Molecular Characterization of Peripheral Extracellular Vesicles in Clinically Isolated Syndrome: Preliminary Suggestions from a Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Extracellular Vesicles Purification
2.3. Total RNA Isolation
2.4. Small RNA Deep Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatic and Statistical Analysis of Small RNA Data
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Take-Home Messages
- The analysis of EVs contents (especially sRNAs) may help to provide more information on their functional role(s) in several diseases; EVs contents may also be used for the isolation of circulating biomarkers (e.g., miRNAs).
- Few studies have investigated both the EV classes (Microvesicles and Exosomes) extracted simultaneously from the peripheral blood samples in the same patient, but this strategy should be suggested in order to fully understand the entire molecular picture of a given status.
- smallRNA deep sequencing is a valuable approach for studying the different classes of small non-coding RNA, although a solid bioinformatics support is recommended for the analysis and the interpretation of the obtained results.
- In order to obtain the right amount of evRNAs for the subsequent sRNA-seq analysis, we suggest/recommend to collect a higher quantity of blood samples (at least 20 mL/each) or to pool together samples belonging to different subjects with the same phenotype [34].
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prada, I.; Furlan, R.; Matteoli, M.; Verderio, C. Classical and unconventional pathways of vesicular release in microglia. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 61, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeis, C.; Fröhlich, D.; Kuo, W.P.; Krämer-Albers, E.M. Extracellular vesicles as mediators of neuron-glia communication. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yuan, T.; Tschannen, M.; Sun, Z.; Jacob, H.; Du, M.; Liang, M.; Dittmar, R.L.; Liu, Y.; Liang, M.; et al. Characterization of human plasma-derived exosomal RNAs by deep sequencing. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.P.; Breakefield, X.O. Role of exosomes/microvesicles in the nervous system and use in emerging therapies. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngolab, J.; Trinh, I.; Rockenstein, E.; Mante, M.; Florio, J.; Trejo, M.; Masliah, D.; Adame, A.; Masliah, E.; Rissman, R.A. Brain-derived exosomes from dementia with Lewy bodies propagate α-synuclein pathology. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2017, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lööv, C.; Scherzer, C.R.; Hyman, B.T.; Breakefield, X.O.; Ingelsson, M. α-Synuclein in Extracellular Vesicles: Functional Implications and Diagnostic Opportunities. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couch, Y.; Akbar, N.; Davis, S.; Fischer, R.; Dickens, A.M.; Neuhaus, A.A.; Burgess, A.I.; Rothwell, P.M.; Buchan, A.M. Inflammatory Stroke Extracellular Vesicles Induce Macrophage Activation. Stroke 2017, 48, 2292–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáenz-Cuesta, M.; Osorio-Querejeta, I.; Otaegui, D. Extracellular vesicles in multiple sclerosis: What are they telling us? Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 100. [Google Scholar]
