Prediction of Muddy Floods Using High-Resolution Radar Precipitation Forecasts and Physically-Based Erosion Modeling in Agricultural Landscapes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
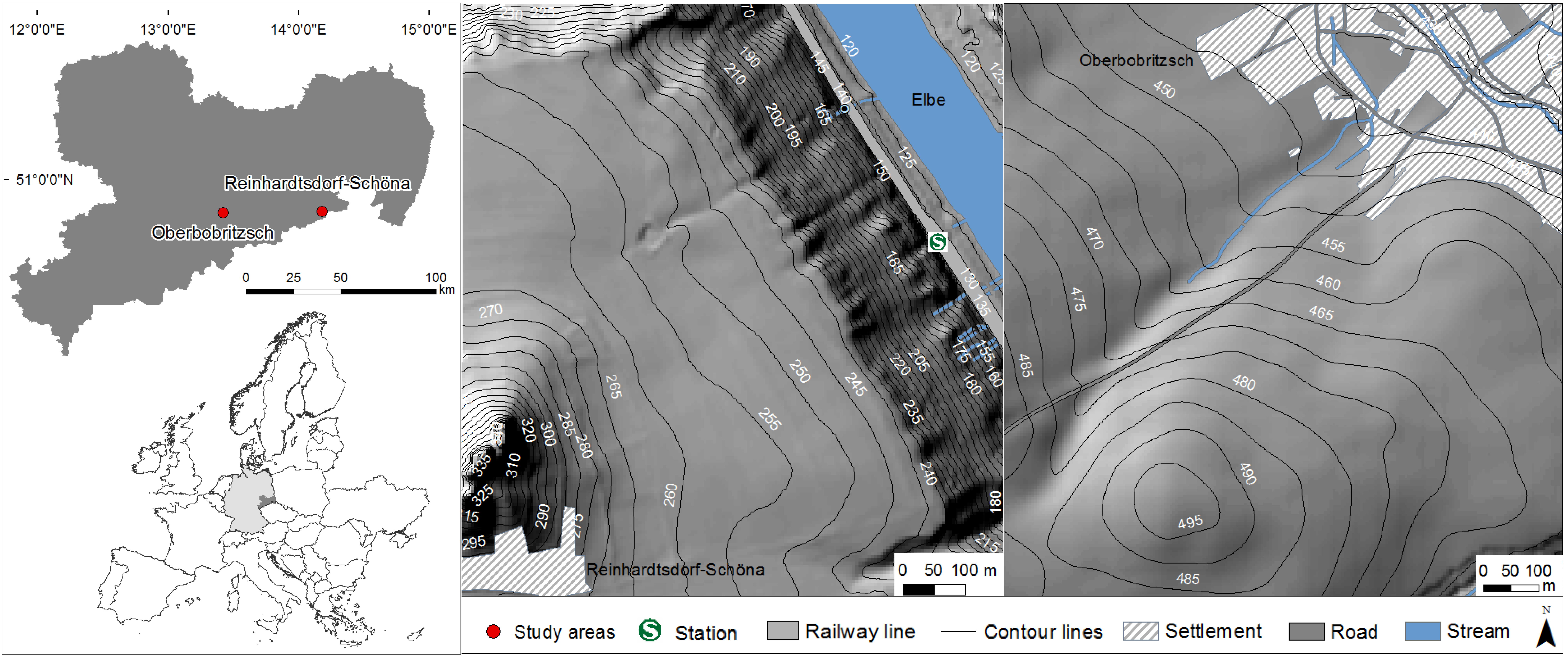
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. High-Resolution Radar Precipitation Data and Forecasts
2.2.1. Data Description
2.2.2. Data Preparation and Analysis
