Comorbidities and Complications in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pulmonary Emphysema
3. Gastroesophageal Reflux
4. Lung Cancer
5. Pulmonary Hypertension
6. Sleep Disorders in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
7. Acute Exacerbation
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cottin, V.; Nunes, H.; Brillet, P.Y.; Delaval, P.; Devouassoux, G.; Tillie-Leblond, I.; Israel-Biet, D.; Court-Fortune, I.; Valeyre, D.; Cordier, J.F.; et al. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: A distinct underrecognised entity. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryerson, C.J.; Hartman, T.; Elicker, B.M.; Ley, B.; Lee, J.S.; Abbritti, M.; Jones, K.D.; King, T.E., Jr.; Ryu, J.; Collard, H.R. Clinical features and outcomes in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2013, 144, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejia, M.; Carrillo, G.; Rojas-Serrano, J.; Estrada, A.; Suárez, T.; Alonso, D.; Barrientos, E.; Gaxiola, M.; Navarro, C.; Selman, M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: Decreased survival associated with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. Chest 2009, 136, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, K.B.; Samet, J.M.; Stidley, C.A.; Colby, T.V.; Waldron, J.A. Cigarette smoking: A risk factor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.R.; Gazzana, M.B.; Barretto, S.S.; Knorst, M.M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema in smokers. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2008, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, J.M.; Collard, H.R. Comorbid Conditions in idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Recognition and Management. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurashima, K.; Takayanagi, N.; Tsuchiya, N.; Kanauchi, T.; Ueda, M.; Hoshi, T.; Miyahara, Y.; Sugita, Y. The effect of emphysema on lung function and survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology 2010, 15, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohashi, Y.; Arai, T.; Sugimoto, C.; Tachibana, K.; Akira, M.; Kitaichi, M.; Hayashi, S.; Inoue, Y. Clinical impact of emphysema evaluated by high-resolution computed tomography on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis diagnosed by surgical lung biopsy. Respiration 2016, 92, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G. Silent gastro-esophageal reflux and microaspiration in IPF: Mounting evidence for anti-reflux therapy? Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 39, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Collard, H.R.; Raghu, G.; Sweet, M.P.; Hays, S.R.; Campos, G.M.; Golden, J.A.; King, T.E., Jr. Does chronic microaspiration cause idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Am. J. Med. 2010, 123, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Ryu, J.H.; Elicker, B.M.; Lydell, C.P.; Jones, K.D.; Wolters, P.J.; King, T.E., Jr.; Collard, H.R. Gastroesophageal Reflux Therapy Is Associated with Longer Survival in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 1390–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Freudenberger, T.D.; Yang, S.; Curtis, J.R.; Spada, C.; Hayes, J.; Sillery, J.K.; Pope, C.E., 2nd; Pellegrini, C.A. High prevalence of abnormal acid gastro-oesophageal reflux in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savarino, E.; Carbone, R.; Marabotto, E.; Furnari, M.; Sconfienza, L.; Ghio, M.; Zentilin, P.; Savarino, V. Gastro-oesophageal reflux and gastric aspiration in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madan, K.; Ahuja, V.; Gupta, S.D.; Bal, C.; Kapoor, A.; Sharma, M.P. Impact of 24-h esophageal pH monitoring on the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease: Defining the gold standard. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 20, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, R.; Lord, C.; Nurko, S. The sensitivity of multichannel intraluminal impedance and the pH probe in the evaluation of gastroesophageal reflux in children. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hila, A.; Agrawal, A.; Castell, D.O. Combined multichannel intraluminal impedance and pH esophageal testing compared to pH alone for diagnosing both acid and weakly acidic gastroesophageal reflux. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S. Bronchoalveolar lavage pepsin in acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 39, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tcherakian, C. Progression of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Lessons from asymetrical disease. Thorax 2011, 66, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Kim, D.S.; Shim, T.S.; Lim, C.M.; Koh, Y.; Lee, S.D.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, W.D.; Lee, J.S.; Song, K.S. Lung cancer in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 17, 1216–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Jeune, I.; Gribbin, J.; West, J.; Smith, C.; Cullinan, P.; Hubbard, R. The incidence of cancer in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and sarcoidosis in the UK. Respir. Med. 2007, 101, 2534–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, Y.; Suda, T.; Naito, T.; Enomoto, N.; Hashimoto, D.; Fujisawa, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Inui, N.; Nakamura, H.; Chida, K. Cumulative incidence of and predictive factors for lung cancer in IPF. Respirology 2009, 14, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karampitsakos, T.; Tzilas, V.; Tringidou, R.; Steiropoulos, P.; Aidinis, V.; Papiris, S.A.; Bouros, D.; Tzouvelekis, A. Lung cancer in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calio, A.; Lever, V.; Rossi, A.; Gilioli, E.; Brunelli, M.; Dubini, A.; Tomassetti, S.; Piciucchi, S.; Nottegar, A.; Rossi, G.; et al. Increased frequency of bronchiolar histotypes in lung carcinomas associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Histopathology 2017, 71, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Kaiser, R.; Mellemgaard, A.; Douillard, J.Y.; Orlov, S.; Krzakowski, M.; von Pawel, J.; Gottfried, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Liao, M.; et al. Docetaxel plus nintedanib versus docetaxel plus placebo in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (LUME-Lung 1): A phase 3, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediavilla-Varela, M.; Boateng, K.; Noyes, D.; Antonia, S.J. The anti-fibrotic agent pirfenidone synergizes with cisplatin in killing tumor cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Bogaard, H.J.; Condliffe, R.; Frantz, R.; Khanna, D.; Kurzyna, M.; Langleben, D.; Manes, A.; Satoh, T.; Torres, F.; et al. Definitions and diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, D42–D50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harari, S.; Elia, D.; Humbert, D. Pulmonary hypertension in parenchymal lung disease: Any future for new therapies? Chest 2018, 153, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottin, V.; Le Pavec, J.; Prevot, G.; Mal, H.; Humbert, M.; Simonneau, G.; Cordier, J.F. Pulmonary hypertension in patients with combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema syndrome. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lettieri, C.J.; Nathan, S.D.; Barnett, S.D.; Ahmad, S.; Shorr, A.F. Prevalence and outcomes of pulmonary arterial hypertension in advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2006, 129, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collum, S.D.; Amione-Guerra, J.; Cruz-Solbes, A.-S.; DiFrancesco, A.; Hernandez, A.M.; Hanmandlu, A.; Youker, K.; Guha, A.; Karmouty-Quintana, H. Pulmonary hypertension associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Current and future perspectives. Can. Respir. J. 2017, 2017, 1430350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shorr, A.F.; Wainwright, J.L.; Cors, C.S.; Lettieri, C.J.; Nathan, S.D. Pulmonary hypertension in patients with pulmonary fibrosis awaiting lung transplant. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 30, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, S.D.; Cottin, V. Pulmonary hypertension in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. In Pulmonary Hypertension (ERS Monograph) Sheffield; Hoeper, M.M., Humbert, M., Eds.; European Respiratory Society: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 148–160. [Google Scholar]
- Minai, O.A.; Santacruz, J.F.; Alster, J.M.; Budev, M.M.; McCarthy, K. Impact of pulmonary hemodynamics on 6-min walk test in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Med. 2009, 106, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galie, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachieri, J.L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A.; Simonneau, G.; Peacock, A.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Beghetti, M.; et al. ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 903–975. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kimura, A.; Taniguchi, H.; Kondoh, Y.; Kimura, T.; Kataoka, K.; Nishiyama, O.; Aso, H.; Sakamoto, K.; Hasegawa, Y. Pulmonary hypertension as a prognostic indicator at initial evaluation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respiration 2013, 85, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boer, K.; Lee, J.S. Under-recognised co-morbidities in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A review. Respirology 2016, 21, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, S.D.; Shlobin, O.A.; Barnett, S.D.; Saggar, R.; Belperio, J.A.; Ross, D.J.; Ahmad, S.; Saggar, R.; Libre, E.; Lynch, J.P., 3rd; et al. Right ventricular systolic pressure by echocardiography as a predictor of pulmonary hypertension in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Med. 2008, 102, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkukhun, L.; Wang, X.F.; Ahmed, M.K.; Baumgartner, M.; Budev, M.M.; Dweik, R.A.; Tonelli, A.R. Non-invasive screening for pulmonary hypertension in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Med. 2016, 117, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, S.D.; Shlobin, O.A.; Ahmad, S.; Urbanek, S.; Barnett, S.D. Pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary function testing in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2007, 131, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, T.; Kondoh, Y.; Taniguchi, H.; Yagi, M.; Matsuda, T.; Kimura, T.; Kataoka, K.; Johkoh, T.; Ando, M.; Hashimoto, N.; et al. A scoring system to predict the elevation of mean pulmonary arterial pressure