Abstract
Wind-blown sand concentrations decay rapidly and in an orderly manner with height above the surface. The saltation flux profiles are of interest to understand wind and sand interactions and for fundamental measurement and modeling of associated transport rates. This study compares methods to measure and represent aeolian sand flux profiles. We measured vertical flux profiles and used quality-controlled data to test power, logarithmic, and exponential functions to reproduce the profiles. These results are used in a pragmatic assessment of the efficiency of reproducing flux profiles from vertically discontinuous arrays of traps or sensors compared to profiles obtained from continuous vertical arrays of segmented traps. Our analysis corroborates previous findings demonstrating that exponential decay functions are statistically the best method to approximate flux profiles. The results are used in a novel application to compare flux profiles reproduced from vertically discontinuous arrays of devices with those obtained from continuous vertical arrays comprising nine mesh-style traps. The results indicate that discontinuous arrays of 3, 4, 5, or 6 devices deployed less than 200 mm from the surface will effectively reproduce results from the continuous array, with average errors less than 3%. Errors increase when devices are at greater heights or as the number of devices decreases. Discontinuous arrays typically do not capture creep transport which would contribute to error in our comparisons. Therefore, creep must comprise less than 3% of total aeolian sand flux, contradicting typical assumptions of 25%.
1. Introduction
Most wind-blown sand moves via saltation [1]. The trajectories of saltating grains are determined by the ballistic variables of launch angle, launch speed, wind speed (or wind shear velocity), and altered by in-flight grain-grain collisions. The intensity of saltation decays rapidly with height above the surface under equilibrium (or saturated) transport, resulting in the development of a characteristic flux profile. Measuring this bulk manifestation of saltation trajectories is critical for deciphering the interactions between wind and the sand it transports, and is fundamental to modeling and field validation of aeolian transport rates. As eloquently stated by Butterfield [2] (p. 393): “Vertical profiles of horizontal mass flux…are significant for the reliable prediction of transport rate and for verification of …numerical models…”.
Models of aeolian sand transport rely, implicitly or explicitly, on an understanding of the trajectories and quantities of saltating grains [3,4,5,6,7] and the characterization of the grain concentration profile above the surface [2,8,9,10,11,12]. A number of functions have been proposed as best representing the rapid decrease in flux away from the bed, including power functions [2,8,9,13,14,15,16,17,18], logarithmic functions [11,19,20,21], and exponential decay functions [9,10,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39] (among many others). Characterization of saltation flux profiles requires measurement of transport at three or more elevations within the saltation layer. Sets of sand traps and saltation sensing instruments of different designs and configurations have been used in wind tunnels or field environments to obtain these measurements.
Continuous arrays of vertically segmented sand traps capture all the sand blowing past a particular wind-perpendicular length (total load) spanning the height from the sand surface to the top of the saltation layer. The more traps between these two levels, the greater the detail that can be gained concerning the distribution of sand mass. Using this approach, traps should capture all grains passing through the plane of the trap openings, whether they move by saltation, reptation, or creep, assuming 100% trap efficiency. In many cases, however, vertical arrays are discontinuous, i.e., there are vertical gaps between traps or sensors where portions of the saltation profile are not measured but inferred through curve-fitting.
Several trap designs have been developed for deployment as continuous arrays, a term we use to distinguish these total load systems from vertically integrating, total-load traps, such as those designed by Leatherman [40] and Rosen [41], Jackson [42], or Nickling and McKenna-Neuman [43], for example. Perhaps the first continuous array was that of Bagnold [44] (c.f. his Figure 3), who deployed a trap about 0.75 m in height with 15 openings of about 505 mm each for use in his desert studies. A smaller example, with 30 segments with 10 mm × 10 mm openings was used by Ni et al. [16] in their wind tunnel experiments. Another version of this trap that was more aerodynamically sound, thus more efficient, was developed by Dong et al. [32]. Their WITSEG sampler features 60 openings 10 mm high and 5 mm wide. A similar trap, the LLDSEG [45], comprised 50 20 × 20 mm traps in a 1 m high array. Rotnicka [46] used a continuous trap with 40 openings 127 mm high and 10 mm wide. Stacks of hose-style or mesh-style traps with dimensions 25 mm, 50 mm, or 100 mm high and 100 mm wide were used in different deployments by Ellis et al. [10], Li et al. [47], Farrell and Sherman [48], Swann et al. [49], and Strypsteen et al. [50]. Continuous arrays often require real-time monitoring during active sand transport events to avoid their filling and blockage.
Discontinuous traps or sensor arrays (jointly termed devices herein) include vertical gaps between adjacent traps and a gap between the lowest device and the sand surface. These devices can be mechanical traps, or optical, acoustic, or piezoelectric sensors. Examples of discontinuous arrays are summarized in Table 1. Any gap in measuring the vertical profile causes a loss of information that is addressed by integrating the area under a fitted curve to estimate the total flux. The degree to which such estimations of sand flux might be degraded is assumed to be small, but is, in fact, unknown. Further, because discontinuous arrays have a gap between the surface and the bottom of the lowest device, they cannot measure creep transport, often reported to represent a substantial proportion of the total flux [51]; thus also representing a potential source of substantial flux estimation error. Discontinuous arrays are often deployed in field conditions where real-time monitoring is not feasible because of logistical constraints, or, as in the case of saltation sensors, physical instrument limitations. In either case, the elevations and spacings of such devices are key elements of experimental design.

Table 1.
Examples of studies measuring saltation flux with discontinuous arrays of sand traps or saltation sensors.