2.2.3. Comparison of Radar Precipitation Data and Rain Gauge Data
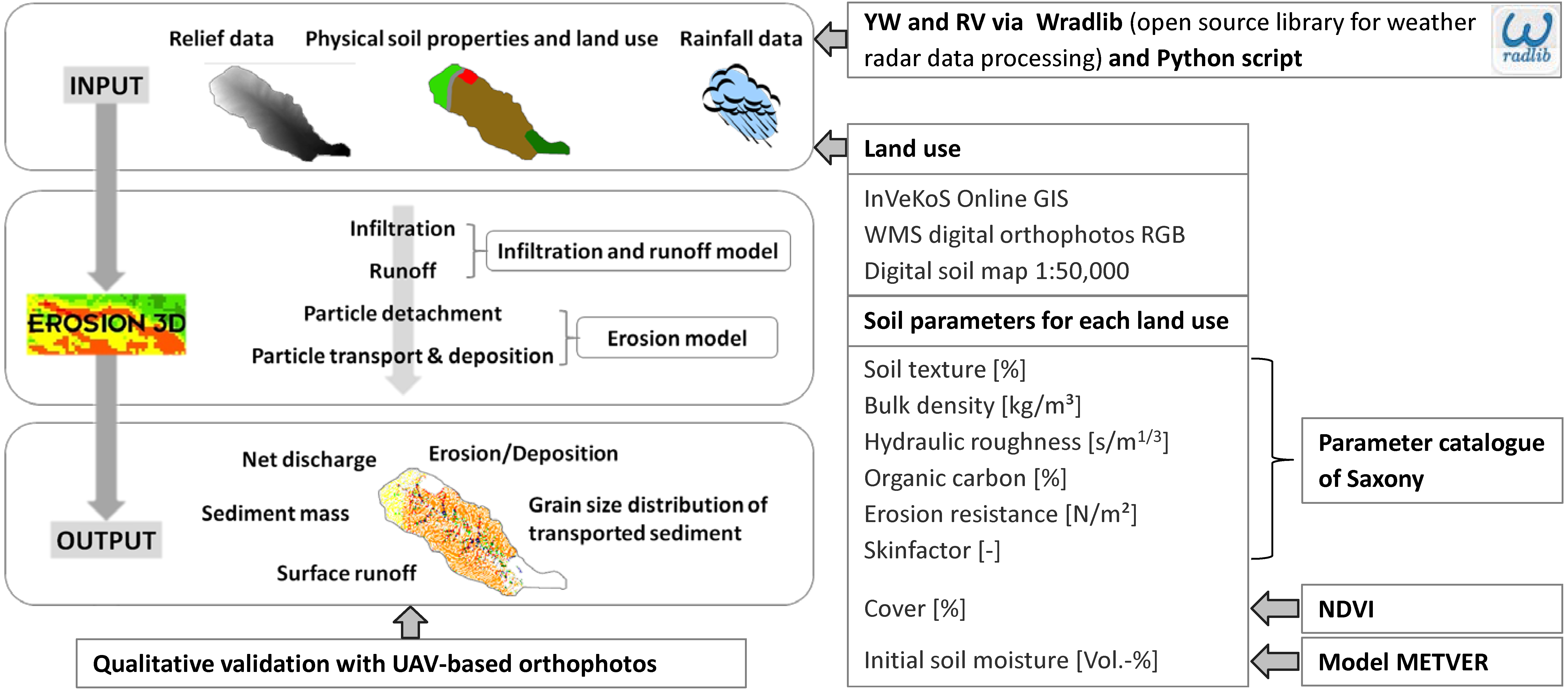
2.3. High-Resolution Physically-Based Erosion Modeling Using EROSION 3D
2.3.1. Modeling Approach
- bulk density [kg/m3]
- organic carbon [% by weight]
- initial soil moisture [% by volume]
- hydraulic roughness [s/m1/3]
- resistance to erosion [N/m2]
- cover [%], and
- soil texture [% by weight] [39].
