Sociodemographic Factors, Healthy Habits, and Quality of Life in Relation to Insulin Resistance Risk in a Large Cohort of Spanish Workers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
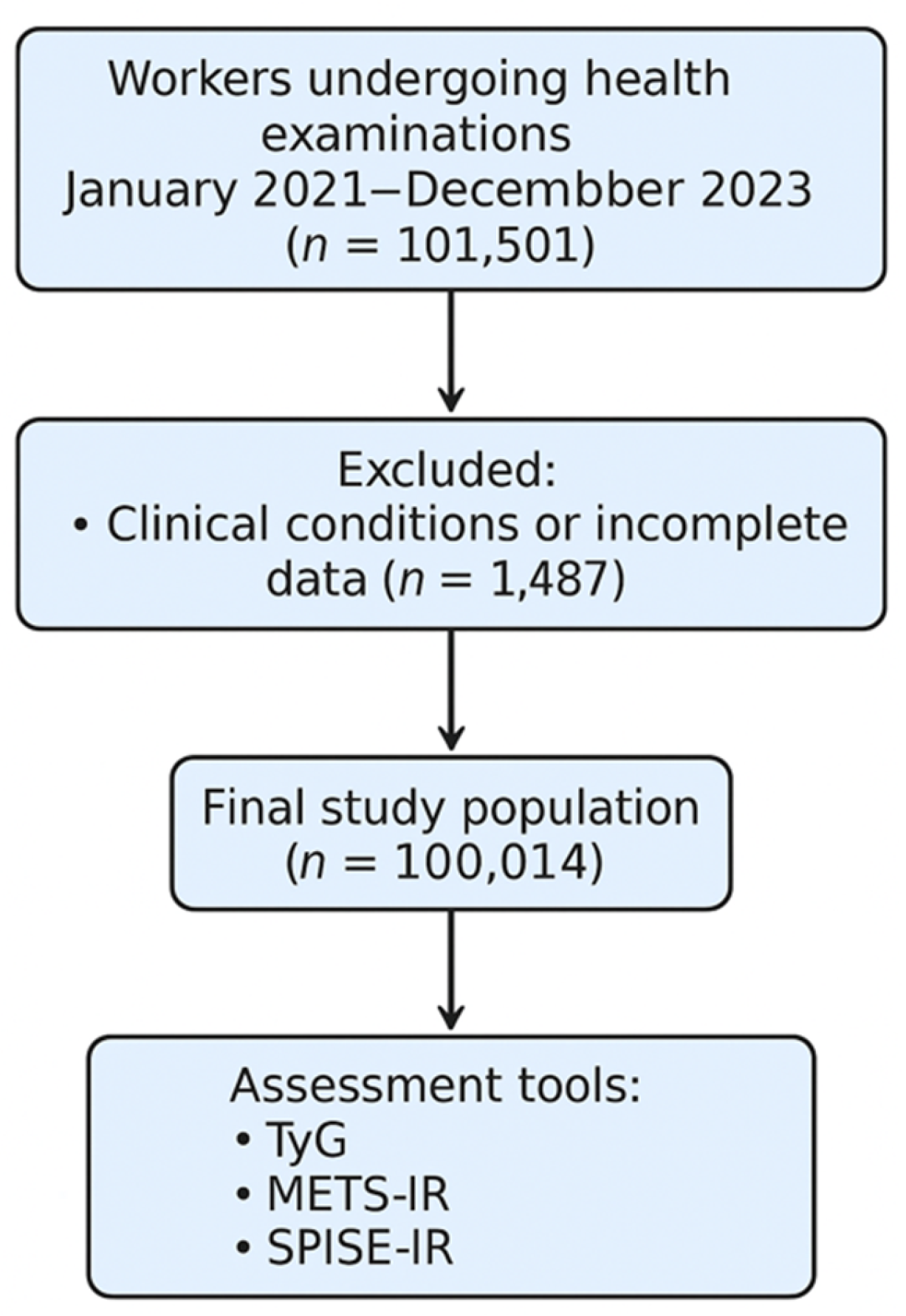
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Anthropometric and Clinical Measurements
2.4. Assessment of Insulin Resistance
- The Triglyceride-Glucose Index (TyG) was calculated as: TyG = ln [fasting triglycerides (mg/dL) × fasting glucose (mg/dL)/2] high risk ≥ 8.5 [39].
- The Metabolic Score for Insulin Resistance (METS-IR) was calculated as: METS-IR = ln [2 × fasting glucose (mg/dL) + triglycerides (mg/dL)] × BMI (kg/m2)/ln [HDL cholesterol (mg/dL)] High values ≥ 50 [40].
