Using Historical Precipitation Patterns to Forecast Daily Extremes of Rainfall for the Coming Decades in Naples (Italy)
Abstract
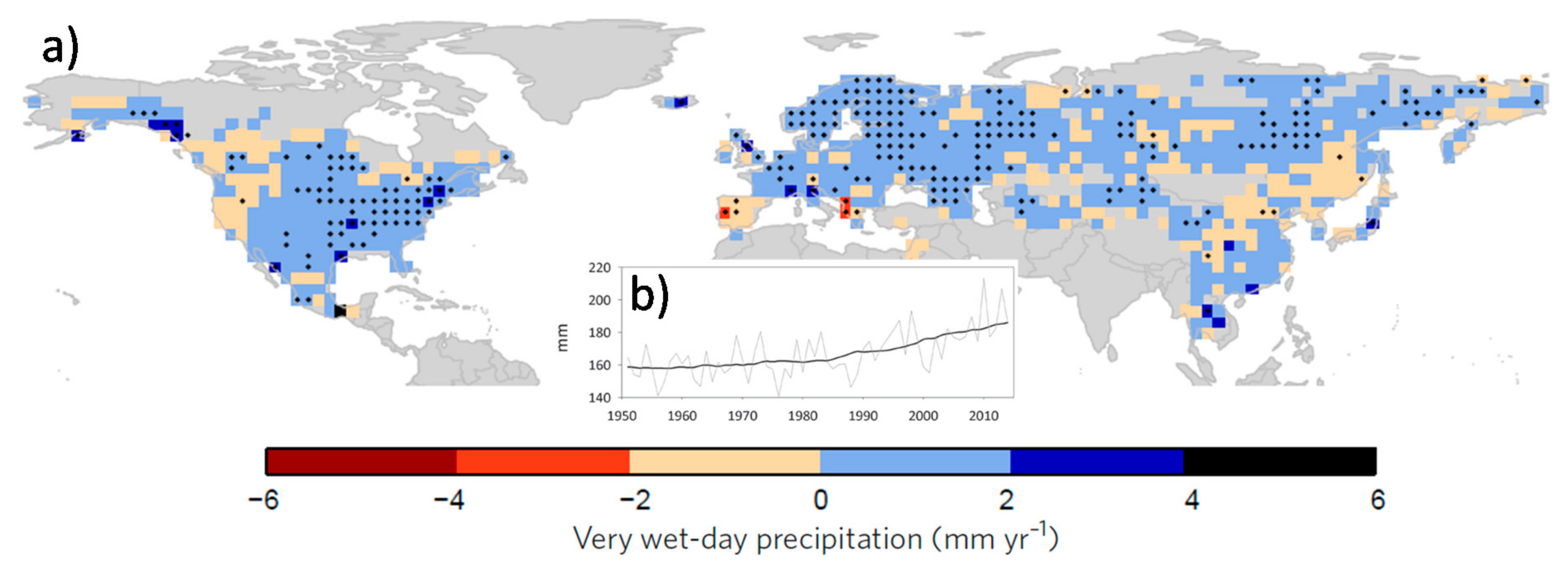
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Data Sources
2.2. Statistical Model
3. Results and Discussion
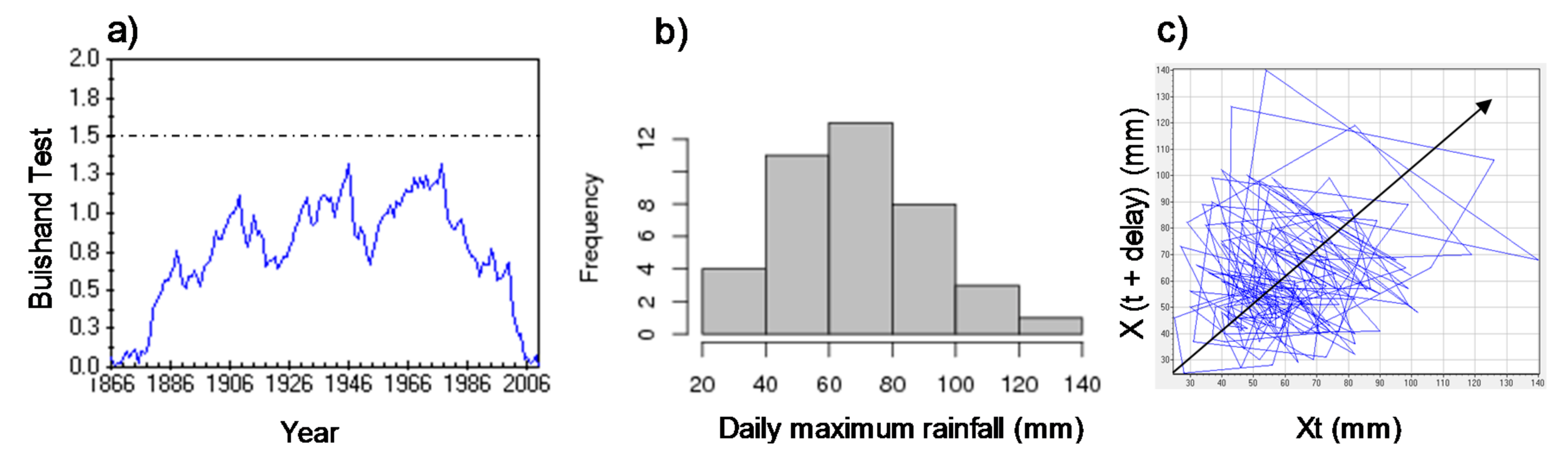
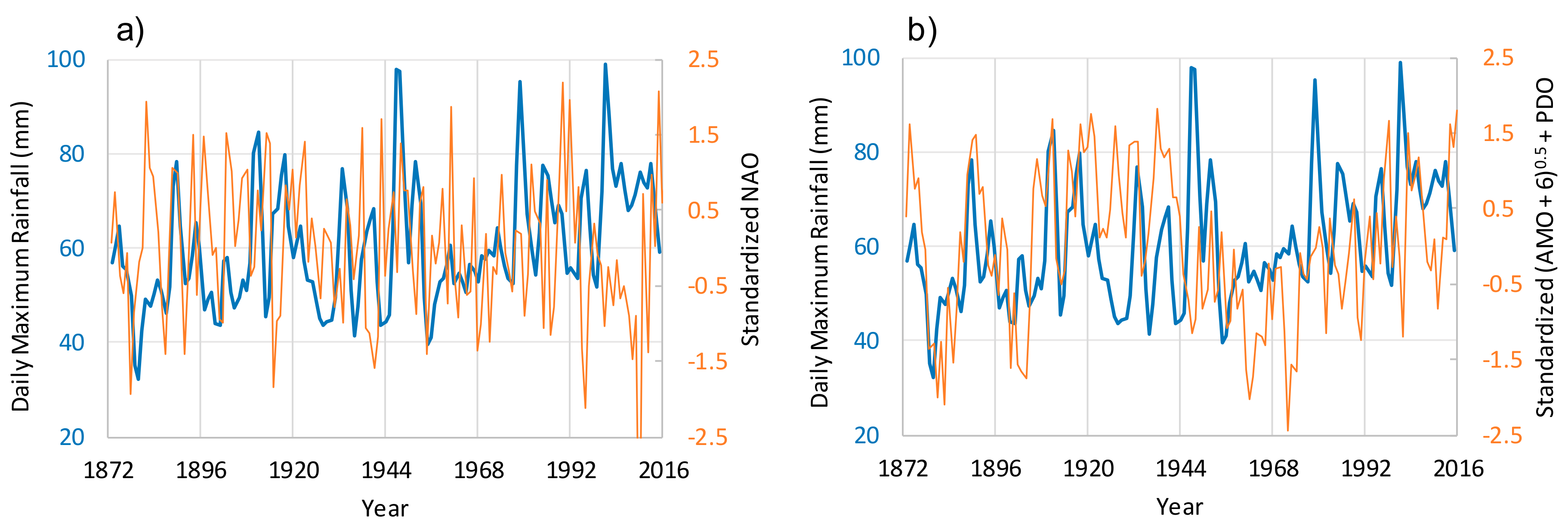
3.1. Exploratory Data Analysis
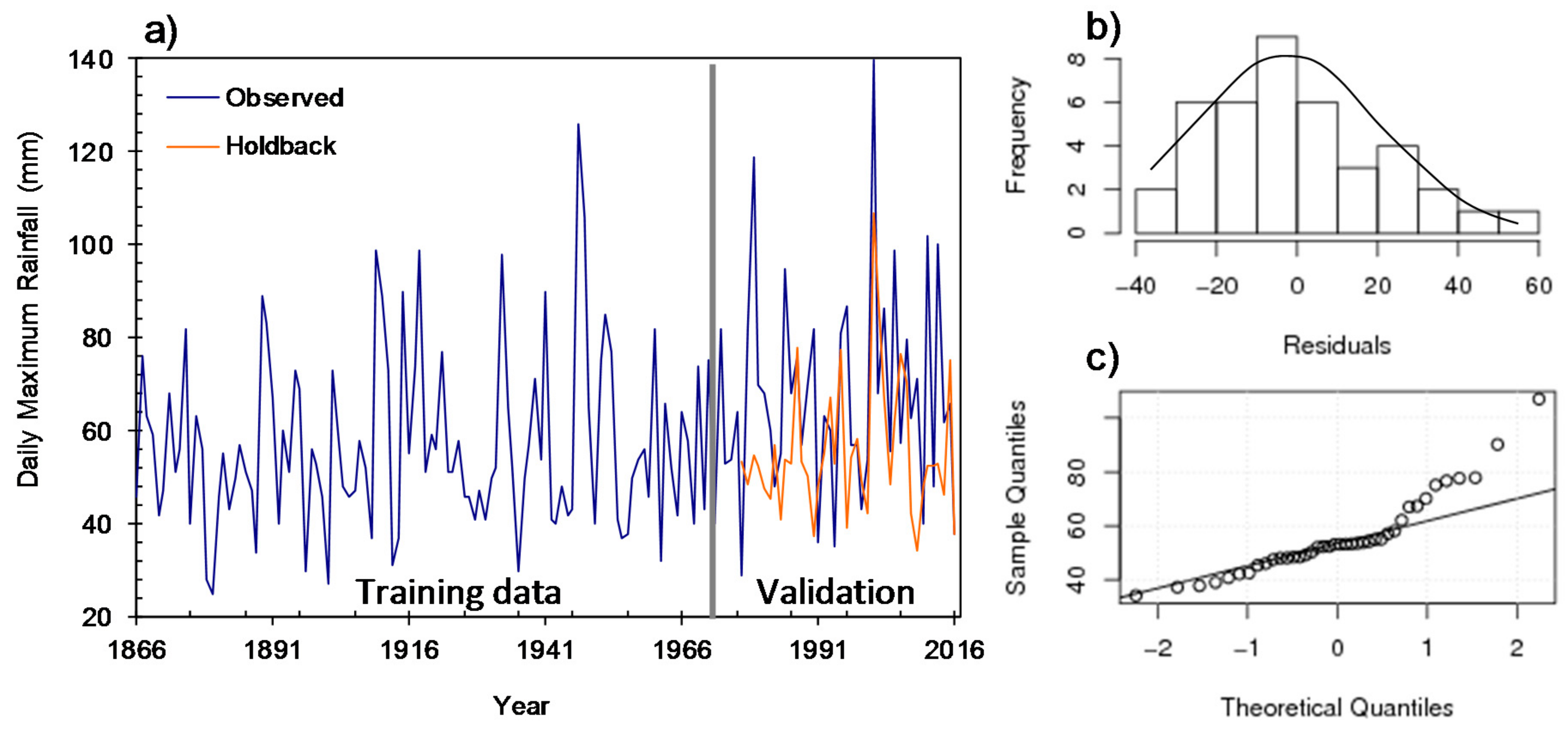
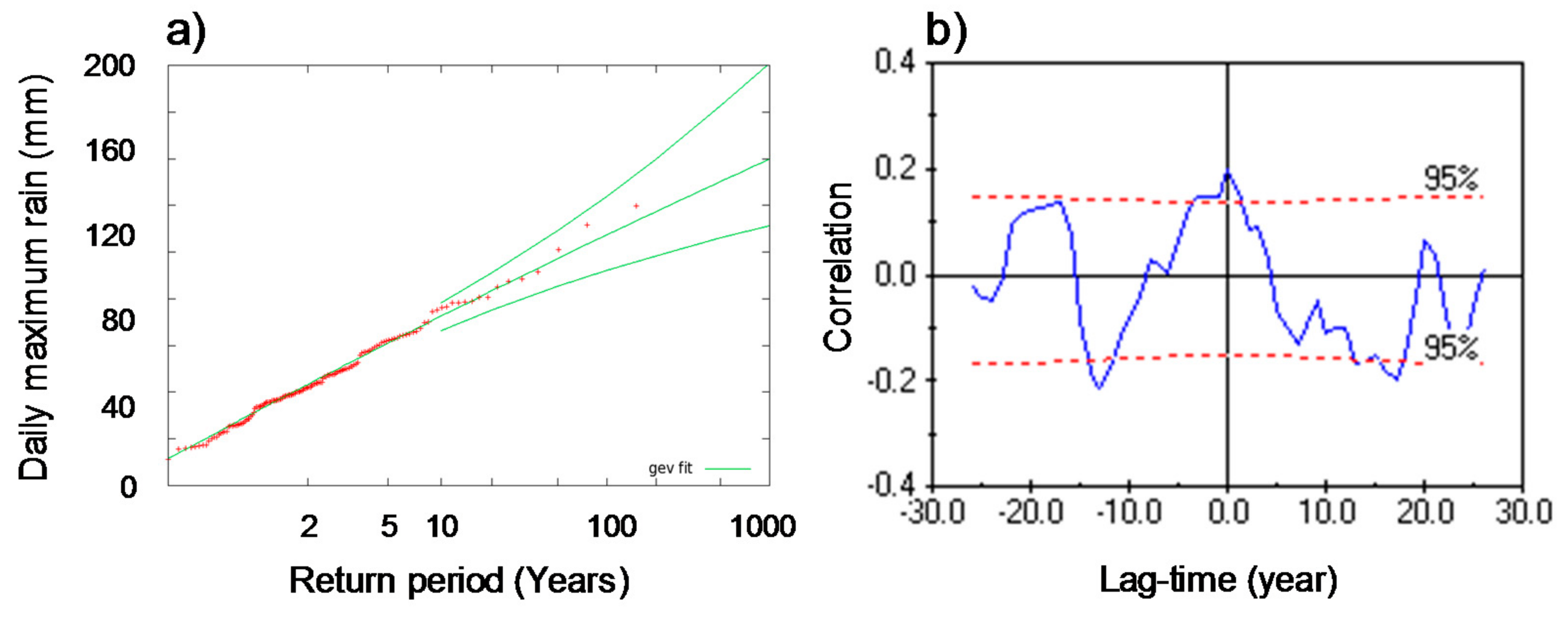
3.2. Validation Test
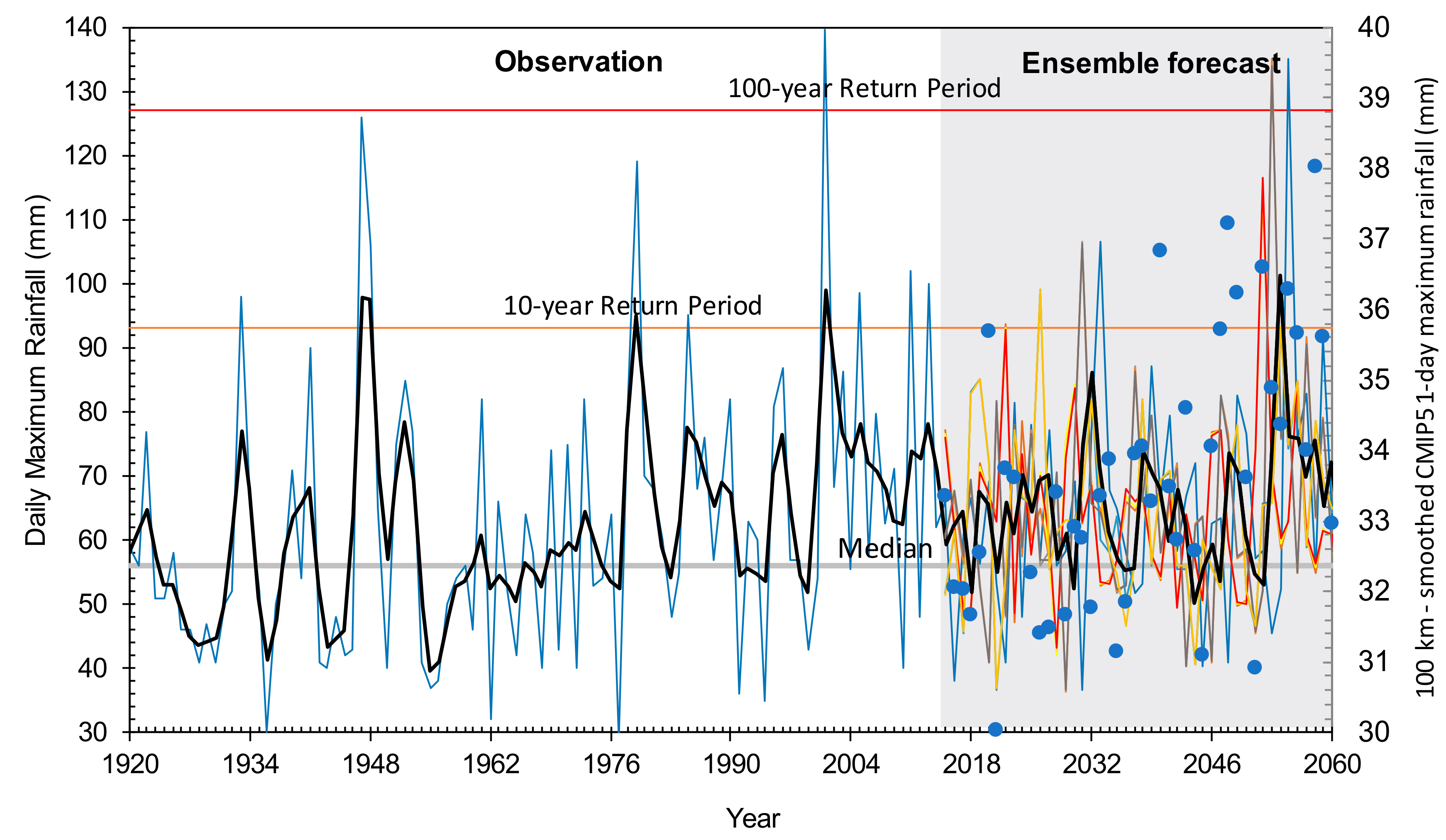
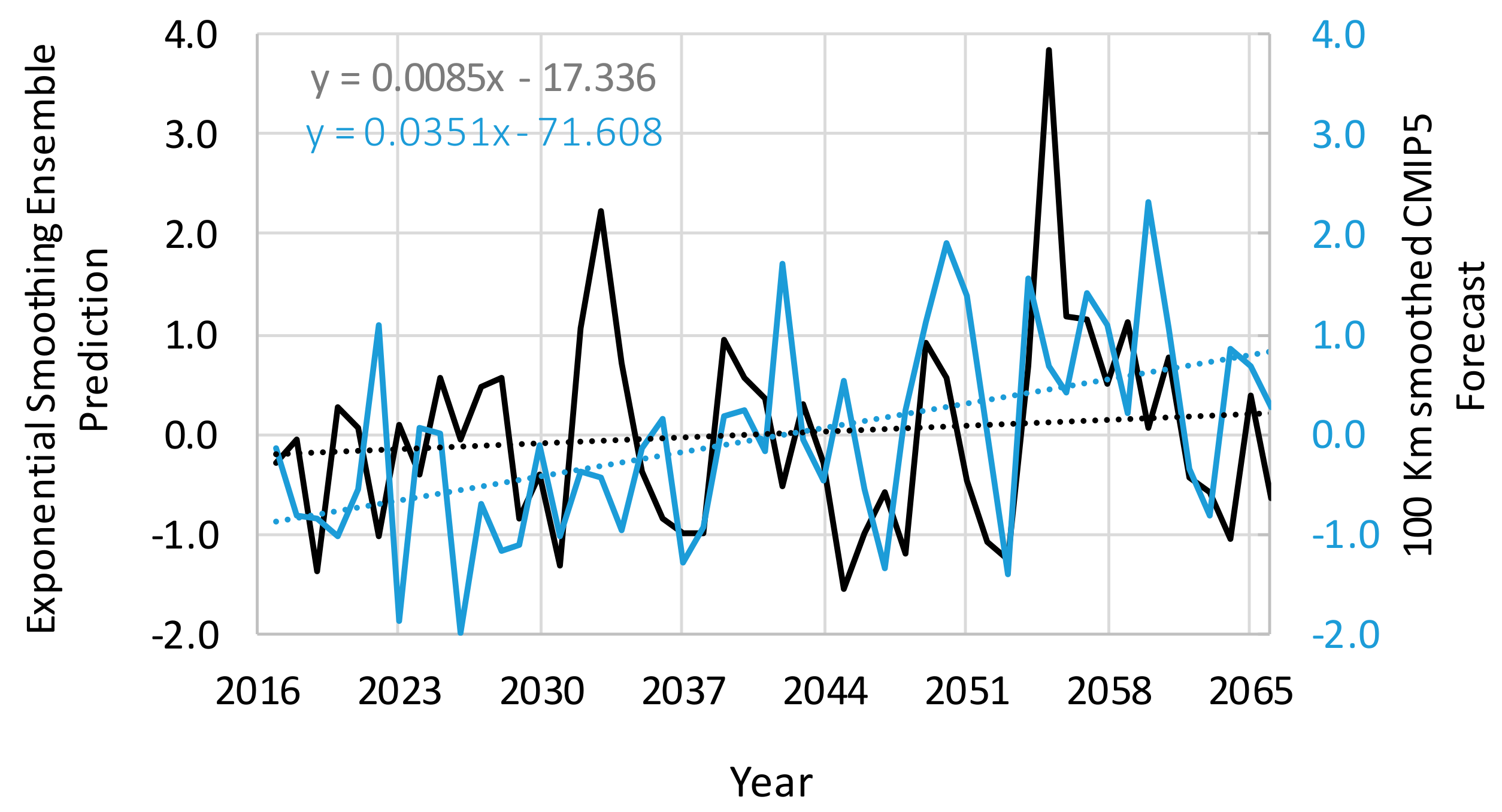
3.3. Simulation Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, J.; Screen, J.A.; Furtado, J.C.; Barlow, M.; Whittleston, D.; Coumou, D.; Francis, J.; Dethloff, K.; Entekhabi, D.; Overland, J.; et al. Recent Arctic amplification and extreme mid-latitude weather. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Fu, Q. Sensitivity of precipitation extremes to radiative forcing of greenhouse gases and aerosols. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 9860–9868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnell, N.W.; Delaney, E.K. Adapting to climate change: Public water supply in England and Wales. Clim. Chang. 2006, 78, 227–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, X.; Shen, Y.; Xu, C.; Shi, Y.; Giorgi, F. A daily temperature dataset over China and its application in validating a RCM simulation. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 26, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazeleger, W.; van den Hurk, B.J.J.M.; Min, E.; van Oldenborgh, G.J.; Petersen, A.C.; Stainforth, D.A.; Vasileiadou, E.; Smith, L.A. Tales of future weather. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dünkeloh, A.; Jacobeit, J. Circulation dynamics of Mediterranean precipitation variability. Int. J. Climatol. 2003, 23, 1843–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triacca, U.; Attanasio, A.; Pasini, A. Anthropogenic global warming hypothesis: Testing its robustness by Granger causality analysis. Environmetrics 2013, 24, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocchi, F.; Pasini, A. Climate model pluralism beyond dynamical ensembles. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2017, 8, e477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasini, A.; Racca, P.; Amendola, S.; Cartocci, G.; Cassardo, C. Attribution of recent temperature behaviour reassessed by a neural-network method. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, C.A.; Hsu, K.J. Geophysical, archaeological, and historical evidence support a solar-output model for climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12433–12438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.S.; Karl, T.R.; Reynolds, R.W. How accurate are climate simulations? Science 2002, 296, 483–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, A.J.; Hillaire-Marcel, C. Global warming and the next ice