Abstract
Hypoxia is characterized as one of the main consequences of sepsis, which is recognized as the leading cause of death in intensive care unit (ICU) patients. In this study, we aimed to examine whether the expression levels of genes regulated under hypoxia could be utilized as novel biomarkers for sepsis prognosis in ICU patients. Whole blood expression levels of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF1A), interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15), hexokinase 2 (HK2), lactate dehydrogenase (LDHA), heme oxygenase-1 (HMOX1), erythropoietin (EPO), and the vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) were measured on ICU admission in 46 critically ill, initially non-septic patients. The patients were subsequently divided into two groups, based on the development of sepsis and septic shock (n = 25) or lack thereof (n = 21). HMOX1 mRNA expression was increased in patients who developed sepsis/septic shock compared to the non-septic group (p < 0.0001). The ROC curve, multivariate logistic regression, and Kaplan–Meier analysis demonstrated that HMOX1 expression could be utilized for sepsis and septic shock development probability. Overall, our results indicate that HMOX1 mRNA levels have the potential to be a valuable predictive factor for the prognosis of sepsis and septic shock in ICU patients.
1. Introduction
Sepsis is a complex disorder, defined as a life-threatening organ dysfunction attributed to dysregulated host response to infection [1]. In recent years, sepsis has become the main cause of mortality in intensive care units (ICUs) [2]. Septic shock is a subset of sepsis with a greater mortality risk, attributed to profound circulatory, cellular, and metabolic abnormalities [1]. Mitochondrial dysfunction and hypoxia have been linked to cell injury and sepsis-induced organ dysfunction, although to this day the exact molecular mechanisms in play have not been fully elucidated [3]. The discovery of novel markers with prognostic and/or diagnostic significance is crucial so that in combination with modern treatments, the outcome of septic patients can be improved [4].
In cases where oxygen levels are reduced, the hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are responsible for regulating the cellular response [5]. HIFs are heterodimeric transcription factors, which consist of two subunits, an oxygen-sensitive (α-subunit) and a constitutively expressed subunit (β-subunit) [6]. HIF regulation under hypoxia is achieved in part through the negative feedback loop between itself and the interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) protein, a member of the ubiquitin family [7]. ISG15 is a secreted protein with a molecular weight of 15 kDa, strongly induced by type I interferons, with a main role in protein ISGylation [8]. HIF stabilization due to hypoxia leads to the increased expression of ISG15, which in turn neutralizes the formation of the HIF-1α heterodimer. In sepsis, HIF-1α has been described as a key component in numerous phases of inflammatory responses [9]. In addition to inflammation, HIF-1α exerts a significant effect on cell metabolism, regulating the expression of genes related to glycolytic metabolism. During sepsis, HIF-1α, in combination with other driving factors, is responsible for the metabolic switch of immune cells from oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis, an event known as the Warburg effect, enabling cell proliferation and the cytokine storm described in sepsis [10]. Hexokinase 2 (HK2) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDHA) are among the glycolytic genes induced by HIF-1α [11,12,13]. HK2 is the first rate-limiting enzyme of glycolysis, catalyzing the phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate (G-6P), while LDHA is responsible for the reversible enzymatic conversion of pyruvate to lactate [14,15].
Except for enzymes contributing to metabolic pathways, under hypoxia, HIFs regulate several genes with central roles in sepsis, including heme oxygenase-1 (HMOX1), erythropoietin (EPO), and the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGFA) [16,17,18,19]. Heme oxygenase (HO-1) scavenges heme that is released into the circulatory system during sepsis-induced red blood cell lysis and subsequent oxidation of hemoglobin [20]. By degrading heme, HO-1 exerts a potent cytoprotective role in the lungs [21]. Recent studies have demonstrated that HO-1 alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting Golgi stress, as well as endoplasmic reticulum stress [22,23].
Furthermore, EPO regulates bone marrow erythropoiesis via interaction with the surface receptor EPO-R, and its potential utility as a therapeutic treatment in sepsis has been rigorously studied, presenting a strong anti-apoptotic, cytoprotective, and anti-inflammatory effect in several animal models [24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. Lastly, VEGFA retains central roles in cell migration, as well as in vessel formation and permeability [31]. Recent evidence supports that the excessive release of VEGFA from pulmonary vascular endothelial cells could be associated with the development of non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema in sepsis-associated lung injury [32].
The aim of this study was to investigate the gene expression profile of HIF1A, ISG15, HK2, LDHA, HMOX1, EPO, and VEGFA under the setting of sepsis and septic shock, and furthermore to evaluate whether any of these molecules has potential value as a prognostic factor. To this end, we examined the mRNA expression levels in whole blood samples of patients admitted to the ICU who developed sepsis and septic shock or not.
2. Materials and Methods
The “Evangelismos” Hospital Research Ethics Committee (80/01-02-2010) approved this observational study. All study procedures were performed after obtaining informed written consent from the patients’ next of kin, and were in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration.
2.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
The flow chart of the enrolment is depicted in Figure 1. The screening took place from 20 September 2010 to 15 February 2016. The exclusion criteria were as follows: sepsis on ICU admission or sepsis development within the first 48 h post-ICU admission, age < 18, positive pregnancy test, presence of malignant neoplasm, brain death, contagious diseases (human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis), ICU length of stay < 3 days, no need for intubation, transfer from another ICU, and oral intake of corticosteroids at an equivalent dosage of ≥1 mg/kg prednisone/day for a period greater than one month. In total, 334 ICU patients were initially screened for eligibility over the study period. Enrolled patients were assigned to two groups based on the development of sepsis and septic shock during their ICU stay, according to the Sepsis-3 guidelines [1]. Sepsis is defined as life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection (increase in the sepsis-related sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score of 2 points or more). Septic shock is a subset of sepsis in which patients are identified by a vasopressor requirement to maintain a mean arterial pressure of 65 mm Hg or greater and serum lactate levels >2 mmol/L in the absence of hypovolemia. Those who did not develop sepsis during their ICU stay (non-septic patients) constituted the control group, while patients who developed it were assigned to the sepsis and septic shock group (septic patients).
