Seafloor Characterization Using Multibeam Echosounder Backscatter Data: Methodology and Results in the North Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Least Squares Cubic Spline Approximation (LS-CSA)
2.1. Background and Objectives
2.2. Principle of LS-CSA
3. Seafloor Characterization Using Proposed Method
3.1. Application of Bayesian Method
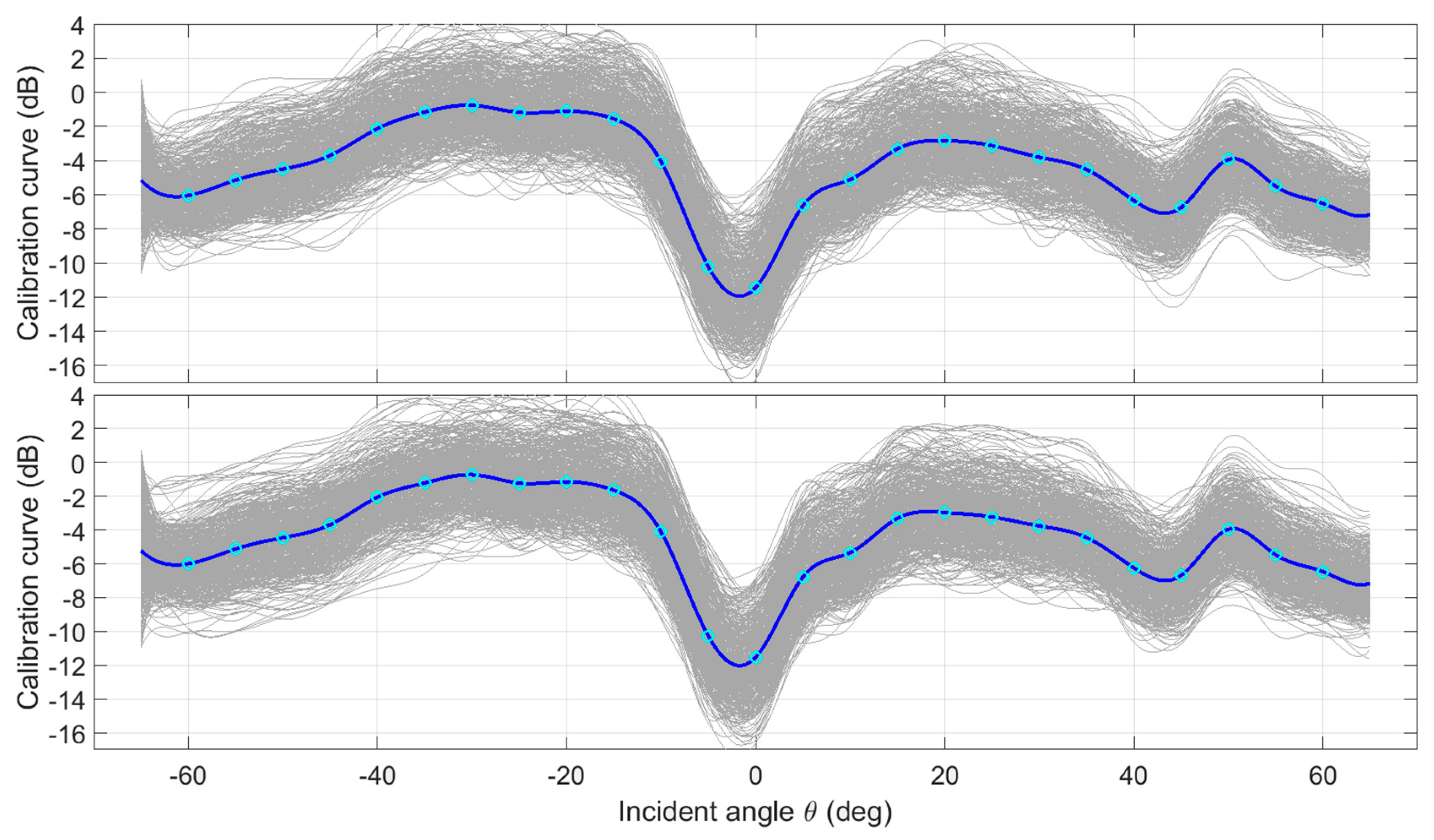
3.2. Estimation of Angular Calibration Curve
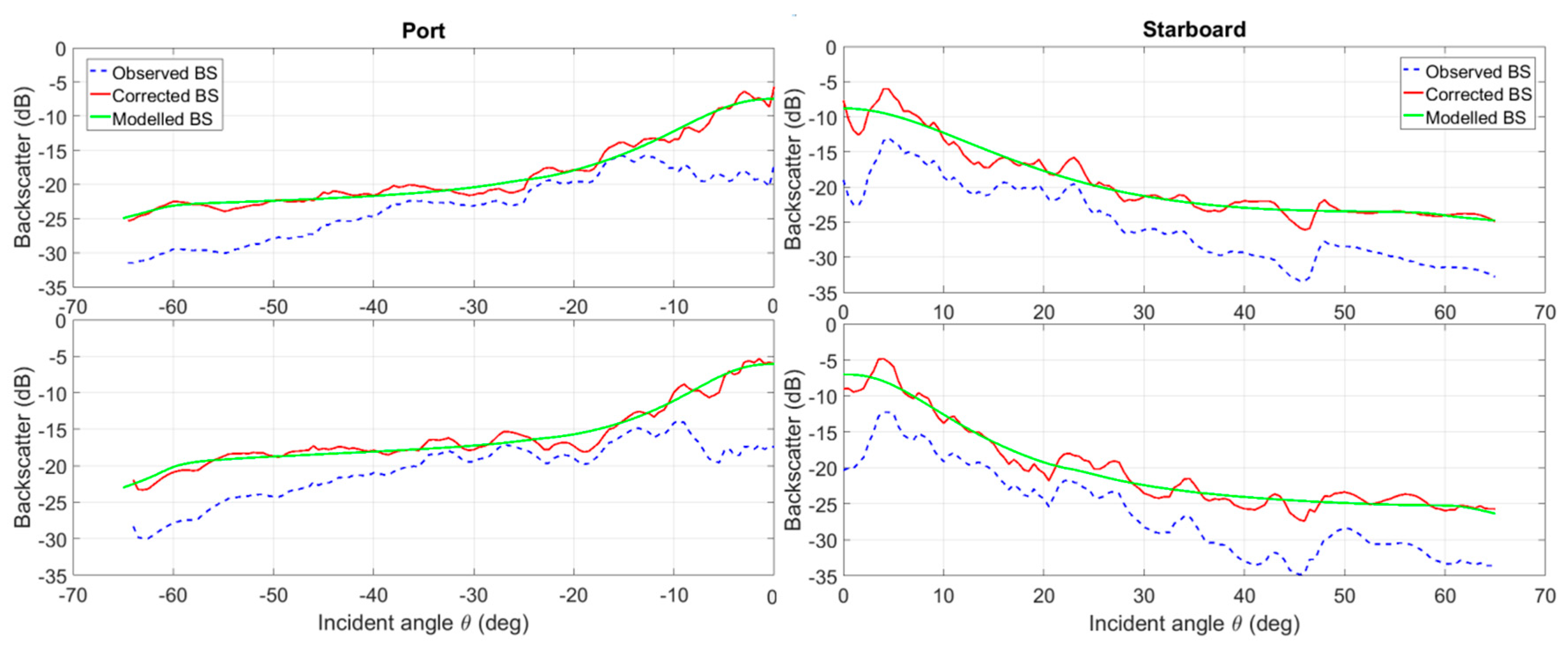
3.3. Model Inversion Using Optimization Method
4. Application to MBES Dataset in Brown Bank
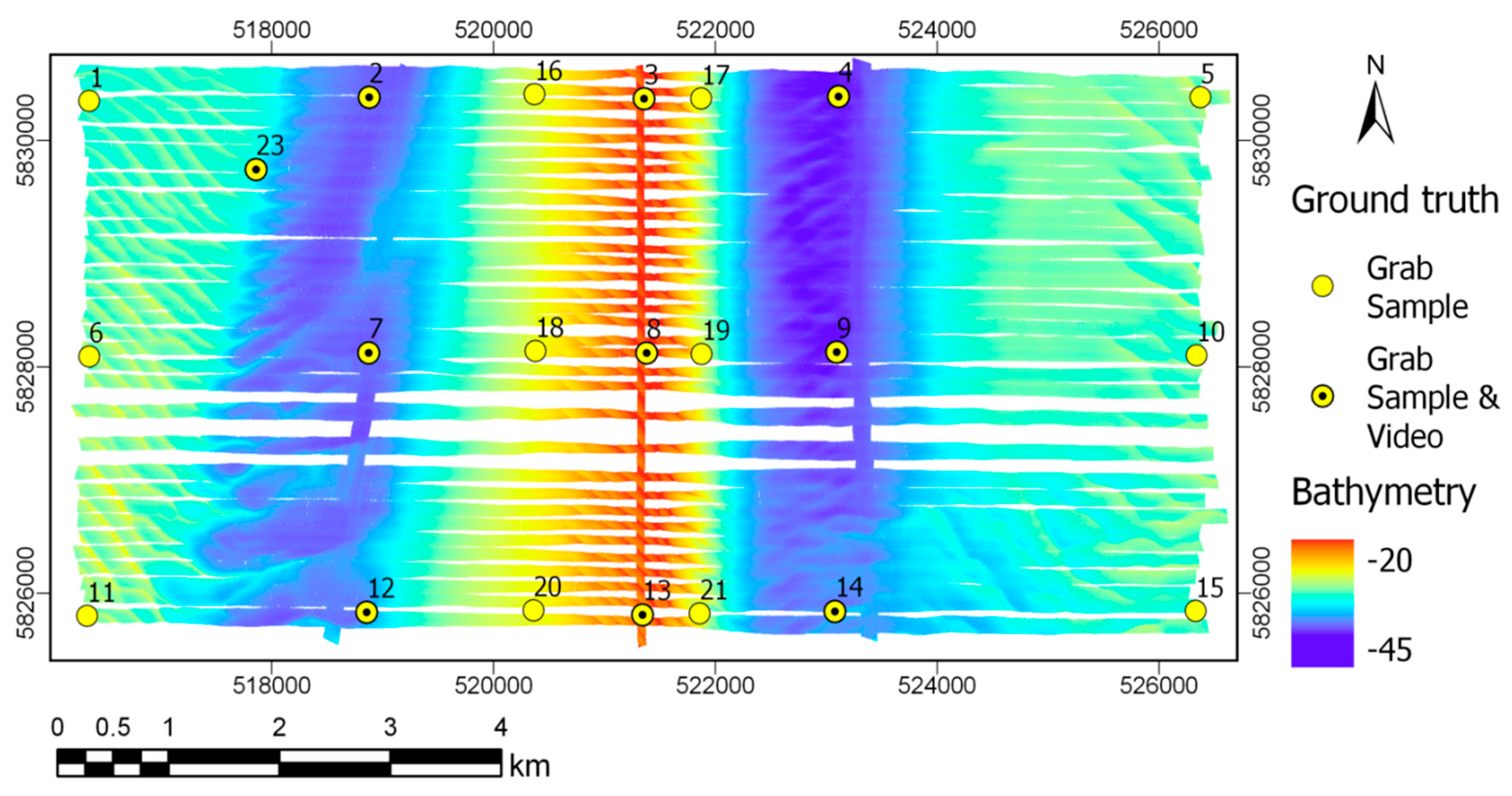
4.1. Study Area and Data Description
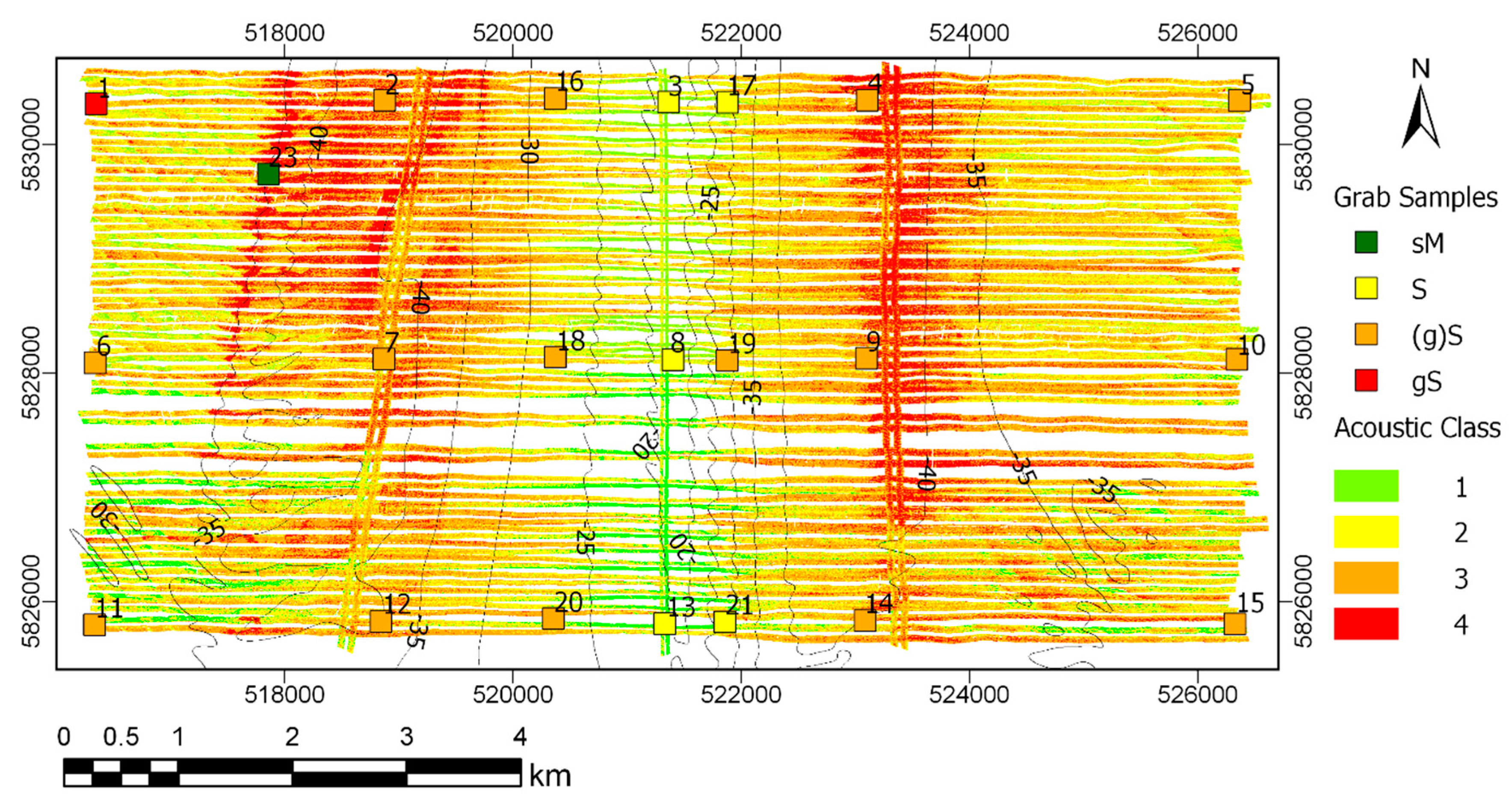
4.2. Bayes Classification Results
4.3. Calibration of MBES
4.4. Estimating Geoacoustic Parameters
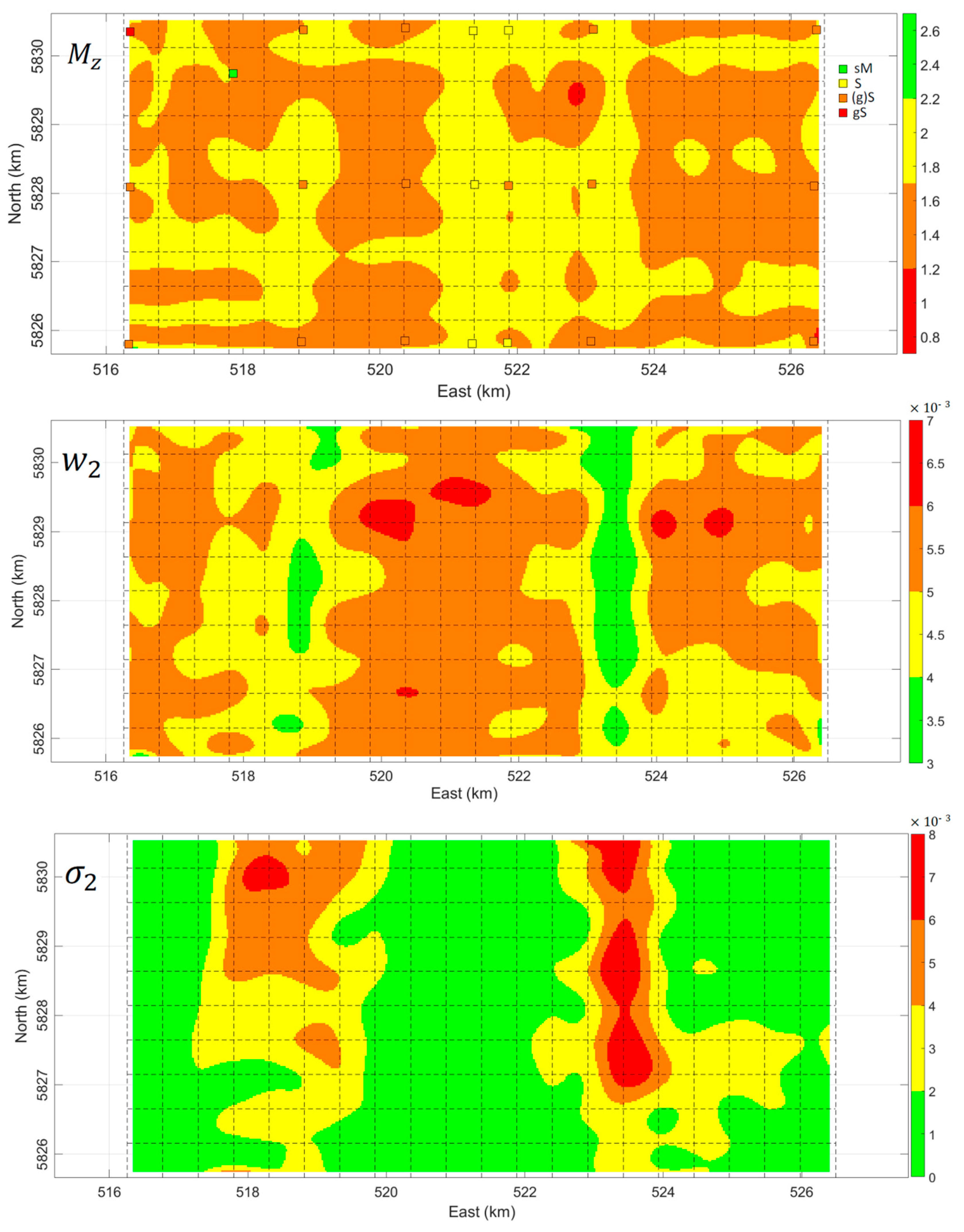
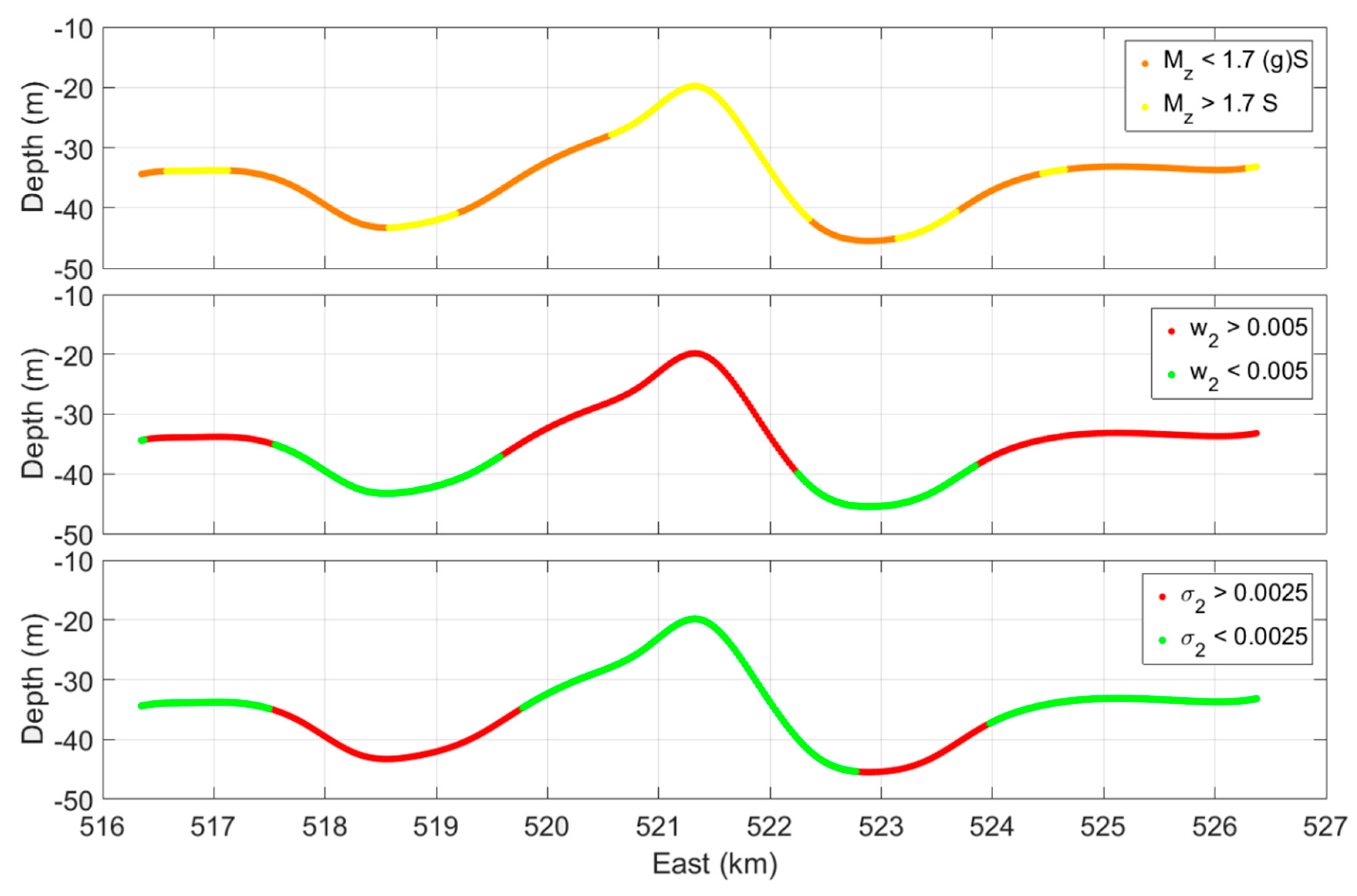
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Acoustic Classes vs. Geoacoustic Parameters
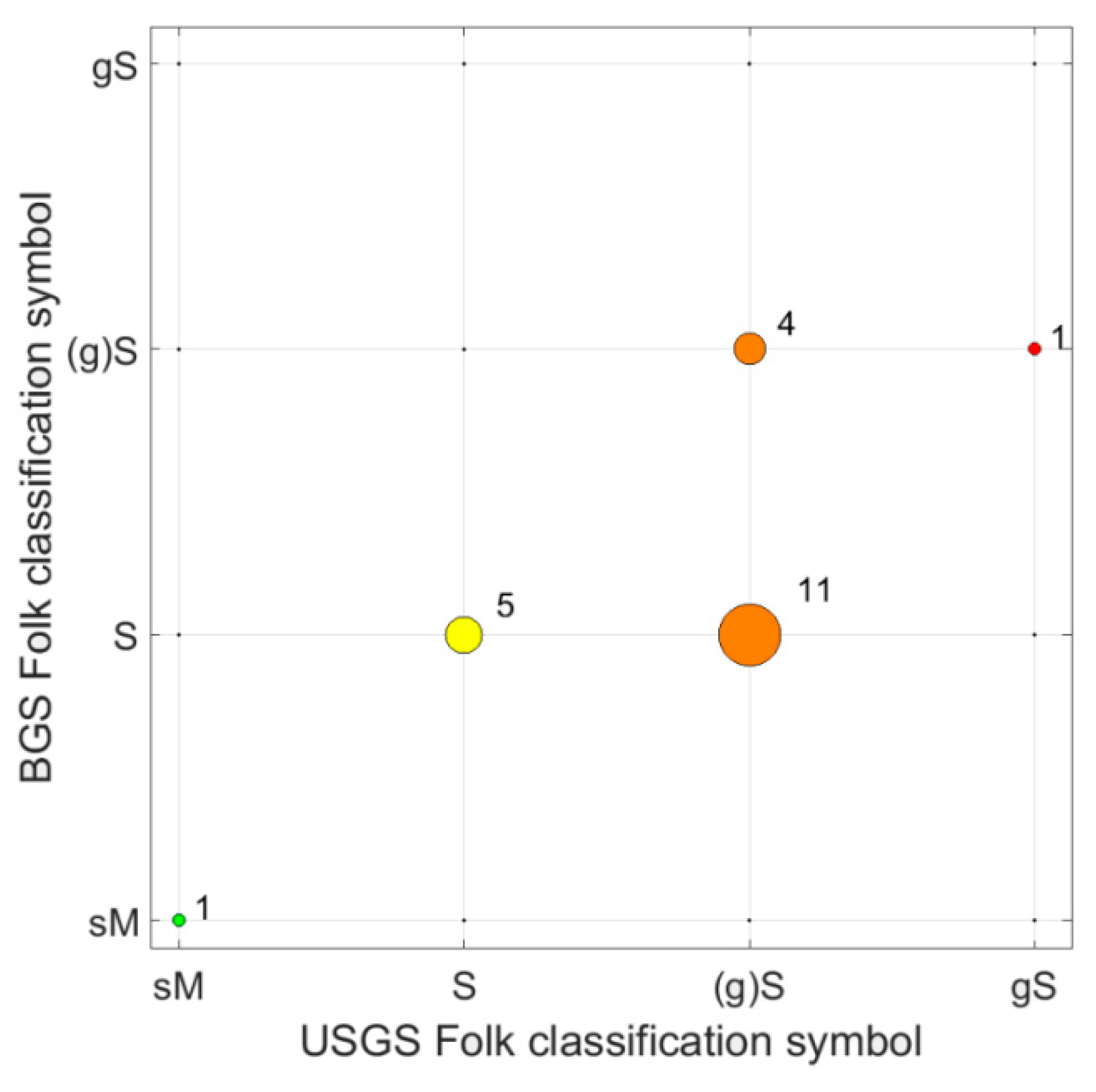
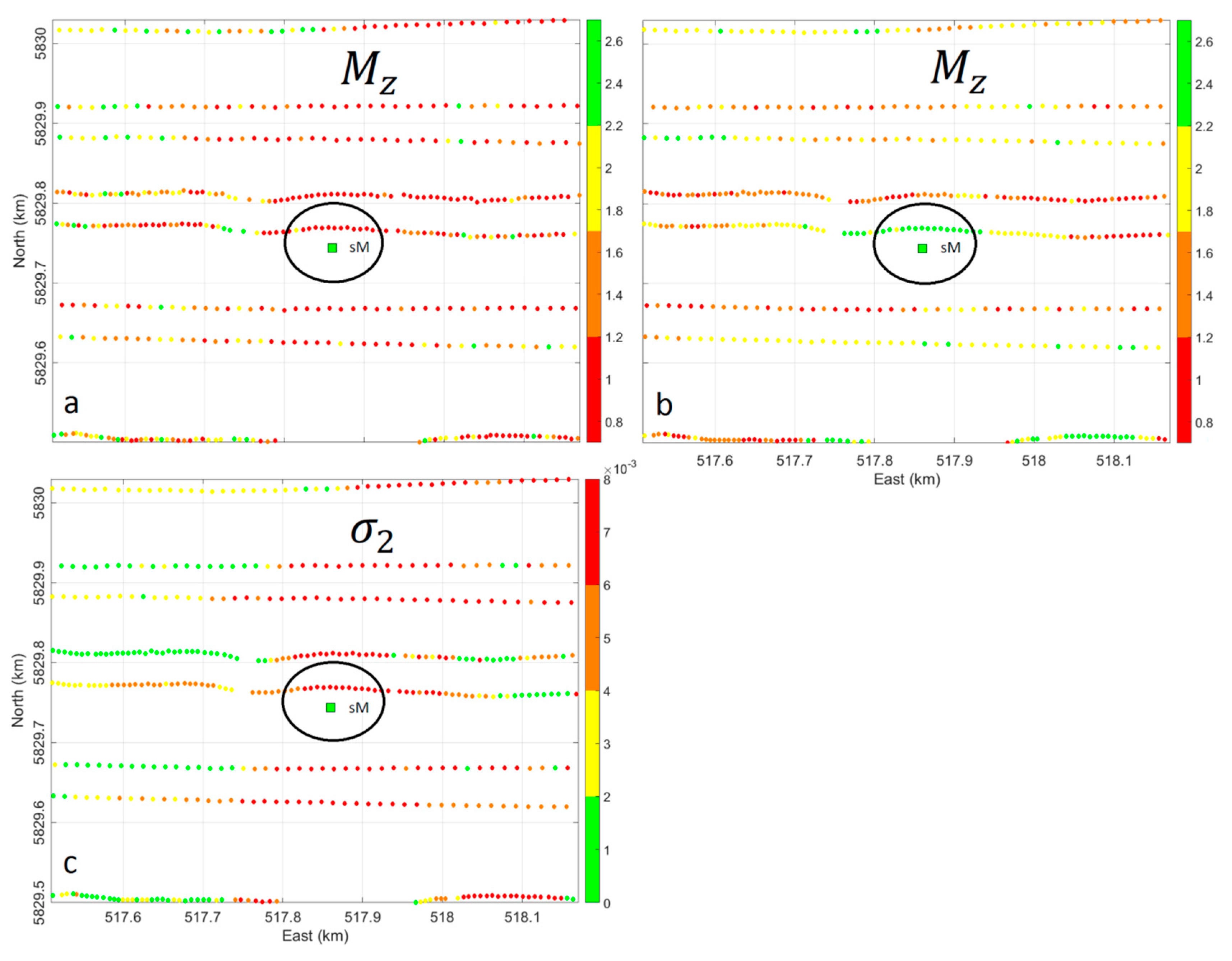
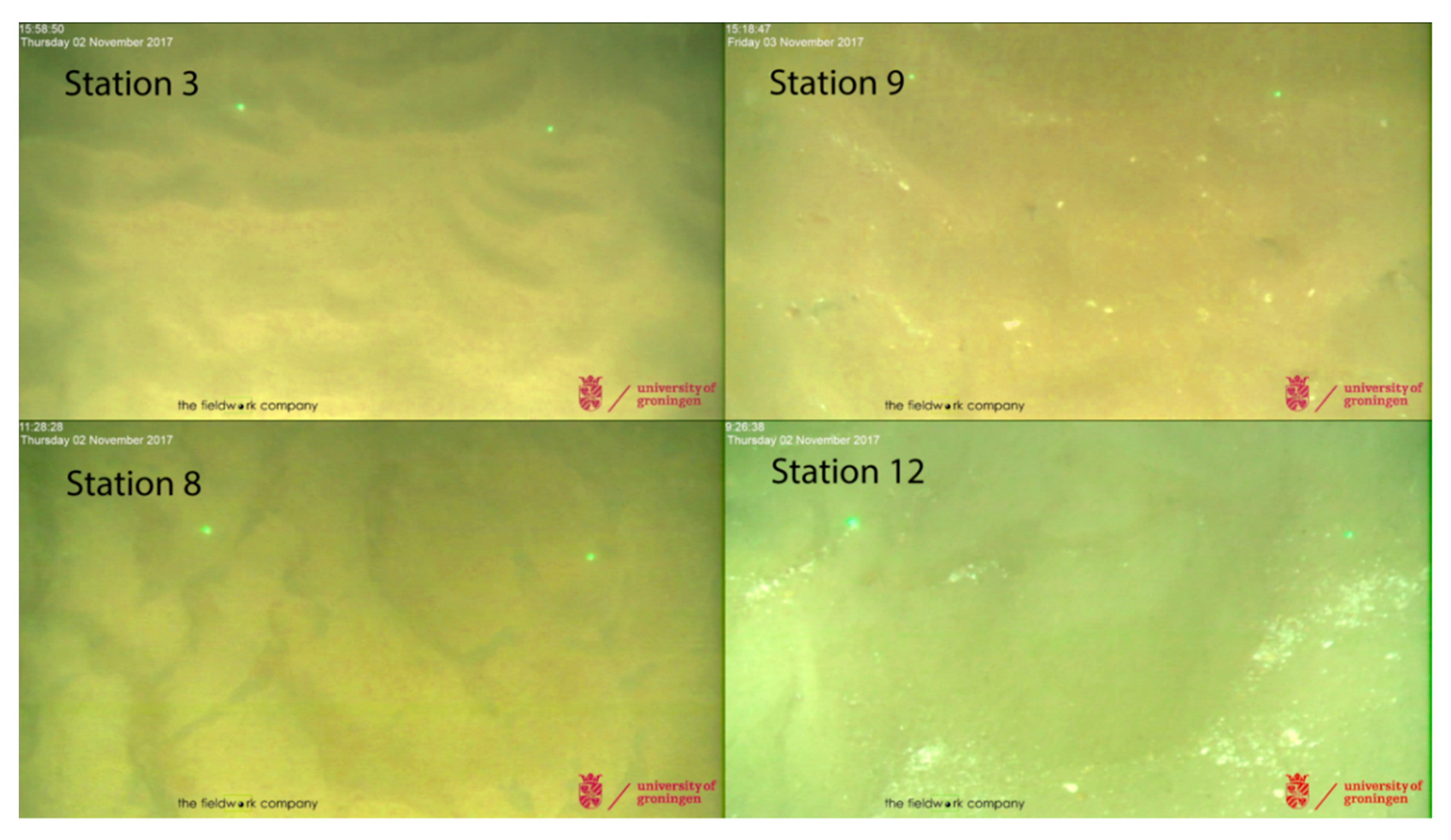