age. Science 2004, 304, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, G.H.; Baker, M.B. Why is climate sensitivity so unpredictable? Science 2007, 318, 629–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knutti, R.; Krähenmann, S.; Frame, D.J.; Allen, M.R. Comment on “Heat capacity, time constant, and sensitivity of Earth’s climate system” by S.E. Schwartz. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D15103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Fasullo, J.T. Tracking Earth’s energy. Science 2010, 328, 316–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtado, J.C.; Di Lorenzo, E.; Schneider, N.; Bond, N.A. North Pacific decadal variability and climate change in the IPCC AR4 models. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 3049–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zwiers, F.W.; Li, G.; Wan, H.; Cannon, A.J. Complexity in estimating past and future extreme short-duration rainfall. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroe-Kunold, E.; Stadnytska, T.; Werner, J.; Braun, S. Estimating long-range dependence in time series: An evaluation of estimators implemented in R. Behav. Res. Meth. 2009, 41, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leith, C. Climate response and fluctuation-dissipation. J. Atmos. Sci. 1975, 32, 2022–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbold, P.; Granger, C.W.J. Experience with forecasting univariate time series and the combination of forecasts. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A 1974, 137, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, C.C. Forecasting seasonals and trends by exponentially weighted moving averages. Int. J. Forecast. 2004, 20, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control; Holden Day: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, E.S., Jr. Exponential smoothing: The state of the art—Part II. Int. J. Forecast. 