Bagnold [1] appears to have also devised the first discontinuous trap array when he used a set of glass tubes, adjusted vertically, in his wind tunnel experiments. Other systems for discontinuous flux profile measurement have been developed; the three described by Rasmussen and Mikkelsen [20], for example. Practice, however, has led to two types of traps being most used in field studies: the Big Springs Number Eight (BSNE) and the modified Wilson and Cook (MWAC) traps [66]. The BSNE trap was first described by Fryrear [67] as a device intended to catch blowing sand and dust. The trap is 20 mm wide and 50 mm tall with a vane at its rear so that it could rotate to align itself with an incident wind, and this remains the common configuration. The Wilson and Cook trap [68] comprises a sample bottle with inlet and outlet glass tubes to allow airflow through the trap while allowing sediments to collect in the trap (a plastic bottle). The MWAC version [69,70] links several individual traps and includes a vane so that the array will align itself with wind direction. The “swinging trap” [65] is another efficient, self-aligning device that can be used in discontinuous vertical arrays.
Small optical, acoustic, and piezoelectric sensors have also been used to measure vertical profiles of saltation by producing what are essentially point source data. Laser particle counters (e.g., the Wenglor fork laser particle counter) are the most common electronic saltation sensors used to detect the passage of saltating grains and arrays of them can reproduce flux profiles [35,36,61,62,64]. Acoustic sensors [71,72,73] and piezoelectric sensors [56,58,74,75,76] have the capacity for flux profile measurement, but are not often used for that purpose. Discontinuous arrays of these sensors can be used to develop saltation profiles comprising grain counts rather than mass flux. Their signals can be calibrated against trap data, for example, to estimate sand transport rates [62,70,77].
Here, we compare methods used to measure and represent aeolian sand flux profiles in field environments. We measured vertical flux profiles at three sites and used quality-controlled data (R2 > 0.99) to compare the qualities of representation of the data associated with fitting power, logarithmic, and exponential functions. Those results are used in a novel and pragmatic assessment of the efficiency of reproducing flux profiles from vertically discontinuous arrays of traps or sensors as compared to profiles obtained from continuous vertical arrays of segmented traps.
2. Study Sites
Multiple study sites were selected for this study as a means of avoiding potential site-specific influences on sand flux profiles. Sites were selected with long (>50 m), flat, and unobstructed fetches. Flux profile data were collected from three field sites in the Jericoacoara National Park, Ceará, Brazil (Figure 1 and Figure 2) in October 2022. All sites were selected to minimize distortions in wind and sand flux caused by local topography. Site 1 was on top of an unvegetated barchan horn (2°49′30.90″ S; 40°29′08.88″ W), adjacent to, but unaffected by, the Jericoaocoara-Jijoca trail. The unobstructed fetch length was about 80 m. Surface sediments were clean and dry, with a median grain size, d50, of 392 μm. Site 2 was approximately 1 km east of Site 1, and was also on top of an unvegetated barchan horn (2°49′32.58″ S; 40°28′37.80″ W). The unobstructed fetch length was about 70 m. Surface sediments were clean and dry, with a d50 of 391 μm. Site 3 was approximately 3 km southwest of the Jericoacoara National Park headquarters (2°49′01.44″ S; 40°32′02.72″ W). The location was on a low-tide terrace with an unobstructed fetch length of about 200 m. This site was chosen as a contrast to Sites 1 and 2, as its surface sediments were clean but wet, with a d50 of 225 μm. The sand surface was also damp during sampling, acting as a transport surface with minimal exchange between saltating sands and the surface sediments.
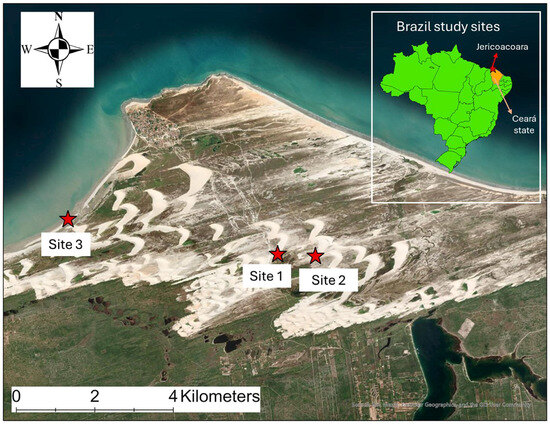
Figure 1.
Locations of the three study sites in Jericoacoara National Park, Ceará State, Brazil, shown on satellite imagery (source: Esri, Maxar, Earthstar Geographics, and the GIS User Community).
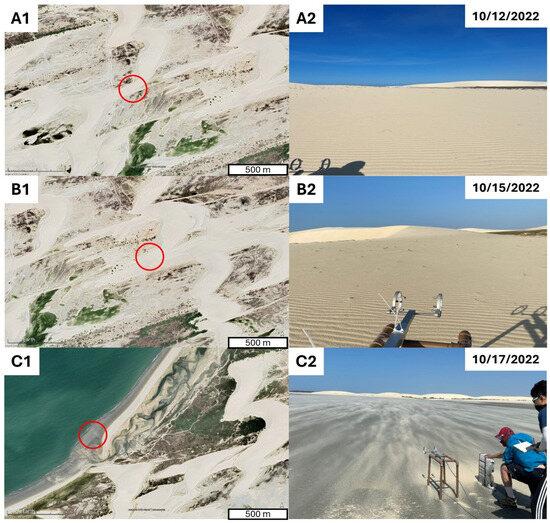

Figure 2.
Details of the three study sites, indicated with red circles. (A1) is a Google Earth image (19 October 2021) of the general Site 1 environment and (A2) is the upwind perspective during data collection. (B1) is a Google Earth image (19 October 2021) of the general Site 2 environment and (B2) is the upwind perspective during data collection. (C1) is a Google Earth image (19 October 2021) of the general Site 3 environment and (C2) is the upwind perspective during data collection. The nine trap, vertically continuous array is visible in the lower right of (C2).