- The Single Point Insulin Sensitivity Estimator for Insulin Resistance (SPISE-IR) was derived from SPISE as follows: SPISE = 600 × HDL-cholesterol0.185/(triglycerides0.2 × BMI1.338)
2.5. Lifestyle Assessment
- Adherence to the Mediterranean diet was assessed using the 14-item Mediterranean Diet Adherence Screener (MEDAS-14), validated in the PREDIMED study [41]. A score ≥9 was considered indicative of good adherence.
- Physical activity was evaluated using the short form of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ-SF), which assesses frequency and intensity of physical activity over the past seven days. Participants were classified as physically active or inactive according to established MET-min/week thresholds [42].
- Smoking status was self-reported and categorized as current smoker or non-smoker.
2.6. Sociodemographic and Occupational Classification
2.7. Quality of Life Assessment
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with the Existing Literature
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
4.3. Key Contributions
4.4. Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Ethical Approval and Regulatory Compliance
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1.1. SF-12 Health Survey (English Version)
- In general, would you say your health is:
- 2.
- Compared to one year ago, how would you rate your health in general now?
- 3.
- The following questions are about activities you might do during a typical day. Does your health now limit you in these activities? If so, how much?
- Moderate activities (e.g., moving a table, vacuuming, bowling, or playing golf)
- ( ) Yes, limited a lot ( ) Yes, limited a little ( ) No, not limited at all
- b.
- Climbing several flights of stairs
- ( ) Yes, limited a lot ( ) Yes, limited a little ( ) No, not limited at all
- 4.
- During the past 4 weeks, have you had any of the following problems with your work or other regular daily activities as a result of your physical health?
- Accomplished less than you would like
- ( ) Yes ( ) No
- b.
- Were limited in the kind of work or other activities
- ( ) Yes ( ) No
- 5.
- During the past 4 weeks, have you had any of the following problems with your work or other regular daily activities as a result of any emotional problems (such as feeling depressed or anxious)?
- Accomplished less than you would like
- ( ) Yes ( ) No
- b.
- Didn’t do work or other activities as carefully as usual
- ( ) Yes ( ) No
- 6.
- During the past 4 weeks, how much did pain interfere with your normal work (including both work outside the home and housework)?( ) Not at all ( ) A little bit ( ) Moderately ( ) Quite a bit ( ) Extremely
- 7.
- These questions are about how you feel and how things have been with you during the past 4 weeks.
- Have you felt calm and peaceful?
- Did you have a lot of energy?
- Have you felt downhearted and blue?
- 8.
- During the past 4 weeks, how much of the time has your physical health or emotional problems interfered with your social activities (like visiting with friends, relatives, etc.)?
Appendix A.1.2. Scoring and Interpretation
- Physical Component Summary (PCS)
- Mental Component Summary (MCS)
- Below 50: Below average health status
- 50: Average health status
- Above 50: Better than average health status
References
- Li, M.; Chi, X.; Wang, Y.; Setrerrahmane, S.; Xie, W.; Xu, H. Trends in insulin resistance: Insights into mechanisms and therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, C.S. Insulin Resistance: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies. Diabetes Metab. J. 2022, 46, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Berger, D.; Barroso, I.; Soos, M.; Yeo, G.; Schafer, A.J.; O’Rahilly, S.; Whitehead, J.P. Genetic variants of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) in syndromes of severe insulin resistance. Functional analysis of Ala513Pro and Gly1158Glu IRS-1. Diabet. Med. 2002, 19, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta-Martinez, M.; Cabail, M.Z. The PI3K/Akt Pathway in Meta-Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- van Gerwen, J.; Shun-Shion, A.S.; Fazakerley, D.J. Insulin signalling and GLUT4 trafficking in insulin resistance. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2023, 51, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yazıcı, D.; Sezer, H. Insulin Resistance, Obesity and Lipotoxicity. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 960, 277–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangwung, P.; Petersen, K.F.; Shulman, G.I.; Knowles, J.W. Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Insulin Resistance, and Potential Genetic Implications. Endocrinology 2020, 161, bqaa017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Luc, K.; Schramm-Luc, A.; Guzik, T.J.; Mikolajczyk, T.P. Oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in prediabetes and diabetes. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 70, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Meng, Y.; He, S.; Tan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zheng, W. Macrophages, Chronic Inflammation, and Insulin Resistance. Cells 2022, 11, 3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Marušić, M.; Paić, M.; Knobloch, M.; Liberati Pršo, A.M. NAFLD, Insulin Resistance, and Diabetes Mellitus Type 2. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 2021, 6613827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hill, M.A.