Stability of Individuals during Urban Inundations: What Should We Learn from Field Observations?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Field Observations and Materials
3. Results: Stability of Individuals in Floodwaters
4. Discussion and Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jonkman, S.N. Global perspectives on loss of human life caused by floods. Nat. Hazards 2005, 34, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkman, S. Loss of Life Due to Floods: General Overview. In Drowning; Bierens, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 957–965. [Google Scholar]
- Lemperiere, F. Dams that have failed by Flooding: An Analysis of 70 Failures. Int. Water Power Dam Constr. 1993, 45, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lenderink, G.; Van Meijgaard, E. Increase in hourly precipitation extremes beyond expectations from temperature changes. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.-K.; Zhang, X.; Zwiers, F.W.; Hegeri, G.C. Human contribution to more-intense precipitation extremes. Nature 2011, 470, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, R.; Feyen, L.; Watkiss, P. Climate change and river floods in the European Union: Socio-economic consequences and the costs and benefits of adaptation. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 1737–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruwier, M.; Erpicum, S.; Pirotton, M.; Archambeau, P.; Dewals, B. Assessing the operation rules of a reservoir system based on a detailed modelling chain. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. World Urbanizations Prospects: The 2014 Revision; Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division, United Nations Population Division New York: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. World Population Prospects: The 2015 Revision; Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division, United Nations Population Division New York: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Güneralp, B.; Güneralp, I.; Liu, Y. Changing global patterns of urban exposure to flood and drought hazards. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2015, 31, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abt, S.R.; Wittler, R.J.; Taylor, A.; Love, D.J. Human stability in a high flood hazard. Water Resour. Bull. 1989, 25, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, Y.; Ishigaki, T.; Baba, Y.; Toda, K. Safety Analysis of Evacuation Routes Considering Elderly Persons during Underground Flooding. J. Hydrosci. Hydraul. Eng. 2010, 28, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Australian Rainfall and Runoff. Australian Rainfall and Rrunoff Revision Project 10: Appropriate Safety Criteria for People; No. P10/S1/006; Australian Rainfall and Runoff: Sydney, Australia, 2010; p. 31.
- Xia, J.; Falconer, R.A.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, X. New criterion for the stability of a human body in floodwaters. J. Hydraul. Res. 2014, 52, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Deng, S.; Chen, Q.; Guo, P.; Falconer, R.A. Stability Criterion for People in Floods for various Slopes. Water Manag. 2016, 169, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z. Disaster Aftermath. In Encyclopedia of Public Health; Springer-Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, D.N.; Cox, R.J. Stability of Children on Roads Used as Floodways; Technical Report No.73/13; Water Research Laboratory of the University of New South Wales: Manly Vale, Australia, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Karvonen, R.A.; Hepojoki, H.K.; Huhta, H.K.; Louhio, A. The Use of Physical Models in Dam-Break Analysis; RESCDAM Final Report; Helsinki University of Technology: Helsinki, Finland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Gomariz, E.; Gomez, M.; Russo, B. Experimental study of the stability of pedestrians exposed to urban pluvial flooding. Nat. Hazards 2016, 82, 1259–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.Z.; Chanson, H. Physical Modelling of Tidal Bore Dyke Overtopping: Implication on Individuals’ Safety. In Proceedings of the 36th IAHR World Congress, The Hague, The Netherlands, 28 June–3 July 2015; pp. 3824–3831. [Google Scholar]
- Milanesi, L.; Pilotti, M.; Ranzi, R. A conceptual model of people’s vulnerability to floods. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrighi, C.; Oumeraci, H.; Castelli, F. Hydrodynamics of pedestrians’ Instability in Floodwaters. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Endoh, K.; Muro, Z.I. Experimental Study on People’s Safety against Overtopping Waves on Breakwaters. Rep. Port Harb. Inst. 1992, 34, 4–31. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Cox, R.J.; Yee, M.; Ball, J.E. Safety of People in Flooded Streets and Floodways. In Proceedings of the 8th National Conference on Hydraulics in Water Engineering, Gold Coast, Australia, 13–16 July 2004; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hanes, D.M. Human instability related to drowning risk in surf zones for novice beachgoers or weak swimmers. Nat. Hazards 2016, 83, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkman, S.N.; Penning-Rowsell, E. Human Instability in Flood Flows. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2008, 44, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanesi, L.; Pilotti, M.; Bacchi, R. Using web-based observations to identify thresholds of a person’s stability in a flow. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 7793–7805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, G.; Camilli, S.; Quagliarini, E.; D’Orazio, M. Flooding risk in existing urban environment: From human behavioral patterns to a microscopic simulation model. Energy Procedia 2017, 134, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanson, H.; Brown, R.; McIntosh, D. Human body stability in floodwaters: The 2011 flood in Brisbane CBD. In Proceedings of the 5th IAHR International Symposium on Hydraulic Structures (ISHS2014), Brisbane, Australia, 25–27 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chanson, H. The 2010–2011 floods in Queensland (Australia): Observations, first comments and personal experience. J. Houille Blanche 2011, 1, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanson, H.; Brown, R. Turbulence in an Inundated Urban Environment during a Major Flood: Implications in terms of People Evacuation and Sediment Deposition. Mech. Ind. 2014, 15, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Agnew, P.; Association, F. Flood Horror and Tragedy; Agnew School Parents & Friends Association, Southern Education Managements: Tingalpa, Australia, 2011; p. 344. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.; Chanson, H. Turbulence and Suspended Sediment Measurements in an Urban Environment during the Brisbane River Flood of January. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 139, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Rainfall and Runoff. Australian Rainfall and Runoff Revision Project 10: Appropriate Safety Criteria for People. Australian Rainfall and Runoff: A Guide to Flood Estimation, Commonwealth of Australia; Australian Government Geosciences Australia: Sydney, Australia, 2012.