in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1701311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Egan, J.J.; Kawut, S.M.; Flaherty, K.R.; Martinez, F.J.; Nathan, S.D.; Wells, A.U.; Collard, H.R.; et al. Treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with ambrisentan: A parallel, randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 641–649, Erratum in Ann. Intern. Med. 2014, 160, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Clinical Research Network. A controlled trial of sildenafil in advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 3, 620–628. [Google Scholar]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Behr, J.; Held, M.; Grunig, E.; Vizza, C.D.; Vonk-Noordegraaf, A.; Lange, T.J.; Claussen, M.; Grohé, C.; Klose, H.; et al. Pulmonary hypertension in patients with chronic fibrosing idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mermigkis, C.; Bouloukaki, I.; Schiza, S. Sleep as a new target for improving outcomes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2017, 152, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mermigkis, C.; Bouloukaki, I.; Antoniou, K.; Papadogiannis, G.; Giannarakis, I.; Varouchakis, G.; Siafakas, N.; Schiza, S.E. Ostructive sleep apnea should be treated in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sleep Breath. 2015, 19, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mermigkis, C.; Sagaki, E.; Tryfon, S.; Schiza, S.; Amfilochiou, A.; Polychronopoulos, V.; Panagou, P.; Galanis, N.; Kallianos, A.; Mermigkis, D.; et al. How common is sleep-disordered breathing in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Sleep Breath. 2010, 14, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, H.L.; Masson, W.R.; Parnell, J.A.; Rice, T.W.; Loyd, J.E.; Milstone, A.P.; Collard, H.R.; Malow, B.A. Obstructive sleep apnea is common in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2009, 136, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, M.; Olson, A.L.; Huie, T.J.; Solomon, J.J.; Fernandez-Perez, E.R.; Brown, K.K.; Hanna, P.; Lee-Chiong, T.; Swigris, J.J. Obstructive sleep apnea does not promote esophageal reflux in fibrosing interstitial lung disease. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Padilla, R.; West, P.; Lertzman, M.; Kryger, M. Breathing during sleep in patients with interstitial lung disease. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1985, 132, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Corte, T.J.; Wort, S.J.; Talbot, S.; Macdonald, P.M.; Hansel, D.M.; Polkey, M.; Renzoni, E.; Maher, T.M.; Nicholson, A.G.; Wells, A.U. Elevated nocturnal desaturation index predicts mortality in interstitial lung disease. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2012, 29, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Collard, H.R.; Ryerson, C.J.; Corte, T.J.; Jenkins, G.; Kondoh, Y.; Lederer, D.J.; Lee, J.S.; Maher, T.M.; Wells, A.U.; Antoniou, K.M.; et al. Acute exacerbationa of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An international Working Group Report. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Park, J.H.; Park, B.K.; Lee, J.S.; Nicholson, A.G.; Colby, T. Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Frequency and clinicalfeatures. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemptinne, Q.; Remmelink, M.; Brimioulle, S.; Salmon, I.; Vincent, J.L. ARDS: A clinicopathological confrontation. Chest 2009, 135, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, K.; Ishimoto, H.; Yamada, S.; Kushima, H.; Ishii, H.; Imanaga, T.; Harada, T.; Ishimatsu, Y.; Matsumoto, N.; Naito, K.; et al. Autopsy analyses in acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon-Blancal, V.; Freynet, O.; Nunes, H.; Bouvry, D.; Naggara, N.; Brillet, P.Y.; Denis, D.; Cohen, Y.; Vincent, F.; Valeyre, D.; et al. Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Outcome and prognostic factors. Respiration 2012, 83, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondoh, Y.; Taniguchi, H.; Katsuta, T.; Kataoka, K.; Kimura, T.; Nishiyama, O.; Sakamoto, K.; Johkoh, T.; Nishimura, M.; Ono, K.; et al. Risk factors of acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2010, 27, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Natsuizaka, M.; Chiba, H.; Kuronuma, K.; Otsuka, M.; Kudo, K.; Mori, M.; Bando, M.; Sugiyama, Y.; Takahashi, H. Epidemiologic survey of Japanese patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and investigation of ethnic differences. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
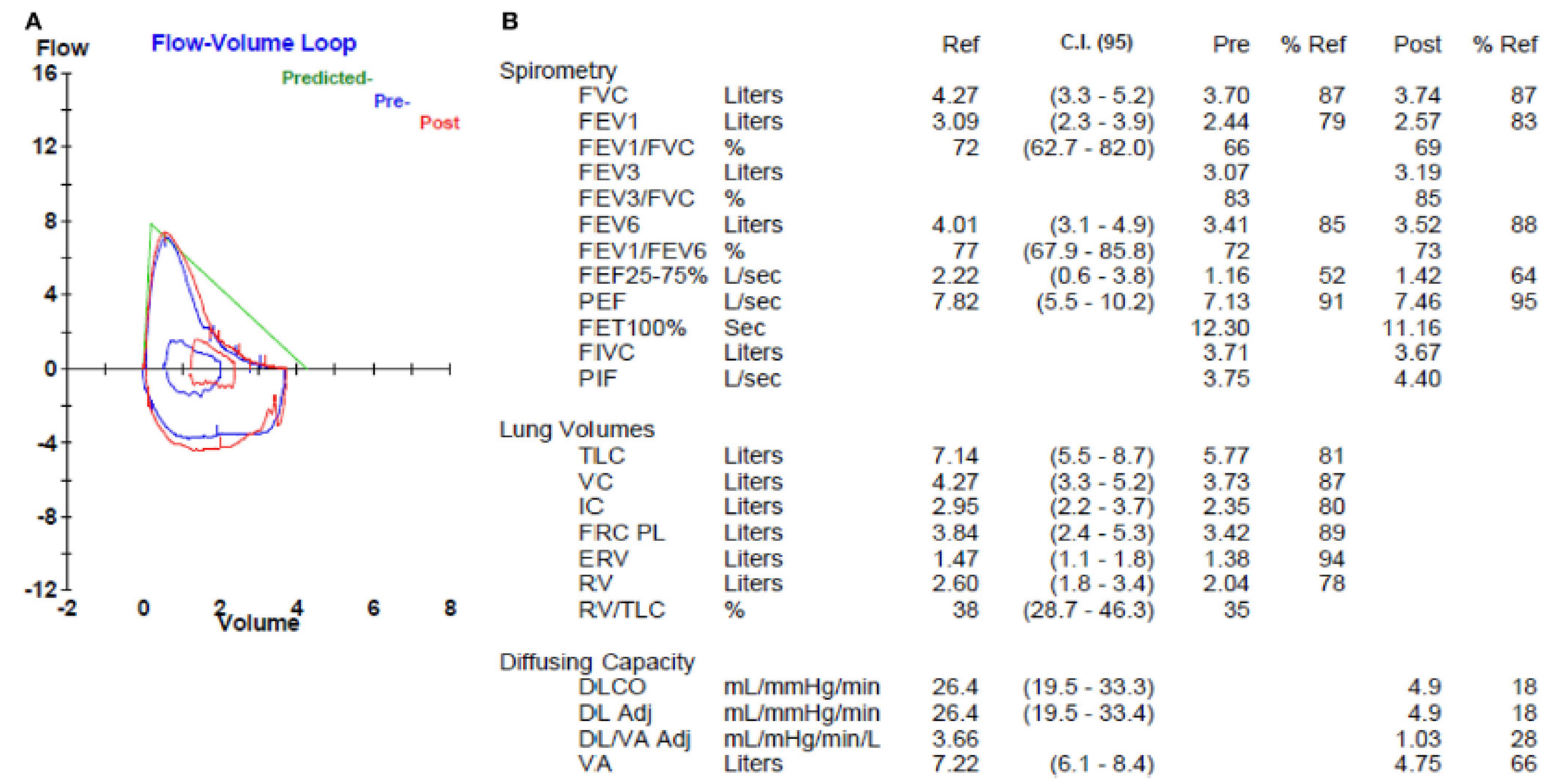
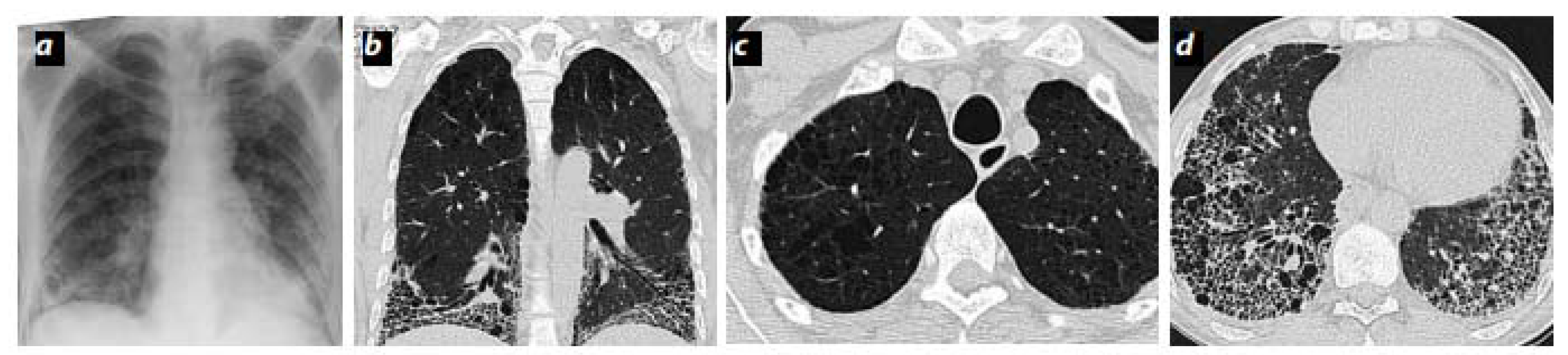
| Terminology | Haemodynamics (Right Heart Catetherization) |
|---|---|
| COPD/IPF/CPFE without PH | mPAP < 25 mmHg |
| COPD/IPF/CPFE with PH | mPAP ≥ 25 mmHg |
| COPD/IPF/CPFE with severe PH | mPAP > 35 mmHg, or mPAP ≥ 25 mmHg in the presence of low cardiac output (CI < 2.5 L/min/m2, not explained by other causes) |
| Sleep Macro and Microarchitecture | Increased Stage N1 Sleep, Arousal Index, WASO Decreased REM, Slow-Wave Sleep, and Sleep Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Respiratory pattern | Increased respiratory frequency during sleep |
| Rapid and shallow breathing (especially during REM sleep) | |
| Nocturnal oxygenation parameters | Episodic desaturation during REM sleep |
| Desaturation during NREM sleep | |
| Desaturation due to respiratory events (apneas and hypopneas) | |
| Sleep-disordered breathing and other sleep problems | Increased incidence of OSA |
| Increased periodic leg movements during sleep Insomnia | |
| Nocturnal cough |
| Revised Definition |
| Acute, clinically significant respiratory deterioration characterized by evidence of new widespread alveolar abnormality |
| Revised Diagnostic Criteria |
| Previous or concurrent diagnosis of IPF |
| Acute worsening of development of dyspnea typically with less than one-month duration |
| CT scan with new bilateral ground-glass opacity and/or consolidation superimposed on a background with usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) pattern |
| Deterioration not fully explained by cardiac failure or fluid overload |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cano-Jiménez, E.; Hernández González, F.; Peloche, G.B. Comorbidities and Complications in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci6030071
Cano-Jiménez E, Hernández González F, Peloche GB. Comorbidities and Complications in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Medical Sciences. 2018; 6(3):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci6030071
Chicago/Turabian StyleCano-Jiménez, Esteban, Fernanda Hernández González, and Guadalupe Bermudo Peloche. 2018. "Comorbidities and Complications in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis" Medical Sciences 6, no. 3: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci6030071
APA StyleCano-Jiménez, E., Hernández González, F., & Peloche, G. B. (2018). Comorbidities and Complications in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Medical Sciences, 6(3), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci6030071




