Abstract
In this paper, the thermal decomposition kinetics of a class of minerals that we call White Soft Minerals (WSMs) is studied by means of theoretical and experimental methods, in connection to the transport of extraterrestrial organic matter to Earth and the possible use of the decomposition reaction in the characterization of these minerals in space. WSMs include, under a single denomination, carbonates and sulphates of Mg, Fe, and Ca. To improve the present knowledge of the properties of such materials, we use the following techniques: kinetic models for chemical decomposition, atmospheric entry models, spectroscopy, and gravimetric analyses. Model results show that the atmospheric entry of WSM grains is strongly affected by their thermal decomposition. The decomposition reaction, being strongly endothermic, tends to significantly lower the grain temperature during the atmospheric entry, especially at high altitudes and for grazing entries. A previously proposed infrared spectroscopic technique to evaluate the degree of advancement of the reaction is found to be in good agreement with gravimetric measurements for calcium carbonate. The numerical model developed for the atmospheric entry scenarios is used to interpret experimental results. These main findings show that an additional contribution to the reaction enthalpy is needed to reproduce the experimental results, suggesting that the present theoretical model needs improvements such as the account of gas diffusion in the materials.
1. Introduction
One of the most exciting perspectives in astrochemistry lies in the role played by the molecules discovered in space: they may have a crucial importance in the Earth’s chemical evolution and in the origin of life on Earth. The possibility of extraterrestrial organic matter delivery to Earth by way of meteorites of cometary origin has been much studied in the literature [1,2]. A more extreme possibility, highly controversial but recurrently taken into consideration in astrobiology, is panspermia, i.e., the proposal that life, not just organic molecules, is disseminated by dust or meteoroids, via interplanetary or interstellar processes that last hundreds of thousands of years [3,4]. This theory is supported by meteorite samples of Martian origin, for example the very well-known ALH84001, which features complex magnetite structures associated with Mg/Ca/Fe carbonate globules and morphologically close to those produced by magnetotactic bacteria on Earth [5].
Life-related molecules, which are particularly thermolabile, could reach the Earth’s surface inside solid particles or grains. In this case, the mineral composition of these grains could provide the necessary thermal protection against the high temperatures reached during the first stages of the atmospheric entry process [6,7].
The most interesting mineral phases that are often associated with organic matter are Mg-, Ca-, and Fe-carbonates [8,9,10]. It has been shown that the carbonate matrix can host and protect organic material against relatively high temperatures [11,12]. Similar considerations apply to some sulphates, in particular gypsum, and some phyllosilicates. These materials may be collectively addressed as White Soft Minerals (WSMs). They share several properties: they are usually white in micro-crystal forms, sometimes yellowish if Fe is present; they are relatively soft (lower than 4 in Mohs’ scale of mineral hardness); they have some affinity with water, sometimes presenting one or several hydrated phases; and they have a decomposition and/or dehydration reaction, allowing important heat dissipation at moderate temperatures in vacuum. WSMs include magnesite, dolomite, calcite, aragonite, siderite, anhydrite, gypsum, bassanite, and whewellite. This class of minerals crosses the boundaries between mineralogical classifications, since it includes carbonates, sulphates, and even organic minerals such as whewellite. These minerals have been the subject of much research in astrobiology [5,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24].
The detection of carbonates and sulphates on the surface of several bodies of our Solar System has become more frequent due to the advancement of technology in the design of space missions. For example, an increasing planetological and paleontological interest in the detection of the presence of such kind of minerals on surface of Mars [13,14,15,16,17,18] and in Martian meteorites [5,19,20,21,22,23,24] has arisen, in close association with the search for extinct forms of life [5,21,22,25,26]. Spectroscopic evidence confirms the presence of carbonates on the dark surface of Ceres, the largest object in the main asteroid belt [27,28], suggesting the presence of a local hydrothermal process and, consequently, a possible environment favorable for a prebiotic chemistry [29,30]. In addition, carbonates have been also detected in cometary dust [31] and comas [32], suggesting that such minerals are more widespread than we thought in the past.
In order to evaluate the thermal behavior of sub-mm grains during the atmospheric entry process, it is necessary to develop numerical models of this process as those built in the past in the case of silicates [33]. The first actual atmospheric entry scenarios for carbonate and sulphate grains have been published by some of the present authors [34,35,36]. The entry model was realized to provide evidence that carbonate and sulphate decomposition might act as possible cooling mechanism, in the delivery of organic matter from space to Earth [37].
In the past, the thermal decomposition of WSMs has found other applications in the context of astrobiology. For example, laboratory studies have demonstrated that if calcite (of biotic or abiotic origin) is subjected to thermal process at moderate temperature (485 C), the resulting partial decomposition of this carbonate, evaluated by IR spectroscopy, may provide precious information about its degree of biogenicity [38,39,40,41,42].
In view of its importance, in this work, the decomposition reaction is studied using several tools: kinetic model for chemical composition and entry models coupled with experimental (spectroscopic and gravimetric) analyses.
2. Evaluation of Delivery Scenarios Involving WSMs: Computer Modelling
Micrometeoroids are sub-millimeter dust particles that represent most of the minor bodies in the inner Solar System [43]. They are among the most primitive objects in space, suggesting they might represent one of the most important keys in understanding the chemistry of the early Solar System [44,45]. When micrometeoroids enter the atmosphere, they are called micrometeors and dominate the annual flux of extraterrestrial material entering the Earth’s atmosphere, with an estimate flux of approximately kg per year [46]. An analysis of the available data about the distribution of grain dimensions actually entering the Earth’s atmosphere shows that the most common grain size range is 0.01–1 mm [1]. Since over 90% of extraterrestrial material which bombards the Earth’s surface every year is of sub-millimeter size, it is clear that the study of these materials is fundamental to understand the role of small bodies in space and in our Solar System. While entering the Earth’s atmosphere, micrometeoroids experience several physical and chemical modifications: collisions with atmospheric atoms, sputtering, heating, deceleration, evaporation, ablation, and thermal decomposition.
Grains of comparable dimension and with WSM composition are being increasingly detected inside meteorites as minor components [20]. Although pure WSMs are not presently known as independent objects entering the atmosphere, these grains may be the product of fragmentation of larger bodies. Additionally, it is much likely that individual micrometeorites consisting of these minerals are presently not recognized as such. Moreover, the survival of microfossils in artificial meteorites with sedimentary composition has been already studied [47].
The entry model presented in this work comes essentially from the one developed by Love and Brownlee [33], but it has been extended to undertake the studies of the proposed materials (magnesite, calcite, siderite, anhydrite). The present model includes a 2D geometry, the real non-isothermal atmospheric profile, power balance, evaporation, ablation, and radiation losses; furthermore, it includes additional features such as chemical changes, stoichiometry, and chemical effects in power balance. Micrometeoroids are treated as homogeneous, isothermal spheres, where the density is assumed to be constant at 3 g/cm for grains initially composed of MgCO, CaCO, and CaSO, and at 4.8 g/cm for those initially composed of FeCO. These numbers are very close to the average densities of the mineral and the corresponding oxide, in all cases of study. The isothermal hypothesis is supported by the Biot number analysis: considering the temperatures and the grain radii involved in our case studies, the Biot number is much smaller than one (∼), so the body temperature can be considered uniform [35,36].
The atmospheric entry model is two-dimensional, in the vertical entry plane : it includes the effects of gravity, drag forces, and the Earth’s curvature. The interaction between the micrometeoroid and the atmosphere is direct, with no effect due to fluid-dynamics. The sub-mm size of the grain is much smaller than the mean free path of the air molecule at the considered altitudes: this last physical quantity can be estimated from the laws of kinetic theory based on the air density (where h is the quota), and reaches a value comparable with the diameter of the grain only at 60 km, where the grain is already subsonic. Therefore, shocks and hydrodynamics can be neglected.