3. Methods
3.1. Data Collection
Continuous, vertical arrays of 9 mesh traps [78] were used to collect sand to measure transport rates and construct flux profiles. These traps were 100 mm wide with opening heights of 25, 25, 25, 25, 50, 50, 50, 100, and 100 mm (upward from the bed) for the 9-trap stack. The trap openings were oriented perpendicular to the wind direction, and sample durations varied from 2 to 15 min, depending on the transport rates. Sampling durations were shorter for faster transport rates to avoid filling the smaller traps at or near the bed and thereby degrading trap efficiencies. All samples were weighed with an electronic balance with an accuracy of 0.1 g. Samples from Site 3 were dried before weighing. Ten profile datasets were obtained from Site 1; 18 from Site 2; and 8 from Site 3. Details of each dataset may be found in Zhang et al. [79].
3.2. Evaluating Saltation Flux Distribution Models
The trap data were used to evaluate the performances of power, logarithmic, and exponential functions and their abilities to accurately reproduce the measured sand transport. Following the protocols described in Ellis et al. [10], the sand mass,
(g) collected in a vertical trap was converted to a relative percent value (qni) by normalizing the trap height:
where M is the total amount of sand mass captured during the run, and hti and hbi are the elevations of the top (t) and bottom (b) of trap i. Finding a representative height for each vertical trap is a necessary prerequisite to curve-fitting for profile characterization with power, logarithmic, and exponential curves. In general, there are two approaches to represent mean trap center height (hi): arithmetic mean centering () or geometric mean centering (). When using geometric centering, it is necessary to specify a non-zero elevation for the bottom of the bottom trap so that GC ≠ 0. We evaluated three ways to specify hbi: (1) as equal to 1 mm, (2) as equal to the median grain diameter (d50), and (3) as equal to the grain roughness length, estimated as d50/15. Twelve curve-fitted results were compared for each vertical profile dataset by using power (Equation (2)), logarithmic (Equation (3)), and exponential (Equation (4)) functions and with the representative average trap elevations set using arithmetic and geometric centering, with three versions of the latter corresponding to the method of specifying hbi.
Three criteria were used to assess the quality of curve-fitting from each of the twelve approaches: (1) coefficients of determination, R2; (2) root mean square errors, RMSE; and (3) the average, absolute difference (% error) in masses caught in the bottom traps.
3.3. Comparing Continuous and Discontinuous Array Estimates of Total Sand Flux
The results of the curve-fitting exercise were used to assess the performances of discontinuous trap and sensor arrays relative to continuous trap arrays. We evaluated simulated flux estimates that might be associated with deployments of vertical arrays of 3 to 6 BSNE, MWAC, Wenglor, or other traps or sensors. In all cases, it is assumed that traps and sensors are 100% efficient, although we know that is an idealization [70,80,81]. The elevations used for the different arrays were the averages for our nine trap centers (based on geometric centering): 2.95, 35.36, 61.24, 86.60, 122.47, 173.21, 223.61, 295.80, and 396.86 mm, respectively. The value for the bottom trap center is the mean based on the different grain sizes from the flux profiles, and the standard deviation was 0.40 mm. We did not test two device profiles as exponential curves require at least three points.
The assessment of error for each flux profile comparison was calculated as follows:
where is the predicted transport rate at trap height . These errors were then averaged for each discontinuous array configuration.
4. Results
The results of assessing the flux profile curve-fitting methods are summarized in Table 2. Coefficients of determination, R2, for the four exponential approaches exceeded 0.99, with little difference between them. Goodness of fits for the logarithmic approaches were not as tight as those for the exponential curves, but were still quite strong, with R2 exceeding 0.90, but with a range of about 10%. The power model results were least accurate, with R2 ranging from about 0.76 to 0.92. The results from the root mean square error assessment also favor exponential fits, with RMSE all less than 0.33%. RMSE for the logarithmic curves ranged from about 0.74 to 1.32%. Again, the results from fitting a power function were least accurate, with RMSE ranging from about 1.21 to 2.10%. Assessment of the average, absolute differences (% error) in sand masses caught in the bottom traps yields similar results in support of exponential distributions as best representing flux profiles, with such errors ranging from about 1.9 to 2.9%. The corresponding ranges for logarithmic and power functions were 4.3 to 9.9% and 4.9 to 6.5%, respectively.

Table 2.
Statistical summary of the accuracy of different approaches to approximate vertical sand flux profiles.
Differences in the quality of exponential curve-fitting approaches were small, and it could be argued that they are trivial. Nevertheless, we opted to test the continuous and discontinuous flux profile approaches using the exponential fit based on geometric centers with the bottom of the bottom trap estimated using the surface roughness length approximation of d50/15. Coefficients of determination from the four approaches vary only at the third decimal place. The roughness-length based fit, however, yields the smallest RMSE and % error in the bottom trap. The latter, especially, might prove important for interpreting other aspects of the transport system, such as mean saltation height or reptation flux, with the latter occurring within 10 mm of the surface [3,82,83].
