Gestational Geophagia Affects Nephrocardiac Integrity, ATP-Driven Proton Pumps, the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System, and F2-Isoprostane Status
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mating and Housing
2.2. Animal Diet
2.2.1. Analysis of Renal Hemodynamics
2.2.2. Determination of Cardiovascular Integrity
2.2.3. Analysis of Total and P-type ATPases (Proton Pumps)
2.2.4. Measurement of the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System Activities
2.2.5. Oxidative Stress Markers
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Clay Beverage on Body and Organ Weights and Renal Hemodynamics during Early and Late Gestation
3.2. Implication of Gestational Clay Beverage Intake on Cardiovascular Integrity
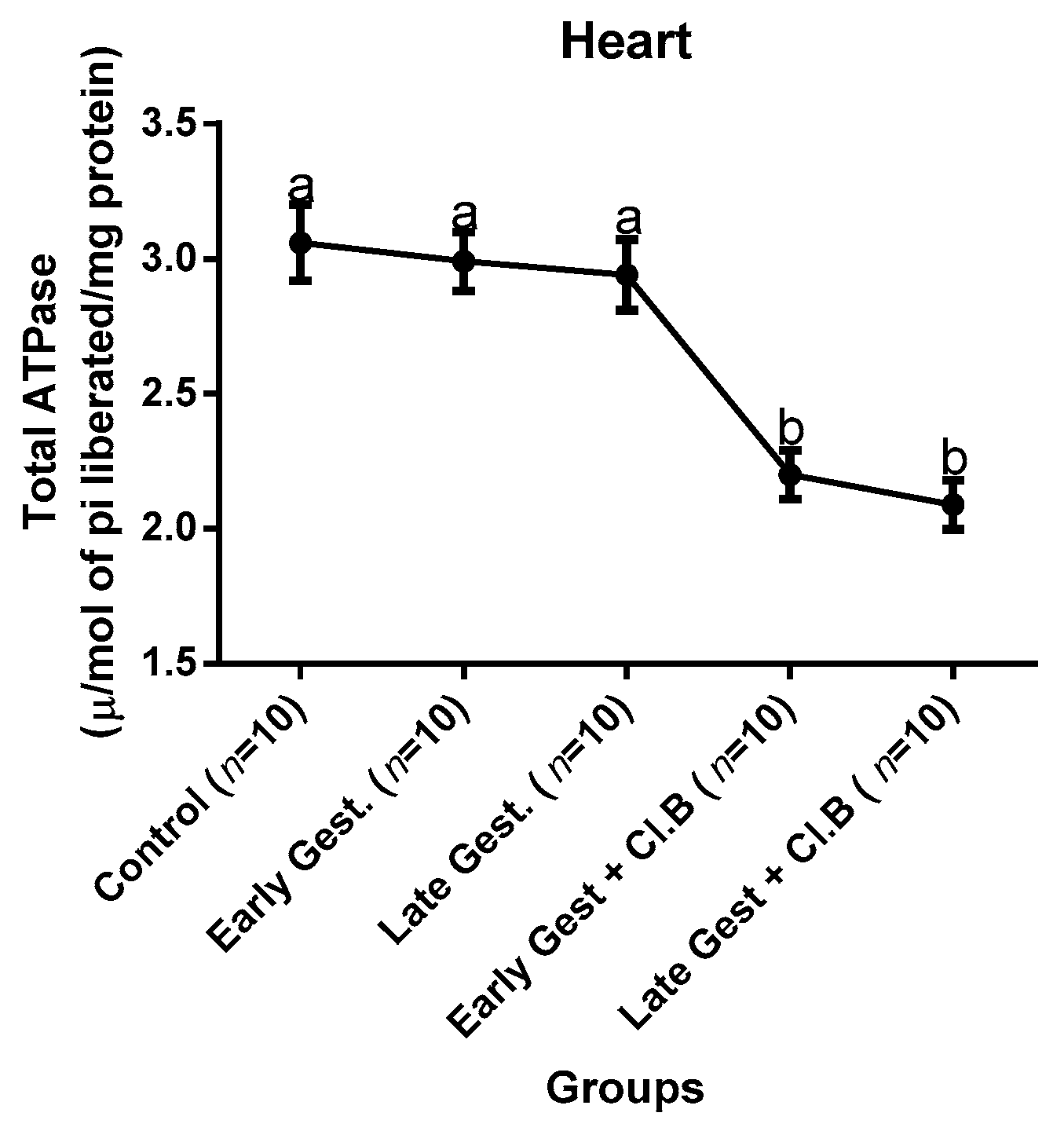
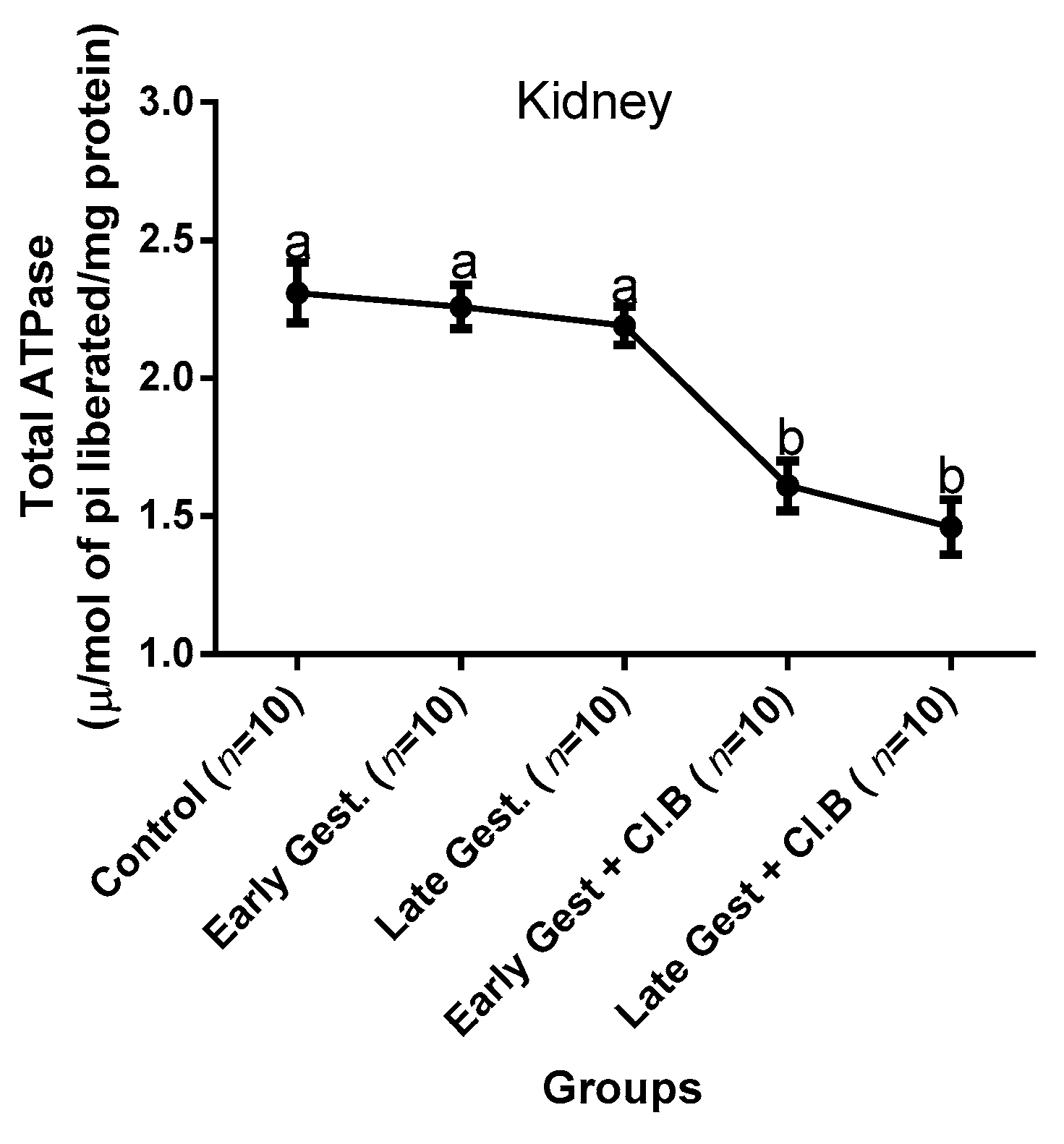
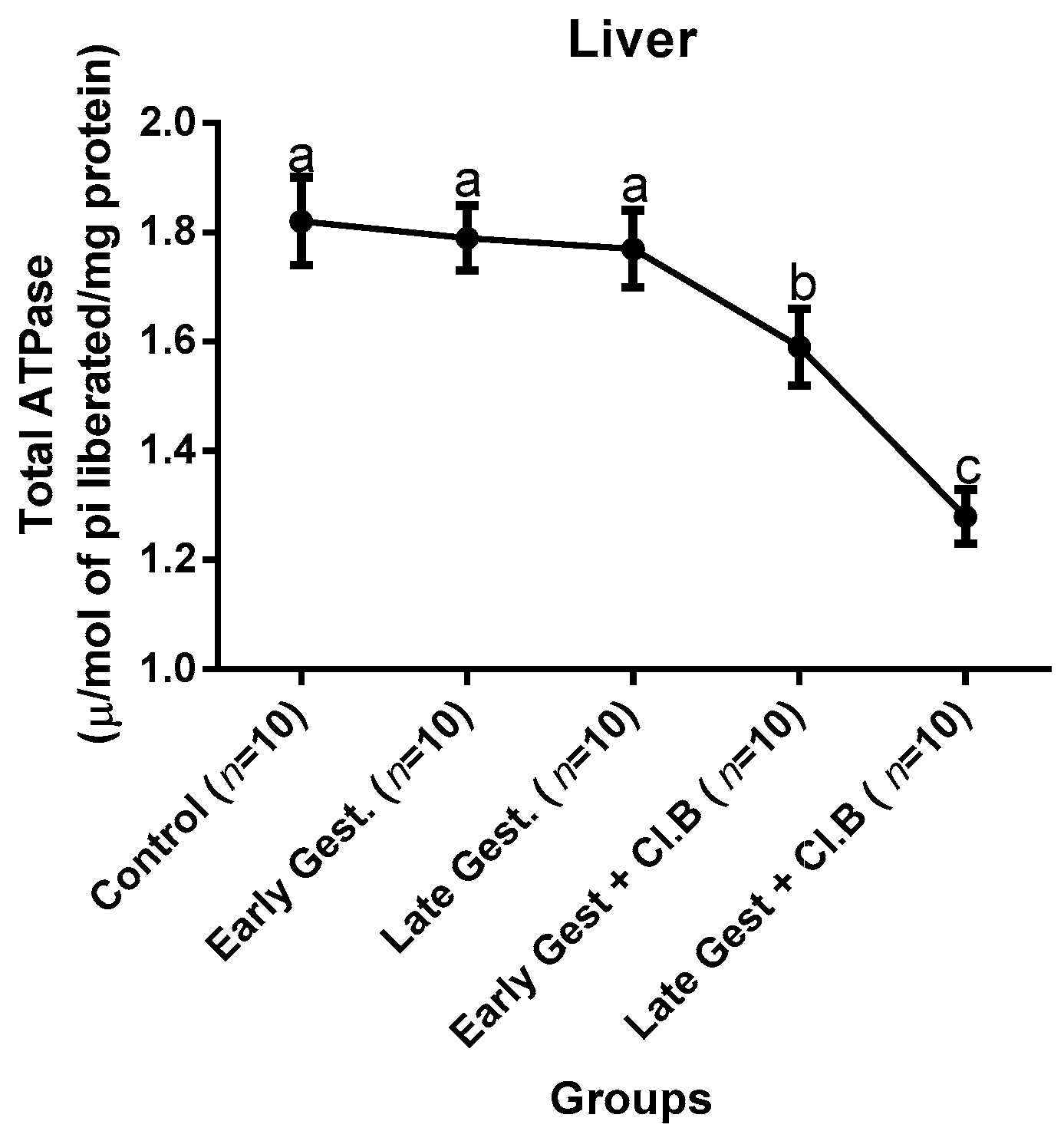
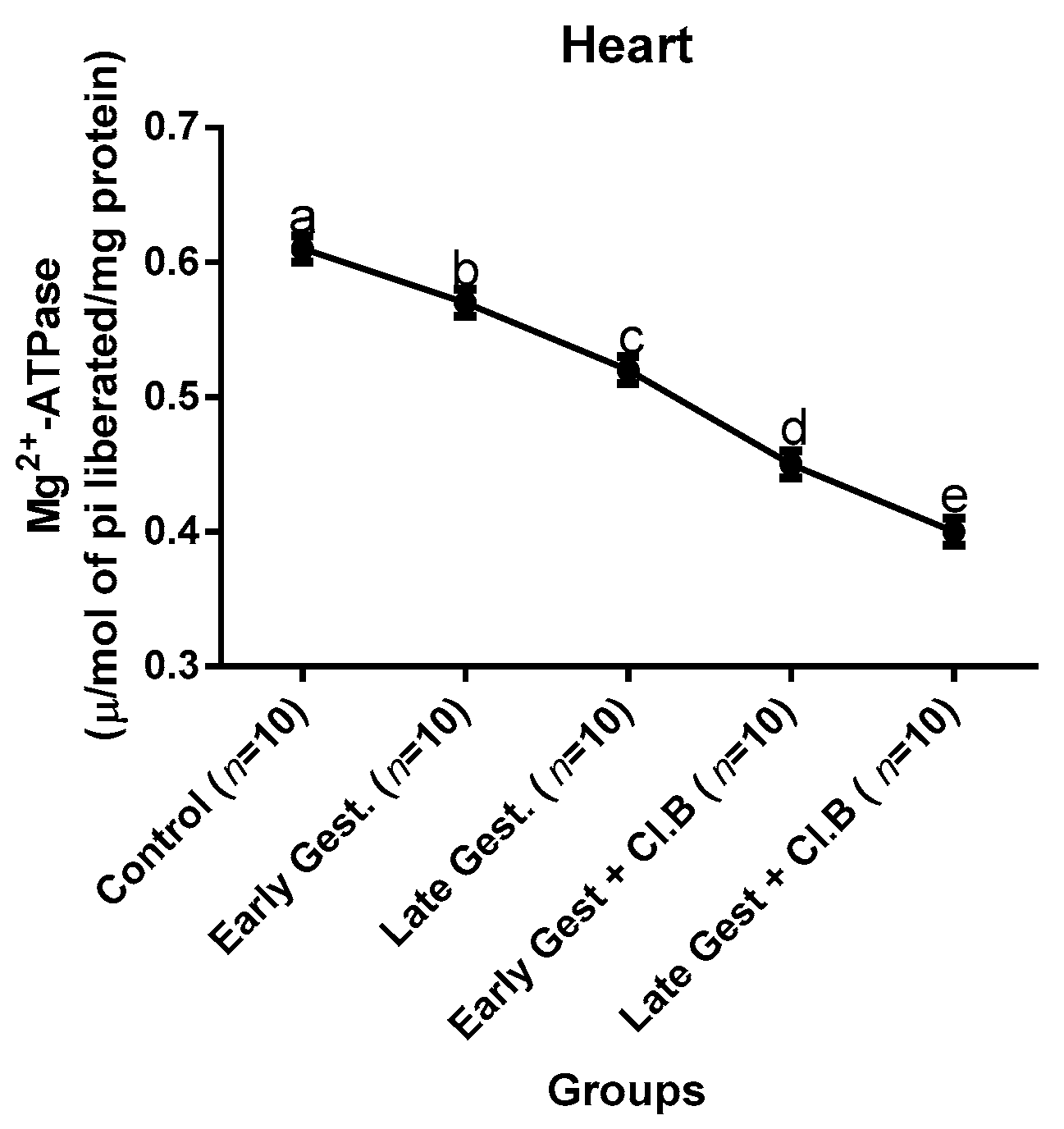
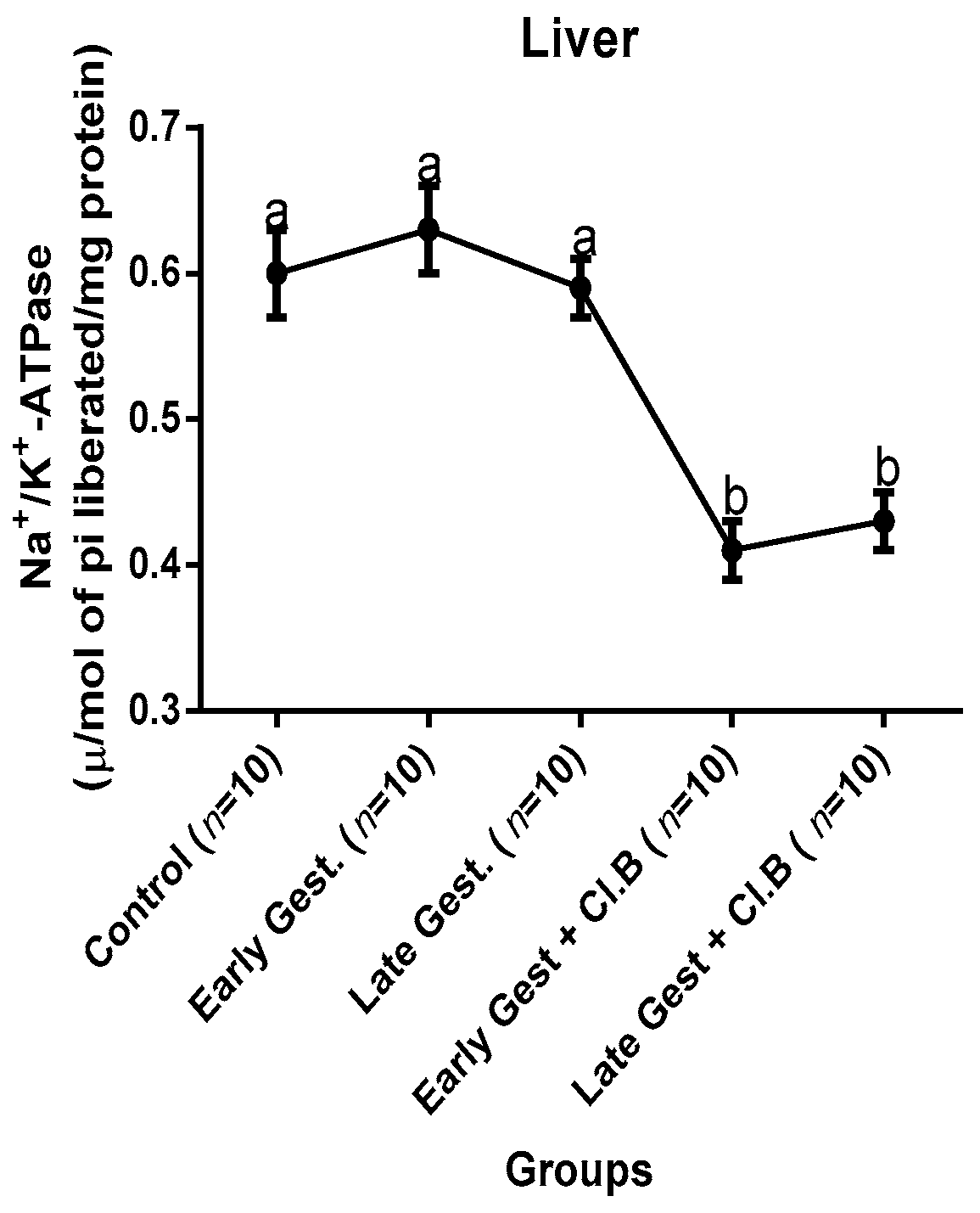
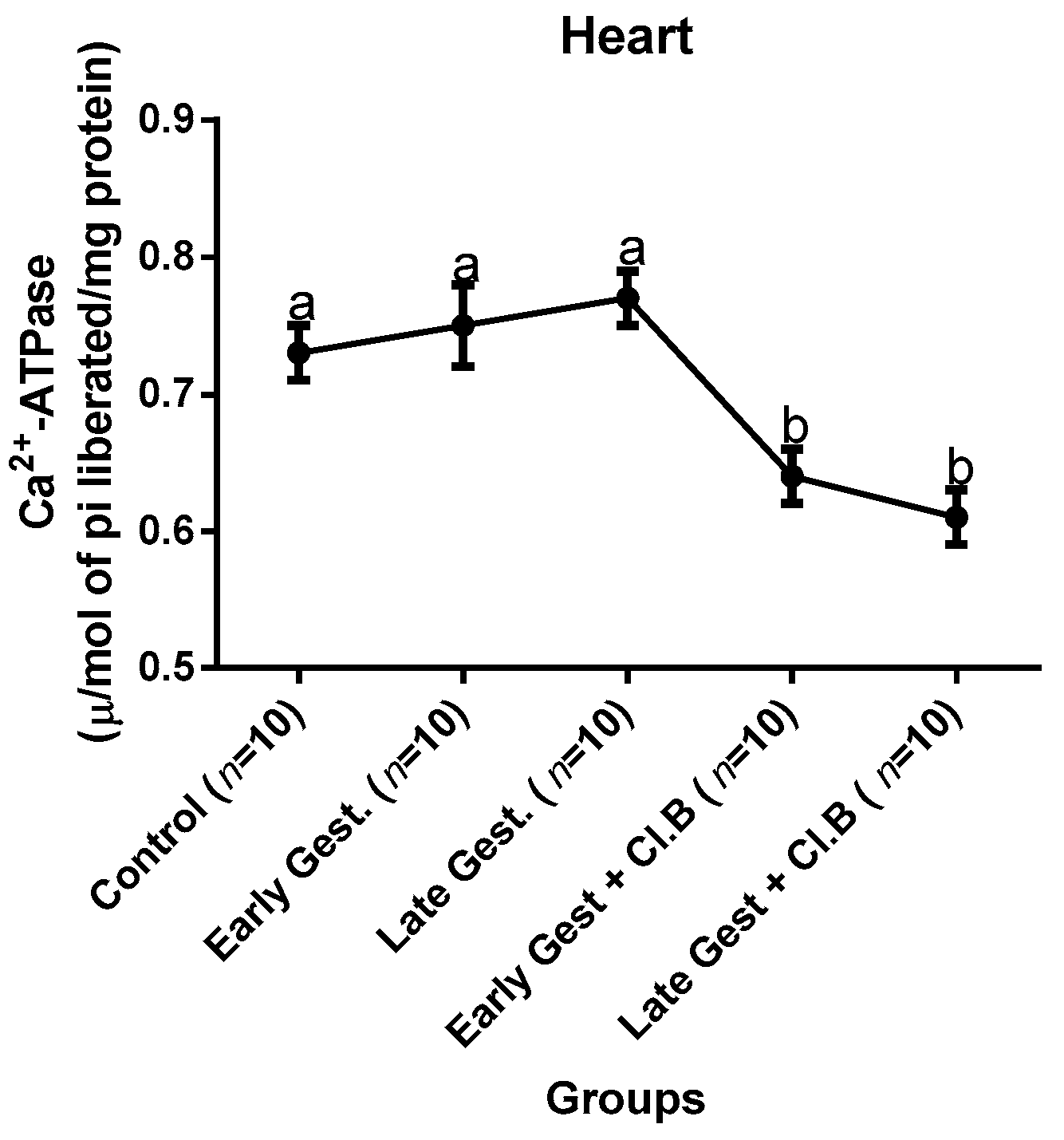
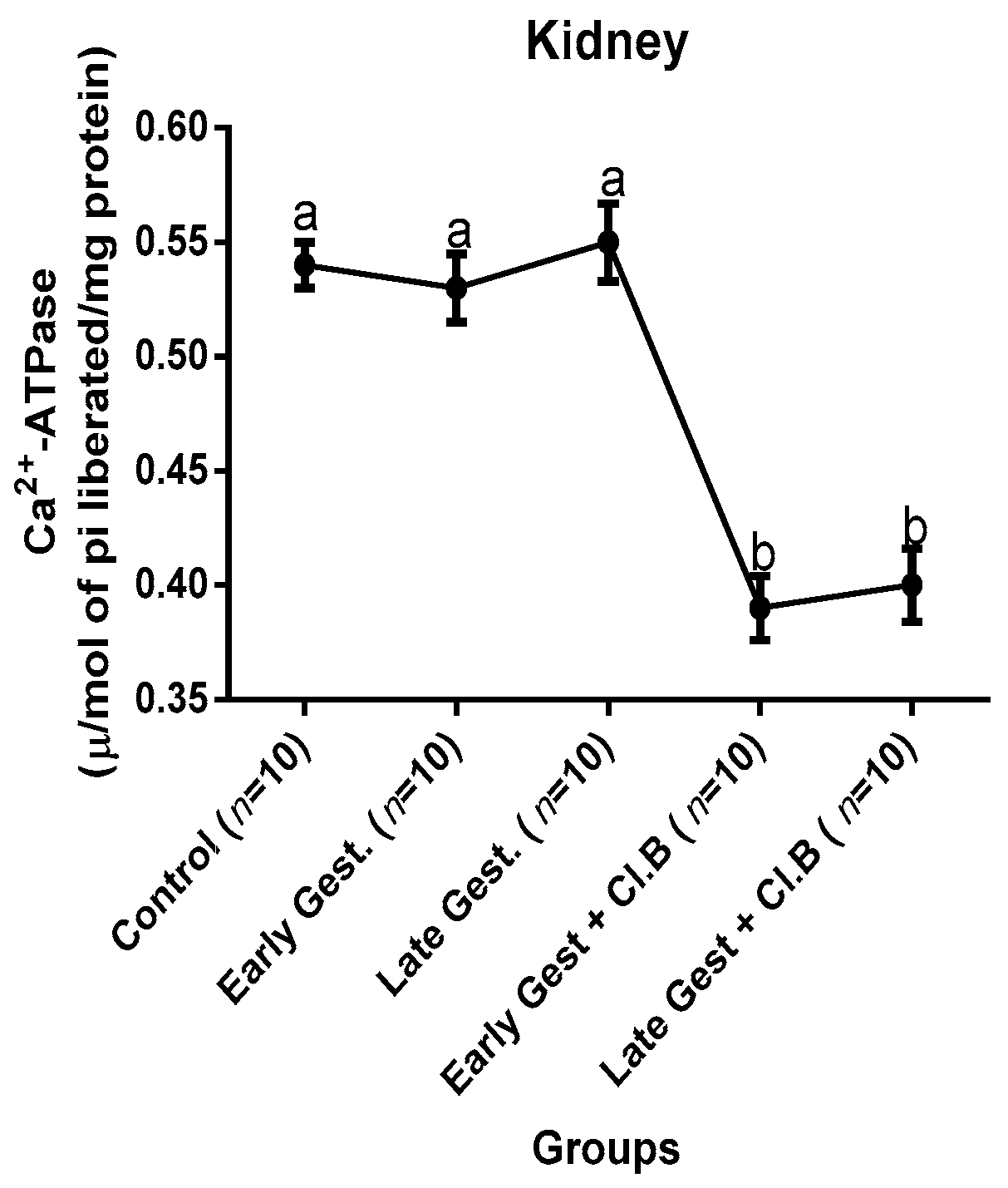
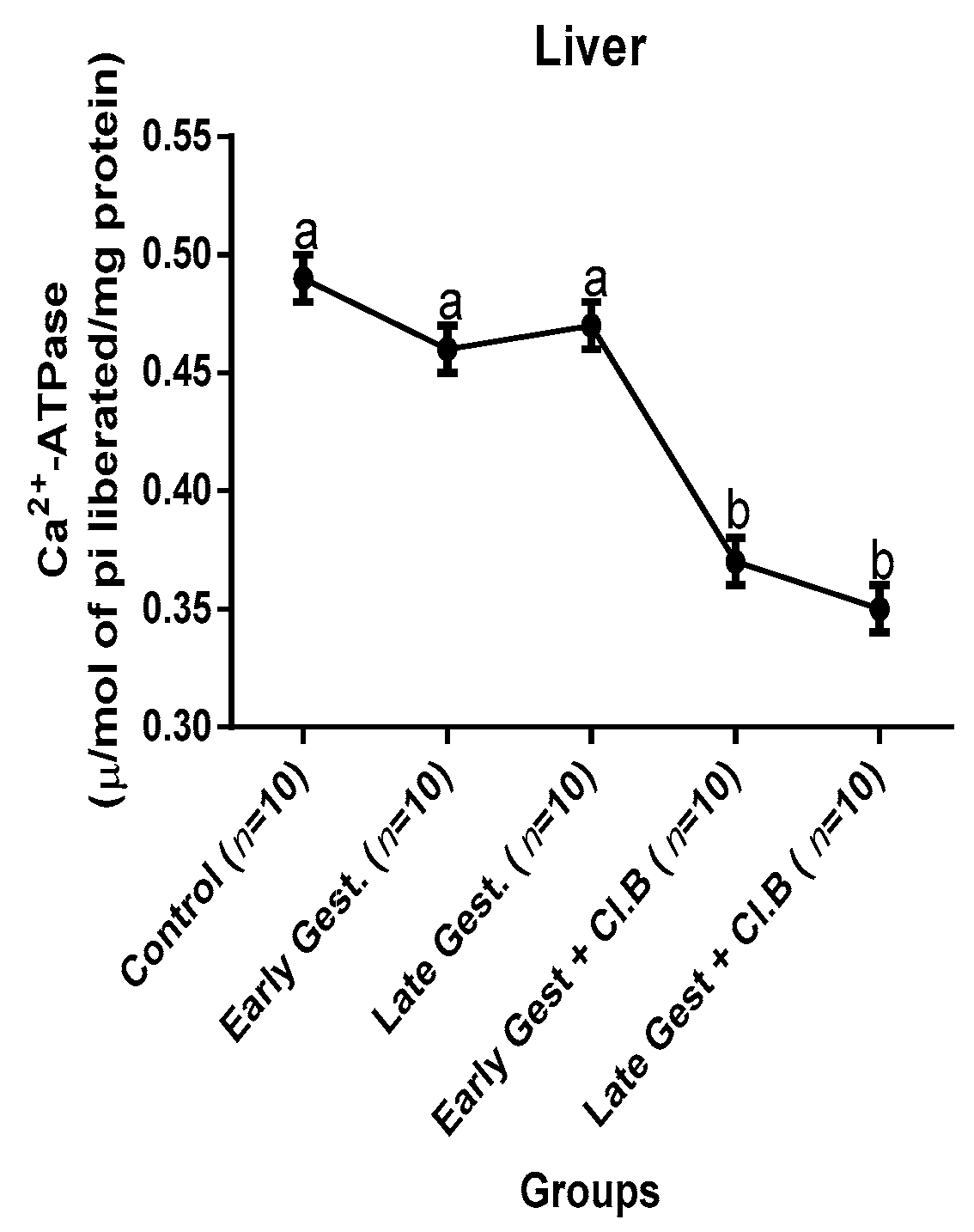
3.3. Relationship between Gestational Clay Beverage Intake and the Expression of Various Proton Pumps from Tissue Homogenates
3.4. The Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone Activities Concentration after Clay Beverage Consumption by Rat Dams
3.5. Oxidative Stress Markers and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities during Gestational Clay Beverage Consumption
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soma-Pillay, P.; Nelson-Piercy, C.; Tolppanen, H.; Mebazaa, A. Physiological changes in pregnancy. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2016, 27, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, S.; Figueiredo, N.; Borges, A.; São Jose Pais, M.; Freitas, L.; Moura, P. Acute kidney injury in pregnancy: A clinical challenge. J. Nephrol. 2012, 25, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, K.L.; Lafayette, R.A. Renal Physiology of Pregnancy. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2013, 20, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siribamrungwong, M.; Chinudomwong, P. Relation between acute kidney injury and pregnancy-related factors. J. Acute Dis. 2016, 5, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsuwaida, A. Challenges in diagnosis and treatment of acute kidney injury during pregnancy. Nephro-Urol. Mon. 2012, 4, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.E.; George, E.M.; Granger, J.P. El corazón durante el embarazo. Rev. Española De Cardiol. 2011, 64, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsueh, W.A.; Luetscher, J.A.; Carlson, E.J.; Grislis, G.; Fraze, E.; Mchargue, A. Changes in Active and Inactive Renin throughout Pregnancy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1982, 54, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Gallery, E.D.; Ross, M.R.; Esber, R.P. Sodium excretion in normal and hypertensive pregnancy: A prospective study. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1988, 159, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawass, N.E.; Alnozha, M.M.; Kolawole, T. Adult geophagia—Report of three cases with review of the literature. Trop. Geogr. Med. 1987, 39, 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Woywodt, A.; Kiss, A. Geophagia: The history of earth-eating. J. R. Soc. Med. 2002, 95, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njiru, H.; Elchalal, U.; Paltiel, O. Geophagy during Pregnancy in Africa: A Literature Review. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2011, 66, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, S.L.; Rasmussen, K.M.; Kavle, J.A.; Farag, T.H.; Hajji, H.; Khalfan, S.S.; Tielsch, J.M. Association of Pica with Anemia and Gastrointestinal Distress among Pregnant Women in Zanzibar, Tanzania. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekong, M.B.; Akpantah, A.O.; Ibok, O.S.; Eluwa, M.A.; Ekanem, T.B. Differential effects of calabash chalk on the histology of liver of adult Wistar rats. Internet J. Health 2009, 8, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Akpantah, A.O.; Ibok, O.S.; Ekong, M.B.; Eluwa, M.A.; Bassey, E.T. The effect of calabash chalk on some hematological parameters in female adult Wistar rats. Turk. J. Hematol. 