Concerning the thermochemistry of the entry process [33], the input heat flux delivered as heat to the grain is the rate at which the kinetic energy is deposited into it:
r is the grain radius, v is its entry speed, is the atmospheric density, and is the heat transfer coefficient in a collision between two free atoms [48]:
where and is the atomic weight of the chemical species involved. This approximation is based on a very simple individual rigid sphere collision which is probably reasonable at the high speeds corresponding to peak temperatures (several thousands of m/s). For all the cases of study, = 0.4 has been set.
The input heat flux is balanced by radiative and evaporative energy losses:
where is the body emissivity (here, we assume ), is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant, T is the temperature, is the latent heat of vaporization, (cgs units), is the vapor pressure, and is the molecular weight. All evaporation is assumed to take place in vacuum, since the partial pressure of CO (or SO), at the given altitude, is negligible.
Since evaporation affects both particle’s temperature and mass, it is possible to evaluate the mass loss rate:
The kinetic of carbonate decomposition has been extensively studied [49], although several aspects are still poorly characterized. As it is well known, at sufficiently high temperatures (∼800–900 C), carbonates decompose into oxide and carbon dioxide: . Therefore, during the atmospheric entry, grains with carbonate composition are expected to be enriched with oxides and depleted of the initial carbonate amount. This process, being endothermic, may contribute to the thermal protection of the encapsulated organic matter. However, the decomposition kinetic under such peculiar conditions is not well understood.
The present decomposition model is based on a well-mixed and ideal solid mixture, and it allows a first evaluation of grains behavior during their passage through the Earth’s atmosphere. The material is assumed to be porous enough to allow the CO diffusion and the chemical mixing. The Langmuir law allows to calculate the evaporation rate J expressed in molecules per unit time and area, in terms of the vapor pressure of the solid mixture carbonate/oxide [37]:
where R is the ideal gas constant, M is the molar mass of the gas component, is the partial pressure of the gas component, and k is the Boltzmann constant. The vapor pressure of the solid mixture XCO/XO can be estimated using Raoult’s law:
where is the reference pressure for the thermodynamic data. In this case, Pa. represents the mole fraction of carbonate in the grain and the Gibbs energy is calculated using specific thermodynamic data of enthalpy of formation (kJ mol) and entropy (J mol K) related to the chemical species involved.
is evaluated using stoichiometry:
where m is the mass of the grain at temperature T, represents the mass of the object when it is totally composed by carbonate, and is the minimum mass in which all carbonate is turned into oxide:
where and are the molecular weights, respectively of the pure oxide and of the carbonate.
Identical considerations can be extended to the sulphate case of study, keeping in mind that anhydrous calcium sulphate CaSO decomposes into calcium oxide and sulfur trioxide, with their respective thermodynamic data; more in general, the following reaction occurs: .
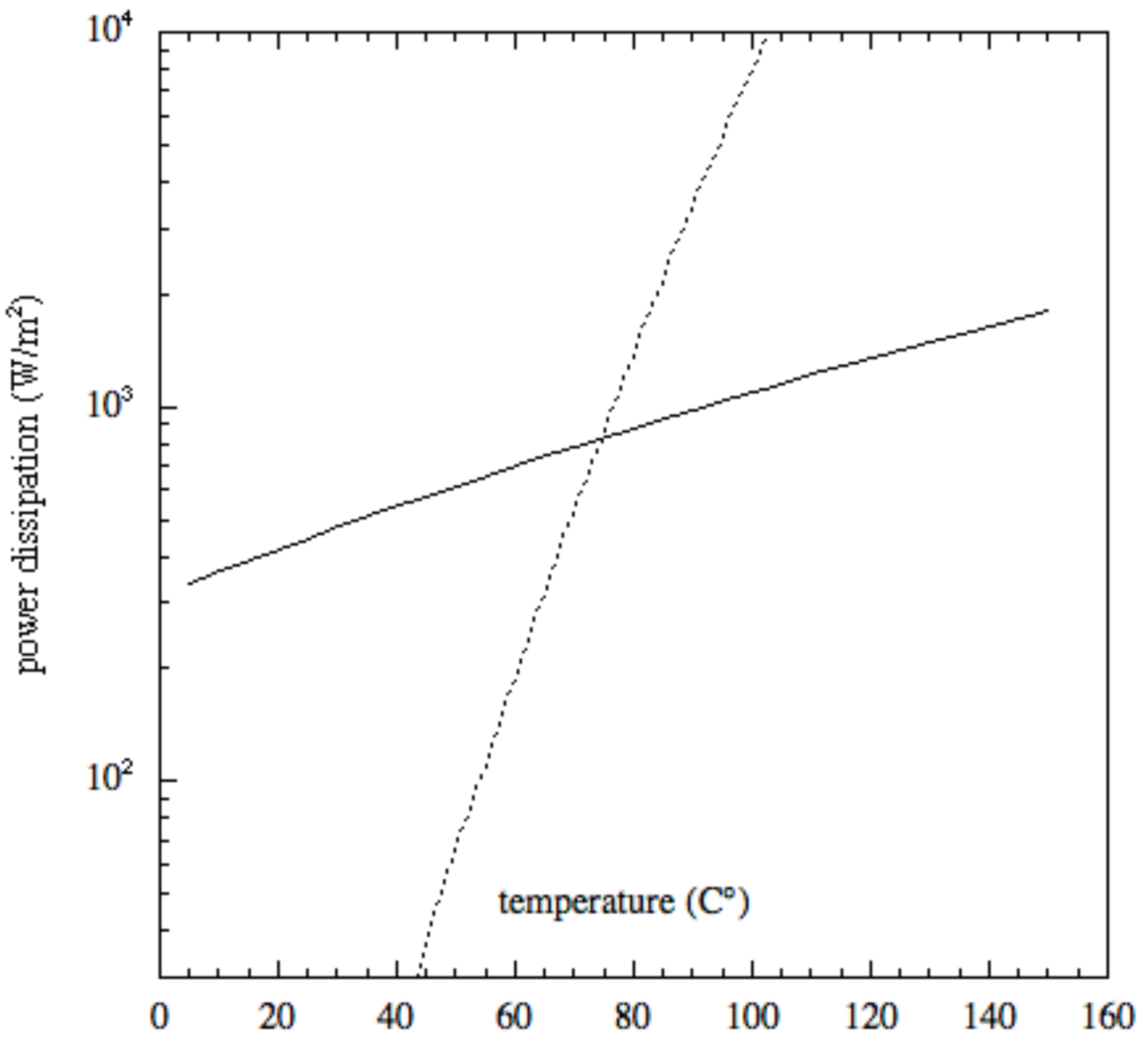
An evaluation of the radiative (calculated by means of the blackbody relation) and evaporative (Langmuir law) energy loss contributions concerning magnesite is plotted in Figure 1. The power dissipation in Figure 1 is calculated using Equation (3). Even if radiative losses are of the utmost importance, it is evident from Figure 1 that evaporation becomes the predominant contribution at high temperatures.
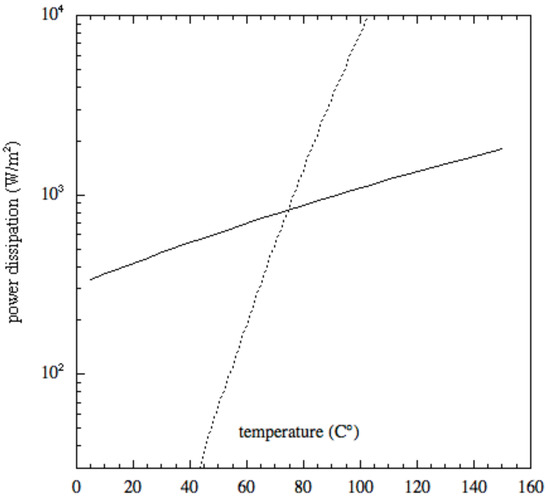
Figure 1.
Energy loss contribution of magnesite MgCO: the solid line represents the radiative loss, the dashed line stands for the evaporation loss.