The results of comparing sand transport measured via continuous trap arrays with discontinuous trap or sensor arrays are summarized in Figure 3. Using the geometrically derived trap centers from our nine trap arrays, we derived error statistics for different deployment of 3, 4, 5, and 6 trap, discontinuous arrays. We assumed that none of the discontinuous arrays measured sand flux below 25 mm. Therefore, there were 28 combinations of six traps, 56 of five traps, 70 of four traps, and 56 of three traps. Figure 3 presents histograms of error statistics for the best and worst array configurations, and for averages of all, according to number of traps and their respective elevations. For the configurations demonstrating the least error, the number of traps deployed causes trivial differences in the quality of the curve-fitting and integration, thus flux prediction. The elevations used for the respective arrays were more important in determining profile quality. For the different numbers of traps, lower elevations produced the best results. For all the possible six device array combinations, the mean error averaged 5.82% with a standard deviation of 5.84%, with a mean error ranging from 4.77 to 9.03%. For a five-device array the comparable statistics were 6.34%, 6.17%, and 4.78 to 11.32%. For arrays of four or three devices, these same statistics were 7.07%, 6.60%, and 4.79 to 17.10%, and 8.32%, 8.00%, and 4.83 to 20.93%, respectively. The distribution of errors for the best performing arrays was almost identical, whereas the distributions of greatest errors depended greatly on the number of traps and their elevations.
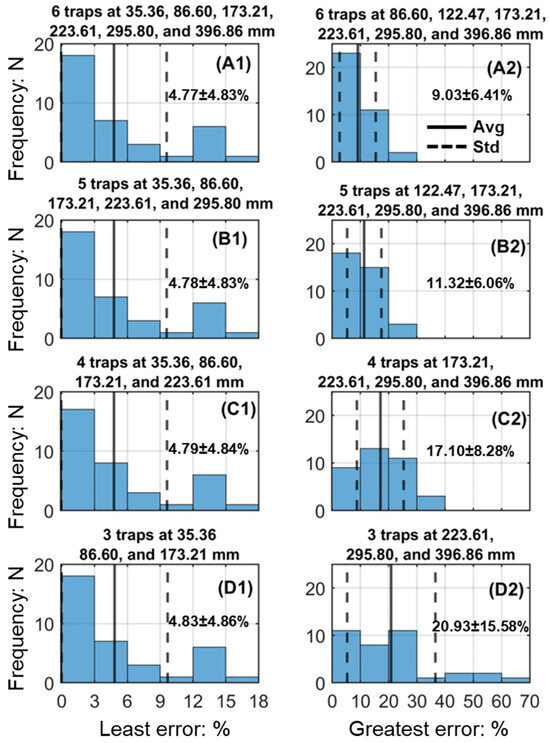
Figure 3.
Histograms illustrating least (A1,B1,C1,D1) and greatest errors (A2,B2,C2,D2) associated with different elevation configurations for sets of 3 (A), 4 (B), 5 (C), and 6 (D) traps or sensors.
5. Discussion
Our statistical results from evaluating curve-fitting methods contradict Ellis et al.’s [10] recommendation to use 1 mm as the bottom elevation of a surface trap for establishing a geometrically averaged trap center because using a roughness length estimate for the bed elevation provides slightly better curve fits to the measurements. We note, however, that the differences between using 1 mm and d50/15 are marginal, and the former is more easily applicable for cases when grain size data are unavailable.
When discontinuous arrays are deployed low in the saltation cloud (as is the case for our least error results (Figure 3)), the results of the assessment of curve-fitting with discontinuous arrays compared to continuous arrays show essentially no difference in performance when considering deployments of three, four, five, or six vertically deployed devices, implying that three trap/sensor arrays are sufficient for accurate flux profile integration. If the minimum criteria for an array of three is met, this also contradicts the recommendation of Ellis et al. [10] that more traps are better than fewer. It is also clear, however, that the vertical distribution of traps or sensors profoundly affects the magnitude of potential error. The least error profiles in this study are associated with arrays where the sets of devices are closest to the bed (elevations less than 200 mm), whereas the greatest errors are associated with arrays where the sets of devices are farthest from the bed. Other array configurations, i.e., mixes of low and high devices, produce mean error results intermediate to the extremes. Zhang [84] includes a user-friendly MATLAB R2023b script as an analytical tool to allow other aeolian scientists to estimate potential errors for any combination of discontinuous device arrays, based on the nine index heights of our continuous profile.
The results depicted in Figure 3 for the best array configurations (least error) also indicate six profile cases where the error is larger than 10%. All these profiles are from Site 3 with a damp sand surface and there is a seventh Site 3 profile also with a large error—15.7%. The analysis summarized in Table 2 and Figure 3 was repeated with the exclusion of the data from all eight Site 3 profiles (Figure 4). The evaluation of curve-fitting approaches summarized in Table 2 indicates no statistically significant differences between data from the barchan sites and the beach site, or from the combined dataset. In each case, the value of R2 is 0.99 for exponential functions. Omitting Site 3 data reduces the least error for the different numbers of traps or sensors from about 4.8% to about 2.5 to 2.6%, again with trivial differences based on the number of traps. For the configurations with the greatest errors, the omission of Site 3 data reduced the range of average errors from 9.0 to 20.9% to 7.9 to 15.9%.
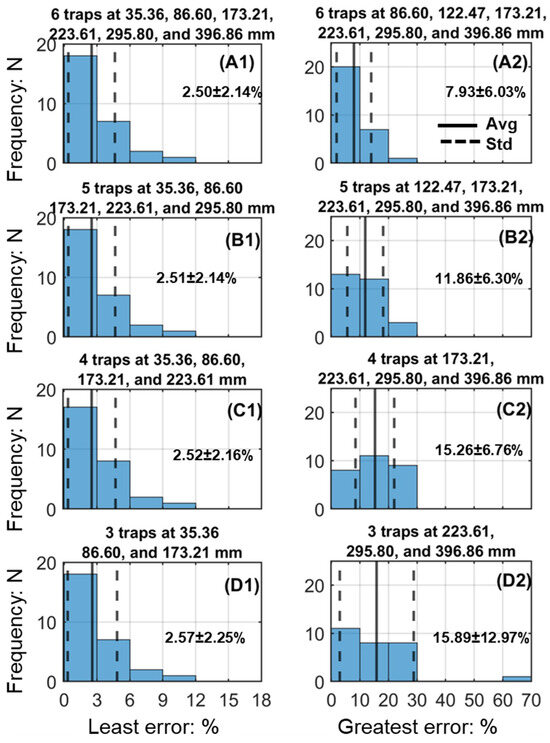
Figure 4.