2.3.2. Model Parameterization
2.3.3. Derivation of E 3D’s Soil Parameter ‘Cover’ from NDVI
2.4. Qualitative Model Validation by UAV Monitoring
3. Results
3.1. High-Resolution Radar Precipitation Data and Forecasts
3.1.1. Comparison of Radar Precipitation Data and Rain Gauge Data
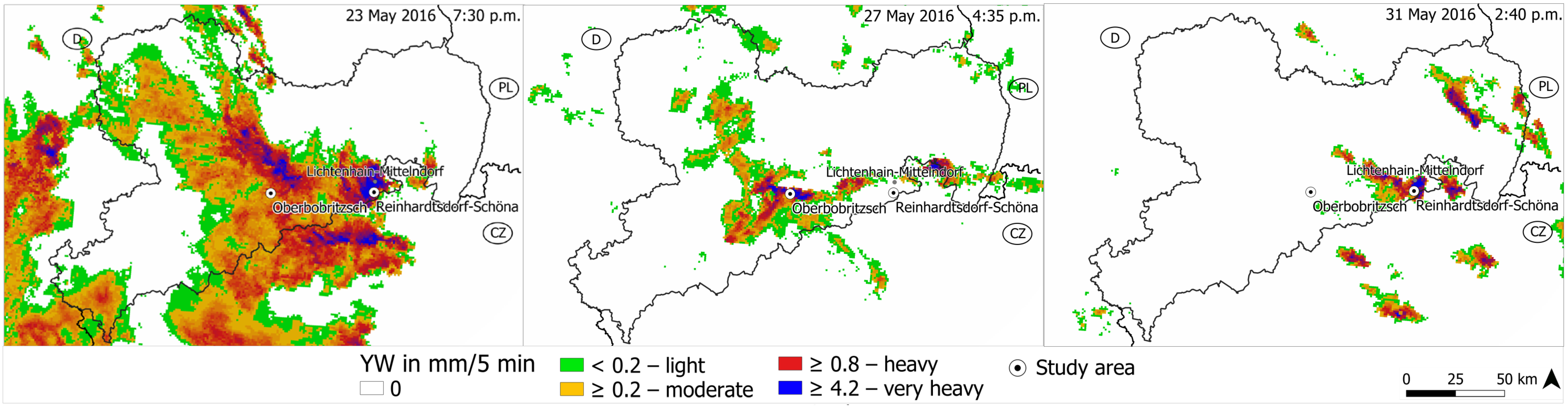
3.1.2. The Storm Events by Radar Images
3.1.3. The Radar Precipitation Forecasts
3.2. High-Resolution Physically-Based Erosion Modeling Using EROSION 3D
3.2.1. Reconstruction and Qualitative Validation of the Muddy Floods
3.2.2. Forecast of the Muddy Floods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DLM | Digital Landscape Model |
| DTM | Digital Terrain Model |
| DWD | German term, abbreviated from Deutscher Wetterdienst meaning German Meteorological Service |
| E 3D | EROSION 3D Soil Erosion Model |
| GIS | Geographic Information Systems |
| KOSTRA-DWD-2010R | German term, abbreviated from KOordinierte STarkniederschlagsRegionalisierung und -Auswertung des DWD meaning coordinated regionalization and analysis of heavy precipitation by the DWD |
| METVER | German term, abbreviated from METeorologisches VERdunstungsmodell, meaning meteorological evaporation model |
| NDVI | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index |
| RADKLIM | German term, abbreviated from RADarKLIMatologie, meaning radar climatology |
| RADOLAN | German term, abbreviated from RADar-OnLine-ANeichung meaning radar online adjustment |
| RADVOR | German term, abbreviated from RADar-NiederschlagsVORhersage, meaning radar precipitation forecast |
| SfM | Structure from Motion |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| USLE | Universal Soil Loss Equation |
References
- Boardman, J. A short history of muddy floods. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 21, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boardman, J.; Vandaele, K.; Evans, R.; Foster, I. Off-site impacts of soil erosion and runoff: Why connectivity is more important than erosion rates. Soil Use Manag. 2019, 35, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltner, A.; Baumgart, P.; Maas, H.-G.; Faust, D. Multi-temporal UAV data for automatic measurement of rill and interrill erosion on loess soil. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2015, 40, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, H.-P.; Brümmer, G.W.; Fleige, H.; Horn, R.; Kandeler, E.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Kretzschmar, R.; Stahr, K.; Wilke, B.-M. Scheffer/Schachtschabel Soil Science, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ad-hoc-Arbeitsgruppe Boden der Staatlichen Geologischen Dienste und der Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe. Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung, 5th ed.; E. Schweizerbart‘sche Verlagsbuchhandlung (Nägele und Obermiller): Stuttgart, Germany, 2005; pp. 1–438. [Google Scholar]
- Ziese, M.; Junghänel, T.; Becker, A. Andauernde Großwetterlage Tief Mitteleuropa Entfaltet Ihr Unwetterpotential mit Starken Gewittern und Massiven Schadensgeschehen in Deutschland. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/DE/leistungen/besondereereignisse/niederschlag/20160603_starkregen_mai-2016_meldung.html (accessed on 18 July 2019).
- Bronstert, A.; Agarwal, A.; Boessenkool, B.; Fischer, M.; Heistermann, M.; Köhn-Reich, L.; Moran, T.; Wendi, D. Die Sturzflut von Braunsbach am 29. Mai 2016—Entstehung, Ablauf und Schäden eines “Jahrhundertereignisses”. Teil 1: Meteorologische und hydrologische Analyse. The Braunsbach Flashflood of Mai 29th, 2016—Origin, Pathways and Impacts of an Extreme Hydro-Meteorological Event. Part 1: Meteorological and Hydrological Analysis. Hydrol. Wasserbewirtsch. 2017, 61, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- earth-chronicles.com. A Landslide Disrupted Rail Service between Dresden and Prague. Available online: http://earth-chronicles.com/natural-catastrophe/a-landslide-disrupted-rail-service-between-dresden-and-prague.html (accessed on 14 September 2016).