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.; Jia, G.; Parrish, A.R.; Sowers, J.R. Insulin resistance, cardiovascular stiffening and cardiovascular disease. Metabolism 2021, 119, 154766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Manent, J.I.; Tomás-Gil, P.; Coll-Villalonga, J.L.; Marti-Lliteras, P.; López-González, A.A.; Paublini, H. Association between atherogenic dyslipidemia and lipid triad with cardiovascular risk scales in 418.343 Spanish workers. Acad. J. Health Sci. 2024, 39, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Z.; Shi, R. Association between insulin resistance and uncontrolled hypertension and arterial stiffness among US adults: A population-based study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- McCormick, N.; O’Connor, M.J.; Yokose, C.; Merriman, T.R.; Mount, D.B.; Leong, A.; Choi, H.K. Assessing the Causal Relationships Between Insulin Resistance and Hyperuricemia and Gout Using Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 2096–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tanase, D.M.; Gosav, E.M.; Costea, C.F.; Ciocoiu, M.; Lacatusu, C.M.; Maranduca, M.A.; Ouatu, A.; Floria, M. The Intricate Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), Insulin Resistance (IR), and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 3920196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xu, Y.; Qiao, J. Association of Insulin Resistance and Elevated Androgen Levels with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS): A Review of Literature. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 9240569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, T.; Kang, J. Relationship between obstructive sleep apnea, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome: A nationwide population-based survey. Endocr. J. 2023, 70, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scurt, F.G.; Ganz, M.J.; Herzog, C.; Bose, K.; Mertens, P.R.; Chatzikyrkou, C. Association of metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease. Obes. Rev. 2024, 25, e13649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; van Dijk, K.W.; Wijsman, C.A.; Rozing, M.P.; Mooijaart, S.P.; Beekman, M.; Slagboom, P.E.; Jukema, J.W.; Noordam, R.; van Heemst, D. Differential insulin sensitivity of NMR-based metabolomic measures in a two-step hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp study. Metabolomics 2021, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ormsbee, J.J.; Burden, H.J.; Knopp, J.L.; Chase, J.G.; Murphy, R.; Shepherd, P.R.; Merry, T. Variability in Estimated Modelled Insulin Secretion. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2022, 16, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Renklint, R.; Chninou, Y.; Heni, M.; Fritsche, A.; Haering, H.U.; Wagner, R.; Otten, J. Surrogate measures of first-phase insulin secretion versus reference methods intravenous glucose tolerance test and hyperglycemic clamp: A systematic review and meta-analyses. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care. 2024, 12, e004256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tahapary, D.L.; Pratisthita, L.B.; Fitri, N.A.; Marcella, C.; Wafa, S.; Kurniawan, F.; Rizka, A.; Tarigan, T.J.E.; Harbuwono, D.S.; Purnamasari, D.; et al. Challenges in the diagnosis of insulin resistance: Focusing on the role of HOMA-IR and Tryglyceride/glucose index. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2022, 16, 102581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosoratto, J.; Carriedo, B.; Cantón, C. Cardiometabolic risk level in 43074 Spanish office workers: Associated variables. Acad. J. Health Sci. 2024, 39, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzanero, R.Z.; López-González, A.A.; Tomás-Gil, P.; Paublini, H.; Martínez-Jover, A.; Ramírez-Manent, J.I. Cardiometabolic risk assessment in 28300 spanish waiters. Acad. J. Health Sci. 2023, 39, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Zhao, X.; Li, S.; Miao, G.; Bai, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, W.; Zhao, X. Metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR) predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in the general population: Evidence from NHANES 2001-2018. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vicente-Herrero, M.T.; Egea-Sancho, M.; Ramírez Iñiguez de la Torre, M.V.; López-González, A.A. Relación de los índices de adiposidad visceral (VAI) y adiposidad disfuncional (DAI) con las escalas de riesgo de resistencia a la insulina y prediabetes. Acad. J. Health Sci. 2024, 39, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, J.; Zethelius, B. SPISE and other fasting indexes of insulin resistance: Risks of coronary heart disease or type 2 diabetes. Comparative cross-sectional and longitudinal aspects. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 124, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sastre-Alzamora, T.; Tomás-Gil, P.; Paublini, H.; Pallarés, L.; Ramírez-Manent, J.I.; López-González, A.A. Relationship between heart age and insulin resistance risk scales in 139634 Spanish workers. Acad. J. Health Sci. 2024, 39, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ding, X.; Lan, Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, S.; Wu, D. Multi-trajectories of triglyceride-glucose index and lifestyle with Cardiovascular Disease: A cohort study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aguiló Juanola, M.C.; López-González, A.A.; Tomás-Gil, P.; Paublini, H.; Tárraga-López, P.J.; Ramírez-Manent, J.I. Influence of tobacco consumption on the values of different insulin resistance risk scales and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatic fibrosis scales in 418,343 spanish people. Acad. J. Health Sci. 2024, 39, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraldstad, K.; Wahl, A.; Andenæs, R.; Andersen, J.R.; Andersen, M.H.; Beisland, E.; Borge, C.R.; Engebretsen, E.; Eisemann, M.; Halvorsrud, L.; et al. A systematic review of quality of life research in medicine and health sciences. Qual. Life Res. 2019, 28, 2641–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Abrantes, L.C.S.; Morais, N.d.S.d.; Gonçalves, V.S.S.; Ribeiro, S.A.V.; Sediyama, C.M.N.d.O.; Franceschini, S.D.C.C.; Amorim, P.R.d.S.; Priore, S.E. Physical activity and quality of life among college students without comorbidities for cardiometabolic diseases: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Qual. Life Res. 2022, 31, 1933–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lin, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, X.; Wan, C. Comparing the reliability and validity of the SF-36 and SF-12 in measuring quality of life among adolescents in China: A large sample cross-sectional study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2020, 18, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jankowska, A.; Golicki, D. Self-reported diabetes and quality of life: Findings from a general population survey with the Short Form-12 (SF-12) Health Survey. Arch. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ghali, H.; Elhraiech, A.; Ben Souda, H.; Karray, M.; Pavy, B.; Zedini, C. Impact of therapeutic education on quality of life in coronary patients: Interventional study. Tunis. Med. 2024, 102, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Constantin-Teodosiu, D.; Constantin, D. Molecular Mechanisms of Muscle Fatigue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Eriksson, M.C.M.; Lundgren, J.; Hellgren, M.; Li, Y.; Björkelund, C.; Lindblad, U.; Daka, B.; Mendoza-Nuñez, V.M. Association between low internal health locus of control, psychological distress and insulin resistance. An exploratory study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, J.R.; Kim, H.N.; Song, S.W. Associations among inflammation, mental health, and quality of life in adults with metabolic syndrome. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2018, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sun, Y.; Ji, H.; Sun, W.; An, X.; Lian, F. Triglyceride glucose (TyG) index: A promising biomarker for diagnosis and treatment of different diseases. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2025, 131, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; Huo, X.; Zuo, X.; Zhao, L.; Liu, L.; Sun, L.; Chen, X. Association of metabolic score for visceral fat with all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and cancer mortality: A prospective cohort study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 5870–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Barquero, S.; Crovetto, F.; Estruch, R.; Ruiz-León, A.M.; Larroya, M.; Sacanella, E.; Casanovas-Garriga, F.; Casas, I.; Nakaki, A.; Youssef, L.; et al. Validation of a pregnancy-adapted Mediterranean Diet Adherence Screener (preg-MEDAS): A validation study nested in the Improving Mothers for a better PrenAtal Care Trial BarCeloNa (IMPACT BCN) trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 120, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestre Font, M.; Busquets-Cortés, C.; Ramírez-Manent, J.I.; Vallejos, D.; Sastre Alzamora, T.; López-González, A.A. Influence of sociodemographic variables and healthy habits on the values of cardiometabolic risk scales in 386924 spanish workers. Acad. J. Health Sci. 2024, 39, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Salvany, A.; Bacigalupe, A.; Carrasco, J.M.; Espelt, A.; Ferrando, J.; Borrell, C.; del Grupo de Determinantes Sociales de la Sociedad Española de Epidemiología. Propuestas de clase social neoweberiana y neomarxista a partir de la Clasificación Nacional de Ocupaciones. Gac. Sanit. 2013, 27, 263–272. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawkes, L.S.; Roh, T.; McDonald, T.J.; Horney, J.A.; Chiu, W.A.; Sansom, G.T. Using the 12-item short-form health survey (SF-12) to evaluate self-rated health in an environmental justice community. Arch. Public. Health. 2024, 82, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mestre-Font, M.; Busquets-Cortés, C.; Ramírez-Manent, J.I.; Tomás-Gil, P.; Paublini, H.; López-González, A.A. Influence of sociodemographic variables and healthy habits on the values of type 2 diabetes risk scales. Acad. J. Health Sci. 2024, 39, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, A.; Doustmohammadian, A.; Shamshirgaran, S.M.; Aminisani, N.; Azimi-Nezhad, M.; Abasi, H.; Hariri, M. Association Between Metabolic Syndrome and Health-Related Quality of Life in Older Adults: Findings from the IRanian Longitudinal Study on Ageing. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2024, 22, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-C.; Chang, H.-T.; Chiang, S.-C.; Chen, H.-S.; Lin, M.-H.; Chen, T.-J.; Hwang, S.-J. Sex differences in relationships between metabolic syndrome components and factors associated with health-related quality of life in middle-aged adults living in the community: A cross-sectional study in Taiwan. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2018, 16, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, C.-C.; Chang, H.-T.; Chiang, S.-C.; Chen, H.-S.; Lin, M.-H.; Chen, T.-J.; Hwang, S.-J. Diabesity and Dietary Interventions: Evaluating the Impact of Mediterranean Diet and Other Types of Diets on Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Management. Nutrients 2023, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrou, I.; Tsigos, C.; Mavrogianni, C.; Cardon, G.; Van Stappen, V.; Latomme, J.; Kivelä, J.; Wikström, K.; Tsochev, K.; Nanasi, A.; et al. Sociodemographic and lifestyle-related risk factors for identifying vulnerable groups for type 2 diabetes: A narrative review with emphasis on data from Europe. BMC Endocrine Disorders 2020, 20 (Suppl. 1), 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaravadi, S.K.; Maiya, G.A.; Vaishali, K.; Shastry, B.A. Effectiveness of structured exercise program on insulin resistance and quality of life in type 2 diabetes mellitus–A randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0302831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, S.; Choi, D.-W.; Ju, Y.J.; Park, E.C. Association of self-reported sedentary time with insulin resistance among Korean adults without diabetes mellitus: A cross sectional study. BMC Public. Health 2018, 18, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetrani, C.; Verde, L.; Colao, A.; Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G. The Mediterranean Diet: Effects on Insulin Resistance and Secretion in Individuals with Overweight or Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazukauskiene, N.; Podlipskyte, A.; Varoneckas, G.; Mickuviene, N. Health-related quality of life and insulin resistance over a 10-year follow-up. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hertfordshire Cohort Study. Available online: https://www.mrc.soton.ac.uk/herts/ (accessed on 29 July 2025).