The model has been implemented as a native Fortran code; the second-order Leapfrog method is used, with a time step of 1 ms. Grain chemical compositions, their diameters, entry speeds (not less than the Earth’s escape velocity 11.2 km/s), and entry angles (0 indicates vertical downward fall) are free parameters. All simulations begin at the quota h of 190 km and stop when the micrograin becomes subsonic: at this point, the survived grain falls to the ground with its terminal speed, in which viscosity balances gravity. From about 60 km downwards, further heating mechanisms, e.g., the presence of the air cap, may provide additional thermal mitigation, which might be able to produce an even more favorable scenario of organic matter delivery. These mechanisms are not considered in this study: as already mentioned, the mean free path of air molecules decreases rapidly with altitude and becomes comparable with micrograin dimensions at about 60 km downwards.
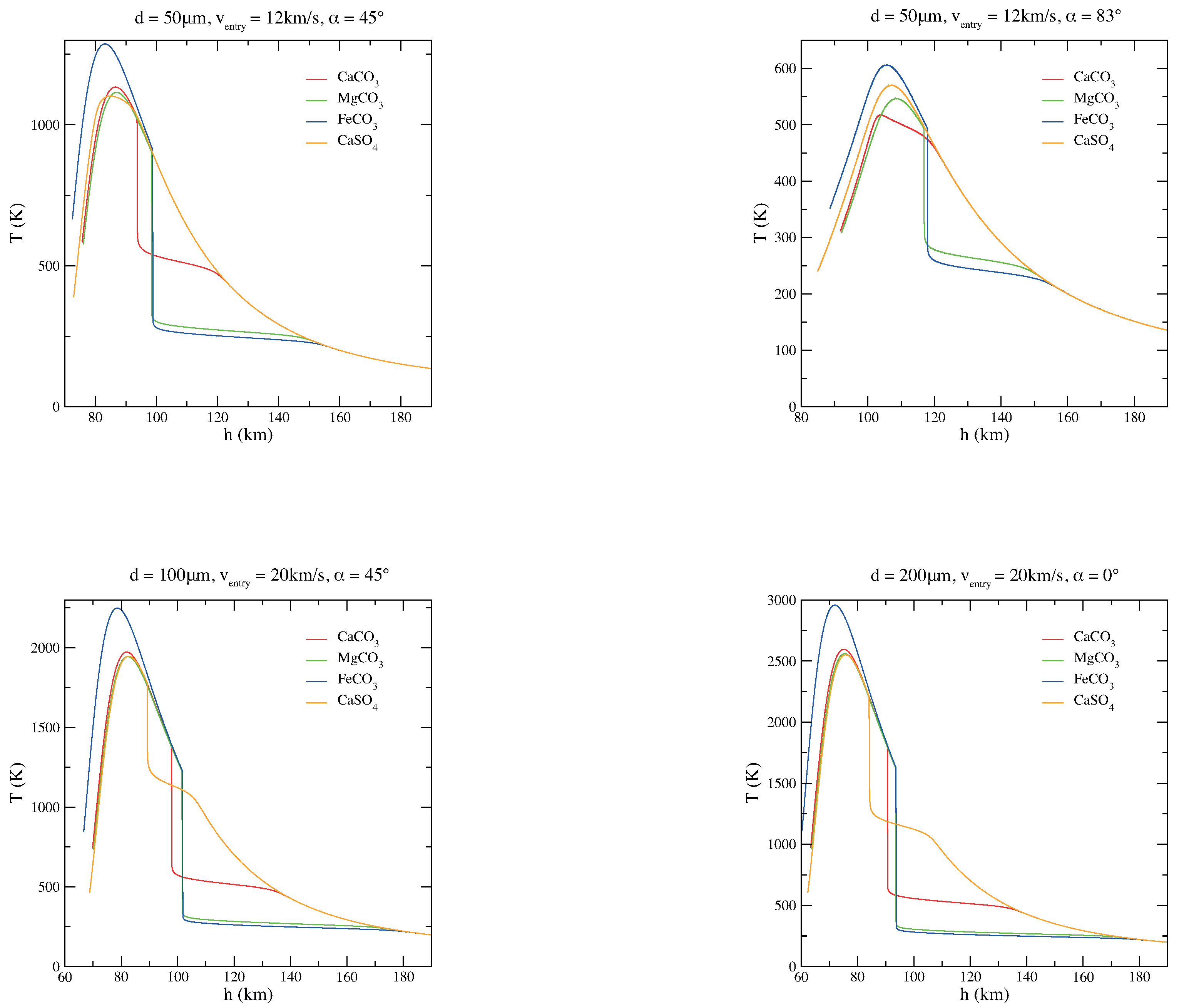
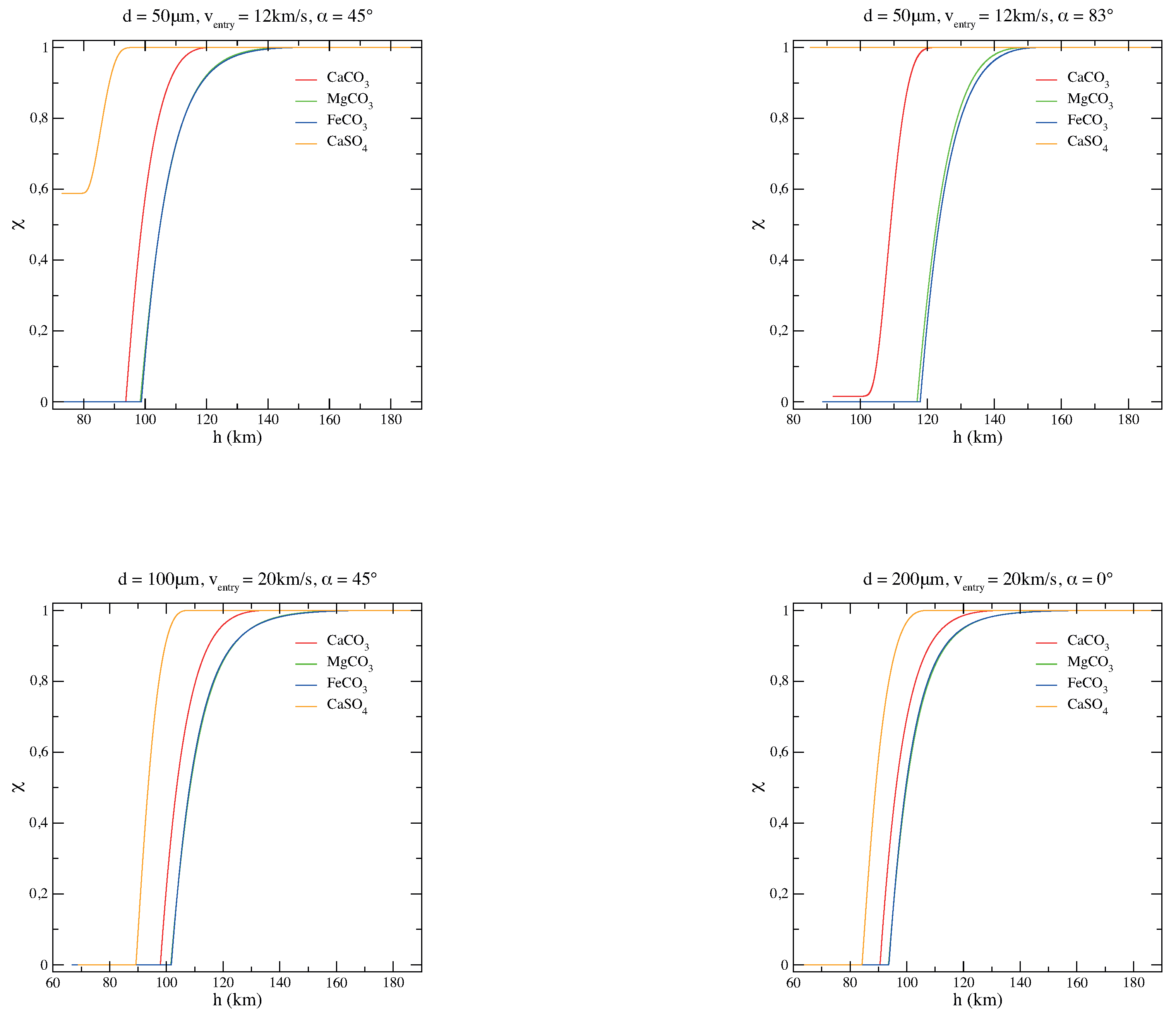
To get a better understanding of the grain behavior depending on its chemical composition, comparisons of the thermal histories of magnesite, siderite, calcite, and anhydrite micrograins are plotted as a function of the quota h (Figure 2). Figure 3, instead, shows the carbonate/sulphate fractions of the corresponding entry scenarios of Figure 2. As it is clear from Figure 2 and Figure 3, the composition of the original carbonate micrograin changes very fast while entering the atmosphere: during the descent, it releases CO and becomes a solid mixture of carbonate and oxide. When CO is completely evaporated and the grain becomes pure oxide, the grain mass does not change anymore and the temperature increases dramatically, only mitigated by blackbody radiation [34,35]. On the other hand, a sulphate micrograin can survive the atmospheric entry with a partial decomposition [36].