- Radio Leipzig. Unwetter Sorgt für Schäden in Sächsischer Schweiz. Available online: www.radioleipzig.de/beitrag/unwetter-sorgt-fuer-schaeden-in-saechsischer-schweiz-230485 (accessed on 23 July 2018).
- TAG24.de. Heftiges Unwetter löst Schlammlawine aus. Available online: https://www.tag24.de/nachrichten/freiberg-mittelsachsen-unwetter-tobt-ueber-sachsen-schlammlawine-69045 (accessed on 23 July 2019).
- DWA-Themen. Niederschlagserfassung Durch Radar und Anwendung in Der Wasserwirtschaft—T2/2017; Deutsche Vereinigung für Wasserwirtschaft, Abwasser und Abfall e. V.: Hennef, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–99. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, F.K.; Winterrath, T.; Junghänel, T.; Walawender, E.; Auerswald, K. Mean annual precipitation erosivity (R factor) based on RADKLIM Version 2017.002. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, F.; Hauck, J.; Brandhuber, R.; Weigl, E.; Maier, H.; Auerswald, K. Spatio-temporal variability of erosivity estimated from highly resolved and adjusted radar rain data. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 223, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, F.K.; Kistler, M.; Brandhuber, R.; Maier, H.; Treisch, M.; Auerswald, K. Validation of official erosion modelling based on high-resolution radar rain data by aerial photo erosion classification. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, F.K.; Winterrath, T.; Auerswald, K. Temporal- and spatial-scale and positional effects on rain erosivity derived from point-scale and contiguous rain data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6505–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winterrath, T.; Brendel, C.; Hafer, M.; Junghänel, T.; Klameth, A.; Lengfeld, K.; Walawender, E.; Weigl, E.; Becker, A. RADKLIM Version 2017.002: Reprocessed gauge-adjusted radar data, one-hour precipitation sums (RW). 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J. Entwicklung und Anwendung eines physikalisch begründeten Simulationsmodells für die Erosion geneigter, landwirtschaftlicher Nutzflächen. Berl. Geogr. Abh. 1996, 61, 1–148. [Google Scholar]
- Deumlich, D. Nutzung Von RADOLAN-Daten Zur Retrospektiven Analyse Von Erosionsereignissen. In Proceedings of the Berichte der DBG: Böden verstehen-böden nutzen-böden fit machen, Berlin, Germany, 3–9 September 2011; Available online: http://eprints.dbges.de/609/ (accessed on 21 July 2019).
- Hänsel, P.; Kaiser, A.; Buchholz, A.; Böttcher, F.; Langel, S.; Schmidt, J.; Schindewolf, M. Mud flow reconstruction by means of physical erosion modeling, high-resolution radar-based precipitation data and UAV monitoring. Geosciences 2018, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterrath, T.; Brendel, C.; Hafer, M.; Junghänel, T.; Klameth, A.; Lengfeld, K.; Walawender, E.; Weigl, E.; Becker, A. RADKLIM Version 2017.002: Reprocessed quasi gauge-adjusted radar data, 5-minute precipitation sums (YW). 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OSM Boundaries Map 4.4.6. Wambachers-OSM. Available online: https://wambachers-osm.website/boundaries/ (accessed on 28 September 2018).
- DWD Climate Data Center (CDC): Multi-Annual Station Means for the Climate Normal Reference Period 1981–2010, for Current Station Location and for Reference Station Location. Available online: https://opendata.dwd.de/climate_environment/CDC/observations_germany/climate/multi_annual/mean_81-10/ (accessed on 21 July 2019).
- BK 50 2012: Sächsisches Landesamt für Umwelt, Landwirtschaft und Geologie. Available online: https://www.umwelt.sachsen.de/umwelt/boden/27787.htm (accessed on 21 July 2018).
- DWD Climate Data Center (CDC): Historical Daily Precipitation Observations for Germany; Version v007 (Daily Precipitation Data). 2019. Available online: https://opendata.dwd.de/climate_environment/CDC/observations_germany/climate/daily/more_precip/historical/ (accessed on 21 July 2019).