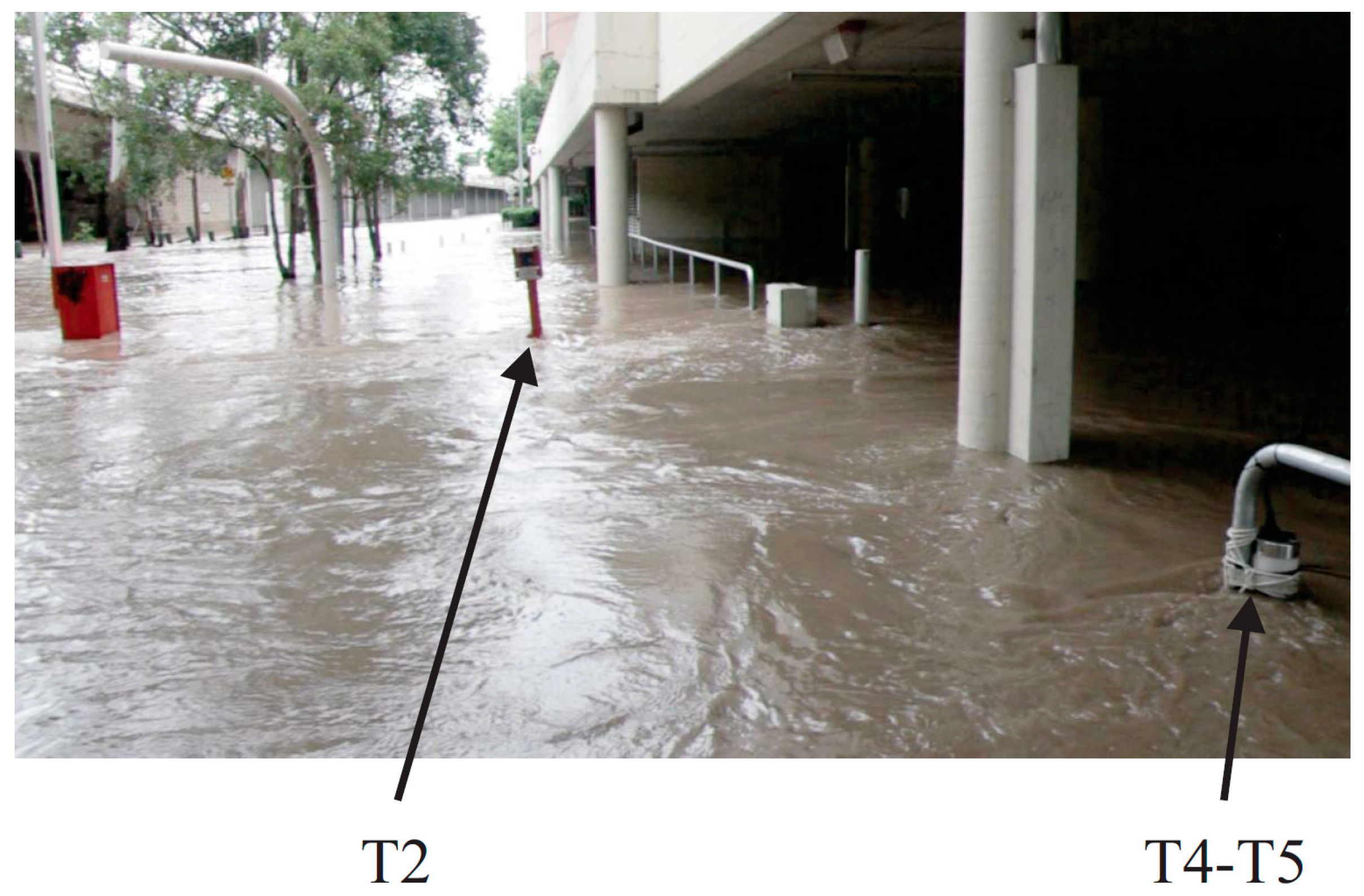
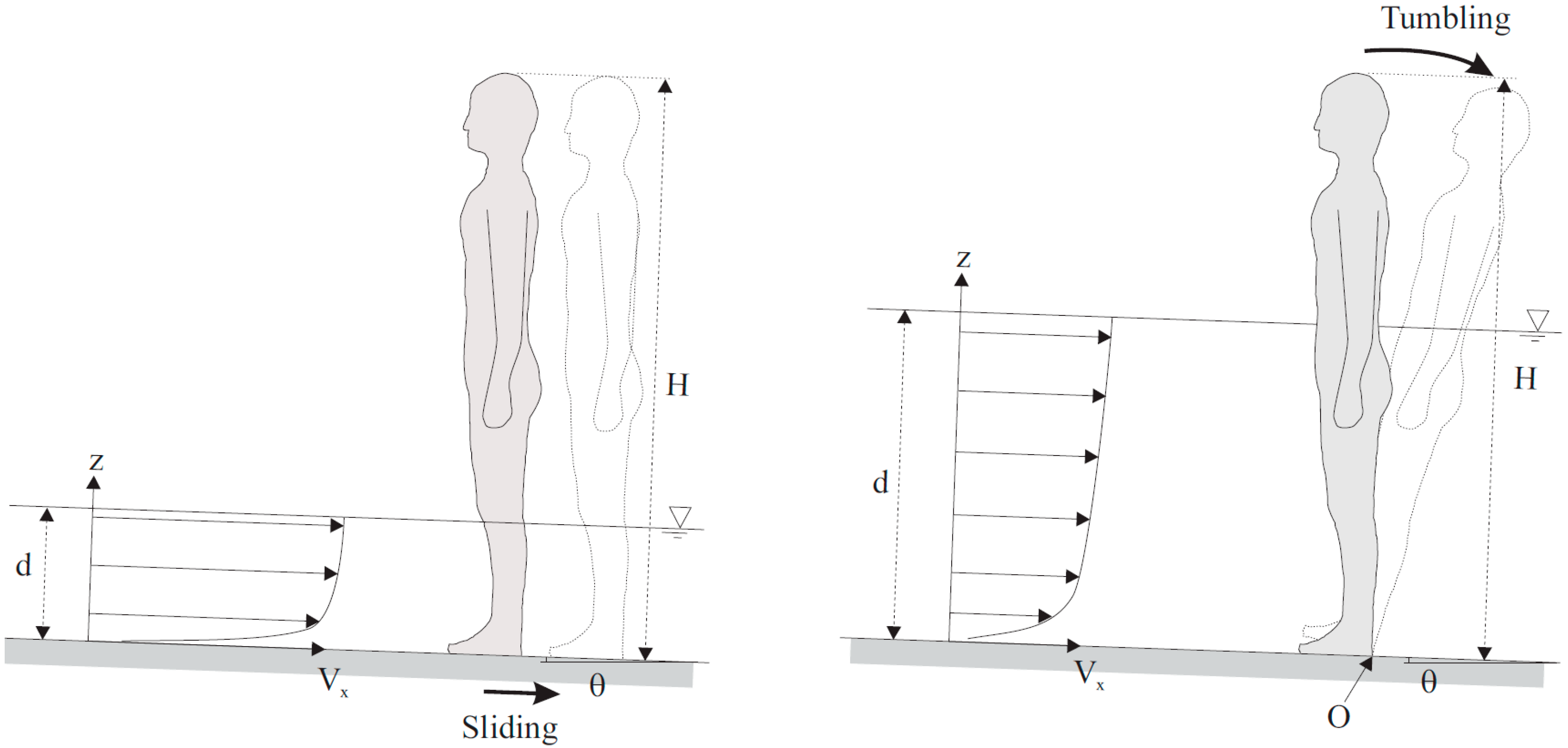
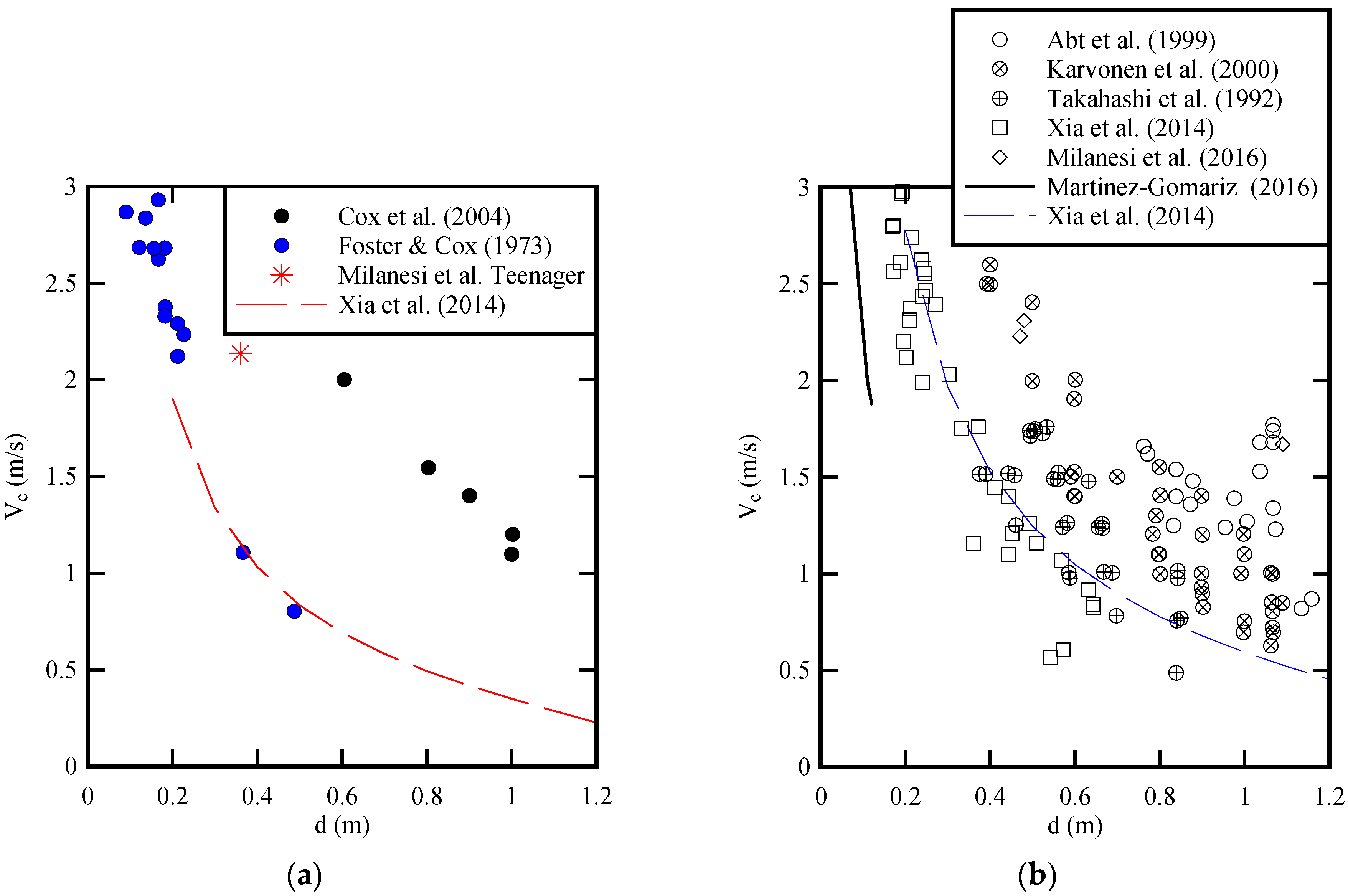


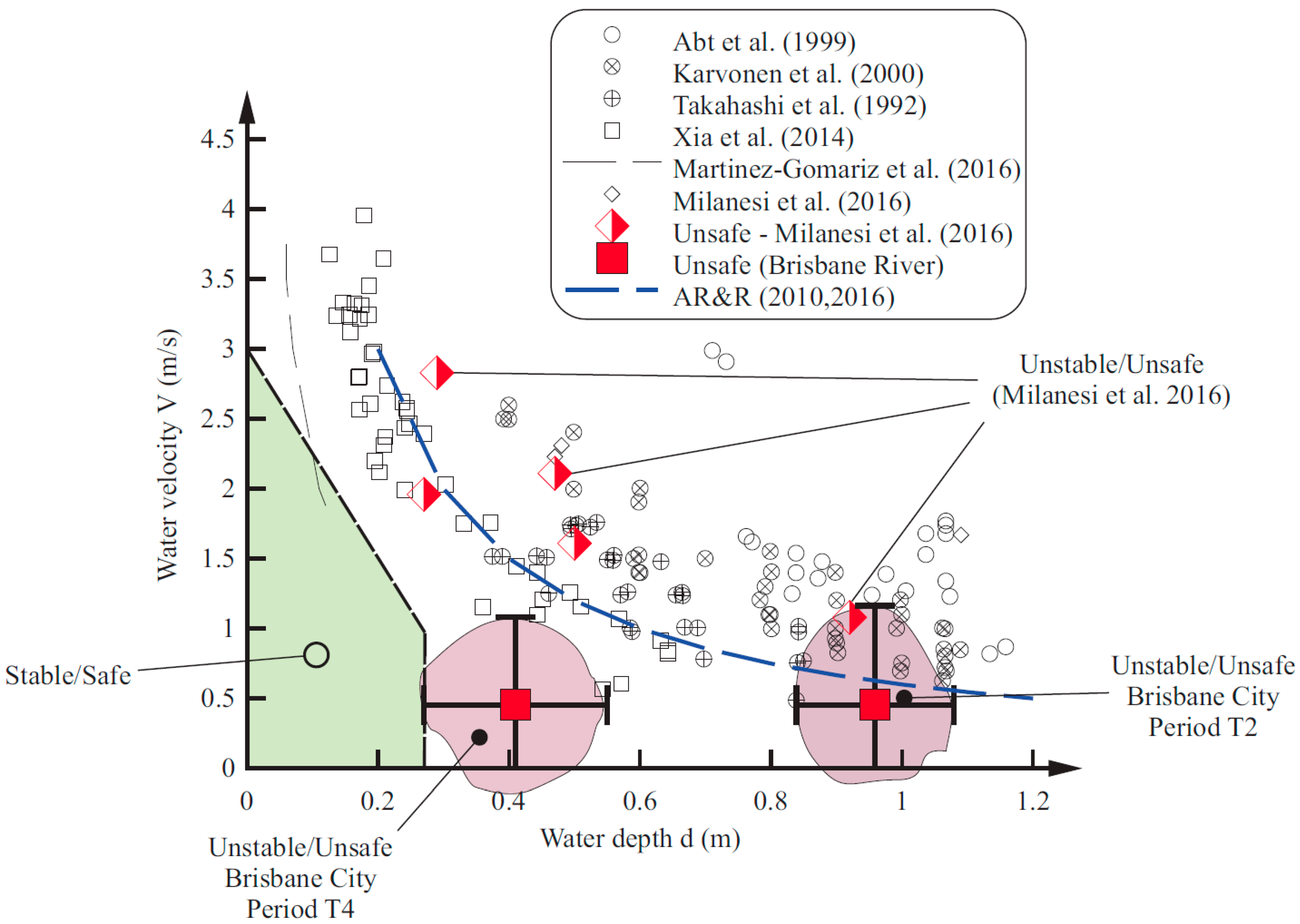
| Period | ZADV (m) | Velocity Data Set | Water Depth (m) | Mean Velocity (m/s) | Std Velocity (m/s) | Velocity Data Range (m/s) | Individual Stability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2 | 0.35 | 800,000 samples (4.4 h) | 0.8–1.0 | 0.454 | 0.170 | −0.36/+1.17 | Unstable & Unsafe |
| T4 | 0.083 | 685,884 samples (3.8 h) | 0.6–0.4 | 0.455 | 0.123 | −0.23/+1.09 | Unstable & Unsafe |
| T5 | 0.083 | 196,762 samples (1.1 h) | 0.3–0.1 | 0.0065 | 0.031 | −0.12/+0.15 | Stable & Safe |
| No. | Height (m) | Mass (kg) | Age | Male/Female |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.75 | 75 | 49 | M |
| 2 | 1.75 | 74 | 51 | M |
| 3 | 1.79 | 120 | 60 | M |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chanson, H.; Brown, R. Stability of Individuals during Urban Inundations: What Should We Learn from Field Observations? Geosciences 2018, 8, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8090341
Chanson H, Brown R. Stability of Individuals during Urban Inundations: What Should We Learn from Field Observations? Geosciences. 2018; 8(9):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8090341
Chicago/Turabian StyleChanson, Hubert, and Richard Brown. 2018. "Stability of Individuals during Urban Inundations: What Should We Learn from Field Observations?" Geosciences 8, no. 9: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8090341
APA StyleChanson, H., & Brown, R. (2018). Stability of Individuals during Urban Inundations: What Should We Learn from Field Observations? Geosciences, 8(9), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8090341