- Verderio, C.; Muzio, L.; Turola, E.; Bergami, A.; Novellino, L.; Ruffini, F.; Riganti, L.; Corradini, I.; Francolini, M.; Garzetti, L.; et al. Myeloid microvesicles are a marker and therapeutic target for neuroinflammation. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 4, 610–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownlee, W.J.; Miller, D.H. Clinically isolated syndromes and the relationship to multiple sclerosis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáenz-Cuesta, M.; Irizar, H.; Castillo-Triviño, T.; Muñoz-Culla, M.; Osorio-Querejeta, I.; Prada, A.; Sepúlveda, L.; López-Mato, M.P.; López de Munain, A.; Comabella, M.; et al. Circulating microparticles reflect treatment effects and clinical status in multiple sclerosis. Biomark. Med. 2014, 8, 653–661. [Google Scholar]
- Vlassov, A.V.; Magdaleno, S.; Setterquist, R.; Conrad, R. Exosomes: Current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Amigorena, S.; Raposo, G.; Clayton, A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2006, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescitelli, R.; Lasser, C.; Szabo, T.G.; Kittel, A.; Eldh, M.; Dianzani, I.; Buzás, E.I.; Lötvall, J. Distinct RNA profiles in subpopulations of extracellular vesicles: Apoptotic bodies, microvesicles and exosomes. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conesa, A.; Madrigal, P.; Tarazona, S.; Gomez-Cabrero, D.; Cervera, A.; McPherson, A.; Szcześniak, M.W.; Gaffney, D.J.; Elo, L.L.; Zhang, X.; et al. A survey of best practices for RNA-seq data analysis. Genome Biol. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcel, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedländer, M.R.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Li, N.; Chen, W.; Rajewsky, N. miRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 1, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, D.J.; Franklin, J.L.; Dou, Y.; Liu, Q.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Beckler, M.D.; Weaver, A.M.; Vickers, K.; Prasad, N.; Levy, S.; et al. KRAS-dependent sorting of miRNA to exosomes. eLife 2015, 4, e07197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevanato, L.; Thanabalasundaram, L.; Vysokov, N.; Sinden, J.D. Investigation of content, stoichiometry and transfer of miRNA from human neural stem cell line derived exosomes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolte-‘t Hoen, E.N.M.; Buermans, H.P.J.; Waasdorp, M.; Stoorvogel, W.; Wauben, M.H.M.; ‘t Hoen, P.A.C. Deep sequencing of RNA from immune cell-derived vesicles uncovers the selective incorporation of small non-coding RNA biotypes with potential regulatory functions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 9272–9285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Balkom, B.W.M.; Eisele, A.S.D.; Pegtel, M.; Bervoets, S.; Verhaar, M.C. Quantitative and qualitative analysis of small RNAs in human endothelial cells and exosomes provides insights into localized RNA processing, degradation and sorting. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 26760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Hou, D.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Bian, Z.; Liang, X.; Cai, X.; et al. Exogenous plant MIR168a specifically targets mammalian LDLRAP1: Evidence of cross-kingdom regulation by microRNA. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selmaj, I.; Cichalewska, M.; Namiecinska, M.; Galazka, G.; Horzelski, W.; Selmaj, K.W.; Mycko, M.P. Global Exosome Transcriptome Profiling Reveals Biomarkers for Multiple Sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vistbakka, J.; Elovaara, I.; Lehtimäki, T.; Hagman, S. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers in progressive multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2017, 23, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pienimaeki-Roemer, A.; Konovalova, T.; Musri, M.M.; Sigruener, A.; Boettcher, A.; Meister, G.; Schmitz, G. Transcriptomic profiling of platelet senescence and platelet extracellular vesicles. Transfusion 2017, 57, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouin, K.; Peck, K.; Antes, T.; Johnson, J.L.; Li, C.; Vaturi, S.D.; Middleton, R.; de Couto, G.; Walravens, A.S.; Rodriguez-Borlado, L.; et al. A comprehensive method for identification of suitable reference genes in extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1347019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodosthenous, R.S.; Coull, B.A.; Lu, Q.; Vokonas, P.S.; Schwartz, J.D.; Baccarelli, A.A. Ambient particulate matter and microRNAs in extracellular vesicles: A pilot study of older individuals. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Lv, W.; Hu, X. Altered microRNA profiles in cerebrospinal fluid exosome in Parkinson disease and Alzheimer disease. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 37043–37053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S.B.; Zhang, H.; Cai, T.T.; Liu, Y.N.; Ni, J.J.; He, J.; Peng, J.Y.; Chen, Q.Y.; Mo, H.Y.; Jun-Cui; et al. Exosomal miR-24-3p impedes T-cell function by targeting FGF11 and serves as a potential prognostic biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2016, 40, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugli, G.; Cohen, A.M.; Bennett, D.A.; Shah, R.C.; Fields, C.J.; Hernandez, A.G.; Smalheiser, N.R. Plasma Exosomal miRNAs in Persons with and without Alzheimer Disease: Altered Expression and Prospects for Biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Qiupeng, Z.; Chunyang, B.; Li, S.; Guo, W.; Zhao, J.; Chen, D.; Gu, J.; He, X.; Huanget, S. Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: A promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 981–984. [Google Scholar]
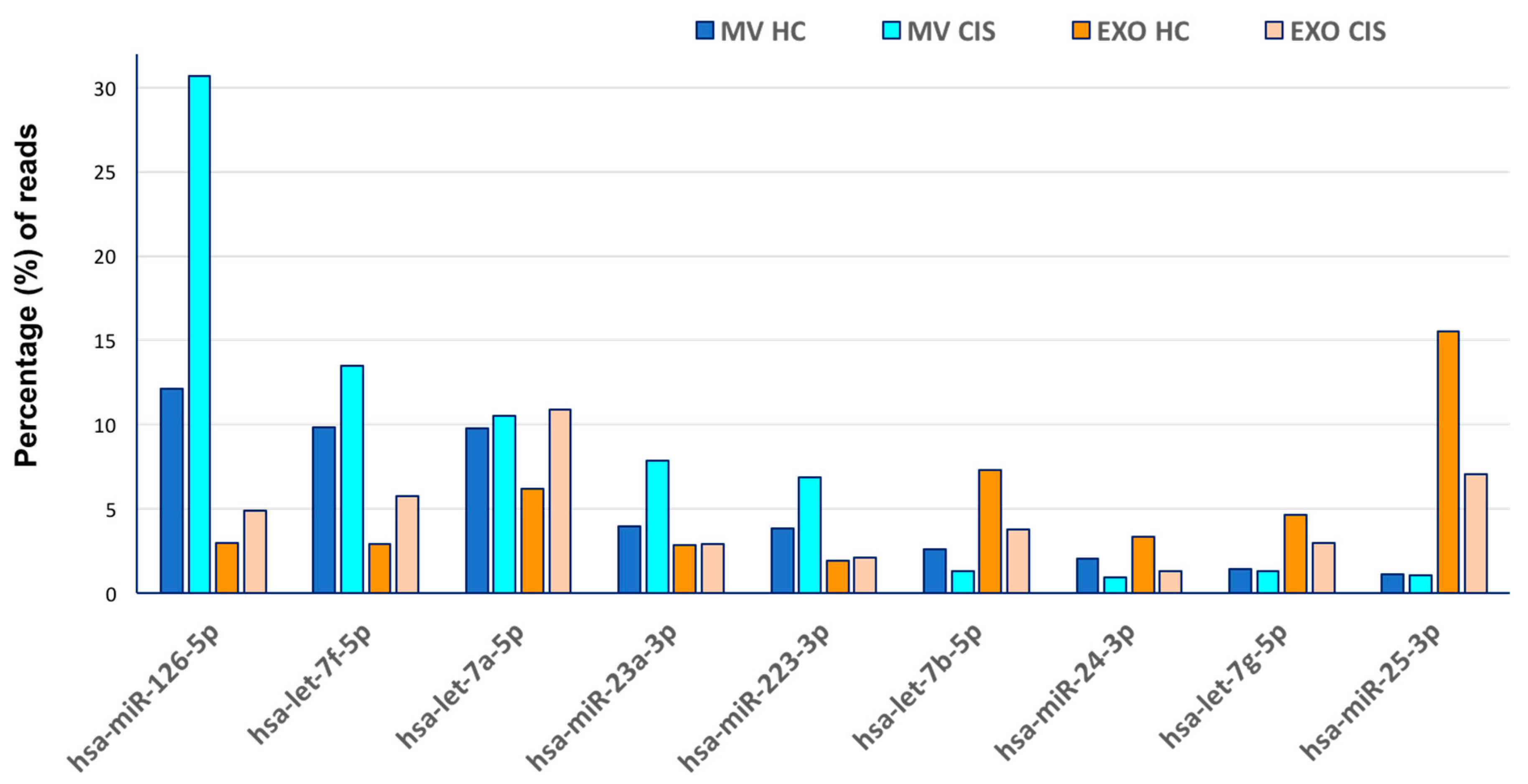
| Microvesicles | Exosomes | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HC-1 | HC-2 | CIS-1 | HC-3 | CIS-2 | ||||||
| Read Count | % | Read Count | % | Read Count | % | Read Count | % | Read Count | % | |
| Raw reads | 12,031,509 | 26,023,784 | 23,176,535 | 57,568,091 | 17,246,086 | |||||
| Clean reads (mapped/unmapped) | 3,851,795 | 18,679,042 | 7,845,182 | 39,163,534 | 10,030,669 | |||||