- DWD RADOLAN Produktübersicht. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/DE/leistungen/radolan/radolan.html (accessed on 16 July 2019).
- DWD Erhöhung Der Zeitlichen Taktrate Der Nationalen Standard-Aneichung (RW) Von Einer Stunde Auf Zehn Minuten. RADOLAN-Info Nr. 47. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/DE/leistungen/radolan/radolan_info/radolan_info_nr_47.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=2 (accessed on 11 July 2019).
- DWD RADKLIM. Erstellung Einer Radargestützten Hochaufgelösten Niederschlagsklimatologie für Deutschland zur Auswertung Der Rezenten Änderungen Des Extremverhaltens Von Niederschlag. Beschreibung des Kompositformats und Der Verschiedenen Reprozessierungsläufe; Version 1.0. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/EN/ourservices/radarklimatologie/format_description_in_german.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=2 (accessed on 16 July 2019).
- DWD RADVOR-Kurzbeschreibung. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/EN/ourservices/radvor/radvor.html (accessed on 15 July 2019).
- DWD Operationalisierung von RADVOR(RY) am 25.11.2015, 11:30 MEZ, erfolgt. RADVOR-Info Nr. 18. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/DE/leistungen/radvor/radvor_info/radvor_op_info_nr_18.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=2 (accessed on 22 July 2019).
- DWD RADVOR-OP Kurzbeschreibung. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/DE/fachnutzer/wasserwirtschaft/unsere_leistungen/radarniederschlagsprodukte/radvor_opkurzbeschreibung_pdf.html (accessed on 17 July 2019).
- Open Data Server DWD 2019. Data Source: Deutscher Wetterdienst. Radolan. Available online: https://opendata.dwd.de/weather/radar/radolan/ (accessed on 11 July 2019).
- DWD RADOLAN/RADVOR. Hoch aufgelöste Niederschlagsanalyse und –vorhersage auf der Basis quantitativer Radar- und Ombrometerdaten für grenzüberschreitende Fluss-Einzugsgebiete von Deutschland im Echtzeitbetrieb Beschreibung des Kompositformats; Version 2.4.5. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/DE/leistungen/radolan/radolan.html (accessed on 15 July 2019).
- Heistermann, M.; Jacobi, S.; Pfaff, T. Technical Note: An open source library for processing weather radar data (wradlib). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DWD Wetterlexikon. Available online: www.dwd.de/lexikon (accessed on 22 July 2019).
- QGIS 2018. QGIS Version 3.0.1—Girona 64 bit. Available online: https://www.qgis.org (accessed on 10 April 2018).
- DWD Climate Data Center (CDC): Grids of Return Periods of Heavy Precipitation (Design Precipitation) over Germany (KOSTRA-DWD); Version 2010R. Available online: https://opendata.dwd.de/climate_environment/CDC/grids_germany/return_periods/precipitation/KOSTRA/KOSTRA_DWD_2010R/ (accessed on 12 July 2019).
- DWD Climate Data Center (CDC): Historical 1 Minute Precipitation Observations for Germany; Version v007. 2019. Available online: https://opendata.dwd.de/climate_environment/CDC/observations_germany/climate/1_minute/precipitation/historical/2016/ (accessed on 11 July 2019).
- DWD Climate Data Center (CDC): Historical Daily Precipitation Observations for Germany; Version v007 (Every Minute Precipitation Data). 2019. Available online: https://opendata.dwd.de/climate_environment/CDC/observations_germany/climate/daily/more_precip/historical/ (accessed on 21 July 2019).