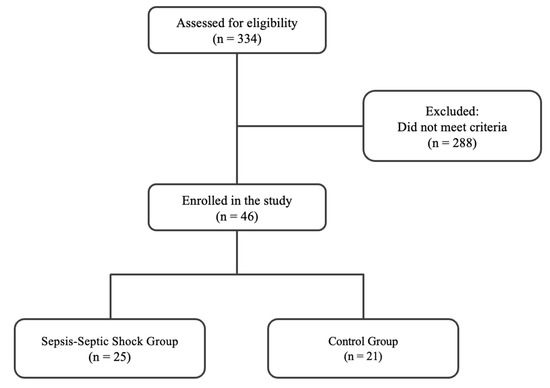
Figure 1.
Flow chart of patient enrollment.
2.2. Total RNA Extraction
Venous blood samples were obtained at various time points (Tempus RNA tubes, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The first blood sample was drawn on ICU admission (within 24 h). For patients who subsequently developed sepsis and septic shock, 2 more blood samples were obtained within 6 h of their development, respectively. For non-septic patients, a second blood sample was drawn at ICU discharge. The corresponding kit was utilized to isolate total RNA from the peripheral blood, per the manufacturer’s instructions. The concentration and quality of isolated total RNA were measured with a spectrophotometer at 260/280 nm.
2.3. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
cDNA was synthesized from the isolated total RNA (Nippon Genetics, Duren, Germany), and the quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) method (Kapa SYBR® Green PCR Master Mix, Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) was used to measure HIF1A, HMOX1, EPO, ISG15, LDHA, HK2, and VEGFA mRNA expression using the specific primer sets listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Primer pairs used in quantitative real-time PCR experiments.
Quantitative real-time PCR was performed in 96-well plates (CFX Connect thermocycler, Biorad, Hercules, CA, USA). The comparative CT method 2−ΔΔCT [33] was applied using GAPDH mRNA expression levels for normalization of the target gene expression levels. ICU admission values within each group were used as the control.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Data are presented either as individual values, mean ± SD for normally distributed data, or median with interquartile range (IQR) for skewed data. Comparisons between the two groups were performed using Student’s t-test, the non-parametric Mann–Whitney test, the paired non-parametric Wilcoxon test, or the chi-square test, as appropriate. Comparisons between three groups were performed using the paired non-parametric Friedman test. Spearman’s coefficient was used to test correlations. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was generated using the development of sepsis/septic shock in the ICU or its absence as the classification variable, and HMOX1 DCt values on ICU admission as the prognostic variable. In qPCR, Ct values represent the number of amplification cycles required to reach the signal threshold. DCt is defined as the difference between the Ct value of the target gene (HMOX1) and the control gene (GAPDH). The optimal cut-off value for risk for sepsis/septic shock onset prediction was calculated as the point with the greatest combined sensitivity and specificity (Youden index). Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed to identify potential risk factors for sepsis/septic shock development in the ICU. The whole patient cohort was dichotomized above and below the cut-off value determined from the ROC curve, and the Kaplan–Meier method was subsequently used for sepsis/septic shock probability estimation, using the log-rank test for comparison. All p-values are two-sided; significance was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
A total of 46 (32 male and 14 female) critically ill, mechanically ventilated, initially non-septic patients were enrolled in the study. These patients suffered from surgical, medical, and trauma-related pathologies. A total of 25 patients (19 male and 6 female) subsequently developed sepsis (on day 5 (IQR: 3–8)) and septic shock (on day 12 (IQR: 8–17)) during their ICU stay (septic patients), while the remaining 21 patients (13 male and 8 female) did not develop sepsis during their ICU stay (non-septic patients) and were used as a control group. All 25 patients who developed sepsis/septic shock had positive biological fluid cultures. In 23 of our septic patients (92%), sepsis originated from a lung infection. The infections were mainly due to Gram-negative bacteria (88%, mostly Acinetobacter baumannii and Klebsiella pneumoniae). Clinical data and blood samples were acquired from all the patients enrolled. The characteristics of the two patient groups upon admission are presented in Table 2. In septic patients, the SOFA score was higher. Additionally, the same group presented an extended duration of mechanical ventilation and length of stay in the ICU in comparison to non-septic patients.

Table 2.
Demographic information, clinical characteristics, and laboratory data of critically ill patients on ICU admission.
