Forecasting Environmental Drivers and Invasion Risk of Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) and Pterois miles (Bennett, 1828) in the Pagasitikos Gulf (Greece)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
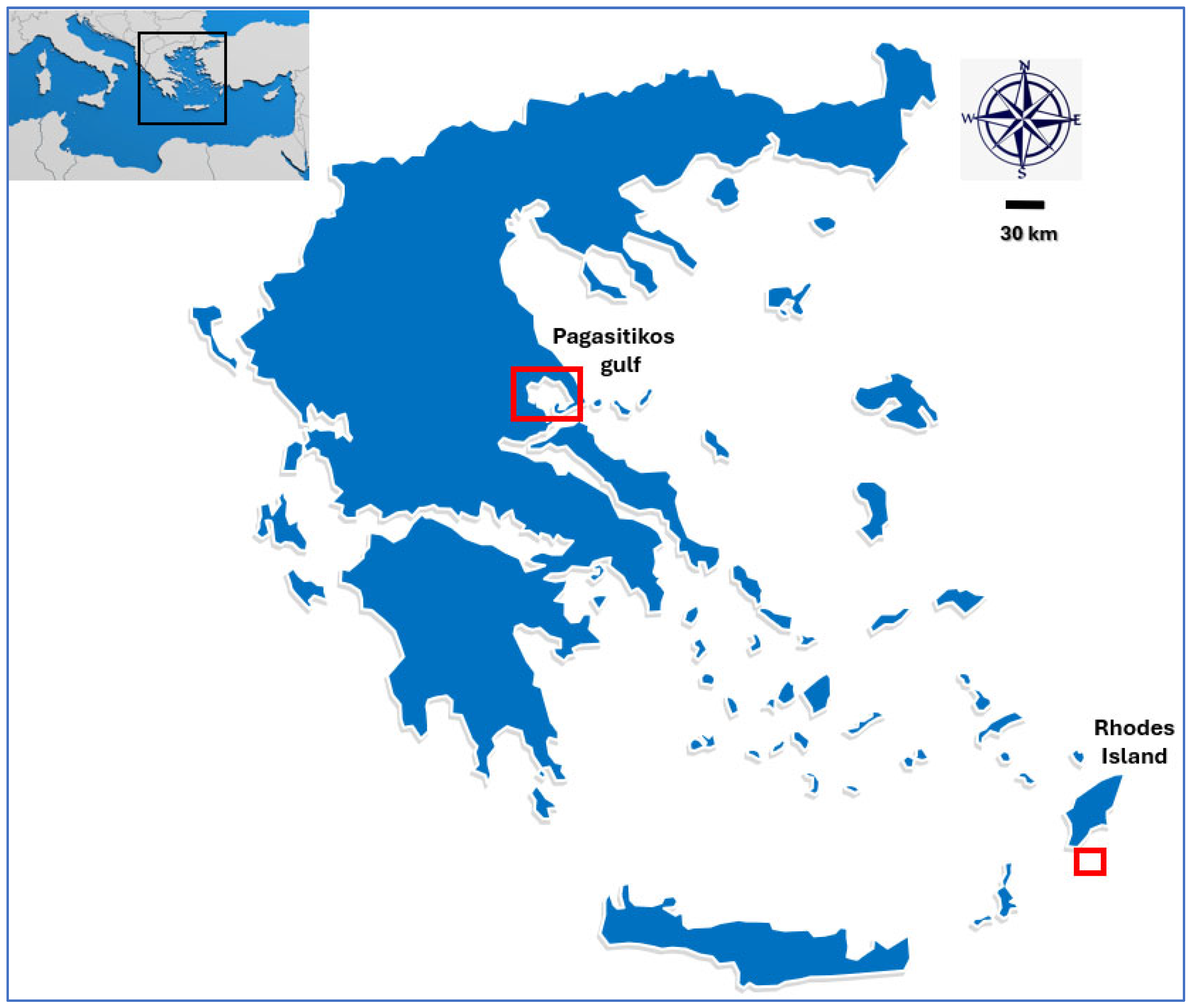
2.1. Data Acquisition and Study Area
2.2. Statistical Analysis
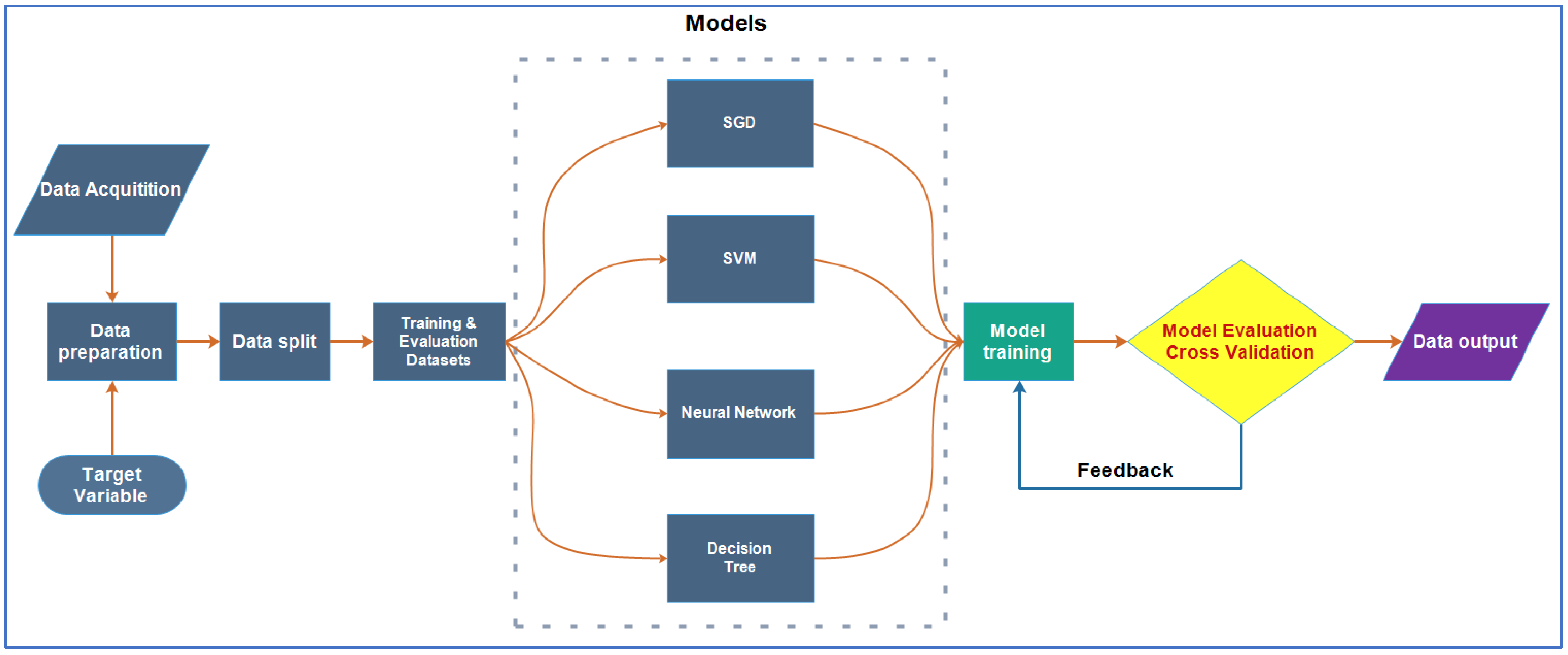
2.3. Machine Learning
2.4. Description of ML Algorithms
2.5. Assessment of Model Performance
2.5.1. Area Under the Receiver-Operating Characteristic Curve (AUC)
2.5.2. Classification Accuracy (CA)
2.5.3. F1 Score
2.5.4. Precision
2.5.5. Recall
2.5.6. Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC)
2.6. Environmental Drivers and Thresholds for Species Establishment in South Aegean
2.7. Environmental Drivers and Thresholds for Species Establishment in the Pagasitikos Gulf
2.8. Forecast of Environmental Parameters at the Pagasitikos Gulf
2.9. Evaluation of Species Establishment Potential in the Pagasitikos Gulf
3. Results
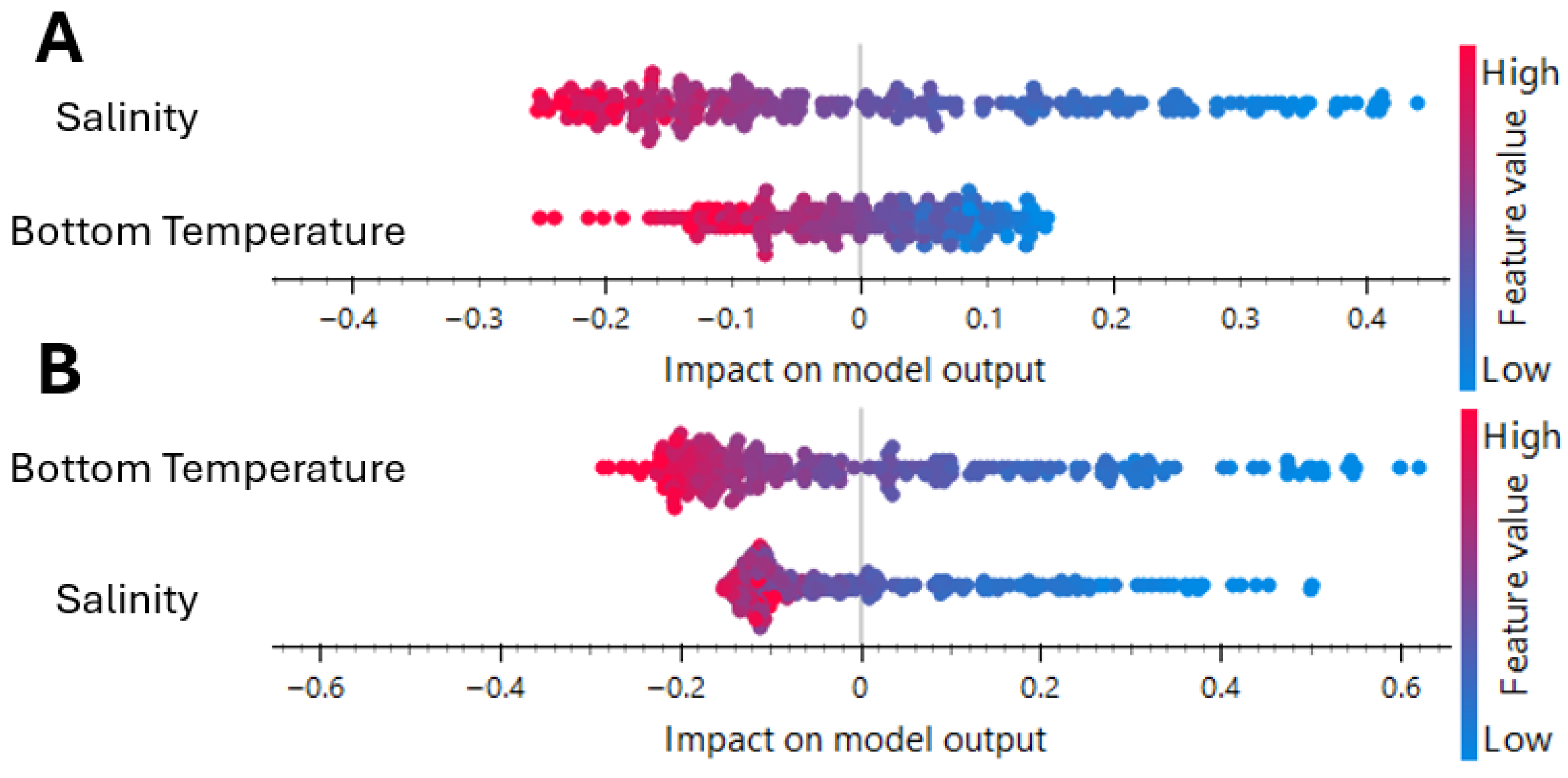
3.1. Factors Affecting Species Establishment
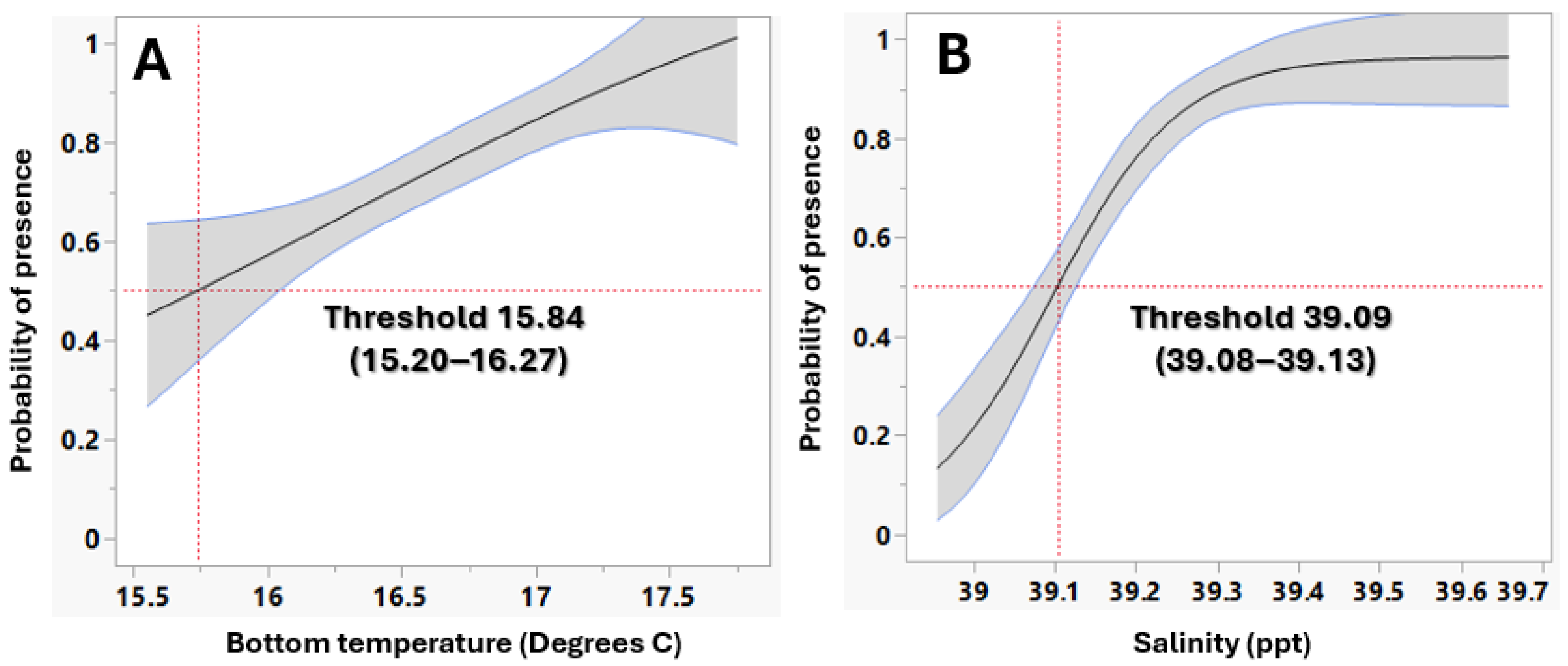
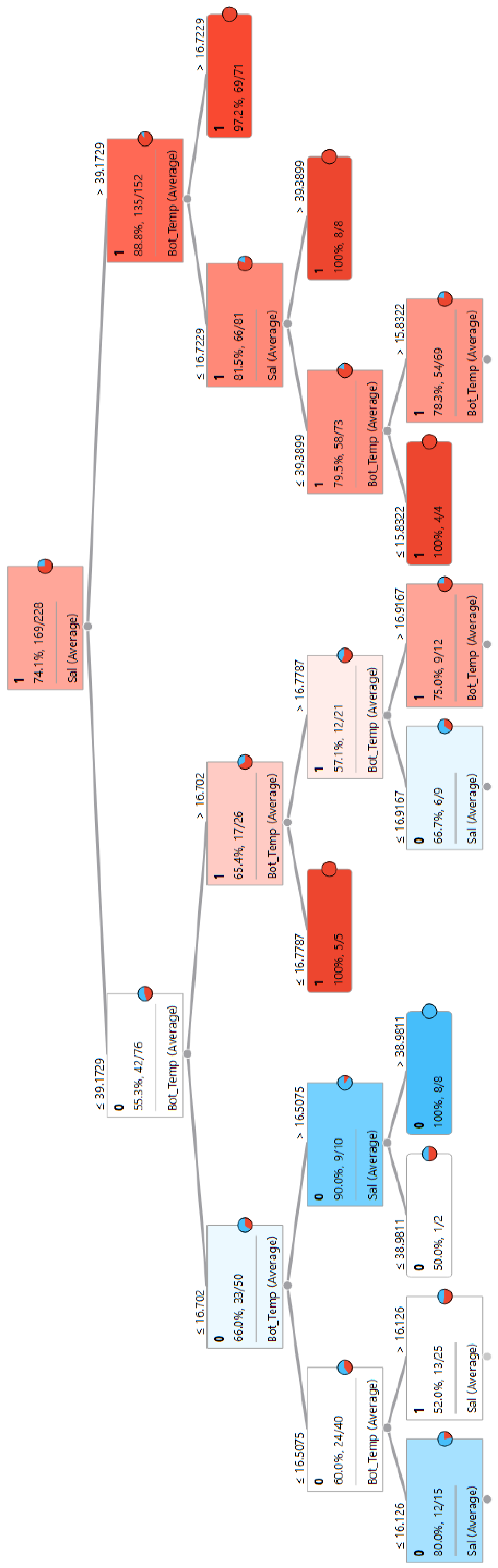
3.1.1. L. sceleratus Establishment in Rhodes
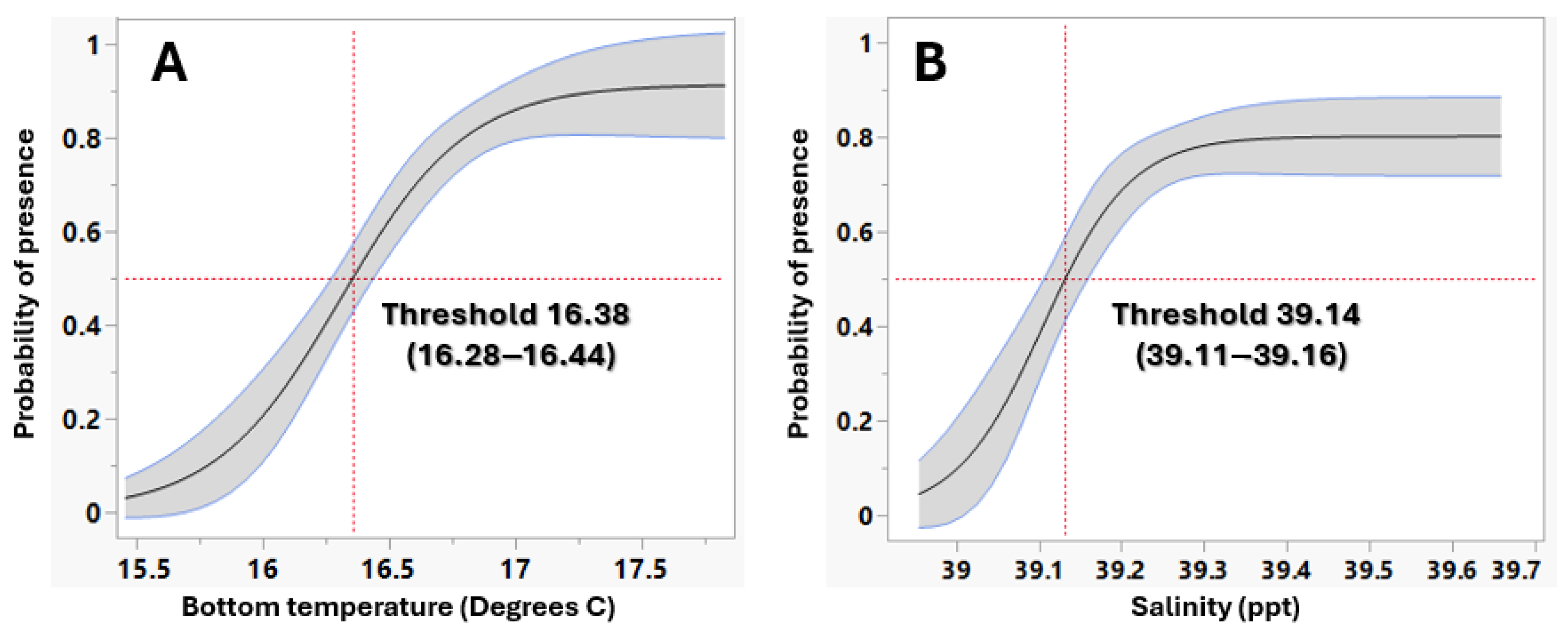
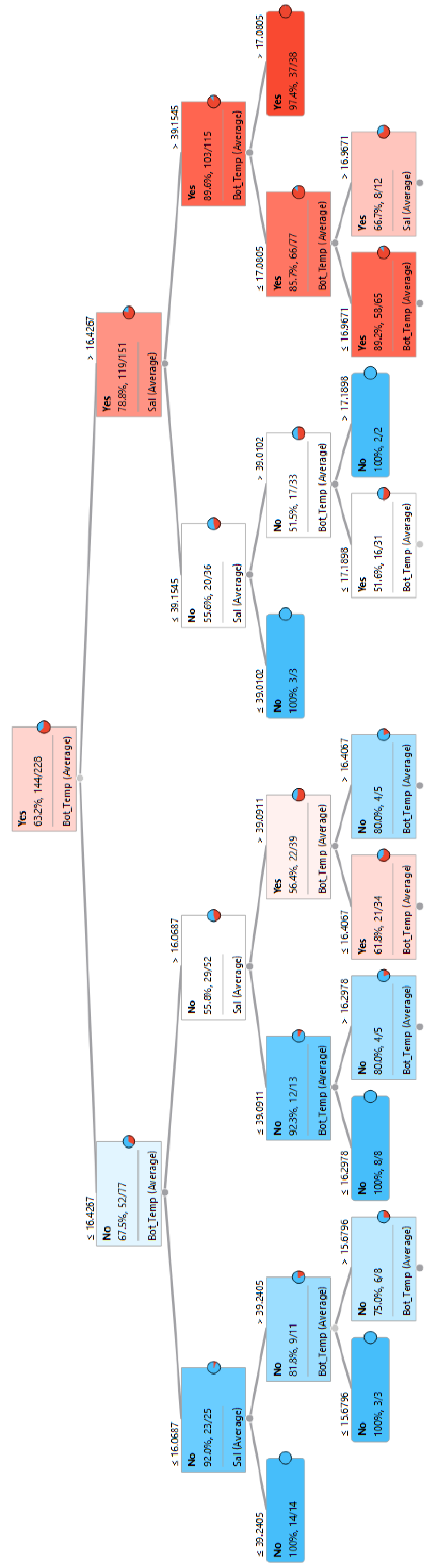
3.1.2. P. miles Establishment in Rhodes
3.2. ML Model Configuration and Performance for Each Species’ Establishment
3.3. Identification of Key Environmental Parameters and Threshold Values for the Pagasitikos Gulf Establishment
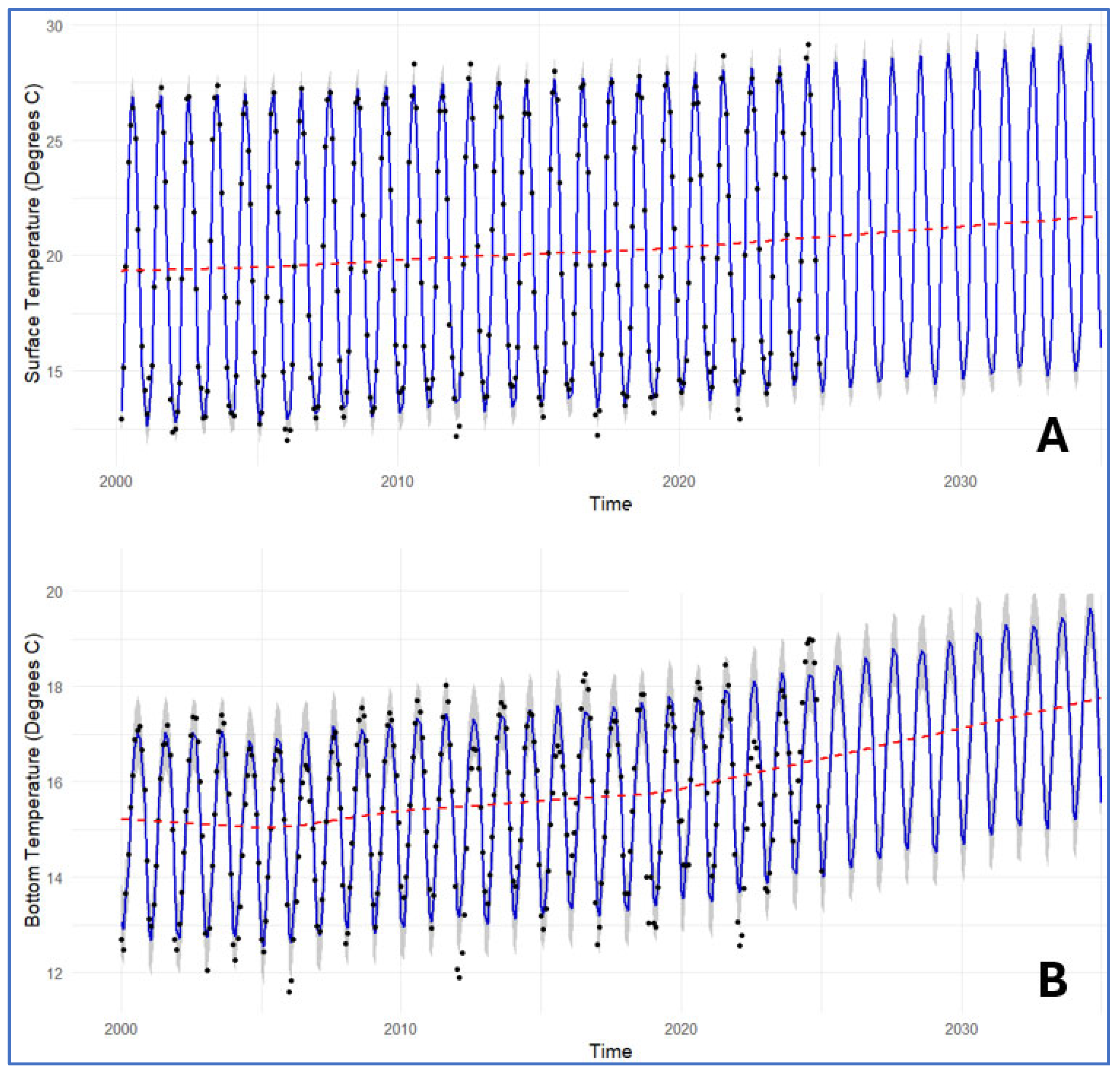
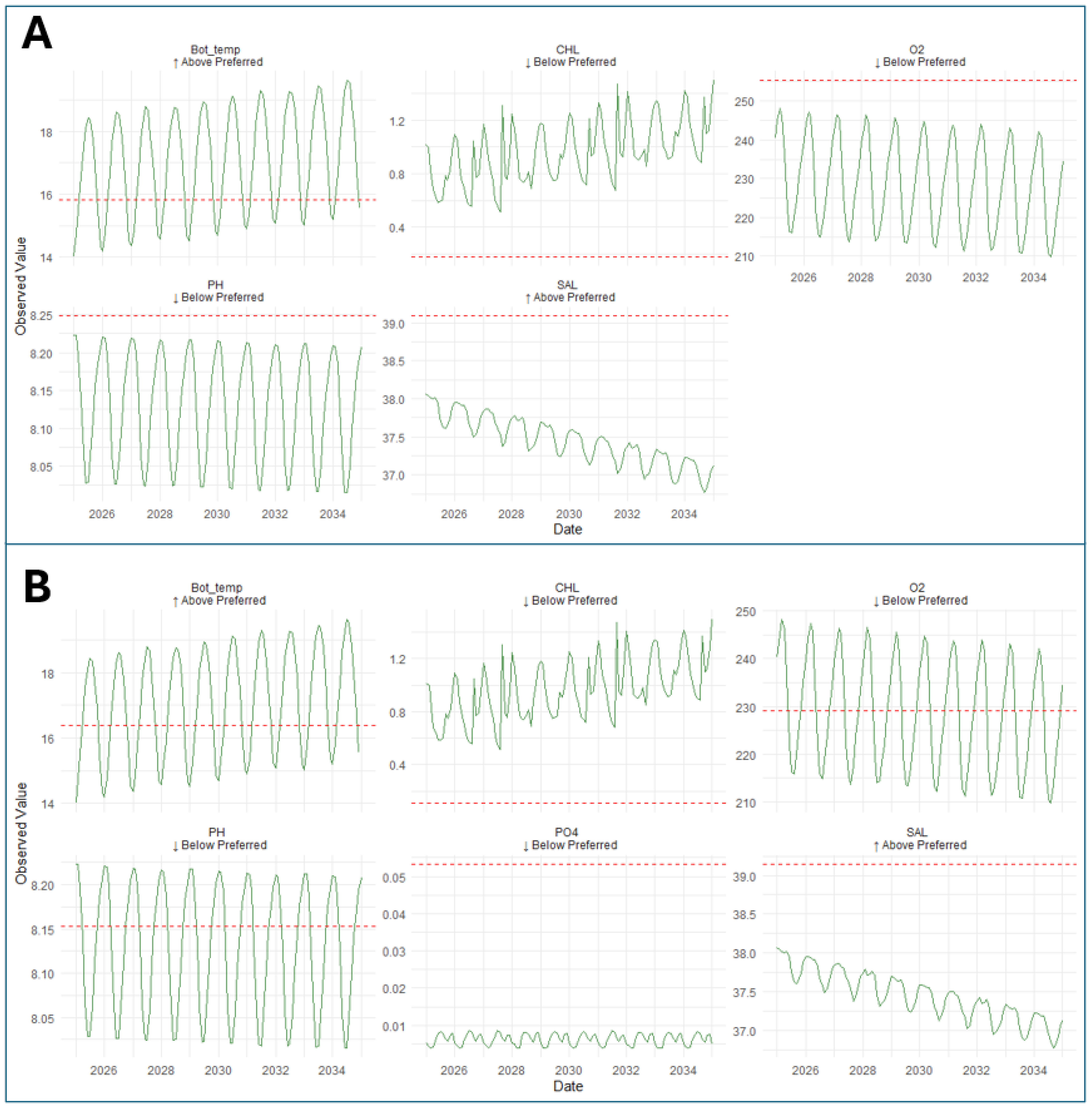
3.4. Forecast of Environmental Parameters at the Pagasitikos Gulf
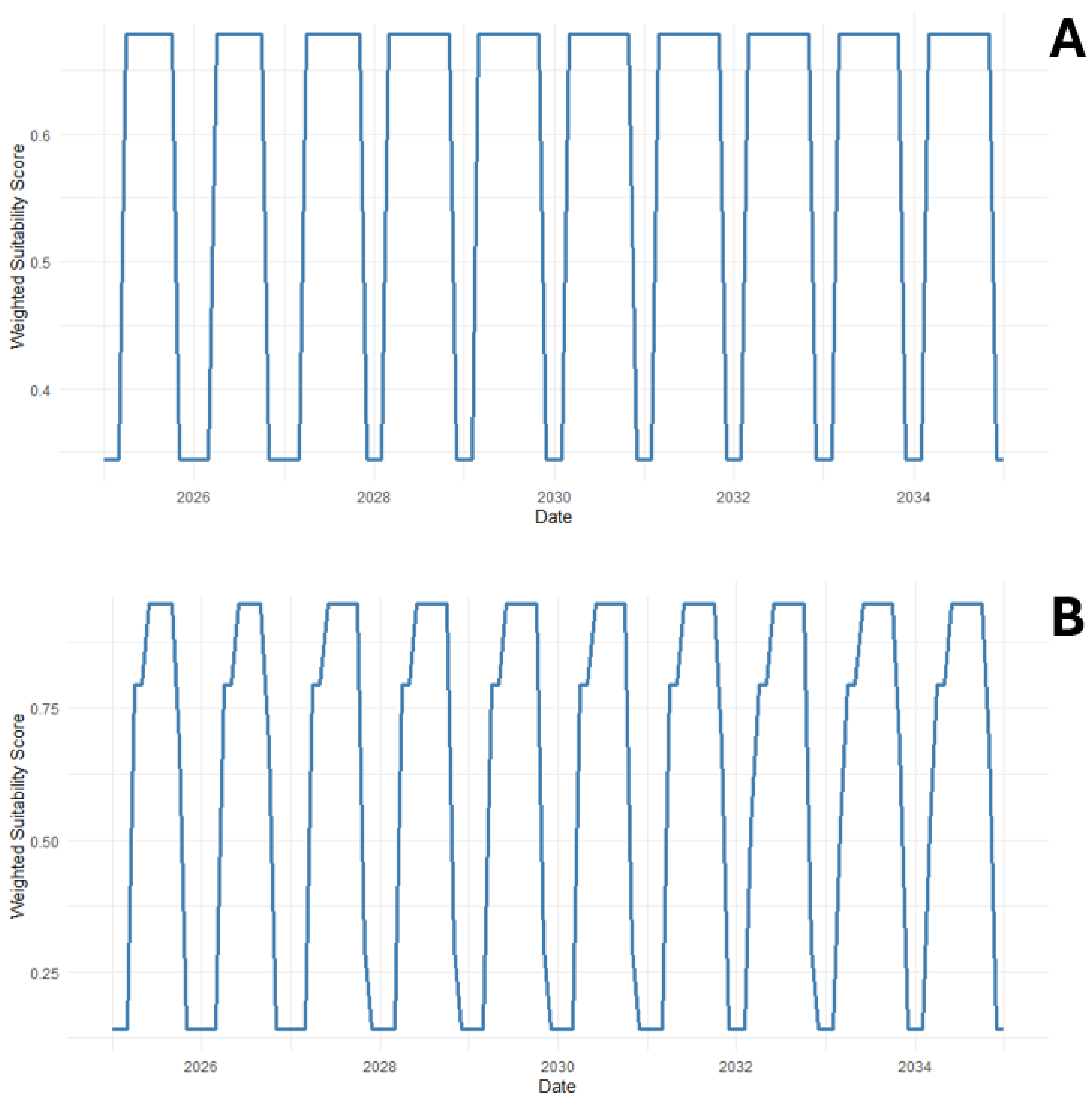
3.5. Evaluation of Species Establishment Potential in the Pagasitikos Gulf
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costello, M.J.; Coll, M.; Danovaro, R.; Halpin, P.; Ojaveer, H.; Miloslavich, P. A Census of Marine Biodiversity Knowledge, Resources, and Future Challenges. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rilov, G.; Galil, B. Marine Bioinvasions in the Mediterranean Sea—History, Distribution and Ecology. In Biological Invasions in Marine Ecosystems; Rilov, G., Crooks, J.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 204, pp. 549–575. ISBN 978-3-540-79236-9. [Google Scholar]
- Galil, B.S. Alien Species in the Mediterranean Sea—Which, When, Where, Why? Hydrobiologia 2008, 606, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenetos, A.; Gofas, S.; Morri, C.; Rosso, A.; Violanti, D.; Garcia Raso, J.E.; Cinar, M.E.; Almogi-Labin, A.; Ates, A.S.; Azzurro, E.; et al. Alien Species in the Mediterranean Sea by 2012. A Contribution to the Application of European Union’s Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). Part 2. Introduction Trends and Pathways. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2012, 13, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelist, D.; Rilov, G.; Golani, D.; Carlton, J.T.; Spanier, E. Restructuring the S Ea: Profound Shifts in the World’s Most Invaded Marine Ecosystem. Divers. Distrib. 2013, 19, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavruk, S.; Avsar, D. Non-Native Fishes in the Mediterranean from the Red Sea, by Way of the Suez Canal. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2008, 18, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, I.M.; Smith, N.S. The Lionfish Pterois Sp. Invasion: Has the Worst-case Scenario Come to Pass? J. Fish Biol. 2018, 92, 660–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streftaris, N.; Zenetos, A. Alien Marine Species in the Mediterranean-the 100 ‘Worst Invasives’ and Their Impact. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2006, 7, 87–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, I.M.; Green, S.J.; Hixon, M.A. Predatory Fish Invaders: Insights from Indo-Pacific Lionfish in the Western Atlantic and Caribbean. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 164, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondylatos, G.; Theocharis, A.; Mandalakis, M.; Avgoustinaki, M.; Karagyaurova, T.; Koulocheri, Z.; Vardali, S.; Klaoudatos, D. The Devil Firefish Pterois miles (Bennett, 1828): Life History Traits of a Potential Fishing Resource in Rhodes (Eastern Mediterranean). Hydrobiology 2024, 3, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, P.G.; Frazer, T.K.; Jacoby, C.A.; Yanong, R.P.E. Reproductive Biology of Invasive Lionfish (Pterois spp.). Front. Mar. Sci. 2015, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerson, L.A.; Mooney, H.A. Invasive Alien Species in an Era of Globalization. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2007, 5, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebens, H.; Gastner, M.T.; Blasius, B. The Risk of Marine Bioinvasion Caused by Global Shipping. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, A.; Larrinaga, A.R.; Neto, J.M.; Troncoso, J.; Méndez, G.; Domínguez-Lapido, P.; Ovejero, A.; Pereira, L.; Mouga, T.M.; Gaspar, R.; et al. Spotting Intruders: Species Distribution Models for Managing Invasive Intertidal Macroalgae. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 281, 111861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, K.E.; Lynch, S.A.; McAllen, R.; O’Riordan, R.M.; Culloty, S.C. Assessing the Potential for Invasive Species Introductions and Secondary Spread Using Vessel Movements in Maritime Ports. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 177, 113496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainka, S.A.; Howard, G.W. Climate Change and Invasive Species: Double Jeopardy. Integr. Zool. 2010, 5, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.; King, N.G.; Wilmes, S.B.; Moore, P.J. Summer and Winter Marine Heatwaves Favor an Invasive Over Native Seaweeds. J. Phycol. 2020, 56, 1591–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzurro, E.; Smeraldo, S.; D’Amen, M. Spatio-temporal Dynamics of Exotic Fish Species in the Mediterranean Sea: Over a Century of Invasion Reconstructed. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 6268–6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowicz, J.J.; Terwin, J.R.; Whitlatch, R.B.; Osman, R.W. Linking Climate Change and Biological Invasions: Ocean Warming Facilitates Nonindigenous Species Invasions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15497–15500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorte, C.J.B.; Williams, S.L.; Zerebecki, R.A. Ocean Warming Increases Threat of Invasive Species in a Marine Fouling Community. Ecology 2010, 91, 2198–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kletou, D.; Hall-Spencer, J.M.; Kleitou, P. A Lionfish (Pterois miles) Invasion Has Begun in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2016, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, F.; Valiente, J.A.; Khodayar, S. A Warming Mediterranean: 38 Years of Increasing Sea Surface Temperature. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, S.; Martínez, B.D.-C.; Olabarria, C. Predicting Habitat Suitability for Alien Macroalgae in Relation to Thermal Niche Occupancy. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 208, 116953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogirou, S.; Wennhage, H.; Pihl, L. Non-Indigenous Species in Mediterranean Fish Assemblages: Contrasting Feeding Guilds of Posidonia Oceanica Meadows and Sandy Habitats. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 96, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondylatos, G.; Kallias, I.; Vafidis, D.; Exadactylos, A.; Theocharis, A.; Mavrouleas, D.; Kalaentzis, K.; Avgoustinaki, M.; Conides, A.; Klaoudatos, D. The Length-Weight Relationship of Indigenous and Non-Indigenous Fish Species from the Small-Scale Fisheries of Rhodes Greece. Int. Aquat. Res. 2024, 16, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, E.; Dominguez Almela, V. Modelling the Rise of Invasive Lionfish in the Mediterranean. Mar. Biol. 2025, 172, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coro, G.; Vilas, L.G.; Magliozzi, C.; Ellenbroek, A.; Scarponi, P.; Pagano, P. Forecasting the Ongoing Invasion of Lagocephalus sceleratus in the Mediterranean Sea. Ecol. Modell. 2018, 371, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyol, O.; Ünal, V.; Ceyhan, T.; Bilecenoglu, M. First Confirmed Record of Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) in the Mediterranean Sea. J. Fish Biol. 2005, 66, 1183–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsini, M.; Margies, P.; Kondilatos, G.; Economidis, P.S. Three New Exotic Fish Records from the SE Aegean Greek Waters. Sci. Mar. 2006, 70, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, S.; Corsini-Foka, M.; Sioulas, A.; Wennhage, H.; Pihl, L. Diversity, Structure and Function of Fish Assemblages Associated with Posidonia oceanica Beds in an Area of the Eastern Mediterranean Sea and the Role of Non-indigenous Species. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 77, 2338–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinar, M.E.; Bilecenoglu, M.; Ozturk, Β.; Katagan, Τ.; Yokes, Μ.Β.; Aysel, V.; Dagli, E.; Acik, S.; Ozcan, T.; Erdogan, H. An Updated Review of Alien Species on the Coasts of Turkey. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2011, 12, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilecenoğlu, M.; Öztürk, B. Possible Intrusion of Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) to the Turkish Black Sea Coast. J. Black Sea/Mediterr. Environ. 2018, 24, 272–276. [Google Scholar]
- Azzurro, E.; Bariche, M. The Long Reach of the Suez Canal: Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) an Unwanted Indo-Pacific Pest at the Atlantic Gate. BioInvasions Rec. 2020, 9, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosker, A.R.; Özogul, F.; Durmus, M.; Ucar, Y.; Ayas, D.; Regenstein, J.M.; Özogul, Y. Tetrodotoxin Levels in Pufferfish (Lagocephalus sceleratus) Caught in the Northeastern Mediterranean Sea. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünal, V.; Bodur, H.G. The Socio-Economic Impacts of the Silver-Cheeked Toadfish on Small-Scale Fishers: A Comparative Study from the Turkish Coast. Su Ürünleri Derg. 2017, 34, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katikou, P.; Georgantelis, D.; Sinouris, N.; Petsi, A.; Fotaras, T. First Report on Toxicity Assessment of the Lessepsian Migrant Pufferfish Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) from European Waters (Aegean Sea, Greece). Toxicon 2009, 54, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogirou, S. Ecological Characteristics of the Invasive Pufferfish Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea—A Case Study from Rhodes. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2013, 14, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golani, D.; Sonin, O. New Records of the Red Sea Fishes, Pterois miles (Scorpaenidae) and Pteragogus pelycus (Labridae) from the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Jpn. J. Ichthyol. 1992, 39, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, A.C.; Chartosia, N.; Hall-Spencer, J.M.; Kleitou, P.; Jimenez, C.; Antoniou, C.; Hadjioannou, L.; Kletou, D.; Sfenthourakis, S. Genetic Data Suggest Multiple Introductions of the Lionfish (Pterois miles) into the Mediterranean Sea. Diversity 2019, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, M.E.; Miller, J.M.; Whitfield, P.E.; Hare, J.A. Thermal Tolerance and Potential Distribution of Invasive Lionfish (Pterois volitans/miles Complex) on the East Coast of the United States. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 283, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, B.D.; Horodysky, A.Z.; Kerstetter, D.W. Hot or Not? Comparative Behavioral Thermoregulation, Critical Temperature Regimes, and Thermal Tolerances of the Invasive Lionfish Pterois Sp. versus Native Western North Atlantic Reef Fishes. Biol. Invasions 2018, 20, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.A.; Whitfield, P.E. Biology, Ecology, Control and Management of the Invasive Indo-Pacific Lionfish: An Updated Integrated Assessment. NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS NCCOS 99; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Peake, J.; Bogdanoff, A.K.; Layman, C.A.; Castillo, B.; Reale-Munroe, K.; Chapman, J.; Dahl, K.; Patterson Iii, W.F.; Eddy, C.; Ellis, R.D.; et al. Feeding Ecology of Invasive Lionfish (Pterois volitans and Pterois miles) in the Temperate and Tropical Western Atlantic. Biol. Invasions 2018, 20, 2567–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koilakos, S.M.; Georgatis, I.; Leonardos, I. Feeding Strategies and Biological Traits of the Lessepsian Migrant Pterois miles (Bennett, 1828) in the Messenian Gulf, SW Greece. Fishes 2024, 9, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondylatos, G.; Vagenas, G.; Kalaentzis, K.; Mavrouleas, D.; Conides, A.; Karachle, P.K.; Corsini-Foka, M.; Klaoudatos, D. Exploring the Structure of Static Net Fisheries in a Highly Invaded Region: The Case of Rhodes Island (Eastern Mediterranean). Sustainability 2023, 15, 14976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisan, A.; Petitpierre, B.; Broennimann, O.; Daehler, C.; Kueffer, C. Unifying Niche Shift Studies: Insights from Biological Invasions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherst, R.W. Climate Change and Invasive Species: A Conceptual Framework. In Invasive Species in a Changing World; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; pp. 211–240. [Google Scholar]
- Jeschke, J.M.; Strayer, D.L. Usefulness of Bioclimatic Models for Studying Climate Change and Invasive Species. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1134, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Thuiller, W.; Miaud, C. Prediction and Validation of the Potential Global Distribution of a Problematic Alien Invasive Species—The American Bullfrog. Divers. Distrib. 2007, 13, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidegain, G.; Bárcena, J.F.; García, A.; Juanes, J.A. Predicting Coexistence and Predominance Patterns between the Introduced Manila Clam (Ruditapes philippinarum) and the European Native Clam (Ruditapes decussatus). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 152, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, A.T.; Robins, C.R. Using Ecological-Niche Modeling to Predict Barred Owl Invasions with Implications for Spotted Owl Conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2003, 17, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellin, C.; Lurgi, M.; Matthews, S.; MacNeil, M.A.; Caley, M.J.; Bax, N.; Przeslawski, R.; Fordham, D.A. Forecasting Marine Invasions under Climate Change: Biotic Interactions and Demographic Processes Matter. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 204, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos-Júnior, L.A.; Barbosa, N.P.U.; Moulton, T.P.; Creed, J.C. Ecological Niche Model Used to Examine the Distribution of an Invasive, Non-Indigenous Coral. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 103, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Huang, Y.; Fang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Chang, J. Non-Native Species in Marine Protected Areas: Global Distribution Patterns. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2024, 22, 100453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, C. Species Distribution Modelling of Invasive Alien Species; Pterois miles for Current Distribution and Future Suitable Habitats. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2020, 6, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, C.; Galanidi, M.; Zenetos, A.; Corsini-Foka, M.; Giovos, I.; Karachle, P.K.; Fournari–Konstantinidou, I.; Kytinou, E.; Issaris, Y.; Azzurro, E. Updating the Occurrences of Pterois miles in the Mediterranean Sea, with Considerations on Thermal Boundaries and Future Range Expansion. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2020, 21, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marine|Copernicus. Available online: https://www.copernicus.eu/en/copernicus-services/marine (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Escudier, R.; Clementi, E.; Omar, M.; Cipollone, A.; Pistoia, J.; Aydogdu, A.; Drudi, M.; Grandi, A.; Lyubartsev, V.; Lecci, R.; et al. Mediterranean Sea Physical Reanalysis (CMEMS MED-Currents) (Version 1) [Data Set]; Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service: Toulouse, France, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudier, R.; Clementi, E.; Cipollone, A.; Pistoia, J.; Drudi, M.; Grandi, A.; Lyubartsev, V.; Lecci, R.; Aydogdu, A.; Delrosso, D. A High Resolution Reanalysis for the Mediterranean Sea. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 702285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, T.; Escudier, R.; Pistoia, J.; Aydogdu, A.; Omar, M.; Clementi, E.; Cipollone, A.; Drudi, M.; Grandi, A.; Mariani, A.; et al. Mediterranean Sea Physical Reanalysis INTERIM (CMEMS MED-Currents, E3R1i System) (Version 1) [Data Set]; Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service: Toulouse, France, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudier, R.; Clementi, E.; Nigam, T.; Pistoia, J.; Grandi, A.; Aydogdu, A.; Miraglio, P. Synthesis Quality Overview Document (SQO) for Mediterranean Sea Physics Reanalysis; Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service: Toulouse, France, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Teruzzi, A.; Di Biagio, V.; Feudale, L.; Bolzon, G.; Lazzari, P.; Salon, S.; Coidessa, G.; Cossarini, G. Mediterranean Sea Biogeochemical Reanalysis (CMEMS MED-Biogeochemistry, MedBFM3 System) (Version 1) [Data Set]; Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service: Toulouse, France, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossarini, G.; Feudale, L.; Teruzzi, A.; Bolzon, G.; Coidessa, G.; Solidoro, C.; Di Biagio, V.; Amadio, C.; Lazzari, P.; Brosich, A. High-Resolution Reanalysis of the Mediterranean Sea Biogeochemistry (1999–2019). Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 741486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecci, Ρ.; Drudi, Μ.; Grandi, A.; Clementi, Ε. Product User Manual for Mediterranean Sea Physical Reanalysis Product, EU Copernicus Marine Service—Public Ref: CMEMS-MED-PUM-006-004; Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service: Toulouse, France, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Teruzzi, A.; Di Biagio, V.; Feudale, L.; Bolzon, G.; Lazzari, P.; Salon, S.; Coidessa, G.; Cossarini, G. Quality Information Document for MED MFC Products MEDSEA_MULTIYEAR_BGC_006_008, Ref: CMEMS-MED-QUID-006-008, Issue 3.2; Copernicus Marine Service: Toulouse, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Volpe, G.; Colella, S.; Brando, V.E.; Forneris, V.; La Padula, F.; Di Cicco, A.; Sammartino, M.; Bracaglia, M.; Artuso, F.; Santoleri, R. Mediterranean Ocean Colour Level 3 Operational Multi-Sensor Processing. Ocean Sci. 2019, 15, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthon, J.-F.; Zibordi, G. Bio-Optical Relationships for the Northern Adriatic Sea. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colella, S.; Böhm, E.; Cesarini, C.; Jutard, Q.; VE, B. Product User Manual for Ocean Colour Products, EU Copernicus Marine Service—Public Ref: CMEMS-OC-PUM-5.0; Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service: Toulouse, France, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- NASA Ocean Biology Processing Group. Sea-viewing Wide Field-of-view Sensor (SeaWiFS) Level-2 Ocean Color Data, version R2018.8; NASA Ocean Biology Distributed Active Archive Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA Ocean Color. Available online: https://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov/resources/atbd/sst/ (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- QGIS Development Team. QGIS Geographic Information System (Version 3.44.2) [Computer software]. Open Source Geospatial Foundation. 2025. Available online: https://www.qgis.org (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Şahin, M.; Aybek, E. Jamovi: An Easy to Use Statistical Software for the Social Scientists. Int. J. Assess. Tools Educ. 2019, 6, 670–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, R.E.; Havel, J.E. Introductory Biological Statistics; Waveland Press: Long Grove, IL, USA, 2006; ISBN 1577663802. [Google Scholar]
- Figard, S. Introduction to Biostatistics with JMP; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2019; ISBN 1635267188. [Google Scholar]
- Sall, J.; Stephens, M.L.; Lehman, A.; Loring, S. JMP Start Statistics: A Guide to Statistics and Data Analysis Using JMP; Sas Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2017; ISBN 1629608785. [Google Scholar]
- Gareth, J.; Witten, D.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. An Introduction to Statistical Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 112. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.-J.; Yang, M.; Ren, Z.J. Machine Learning in Environmental Research: Common Pitfalls and Best Practices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 17671–17689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demšar, J.; Curk, T.; Erjavec, A.; Gorup, Č.; Hočevar, T.; Milutinovič, M.; Možina, M.; Polajnar, M.; Toplak, M.; Starič, A. Orange: Data Mining Toolbox in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2013, 14, 2349–2353. [Google Scholar]
