An Integrated Model of Destination Attractiveness and Tourists’ Environmentally Responsible Behavior: The Mediating Effect of Place Attachment
Abstract
1. Introduction
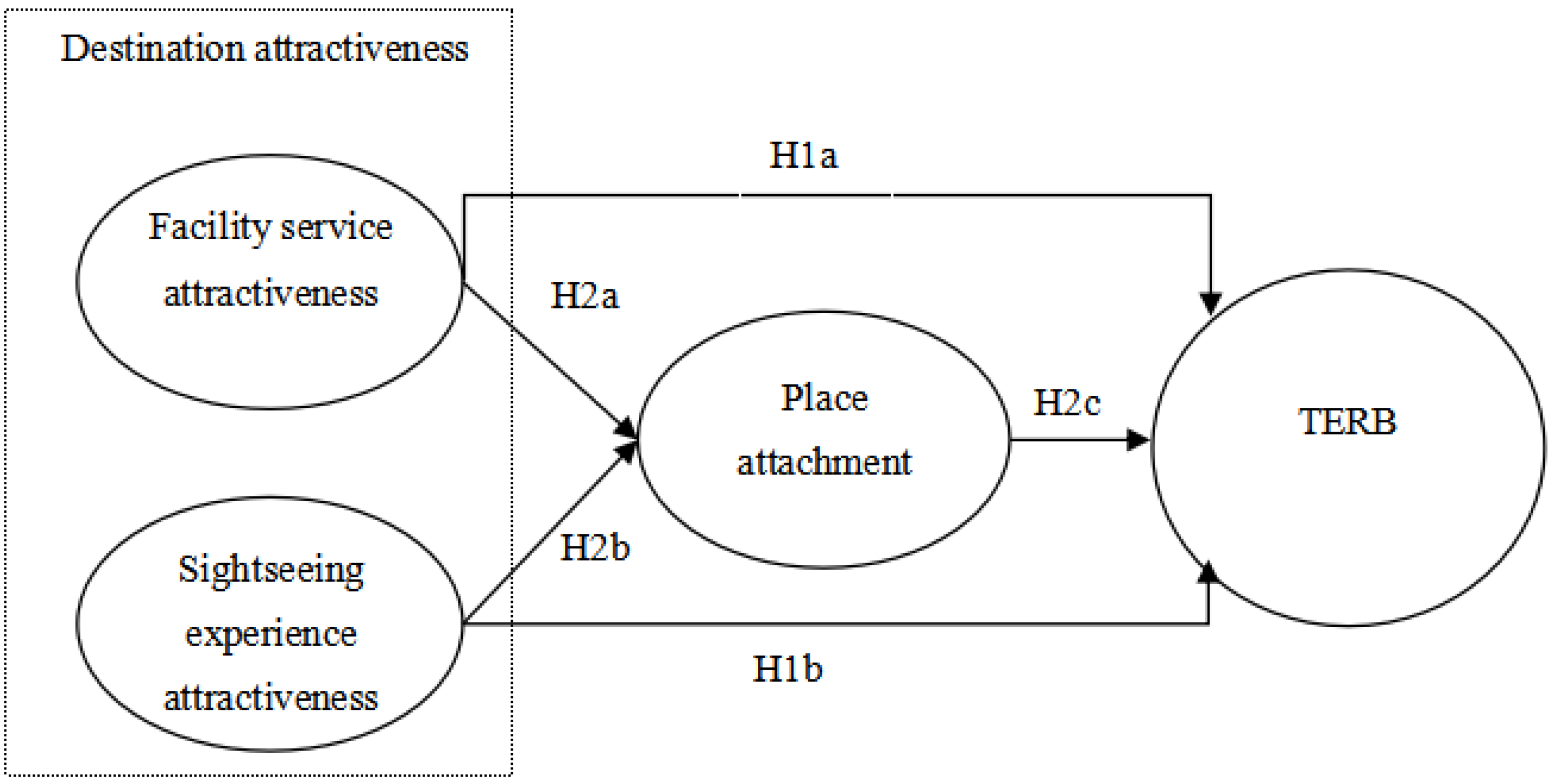
2. Literature Review and Hypothesis
2.1. Theoretical Foundation
2.2. Relationship between Destination Attractiveness and TERB
2.3. Mediating Role of Place Attachment
3. Methodology
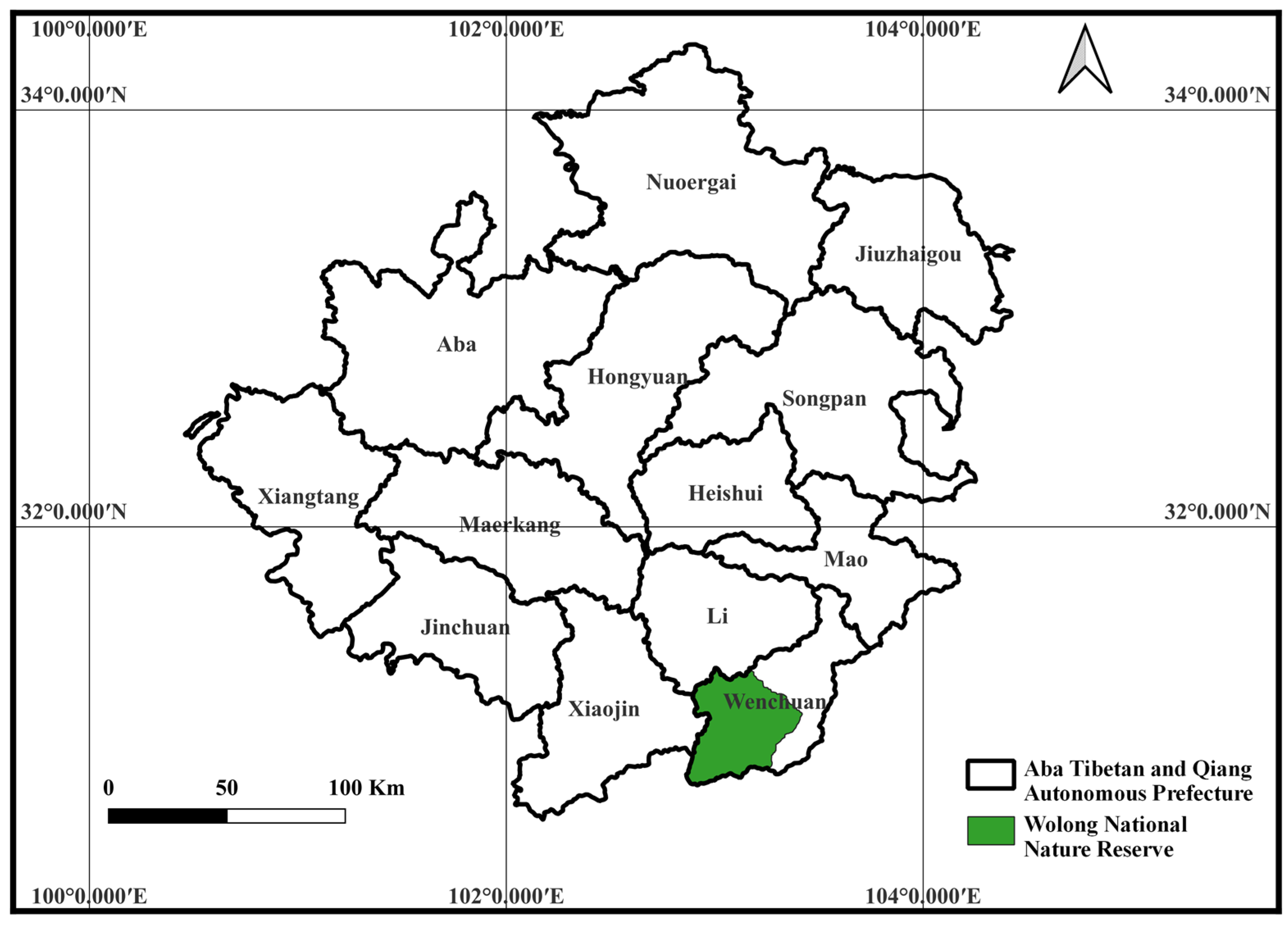
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Questionnaire and Measurement Scale Design
- (1)
- (2)
- (3)
| Construct | Item | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Facility service attractiveness | A1: This destination has good accommodations. A2: This destination has easy access to transportation nearby. A3: This destination provides me with a lot of leisure fun. | Hu (1993) and Liu (2017) [31,57] |
| Sightseeing experience attractiveness | B1: This destination has beautiful scenery. B2: This destination has profound cultural heritage. | |
| Place attachment | C1: This destination is a special place for me. C2: The experience of traveling to this destination is unique. C3: This destination gives me more satisfaction than other national parks. C4: I like this destination more than other parks. | Zhou (2014) and Scanell (2010) [54,58] |
| TERB | E1: I will obey the policy regarding not entering the national park protection area. E2: I will convince my peers to adopt environmental protection behaviors. E3: I will avoid disturbing the flora and fauna in the scenic area during the tour. E4: I will voluntarily reduce or stop the corresponding activities if the scenic spot needs to be restored. | He (2018) and Wu (2022) [5,59] |
3.3. Data Collection
4. Data Analysis
4.1. Exploratory Factor Analysis
4.2. Reliability Test
4.3. Test Validity
5. Hypothesis Testing
6. Mediating Effect Test
7. Discussion and Conclusions
7.1. Discussion
7.2. Theoretical Contributions
7.3. Practical Implications
7.4. Conclusions
8. Limitations and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, Z.; Chen, X. The Effect of Tourism Experience on Tourists’ Environmentally Responsible Behavior at Cultural Heritage Sites: The Mediating Role of Cultural Attachment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 565. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Li, L. Sustainable development of tourism under the background of low-carbon and green economy. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8587024. [Google Scholar]
- Akhshik, A.; Rezapouraghdam, H.; Ramkissoon, H. Industrialization of nature in the time of complexity unawareness: The case of Chitgar Lake, Iran. J. Hosp. Tour. Res. 2022, 46, 583–606. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, X.; Sun, F.; Xiao, M.; Shi, Q. Examining the dimensions and mechanisms of tourists’ environmental behavior: A theory of planned behavior approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 123007. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.C.; Hsieh, C.-M.; Yang, C.-H.; Huang, W.-S.; Ku, G.C.-M. Mediating role of attitudinal and behavioral loyalty between destination attractiveness and environmentally responsible behavior based on Stimulus-Organism-Response model. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2022, 27, 712–725. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, Y.-T.H.; Lee, W.-I.; Chen, T.-H. Environmentally responsible behavior in ecotourism: Exploring the role of destination image and value perception. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2014, 19, 876–889. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Liu, M.; Wei, M. Host sincerity and tourist environmentally responsible behavior: The mediating role of tourists’ emotional solidarity with hosts. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2021, 19, 100548. [Google Scholar]
- Obradović, S.; Stojanović, V.; Tešin, A.; Šećerov, I.; Pantelić, M.; Dolinaj, D. Memorable Tourist Experiences in National Parks: Impacts on Future Intentions and Environmentally Responsible Behavior. Sustainability 2023, 15, 547. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, T.-M.; Wu, H.C.; Huang, L.-M. The influence of place attachment on the relationship between destination attractiveness and environmentally responsible behavior for island tourism in Penghu, Taiwan. J. Sustain. Tour. 2013, 21, 1166–1187. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, M. An empirical study on the effect of attractiveness of ecotourism destination on experiential value and revisit intention. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2016, 15, 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Reitsamer, B.F.; Brunner-Sperdin, A.; Stokburger-Sauer, N.E. Destination attractiveness and destination attachment: The mediating role of tourists’ attitude. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2016, 19, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- de Araújo, A.F.; Andrés Marques, M.I.; Candeias, M.T.R.; Vieira, A.L. Willingness to Pay for Sustainable Destinations: A Structural Approach. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2548. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Liu, C.-R.; Huang, W.-S.; Chen, S.-P. Destination fascination and destination loyalty: Subjective well-being and destination attachment as mediators. J. Travel Res. 2020, 59, 496–511. [Google Scholar]
- Thio, S.; Jokom, R.; Widjaja, D.C. The contribution of perceived food consumption value on destination attractiveness and revisit intention. J. Culin. Sci. Technol. 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, I.K.V.; Ryan, C. Destination attractiveness and place attachment: A multi-group analysis of visitors from the Greater China Region. Tour. Recreat. Res. 2021, 23, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, J. Antecedents and consequences of place attachment: A comparison of Chinese and Western urban tourists in Hangzhou, China. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2016, 5, 86–96. [Google Scholar]
- Shaykh-Baygloo, R. Foreign tourists’ experience: The tri-partite relationships among sense of place toward destination city, tourism attractions and tourists’ overall satisfaction-Evidence from Shiraz, Iran. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2021, 19, 100518. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Thapa, B. Perceived value and flow experience: Application in a nature-based tourism context. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2018, 8, 373–384. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.; Jang, S.S.; Zhao, Y. Understanding tourists’ environmentally responsible behavior at coastal tourism destinations. Mar. Policy 2022, 143, 105178. [Google Scholar]