3.2. mRNA Expression of Hypoxia-Regulated Genes in ICU Patients
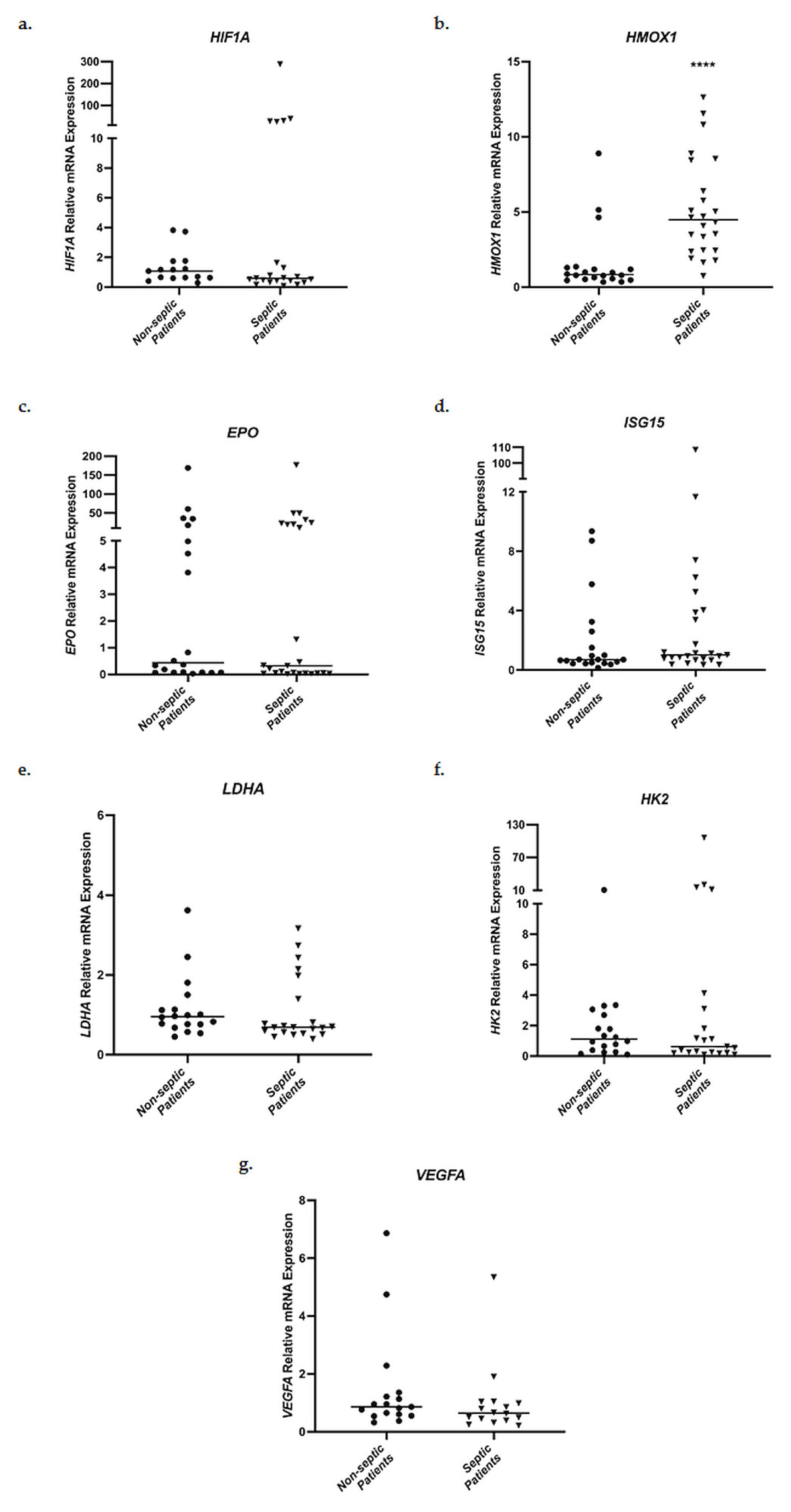
Relative messenger RNA expression levels of HIF1A, HMOX1, EPO, ISG15, LDHA, HK2, and VEGFA in whole blood samples were evaluated in the two groups of patients admitted to the ICU, septic patients and non-septic patients. Initially, ICU admission mRNA levels were compared between the two groups (Figure 2). No statistically significant differences in mRNA expression were observed for HIF1A, EPO, ISG15, LDHA, HK2, and VEGFA. However, septic patients presented significantly elevated HMOX1 mRNA levels on ICU admission, in comparison to non-septic patients (Figure 2b). Specifically, septic patients showed a 4.48-fold increase (interquartile range (IQR), 2.44–7.93) in HMOX1 mRNA expression in comparison to 0.83-fold (0.54–1.26, p < 0.0001) in the non-septic patient control group.
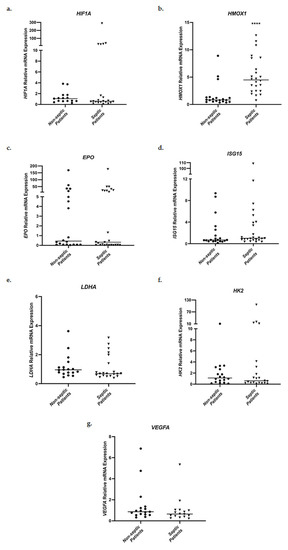
Figure 2.
Distribution of HIF1A (a), HMOX1 (b), EPO (c), ISG15 (d), LDHA (e), HK2 (f), and VEGFA (g) relative mRNA expression in whole blood samples on ICU admission of non-septic patients and septic patients. Data are presented as scatter plots. Line in the middle: median. **** p < 0.0001 vs. non-septic patients by the Mann–Whitney test.
Additionally, the mRNA expression levels of the above-mentioned genes were measured on ICU admission, sepsis, and septic shock for the septic group, and on admission and discharge for the non-septic group (Supplementary Materials, Figure S1). HIF1A mRNA levels exhibited a 0.69-fold (0.43–0.96; p < 0.05) decrease at septic shock compared to values on admission (Figure S1a). On the contrary, HK2 mRNA levels presented a 1.56-fold (0.92–2.63; p < 0.05) increase at septic shock (Figure S1e). The non-septic patients exhibited decreased HK2 and LDHA mRNA expression at discharge. Specifically, LDHA mRNA expression (Figure S1d) showed a 0.82-fold (0.60–0.89; p < 0.001) decrease, while for HK2 (Figure S1e) we calculated a 0.77-fold decrease (0.51–1.08; p < 0.05).
