Major Strike-Slip Faults Identified Using Satellite Data in Central Borneo, SE Asia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
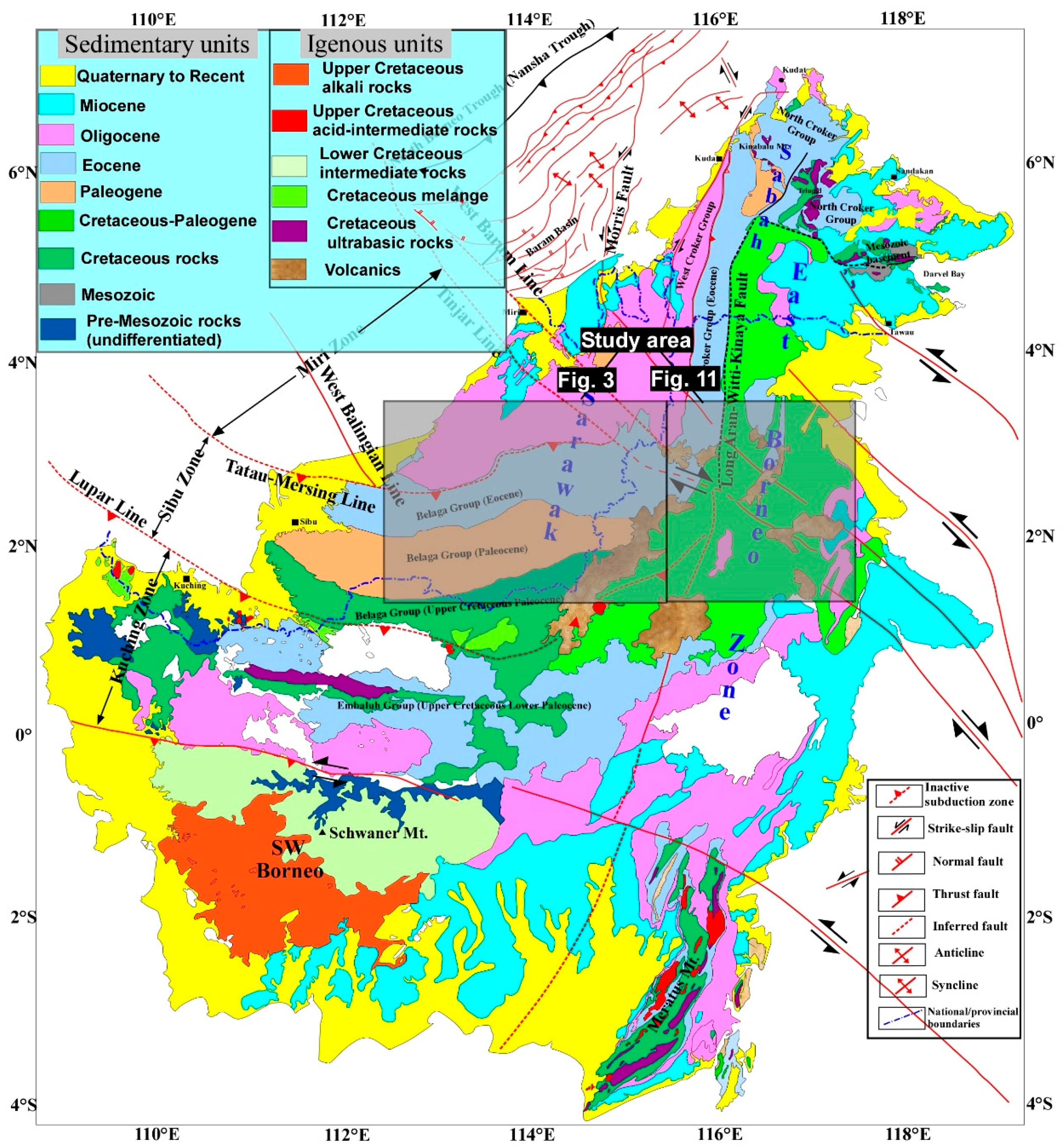
2. Regional Tectonic Setting
3. Instrumental Seismicity
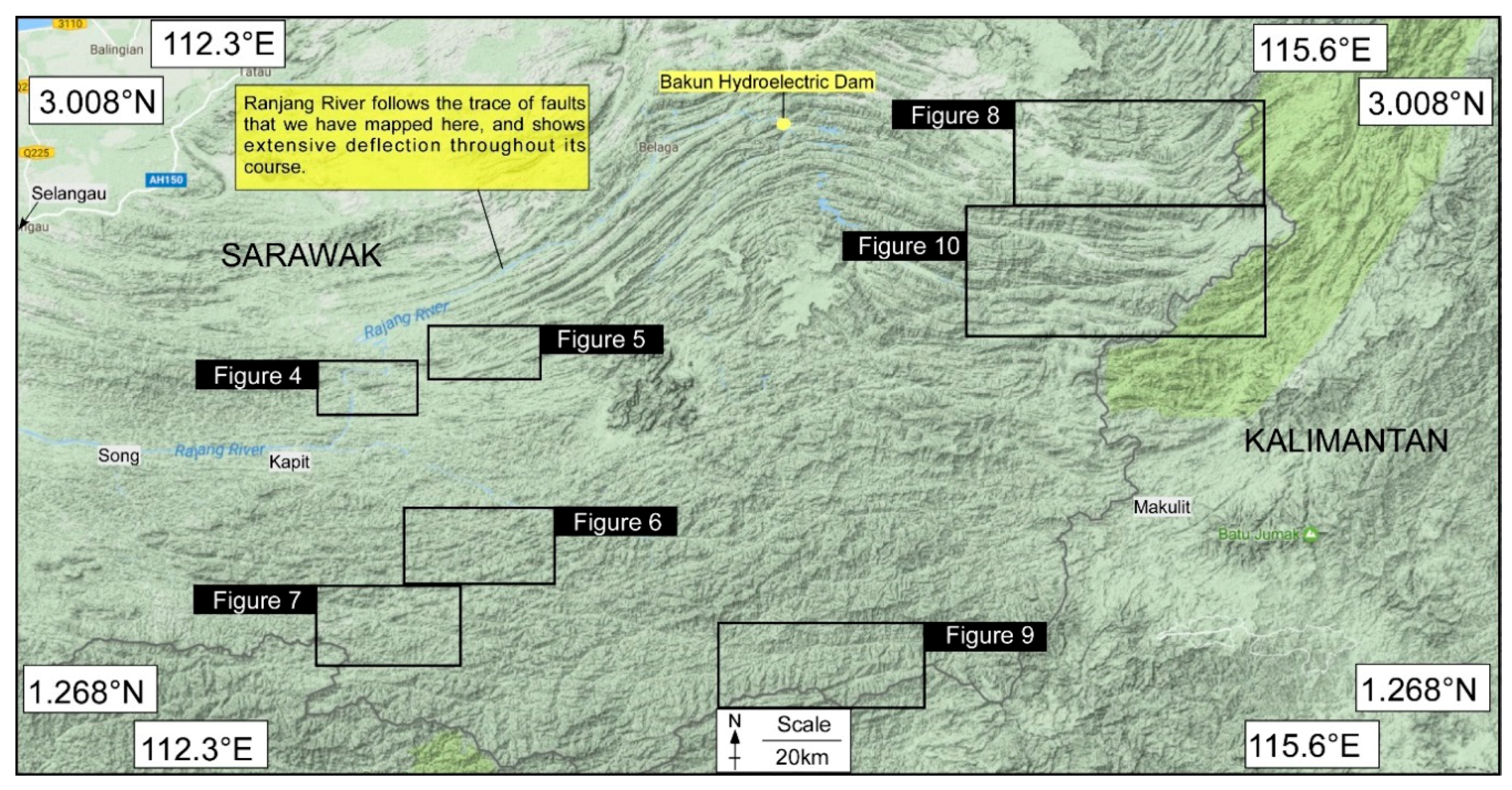
4. Methodology
Limitation of Google Maps
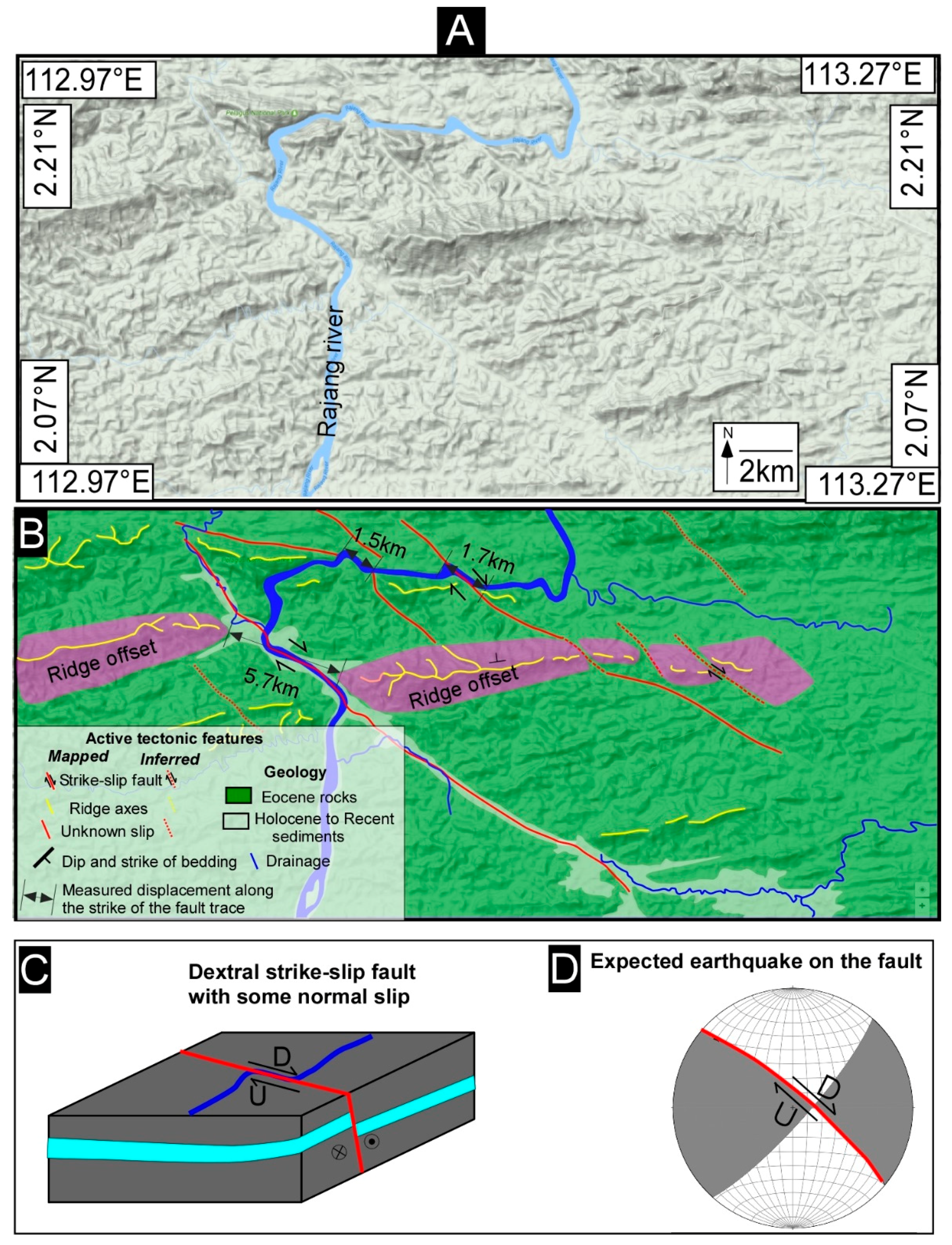
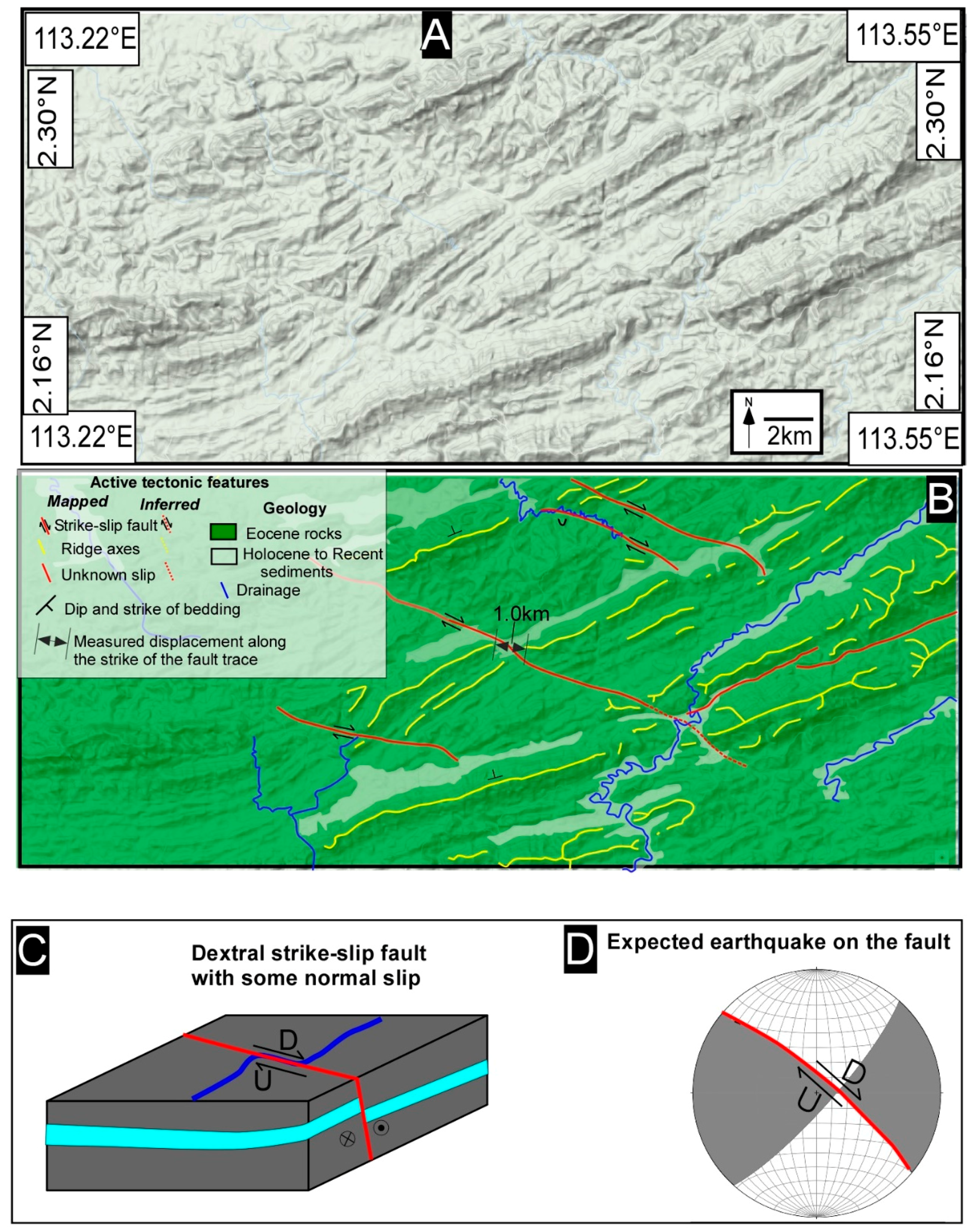
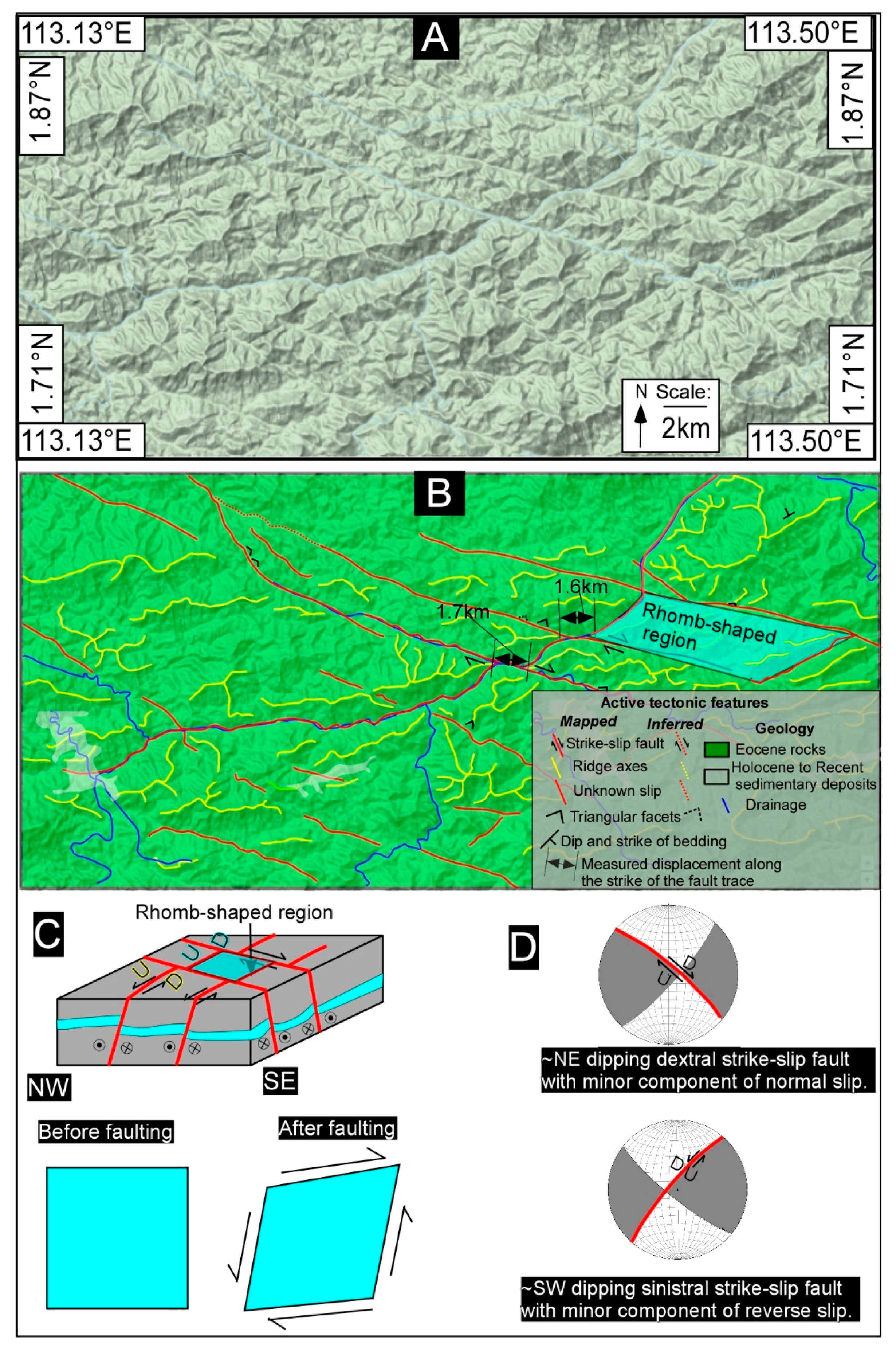
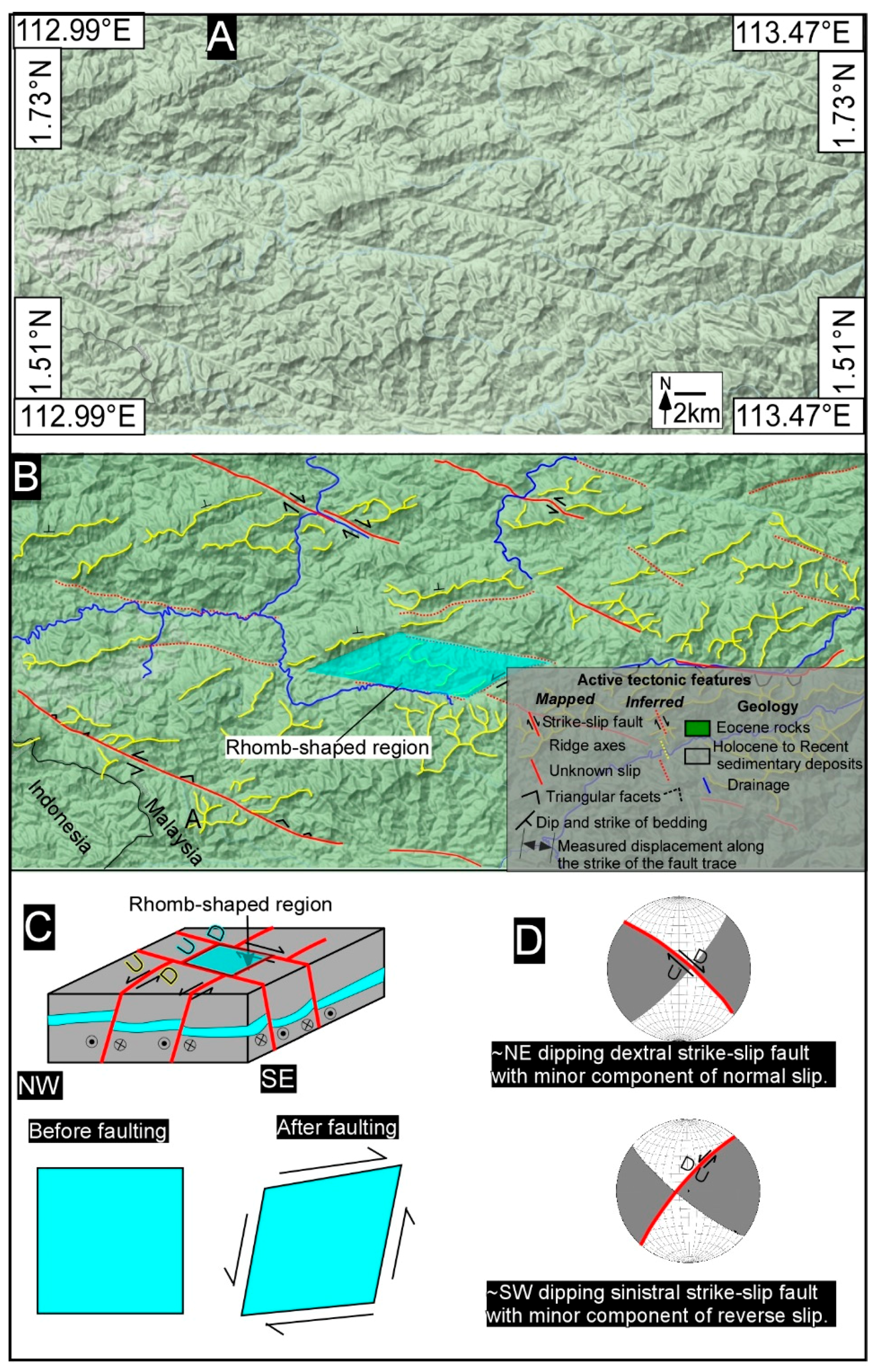
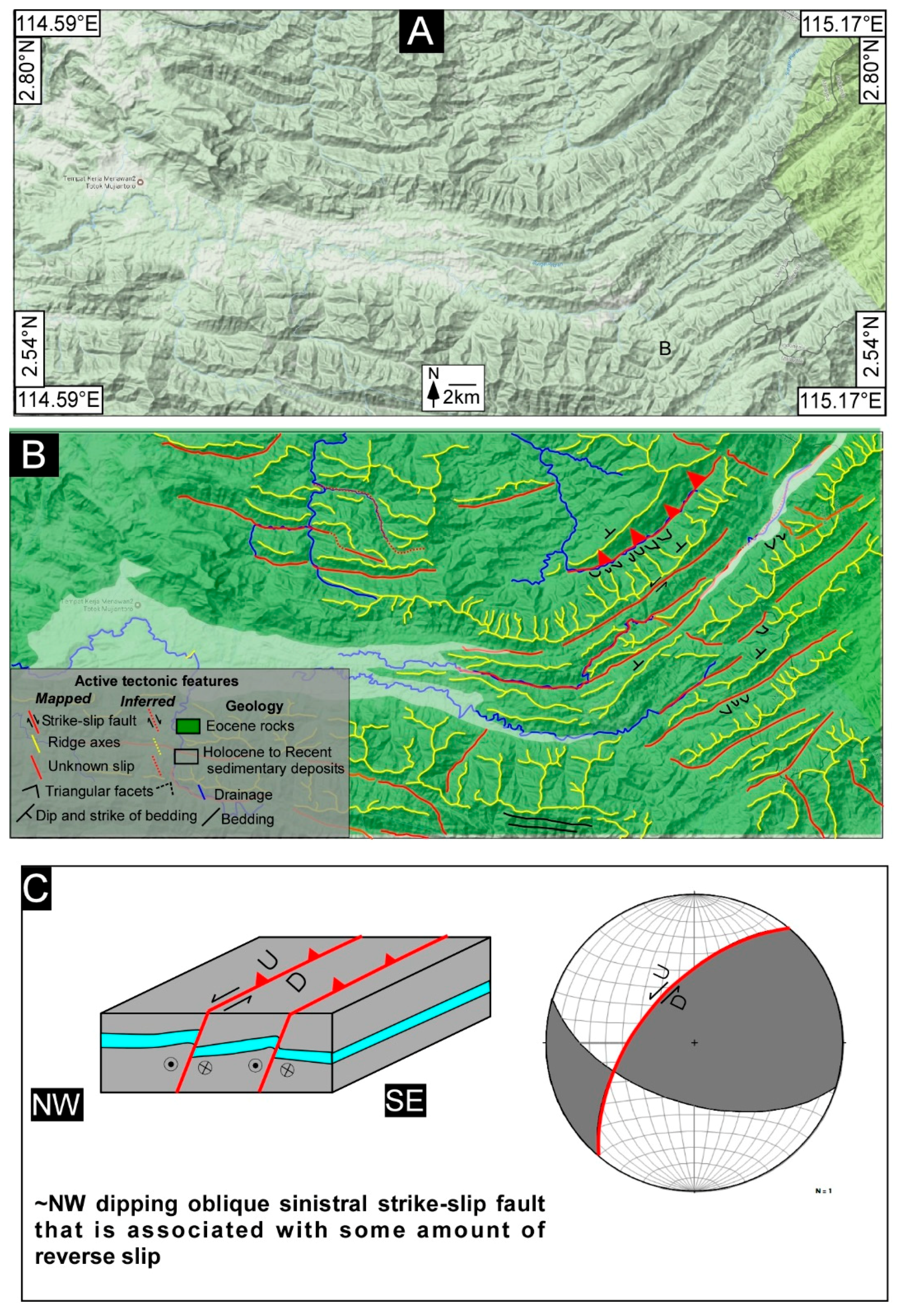
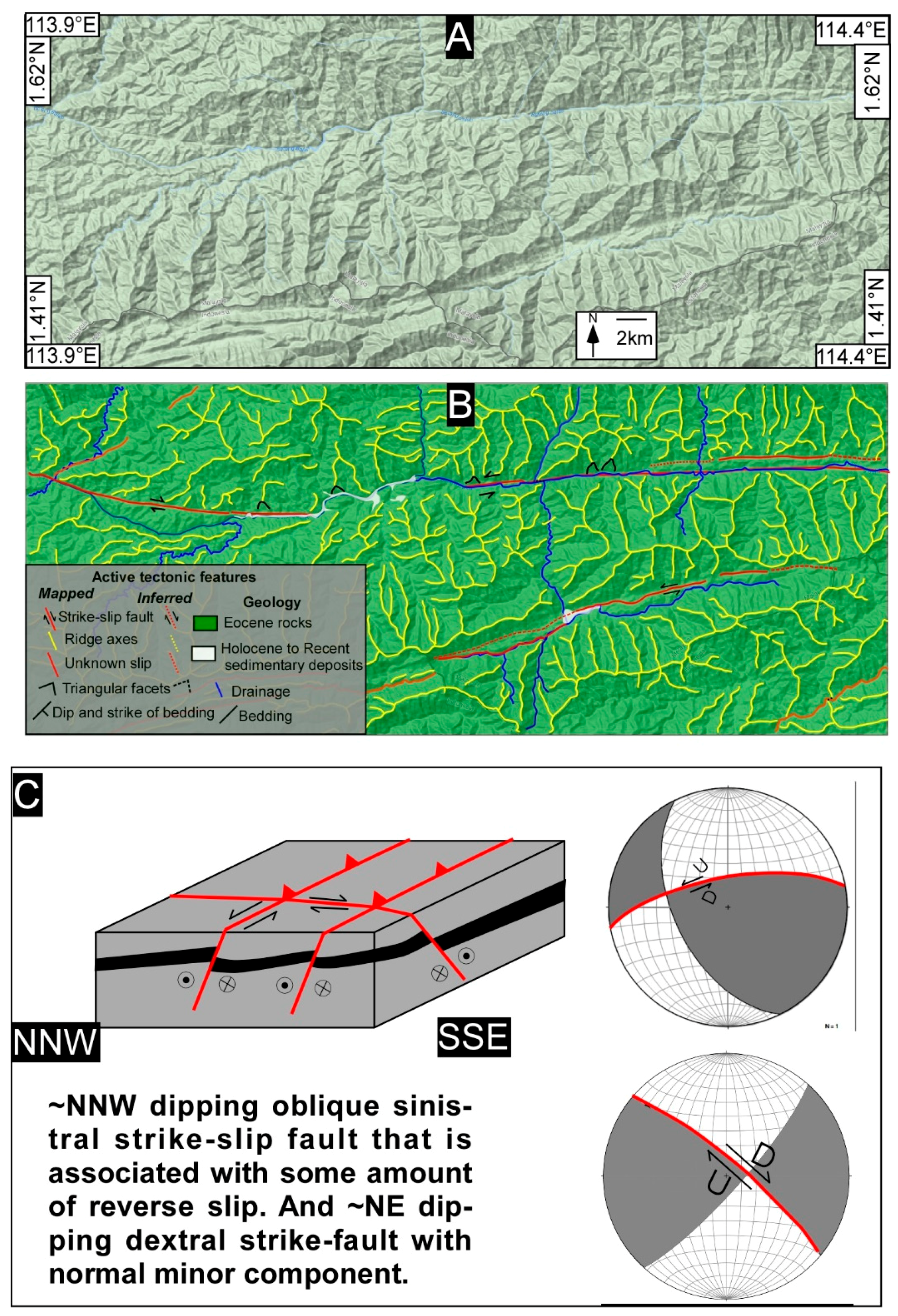
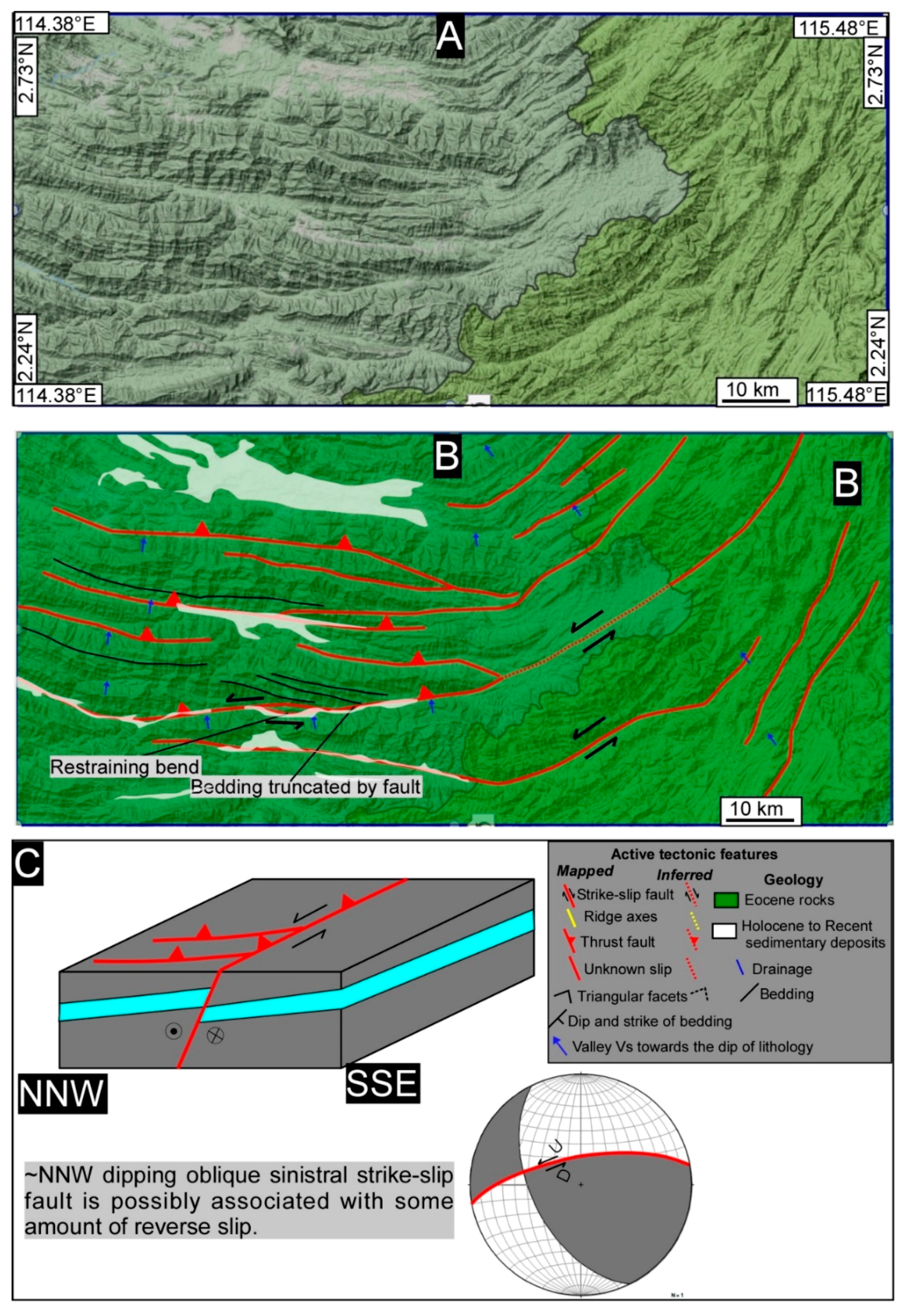