- Safshekan, S.; Ozturen, A.; Ghaedi, A. Residents’ environmentally responsible behavior: An insight into sustainable destination development. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2020, 25, 409–423. [Google Scholar]
- Confente, I.; Scarpi, D. Achieving environmentally responsible behavior for tourists and residents: A norm activation theory perspective. J. Travel Res. 2021, 60, 1196–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer, L.; Chen, N.; Lee, J. The role of place attachment in tourism research. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2019, 36, 645–652. [Google Scholar]
- Ramkissoon, H.; Smith, L.D.G.; Weiler, B. Testing the dimensionality of place attachment and its relationships with place satisfaction and pro-environmental behaviours: A structural equation modelling approach. Tour. Manag. 2013, 36, 552–566. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, L.; Weiss, J. Evidence on the Relationship between Place Attachment and Behavioral Intentions between 2010 and 2021: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuksel, A.; Yuksel, F.; Bilim, Y. Destination attachment: Effects on customer satisfaction and cognitive, affective and conative loyalty. Tour. Manag. 2010, 31, 274–284. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, S.P. Place attachment and tourism marketing: Investigating international tourists in Singapore. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2012, 14, 139–152. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Qiu, H.; Morrison, A.M.; Wei, W.; Zhang, X. Landscape and unique fascination: A dual-case study on the antecedents of tourist pro-environmental behavioral intentions. Land 2022, 11, 479. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, R.; Xiao, X.; Wei, Z.; Yang, J.; Gao, Y.n.; Lu, S. How to coordinate the use and conservation of natural resources in protected areas: From the perspective of tourists’ natural experiences and environmentally responsible behaviours. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1944. [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg, S.; Schmidt, P. Incentives, morality, or habit? Predicting students’ car use for university routes with the models of Ajzen, Schwartz, and Triandis. Environ. Behav. 2003, 35, 264–285. [Google Scholar]
- Bagozzi, R.P. The self-regulation of attitudes, intentions, and behavior. Soc. Psychol. Q. 1992, 55, 178–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ritchie, J.B. Measuring destination attractiveness: A contextual approach. J. Travel Res. 1993, 32, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Formica, S.; Uysal, M. Destination attractiveness based on supply and demand evaluations: An analytical framework. J. Travel Res. 2006, 44, 418–430. [Google Scholar]
- Formica, S. Destination Attractiveness as a Function of Supply and Demand Interaction; Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Perdue, R.R. The influence of image on destination attractiveness. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2011, 28, 225–239. [Google Scholar]