3.3. HMOX1 mRNA Expression as a Prognostic Factor for Sepsis and Septic Shock
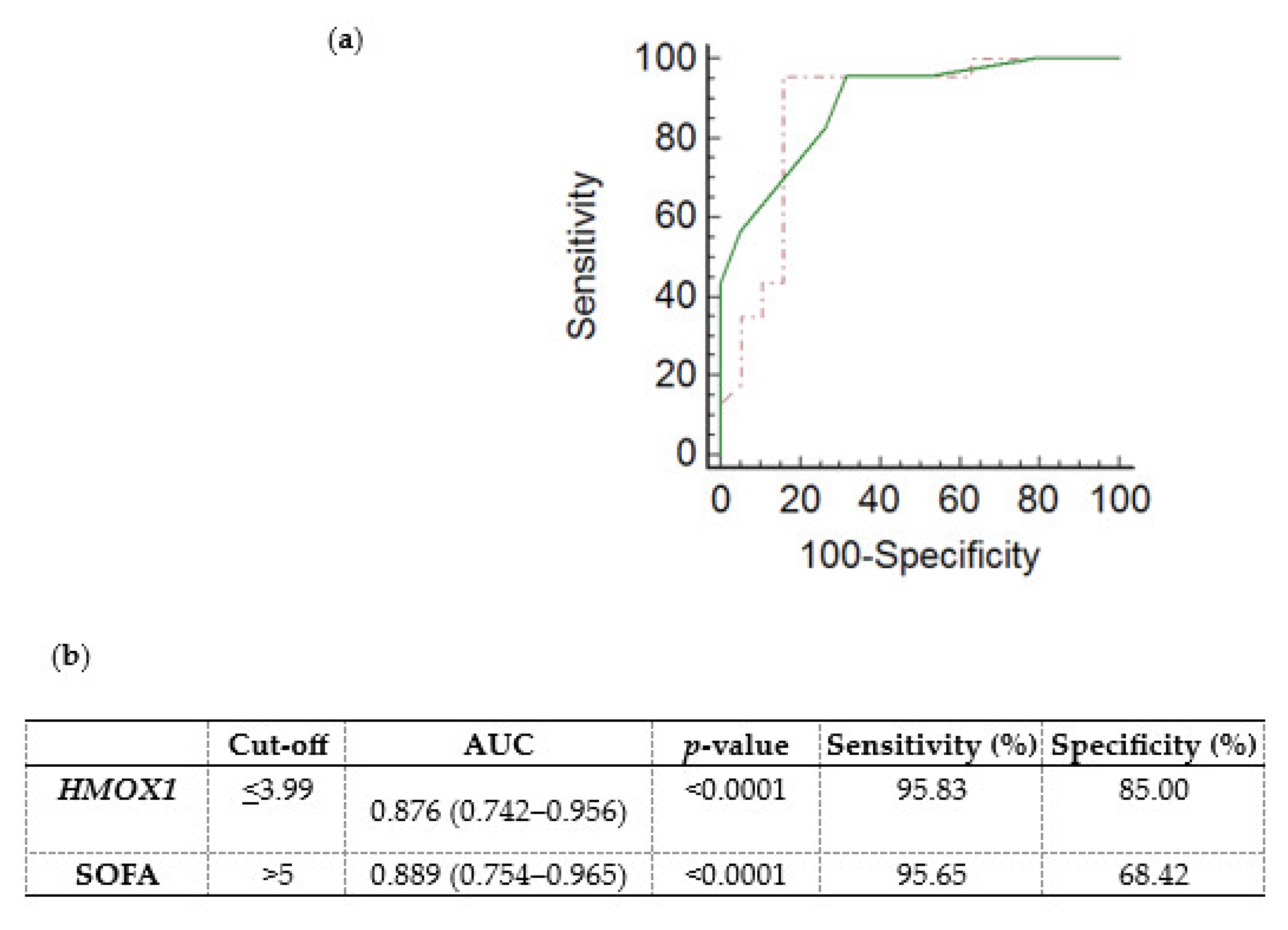
A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was generated, using the ICU admission HMOX1 DCt values, to determine whether HMOX1 levels could predict the subsequent development of sepsis and septic shock in critically ill, initially non-septic patients. Non-septic patients exhibited higher DCt values (4.97; (4.36–5.60)), and thus lower mRNA expression, in comparison to septic patients (2.54; (1.72–3.42), p < 0.0001). The ROC curve of sepsis/septic shock development probability presented an area under the curve (AUC) equal to 0.876 (0.742–0.956, Figure 3a,b; p < 0.0001). The cut-off was determined by the Youden index at ≤3.99. The generated ROC curve was compared with the ROC curve of the SOFA score (Figure 3a; p = 0.83).
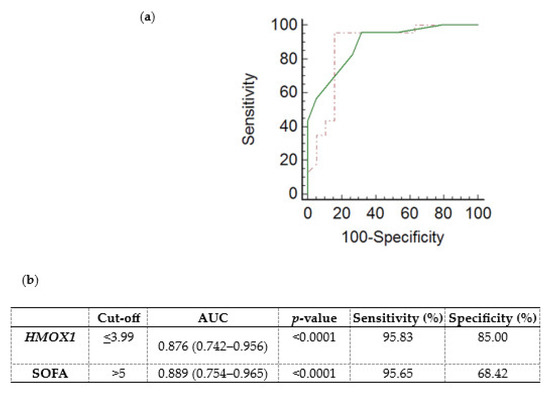
Figure 3.
Whole blood HMOX1 mRNA expression levels and probability of sepsis/septic shock development in critically ill, initially non-septic patients. (a) Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were generated for HMOX1 DCt values (dashed red line) and the SOFA score (solid green line) for the probability of sepsis/septic shock development in initially non-septic patients admitted to the ICU. (b) Table listing the cut-off values (Youden index), the area under the curve (AUC), and the sensitivity and specificity for HMOX1 and SOFA score of the respective ROC curves.
Furthermore, a logistic regression analysis was performed to investigate the possible association between ICU admission HMOX1 expression levels and the risk of sepsis/septic shock development (Table 3). The univariate model showed that lower HMOX1 DCt values, corresponding to higher mRNA expression, correlated with an increased risk of sepsis/septic shock development (odds ratio (O.R.) = 0.259, 95% C.I. = 0.125–0.534, and p < 0.0001). Multivariate analysis was performed to correct for potential confounding factors, including SOFA score, age (continuous variables), and sex (categorical). According to our results, lower HMOX1 DCt values may serve as a stand-alone marker for sepsis/septic shock development (adjusted O.R. = 0.258, 95% C.I. = 0.097–0.686, and p = 0.007).

Table 3.
Results from the univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis.