- Ruder, S. An Overview of Gradient Descent Optimization Algorithms. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.04747. [Google Scholar]
- Bottou, L. Stochastic Gradient Descent Tricks. In Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 421–436. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, W.S. What Is a Support Vector Machine? Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1565–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisner, D.A.; Schnyer, D.M. Chapter 6—Support Vector Machine. In Machine Learning: Methods and Applications to Brain Disorders; Mechelli, A., Vieira, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 101–121. ISBN 978-0-12-815739-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wallisch, P.; Lusignan, M.E.; Benayoun, M.D.; Baker, T.I.; Dickey, A.S.; Hatsopoulos, N.G. Chapter 36—Neural Networks Part I: Unsupervised Learning. In MATLAB for Neuroscientists: An Introduction to Scientific Computing in MATLAB, 2nd ed.; Wallisch, P., Lusignan, M.E., Benayoun, M.D., Baker, T.I., Dickey, A.S., Hatsopoulos, N., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 489–500. ISBN 978-0-12-383836-0. [Google Scholar]
- Politikos, D.V.; Petasis, G.; Chatzispyrou, A.; Mytilineou, C.; Anastasopoulou, A. Automating Fish Age Estimation Combining Otolith Images and Deep Learning: The Role of Multitask Learning. Fish. Res. 2021, 242, 106033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, J.R. Induction of Decision Trees. Mach. Learn. 1986, 1, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsiantis, S.B.; Zaharakis, I.D.; Pintelas, P.E. Machine Learning: A Review of Classification and Combining Techniques. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2006, 26, 159–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olden, J.D.; Lawler, J.J.; Poff, N.L. Machine Learning Methods Without Tears: A Primer for Ecologists. Q. Rev. Biol. 2008, 83, 171–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, J.A.; McNeil, B.J. The Meaning and Use of the Area under a Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve. Radiology 1982, 143, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, M.; Lapalme, G. A Systematic Analysis of Performance Measures for Classification Tasks. Inf. Process. Manag. 2009, 45, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.M.W. Evaluation: From Precision, Recall and F-Measure to ROC, Informedness, Markedness and Correlation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.16061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, B.W. Comparison of the Predicted and Observed Secondary Structure of T4 Phage Lysozyme. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct. 1975, 405, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Jurman, G. The Advantages of the Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC) over F1 Score and Accuracy in Binary Classification Evaluation. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawcett, T. An Introduction to ROC Analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Valverde, A. Insights into the Area under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (AUC) as a Discrimination Measure in Species Distribution Modelling. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 21, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, A.H.; Bell, J.F. A Review of Methods for the Assessment of Prediction Errors in Conservation Presence/Absence Models. Environ. Conserv. 1997, 24, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofaer, H.R.; Flather, C.H.; Skagen, S.K.; Steen, V.A.; Noon, B.R. Clustering and Ensembling Approaches to Support Surrogate-based Species Management. Divers. Distrib. 2019, 25, 1246–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Erion, G.; Chen, H.; DeGrave, A.; Prutkin, J.M.; Nair, B.; Katz, R.; Himmelfarb, J.; Bansal, N.; Lee, S.-I. From Local Explanations to Global Understanding with Explainable AI for Trees. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2020, 2, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goutte, C.; Gaussier, E. A Probabilistic Interpretation of Precision, Recall and F-Score, with Implication for Evaluation. In Advances in Information Retrieval, Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Retrieval, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 21–23 March 2005; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 345–359. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.; Goadrich, M. The Relationship between Precision-Recall and ROC Curves. In Proceedings of the 23rd international Conference on Machine Learning, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 25–29 June 2006; pp. 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Wisz, M.S.; Guisan, A. Do Pseudo-Absence Selection Strategies Influence Species Distribution Models and Their Predictions? An Information-Theoretic Approach Based on Simulated Data. BMC Ecol. 2009, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.; Ferrier, S. Evaluating the Predictive Performance of Habitat Models Developed Using Logistic Regression. Ecol. Modell. 2000, 133, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagarakis, K.; Libralato, S.; Giannoulaki, M.; Touloumis, K.; Somarakis, S.; Machias, A.; Frangoulis, C.; Papantoniou, G.; Kavadas, S.; Stoumboudi, M.T. Drivers of the North Aegean Sea Ecosystem (Eastern Mediterranean) Through Time: Insights From Multidecadal Retrospective Analysis and Future Simulations. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 919793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.J.; Letham, B. Forecasting at Scale. Am. Stat. 2018, 72, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitriou, E.; Efstratiadis, A.; Zotou, I.; Papadopoulos, A.; Iliopoulou, T.; Sakki, G.-K.; Mazi, K.; Rozos, E.; Koukouvinos, A.; Koussis, A.D. Post-Analysis of Daniel Extreme Flood Event in Thessaly, Central Greece: Practical Lessons and the Value of State-of-the-Art Water-Monitoring Networks. Water 2024, 16, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C.; Ljung, G.M. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control, 3rd ed.; Grant, J., Riker, E., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; ISBN 1118674928. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Sievert, C. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Hosmer, D.W., Jr.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 1118548353. [Google Scholar]
- Guisan, A.; Zimmermann, N.E. Predictive Habitat Distribution Models in Ecology. Ecol. Modell. 2000, 135, 147–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Leathwick, J.R.; Hastie, T. A Working Guide to Boosted Regression Trees. J. Anim. Ecol. 2008, 77, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, J.T. Biological Invasions and Cryptogenic Species. Ecology 1996, 77, 1653–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolar, C.S.; Lodge, D.M. Progress in Invasion Biology: Predicting Invaders. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2001, 16, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crafton, R.E. Modeling Invasion Risk for Coastal Marine Species Utilizing Environmental and Transport Vector Data. Hydrobiologia 2015, 746, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowicz, J.J.; Whitlatch, R.B.; Osman, R.W. Species Diversity and Invasion Resistance in a Marine Ecosystem. Science 1999, 286, 1577–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, R.N.; Simberloff, D.; Mark Lonsdale, W.; Evans, H.; Clout, M.; Bazzaz, F.A. Biotic Invasions: Causes, Epidemiology, Global Consequences, and Control. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 689–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, C.D.; Wallentinus, I. Can Species Traits Be Used to Predict Marine Macroalgal Introductions? Biol. Invasions 2005, 7, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimbro, D.L.; Cheng, B.S.; Grosholz, E.D. Biotic Resistance in Marine Environments. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciardi, A.; Hoopes, M.F.; Marchetti, M.P.; Lockwood, J.L. Progress toward Understanding the Ecological Impacts of Nonnative Species. Ecol. Monogr. 2013, 83, 263–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, B.; Drake, J.M.; Lodge, D.M. Predicting Invasions: Propagule Pressure and the Gravity of Allee Effects. Ecology 2004, 85, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.L.; Grosholz, E.D. The Invasive Species Challenge in Estuarine and Coastal Environments: Marrying Management and Science. Estuaries Coasts 2008, 31, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varsamos, S.; Nebel, C.; Charmantier, G. Ontogeny of Osmoregulation in Postembryonic Fish: A Review. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2005, 141, 401–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, E.T.; McCormick, S.D. Euryhalinity in an Evolutionary Context; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, D.; Claiborne, J.; Currie, S. The Physiology of Fishes, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; ISBN 100017459X. [Google Scholar]
- Bœuf, G.; Payan, P. How Should Salinity Influence Fish Growth? Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2001, 130, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Wallentinus, I.; Zenetos, A.; Leppäkoski, E.; Çinar, M.E.; Oztürk, B.; Grabowski, M.; Golani, D.; Cardoso, A.C. Impacts of Invasive Alien Marine Species on Ecosystem Services and Biodiversity: A Pan-European Review. Aquat. Invasions 2014, 9, 391–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siokou-Frangou, I.; Christaki, U.; Mazzocchi, M.G.; Montresor, M.; Ribera d’Alcalá, M.; Vaqué, D.; Zingone, A. Plankton in the Open Mediterranean Sea: A Review. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 1543–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barale, V.; Jaquet, J.-M.; Ndiaye, M. Algal Blooming Patterns and Anomalies in the Mediterranean Sea as Derived from the SeaWiFS Data Set (1998–2003). Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3300–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somero, G.N. The Physiology of Climate Change: How Potentials for Acclimatization and Genetic Adaptation Will Determine ‘Winners’ and ‘Losers’. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petihakis, G.; Triantafyllou, G.; Pollani, A.; Koliou, A.; Theodorou, A. Field Data Analysis and Application of a Complex Water Column Biogeochemical Model in Different Areas of a Semi-Enclosed Basin: Towards the Development of an Ecosystem Management Tool. Mar. Environ. Res. 2005, 59, 493–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousbouras, G.; Angelidis, P. Hydrodynamic Simulation of the Pagasitikos Gulf, Greece. Comput. Water Energy Environ. Eng. 2023, 13, 58–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabrah, M.; El-Ganainy, A.; Zaky, M.A. Biology and Toxicity of the Pufferfish Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) from the Gulf of Suez. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2006, 32, 283–297. [Google Scholar]