- Laws, E. Tourist Destination Management: Issues, Analysis and Policies; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Das, D.; Sharma, S.K.; Mohapatra, P.K.; Sarkar, A. Factors influencing the attractiveness of a tourist destination: A case study. J. Serv. Res. 2007, 7, 103–134. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Hultman, M.; Eisingerich, A.B.; Wei, X. How does brand loyalty interact with tourism destination? Exploring the effect of brand loyalty on place attachment. Ann. Tour. Res. 2020, 81, 102879. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.-S.; Lin, C.-H.; Morais, D.B. Antecedents of attachment to a cultural tourism destination: The case of Hakka and non-Hakka Taiwanese visitors to Pei-Pu, Taiwan. J. Travel Res. 2005, 44, 221–233. [Google Scholar]
- Henkel, R.; Henkel, P.; Agrusa, W.; Agrusa, J.; Tanner, J. Thailand as a tourist destination: Perceptions of international visitors and Thai residents. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2006, 11, 269–287. [Google Scholar]
- Nadzirah, M.; Yuhanis, A.A.; Khairil, W.A.; Zaiton, S. Influence of destination attractiveness on place satisfaction and environmentally responsible behaviour in Marine Parks. J. Sustain. Sci. Manag. 2020, 15, 52–67. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.H.; Jan, F.-H.; Yang, C.-C. Conceptualizing and measuring environmentally responsible behaviors from the perspective of community-based tourists. Tour. Manag. 2013, 36, 454–468. [Google Scholar]
- Gezhi, C.; Xiang, H. From good feelings to good behavior: Exploring the impacts of positive emotions on tourist environmentally responsible behavior. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2022, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, L.T.; Ma, A.T.; Lam, T.W.; Chow, A.S.; Fok, L.; Cheang, C.C. Predictors of the environmentally responsible behaviour of participants: An empirical investigation of interpretative dolphin-watching tours. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 23, e01153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Swanson, S.R. The effect of destination social responsibility on tourist environmentally responsible behavior: Compared analysis of first-time and repeat tourists. Tour. Manag. 2017, 60, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Bai, K.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. Which factors influence individual pro-environmental behavior in the tourism context: Rationality, affect, or morality? Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2021, 26, 516–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Su, K.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Wen, Y. The impact of tourist cognition on willing to pay for rare species conservation: Base on the questionnaire survey in protected areas of the Qinling region in China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 33, e01952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Zhang, J.; Lu, S.; Li, L. Relationship between specific attributes of place, tourists’ place attachment and pro-environment behavioral intentions in Jiuzhaigou. Prog. Geogr 2014, 33, 411–421. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, F.; Hongliang, Q.; Xuefei, W. Tourist destination image, place attachment and tourists’ environmentally responsible behavior: A case of Zhejiang tourist resorts. Tour. Trib./Lvyou Xuekan 2014, 29, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Xie, J.; Guo, Y. Empirical Research of Impacts for Place Attachment on Environmental Responsibility Behavior in Oasis Cities—Take Zhangye National Wetland Park for an Example. Resour. Dev. Mark. 2017, 33, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Ma, B.; Zhang, Y. Research on The Relationship among Local Knowledge Demand, Place Attachment and Environmental Responsibility Behaviors: Take Three-Rivers-Source National Park as an Example. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2019, 13, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo, M.C.; Hernandez, B. Place attachment: Conceptual and empirical questions. J. Environ. Psychol. 2001, 21, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-F.; Phou, S. A closer look at destination: Image, personality, relationship and loyalty. Tour. Manag. 2013, 36, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.-M.; Kim, K.-S.; Yim, B.H. The mediating effect of place attachment on the relationship between golf tourism destination image and revisit intention. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2017, 22, 1182–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, Q.; Zhu, L. Outcome efficacy, people-destination affect, and tourists environmentally responsible behavior intention: A revised model based on the theory of planned behavior. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Humanit. Soc. Sci.) 2014, 44, 88–98. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Lin, X.; Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, M. Experiential Value, Place Attachment, and Environmentally Responsible Behavior of Forest Health Tourism—A Case of China. Forests 2022, 13, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Wang, H. Participation, income growth and poverty alleviation in payments for ecosystem services: The case of China’s Wolong Nature Reserve. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 196, 107433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-R.; Wang, Y.-C.; Huang, W.-S.; Chen, S.-P. Destination fascination: Conceptualization and scale development. Tour. Manag. 2017, 63, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scannell, L.; Gifford, R. The relations between natural and civic place attachment and pro-environmental behavior. J. Environ. Psychol. 2010, 30, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Hu, D.; Su, L. Destination resident’s perceived justice, relational quality, and environmentally responsible behavior. Tour. Trib. 2018, 33, 117–131. [Google Scholar]
- Lochrie, S.; Baxter, I.W.; Collinson, E.; Curran, R.; Gannon, M.J.; Taheri, B.; Thompson, J.; Yalinay, O. Self-expression and play: Can religious tourism be hedonistic? Tour. Recreat. Res. 2019, 44, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 382–388. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Kim, H.J.; Liang, M.; Ryu, K. Interrelationships between tourist involvement, tourist experience, and environmentally responsible behavior: A case study of Nansha Wetland Park, China. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2018, 35, 856–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-T.; Zhu, D.; Liu, C.; Kim, P.B. A systematic review of empirical studies of pro-environmental behavior in hospitality and tourism contexts. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2022, 34, 3982–4006. [Google Scholar]