| Mapped ncRNA | ||||||||||
| miRNA | 73,459 | 1.91 | 143,322 | 0.77 | 1,382,492 | 17.62 | 829,102 | 2.12 | 91,160 | 0.91 |
| miRNA_primary_transcript | 13,089 | 0.34 | 12,758 | 0.07 | 66,145 | 0.84 | 5,419,917 | 13.84 | 520,722 | 5.19 |
| piRNA | 70,927 | 1.84 | 497,413 | 2.66 | 653,901 | 8.34 | 1,587,896 | 4.05 | 172,016 | 1.71 |
| misc_RNA | 52,601 | 1.37 | 273,814 | 1.47 | 119,722 | 1.53 | 178,440 | 0.46 | 77,591 | 0.77 |
| rRNA | 34,888 | 0.91 | 786,417 | 4.21 | 36,569 | 0.47 | 3,971,869 | 10.14 | 534,541 | 5.33 |
| snoRNA | 754 | 0.02 | 1330 | 0.01 | 3442 | 0.04 | 72,452 | 0.18 | 15,955 | 0.16 |
| snRNA | 2091 | 0.05 | 14,445 | 0.08 | 11,740 | 0.15 | 95,877 | 0.24 | 83,351 | 0.83 |
| SRP_RNA | 2810 | 0.07 | 22,088 | 0.12 | 7666 | 0.10 | 10,246 | 0.03 | 829 | 0.01 |
| tRNA | 12,925 | 0.34 | 465,531 | 2.49 | 42,955 | 0.55 | 276,975 | 0.71 | 23,337 | 0.23 |
| vault_RNA | 106 | 0.001 | 2331 | 0.01 | 793 | 0.001 | 14,463 | 0.04 | 2120 | 0.02 |
| Y_RNA | 27,020 | 0.70 | 276,914 | 1.48 | 454,862 | 5.80 | 390,174 | 1.00 | 31,963 | 0.32 |
| antisense | 28,863 | 0.75 | 90,018 | 0.48 | 44,561 | 0.57 | 347,191 | 0.89 | 95,003 | 0.95 |
| lincRNA | 573,422 | 14.89 | 215,484 | 1.15 | 338,285 | 4.31 | 1,227,887 | 3.14 | 1,289,945 | 12.86 |
| lncRNA | 158,954 | 4.13 | 214,994 | 1.15 | 102,465 | 1.31 | 279,388 | 0.71 | 177,791 | 1.77 |
| processed_transcript | 134,450 | 3.49 | 268,735 | 1.44 | 128,558 | 1.64 | 264,513 | 0.68 | 121,479 | 1.21 |
| retained_intron | 102,548 | 2.66 | 180,506 | 0.97 | 126,455 | 1.61 | 530,026 | 1.35 | 228,149 | 2.27 |
| Unmapped ncRNA | ||||||||||
| Human genome (GRCh38) | 856,079 | 22.23 | 1,643,508 | 8.80 | 1,975,727 | 25.18 | 16,540,083 | 42.23 | 5,153,999 | 51.38 |
| unmapped Human genome | 1,706,809 | 44.31 | 13,569,434 | 72.65 | 2,348,844 | 29.94 | 7,127,035 | 18.20 | 1,410,718 | 14.06 |
| MVs | EXOs | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCs-1-2 | CIS-1 | HC-3 | CIS-2 | ||||||||
| Transcript ID | Read Count * | % | Transcript ID | Read Count | % | Transcript ID | Read Count | % | Transcript ID | Read Count | % |
| hsa-miR-126-5p | 33,125.28 | 12.11 | hsa-miR-126-5p | 775,815 | 30.67 | hsa-miR-25-3p | 129,373 | 15.46 | hsa-let-7a-5p | 24,658 | 10.88 |
| hsa-let-7f-5p | 26,785.99 | 9.80 | hsa-let-7f-5p | 341,213 | 13.49 | hsa-let-7b-5p | 60,980 | 7.29 | hsa-miR-25-3p | 15,906 | 7.02 |
| hsa-let-7a-5p | 26,706.14 | 9.77 | hsa-let-7a-5p | 266,308 | 10.53 | hsa-miR-451a | 60,215 | 7.20 | hsa-miR-3908 | 15,510 | 6.84 |
| hsa-miR-142-3p | 16,230.72 | 5.94 | hsa-miR-23a-3p | 199,088 | 7.87 | hsa-let-7a-5p | 51,475 | 6.15 | hsa-let-7f-5p | 13,026 | 5.75 |
| hsa-miR-1246 | 15,182.89 | 5.55 | hsa-miR-223-3p | 172,699 | 6.83 | hsa-let-7g-5p | 38,560 | 4.61 | hsa-miR-126-5p | 11,069 | 4.88 |
| hsa-miR-126-3p | 11,081.05 | 4.05 | hsa-miR-150-5p | 113,228 | 4.48 | hsa-miR-19b-3p | 28,400 | 3.39 | hsa-miR-5096 | 10,094 | 4.45 |
| hsa-miR-23a-3p | 10,809.96 | 3.95 | hsa-miR-151a-3p | 34,022 | 1.35 | hsa-miR-24-3p | 28,108 | 3.36 | hsa-let-7b-5p | 8506 | 3.75 |
| hsa-miR-223-3p | 10,415.68 | 3.81 | hsa-let-7b-5p | 33,279 | 1.32 | hsa-miR-1246 | 26,006 | 3.11 | hsa-miR-1273c | 7323 | 3.23 |