2010, 27, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekong, M.B.; Peter, A.I.; Ekanem, T.B.; Eluwa, M.A.; Mbadugha, C.C.; Osim, E.E. Calabash Chalk’s Geophagy Affects Gestating Rats’ Behavior and the Histomorphology of the Cerebral Cortex. Int. J. Brain Sci. 2014, 2014, 394847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadi, P.U.; Agomuo, E.N.; Bob-Chile Agada, A.I.; Njoku, U.C.; Ifeanacho, M.O.; Okereke, J.C.; Osuoha, J.O. Toxicities of selected medicinal plants and floras of lower phyla. Alex. J. Med. 2018, 54, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horder, M.; Elser, R.C.; Gerhardt, W.; Matthieu, M.; Sampson, E.J. Approved recommendation on IFCC methods for the measurement of catalytic concentration of enzymes. Part 7. IFCC method for creatine kinase (ATP:creatine N-phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.3.2). EurJ. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem 1991, 29, 435–456. [Google Scholar]
- Schulpis, K.H.; Giannoulia-Karantana, A.; Papaconstantinou, E.D.; Parthimos, T.; Tjamouranis, I.; Tsakiris, S. Erythrocyte membrane Na+,K+-ATPase and Mg2+-ATPase activities in subjects with methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) 677 C→T genotype and moderate hyperhomocysteinaemia. The role of L-phenylalanine and L-alanine. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2006, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentzer, W.C.; August, C.S.; Nathan, D.G. The effects of androgen administration in sickle cell anemia. Pediatr. Res. 1969, 3, 378. [Google Scholar]
- Su-Hong, C.; Qi, C.; Bo, L.; Jian-Li, G.; Jie, S.; Gui-Yuan, L. Antihypertensive Effect of Radix Paeoniae Alba in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats and Excessive Alcohol Intake and High Fat Diet Induced Hypertensive Rats. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 731237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krohne-Ehrich, G.; Schirmer, R.H.; Untucht-Grau, R. Glutathione reductase from human erythrocytes. Isolation of the enzyme and sequence analysis of the redox-active peptide. Eur. J. Biochem 1977, 80, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Manchali, S.; Chidambara, M.K.N.; Patil, B.S. Crucial facts about health benefits of popular cruciferous vegetables. J. Funct. Foods. 2012, 4, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105(C), 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Jeyabalan, A.; Conrad, K.P. Renal function during normal pregnancy and preeclampsia. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 2425–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, W.; Lafayette, R.A. Renal function in normal and disordered pregnancy. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2014, 23, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrad, K.P.; Lindheimer, M.D. Renal and cardiovascular alterations. In Chesley’s hypertensive disorders in pregnancy, 2nd ed.; Lindheimer, M.D., Roberts, J.M., Cunningham, F.G., Eds.; Appleton & Lange: Stamford, CT, USA, 1999; pp. 263–326. [Google Scholar]
- Kraut, J.A.; Madias, N.E. Serum Anion Gap: Its Uses and Limitations in Clinical Medicine. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 2, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Felstead, D.; Doraiswami, M.; Stocks, G.M.; Waheed, U. Acute starvation in pregnancy: A cause of severe metabolic acidosis. Int. J. Obstet. Anesthesia 2011, 20, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, M.K.; Saxena, S.V.; Khullar, M.; Sawhney, H.; Vasishta, K. Role of anion gap and different electrolytes in hypertension during pregnancy (preeclampsia). Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 282, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E.N.; Forman, J.P.; Farwell, W.R. Serum anion gap and blood pressure in the national health and nutrition examination survey. Hypertension 2007, 50, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaraj, G.; Desai, P.B.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Hull, V.V.; Math, A.A.K.; Vernekar, S.N. Markers of renal function tests. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2010, 2, 170–173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, F. Association between resting heart rate and coronary artery disease, stroke, sudden death and noncardiovascular diseases: A meta-analysis. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2016, 188, E384–E392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.X.; Arany, Z. Maternal cardiac metabolism in pregnancy. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 101, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aune, D.; Sen, A.; ó’Hartaigh, B.; Janszky, I.; Romundstad, P.R.; Tonstad, S.; Vatten, L.J. Resting heart rate and the risk of cardiovascular disease, total cancer, and all-cause mortality—A systematic review and dose—Response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 27, 504–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amir, K.A.; Chen, S.X.; Arsura, E.L.; Bobba, R.K. Elevation of Serum Creatine Phosphokinase in Hospitalized Patients. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 338, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunau, B.E.; Pourvali, R.; Wiens, M.O.; Levin, A.; Li, J.; Grafstein, E.; Scheuermeyer, F.X. Characteristics and Thirty-day Outcomes of Emergency Department Patients With Elevated Creatine Kinase. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2014, 21, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patanè, S.; Marte, F.; Di Bella, G.; Davi’, M. Abnormal troponin I levels during pregnancy without acute coronary syndrome and without hypertensive disorders. Int. J. Cardiol. 2008, 128, e47–e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, S.M.; O’Gorman, T.; Finn, J.; Grimes, H.; Daly, K.; Morrison, J.J. Cardiac troponin I in pre-eclampsia and gestational hypertension. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2000, 107, 1417–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherd, A.A.; Helmi, N.; Balamash, K.S.; Kumosani, T.A.; AL-Ghamdi, S.A.; Qari, M.; Huwait, E.A.; Yaghmoor, S.S.; Nabil, A.; AL-Ghamdi, M.A.; et al. Changes in erythrocyte ATPase activity under different pathological conditions. Afr. Health Sci. 2018, 17, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irani, R.A.; Xia, Y. Renin Angiotensin Signaling in Normal Pregnancy and Preeclampsia. Semin. Nephrol. 