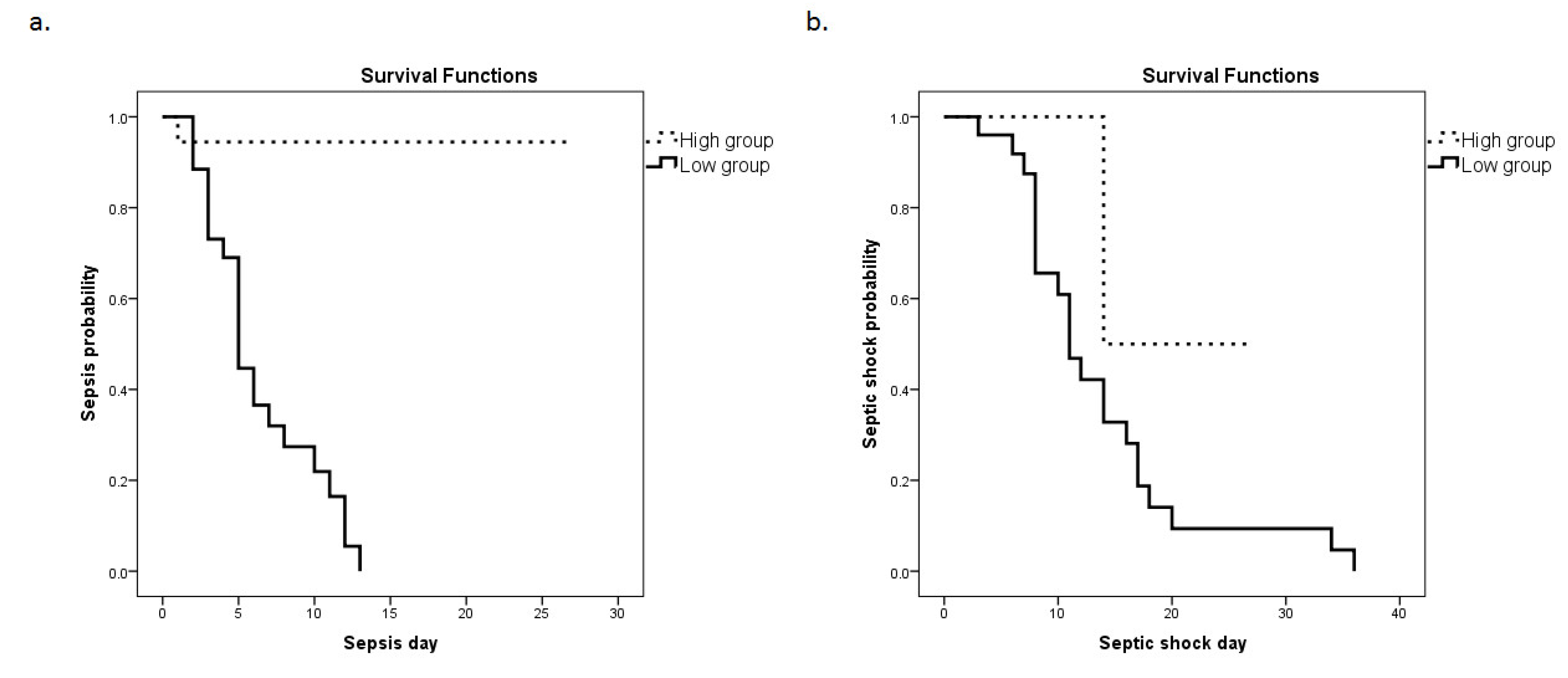
Subsequently, a Kaplan–Meier analysis was performed (Figure 4a,b). The ICU cohort was dichotomized above (high group) and below (low group) the cut-off value determined from the ROC curve using the Youden index (3.99). The probability for the development of sepsis and septic shock was significantly elevated in the low groups (corresponding to higher mRNA expression). Specifically, the median time for sepsis development was 6 (5–8) days following admission to the ICU for the HMOX1 low group in comparison to 25 (23–28) days for the HMOX1 high group (p < 0.0001). For septic shock development, the median time for the HMOX1 low group was 13 (10–19) days, whereas for the HMOX1 high group, it was 21 (11–30) days (p = 0.04).
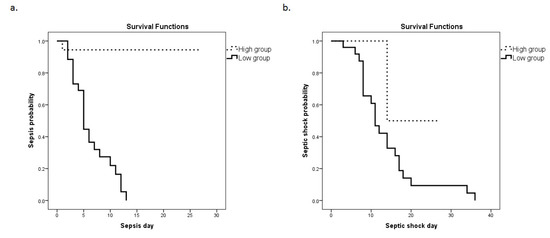
Figure 4.
HMOX1 expression levels and sepsis or septic shock development probability. The Kaplan–Meier method was used for sepsis (a) and septic shock (b) probability estimation, and the log-rank test for two-group comparison. The patient cohort was dichotomized above and below the cut-off value (3.99), as determined by the ROC curve. Dashed lines: ≥3.99 (high group); solid lines: <3.99 (low group). (a) The respective median time to sepsis development was 6 (95% C.I. = 5–8) days for the low group, and 25 (23–28) days for the high group (p-value < 0.0001). (b) The respective median times to septic shock development were 13 (10–19) days for the low group and 21 (11–30) days for the high group (p-value = 0.04).