2006, 22, 637–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClain, J.O. Dynamics of exponential smoothing with trend and seasonal terms. Manag. Sci. 1974, 20, 1300–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.W. Exponential smoothing with a damped multiplicative trend. Int. J. Forecast. 2003, 19, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Koehler, A.B.; Ord, J.K.; Snyder, R.D. Forecasting with Exponential Smoothing: The State Space Approach; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Crevits, R.; Croux, C. Forecasting Using Robust Exponential Smoothing with Damped Trend and Seasonal Components; Working Papers Department of Decision Sciences and Information Management 588812; Faculty of Economics and Business, Department of Decision Sciences and Information Management: Leuven, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Monfared, M.A.S.; Ghandali, R.; Esmaeili, M. A new adaptive exponential smoothing method for non-stationary time series with level shifts. J. Ind. Eng. Int. 2014, 10, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vennari, C.; Parise, M.; Santangelo, N.; Santo, A. A database on flash flood events in Campania, southern Italy, with an evaluation of their spatial and temporal distribution. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 2485–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henfrey, A. The Vegetation of Europe: Its Conditions and Causes; J. van Voorst: London, UK, 1852. [Google Scholar]
- Wigley, T.M.L. Future climate of the Mediterranean Basin with particular emphasis in changes in precipitation. In Climate Change in the Mediterranean; Jeftic, L., Milliman, J.D., Sestini, G., Eds.; Edward Arnold: London, UK, 1992; pp. 15–44. [Google Scholar]
- Smooth Forecast. Available online: http://smoothforecast.com (accessed on 5 August 2018).
- Wessa, P. Free Statistics Software, Office for Research Development and Education. version 1.1.23-r7. 2012. Available online: https://www.wessa.net (accessed on 5 August 2018).