- Von Werner, M. Erosion-3D Benutzerhandbuch; Version 3.0.; Michael von Werner: Berlin, Germany, 2002; pp. 1–82. [Google Scholar]
- Klik, A.; Zartl, A.S.; Hebel, B.; Schmidt, J. Comparing RUSLE, EROSION 2D/3D, and WEPP Soil Loss Calculations with Four Years of Observed Data. In Proceedings of the ASAE, Annual International Meeting, Orlando, FL, USA, 11–16 July 1998. ASAE No. 982055. [Google Scholar]
- Jetten, V.; de Roo, A.; Favis-Mortlock, D. Evaluation of field-scale and catchment-scale soil erosion models. Catena 1999, 37, 521–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.; von Werner, M.; Michael, A. Application of the EROSION 3D Model to the Catsop Watershed, The Netherlands. Catena 1999, 37, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebel, B. Validierung numerischer Erosionsmodelle in Einzelhang und Einzugsgebietsdimension. Phys. Baseler Beitr. Zur Phys. 2003, 32, 1–181. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, A.; Schmidt, J.; Enke, W.; Deutschländer, T.; Malitz, G. Impact of expected increase in precipitation intensities on soil loss—Results of comparative model simulations. Catena 2005, 61, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schob, A.; Schmidt, J.; Tenholtern, R. Derivation of site-related measures to minimise soil erosion on the watershed scale in the Saxonian loess belt using the model EROSION 3D. Catena 2006, 68, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilde, M. Modelling Soil Erosion in the Zhifanggou-Watershed on the Chinese Loess Plateau using EROSION 2/3D; TU Bergakademie Freiberg: Freiberg, Germany, 2008; 79p. [Google Scholar]
- Seidel, N. Untersuchung der Wirkung Verschiedener Landnutzungen auf Oberflächenabfluss und Bodenerosion mit einem Simulationsmodell. Ph.D. Thesis, TU Bergakademie Freiberg, Freiberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Schindewolf, M.; Schmidt, W. Validierung EROSION 3D—Prüfung und Validierung des neu entwickelten Oberflächenabflussmoduls des Modells EROSION 3D im Zusammenhang mit Maßnahmen des vorsorgenden Hochwasserschutzes auf landwirtschaftlich genutzten Flächen. Schri. Landesamtes Umwelt Landwirtsch. Geol. 2009, 15, 1–121. Available online: https://nbn-resolving.org/urn:nbn:de:bsz:14-ds-1244617738468-42743 (accessed on 23 July 2019).
- Schindewolf, M. Prozessbasierte Modellierung von Erosion, Deposition und Partikelgebundenem Nähr- und Schadstofftransport in der Einzugsgebiet- und Regionalskala. Ph.D. Thesis, TU Bergakademie Freiberg, Freiberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Steinz, A. Prozessbasierte Ermittlung des Jährlichen Partikelgebundenen Schwermetallaustrages im Einzugsgebiet der Mulde. Master’s Thesis, TU Bergakademie Freiberg, Freiberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Starkloff, T.; Stolte, J. Applied comparison of the erosion risk models EROSION 3D and LISEM for a small catchment in Norway. Catena 2014, 118, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schindewolf, M.; Kaiser, A.; Buchholz, A.; Schmidt, J. Development of a flash flood warning system based on real-time radar data and process-based erosion modelling. In EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts; EGU2017-18057; EGU General Assembly: Vienna, Austria, 2017; Volume 19. [Google Scholar]
- LfUG. Bodenerosionsmessprogramm Sachsen—Auswertung der Beregnungsversuche 1–28 vom 04.-31.10.1993; LfUG: Freiberg, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- LfUG. Bodenerosionsmessprogramm Sachsen—Auswertung der Beregnungsversuche 29–49 vom 02.-12.05.1994; LfUG: Freiberg, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- LfUG. Bodenerosionsmessprogramm Sachsen—Auswertung der Beregnungsversuche 50–76 vom 26.09.-12.10.1994; LfUG: Freiberg, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- LfUG. Bodenerosionsmessprogramm Sachsen—Auswertung der Beregnungsversuche 77–94 vom 09.05.-19.5.1995; LfUG: Freiberg, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- LfUG. Bodenerosionsmessprogramm Sachsen—Auswertung der Beregnungsversuche 95–116 vom 03.10.-13.10.1996; LfUG: Freiberg, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, J. A mathematical model to simulate rainfall erosion. In Erosion, Transport and Deposition Processes—Theories and Models; Catena Supplement; Bork, H.-R., de Ploey, J., Schick, A.P., Eds.; Catena Verlag: Cremlingen-Destedt, Germany, 1991; Volume 19, pp. 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, J. Modeling long term soil loss and landform change. In Overland Flow—Hydraulics and Erosion Mechanics; Parson, A.J., Abrahams, A.D., Eds.; UCL Press: London, UK, 1992; pp. 409–433. [Google Scholar]