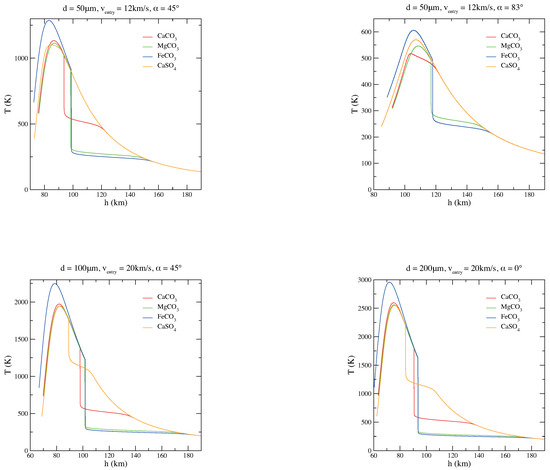
Figure 2.
Comparisons among MgCO, CaCO, FeCO, and CaSO micrograin thermal histories for various diameters (d), velocities (v), and entry angles () of the particle.
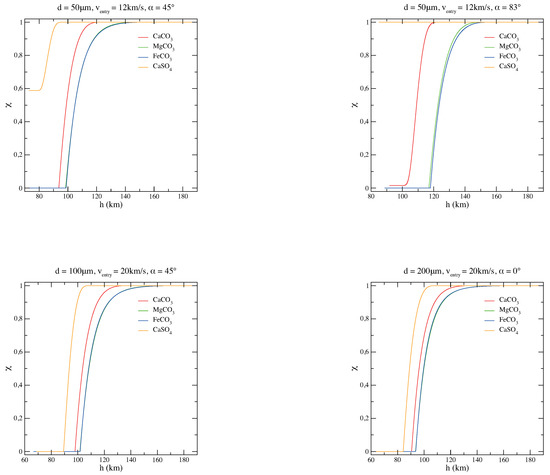
Figure 3.
Carbonate/sulphate fraction of the corresponding entry scenarios of MgCO, CaCO, FeCO, and CaSO micrograins for various diameters (d), velocities (v), and entry angles () of the particle.
The difference observed in these thermal trends is due to the different decomposition reaction enthalpies of the considered materials; in particular = 100.59 kJ mol, = 178.29 kJ mol, = 91.99 kJ mol, = 403.7 kJ mol at 298 K (here, we have assumed independent of the grain temperature; in other words, we have not corrected for the specific heat as in a previous study on MgCO [37], since the effect is relatively small, ∼10 kJ/mol). It is evident that a smaller enthalpy leads to higher decomposition temperatures, consequently to a lower volatility and a greater dissipation; indeed, by passing from siderite and magnesite to calcite and anhydrite, the grain offers a better thermal protection against chemical decomposition of life-related molecules present inside the grain.
As shown in Figure 2, in view of its interesting intermediate volatility between carbonates and silicates, CaSO may actually reduce the intensity and the duration of the heat peak in a substantial way. More volatile materials can keep a very low equilibration temperature, but the chemical reservoir of carbonates is soon exhausted. In the most probable entry conditions, this occurs in the case of CaCO particles at high altitudes (∼100 km). A grain of CaSO can keep strong chemical cooling until an altitude of about 80 km is reached. On the other hand, the higher standard formation enthalpy of silicates leads to such a low volatility that temperatures are substantially controlled by radiation.
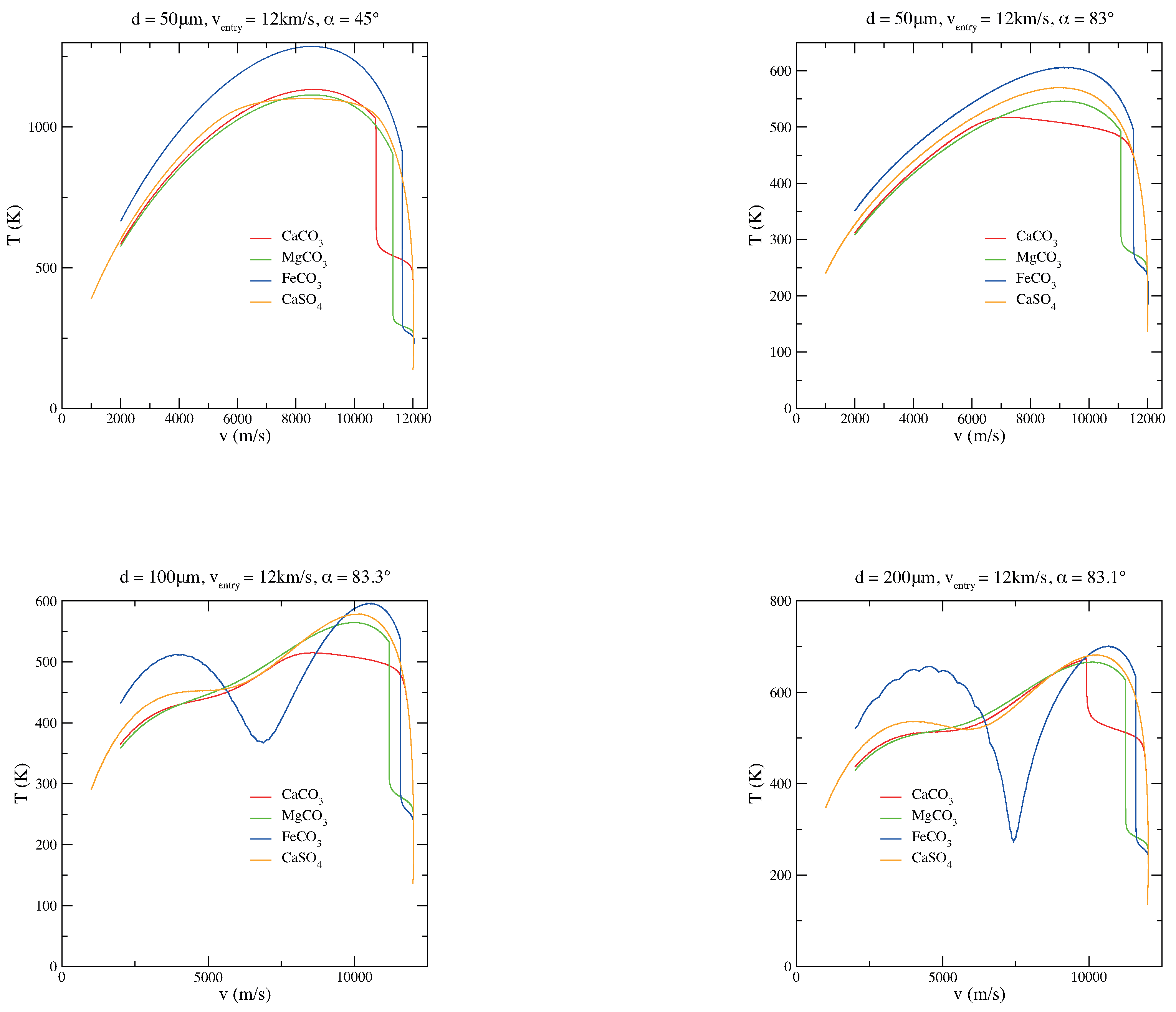
In Figure 4, few plots concerning the velocity trend during the micrometeoroid descent through the atmosphere are shown. When entry angles are grazing (low entry angles with respect to the horizontal plane), the micrometeoroid tries to escape the atmosphere; when a “limit” entry angle is reached, the grain bounces on the top of the atmosphere, as it is evident from Figure 4. When the micrometeoroid overcomes this “limit” angle, it goes off the atmosphere. Usually, the “limit” angle is in the range of 83.0 to 83.7. Moreover, grazing trajectories represent the main scenario in which larger grains can survive the atmospheric entry without melting [33,50]: it must be noted that the peak temperatures in grazing entries are lower (top right panel in Figure 2).