- Veasna, S.; Wu, W.-Y.; Huang, C.-H. The impact of destination source credibility on destination satisfaction: The mediating effects of destination attachment and destination image. Tour. Manag. 2013, 36, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| X2/df | RMSEA | GFI | AGFI | CFI | IFI | TLI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <3 | <0.08 | >0.8 | >0.8 | >0.9 | >0.9 | >0.9 |
| 1.435 | 0.049 | 0.956 | 0.941 | 0.984 | 0.987 | 0.976 |
| Latent Variables | Measurement Item | Standardized Load | t-Value | Composite Reliability | Cronbach’s α Value | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Facility service attractiveness | A1 A2 A3 | 0.728 0.765 0.828 | 8.185 7.764 | 0.74 | 0.815 | 0.51 |
| Sightseeing experience attractiveness | B1 B2 | 0.688 0.755 | - 8.357 | 0.69 | 0.746 | 0.50 |
| Place attachment | C1 | 0.728 | 0.87 | 0.887 | 0.63 | |
| C2 | 0.813 | 11.256 | ||||
| C3 | 0.826 | 11.574 | ||||
| C4 | 0.792 | 10.689 | ||||
| TERB | 0.85 | 0.814 | 0.62 | |||
| E1 | 0.774 | 10.768 | ||||
| E2 | 0.768 | 11.462 | ||||
| E3 | 0.845 | 12.316 | ||||
| E4 | 0.802 | |||||
| Overall scale | 0.916 |
| Path Relationship | Standardized Path Coefficient | S.E. | C.R. | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1a: Facility service attractiveness → Place attachment | 0.835 | 0.146 | 3.187 | *** |
| H1b: Sightseeing experience attractiveness → Place attachment | 0.792 | 0.165 | 3.731 | *** |
| H2a: Facility service attractiveness → TERB | 0.699 | 0.476 | 4.586 | *** |
| H2b: Sightseeing experience attractiveness → TERB | 0.851 | 0.254 | 3.496 | *** |
| H2c: Place attachment → TERB | 0.822 | 0.153 | 4.674 | *** |
| Path | Indirect Effect | Percentile Inspection of 95% |
|---|---|---|
| Facility service attraction → Place attachment → TERB | 0.072 | [0.064, 0.116] |
| Sightseeing experience attractiveness → Place attachment → TERB | 0.081 | [0.053, 0.097] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Liao, C.; Law, R.; Zhang, M. An Integrated Model of Destination Attractiveness and Tourists’ Environmentally Responsible Behavior: The Mediating Effect of Place Attachment. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13030264
Li T, Liao C, Law R, Zhang M. An Integrated Model of Destination Attractiveness and Tourists’ Environmentally Responsible Behavior: The Mediating Effect of Place Attachment. Behavioral Sciences. 2023; 13(3):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13030264
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ting, Chenmei Liao, Rob Law, and Mu Zhang. 2023. "An Integrated Model of Destination Attractiveness and Tourists’ Environmentally Responsible Behavior: The Mediating Effect of Place Attachment" Behavioral Sciences 13, no. 3: 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13030264
APA StyleLi, T., Liao, C., Law, R., & Zhang, M. (2023). An Integrated Model of Destination Attractiveness and Tourists’ Environmentally Responsible Behavior: The Mediating Effect of Place Attachment. Behavioral Sciences, 13(3), 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13030264