- Von Werner, M. GIS-orientierte Methoden der Digitalen Reliefanalyse zur Modellierung von Bodenerosion in Kleinen Einzugsgebieten. Ph.D. Thesis, Freie Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Green, W.H.; Ampt, G.A. Studies on soil physics. J. Agric. Sci. 1911, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Werner, M. Abschätzung Des Oberflächenabflusses Und Der Wasserinfiltration Auf landwirtschaftlich Genutzten Flächen Mit Hilfe Des Modells EROSION 3D; Endbericht; GeoGnostic: Berlin, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kunth, F.; Kaiser, A.; Vláčilová, M.; Schindewolf, M.; Schmidt, J. Extensive Rill Erosion and Gullying on Abandoned Pit Mining Sites in Lusatia, Germany; EGU General Assembly: Vienna, Austria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, A.; Schmidt, J.; Schmidt, W. Band II: Parameterkatalog Sachsen Anwendung. In EROSION 2D/3D—Ein Computermodell zur Simulation der Bodenerosion durch Wasser; Sächsische Landesanstalt für Landwirtschaft, Sächsisches Landesamt für Landwirtschaft, Umwelt und Geologie: Dresden, Freiberg, Germany, 1996; p. 121. [Google Scholar]
- Seibert, S.; Auerswald, K.; Fiener, P.; Disse, M.; Martin, W.; Haider, J.; Michael, A.; Gerlinger, K. Surface runoff from arable land—A homogenized data base of 726 rainfall simulation experiments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LfL. Erarbeitung der Digitalen Datengrundlage für die Anwendung von EROSION-3D auf Mesoskaliger Maßstabsebene mit Durchführung einer Erosionssimulation für das zu Bearbeitende Gebiet, Endbericht des FuE-Vorhabens der LfL; GeoGnostics: Leipzig/Berlin, Germany, 2005; pp. 1–88. [Google Scholar]
- Schindewolf, M.; Schmidt, J.; von Werner, M. Modeling soil erosion and resulting sediment transport into surface water courses on regional scale. ZfG Suppl. Issues 2013, 57, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DTM2 2016: Staatsbetrieb Geobasisinformation und Vermessung Sachsen. Kachelnummer 4445636 und 4445638. State 2005. Available online: http://www.landesvermessung.sachsen.de/inhalt/produkte/dhm/dgm/dgm.html (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- DTM10: Staatsbetrieb Geobasisinformation und Vermessung Sachsen. Kachelnummer 3905634, 3925634, 3905632 und 3925632. State 2013. Available online: http://www.landesvermessung.sachsen.de/inhalt/produkte/dhm/dgm/dgm.html (accessed on 23 July 2019).
- InVeKoS Online GIS v6.1. 2018: Sächsisches Staatsministerium für Umwelt und Landwirtschaft. Available online: https://www.smul.sachsen.de/gis-online/Default.aspx (accessed on 21 July 2018).
- WMS Digitale Orthophotos (RGB) 2015: Staatsbetrieb Geobasisinformation und Vermessung Sachsen. Available online: https://geodienste.sachsen.de/wms_geosn_dop-rgb/guest? (accessed on 21 July 2018).
- ArcGIS 2015. Esri ArcGIS 10.4.1 for Desktop, Version 10.4.1.5686. Available online: https://www.esri.de/support-de/produkte/startset-arcgis-104 (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Arévalo, S.A. Simulation of a Local Flood Event in a Settling Area with EROSION 3D. Diploma Thesis, TU Bergakademie Freiberg, Freiberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zemke, J. Runoff and Soil Erosion Assessment on Forest Roads Using a Small Scale Rainfall Simulator. Hydrology 2016, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.; Müller, G. Berechnung der Verdunstung landwirtschaftlicher Produktionsgebiete, 1. Mitteilung. Z. Meteorol. 1988, 38, 332–336. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, J.; Müller, G. Berechnung der Verdunstung landwirtschaftlicher Produktionsgebiete, 2. Mitteilung. Z. Meteorol. 1988, 38, 361–365. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, J.; Müller, G. Berechnung der Verdunstung landwirtschaftlicher Produktionsgebiete, 3. Mitteilung. Z. Meteorol. 1989, 39, 142–149. [Google Scholar]
- Wendling, U.; Schellin, H.-G. Neue Ergebnisse zur Berechnung der potentiellen Evapotranspiration. Z. Meteorol. 1986, 36, 214–217. [Google Scholar]
- Turc, L. Évaluation des besoins en eau d’irrigation, évapotranspiration potentielle, formule simplifiée et mise à jour. Ann. Agron. 1961, 12, 13–49. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, J.; Böttcher, F.; Schmidt, M. Bestimmung bodenabhängiger Klimafeuchtezahlen für verschiedene Standorte in den mittleren und nordöstlichen Regionen Deutschlands. Hercynia, N. F. 2008, 41, 189–200. [Google Scholar]
- Land Viewer 2018: EOS Data Analytics, Inc. Available online: https://eos.com/landviewer (accessed on 21 July 2018).