3.4. Correlations of HIF-Regulated Gene Expression on ICU Admission
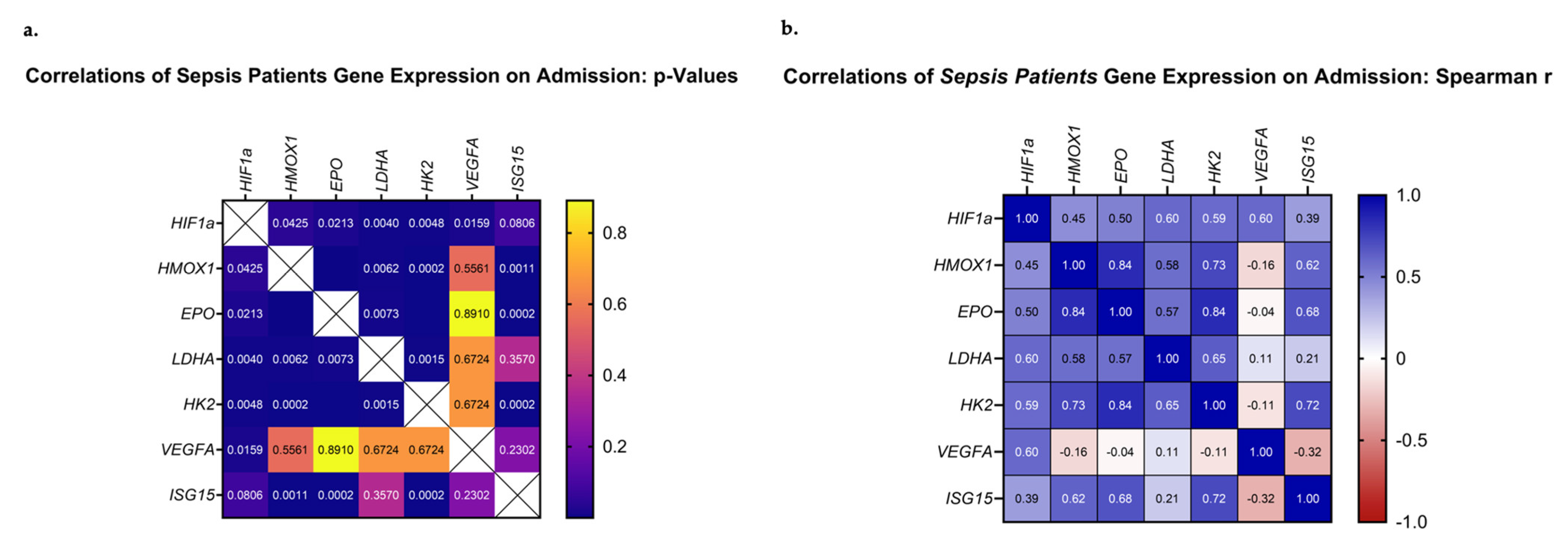
The next step in our analysis was to evaluate whether the above-mentioned genes presented any correlations between their mRNA expression patterns. Our analysis focused on the mRNA expression levels of the septic patient group. Upon admission, all studied genes, except for VEGFA, correlated significantly with each other and demonstrated positive Spearman coefficient correlation values (Figure 5a,b). VEGFA mRNA levels correlated only with HIF1A (p = 0.002, rs = 0.60). Most importantly, the highest Spearman values were calculated for pairs involving EPO, HMOX1, HK2, and ISG15 (EPO–HMOX1, p < 0.0001, rs = 0.84; EPO–HK2, p < 0.0001, rs = 0.84; HMOX1–HK2, p = 0.0002, rs = 0.73, ISG15 –HK2, p = 0.0002, rs = 0.72; ISG15–EPO, p = 0.0002, rs = 0.69; and ISG15–HMOX1, p = 0.0011, rs = 0.62). Additionally, pairs involving HIF1A, LDHA, and HK2 presented high Spearman values (HIF1A–LDHA, p = 0.006, rs = 0.60; HIF1A–HK2, p = 0.005, rs = 0.59; and LDHA–HK2, p = 0.002, rs = 0.65). Lastly, worth noting is the fact that ISG15 mRNA expression demonstrated a positive correlation with the day of sepsis development (ISG15–day of sepsis, p = 0.035, rs = 0.42), while it tended to correlate with the day of septic shock development (ISG15–day of septic shock, p = 0.059, rs = 0.39). The same trend was observed for EPO mRNA expression (EPO–day of sepsis, p = 0.10, rs = 0.34; EPO–day of shock, p = 0.08, rs = 0.36). A larger cohort of patients could prove beneficial in elucidating the true relationship between the two.
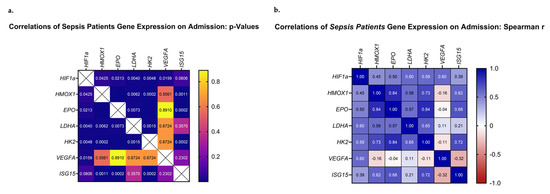
Figure 5.
Correlations of HIF1A, HMOX1, EPO, LDHA, ISG15, HK2, and VEGFA relative mRNA expression on ICU admission. (a) The p-values and (b) Spearman r values of each pair are presented as heat maps.
4. Discussion
Hypoxia is established as one of the main consequences of sepsis. Thus, the present study aimed to analyze whether genes with central roles in sepsis, known to be regulated by HIFs, exhibit a differential expression pattern in patients admitted to the ICU. Our study focused on analyzing gene expression patterns during admission, sepsis, and septic shock, as well as investigating differences on admission among initially non-septic patients who eventually developed or not sepsis/septic shock in the ICU. Our findings suggest that HMOX1 mRNA expression on ICU admission could be useful as a prognostic marker for sepsis and septic shock development.
To this day, few studies have explored heme oxygenase expression in septic patients and its importance as a prognostic factor. In these studies, the serum or plasma levels of heme oxygenase (HO-1) protein were measured, with little to no data regarding HMOX1 mRNA expression in sepsis patients. Xia et al. studied a cohort of septic and non-septic patients suffering from acute kidney injury (AKI) and demonstrated that the septic-AKI group presented elevated serum HO-1 protein levels in comparison to the non-septic-AKI group. They proposed that the extent of AKI progression in septic patients could be predicted by the increase in serum HO-1 levels [34]. Additionally, a study performed by Chen et al. demonstrated that in a cohort of COVID-19 patients, serum HO-1 protein levels were significantly elevated in those suffering from sepsis. When the septic patients were divided into survivors and non-survivors, the latter subgroup presented higher serum HO-1 levels [35]. Furthermore, another recent study showed that in a group of 70 patients diagnosed with sepsis, high HO-1 plasma levels measured on admission were significantly associated with disease severity and mortality [36].
In our cohort of ICU-admitted patients, we found that HMOX1 mRNA expression on ICU admission was significantly elevated in the septic patient group. ROC curve analysis in combination with multivariate regression analysis indicated that HMOX1 levels could be used as an independent prognostic factor for patients with a higher risk of developing sepsis and septic shock. Furthermore, the Kaplan–Meier analysis demonstrated that patients with higher HMOX1 expression have a higher probability of developing sepsis and septic shock compared to those with a lower expression.
