Older Adults and Clutter: Age Differences in Clutter Impact, Psychological Home, and Subjective Well-Being
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Psychological Home, Subjective Well-Being, and Clutter
1.2. Life Course Perspectives
1.3. Hypotheses
2. Method
2.1. Participants
2.2. Psychometric Scales
3. Results
3.1. Analysis Plan and Preliminary Results
3.2. Primary Analyses
4. Discussion
Limitations and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roster, C.A.; Ferrari, J.R.; Jurkat, M.P. The dark side of home: Assessing possession ‘clutter’ on subjective well-being. J. Environ. Psychol. 2016, 46, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crum, K.P.; Ferrari, J.R. Toward an understanding of psychological home and clutter with emerging adults: Relationships over relics. N. Am. J. Psychol. 2019, 21, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Crum, K.P.; Ferrari, J.R. Psychological home, clutter, and place attachment predicting life satisfaction among women of color: Home is beyond physical space. J. Contemp. Res. Soc. Sci. 2019, 1, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, J.R.; Roster, C.A. Delaying disposing: Examining the relationship between procrastination and clutter across generations. Curr. Psychol. 2018, 37, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prohaska, V.; Celestino, D.; Dangleben, T.; Sanchez, P.; Sandoval, A. Assessing “clutter” and related constructs with a non-white, urban sample. Curr. Psychol. 2018, 32, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, C.J.; Hart, R. Home and the extended-self: Exploring associations between clutter and wellbeing. J. Environ. Psychol. 2021, 73, 101553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmon, S.T.; Whitcomb, S.R.; Synder, C.R. Psychological home. In Psychological Sense of Community: Research, Applications, and Implications; Fisher, A.T., Sonn, C.C., Bishop, B.J., Eds.; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Mallett, S. Understanding home: A critical review of the literature. Sociol. Rev. 2004, 52, 62–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, F.M.; Withey, S.B. Social Indicators of Well-Being: America’s Perception of Life Quality; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Bratskier, K. This is the Secret to Staying Happy in Old Age. Huffington Post, 11 March 2016. Available online: https://www.huffpost.com/entry/secret-to-life-long-happiness_n_56e063bee4b0860f99d777d4(accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Gregiore, C. Older People are Happier than You. Why? CNN, 24 April 2015. Available online: https://www.cnn.com/2015/04/24/health/old-people-happy/index.html(accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Isaacowitz, D. Why are Older People Happier? Association for Psychological Science, 5 January 2012. Available online: https://www.psychologicalscience.org/news/releases/better-research-is-needed-to-understand-why-elders-are-happier.html(accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Leland, J. Want to be happy? Think like an Old Person. New York Times, 29 December 2017. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2017/12/29/nyregion/want-to-be-happy-think-like-an-old-person.html(accessed on 20 January 2022).