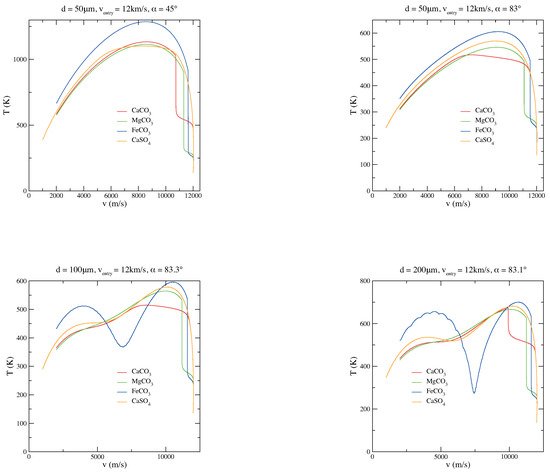
Figure 4.
Comparisons among MgCO, CaCO, FeCO, and CaSO micrograin velocity trend in the case of various diameters (d), velocities (v), and entry angles () of the particle.
Since the thermal decomposition reaction significantly affects the thermal load and the dynamics of the atmospheric entry of these minerals in an organic matter delivery or panspermia scenario, a better characterization of this reaction may represent a desirable goal of research in astrobiology.
3. Theory and Experiment: Calcite Decomposition
In the past, different experimental techniques such as IR spectroscopy, gravimetry, Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), and Energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis have been used to investigate spectral, morphological, and compositional modifications induced by thermal processing on different samples [38,39,40,41,42]. The goal was to develop a method able to discriminate biogenic carbonate samples from their abiogenic counterparts, to determine the degree of biogenicity of different samples. Comparing the IR transmission spectra of biotic and abiotic Ca-carbonates, before and after thermal processing at 485 C for 3.5 h, it was observed that only biotic carbonates undergo partially the transformation into CaO, while those of abiotic origin require higher temperatures. The IR spectroscopy method, supported also by results from SEM and EDX analyses, has been successfully applied to several cases such as:
- problematic carbonate samples, in which there is no clear evidence of controlled or induced biomineralization [40];
- microbialites, i.e., bio-induced carbonate deposits, and stromatolites, i.e., the laminated fabric of microbialites, some of which are among the most primitive traces of biological activity on Earth [41];
- different parts of the same carbonate rock to discriminate the presence, nature and degree of biogenicity of various micrite types (i.e., detrital vs autochthonous) and to distinguish them from the skeletal grains, each one characterized by different organic matter content [42].
In the present work, taking the advantage of the great improvement given by research on the knowledge of the endothermic transformation, we used the spectroscopic method to monitor the thermal process which micrometeoroids of carbonate composition experience when they pass through the Earth’s atmosphere. To test the model discussed in Section 2, we analyzed the thermal decomposition of CaCO from the spectroscopic, morphological, and compositional point of view introducing gravimetric studies to better quantify the loss of CO in the transformation into CaO.
To this aim, a piece of limestone of abiotic origin, collected near Lecce, Italy, and composed of more than 98% of CaCO in the calcite polymorphic form [51] was ground in a Retsch mechanical mortar grinder (RM100) and the fraction in the 20–50 m size range was selected using a sieve in a Retsch laboratory sieve shaker (AS200 basic). This selected sample (hereafter named S1) was thermally processed under vacuum (10–10 mbar), for 3.5 h, at several temperatures by using a Carbolite furnace able to reach temperatures up to 1200 C. The various temperatures were chosen in the range 420 C–1150 C (693 K–1423 K) (see Table 1) to carefully monitor the resulting process of decomposition of CaCO into CaO (see Section 2) from a spectroscopic point of view using a Perkin Elmer Frontier IR Fourier Transform spectrometer after the processing. The result was then compared to the spectrum of the same sample S1 at room temperature (25 C or 298 K) before introducing it in the oven. For some of the most significant temperatures listed above (see Table 1), precise gravimetry measurements, by Sartorius semi-micro balance Genius ME215S, were also taken before and after the thermal processing.

Table 1.
Selected temperatures (in C and K) and experimental values of and with respective uncertainties for the sample S1.
With the grain radius as free parameter and with the use of the thermodynamic data referring to CaCO available in the literature, the model discussed in Section 2 was used to simulate the calcite micrograin decomposition inside the experimental equipment, with the input heat flux from the oven (assumed as a black body):
counterbalanced by the radiative energy loss:
and by evaporative energy loss:
with a final time of h. In Equation (11), represent the latent heat of vaporization and is the additional enthalpy associated with additional processes that differ from decomposition. The numerical code can calculate the equilibrium temperature at which the sum of radiative and evaporative losses equals the input heat flux, , by means of a binary algorithm.
The parameter, introduced in Section 2, allows us to control the carbonate fraction during the decomposition process. is calculated theoretically by means of Equation (7):
From the experimental point of view, the equation is similar in the case of gravimetric measurements:
where are the experimental values, corresponding to m values, measured with an accuracy of 10 g.
Regarding the spectroscopic measurements, as the samples decompose when treated at increasingly higher temperatures, the IR spectrum of CaCO gradually changes to that of CaO when the whole transformation has taken place.
This spectral behavior can be quantified using the slope variation index D [38,39,40,42]:
where and represent the values of transmittance for processed and unprocessed samples (subscripts p and u respectively), while cm and cm are two wavenumbers chosen in the spectral range at which the difference in the spectral slope is more evident.
The values of the spectroscopic measurements is therefore calculated as follows:
where D is the value obtained with Equation (14) for the spectrum of the processed sample, is the value for the spectrum of the same sample before the thermal processing (i.e., at room temperature), and corresponds to the D value for which the final step of the transformation of CaCO to CaO is experimentally reached. The uncertainty about is related to that about the spectral index D. The latter refers to the larger between the experimental error of a single transmittance spectrum and the uncertainty linked to the statistical dispersion, calculated considering different spectra relative to various measurements of the same sample.