Histograms illustrating least (A1,B1,C1,D1) and greatest errors (A2,B2,C2,D2) associated with different elevation configurations for sets of 3 (A), 4 (B), 5 (C), and 6 (D) traps or sensors when data from Site 3 are excluded.
After removing the Site 3 data, for all the possible six-trap or sensor arrays, the mean error averages 3.48% with a standard deviation of 3.21%, with an error range from 2.50 to 7.93%. For a five-device array, the comparable statistics are 4.10%, 3.88%, and 2.51 to 11.86%. For arrays of four or three devices, the statistics are 5.02%, 4.82%, and 2.52 to 15.26%, and 6.51%, 6.86%, and 2.57 to 19.87%, respectively. The difference in the averages of errors for the best performing arrays is trivial (less than 5% difference), whereas the distributions of greatest errors again show great dependence on the number of traps and their elevations.
Figure 5A depicts the fitted curves averaged from Site 1 and 2 data for continuous and six discontinuous trap arrays, using the least error configuration. The two curves match closely, unlike the case for a similar treatment of the Site 3 data (Figure 5B). The discontinuous array, missing the bottom of the flux profile, puts great weight on its bottom trap (with a 35.36 mm center height) for curve-fitting whereas the continuous array weights most heavily on its bottom trap (with an elevation of 2.95 mm). The relatively fine beach sands have lower mean saltation trajectories than those of coarser sediments at Sites 1 and 2, despite the near-inelastic transport surface. This causes the substantial overprediction of near-bed transport based on curves fit to the discontinuous array profiles. We speculate that analogous discrepancies might arise with transport over similarly inelastic surfaces, such as those with crusted sand or sediment beds of larger caliber than the saltating sands. This corresponds with the findings of Bagnold [1], Namikas et al. [85], Dong et al. [86], and Ho et al. [87], among many others.
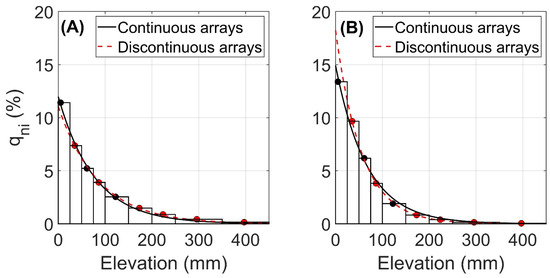
Figure 5.
Average flux profiles comparing continuous (black lines) and discontinuous (least error, red dashed lines) curves. (A) Fitted flux profiles from Site 1 and 2 data. (B) Fitted flux profiles from Site 3 data.
We noted earlier that discontinuous arrays that did not include a surface level trap would not catch any creep transport, often assumed to represent about 25% of the total transport [44,51]. The discontinuous arrays modeled here, for example, would not measure any sand moving within 10 mm of the surface, well above the thickness of the creep (reptation) layer, causing an error proportional to the creep load. The results of this study strongly support the notion that the contribution of creep transport to total aeolian sand flux is minor because the differences between continuous arrays and discontinuous arrays (with all devices below 200 mm) are less than 3%. That figure is in broad agreement with some of the studies reported in Zhang et al. [51]. Some portion of the differences found between the continuous and discontinuous arrays can be attributed to the latter missing creep flux, but that portion must be less than the average errors found. This is especially the case because our error statistics are based on averaging the absolute values of difference percentages to include positive (over prediction) and negative (under prediction) differences.
6. Conclusions
This study assesses the abilities of exponential, logarithmic, and power functions to approximate vertical aeolian flux profiles produced from a curated set of measurements from three field sites using only profiles with R2 > 0.99 for fitted curves. Further, using an innovative approach, we compared the quality-controlled flux measurements from vertically continuous trap arrays with the results of simulated discontinuous arrays comprising three to six devices. The research leads us to three conclusions.
- Saltation flux profiles decay exponentially with height above the surface. Our analysis indicates that exponential functions (RMSE 0.29–0.33; bottom trap absolute error 1.9–2.9%) are much better at fitting the empirical profiles than either the logarithmic (RMSE 0.74–1.32; bottom trap absolute error 4.3–9.9%) or power functions (RMSE 1.21–2.10; bottom trap absolute error 4.9–6.5%). These results support findings from previous research (e.g., Ellis et al. [10], among many others) but contradict those studies that suggest logarithmic or power functions more closely approximate measured flux profiles. Geometric averaging to represent trap centers produces results superior to arithmetic centering, but using 1 mm, median grain size, or grain roughness length to represent the bottom of the bottom trap causes trivial differences.
- The number of traps or sensors in a discontinuous array is secondary to the heights of the devices above the surface in terms of contributing to the magnitude of potential error in fitted model predictions. Average errors, relative to the continuous profile data for arrays comprising 3, 4, 5, or 6 devices, average only about 2.5% when the installations are as close as feasible to a non-cohesive sand surface. This discounts the results for saltation over a moist surface, i.e., Site 3 data in this study. When discontinuous arrays comprise measurements at greater distances from the surface, errors average almost 16% for three device configurations.