2011, 31, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świątkowska-Stodulska, R.; Kmieć, P.; Stefańska, K.; Sworczak, K. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in the Pathogenesis of Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2018, 126, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Rana, S.; Karumanchi, S.A. Preeclampsia: The Role of Angiogenic Factors in Its Pathogenesis. Physiology 2009, 24, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malha, L.; Sison, C.P.; Helseth, G.; Sealey, J.E.; August, P. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Profiles in Pregnant Women with Chronic Hypertension, Novelty and Significance. Hypertension 2018, 72, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutunea-Fatan, E.; Abd-Elrahman, K.S.; Thibodeau, J.F.; Holterman, C.E.; Holleran, B.J.; Leduc, R.; Kennedy, C.R.; Gros, R.; Ferguson, S.S. GRK2 knockdown in mice exacerbates kidney injury and alters renal mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinney, E.T.; Shouri, R.; Hunt, R.S.; Ahokas, R.A.; Sibai, B.M. Plasma, urinary, and salivary 8-epi-prostaglandin F2α levels in normotensive and preeclamptic pregnancies. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2000, 183, 874–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palm, M.; Axelsson, O.; Wernroth, L.; Basu, S. F2-Isoprostanes, tocopherols and normal pregnancy. Free. Radic. Res. 2009, 43, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van’t Erve, T.J.; Kadiiska, M.B.; London, S.J.; Mason, R.P. Classifying oxidative stress by F 2 -isoprostane levels across human diseases: A meta-analysis. Redox Boil. 2017, 12, 582–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, G.L.; Musiek, E.S.; Morrow, J.D. F2-Isoprostanes as markers of oxidative stressin vivo: An overview. Biomarkers 2005, 10, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
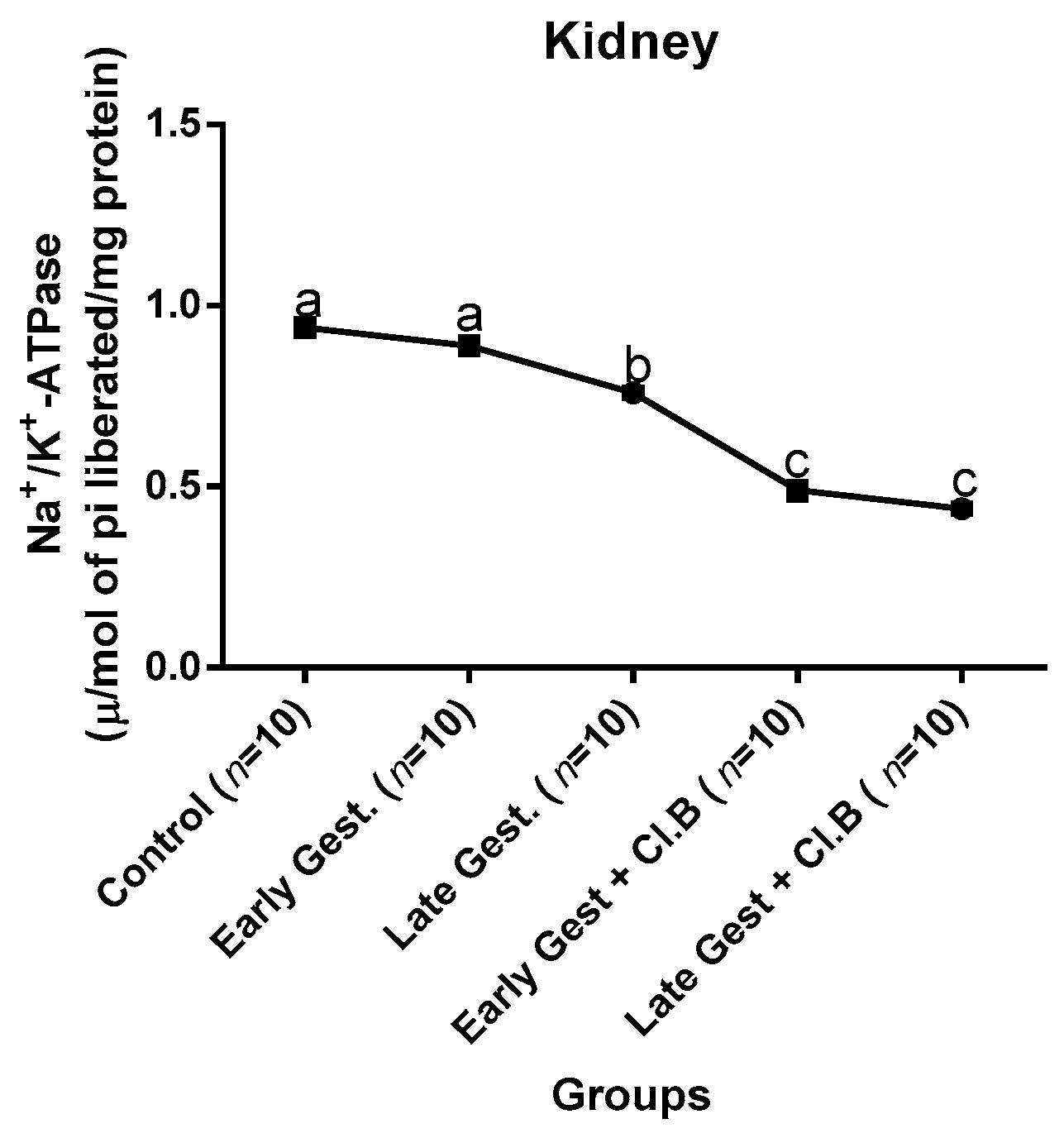