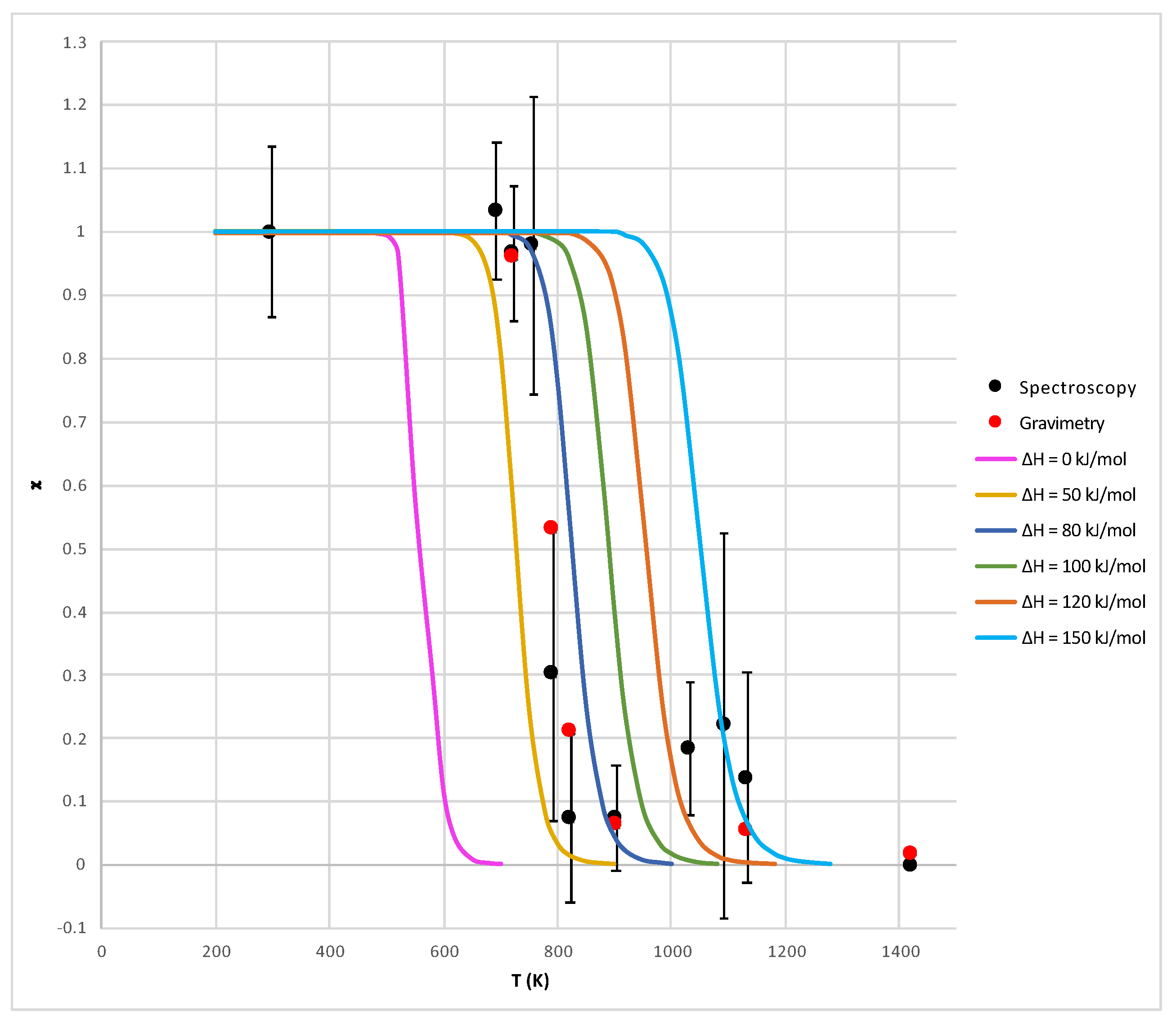
In Figure 5, the parameters and are plotted against temperature and compared with theoretical curves showing obtained with different values of (see Equation (11)). In this figure, the uncertainty about the temperature T is assumed to be only due to the accuracy of the oven thermocouple (±5 C).
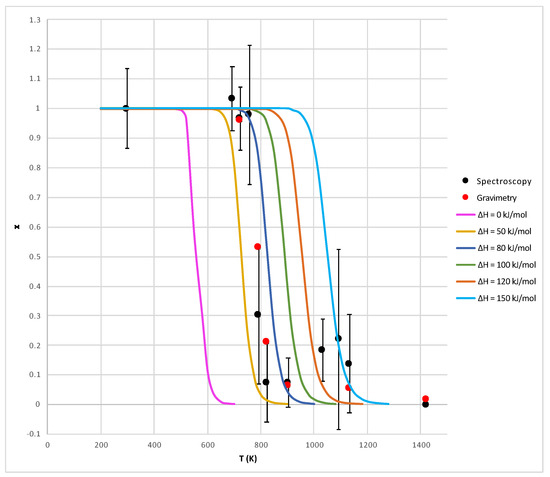
Figure 5.
Comparison between the theoretical values (solid lines) of the parameter obtained by Equation (12) and the experimental ones (circle dots) obtained for sample S1 both by gravimetric (Equation (13)) and spectroscopic (Equation (15)) techniques (see Table 1). The error bars relative to the temperature T (in abscissae) and to (in ordinates) are within the size of the dots. Instead, the error bars relative to (also in ordinates) are obtained as discussed in the text.
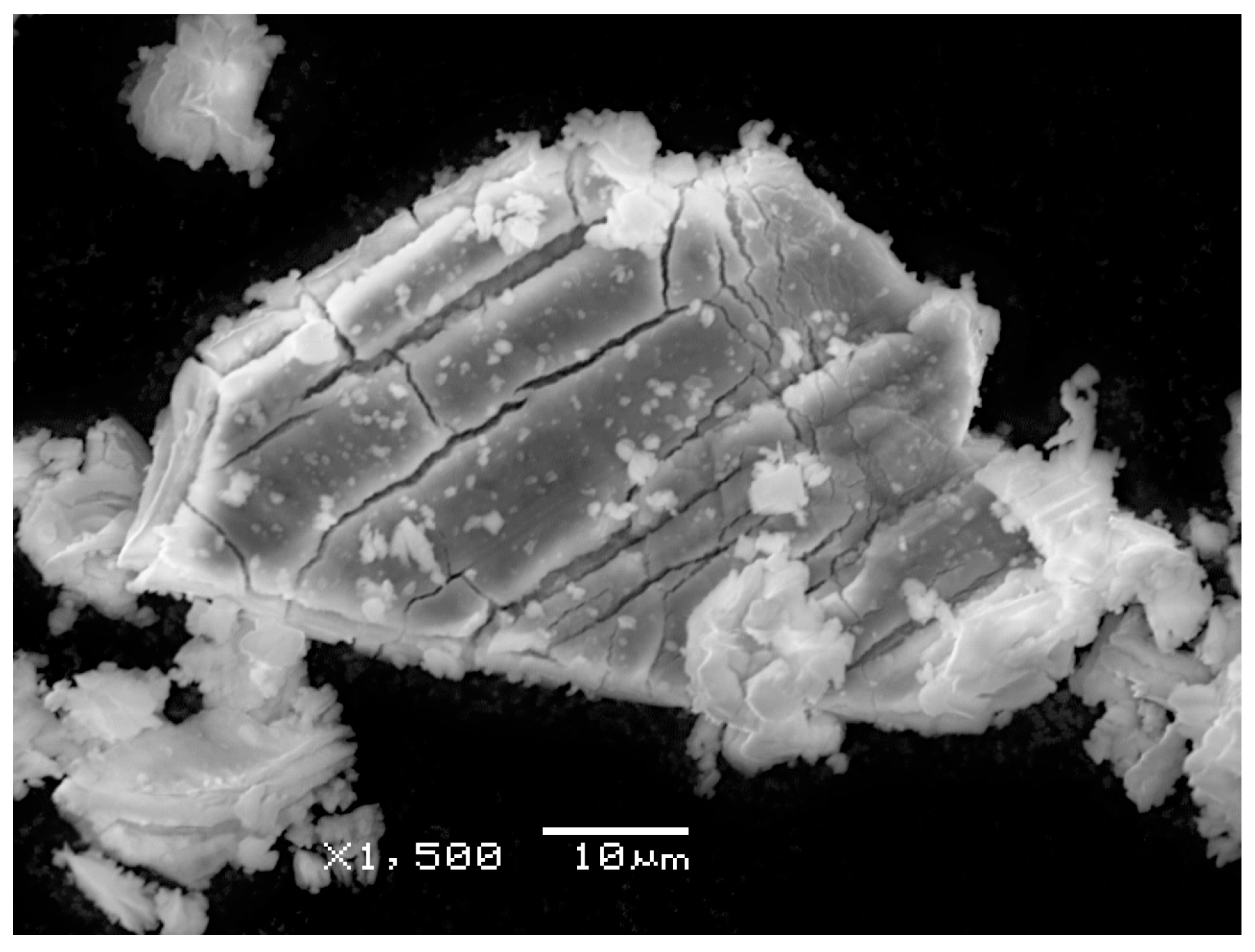
The substantial agreement of the results obtained with the gravimetric and spectroscopic methods, visible in Figure 5, is quite interesting with relevance to future applications: it provides a validation of the spectroscopic method, which can be used without having access to the initial mass of the material (as in the case of most samples in/from space) and without modification in the presence of mixed oxides. The trend between experimental and theoretical curves is the same from a qualitative point of view (especially as far as the gravimetric data are concerned), but it seems that the theoretical model must include a non-zero “additional enthalpy” to fit the experimental data. Currently, it is not very clear how to interpret this enthalpy: it might be an activation enthalpy (due to the presence of barriers to the CO diffusion) or an additional thermal capacity (due to additional surface energy associated with crystal breaking when CO is released). This last possibility is supported by SEM images of the sample S1 heated at high temperatures (1150 C), showing that the processed grains have a strongly fractured structure (Figure 6). The fracturing processes are probably associated with the pressure exerted by CO gas, and the corresponding surface energy has also to be included into the evaluation of the enthalpy of the whole process.