Many studies have indicated a potential prognostic role for several of the molecules investigated in this report. Tamion et al. presented results indicating that in a cohort of 44 septic patients, EPO serum levels on admission were able to predict the outcome of patients [37]. Our results depict a tendency for correlation of EPO mRNA expression with the day of sepsis and septic shock development. Thus, a possible argument arises in relation to the use of EPO as a therapeutic treatment strategy. It could be of interest to examine whether the effect of EPO administration is correlated with the patients’ endogenous levels of EPO expression. Furthermore, ISG15 mRNA expression levels correlated positively with the day of sepsis development, while tending to correlate with the day of septic shock development. Additionally, in patients who developed sepsis, EPO and ISG15 mRNA expression levels at the time of ICU admission were positively correlated. This could be potentially attributed to the involvement of ISG15 in erythropoiesis. Maragno et al. have shown that ISG15 expression is induced during the late stages of erythropoiesis, where EPO retains a crucial role [24,38]. In this context, and consistent with our findings, ISG15 induction is, at least partially, dependent upon EPO receptor signaling and mainly independent of IFN signaling.
The results from a recent meta-analysis have demonstrated that VEGFA levels can also accurately predict sepsis mortality, with non-survivors presenting higher values [39]. Additionally, regarding LDHA, a number of studies have demonstrated that serum lactate levels could be of value in predicting mortality [40,41]. Finally, even though HK2 has not been assigned any prognostic value in sepsis, the enzyme has been significantly associated with mortality in several types of cancer [42,43]. In contrast to these data on protein serum levels, expression of the above-mentioned molecules did not present significant differences between ICU-admitted patients who did or did not develop sepsis. It should be noted though that our study focused on gene expression levels and not the serum levels of their respective products. Despite not presenting an association with any outcome, we showed that all studied genes, except VEGFA, positively correlated on admission in patients who developed sepsis. These results suggest an interplay between these molecules in the setting of sepsis and septic shock and would be interesting to investigate in future larger studies.
It is important to mention the limitations of our study. Initially, this was a single-center study with a limited number of patients. This limitation is derived from our choice of enrolling only patients who developed both sepsis and septic shock in the ICU. A cross-center study with a larger sample size might allow for the generalization of our results. Additionally, the septic patient group did not exhibit high mortality rates, and thus we could not examine the potential value of HMOX1 mRNA expression as a predictive risk factor for ICU outcome. Furthermore, it should be noted that this was an observational study, and hence the mechanisms implicated in the expression of the studied genes were not investigated. HMOX1 expression can be upregulated in response to various cellular stress stimuli, including inflammation, hypoxia–hyperoxia, hyperthermia, ischemia, or radiation.
5. Conclusions
As far as we are aware, this is the first report to assign to HMOX1 expression a possible prognostic role for sepsis development. Our results indicate that ICU admission values of HMOX1 gene expression could reveal patients at risk of developing sepsis and septic shock. Hence, the measurement of HMOX1 gene expression on ICU admission may provide physicians with a useful tool for determining the likelihood of sepsis and septic shock occurrence, allowing for more targeted treatment.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/medsci11020041/s1, Figure S1: Relative mRNA expression of HIF1A (a), HMOX1 (b), EPO (c), LDHA (d), HK2 (e), and VEGFA (f) in whole blood samples, on ICU admission, sepsis, and septic shock (septic patients), and on ICU admission and discharge (non-septic patients).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.G.V. and N.V.; methodology, N.S.L., C.K., A.G.V., E.J., Z.M. and N.V.; validation, A.G.V., N.V., I.D., S.E.O. and A.K.; formal analysis, N.S.L., C.K. and A.G.V.; investigation, N.S.L., C.K. and A.G.V.; resources, A.K.; data curation, N.S.L., C.K., E.J. and Z.M.; writing—original draft preparation, N.S.L., C.K., E.J. and Z.M.; writing—review and editing, A.G.V., N.V., I.D., S.E.O. and A.K.; supervision, A.G.V.; project administration, I.D., S.E.O. and A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the “Evangelismos” Hospital (80/01-02-2010).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all patients involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudd, K.E.; Kissoon, N.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; Bory, S.; Mutahunga, B.; Seymour, C.W.; Angus, D.C.; West, T.E. The global burden of sepsis: Barriers and potential solutions. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M. The role of mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis–induced multi–organ failure. Virulence 2014, 5, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, M.; Perna, B.; Cesaro, A.E.; Maritati, M.; Spampinato, M.D.; Contini, C.; De Giorgio, R. Update on Sepsis and Septic Shock in Adult Patients: Management in the Emergency Department. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 (HIF-1) Pathway. Sci. STKE 2007, 2007, cm8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaelin, W.G., Jr.; Ratcliffe, P.J. Oxygen sensing by metazoans: The central role of the HIF hydroxylase pathway. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.H.; Yang, Y.C.; Hsieh, M.Y.; Yeh, Y.C.; Li, T.K. A negative feedback of the HIF-1a pathway via the interferon-stimulated gene 15 and ISGylation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5927–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perng, Y.C.; Lenschow, D.J. ISG15 in antiviral immunity and beyond. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderhaeghen, T.; Vandewalle, J.; Libert, C. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors in Metabolic Reprogramming during Sepsis. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 1478–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, B.L.; Leite, G.G.F.; Brunialti, M.K.C.; Assuncao, M.; Azevedo, L.C.P.; Freitas, F.; Salomao, R. HIF-1α and Hypoxia Responsive Genes are Differentially Expressed in Leukocytes from Survivors and Non-Survivors Patients During Clinical Sepsis. Shock 2021, 56, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddle, S.R.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, S.; Deeb, S.S.; Malkki, M.; Schneider, B.K.; Allen, C.B.; White, C.W. Hypoxia induces hexokinase II gene expression in human lung cell line A549. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2000, 278, L407–L416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.; Roth, P.; Fang, H.; Wang, G. Transcriptional regulation of genes encoding glycolytic enzymes by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 23757–23763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, H.; Shimoda, L.A.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Semenza, G.L. Analysis of hypoxia-induced metabolic reprogramming. Methods Enzymol. 