| hsa-miR-150-5p | 10,384.42 | 3.80 | hsa-let-7g-5p | 32,259 | 1.28 | hsa-miR-126-5p | 24,775 | 2.96 | hsa-miR-8086 | 6988 | 3.08 |
| hsa-miR-1260b | 8540.57 | 3.12 | hsa-miR-146a-5p | 26,769 | 1.06 | hsa-miR-122-5p | 24,611 | 2.94 | hsa-let-7g-5p | 6770 | 2.99 |
| hsa-let-7b-5p | 7040.47 | 2.57 | hsa-miR-25-3p | 26,213 | 1.04 | hsa-let-7f-5p | 24,091 | 2.88 | hsa-miR-23a-3p | 6519 | 2.88 |
| hsa-miR-191-5p | 5648.99 | 2.07 | hsa-miR-24-3p | 23,816 | 0.94 | hsa-miR-23a-3p | 23,673 | 2.83 | hsa-miR-1290 | 6292 | 2.78 |
| hsa-miR-24-3p | 5522.51 | 2.02 | hsa-miR-1260b | 23,499 | 0.93 | hsa-miR-486-5p | 23,461 | 2.80 | hsa-miR-7704 | 5136 | 2.27 |
| hsa-let-7g-5p | 3832.22 | 1.40 | hsa-miR-126-3p | 22,682 | 0.90 | hsa-miR-92a-3p | 21,203 | 2.53 | hsa-miR-223-3p | 4713 | 2.08 |
| hsa-miR-25-3p | 3070.25 | 1.12 | hsa-miR-21-5p | 21,229 | 0.84 | hsa-miR-223-3p | 15,895 | 1.90 | hsa-miR-1303 | 3914 | 1.73 |
| hsa-miR-146a-5p | 2287.37 | 0.84 | hsa-miR-191-5p | 20,705 | 0.82 | hsa-miR-486-3p | 13,892 | 1.66 | hsa-miR-4279 | 3488 | 1.54 |
| hsa-miR-92a-3p | 2115.47 | 0.77 | hsa-miR-92a-3p | 18,397 | 0.73 | hsa-miR-16-5p | 13,286 | 1.59 | hsa-miR-6087 | 3312 | 1.46 |
| hsa-miR-151a-3p | 1937.60 | 0.71 | hsa-let-7d-3p | 17,960 | 0.71 | hsa-miR-191-5p | 12,984 | 1.55 | hsa-miR-19b-3p | 3103 | 1.37 |
| hsa-miR-342-3p | 1760.54 | 0.64 | hsa-miR-23b-3p | 14,808 | 0.59 | hsa-miR-93-5p | 12,851 | 1.54 | hsa-miR-24-3p | 2979 | 1.31 |
| hsa-miR-486-3p | 1706.72 | 0.62 | hsa-miR-374b-5p | 12,218 | 0.48 | hsa-miR-19a-3p | 11,956 | 1.43 | hsa-miR-6087 | 2622 | 1.16 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nuzziello, N.; Blonda, M.; Licciulli, F.; Liuni, S.; Amoruso, A.; Valletti, A.; Consiglio, A.; Avolio, C.; Liguori, M. Molecular Characterization of Peripheral Extracellular Vesicles in Clinically Isolated Syndrome: Preliminary Suggestions from a Pilot Study. Med. Sci. 2017, 5, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci5030019
Nuzziello N, Blonda M, Licciulli F, Liuni S, Amoruso A, Valletti A, Consiglio A, Avolio C, Liguori M. Molecular Characterization of Peripheral Extracellular Vesicles in Clinically Isolated Syndrome: Preliminary Suggestions from a Pilot Study. Medical Sciences. 2017; 5(3):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci5030019
Chicago/Turabian StyleNuzziello, Nicoletta, Maria Blonda, Flavio Licciulli, Sabino Liuni, Antonella Amoruso, Alessio Valletti, Arianna Consiglio, Carlo Avolio, and Maria Liguori. 2017. "Molecular Characterization of Peripheral Extracellular Vesicles in Clinically Isolated Syndrome: Preliminary Suggestions from a Pilot Study" Medical Sciences 5, no. 3: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci5030019
APA StyleNuzziello, N., Blonda, M., Licciulli, F., Liuni, S., Amoruso, A., Valletti, A., Consiglio, A., Avolio, C., & Liguori, M. (2017). Molecular Characterization of Peripheral Extracellular Vesicles in Clinically Isolated Syndrome: Preliminary Suggestions from a Pilot Study. Medical Sciences, 5(3), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci5030019