- Lin, Y.-H.; Chang, H.-T.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Chen, H.-S.; Chiang, S.-C.; Chen, T.-J.; Hwang, S.-J. Changes in metabolic syndrome affect the health-related quality of life of community-dwelling adults. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Men n = 60,133 | Women n = 39,881 | ||
| Variables | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | p-Value |
| Age (years) | 39.8 (10.3) | 39.2 (10.2) | <0.001 |
| Height (cm) | 174.0 (7.1) | 161.2 (6.6) | <0.001 |
| Weight (kg) | 81.1 (13.8) | 65.4 (13.2) | <0.001 |
| Waist (cm) | 87.7 (9.2) | 73.9 (7.9) | <0.001 |
| Hip (cm) | 100.1 (8.4) | 97.2 (9.0) | <0.001 |
| Systolic BP (mm Hg) | 124.4 (15.1) | 114.3 (14.7) | <0.001 |
| Diastolic BP (mm Hg) | 75.4 (10.6) | 69.6 (10.3) | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 195.8 (38.8) | 194.0 (36.7) | <0.001 |
| HDL-c (mg/dL) | 51.0 (7.0) | 53.7 (7.7) | <0.001 |
| LDL-c (mg/dL) | 120.3 (37.6) | 122.7 (37.3) | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 123.7 (88.7) | 88.1 (46.3) | <0.001 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 88.1 (12.9) | 84.1 (11.6) | <0.001 |
| Variables | n (%) | n (%) | p-value |
| 18–29 years | 10,774 (17.9) | 7747 (19.4) | <0.001 |
| 30–39 years | 19,795 (32.8) | 13,365 (33.5) | |
| 40–49 years | 17,850 (29.7) | 11,626 (29.2) | |
| 50–59 years | 9915 (16.5) | 6121 (15.3) | |
| 60–69 years | 1799 (3.0) | 1022 (2.6) | |
| Social class I | 3208 (5.4) | 2793 (7.0) | <0.001 |
| Social class II | 10,602 (17.6) | 13,255 (33.2) | |
| Social class III | 46,323 (77.0) | 23,833 (59.8) | |
| Smokers | 22,265 (37.0) | 13,040 (32.7) | <0.001 |
| Yes Mediterranean diet | 24,790 (41.2) | 20,344 (51.0) | <0.001 |
| Yes physical activity | 27,551 (45.8) | 20,669 (51.8) | <0.001 |
| TyG Index | METS-IR | SPISE-IR | |||||
| Men | n | Mean (SD) | p-Value | Mean (SD) | p-Value | Mean (SD) | p-Value |
| 18–29 years | 10,774 | 8.1 (0.5) | <0.001 | 34.8 (6.7) | <0.001 | 1.4 (0.4) | <0.001 |
| 30–39 years | 19,795 | 8.4 (0.6) | 38.0 (7.1) | 1.6 (0.5) | |||
| 40–49 years | 17,850 | 8.5 (0.6) | 40.3 (7.4) | 1.8 (0.5) | |||
| 50–59 years | 9915 | 8.6 (0.6) | 42.0 (7.3) | 1.9 (0.5) | |||
| 60–69 years | 1799 | 8.7 (0.5) | 42.6 (6.9) | 1.9 (0.4) | |||
| Social class I | 3208 | 8.3 (0.5) | <0.001 | 38.5 (7.0) | <0.001 | 1.6 (0.4) | <0.001 |
| Social class II | 10,602 | 8.4 (0.6) | 38.7 (7.3) | 1.7 (0.5) | |||
| Social class III | 46,323 | 8.4 (0.6) | 39.0 (7.7) | 1.7 (0.5) | |||