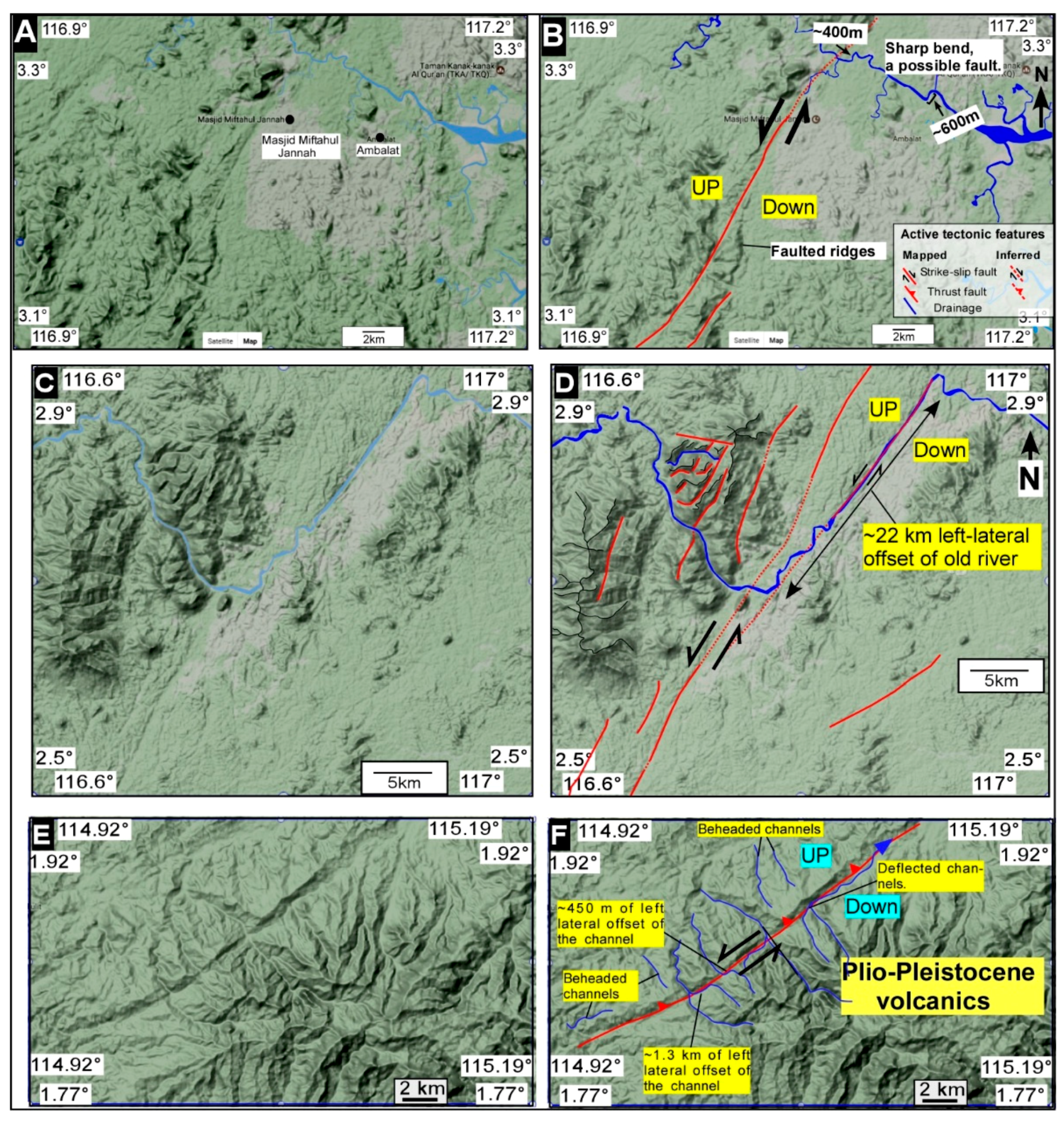
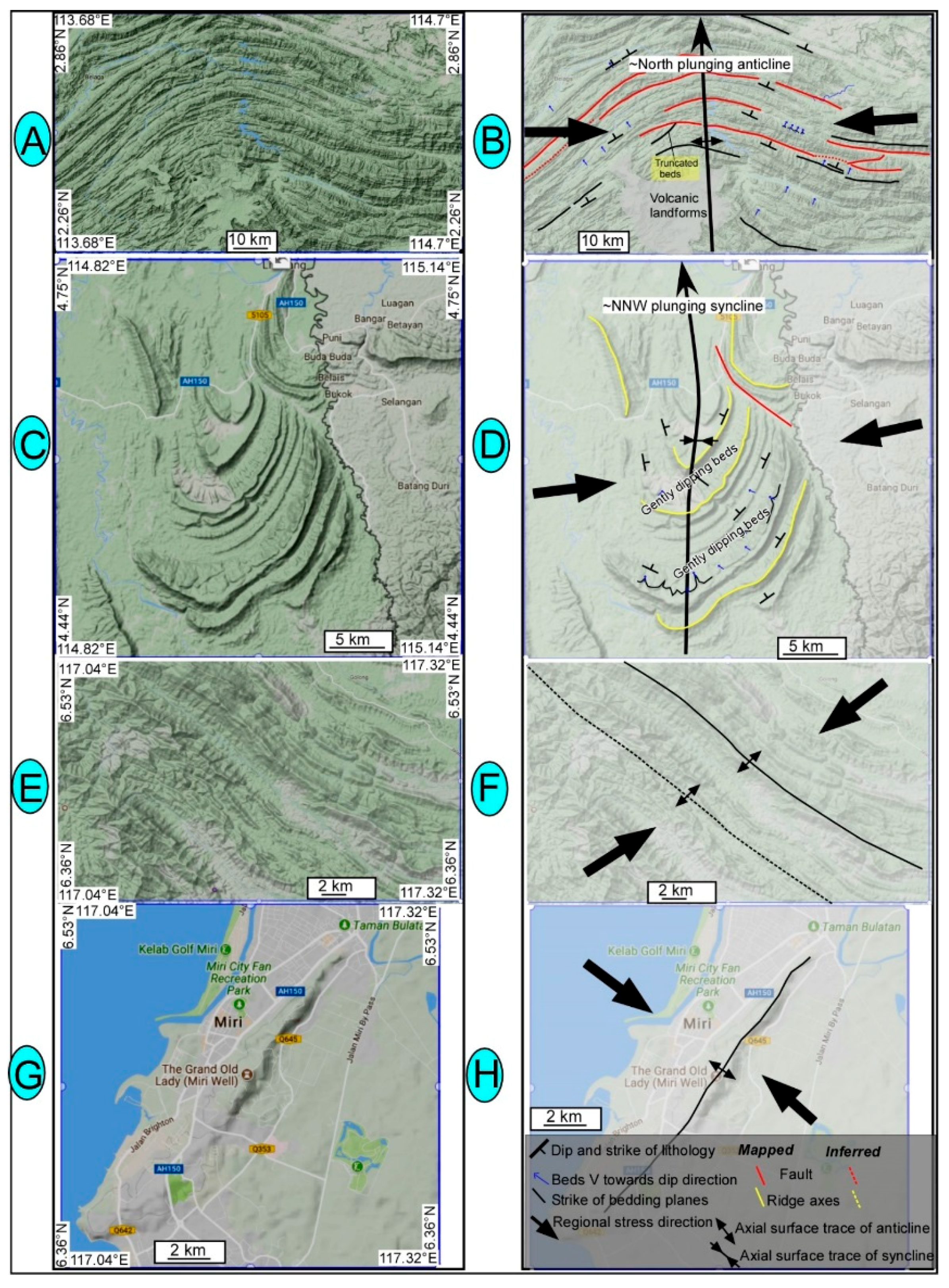
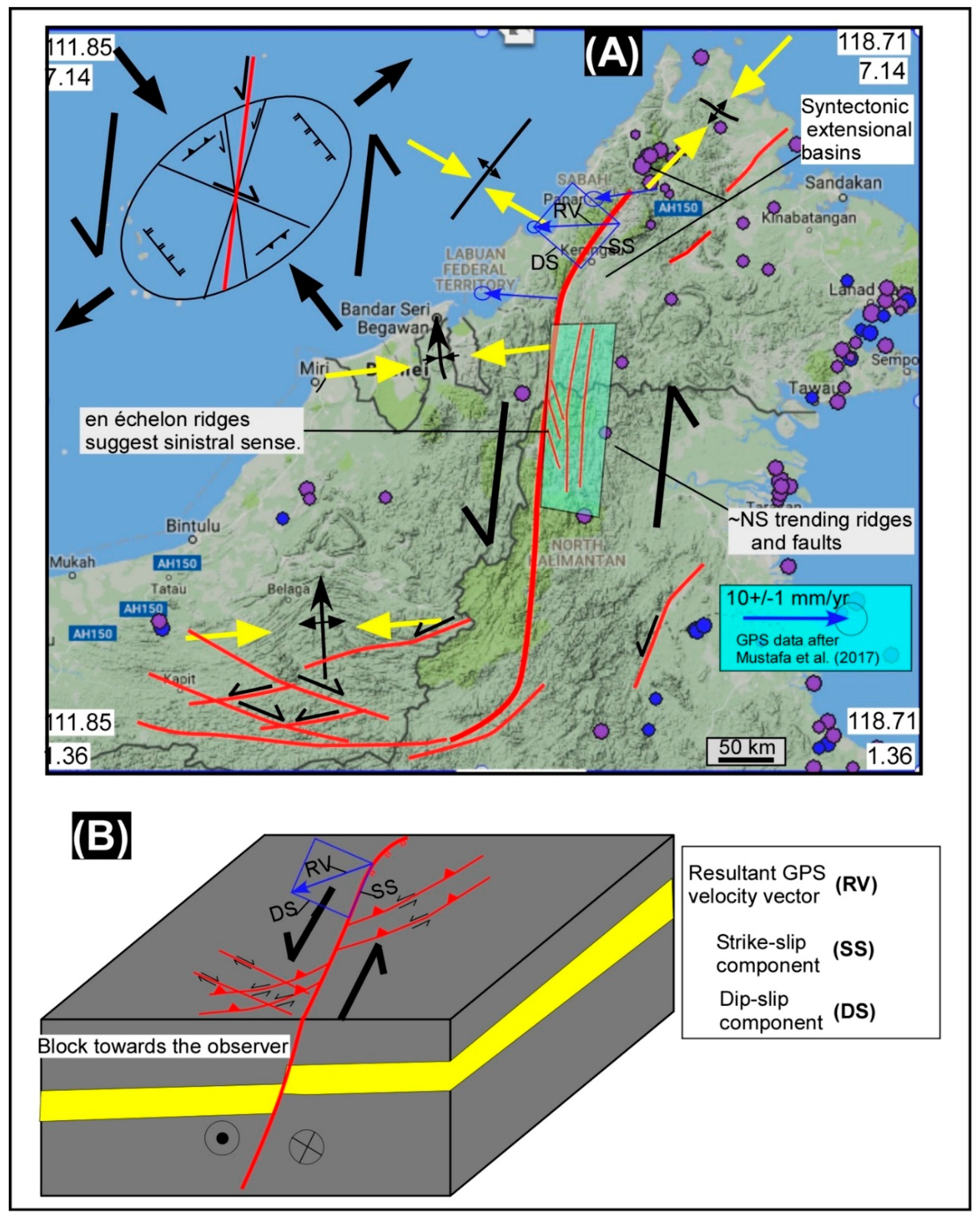
5. Results and Interpretation
5.1. Tectonic Geomorphology
5.2. Regional Folding
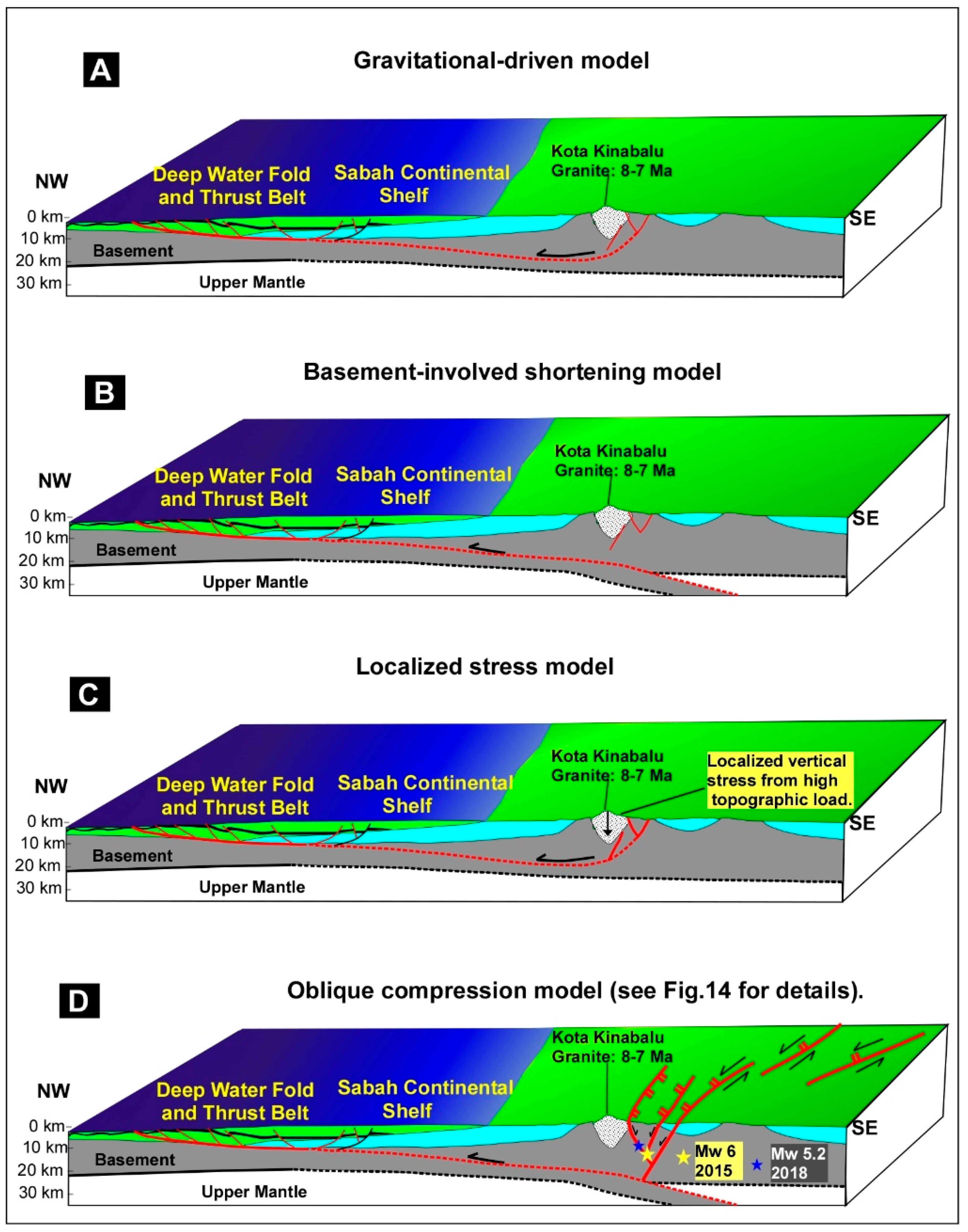
6. Discussion
6.1. Tectonic Geomorphology and Fault Controlled River Patterns of Borneo
6.2. Strike-Slip Faults Are Related to Plate Tectonic Forces
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hutchison, C.S. Geological Evolution of South-East Asia; Clarendon: Oxford, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Tongkul, F. The geology of Northern Sabah, Malaysia: Its relationship to the opening of the South China Sea basin. Tectonophysics 1994, 235, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R. Reconstructing Cenozoic SE Asia. In Tectonic Evolution of SE Asia; Geological Society London Special Publication: London, UK, 1996; Volume 106, pp. 153–184. [Google Scholar]
- Morley, C.K. A tectonic model for the Tertiary evolution of strike-slip faults and rift basins in SE Asia. Tectonophysics 2002, 347, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.; Marco, W.A.; Hattum, V.; Spakman, W. Impact of India-Asia collision on SE Asia: The record in Borneo. Tectonophysics 2008, 451, 366–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, C.K.; King, R.; Hillis, R.; Tingay, M.; Backe, G. Deepwater fold and thrust belt classification, tectonics, structure and hydrocarbon prospectivity. Earth Sci. Rev. 2012, 104, 41–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, C.K. Late Cretaceouse—Early Palaeogene tectonic development of SE Asia. Earth Sci. Rev. 2012, 125, 37–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, C.S. Oroclines and paleomagnetism in Borneo and south-east Asia. Tectonophysics 2010, 496, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, C.S. The north-west Borneo trough. Mar. Geol. 2010, 271, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.W. Southeast Asia reconstruction with a non-rotation Cenozoic Borneo. Geol. Soc. Malays. 1998, 42, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.Z.; Santosh, M.; Jahn, B.M. Evolution of the Asian continent and its continental margins. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 47, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Z.; Santosh, M.; Zhao, G.C.; Zhang, G.W.; Jin, C. Intracontinental deformation in a frontier of super-convergence: A perspective on the tectonic milieu of the South China Block. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 49, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, M.J.; Menier, D.; Siddiqui, N.; Kumar, S.G.; Authemayou, C. Active tectonic deformation along rejuvenated faults in tropical Borneo: Inferences obtained from tectonic-geomorphic evaluation. Geomorphology 2016, 267, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.C.; Li, S.Z.; Guo, L.L.; Jiang, S.H.; Somerville, I.D.; Zhao, S.J.; Zhu, B.D.; Chen, J.; Dai, L.M.; Suo, Y.H.; et al. Mesozoic and Cenozoic accretionary orogenic processes in Borneo and their mechanisms. Geol. J. 2016, 51, 464–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, S.; Wang, X.; Lindsey, E.O.; Tongkul, F.; Tapponnier, P.; Bradley, K.; Chan, C.; Hill, E.M.; Sieh, K. The 2015 M W 6.0 Mt. Kinabalu Earthquake: An Infrequent Fault Rupture within the Crocker Fault System of East Malaysia. Geosci. Lett. 2017, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebby, S.; Tansey, K. Advances in Lithological and Structural Mapping Using Earth Observation Data. Geosciences. 2017. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/geosciences/special_issues/Lithologica-Structural-Mapping (accessed on 4 May 2017).