- Karagiannis, T.; Faloutsos, M.; Molle, M. A user-friendly self-similarity analysis tool. ACM SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 2003, 33, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.C.; Jennings, C.L.; Kulahci, M. Introduction to Time Series Analysis and Forecasting; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, D.G. Judging air quality model performance: A summary of the AMS workshop on dispersion models performance. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1981, 62, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, N.I.A.; Harun, S.; Kassim, A.H.M. Radial basis function modeling of hourly streamflow hydrograph. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2007, 12, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Koehler, A.B. Another look at measures of forecast accuracy. Int. J. Forecast. 2006, 22, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addiscott, T.M.; Whitmore, A.P. Computer-simulation of changes in soil mineral nitrogen and crop nitrogen during autumn, winter and spring. J. Agric. Sci. 1987, 109, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buishand, T.A. Some methods for testing homogeneity of rainfall records. J. Hydrol. 1982, 58, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jens, F. Fractals; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Kamruzzaman, M.; Beecham, S.; Metcalfe, A.V. Non-stationarity in rainfall and temperature in the Murray Darling Basin. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 25, 1659–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quian, B.; Rasheed, K. Hurst exponent and financial market predictability. In Proceedings of the 2nd IASTED International Conference on Financial Engineering and Applications, Cambridge, MA, USA, 8–11 November 2004; pp. 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Miglietta, M.M.; Mazon, J.; Motola, V.; Pasini, V. Effect of a positive Sea Surface Temperature anomaly on a Mediterranean tornadic supercell. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, A.M. Uncertainty in regional climate modelling: A review. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2010, 34, 647–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfahl, S.; O’Gorman, P.A.; Fischer, E.M. Understanding the regional pattern of projected future changes in extreme precipitation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasini, A.; Langone, R. Attribution of precipitation changes on a regional scale by neural network modeling: A case study. Water 2010, 2, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, M.F.; Seidenkrantz, M.-S.; Jacobsen, B.H.; Kuijpers, A. Tracking the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation through the last 8000 years. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scafetta, N. Empirical evidence for a celestial origin of the climate oscillations and its implications. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 2010, 72, 951–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, J.; He, Y.; Guan, Y. Combined effects of the Pacific Decadal Oscillation and El Niño-Southern Oscillation on global land dry-wet changes. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslova, V.N.; Voskresenskaya, E.N.; Maslova, A.S.L. Multidecadal change of winter cyclonic activity in the Mediterranean associated with AMO and PDO. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2017, 6, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diodato, N.; Bellocchi, G. Long-term winter temperatures in central Mediterranean: Forecast skill of an ensemble statistical model. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 116, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diodato, N.; Bellocchi, G.; Fiorillo, F.; Ventafridda, G. Case study for investigating groundwater and the future of mountain spring discharges in Southern Italy. J. Mt. Sci. 2017, 14, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheyas, I.; Smith, L. A neural network approach to time series forecasting. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering, London, UK, 1–3 July 2009; pp. 1292–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Knutti, R.; Furrer, R.; Tebaldi, C.; Cermak, J.; Meehl, G.A. Challenges in combining projections from multiple climate models. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 2739–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diodato, N.; Bellocchi, G. Using Historical Precipitation Patterns to Forecast Daily Extremes of Rainfall for the Coming Decades in Naples (Italy). Geosciences 2018, 8, 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8080293
Diodato N, Bellocchi G. Using Historical Precipitation Patterns to Forecast Daily Extremes of Rainfall for the Coming Decades in Naples (Italy). Geosciences. 2018; 8(8):293. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8080293
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiodato, Nazzareno, and Gianni Bellocchi. 2018. "Using Historical Precipitation Patterns to Forecast Daily Extremes of Rainfall for the Coming Decades in Naples (Italy)" Geosciences 8, no. 8: 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8080293
APA StyleDiodato, N., & Bellocchi, G. (2018). Using Historical Precipitation Patterns to Forecast Daily Extremes of Rainfall for the Coming Decades in Naples (Italy). Geosciences, 8(8), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8080293