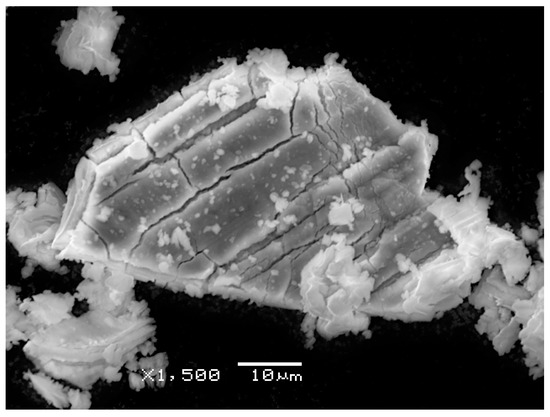

Figure 6.
SEM morphology of a grain of the sample S1 after thermal process at 1150 C (1423 K).
An issue about which not much reliable material has been found is the kinetics of diffusion within the grains. As a matter of fact, it is expected that the decomposition process affects the carbonate fraction close to the surface faster than in the center [52,53]. This process can produce a non-uniform distribution of the carbonate fraction and a more complex kinetics. In future, the inclusion of this effect in the model is the only way to estimate its importance under two different conditions: the entry process and the vacuum heating experiments performed in laboratory.
A non-thermodynamic aspect that may contribute to the decomposition process and explain the quantitative difference between theoretical and experimental data is the nanoporosity of carbonate micrograins. As a matter of fact, these porosities may trap the CO inside the grain, preventing the diffusion process of the gas. In a work by Houst and Wittman [54], the authors analyze the variation of CO diffusivity as a function of porosity, as a consequence of the characteristic microstructure of the material (cement paste), and they conclude that diffusivity depends strongly on the porosity [55].
4. Conclusions
In this paper, we have studied and characterized the thermal decomposition reaction of WSM grains.
Numerical simulations show that this reaction can dissipate considerable amounts of thermal energy when grains of WSMs with sub-mm dimensions enter the atmosphere. The resulting reduction of the equilibration temperatures may represent a crucial point. Our data show that for favorable entry geometries (grazing angles), these minerals may allow the protection of the organic matter possibly enclosed inside the micrograin, thanks to the endothermic decomposition reaction.
The decomposition of a CaCO sample has been characterized by IR spectroscopy and gravimetry and compared with a numerical model. Results show that the experiments can be matched only by including an additional enthalpy contribution, which is not related to the thermodynamics of the reaction. This additional enthalpy has been tentatively interpreted as an effect of barriers to gas diffusion and some evidence from microscopy seems to support this proposal. In view of the widespread findings of WSM samples into meteorites and on the surface of Mars, the experimental study must be extended to other WSMs, in particular gypsum.
The thermal decomposition reaction has an important part to play during the atmospheric entry of these materials, so its characterization, from a theoretical and an experimental point of view, represents a line of future research in the context of geosciences.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.F. and S.L.; methodology, S.F., S.L. and V.O.; software, S.L. and G.M.L.; validation, M.D., S.L., F.M., G.M.L., and V.O.; formal analysis, G.M.L. and S.L.; investigation, M.D., F.M., G.M.L.; resources, S.F. and S.L.; data curation, M.D., F.M., G.M.L.; writing—original draft preparation, G.M.L.; writing—review and editing, M.D., S.L., F.M., G.M.L. and V.O.; visualization, G.M.L.; supervision, S.L. and V.O.; project administration, S.L. and V.O.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
Vincenzo Orofino acknowledges the TAsP and Euclid INFN Projects. This paper is dedicated to the memory of Sergio Fonti, who gave a precious contribution to the realization of the present work and whose premature death hits hard all of us.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jenniskens, P.; Wilson, M.A.; Packan, D.; Laux, C.O.; Krüger, C.H.; Boyd, I.D.; Popova, O.P.; Fonda, M. Meteors: A delivery mechanism of organic matter to the early Earth. Earth Moon Planets 1998, 82, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyba, C.; Sagan, C. Endogenous production, exogenous delivery and impact-shock synthesis of organic molecules: An inventory for the origins of life. Nature 1992, 355, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horneck, G.; Rettberg, P.; Reitz, G.; Panitz, C.; Rabbow, E. Protection of bacterial spores in space, a contribution to the discussion on panspermia. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 2001, 31, 527–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burchell, M.J. Panspermia today. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2004, 3, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, D.S.; Gibson, E.K., Jr.; Thomas-Keprta, K.L.; Vali, H.; Romanek, C.S.; Clemett, S.J.; Chillier, X.D.; Maechling, C.R.; Zare, R.N. Search for past life on Mars: Possible relic biogenic activity in Martian meteorite ALH84001. Science 1996, 273, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glavin, D.P.; Bada, J.L. Survival of amino acids in micrometeorites during atmospheric entry. Astrobiology 2001, 1, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matrajt, G.; Brownlee, D.; Sadilek, M.; Kruse, L. Survival of organic phases in porous IDPs during atmospheric entry: A pulse-heating study. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2006, 41, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, G.; Keller, L.P.; Jacobsen, C.; Wirick, S.; Miller, M.A. Organic carbon in interplanetary dust particles. Bioastronomy 99 2000, 213, 191–194. [Google Scholar]
- Pizzarello, S.; Cooper, G.W.; Flynn, G.J. The nature and distribution of the organic material in carbonaceous chondrites and interplanetary dust particles. Meteorit. Early Sol. Syst. II 2000, 1, 625–651. [Google Scholar]
- Matrajt, G.; Messenger, S.; Brownlee, D.; Joswiak, D. Diverse forms of primordial organic matter identified in interplanetary dust particles. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2012, 47, 525–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, C.A.; Piazolo, S.; Webb, G.E.; Dutkiewicz, A.; George, S.C. In search of early life: Carbonate veins in Archean metamorphic rocks as potential hosts of biomarkers. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 453, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, C.A.; George, S.C. Hydrocarbon biomarkers preserved in carbonate veins of potentially Paleoproterozoic age, and implications for the early biosphere. Geobiology 2018, 16, 577–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gendrin, A.; Mangold, N.; Bibring, J.P.; Langevin, Y.; Gondet, B.; Poulet, F.; Bonello, G.; Quantin, C.; Mustard, J.; Arvidson, R.; et al. Sulfates in Martian layered terrains: the OMEGA/Mars Express view. Science 2005, 307, 1587–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langevin, Y.; Poulet, F.; Bibring, J.P.; Gondet, B. Sulfates in the north polar region of Mars detected by OMEGA/Mars Express. Science 2005, 307, 1584–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlmann, B.L.; Mustard, J.F.; Murchie, S.L.; Poulet, F.; Bishop, J.L.; Brown, A.J.; Calvin, W.M.; Clark, R.N.; Marais, D.J.; Milliken, R.E.; et al. Orbital identification of carbonate-bearing rocks on Mars. Science 2008, 322, 1828–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boynton, W.V.; Ming, D.W.; Kounaves, S.P.; Young, S.M.; Arvidson, R.E.; Hecht, M.H.; Hoffman, J.; Niles, P.B.; Hamara, D.K.; Quinn, R.C.; et al. Evidence for calcium carbonate at the Mars Phoenix landing site. Science 2009, 325, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomba, E.; Zinzi, A.; Cloutis, E.A.; D’Amore, M.; Grassi, D.; Maturilli, A. Evidence for Mg-rich carbonates on Mars from a 3.9 μm absorption feature. Icarus 2009, 203, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, J.J.; Murchie, S.L.; Bishop, J.L.; Ehlmann, B.L.; Milliken, R.E.; Wilhelm, M.B.; Seelos, K.D.; Chojnacki, M. Orbital evidence for more widespread carbonate-bearing rocks on Mars. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2016, 121, 652–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, L.E.; Connelly, J.N.; Nyquist, L.E.; Shih, C.Y.; Wiesmann, H.; Reese, Y. The age of the carbonates in Martian meteorite ALH84001. Science 1999, 286, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas-Keprta, K.L.; Clemett, S.J.; Mckay, D.S.; Gibson, E.K.; Wentworth, S.J. Origins of magnetite nanocrystals in Martian meteorite ALH84001. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 6631–6677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooding, J.L.; Wentworth, S.J.; Zolensky, M.E. Calcium carbonate and sulfate of possible extraterrestrial origin in the EETA 79001 meteorite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooding, J.L.; Wentworth, S.J.; Zolensky, M.E. Aqueous alteration of the Nakhla meteorite. Meteoritics 1991, 26, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treiman, A.H.; Barrett, R.A.; Gooding, J.L. Preterrestrial aqueous alteration of the Lafayette (SNC) meteorite. Meteoritics 1993, 28, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentworth, S.J.; Gooding, J.L. Carbonates and sulfates in the Chassigny meteorite: Further evidence for aqueous chemistry on the SNC parent planet. Meteoritics 1994, 29, 860–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann, E.I.; Wierzchos, J.; Ascaso, C.; Winklhofer, M. Chains of magnetite crystals in the meteorite ALH84001: Evidence of biological origin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 2176–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, E.K., Jr.; McKay, D.S.; Thomas-Keprta, K.L.; Wentworth, S.J.; Westall, F.; Steele, A.; Romanek, C.S.; Bell, M.S.; Toporski, J. Life on Mars: evaluation of the evidence within Martian meteorites ALH84001, Nakhla, and Shergotty. Precambrian Res. 2001, 106, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivkin, A.S.; Volquardsen, E.L.; Clark, B.E. The surface composition of Ceres: Discovery of carbonates and iron-rich clays. Icarus 2006, 185, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sanctis, M.C.; Raponi, A.; Ammannito, E.; Ciarniello, M.; Toplis, M.J.; McSween, H.Y.; Castillo-Rogez, J.C.; Ehlmann, B.L.; Carrozzo, F.G.; Marchi, S.; et al. Bright carbonate deposits as evidence of aqueous alteration on (1) Ceres. Nature 2016, 536, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sanctis, M.C.; Ammannito, E.; McSween, H.Y.; Raponi, A.; Marchi, S.; Capaccioni, F.; Capria, M.T.; Carrozzo, F.G.; Ciarniello, M.; Fonte, S.; et al. Localized aliphatic organic material on the surface of Ceres. Science 2017, 355, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sanctis, M.C.; Vinogradoff, V.; Raponi, A.; Ammannito, E.; Ciarniello, M.; Carrozzo, F.G.; De Angelis, S.; Raymond, C.A.; Russell, C.T. Characteristics of organic matter on Ceres from VIR/Dawn high spatial resolution spectra. Mon. Notices R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 482, 2407–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busemann, H.; Nguyen, A.N.; Cody, G.D.; Hoppe, P.; Kilcoyne, A.L.D.; Stroud, R.M.; Zega, T.; Nittler, L.R. Ultra-primitive interplanetary dust particles from the comet 26P/Grigg-Skjellerup dust stream collection. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 288, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomenkova, M.N.; Kerridge, J.F.; Marti, K.; McFadden, L.A. Compositional trends in rock-forming elements of comet Halley dust. Science 1992, 258, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, S.G.; Brownlee, D.E. Heating and thermal transformation of micrometeoroids entering the Earth’s atmosphere. Icarus 1991, 89, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micca Longo, G.; Longo, S. Thermal decomposition of MgCO3 during the atmospheric entry of micrometeoroids. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2017, 16, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micca Longo, G.; Longo, S. Theoretical analysis of the atmospheric entry of sub-mm meteoroids of MgxCa1−xCO3 composition. Icarus 2018, 310, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micca Longo, G.; Piccinni, V.; Longo, S. Evaluation of CaSO4 micrograins in the context of organic matter delivery: Thermochemistry and atmospheric entry. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisceglia, E.; Micca Longo, G.; Longo, S. Thermal decomposition rate of MgCO3 as an inorganic astrobiological matrix in meteorites. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2017, 16, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orofino, V.; Blanco, A.; D’Elia, M.; Licchelli, D.; Fonti, S. Infrared transmission spectroscopy of carbonate samples of biotic origin relevant to Mars exobiological studies. Icarus 2007, 187, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orofino, V.; Blanco, A.; D’Elia, M.; Fonti, S.; Licchelli, D. Time-dependent degradation of biotic carbonates and the search for past life on Mars. Planet. Space Sci. 2009, 57, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, A.; Orofino, V.; D’Elia, M.; Fonti, S.; Mastandrea, A.; Guido, A.; Russo, F. A spectroscopic method for identifying terrestrial biocarbonates and application to Mars. Icarus 2011, 213, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, A.; Orofino, V.; D’Elia, M.; Fonti, S.; Mastandrea, A.; Guido, A.; Russo, F. Infrared spectroscopy of microbially induced carbonates and past life on Mars. Icarus 2013, 226, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, A.; D’Elia, M.; Orofino, V.; Mancarella, F.; Fonti, S.; Mastandrea, A.; Guido, A.; Tosti, F.; Russo, F. Microbialites vs. detrital micrites: Degree of biogenicity, parameter suitable for Mars analogues. Planet. Space Sci. 2014, 97, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grün, E.; Zook, H.A.; Fechtig, H.; Giese, R.H. Collisional balance of the meteoritic complex. Icarus 1985, 62, 244–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerridge, J.F.; Matthews, M.S. Meteorites and the Early Solar System; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AR, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, G.J.; Keller, L.P.; Feser, M.; Wirick, S.; Jacobsen, C. The origin of organic matter in the solar system: Evidence from the interplanetary dust particles. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 4791–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, S.G.; Brownlee, D.E. A direct measurement of the terrestrial mass accretion rate of cosmic dust. Science 1993, 262, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foucher, F.; Westall, F.; Brandstaetter, F.; Demets, R.; Parnell, J.; Cockell, C.; Edwards, H.; Jean-Michel, B.; Brack, A.; Kurat, G. Testing the survival of microfossils in artificial Martian sedimentary meteorites during entry into Earth’s atmosphere: the STONE 6 experiment. Icarus 2010, 207, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opik, E.J. Physics of Meteor Flight in the Atmosphere; Courier Corporation: Chelmsford, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- L’vov, B.V. Thermal Decomposition of Solids and Melts: New Thermochemical Approach to the Mechanism, Kinetics and Methodology (Vol. 7); Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Briani, G.; Pace, E.; Shore, S.N.; Pupillo, G.; Passaro, A.; Aiello, S. Simulations of micrometeoroid interactions with the Earth atmosphere. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 552, A53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orofino, V.; Blanco, A.; Fonti, S.; Marra, A.C.; Polimeno, N. The complex refractive index of limestone particles: An extension to the FIR range for Mars applications. Planet. Space Sci. 2002, 50, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, A.W.D. The mechanism of the thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1968, 23, 297–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, R. The reversibility of the reaction CaCO3 CaO+ CO2. J. Appl. Chem. Biotechnol. 1973, 23, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houst, Y.F.; Wittmann, F.H. Influence of porosity and water content on the diffusivity of CO2 and O2 through hydrated cement paste. Cement Concr. Res. 1994, 24, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, A.S.; Kim, Y.-Y. Unraveling the internal microstructure of biogenic and bioinspired calcite single crystals. MRS Bull. 2015, 40, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).