| Smokers | 22,265 | 8.5 (0.6 | <0.001 | 39.2 (7.3) | <0.001 | 1.7 (0.5) | <0.001 |
| Non-smokers | 37,868 | 8.4 (0.6) | 38.4 (8.0) | 1.6 (0.5) | |||
| Yes Mediterranean diet | 24,790 | 8.1 (0.4) | <0.001 | 33.5 (3.7) | <0.001 | 1.3 (0.2) | <0.001 |
| Non Mediterranean diet | 35,343 | 8.7 (0.6) | 42.7 (7.3) | 1.9 (0.5) | |||
| Yes physical activity | 27,551 | 8.1 (0.4) | <0.001 | 33.4 (3.6) | <0.001 | 1.3 (0.2) | <0.001 |
| Non physical activity | 32,582 | 8.7 (0.6) | 43.5 (6.9) | 2.0 (0.5) | |||
| SF-12 good | 41,843 | 8.2 (0.4) | <0.001 | 36.1 (5.5) | <0.001 | 1.5 (0.3) | <0.001 |
| SF-12 poor | 18,290 | 8.9 (0.6) | 45.4 (7.7) | 2.1 (0.5) | |||
| Women | n | Mean (SD) | p-value | Mean (SD) | p-value | Mean (SD) | p-value |
| 18–29 years | 7747 | 7.9 (0.5) | <0.001 | 32.4 (7.2) | <0.001 | 1.3 (0.4) | <0.001 |
| 30–39 years | 13,365 | 8.0 (0.5) | 34.0 (7.7) | 1.4 (0.5) | |||
| 40–49 years | 11,626 | 8.1 (0.5) | 36.3 (7.8) | 1.5 (0.5) | |||
| 50–59 years | 6121 | 8.3 (0.5) | 38.4 (7.6) | 1.6 (0.5) | |||
| 60–69 years | 1022 | 8.4 (0.5) | 39.6 (7.2) | 1.7 (0.5) | |||
| Social class I | 2793 | 8.0 (0.4) | <0.001 | 32.9 (7.0) | <0.001 | 1.3 (0.4) | <0.001 |
| Social class II | 13,255 | 8.1 (0.5) | 33.7 (7.2) | 1.4 (0.4) | |||
| Social class III | 23,833 | 8.1 (0.5) | 36.3 (8.1) | 1.5 (0.5) | |||
| Smokers | 13,040 | 8.1 (0.5) | <0.001 | 35.6 (8.0) | <0.001 | 1.5 (0.5) | <0.001 |
| Non Smokers | 26,841 | 8.0 (0.5) | 34.3 (7.6) | 1.4 (0.5) | |||
| Yes Mediterranean diet | 20,344 | 7.9 (0.4) | <0.001 | 30.6 (3.7) | <0.001 | 1.2 (0.2) | <0.001 |
| Non Mediterranean diet | 19,537 | 8.3 (0.5) | 40.0 (8.2) | 1.8 (0.5) | |||
| Yes physical activity | 20,669 | 7.9 (0.4) | <0.001 | 30.2 (3.5) | <0.001 | 1.2 (0.2) | <0.001 |
| Non physical activity | 19,212 | 8.3 (0.5) | 40.5 (7.8) | 1.8 (0.5) | |||
| SF-12 good | 32,173 | 8.0 (0.4) | <0.001 | 33.1 (6.0) | <0.001 | 1.3 (0.3) | <0.001 |
| SF-12 poor | 7708 | 8.5 (0.5) | 44.0 (8.8) | 2.0 (0.6) |
| TyG index High | METS-IR High | SPISE-IR High | |||||
| Men | n | % | p-Value | % | p-Value | % | p-Value |
| 18–29 years | 10,774 | 10.0 | <0.001 | 3.4 | <0.001 | 5.7 | <0.001 |
| 30–39 years | 19,795 | 20.0 | 6.4 | 10.6 | |||
| 40–49 years | 17,850 | 30.6 | 10.1 | 16.9 | |||
| 50–59 years | 9915 | 35.1 | 13.3 | 20.2 | |||
| 60–69 years | 1799 | 35.3 | 13.4 | 20.5 | |||
| Social class I | 3208 | 20.7 | <0.001 | 6.7 | <0.001 | 11.3 | <0.001 |
| Social class II | 10,602 | 24.0 | 7.5 | 12.3 | |||