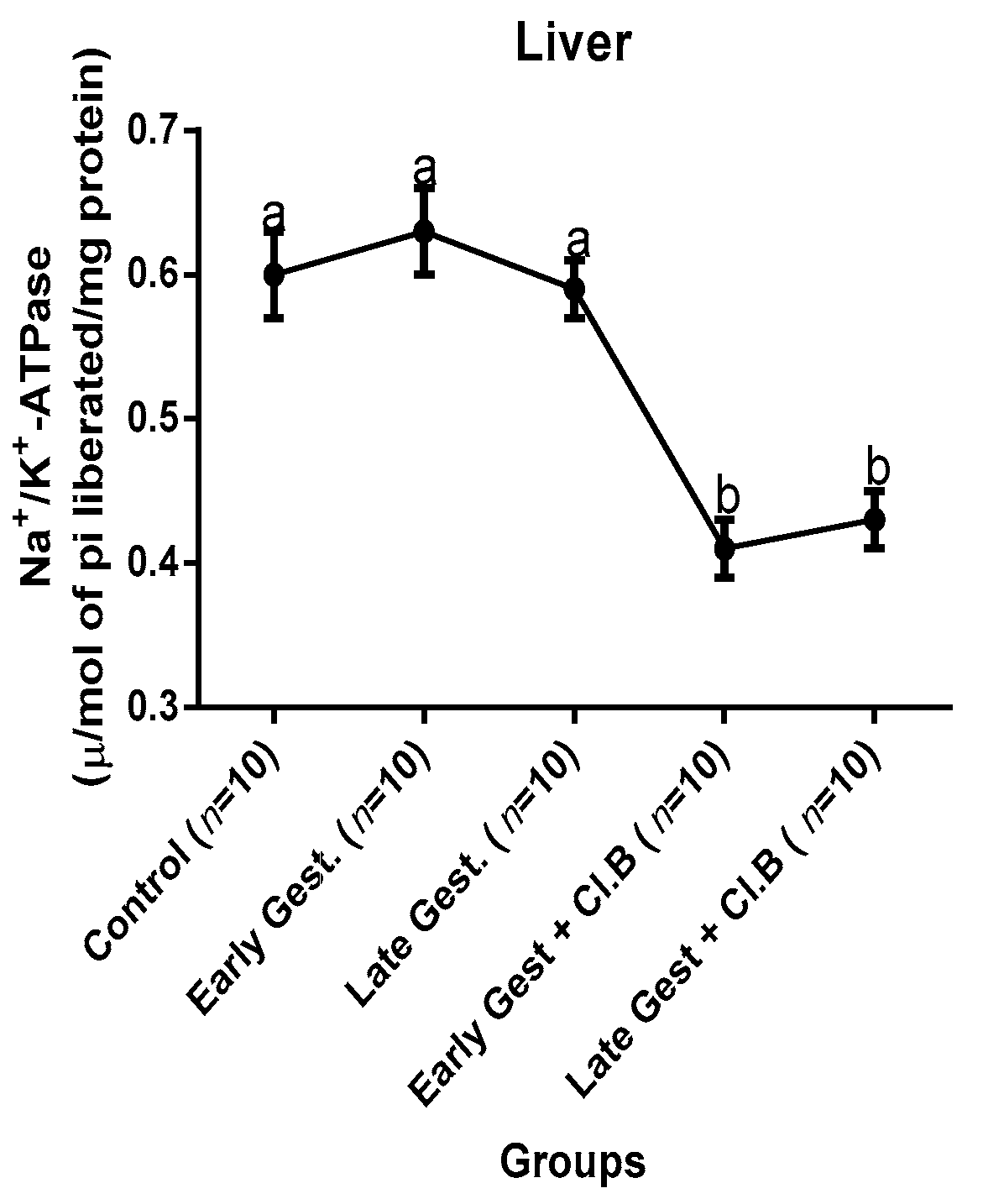
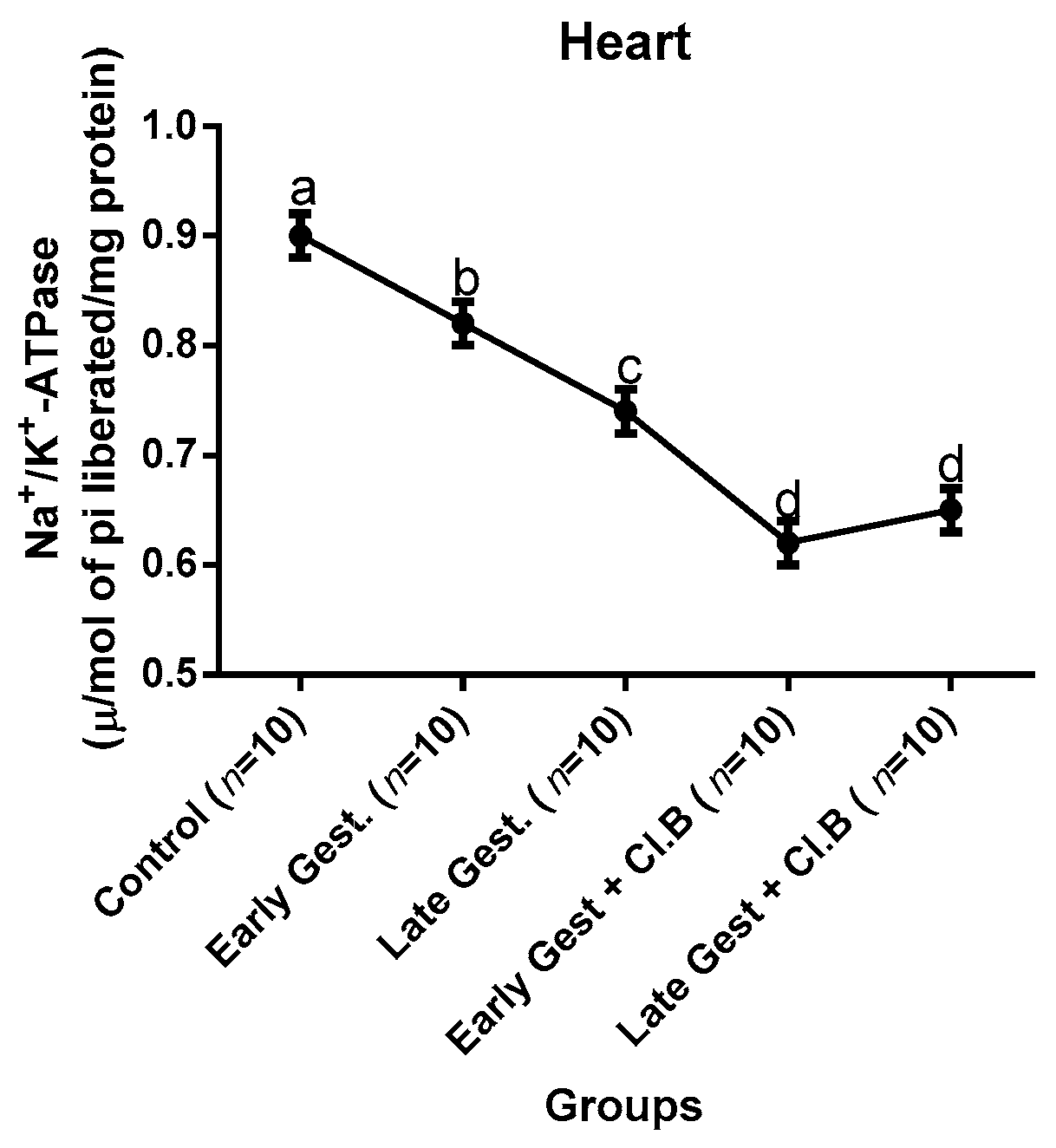
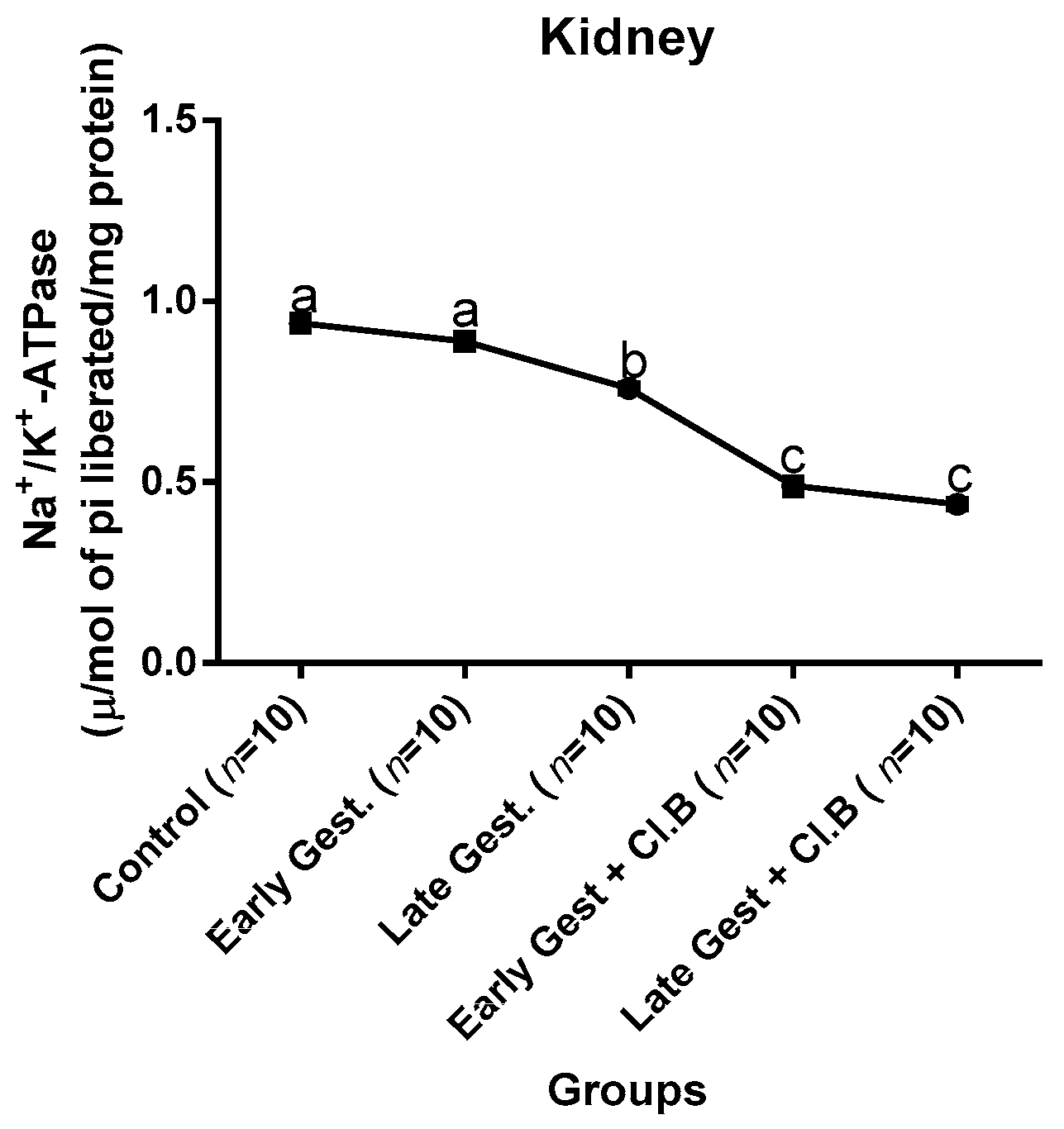
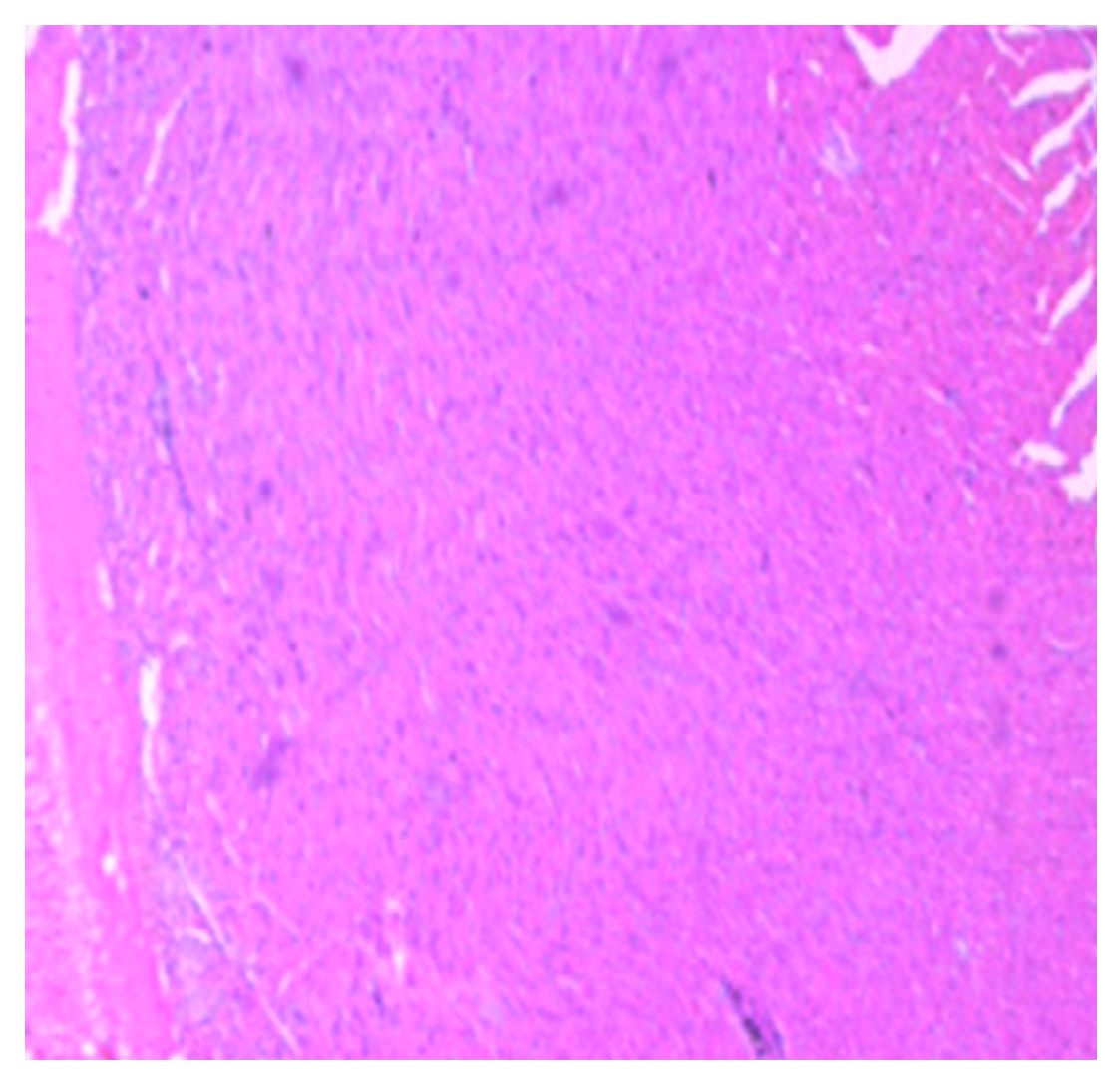
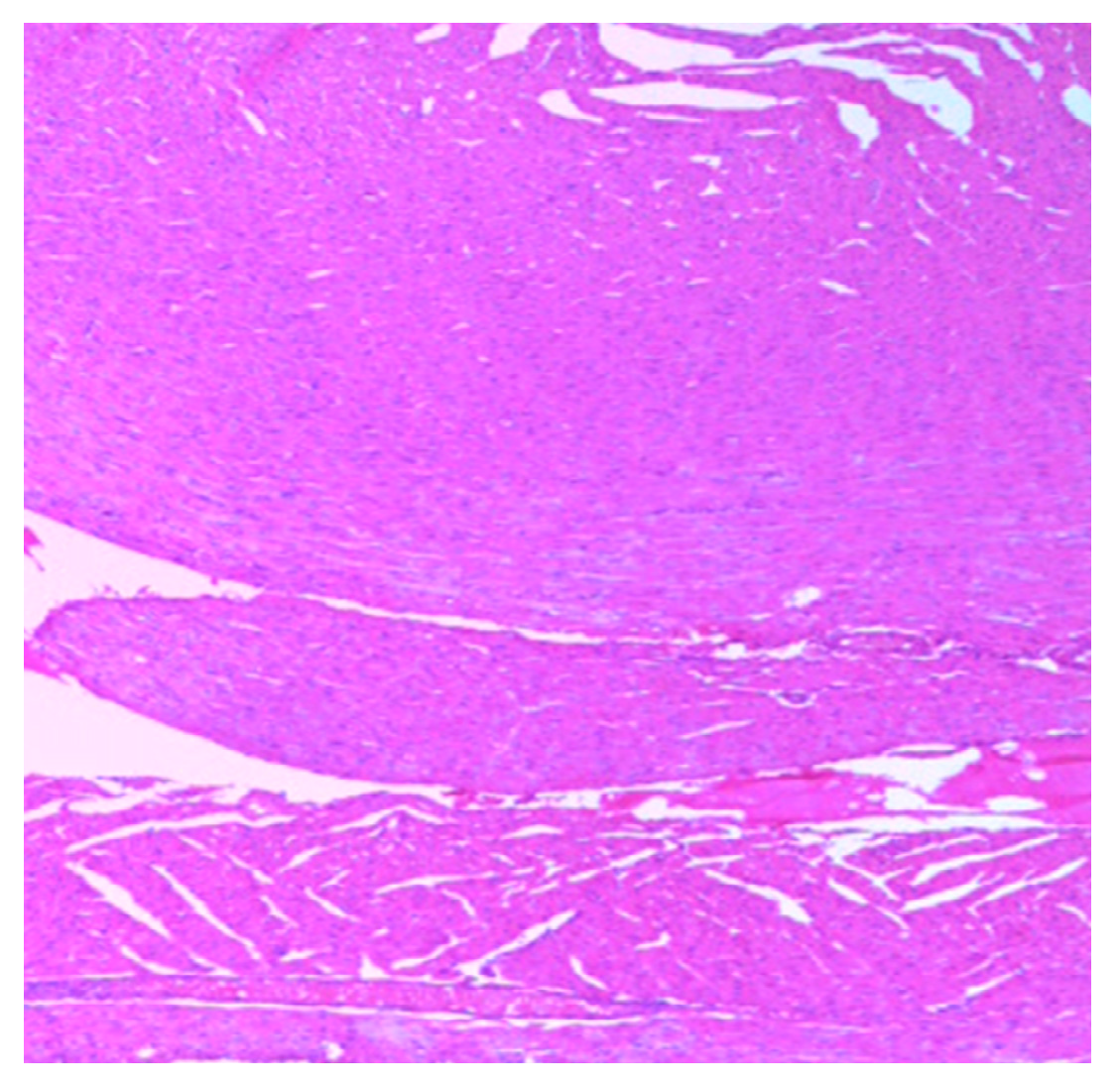
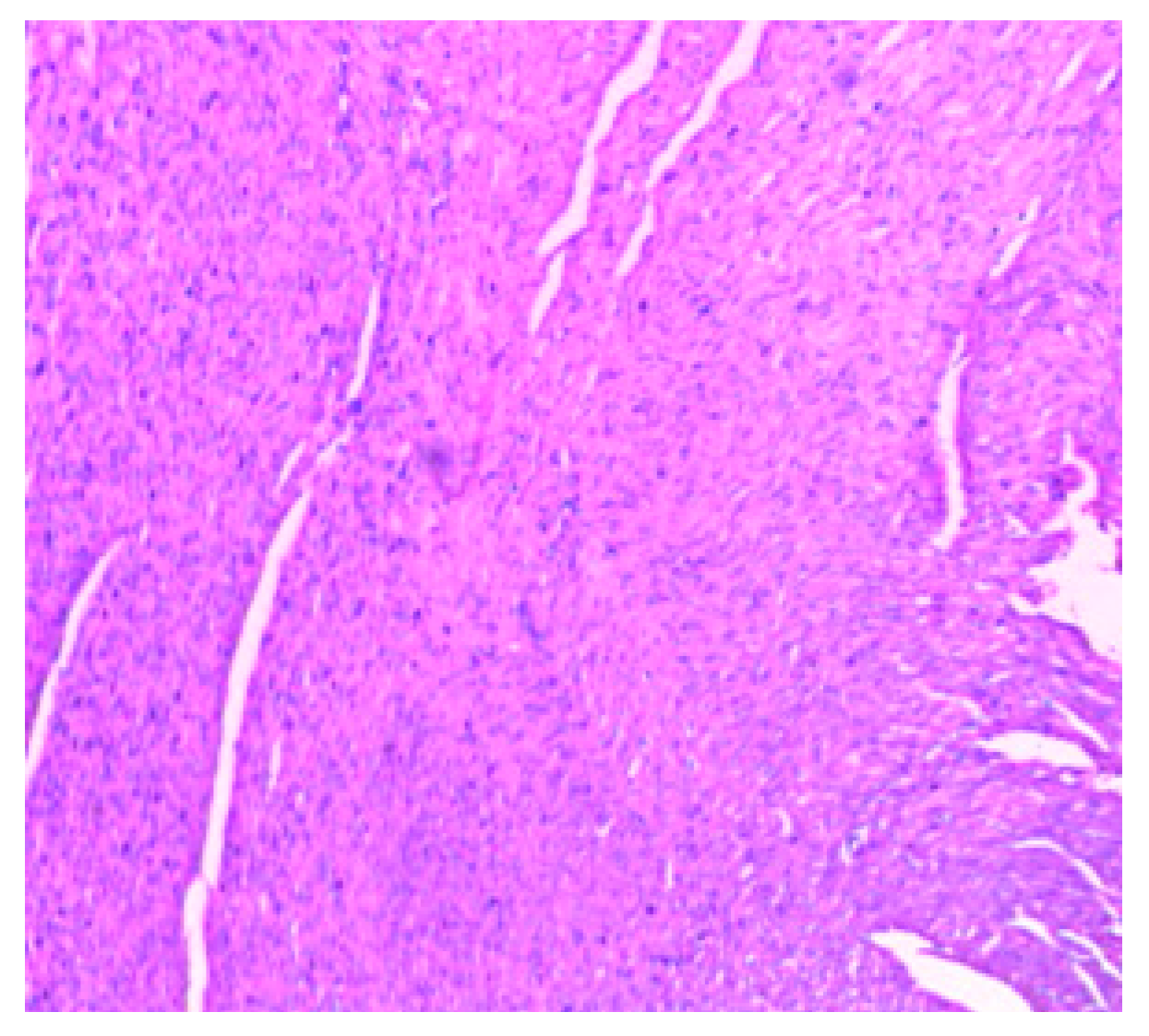
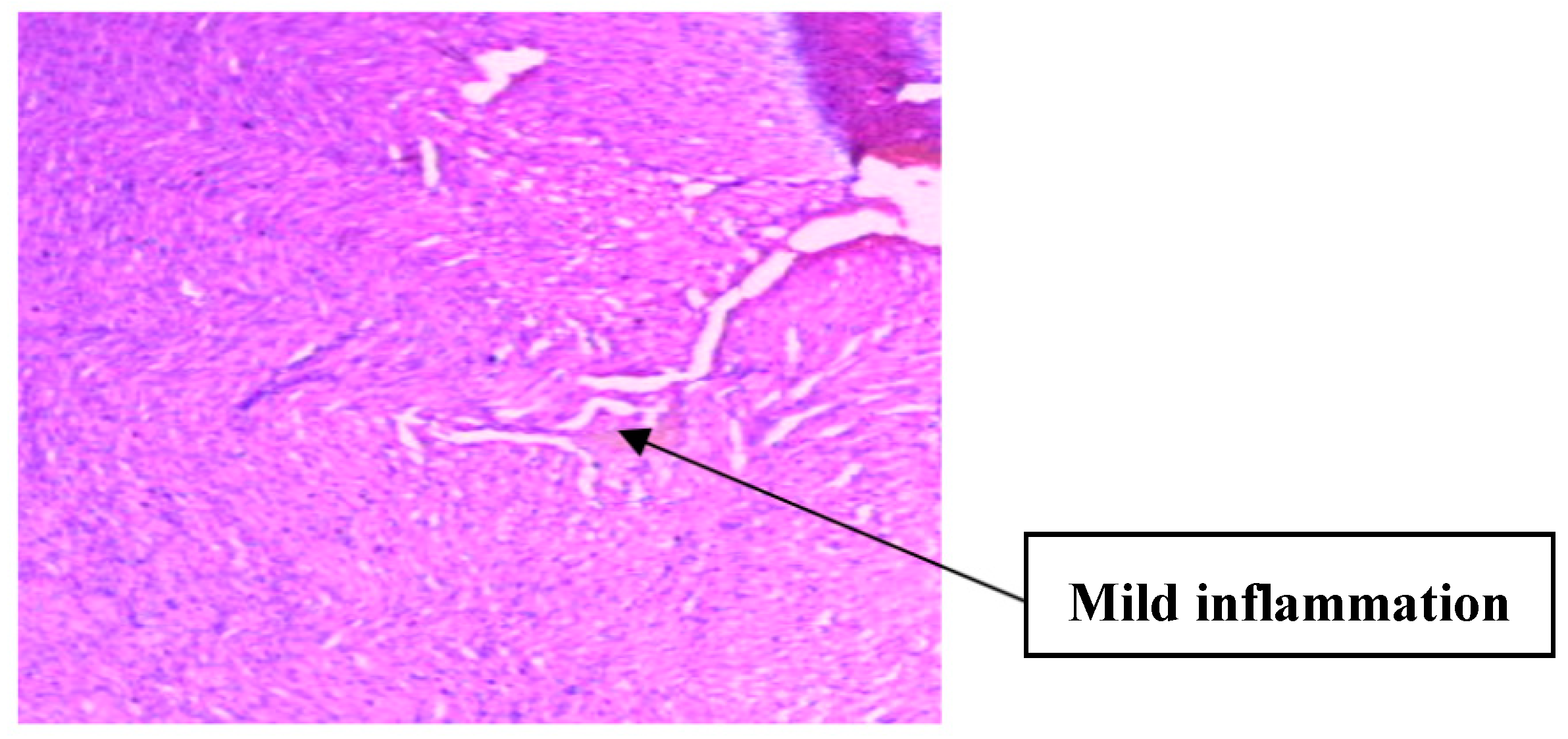
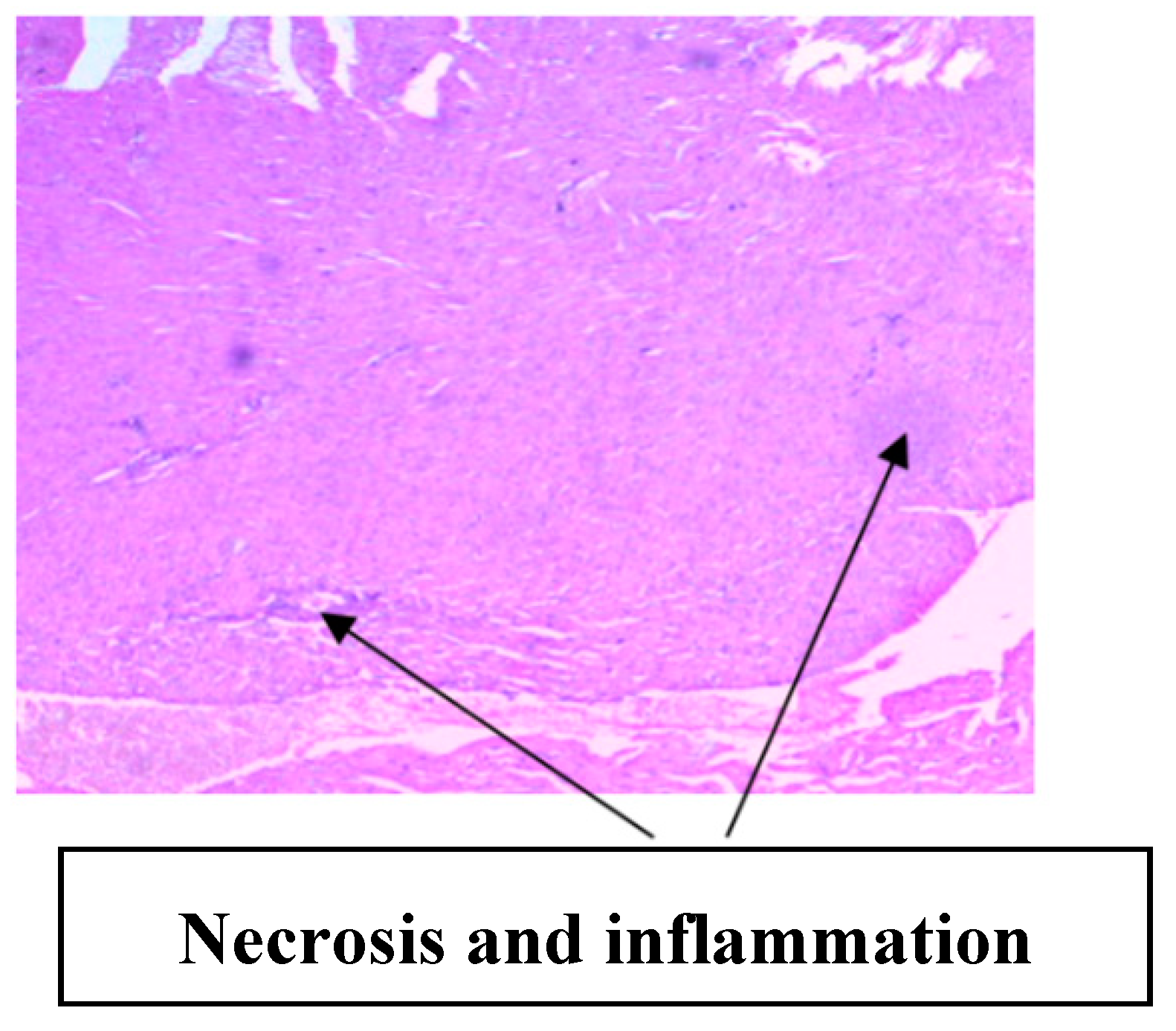
| Parameters | Control (n = 10) | E.G (n = 10) | L.G (n = 10) | E.G + Cl.B (n = 10) | L.G + Cl.B (n = 10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BW (g) | 195.36±7.26a | 253.40±6.44b | 296.05±7.23c | 216.21±4.45d | 237.50±5.21e |
| LW (g) | 9.45±0.62a | 11.31±0.79b | 12.81±1.05b | 9.41±0.40a | 9.83±0.62a |
| KW (g) | 1.94±0.12a | 1.99±0.20a | 1.92±0.33a | 1.84±0.57b | 1.79±0.44b |
| HW | 1.46±0.11a | 1.62±0.15a | 1.50±0.13a | 1.96±0.17b | 1.83±0.13b |
| PW | 0.93±0.08a | 0.90±0.07a | 0.92±0.06a | 0.94±0.07a | 0.95±0.11a |
| DIU (mL) | 4.97±0.21a | 7.25±0.55b | 7.57±0.48b | 3.08±0.33c | 2.59±0.35c |
| GFR * | 0.63±0.06a | 0.84±0.09b | 0.89±0.07b | 0.77±0.08c | 0.70±0.08c |
| Anion gap | 9.97 | 9.76 | 10.07 | 14.18 | 18.50 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 27.01±1.73a | 20.80±2.12b | 18.11±1.19b | 37.36±3.94c | 39.22±2.04c |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.52±0.07a | 0.44±0.05b | 0.41±0.06b | 0.66±0.09c | 0.69±0.05c |
| BUN/Crt | 51.94 | 47.27 | 44.17 | 56.60 | 56.86 |
| Groups | HBR (Beat/Min) | AIP | CRR | AC | CRT-Kin(U/L) | TROP(ng/mL) | LDH (U/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control (n = 10) | 320.5±9.5a | 0.25 | 2.73 | 1.73 | 377.1±11.7a | 3.40±0.4a | 248.3±14.4a |
| E.G (n = 10) | 327.8±8.6a | 0.30 | 2.90 | 1.90 | 382.1±8.9a | 3.51±0.6a | 239.4±17.1a |
| L.G (n = 10) | 349.4±10.1b | 0.31 | 3.00 | 2.00 | 390.8±8.6a | 3.47±0.4a | 259.4±11.9a |
| E.G + Cl.B (n = 10) | 372.3±7.7c | 0.53 | 4.74 | 3.74 | 443.9±14.1b | 4.82±0.6c | 329.7±19.3b |
| L.G + Cl.B (n = 10) | 380.4±11.8c | 0.46 | 4.51 | 3.51 | 470.2±16.6c | 4.99±0.5d | 302.4±16.9b |
| Groups | REN (ng/mL) | ALD (ng/mL) | ANG (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control (n = 10) | 61.8±5.5a | 177.2±13.5a | 76.6±5.1a |