2014, 542, 425–455. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, D.J.; Miyamoto, S. Hexokinase II integrates energy metabolism and cellular protection: Akting on mitochondria and TORCing to autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wyngene, L.; Vandewalle, J.; Libert, C. Reprogramming of basic metabolic pathways in microbial sepsis: Therapeutic targets at last? EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, e8712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chillappagari, S.; Venkatesan, S.; Garapati, V.; Mahavadi, P.; Munder, A.; Seubert, A.; Sarode, G.; Guenther, A.; Schmeck, B.T.; Tümmler, B.; et al. Impaired TLR4 and HIF expression in cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelial cells downregulates hemeoxygenase-1 and alters iron homeostasis in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 307, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, V.H. Regulation of erythropoiesis by hypoxia-inducible factors. Blood Rev. 2013, 27, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, B.L.; Bunn, H.F. Regulation of the Erythropoietin Gene. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 1999, 94, 1864–1877. [Google Scholar]
- Semenza, G.L. HIF-1: Mediator of physiological and pathophysiological responses to hypoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 88, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryter, S.W. Heme Oxgenase-1, a Cardinal Modulator of Regulated Cell Death and Inflammation. Cells 2021, 10, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredenburgh, L.E.; Perrella, M.A.; Mitsialis, S.A. The Role of Heme Oxygenase-1 in Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 36, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yu, J.; Gong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.; Shi, J.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Heme oxygenase-1(HO-1) regulates Golgi stress and attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury through hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α)/HO-1 signaling pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 165, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Xie, X.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Q.; Ge, Z.; Wei, H.; Deng, J.; Xia, Z.; Lian, Q. Heme Oxygenase-1 Reduces Sepsis-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Acute Lung Injury. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 9413876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelkmann, W. Erythropoietin. Front. Horm. Res. 2016, 47, 115–127. [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer, H.E. Erythropoietin: Multiple targets, actions, and modifying influences for biological and clinical consideration. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chancharoenthana, W.; Udompronpitak, K.; Manochantr, Y.; Kantagowit, P.; Kaewkanha, P.; Issara-Amphorn, J.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Repurposing of High-Dose Erythropoietin as a Potential Drug Attenuates Sepsis in Preconditioning Renal Injury. Cells 2021, 10, 3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, S. Protective Effects of Erythropoietin towards Acute Lung Injuries in Rats with Sepsis and Its Related Mechanisms. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2019, 49, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Walden, A.P.; Young, J.D.; Sharples, E. Bench to bedside: A role for erythropoietin in sepsis. Crit. Care 2010, 14, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, K.; Choudhury, S.; Ramasamy, T.; Kesavan, M.; Parida, S.; Singh, T.U. Erythropoietin prevents sepsis-induced clinical severity and haematological changes in mice. Pharma Innov. J. 2020, 9, 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ghezzi, P.; Brines, M. Erythropoietin as an antiapoptotic, tissue-protective cytokine. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11, S37–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.O. Vascular endothelial growth factors and vascular permeability. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 87, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, K.; Saito, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Imbaby, S.; Hattori, K.; Matsuda, N.; Hattori, Y. Vascular endothelial growth factor contributes to lung vascular hyperpermeability in sepsis-associated acute lung injury. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 2365–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.L.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta DeltaC(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Dong, H.; Wu, N.; Wiedermann, C.J.; Andaluz-Ojeda, D.; Chen, H.; Li, N. Heme oxygenase-1 as a predictor of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: A cross-sectional study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Tzeng, I.S.; Tsai, K.W.; Wu, Y.K.; Cheng, C.F.; Lu, K.C.; Chung, H.W.; Chao, Y.C.; Su, W.L. Association between heme oxygenase one and sepsis development in patients with moderate-to-critical COVID-19: A single center, retrospective observational study. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2022, 27, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekregbesi, P.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Bottomley, C.; Riley, E.M.; Mooney, J.P. Relationship between Anaemia, Haemolysis, Inflammation and Haem Oxygenase-1 at Admission with Sepsis: A pilot study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamion, F.; Le Cam-Duchez, V.; Menard, J.F.; Girault, C.; Coquerel, A.; Bonmarchand, G. Erythropoietin and renin as biological markers in critically ill patients. Crit. Care 2004, 8, R328–R335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maragno, A.L.; Pironin, M.; Alcalde, H.; Cong, X.; Knobeloch, K.P.; Tangy., F.; Zhang, D.E.; Ghysdael, J.; Quang, C.T. ISG15 modulates development of the erythroid lineage. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.L.; Peng, Y.; Shen, M.J.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, S.; Xiong, M.C.; Gao, N.; Hu, T.P.; Zhang, G.Q. Prognostic role of elevated VEGF in sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 941257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryoo, S.M.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Lim, K.S.; Huh, J.W.; Hong, S.B.; Lim, C.M.; Koh, Y.; Kim, W.Y. Lactate level versus lactate clearance for predicting mortality in patients with septic shock defined by sepsis-3. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, e489–e495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.G.; Song, J.; Park, D.W.; Moon, S.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.; Cha, J.H. Prognostic value of lactate levels and lactate clearance in sepsis and septic shock with initial hyperlactatemia: A retrospective cohort study according to the Sepsis-3 definitions. Medicine 2021, 100, e24835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, K.; Shi, L.; Xiang, F.; Tao, K.; Wang, G. Prognostic Significance of the Metabolic Marker Hexokinase-2 in Various Solid Tumors: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagiri, M.; Karasawa, H.; Takagi, K.; Nakayama, S.; Yabuuchi, S.; Fujishima, F.; Naitoh, T.; Watanabe, M.; Suzuki, T.; Unno, M.; et al. Hexokinase 2 in colorectal cancer: A potent prognostic factor associated with glycolysis, proliferation and migration. Histol. Histopathol. 2017, 32, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).