- Agisoft 2016. Agisoft PhotoScan Professiona; Version 1.2.5 Build 2735 (64 bit); Agisoft LLC: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2016; Available online: http://www.agisoft.com/ (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Peters, T. Ableitung einer Beziehung zwischen der Radarreflektivität, der Niederschlagsrate und weiteren aus Radardaten abgeleiteten Parametern unter Verwendung von Methoden der multivariaten Statistik. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Fridericiana zu Karlsruhe (TH), Karlsruhe, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Einfalt, T.; Frerk, I. The challenge to estimate extreme precipitation for locations without rain gauges. In Proceedings of the ERAD 2012—The seventh European Conference on Radar in Meteorology and Hydrology, Toulouse, France, 25–29 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- DWD RADOLAN/RADVOR-OP (Sachstand und Ausblick). Available online: https://www.dwd.de/DE/leistungen/radolan/radarniederschlagsprodukte/vortrag_2010_pdf (accessed on 15 December 2017).
- Hänsel, P.; (Technical University Bergakademie Freiberg, Freiberg, Saxony, Germany). Personal photography. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hebenstreit, F.; (DB Netz AG, Dresden, Saxony, Germany). Personal Communication, 2018.
- DWD Änderung des Inputs beim RY-Radarprodukt und zwei neue Summenprodukte. RADOLAN-Info Nr. 45. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/DE/leistungen/radolan/radolan_info/radolan_info_nr_45.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=3 (accessed on 21 July 2019).
- DWD Inbetriebnahme des Ausfallsicherungsradars Borkum und Abschaltung des Radars Emden sowie Änderung des Inputs beim RO- und RZ-Radarprodukt. RADOLAN-Info Nr. 46. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/DE/leistungen/radolan/radolan_info/radolan_info_nr_46.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=2 (accessed on 21 July 2019).
- DWD Start der Bereitstellung der Testproduktion POLARA_*. RADVOR-Info Nr. 19. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/DE/leistungen/radvor/radvor_info/radvor_op_info_nr_19.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=2 (accessed on 21 July 2019).










| Product | Procedure | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| RZ | RADOLAN | real-time, unadjusted to rain gauges |
| RY | RADOLAN | real-time, quality tested, unadjusted to rain gauges |
| YW | RADKLIM | reprocessed, quasi-gauge adjusted |
| RV | RADVOR | real-time, forecasted, basis: RY, unadjusted to rain gauges |
| Intensity | mm/5 min 1 | mm/10 min | mm/hr |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light | <0.2 | <0.5 | <2.5 |
| Moderate | ≥ 0.2–< 0.8 | ≥ 0.5–< 1.7 | ≥ 2.5–< 10.0 |
| Heavy | ≥ 0.8–< 4.2 | ≥ 1.7–< 8.3 | ≥10.0–< 50.0 |
| Very heavy | ≥4.2 | ≥8.3 | ≥50.0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hänsel, P.; Langel, S.; Schindewolf, M.; Kaiser, A.; Buchholz, A.; Böttcher, F.; Schmidt, J. Prediction of Muddy Floods Using High-Resolution Radar Precipitation Forecasts and Physically-Based Erosion Modeling in Agricultural Landscapes. Geosciences 2019, 9, 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9090401
Hänsel P, Langel S, Schindewolf M, Kaiser A, Buchholz A, Böttcher F, Schmidt J. Prediction of Muddy Floods Using High-Resolution Radar Precipitation Forecasts and Physically-Based Erosion Modeling in Agricultural Landscapes. Geosciences. 2019; 9(9):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9090401
Chicago/Turabian StyleHänsel, Phoebe, Stefan Langel, Marcus Schindewolf, Andreas Kaiser, Arno Buchholz, Falk Böttcher, and Jürgen Schmidt. 2019. "Prediction of Muddy Floods Using High-Resolution Radar Precipitation Forecasts and Physically-Based Erosion Modeling in Agricultural Landscapes" Geosciences 9, no. 9: 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9090401
APA StyleHänsel, P., Langel, S., Schindewolf, M., Kaiser, A., Buchholz, A., Böttcher, F., & Schmidt, J. (2019). Prediction of Muddy Floods Using High-Resolution Radar Precipitation Forecasts and Physically-Based Erosion Modeling in Agricultural Landscapes. Geosciences, 9(9), 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9090401