| E.G (n = 10) | 97.4±6.1b | 286.6±18.4b | 104.9±7.2b |
| L.G (n = 10) | 92.2±8.5b | 317.2±16.0c | 99.4±8.0b |
| E.G + Cl.B (n = 10) | 50.5±5.9c | 94.1±7.7d | 53.6±4.2c |
| L.G + Cl.B (n = 10) | 43.3±4.7d | 82.5±8.2e | 55.8±3.9c |
| Group | F2-Isoprostane (pg/mL) | MDA * | GRase ** | CAT (U/mg) | SOD (U/mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control (n = 10) | 21.4±0.04a | 0.48±0.07a | 7.50±1.7a | 59.17±5.3a | 15.50±2.1a |
| E.G (n = 10) | 26.9±0.04b | 0.59±0.06c | 7.71±1.1a | 61.91±3.9a | 19.26±1.8b |
| L.G (n = 10) | 28.0±0.03b | 0.62±0.07c | 8.04±1.5a | 60.27±3.1a | 21.49±2.4b |
| E.G + Cl.B (n = 10) | 37.3±0.06c | 0.79±0.08d | 6.13±1.3b | 46.52±5.9b | 8.30±1.4c |
| L.G + Cl.B (n = 10) | 35.4±0.05c | 0.83±0.06d | 5.93±0.9b | 43.80±4.4b | 8.09±0.8c |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agomuo, E.N.; Amadi, P.U.; Adumekwe, C. Gestational Geophagia Affects Nephrocardiac Integrity, ATP-Driven Proton Pumps, the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System, and F2-Isoprostane Status. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci7020013
Agomuo EN, Amadi PU, Adumekwe C. Gestational Geophagia Affects Nephrocardiac Integrity, ATP-Driven Proton Pumps, the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System, and F2-Isoprostane Status. Medical Sciences. 2019; 7(2):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci7020013
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgomuo, Emmanuel Nnabugwu, Peter Uchenna Amadi, and Chiamaka Adumekwe. 2019. "Gestational Geophagia Affects Nephrocardiac Integrity, ATP-Driven Proton Pumps, the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System, and F2-Isoprostane Status" Medical Sciences 7, no. 2: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci7020013
APA StyleAgomuo, E. N., Amadi, P. U., & Adumekwe, C. (2019). Gestational Geophagia Affects Nephrocardiac Integrity, ATP-Driven Proton Pumps, the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System, and F2-Isoprostane Status. Medical Sciences, 7(2), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci7020013