- MacMillian, A. Happiness Linked to Longer Life. CNN Health, 20 July 2018. Available online: https://www.cnn.com/2011/10/31/health/happiness-linked-longer-life/index.html(accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Netburn, D. The Aging Paradox: The Older We Get, the Happier We Are. Los Angeles Times, 24 August 2016. Available online: https://www.latimes.com/science/sciencenow/la-sci-sn-older-people-happier-20160824-snap-story.html(accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Oaklander, M. Older People are Happier than People in Their 20s. TIME, 24 August 2016. Available online: https://time.com/4464811/aging-happiness-stress-anxiety-depression/(accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Tanner, L. Research: Older Adults are Happiest Americans. ABC News, 20 April 2008. Available online: https://abcnews.go.com/Technology/story?id=4688191&page=1(accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Yang, P.Q.; Leone, E. Are older people really happier than younger people? J. Public Prof. Sociol. 2021, 13, 2. Available online: https://digitalcommons.kennesaw.edu/jpps/vol13/iss1/2 (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Bowling, A. Do older and younger people differ in their reported well-being? A national survey of adults in Britain. Fam. Pract. 2011, 28, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, J.R.; Swanson, H.L.; Patel, D.A. Office clutter: Comparing lower and upper-level employees on work-related criteria. Int. J. Psychol. Res. Rev. 2021, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, J.R.; Swanson, H.L.; Patel, D.A. The impact of office clutter on remote working: “I can’t work with all this stuff!”. N. Am. J. Psychol. 2021, 23, 155–172. [Google Scholar]
- Girts, J.A. Clutter and self-extension tendencies: Predictors of life satisfaction among emerging adults. Coll. Sci. Health Theses Diss. 2019. Available online: https://via.library.depaul.edu/csh_etd/307 (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Mayer, K.U. New directions in life course research. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 2009, 35, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elder, G.H. The Life Course in Time and Place; Heinz, W.R., Marshall, V.W., Eds.; Aldine de Gruyter: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, K.U. Whose lives? How history, societies and institutions define and shape life courses. Res. Hum. Dev. 2004, 3, 161–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settersten, R.A. (Ed.) Propositions and controversies on life-course scholarship. In Invitation to the Life Course: Toward New Understandings of Later Life; Routeledge: London, UK, 2003; pp. 15–48. [Google Scholar]
- Institute for Challenging Disorganization. (n.d.). Available online: https://www.challengingdisorganization.org (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Diener, E.; Emmons, R.A.; Larsen, R.J.; Griffin, S. The satisfaction with life scale. J. Personal. Assess. 1985, 49, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, W.M. Development of reliable and valid short forms of the Marlowe-Crowne social desirability scale. J. Clin. Psychol. 1982, 38, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Jamovi Project (2021). jamovi (Version 2.0) [Computer Software]. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. (Version 4.0) [Computer Software]. 2021. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Kim, S. ppcor: Partial and Semi-Partial (Part) Correlation. [R package]. 2015. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=ppcor (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- George, L.K. Sociological perspectives on life transitions. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 1993, 19, 353–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, P.; Marshall, V.; House, J.; Lantz, P. The social structuring of mental health over the adult life course: Advancing theory in the sociology of aging. Soc. Forces 2011, 89, 1287–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Demographic Category | Older Adults (n = 225) | Younger Adults (n = 225) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | ||
| Gender | |||||