- Hall, R.; Breitfeld, T.H. Nature and demise of the Proto-South China Sea. Bull. Geol. Soc. Malays. 2017, 63, 61–76. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, A.A. Understanding the recent Sabah Earthquake, and other seismogenic sources in North West Borneo. Sci. Malays. 2016, 12, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, A.A.; Malik, J.N. Four major unknown active faults identified, using satellite data, in India and Pakistan portions of NW Himalaya. Nat. Hazards 2017, 88, 845–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapponnier, P.; Molnar, P. Active faulting and tectonics in China. J. Geophys. Res. 1977, 82, 2905–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, T. Active faults of the Himalaya of India and Nepal. Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Publ. 1989, 232, 243–264. [Google Scholar]
- Sieh, K.; Natawidjaja, D. Neotectonics of the Sumatran fault, Indonesia. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 28295–28326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, J.N.; Nakata, T. Active faults and related Late Quaternary deformation along the northwestern Himalayan Frontal Zone. India Annu. Geophys. 2003, 46, 917–936. [Google Scholar]
- Shyu, J.B.H.; Sieh, K.; Chen, G.; Liu, C.S. Neotectonic architecture of Taiwan and its implications for future large earthquakes. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2005, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.; Yin, A. Active structures of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen and their relationships to earthquake distribution, contemporary strain field, and Cenozoic volcanism. Geosphere 2009, 5, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A. Earthquake geology of the Kashmir Basin and its implication for large earthquakes. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2013, 102, 1957–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, J.N.; Shah, A.A.; Naik, S.P.; Sahoo, S.; Okumura, K.; Patra, N.R. Active fault study along foothill zone of Kumaun Sub-Himalaya: Influence on landscape shaping and drainage evolution. Curr. Sci. 2014, 106, 229–236. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison, C.S. The ‘Rajang Accretionary Prism’ and ‘Lupar Line’ problem of Borneo. In Tectonic Evolution of Southeast Asia; Hall, R., Blundell, D.J., Eds.; Geological Society of London Special Publication: London, UK, 1996; Volume 106, pp. 247–261. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison, C.S. Geology of North-West Borneo; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; p. 421. [Google Scholar]
- Cullen, A. Transverse segmentation of the Baram-Balabac Basin, NW Borneo: Refining the model of Borneo’s tectonic evolution. Pet. Geosci. 2010, 16, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, W. Tectonics of the Indonesian Region; Professional Paper; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1979; Volume 345, pp. 1–23.
- Sapin, F.; Pubellier, M.; Lahfid, A.; Janots, D.; Ringenbach, J.C. Onshore record of the subduction of a crustal salient: Example of the NW Borneo Wedge. Terra Nova 2012, 23, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R. Cenozoic geological and plate tectonic evolution of SE Asia and the SW Pacific: Computer-based reconstructions, model and animations. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2002, 20, 353–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, M.; Ali, J.R.; Moss, S.J.; Frost, G.M.; Richter, B.; Mahfi, A. Paleomagnetism of Borneo. J. Asian Earth Sci. 1999, 17, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omang, S.A.; Barber, A.J. Origin and tectonic significance of the metamorphic rocks associated with the Darvel Bay Ophiolite, Sabah, Malaysia. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 1996, 106, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocco, G.; Mendoza, M.; Velázquez, A. Remote sensing and GIS-based regional geomorphological mapping—A tool for land use planning in developing countries. Geomorphology 2001, 39, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, C.; Delacourt, C.; Allemand, P.; Ledru, P.; Wackerle, R. Using ASTER remote sensing data set for geological mapping, in Namibia. Phys. Chem. Earth 2005, 30, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. Application of logistic regression model and its validation for landslide susceptibility mapping using GIS and remote sensing data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 1477–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R. Flood hazard assessment of 2014 floods in Sonawari sub-district of Bandipore district (Jammu & Kashmir): An application of geoinformatics. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2016, 4, 188–203. [Google Scholar]
- Yeats, R.S.; Sieh, K.; Allen, C.R. The Geology of Earthquakes; Oxford University Press: Beijing, China, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Schumm, S.A. Alluvial river response to active tectonics. In Active Tectonics: Impact on Society; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1986; pp. 80–95. [Google Scholar]
- Burbank, D.W.; Anderson, R.S. Tectonic Geomorphology; Blackwell Science: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001; p. 274. [Google Scholar]
- Marrett, R.A.; Allmendinger, R.W. Kinematic analysis of fault-slip data. J. Struct. Geol. 1990, 12, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benker, S.C.; Langford, R.P.; Pavlis, T.L. Positional accuracy of the Google Earth terrain model derived from stratigraphic unconformities in the Big Bend region, Texas, USA. Geocarto Int. 2011, 26, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potere, D. Horizontal position accuracy of Google Earth’s high-resolution imagery archive. Sensors 2008, 8, 7973–7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, D. The web-wide world. Nature 2006, 439, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, S. Response of alluvial rivers to slow active tectonic movement. Geol. Soc. Am. 1985, 96, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, E.A.; Pinter, N. Active Tectonics: Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999; p. 338. [Google Scholar]
- Replumaz, A.; Tapponnier, P. Reconstruction of the deformed collision zone between India and Asia by backward motion of lithospheric blocks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapponnier, P.; Peltzer, G.; Le Dain, A.Y.; Armijo, R.; Cobbold, P. Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia: New insights from simple experiments with plasticine. Geology 1982, 10, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandal, S.T. The Geology and Hydrocarbon Resources of Negara Brunei Darussalam; Brunei Shell Petroleum: Bandar Seri Begawan, Brunei, 1996; p. 243. [Google Scholar]
- Hesse, S.; Back, S.; Franke, D. The deep-water fold-and-thrust belt offshore NW Borneo: Gravity-driven versus basement-driven shortening. Bull. Geol. Soc. Amst. 2009, 121, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapin, F.; Hermawan, I.; Pubellier, M.; Vigny, C.; Ringenbach, J.C. The recent convergence on the NW Borneo Wedge—A crustal-scale gravity gliding evidenced from GPS. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 193, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottam, M.A.; Hall, R.; Sperber, C.; Kohn, B.P.; Forster, M.A.; Batt, G.E. Neogene rock uplift and erosion in northern Borneo: Evidence from the Kinabalu granite, Mount Kinabalu. J. Geol. Soc. 2013, 170, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongkul, F. Active tectonics in Sabah-seismicity and active faults. Bull. Geol. Soc. Malays. 2017, 64, 27–36. [Google Scholar]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shah, A.A.; Zhafri, M.N.; Delson, J.; Navakanesh, B. Major Strike-Slip Faults Identified Using Satellite Data in Central Borneo, SE Asia. Geosciences 2018, 8, 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8050156
Shah AA, Zhafri MN, Delson J, Navakanesh B. Major Strike-Slip Faults Identified Using Satellite Data in Central Borneo, SE Asia. Geosciences. 2018; 8(5):156. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8050156
Chicago/Turabian StyleShah, Afroz Ahmad, Mohd Noor Zhafri, Jumat Delson, and Batmanathan Navakanesh. 2018. "Major Strike-Slip Faults Identified Using Satellite Data in Central Borneo, SE Asia" Geosciences 8, no. 5: 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8050156
APA StyleShah, A. A., Zhafri, M. N., Delson, J., & Navakanesh, B. (2018). Major Strike-Slip Faults Identified Using Satellite Data in Central Borneo, SE Asia. Geosciences, 8(5), 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8050156