5.2. Grab Sample Ground-Truthing
5.3. Importance of Inversion for Three Parameters
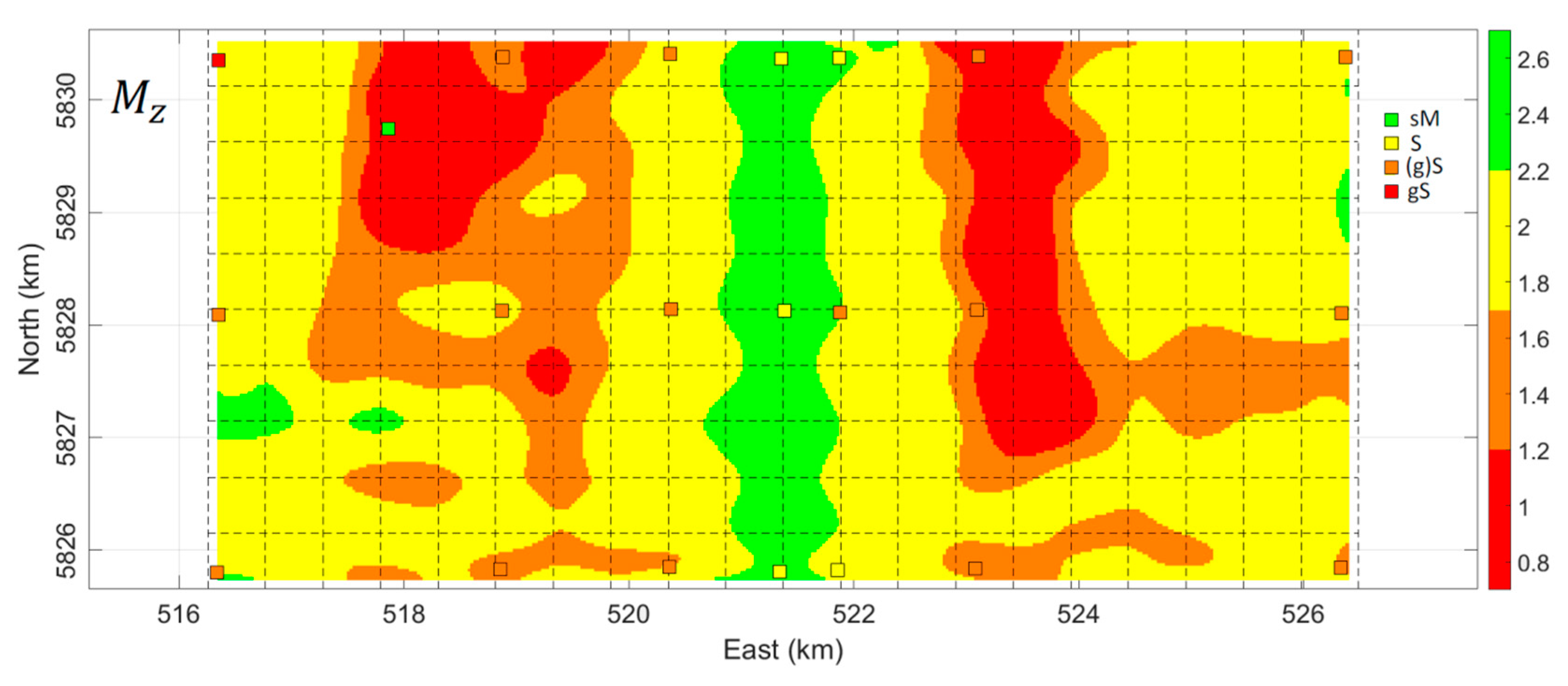
5.4. Brown Bank Sediment Composition
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diesing, M.; Mitchell, P.; Stephens, D. Image-based seabed classification: What can we learn from terrestrial remote sensing? ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 73, 2425–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diesing, M.; Thorsnes, T. Mapping of cold-water coral carbonate mounds based on geomorphometric features: An object-based approach. Geosciences 2018, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, I.; Brown, C. Neural network classification of multibeam backscatter and bathymetry data from Stanton Bank (Area IV). Appl. Acoust. 2009, 70, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, G.Y.; Gayes, P.T.; Van Dolah, R.F.; Schwab, W.C. Spatially quantitative seafloor habitat mapping: Example from the northern South Carolina inner continental shelf. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 59, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J.H.; Danforth, B.; Valentine, P. Areal seabed classification using backscatter angular response at 95 kHz. In Proceedings of the SACLANTCEN Conf on High Frequency Acoustics in Shallow Water, Lerici, Italy, 30 June–4 July 1997; pp. 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, L.; Mayer, L. Remote estimation of surficial seafloor properties through the application angular range analysis to multibeam sonar data. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2007, 28, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarche, G.; Lurton, X.; Verdier, A.-L.; Augustin, J.-M. Quantitative characterisation of seafloor substrate and bedforms using advanced processing of multibeam backscatter—Application to Cook Strait, New Zealand. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, S93–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, L.J. Clustering of cumulative grain size distribution curves for shallow-marine samples with software program CLARA. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2007, 54, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, L.J.; Parnum, I. Acoustic seabed segmentation from direct statistical clustering of entire multibeam sonar backscatter curves. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.J.; Smith, S.J.; Lawton, P.; Anderson, J.T. Benthic habitat mapping: A review of progress towards improved understanding of the spatial ecology of the seafloor using acoustic techniques. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 92, 502–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.J.; Todd, B.J.; Kostylev, V.E.; Pickrill, R.A. Image-based classification of multibeam sonar backscatter data for objective surficial sediment mapping of Georges Bank, Canada. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, S110–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftherakis, D.; Amiri-Simkooei, A.; Snellen, M.; Simons, D.G. Improving riverbed sediment classification using backscatter and depth residual features of multi-beam echo-sounder systems. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 131, 3710–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snellen, M.; Gaida, T.C.; Koop, L.; Alevizos, E.; Simons, D.G. Performance of Multibeam Echosounder Backscatter-Based Classification for Monitoring Sediment Distributions Using Multitemporal Large-Scale Ocean Data Sets. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2018, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiuk, B.; Diesing, M.; Aitken, A.; Brown, C.J.; Edinger, E.N.; Bell, T. A spatially explicit comparison of quantitative and categorical modeling approaches for mapping seabed sediments using random forest. Geosciences 2019, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, D.; Diesing, M. Towards quantitative spatial models of seabed sediment composition. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.J.; Beaudoin, J.; Brissette, M.; Gazzola, V. Multispectral multibeam echo sounder backscatter as a tool for improved seafloor characterization. Geosciences 2019, 9, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscombe, D.; Grams, P.E. Probabilistic substrate classification with multispectral acoustic backscatter: A comparison of discriminative and generative models. Geosciences 2018, 8, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaida, T.C.; Tengku Ali, T.A.; Snellen, M.; Amiri-Simkooei, A.R.; Van Dijk, T.A.G.P.; Simons, D.G. A multispectral Bayesian classification method for increased acoustic discrimination of seabed sediments using multi-frequency multibeam backscatter data. Geosciences 2018, 8, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, D.G.; Snellen, M. A Bayesian approach to seafloor classification using multi-beam echo-sounder backscatter data. Appl. Acoust. 2009, 70, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri-Simkooei, A.; Snellen, M.; Simons, D.G. Riverbed sediment classification using multi-beam echo-sounder backscatter data. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 126, 1724–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.R.; Winebrenner, D.P.; Ishimaru, A. Application of the composite roughness model to high-frequency bottom backscattering. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1986, 79, 1410–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, L.; Brown, C.; Calder, B.; Mayer, L.; Rzhanov, Y. Angular range analysis of acoustic themes from Stanton Banks Ireland: A link between visual interpretation and multibeam echosounder angular signatures. Appl. Acoust. 2009, 70, 1298–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.; Rodrigues, A.; Quartau, R. Acoustic remote characterization of seabed sediments using the Angular Range Analysis technique: The inlet channel of Tagus River estuary (Portugal). Mar. Geol. 2018, 400, 60–75. [Google Scholar]
- Collier, J.; Brown, C. Correlation of sidescan backscatter with grain size distribution of surficial seabed sediments. Mar. Geol. 2005, 214, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APL-UW Model. High-Frequency Ocean Environmental Acoustics Models Handbook; APL-UW Technical Report, No. APL-UW 9407; Williams, K.L., Ed.; Scientific Research: Wuhan, China, 1994; Available online: http://www.dtic.mil/docs/citations/ADB199453 (accessed on 26 June 2019).