| Social class III | 46,323 | 24.6 | 8.6 | 13.9 | |||
| Smokers | 22,265 | 27.5 | <0.001 | 7.9 | <0.001 | 13.8 | <0.001 |
| Non-smokers | 37,868 | 22.4 | 9.0 | 13.2 | |||
| Yes Mediterranean diet | 24,790 | 2.3 | <0.001 | 4.1 | <0.001 | 5.9 | <0.001 |
| Non Mediterranean diet | 35,343 | 39.7 | 10.2 | 14.3 | |||
| Yes physical activity | 27,551 | 1.9 | <0.001 | 3.3 | <0.001 | 4.4 | <0.001 |
| Non physical activity | 32,582 | 43.2 | 12.2 | 16.2 | |||
| SF-12 good | 41,843 | 8.2 | <0.001 | 4.0 | <0.001 | 5.5 | <0.001 |
| SF-12 poor | 18,290 | 61.2 | 10.5 | 16.1 | |||
| Women | n | % | p-value | % | p-value | % | p-value |
| 18–29 years | 7747 | 6.0 | <0.001 | 3.5 | <0.001 | 4.7 | <0.001 |
| 30–39 years | 13,365 | 7.3 | 4.7 | 6.6 | |||
| 40–49 years | 11,626 | 12.5 | 6.6 | 8.9 | |||
| 50–59 years | 6121 | 20.6 | 8.1 | 11.6 | |||
| 60–69 years | 1022 | 26.2 | 10.0 | 15.4 | |||
| Social class I | 2793 | 6.9 | <0.001 | 3.4 | <0.001 | 4.7 | <0.001 |
| Social class II | 13,255 | 9.6 | 4.0 | 5.5 | |||
| Social class III | 23,833 | 12.4 | 6.9 | 9.6 | |||
| Smokers | 13,040 | 11.9 | <0.001 | 6.2 | <0.001 | 8.5 | <0.001 |
| Non Smokers | 26,841 | 10.6 | 4.6 | 6.7 | |||
| Yes Mediterranean diet | 20,344 | 5.1 | <0.001 | 3.8 | <0.001 | 4.9 | <0.001 |
| Non Mediterranean diet | 19,537 | 14.3 | 8.7 | 10.2 | |||
| Yes physical activity | 20,669 | 3.8 | <0.001 | 3.1 | <0.001 | 4.1 | <0.001 |
| Non physical activity | 19,212 | 16.9 | 10.4 | 12.6 | |||
| SF-12 good | 32,173 | 6.5 | <0.001 | 4.2 | <0.001 | 5.0 | <0.001 |
| SF-12 poor | 7708 | 22.3 | 8.0 | 10.1 |
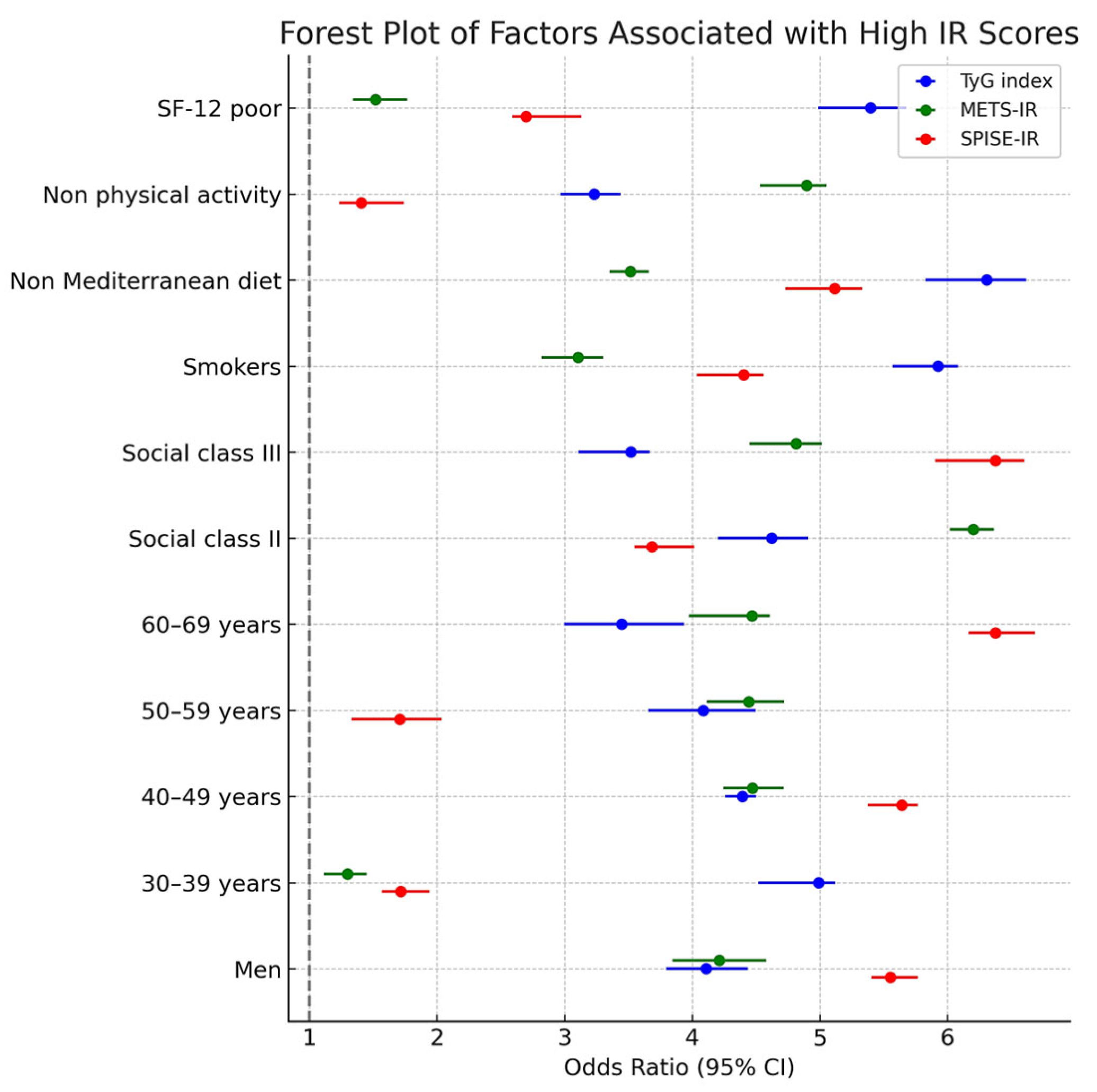
| TyG index High | METS-IR High | SPISE-IR High | ||||
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Women | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Men | 2.35 (2.25–2.46) | <0.001 | 1.85 (1.70–2.01) | <0.001 | 1.26 (1.20–1.33) | <0.001 |
| 18–29 years | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 30–39 years | 1.12 (1.10–1.15) | <0.001 | 1.19 (1.14–1.24) | <0.001 | 1.15 (1.10–1.21) | <0.001 |
| 40–49 years | 1.29 (1.24–1.34) | <0.001 | 1.42 (1.30–1.55) | <0.001 | 1.34 (1.25–1.44) | <0.001 |
| 50–59 years | 1.41 (1.35–1.47) | <0.001 | 2.08 (1.70–2.46) | <0.001 | 1.59 (1.47–1.72) | <0.001 |
| 60–69 years | 1.60 (1.50–1.71) | <0.001 | 3.11 (2.51–3.72) | <0.001 | 1.88 (1.69–2.08) | <0.001 |
| Social class I | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Social class II | 1.15 (1.12–1.18) | <0.001 | 1,15 (1.10–1.21) | <0.001 | 1.19 (1.13 -1.25) | <0.001 |