| Female | 206 | 92.0% | 216 | 96.0% | |
| Male | 18 | 8.0% | 9 | 4.0% | |
| Race | |||||
| White, non-Hispanic | 208 | 94.5% | 203 | 91.4% | |
| Black, non-Hispanic | 5 | 2.3% | 5 | 2.3% | |
| American Indian or Alaska Native | 2 | 0.9% | 1 | 0.5% | |
| Asian/Pacific Islander | 1 | 0.5% | 2 | 0.9% | |
| Hispanic/Latino | 3 | 1.4% | 8 | 3.6% | |
| Relationship Status | |||||
| Married | 114 | 51.4% | 135 | 60.5% | |
| Divorced/Separated | 46 | 20.7% | 30 | 13.5% | |
| Single | 22 | 9.9% | 34 | 15.2% | |
| Widowed | 35 | 15.8% | 12 | 5.4% | |
| Partnered/Cohabitating | 5 | 2.3% | 12 | 5.4% | |
| Housing | |||||
| Own dwelling | 180 | 81.1% | 173 | 77.2% | |
| Rented dwelling | 38 | 17.1% | 44 | 19.6% | |
| Residence Type | |||||
| Detached single-family house | 159 | 71.3% | 165 | 73.7% | |
| Townhouse/Condominium | 25 | 11.2% | 25 | 11.2% | |
| Apartment | 28 | 12.6% | 24 | 10.7% | |
| Duplex | 3 | 1.3% | 5 | 2.2% | |
| Manufactured/Mobile Home | 3 | 1.3% | 5 | 2.2% | |
| Other | 5 | 2.2% | 0 | 0.0% | |
| Cohabitation by Age | |||||
| 6 or younger | 3 | 2.0% | 20 | 13.6% | |
| 7–12 years old | 4 | 2.7% | 30 | 19.4% | |
| 13–17 years old | 2 | 1.4% | 29 | 19.6% | |
| 18–25 years old | 5 | 3.5% | 37 | 25.5% | |
| 26–35 years old | 11 | 7.5% | 20 | 14.1% | |
| 36–45 years old | 9 | 6.0% | 45 | 28.7% | |
| 46–55 years old | 3 | 2.1% | 87 | 54.7% | |
| 56–65 years old | 48 | 30.3% | 114 | 67.1% | |
| 66–75 years old | 160 | 78.4% | 10 | 7.8% | |
| 76+ years old | 45 | 31.0% | 6 | 4.9% | |
| Household Income | |||||
| Less than $20,000 | 16 | 9.2% | 10 | 5.3% | |
| $20,000–$34,999 | 30 | 17.3% | 13 | 7.0% | |
| $35,000–$49,999 | 23 | 13.3% | 35 | 18.7% | |
| $50,000–$74,999 | 38 | 22.0% | 39 | 20.9% | |
| $75,000–$99,999 | 31 | 17.9% | 32 | 17.1% | |
| $100,000 or more | 35 | 20.2% | 58 | 31.0% | |
| M (SD) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.26 (1.63) | [0.97] | −0.490 ** | −0.375 ** | - |
| 4.33 (1.52) | −0.498 ** | [0.91] | 0.292 ** | - |
| 5.65 (0.98) | −0.376 ** | 0.294 ** | [0.86] | - |
| 6.12 (2.86) | 0.147 ** | −0.244 ** | −0.029 | [0.69] |
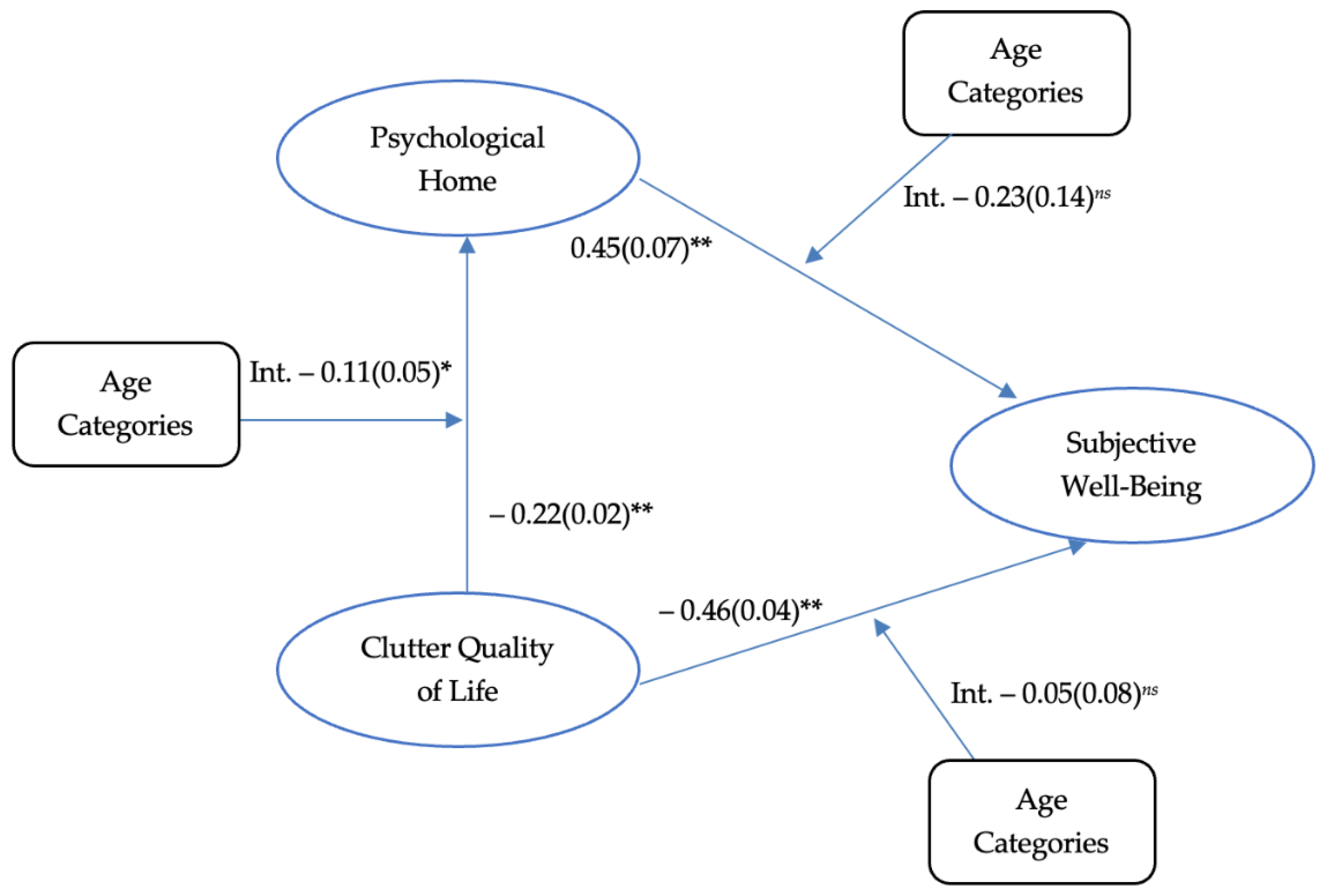
| β | SE | Z | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1: | ||||
| CQLS | −0.22 | 0.023 | −8.83 | <0.001 *** |
| Age Categories | −0.23 | 0.09 | −2.67 | 0.007 * |
| CQLS * Age Categories | −0.11 | 0.05 | −2.26 | 0.024 * |
| Model 2: | ||||
| PSYH | 0.45 | 0.07 | 6.45 | <0.001 *** |
| Age Categories | −0.23 | 0.14 | −1.71 | 0.087 |
| PSYH * Age Categories | −0.23 | 0.14 | −1.62 | 0.106 |
| Model 3: | ||||
| CQLS | −0.46 | −0.04 | −12.03 | <0.001 *** |
| Age Categories | −0.23 | 0.12 | 1.85 | 0.065 |
| CQLS * Age Categories | −0.05 | 0.08 | −0.68 | 0.497 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Swanson, H.L.; Ferrari, J.R. Older Adults and Clutter: Age Differences in Clutter Impact, Psychological Home, and Subjective Well-Being. Behav. Sci. 2022, 12, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12050132
Swanson HL, Ferrari JR. Older Adults and Clutter: Age Differences in Clutter Impact, Psychological Home, and Subjective Well-Being. Behavioral Sciences. 2022; 12(5):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12050132
Chicago/Turabian StyleSwanson, Helena L., and Joseph R. Ferrari. 2022. "Older Adults and Clutter: Age Differences in Clutter Impact, Psychological Home, and Subjective Well-Being" Behavioral Sciences 12, no. 5: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12050132
APA StyleSwanson, H. L., & Ferrari, J. R. (2022). Older Adults and Clutter: Age Differences in Clutter Impact, Psychological Home, and Subjective Well-Being. Behavioral Sciences, 12(5), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12050132