- Bartels, R.H.; Beatty, J.C.; Barsky, B.A. Hermite and Cubic Spline Interpolation. In An Introduction to Splines for Use in Computer Graphics and Geometric Modeling; Morgan Kaufmann: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1998; Chapter 3; pp. 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.K. Feedback, Nonlinear, and Distributed Circuits; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 9–20. ISBN 978-1-4200-5881-9. [Google Scholar]
- Reinsch, C.H. Smoothing by Spline Functions. Numer. Math. 1976, 10, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge, C. Über empirische Funktionen und die Interpolation zwischen äquidistanten Ordinaten. Zeitschrift für Mathematik und Physik 1901, 46, 224–243. [Google Scholar]
- Burden, R.L.; Faires, J.D.; Reynolds, A.C. Numerical Analysis, 6th ed.; Brooks/Cole: Boston, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 120–121. [Google Scholar]
- Lyche, T. Discrete Cubic Spline Interpolation. BIT 1976, 16, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, C.L.; Hanson, R.J. Solving Least Squares Problems; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Luenberger, D.G. Least-Squares Estimation. Optimization by Vector Space Methods; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997; pp. 78–102. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. Adjustment Theory: An Introduction; Series on Mathematical Geodesy and Positioning; Delft University Press: Delft, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zangeneh-Nejad, F.; Amiri-Simkooei, A.R.; Sharifi, M.A.; Asgari, J. Cycle slip detection and repair of undifferenced single-frequency GPS carrier phase observations. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koop, L.; Amiri-Simkooei, A.R.; van der Reijden, K.J.; O’Flynn, S.; Snellen, M.; Simons, D.G. Seafloor classification in a sand wave environment on the Dutch Continental Shelf using multibeam echosounder backscatter data. Geosciences 2019, 9, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boor, C. A Practical Guide to Splines, rev. ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Alevizos, E.; Snellen, M.; Simons, D.G.; Siemes, K.; Greinert, J. Acoustic discrimination of relatively homogeneous fine sediments using Bayesian classification on MBES data. Mar. Geol. 2015, 370, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftherakis, D.; Snellen, M.; Amiri-Simkooei, A.; Simons, D.G.; Siemes, K. Observations regarding coarse sediment classification based on multi-beam echo-sounder’s backscatter strength and depth residuals in Dutch rivers. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 135, 3305–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, E. Prediction of deep-sea sediment properties: State-of-the-art. In Deep-Sea Sediments, Physical and Mechanical Properties; Inderbitzen, A.L., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Snellen, M.; Simons, D.G. An assessment of the performance of global optimisation methods for geoacoustic inversion. J. Comput. Acoust. 2008, 16, 199–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snellen, M.; Siemes, K.; Simons, D.G. Model-based sediment classification using single-beam echosounder signals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 129, 2878–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snellen, M.; Eleftherakis, D.; Amiri-Simkooei, A.R.; Koomans, R.L.; Simons, D.G. An inter-comparison of sediment classification methods based on multi-beam echo-sounder backscatter and sediment natural radioactivity data. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knaapen, M.A. Sandbank occurrence on the Dutch continental shelf in the North Sea. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2009, 29, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, N.C. The Scope of Strategic Environmental Assessment of North Sea Areas SEA3 and SEA2 in Regard to Prehistoric Archaeological Remains. Report TR 014; Department of Trade and Industry: Hong Kong, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Laban, C. Seabed mapping in the Dutch sector of the North Sea. Sea Technol. 2006, 47, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, I.; Larcombe, P. Determining the preservation rating of submerged archaeology in the post-glacial southern North Sea: A first-order geomorphological approach. Environ. Archaeol. 2008, 13, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, T.A.; van Dalfsen, J.A.; van Lancker, V.; van Overmeeren, R.A.; van Heteren, S.; Doornenbal, P.J. Benthic habitat variations over tidal ridges, North Sea, the Netherlands. In Seafloor Geomorphology as Benthic Habitat; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 241–249. [Google Scholar]
- Amiri-Simkooei, A.R.; Hosseini-Asl, M.; Safari, A. Least squares 2D bi-cubic spline approximation: Theory and applications. Measurement 2018, 127, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.L.; Ward, W.C. Brazos River bar [Texas]; a study in the significance of grain size parameters. J. Sedim. Res. 1957, 27, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, D.G.; Snellen, M.; Ainslie, M.A. A multivariate correlation analysis of high-frequency bottom backscattering strength measurements with geotechnical parameters. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2007, 32, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Swart, H.E.; Yuan, B. Dynamics of offshore tidal sand ridges, A review. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2018, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, P.C.; Hulscher, S.; Van Der Meer, F.; Van Dijk, T.; Wientjes, I.G.; van den Berg, J. Grain size sorting over offshore sandwaves: Observations and modeling. In Proceedings of the 5th IAHR Symposium on River, Coastal and Estuarine Morphodynamics, Enschede, The Netherlands, 17–21 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Walgreen, M.; De Swart, H.E.; Calvete, D. A model for grain-size sorting over tidal sand ridges. Ocean Dyn. 2004, 54, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amiri-Simkooei, A.R.; Koop, L.; van der Reijden, K.J.; Snellen, M.; Simons, D.G. Seafloor Characterization Using Multibeam Echosounder Backscatter Data: Methodology and Results in the North Sea. Geosciences 2019, 9, 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9070292
Amiri-Simkooei AR, Koop L, van der Reijden KJ, Snellen M, Simons DG. Seafloor Characterization Using Multibeam Echosounder Backscatter Data: Methodology and Results in the North Sea. Geosciences. 2019; 9(7):292. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9070292
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmiri-Simkooei, Alireza R., Leo Koop, Karin J. van der Reijden, Mirjam Snellen, and Dick G. Simons. 2019. "Seafloor Characterization Using Multibeam Echosounder Backscatter Data: Methodology and Results in the North Sea" Geosciences 9, no. 7: 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9070292
APA StyleAmiri-Simkooei, A. R., Koop, L., van der Reijden, K. J., Snellen, M., & Simons, D. G. (2019). Seafloor Characterization Using Multibeam Echosounder Backscatter Data: Methodology and Results in the North Sea. Geosciences, 9(7), 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9070292