- Azzurro, E.; Soto, S.; Garofalo, G.; Maynou, F. Fistularia commersonii in the Mediterranean Sea: Invasion History and Distribution Modeling Based on Presence-Only Records. Biol. Invasions 2013, 15, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Haweet, A.A.K.; Farrag, M.M.S.; Akel, E.-S.A.; Moustafa, M.A. Puffer Fish Catch in the Egyptian Mediterranean Coast “The Challenged Invaders”. Int. J. Ecotoxicol. Ecobiol. 2016, 1, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Poursanidis, D.; Hoffman, R.; Rizgalla, J.; Rothman, S.B.-S.; Levitt-Barmats, Y.; Hadjioannou, L.; Trkov, D.; Garmendia, J.M.; Rizzo, M. Unpublished Mediterranean Records of Marine Alien and Cryptogenic Species. BioInvasions Rec. 2020, 9, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, T.P.; Pierce, D.W.; AchutaRao, K.M.; Gleckler, P.J.; Santer, B.D.; Gregory, J.M.; Washington, W.M. Penetration of Human-Induced Warming into the World’s Oceans. Science 2005, 309, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poloczanska, E.S.; Brown, C.J.; Sydeman, W.J.; Kiessling, W.; Schoeman, D.S.; Moore, P.J.; Brander, K.; Bruno, J.F.; Buckley, L.B.; Burrows, M.T.; et al. Global Imprint of Climate Change on Marine Life. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, N.; Thingstad, T.F.; Pitta, P.; Psarra, S.; Tanaka, T.; Zohary, T.; Groom, S.; Herut, B.; Mantoura, R.F.C.; Polychronaki, T. Effect of P and N Addition to Oligotrophic Eastern Mediterranean Waters Influenced by Near-Shore Waters: A Microcosm Experiment. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2005, 52, 3054–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béthoux, J.P.; Morin, P.; Ruiz-Pino, D.P. Temporal Trends in Nutrient Ratios: Chemical Evidence of Mediterranean Ecosystem Changes Driven by Human Activity. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2002, 49, 2007–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, E.; Michalak, A.M.; Balaji, V. Eutrophication Will Increase during the 21st Century as a Result of Precipitation Changes. Science 2017, 357, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raitsos, D.E.; Korres, G.; Triantafyllou, G.; Petihakis, G.; Pantazi, M.; Tsiaras, K.; Pollani, A. Assessing Chlorophyll Variability in Relation to the Environmental Regime in Pagasitikos Gulf, Greece. J. Mar. Syst. 2012, 94, S16–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, M.; Cossarini, G.; Lazzari, P.; Lovato, T.; Bolzon, G.; Masina, S.; Solidoro, C.; Salon, S. Acidification, Deoxygenation, and Nutrient and Biomass Declines in a Warming Mediterranean Sea. Biogeosciences 2022, 19, 4035–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellopoulos Theodore, D.; Georgios, P.; Alexandra, P.; Eleni, R.; Ioannis, H.; Catherine, T.; Nikolaos, K.; Sofia, R.; Ioanna, V.; Angeliki, M. The Semi-Enclosed Pagassitikos Gulf Under the Impact of Human Activities. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimarchopoulou, D.; Keramidas, I.; Tsagarakis, K.; Tsikliras, A.C. Ecosystem Models and Effort Simulations of an Untrawled Gulf in the Central Aegean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, e00648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, M.W.; Ballenger, J.C.; Bacheler, N.M.; Bubley, W.J. Tracking an Invasion: How the Distribution and Abundance of Lionfish (Pterois spp.) Has Changed along the US Atlantic Coast. Biol. Invasions 2024, 26, 1669–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojaveer, H.; Galil, B.S.; Minchin, D.; Olenin, S.; Amorim, A.; Canning-Clode, J.; Chainho, P.; Copp, G.H.; Gollasch, S.; Jelmert, A.; et al. Ten Recommendations for Advancing the Assessment and Management of Non-Indigenous Species in Marine Ecosystems. Mar. Policy 2014, 44, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuiller, W.; Lafourcade, B.; Engler, R.; Araújo, M.B. BIOMOD—A Platform for Ensemble Forecasting of Species Distributions. Ecography 2009, 32, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, T.; Elith, J.; Guillera-Arroita, G.; Lahoz-Monfort, J.J. A Review of Evidence about Use and Performance of Species Distribution Modelling Ensembles like BIOMOD. Divers. Distrib. 2019, 25, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisan, A.; Thuiller, W.; Zimmermann, N.E. Habitat Suitability and Distribution Models: With Applications in R; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; ISBN 0521765137. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, M.B.; Luoto, M. The Importance of Biotic Interactions for Modelling Species Distributions under Climate Change. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2007, 16, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisz, M.S.; Pottier, J.; Kissling, W.D.; Pellissier, L.; Lenoir, J.; Damgaard, C.F.; Dormann, C.F.; Forchhammer, M.C.; Grytnes, J.; Guisan, A. The Role of Biotic Interactions in Shaping Distributions and Realised Assemblages of Species: Implications for Species Distribution Modelling. Biol. Rev. 2013, 88, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowen, R.K.; Sponaugle, S. Larval Dispersal and Marine Population Connectivity. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 1, 443–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergés, A.; Steinberg, P.D.; Hay, M.E.; Poore, A.G.B.; Campbell, A.H.; Ballesteros, E.; Heck, K.L., Jr.; Booth, D.J.; Coleman, M.A.; Feary, D.A. The Tropicalization of Temperate Marine Ecosystems: Climate-Mediated Changes in Herbivory and Community Phase Shifts. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20140846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giakoumi, S.; Katsanevakis, S.; Albano, P.G.; Azzurro, E.; Cardoso, A.C.; Cebrian, E.; Deidun, A.; Edelist, D.; Francour, P.; Jimenez, C. Management Priorities for Marine Invasive Species. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simberloff, D.; Martin, J.-L.; Genovesi, P.; Maris, V.; Wardle, D.A.; Aronson, J.; Courchamp, F.; Galil, B.; García-Berthou, E.; Pascal, M.; et al. Impacts of Biological Invasions: What’s What and the Way Forward. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormann, C.F.; Purschke, O.; Marquez, J.R.G.; Lautenbach, S.; Schroeder, B. Components of Uncertainty in Species Distribution Analysis: A Case Study of the Great Grey Shrike. Ecology 2008, 89, 3371–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallien, L.; Douzet, R.; Pratte, S.; Zimmermann, N.E.; Thuiller, W. Invasive Species Distribution Models–How Violating the Equilibrium Assumption Can Create New Insights. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 21, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Measuring Unit |
|---|---|
| Surface Temperature | °C |
| Bottom Temperature | °C |
| Salinity | psu |
| pH | −log[H+] |
| O2 | mmol/m3 |
| Chl_a | mg/m3 |
| NH4 | mmol/m3 |
| NO3 | mmol/m3 |
| PO4 | mmol/m3 |
| L. sceleratus | |||
| Model | Weighted Avg 1 | Rank Score 2 | Ecological Utility 3 |
| Neural Network | 0.72 | 18 (1st) | 0.45 |
| SVM | 0.7 | 15 (2nd) | 0.43 |
| SGD | 0.65 | 10 (3rd) | 0.38 |
| Decision Tree | 0.61 | 8 (4th) | 0.35 |
| P. miles | |||
| Model | Weighted Avg 1 | Rank Score 2 | Ecological Utility 3 |
| Neural Network | 0.754 | 17 (1st) | 0.52 |
| SVM | 0.749 | 14 (2nd) | 0.51 |
| SGD | 0.740 | 13 (3rd) | 0.53 |
| Decision Tree | 0.650 | 7 (4th) | 0.37 |
| Parameter | Pagasitikos Gulf | Rhodes Island | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Temperature (°C) | 19.87 ± 0.29 | 21.43 ± 0.19 | *** |
| Bottom Temperature (°C) | 15.46 ± 0.09 | 16.66 ± 0.03 | *** |
| Salinity (psu) | 38.04 ± 0.02 | 39.25 ± 0.007 | *** |
| O2 (mmol/m3) | 236.00 ± 0.68 | 219.11 ± 0.51 | *** |
| pH (−log[H+]) | 8.15 ± 0.004 | 8.07 ± 0.003 | *** |
| Chl_a (mg/m3) | 0.48 ± 0.029 | 0.06 ± 0.001 | *** |
| NH4 (mmol/m3) | 0.08 ± 0.002 | 0.11 ± 0.001 | *** |
| NO3 (mmol/m3) | 0.18 ± 0.009 | 0.72 ± 0.016 | *** |
| PO4 (mmol/m3) | 0.006 ± 0.001 | 0.012 ± 0.001 | *** |
| Key Environmental Parameters | Threshold for Establishment P. miles | Threshold for Establishment L. sceleratus |
|---|---|---|
| Chlorophyll a | ≤0.1052 mg/m3 | ≤0.1774 mg/m3 |
| Bottom Temperature | ≥16.382 °C | ≥15.84 °C |
| pH | ≤8.1531 | ≤8.249 |
| Salinity | ≥39.144 psu | ≥39.096 psu |
| Dissolved Oxygen | ≤229.07 mmol/m3 | ≤255.37 mmol/m3 |
| Phosphate: | ≤0.05329 mmol/m3 |
| Parameter | Observed | Modeled | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Temperature (°C) | 19.87 ± 5.18 | 21.15 ± 5.15 | ** |
| Bottom Temperature (°C) | 15.46 ± 1.69 | 17.06 ± 1.58 | *** |
| Salinity (psu) | 38.03 ± 0.36 | 37.45 ± 0.31 | *** |
| O2 (mmol/m3) | 235.99 ± 11.73 | 228.79 ± 11.49 | *** |
| pH (−log[H+]) | 8.16 ± 0.07 | 8.13 ± 0.07 | * |
| Chl_a (mg/m3) | 0.48 ± 0.50 | 0.96 ± 0.23 | *** |
| NO3 (mmol/m3) | 0.19 ± 0.16 | 0.06 ± 0.05 | *** |
| NH4 (mmol/m3) | 0.08 ± 0.04 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | *** |
| PO4 (mmol/m3) | 0.0066 ± 0.002 | 0.0062 ± 0.001 | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klaoudatos, D.; Theocharis, A.; Aydin, İ.; Pafras, D.; Karagianni, K.; Domenikiotis, C. Forecasting Environmental Drivers and Invasion Risk of Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) and Pterois miles (Bennett, 1828) in the Pagasitikos Gulf (Greece). Geosciences 2025, 15, 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15090361
Klaoudatos D, Theocharis A, Aydin İ, Pafras D, Karagianni K, Domenikiotis C. Forecasting Environmental Drivers and Invasion Risk of Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) and Pterois miles (Bennett, 1828) in the Pagasitikos Gulf (Greece). Geosciences. 2025; 15(9):361. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15090361
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlaoudatos, Dimitris, Alexandros Theocharis, İlker Aydin, Dimitris Pafras, Kleio Karagianni, and Christos Domenikiotis. 2025. "Forecasting Environmental Drivers and Invasion Risk of Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) and Pterois miles (Bennett, 1828) in the Pagasitikos Gulf (Greece)" Geosciences 15, no. 9: 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15090361
APA StyleKlaoudatos, D., Theocharis, A., Aydin, İ., Pafras, D., Karagianni, K., & Domenikiotis, C. (2025). Forecasting Environmental Drivers and Invasion Risk of Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) and Pterois miles (Bennett, 1828) in the Pagasitikos Gulf (Greece). Geosciences, 15(9), 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15090361