| Social class III | 1.44 (1.37–1.52) | <0.001 | 1.43 (1.35–1.52) | <0.001 | 1.42 (1.32–1.53) | <0.001 |
| Non smokers | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Smokers | 1.50 (1.41–1.60) | <0.001 | 1.14 (1.10–1.19) | <0.001 | 1.21 (1.16–1.27) | <0.001 |
| Yes Mediterranean diet | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Non Mediterranean diet | 2.13 (1.85–2.41) | <0.001 | 2.66 (2.17–3.16) | <0.001 | 2.78 (2.40–3.17) | <0.001 |
| Yes physical activity | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Non physical activity | 5.39 (4.50–6.29) | <0.001 | 6.23 (5.10–7.36) | <0.001 | 6.67 (5.39–7.96) | <0.001 |
| SF-12 good | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| SF-12 poor | 3.83 (3.23–4.24) | <0.001 | 3.29 (2.67–3.92) | <0.001 | 4.11 (3.20–5.01) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marzoa Jansana, M.D.; Tárraga López, P.J.; Guarro Miquel, J.J.; López-González, Á.A.; Riutord Sbert, P.; Busquets-Cortés, C.; Ramírez-Manent, J.I. Sociodemographic Factors, Healthy Habits, and Quality of Life in Relation to Insulin Resistance Risk in a Large Cohort of Spanish Workers. Med. Sci. 2025, 13, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030122
Marzoa Jansana MD, Tárraga López PJ, Guarro Miquel JJ, López-González ÁA, Riutord Sbert P, Busquets-Cortés C, Ramírez-Manent JI. Sociodemographic Factors, Healthy Habits, and Quality of Life in Relation to Insulin Resistance Risk in a Large Cohort of Spanish Workers. Medical Sciences. 2025; 13(3):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030122
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarzoa Jansana, María Dolores, Pedro Juan Tárraga López, Juan José Guarro Miquel, Ángel Arturo López-González, Pere Riutord Sbert, Carla Busquets-Cortés, and José Ignacio Ramírez-Manent. 2025. "Sociodemographic Factors, Healthy Habits, and Quality of Life in Relation to Insulin Resistance Risk in a Large Cohort of Spanish Workers" Medical Sciences 13, no. 3: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030122
APA StyleMarzoa Jansana, M. D., Tárraga López, P. J., Guarro Miquel, J. J., López-González, Á. A., Riutord Sbert, P., Busquets-Cortés, C., & Ramírez-Manent, J. I. (2025). Sociodemographic Factors, Healthy Habits, and Quality of Life in Relation to Insulin Resistance Risk in a Large Cohort of Spanish Workers. Medical Sciences, 13(3), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030122