- In this study, creep/reptation transport is inferred to be a relatively small component of total wind-blown sand flux. Creep would move below the lowest measurement heights of the discontinuous arrays but would be captured in the continuous array data. Thus, the fitted curves would vary to reflect the differences, and this would manifest in error percentages. The close correspondence of the least error discontinuous arrays with continuous profiles suggests, therefore, that creep/reptation proportion of sand transport must average less than the 2.5% average error.
We recognize that these results are not applicable to all possible field environments (e.g., those that are substantially hotter, colder, or wetter) and all possible trap and sensor types. Nevertheless, the viability of most BSNE, MWAC, Wenglor, and other arrays comprising similar devices is validated for most applications, with the provision that the devices are deployed closer to the sand surface than what is commonly reported in the literature. More attention should be paid to the environments where the performances might not be conformal. These include surfaces with non-exponential flux profiles, moist conditions (e.g., Site 3), and locations where sediment sizes are greater or finer than the sands studied here, or where grain size distributions are multimodal.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.J.S. and P.Z.; methodology, D.J.S. and P.Z.; software, P.Z.; validation, P.Z.; formal analysis, A.D.A., J.B., D.J.S., and P.Z.; investigation, A.D.A., A.M.d.C., J.B., J.T.E., E.F., B.L., E.J.R.P., D.J.S., D.L.S., C.S., and P.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, J.B., J.T.E., D.J.S., C.S., and P.Z.; writing—review and editing, A.D.A., A.M.d.C., J.B., J.T.E., E.F., B.L., E.J.R.P., D.J.S., D.L.S., C.S., and P.Z.; visualization, J.B., J.T.E., D.J.S., and P.Z.; funding acquisition, E.J.R.P., D.J.S., and P.Z. Logistics: A.D.A., A.M.d.C., D.J.S., and P.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by a U.S. National Science Foundation grant to D. J. Sherman and P. Zhang (EAR 2027064). E.J.R. Parteli received support through the Heisenberg Program of the German Research Foundation (434377576).
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting our conclusions will be made available at Zenodo.org upon acceptance of the paper. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15778571 (accessed on 16 August 2025) (dataset) and https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15700463 (accessed on 16 August 2025) (code).
Acknowledgments
Fieldwork occurred at sites near Jericoacoara, Ceará, Brazil, with access allowed by the Brazilian Research in the Federal Conservation Units—SISBIO and Jericoacoara National Park.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Christy Swann is employed by the RCOAST Company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Bagnold, R.A. The Movement of Desert Sand. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1936, 157, 594–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, G.R. Near-Bed Mass Flux Profiles in Aeolian Sand Transport: High-Resolution Measurements in a Wind Tunnel. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1999, 24, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreotti, B. A Two-Species Model of Aeolian Sand Transport. J. Fluid Mech. 2004, 510, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, M. On the Rate of Aeolian Sand Transport. Geomorphology 2004, 59, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, D.J.; Li, B. Predicting Aeolian Sand Transport Rates: A Reevaluation of Models. Aeolian Res. 2012, 3, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valance, A.; Rasmussen, K.R.; Ould El Moctar, A.; Dupont, P. The Physics of Aeolian Sand Transport. C. R. Phys. 2015, 16, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pähtz, T.; Tholen, K. Aeolian Sand Transport: Scaling of Mean Saltation Length and Height and Implications for Mass Flux Scaling. Aeolian Res. 2021, 52, 100730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingg, A.W. Wind Tunnel Studies of the Movement of Sedimentary Material. In Proceedings of the 5th Hydraulic Conference Bulletin; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1953; Volume 34, pp. 111–134. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Qian, G.; Luo, W.; Wang, H. Analysis of the Mass Flux Profiles of an Aeolian Saltating Cloud. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.T.; Li, B.; Farrell, E.J.; Sherman, D.J. Protocols for Characterizing Aeolian Mass-Flux Profiles. Aeolian Res. 2009, 1, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.D.; Valance, A.; Dupont, P.; Ould El Moctar, A. Aeolian Sand Transport: Length and Height Distributions of Saltation Trajectories. Aeolian Res. 2014, 12, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.L.; Kok, J.F.; Hugenholtz, C.H.; Barchyn, T.E.; Chamecki, M.; Ellis, J.T. High-Frequency Measurements of Aeolian Saltation Flux: Field-Based Methodology and Applications. Aeolian Res. 2018, 30, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, W.D.; Hopwood, J.M.; Summers, K.J. A Mathematical Model of Suspension with Saltation. Acta Mech. 1995, 108, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterk, G.; Raats, P.A.C. Comparison of Models Describing the Vertical Distribution of Wind-Eroded Sediment. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 1914–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, J.E.; Zobeck, T.M. The Wolfforth Field Experiment: A Wind Erosion Study. Soil Sci. 1996, 161, 616–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.R.; Li, Z.S.; Mendoza, C. Vertical Profiles of Aeolian Sand Mass Flux. Geomorphology 2003, 49, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertia, R.S.; Santra, P.; Kandpal, B.K.; Prasad, R. Mass–Height Profile and Total Mass Transport of Wind Eroded Aeolian Sediments from Rangelands of the Indian Thar Desert. Aeolian Res. 2010, 2, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, C. Field Observations of Sand Flux and Dust Emission above a Gobi Desert Surface. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 1815–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, T.; Iwagaki, Y. On the Effect of Sand Storm in Controlling the Mouth of the Kiku River. Bulletins 1952, 2, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, K.R.; Mikkelsen, H.E. On the Efficiency of Vertical Array Aeolian Field Traps. Sedimentology 1998, 45, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, A.; Dragovich, D.; Dong, Z. Wind-Borne Sand Mass Flux in Vegetated Surfaces–Wind Tunnel Experiments with Live Plants. Catena 2019, 172, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G. Some Aspects of the Eolian Saltation Load. Sedimentology 1964, 3, 257–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerety, K.M.; Slingerland, R. Nature of the Saltating Population in Wind Tunnel Experiments with Heterogeneous Size-Density Sands. Dev. Sedimentol. 1983, 38, 115–131. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, K.R.; Sorensen, M.; Willetts, B.B. Measurement of Saltation and Wind Strength on Beaches; Barndorff-Nielsen, O.E., Moller, J.T., Rasmussen, K.R., Willets, B.B., Eds.; Department of Theoretical Statistics, Aarhus University: Aarhus Centrum, Denmark, 1985; Volume 8, pp. 301–326. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Raupach, M.R. The Overshoot and Equilibration of Saltation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 20559–20564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, B.R.; Mounla, H. An Experimental Study of Froude Number Effect on Wind-Tunnel Saltation. In Aeolian Grain Transport 1; Barndorff-Nielsen, O.E., Willetts, B.B., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1991; Volume 1, pp. 145–157. ISBN 978-3-211-82269-2/978-3-7091-6706-9. [Google Scholar]
- Weinan, C.; Zuotao, Y.; Jiashen, Z.; Zhiwen, H. Vertical Distribution of Wind-Blown Sand Flux in the Surface Layer, Taklamakan Desert, Central ASIA. Phys. Geogr. 1996, 17, 193–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeley, R.; Blumberg, D.G.; Williams, S.H. Field Measurements of the Flux and Speed of Wind-blown Sand. Sedimentology 1996, 43, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-H.; Guo, X.; Zheng, X.J. Experimental Measurement of Wind-Sand Flux and Sand Transport for Naturally Mixed Sands. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 66, 021305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namikas, S.L. Field Measurement and Numerical Modelling of Aeolian Mass Flux Distributions on a Sandy Beach. Sedimentology 2003, 50, 303–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, A.; Wang, X. The Flux Profile of a Blowing Sand Cloud: A Wind Tunnel Investigation. Geomorphology 2003, 49, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. The Blown Sand Flux over a Sandy Surface: A Wind Tunnel Investigation on the Fetch Effect. Geomorphology 2004, 57, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.J.; Li, Z.S.; Ni, J.R. Sidewall Effects of a Wind Tunnel on Wind Velocity and Mass Flux in Aeolian Sand Transport. Geomorphology 2009, 106, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-J.; Luo, S.-H.; He, L.-H. The Characteristic of Streamwise Mass Flux of Windblown Sand Movement. Geomorphology 2012, 139–140, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, B.O.; Davidson-Arnott, R.G.D. Aeolian Particle Flux Profiles and Transport Unsteadiness. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2014, 119, 1542–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.L.; Kok, J.F. Wind-Invariant Saltation Heights Imply Linear Scaling of Aeolian Saltation Flux with Shear Stress. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, S.; Shao, Y.; Parteli, E.J.R. Scaling Laws in Aeolian Sand Transport Under Low Sand Availability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL097767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Wang, H.; An, Z.; Qu, J. Aeolian Sand Transport over a Dry Playa Surface: Sand Flux Density Profiles, Saltation Layer Height, and Flux Scaling Laws and Implications for Dust Emission Dynamics. Catena 2023, 224, 106970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, Z.; Huang, B.; Pu, O. Wind Tunnel Test of Sand Particle Size Distribution along Height in Blown Sand. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leatherman, S.P. A New Aeolian Sand Trap Design. Sedimentology 1978, 25, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, P.S. An Efficient, Low Cost, Aeolian Sampling System. Geol. Surv. Can. Curr. Res. 1978, Part A, 531–532. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, D.W.T. A New, Instantaneous Aeolian Sand Trap Design for Field Use. Sedimentology 1996, 43, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickling, W.G.; McKenna Neuman, C. Wind Tunnel Evaluation of a Wedge-Shaped Aeolian Sediment Trap. Geomorphology 1997, 18, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnold, R.A. The Measurement of Sand Storms. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1938, 167, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Lv, P.; Zhang, Z.; Qian, G.; Luo, W. Aeolian Transport in the Field: A Comparison of the Effects of Different Surface Treatments. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotnicka, J. Aeolian Vertical Mass Flux Profiles above Dry and Moist Sandy Beach Surfaces. Geomorphology 2013, 187, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Sherman, D.J.; Farrell, E.J.; Ellis, J.T. Variability of the Apparent von Kármán Parameter during Aeolian Saltation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, E.J.; Sherman, D.J. Estimates of the Schmidt Number for Vertical Flux Distributions of Wind-Blown Sand. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 165, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, C.; Lee, D.; Trimble, S.; Key, C. Aeolian Sand Transport over a Wet, Sandy Beach. Aeolian Res. 2021, 51, 100712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strypsteen, G.; Delgado-Fernandez, I.; Derijckere, J.; Rauwoens, P. Fetch-driven Aeolian Sediment Transport on a Sandy Beach: A New Study. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2024, 49, 1530–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Sherman, D.J.; Li, B. Aeolian Creep Transport: A Review. Aeolian Res. 2021, 51, 100711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillette, D.A.; Chen, W. Particle Production and Aeolian Transport from a “Supply-limited” Source Area in the Chihuahuan Desert, New Mexico, United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 5267–5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Aqueveque, V.; Alfaro, S.; Muñoz, R.; Rutllant, J.A.; Caquineau, S.; Le Roux, J.P.; Vargas, G. Aeolian Erosion and Sand Transport over the Mejillones Pampa in the Coastal Atacama Desert of Northern Chile. Geomorphology 2010, 120, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnalds, O.; Gisladottir, F.O.; Orradottir, B. Determination of Aeolian Transport Rates of Volcanic Soils in Iceland. Geomorphology 2012, 167–168, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, J.A.; Nickling, W.G.; Tilson, M. Frequency, Magnitude, and Characteristics of Aeolian Sediment Transport: McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2013, 118, 461–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; An, Z.; Zhang, K.; Qu, J.; Han, Q.; Wang, J. Intermittent Aeolian Saltation Over a Gobi Surface: Threshold, Saltation Layer Height, and High-Frequency Variability. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2020, 125, e2019JF005329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, M.J. A New Wind Erosion Sampler Called “Mendeźs Trap (MT)”. Description and Field Performance Test in a Loamy Sand Soil. Aeolian Res. 2022, 56, 100800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, Z.; Han, G.; Tian, J.; Zhang, H.; Tan, L. Aeolian Saltation over Plateau Gobi: Field Studies in the Zhongzaohuo Gobi Area, Northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2024, 250, 105763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strypsteen, G.; Rauwoens, P. Aeolian Sand Transport on a Natural Beach with Shells and Moist Sand Patches. J. Coast. Res. 2023, 39, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelli, N.; Francis, D.; Sow, M.; Fonseca, R.; Alkatheeri, A.; Bosc, E.; Bergametti, G. The Wind-Blown Sand Experiment in the Empty Quarter Desert: Roughness Length and Saltation Characteristics. Earth Space Sci. 2024, 11, e2024EA003512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, N.P.; Wheeler, B.; Edwards, B.L.; Schallner, J.W.; Macanowicz, N.; Van Zee, J.W.; Courtright, E.M.; Cooper, B.; McCord, S.E.; Browning, D.; et al. Magnitude Shifts in Aeolian Sediment Transport Associated With Degradation and Restoration Thresholds in Drylands. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2025, 130, e2024JG008581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson-Arnott, R.G.D.; Bauer, B.O.; Hesp, P.A.; Ollerhead, J.; Delgado-Fernandez, I. Instantaneous and Mean Aeolian Sediment Transport Rate on Beaches: An Intercomparison of Measurements from Two Sensor Types. J. Coast. Res. 2009, I, 297–301. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson-Arnott, R.G.D.; Bauer, B.O.; Walker, I.J.; Hesp, P.A.; Ollerhead, J.; Chapman, C. High-frequency Sediment Transport Responses on a Vegetated Foredune. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2012, 37, 1227–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Campos, L.; Wijnberg, K.M.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. Field Test of the Accuracy of Laser Particle Counters to Measure Aeolian Sediment Flux. Aeolian Res. 2021, 50, 100676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, M.; Nickling, B.; Wakes, S.; Sherman, D.; Konlechner, T.; Jermy, M.; Geoghegan, P. An Efficient, Self-Orienting, Vertical-Array, Sand Trap. Aeolian Res. 2017, 25, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, M.J.; Funk, R.; Buschiazzo, D.E. Field Wind Erosion Measurements with Big Spring Number Eight (BSNE) and Modified Wilson and Cook (MWAC) Samplers. Geomorphology 2011, 129, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryrear, D.W. A Field Dust Sampler. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1986, 41, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.J.; Cooke, R.U. Wind Erosion. In Soil Erosion; Kirkby, M.J., Morgan, R.P.C., Eds.; Landscape Systems; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK; New York, NY, USA; Brisbane, Australia, 1980; pp. 217–251. ISBN 978-0-471-27802-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kuntze, H.; Beinhauer, R.; Tetzlaff, G. Quantification of Soil Erosion by Wind: I. Final Report of the BMFT Project; Institute of Meteorology and Climatology, University of Hannover: Hannover, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Goossens, D.; Nolet, C.; Etyemezian, V.; Duarte-Campos, L.; Bakker, G.; Riksen, M. Field Testing, Comparison, and Discussion of Five Aeolian Sand Transport Measuring Devices Operating on Different Measuring Principles. Aeolian Res. 2018, 32, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaan, W.P.; Van Den Abeele, G.D. Wind Borne Particle Measurements with Acoustic Sensors. Soil Technol. 1991, 4, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.T.; Morrison, R.F.; Priest, B.H. Detecting Impacts of Sand Grains with a Microphone System in Field Conditions. Geomorphology 2009, 105, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poortinga, A.; Van Rheenen, H.; Ellis, J.T.; Sherman, D.J. Measuring Aeolian Sand Transport Using Acoustic Sensors. Aeolian Res. 2015, 16, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockton, P.H.; Gillette, D.A. Field Measurement of the Sheltering Effect of Vegetation on Erodible Land Surfaces. Land Degrad. Dev. 1990, 2, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, A.C.W. Evaluation of Saltation Flux Impact Responders (Safires) for Measuring Instantaneous Aeolian Sand Transport Intensity. Geomorphology 2004, 59, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, D.J.; Li, B.; Farrell, E.J.; Ellis, J.T.; Cox, W.D.; Maia, L.P.; Sousa, P.H.G.O. Measuring Aeolian Saltation: A Comparison of Sensors. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 59, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchyn, T.E.; Hugenholtz, C.H.; Li, B.; Neuman, C.M.; Steven Sanderson, R. From Particle Counts to Flux: Wind Tunnel Testing and Calibration of the ‘Wenglor’ Aeolian Sediment Transport Sensor. Aeolian Res. 2014, 15, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, D.J.; Swann, C.; Barron, J.D. A High-Efficiency, Low-Cost Aeolian Sand Trap. Aeolian Res. 2014, 13, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Araújo, A.; Bae, J.; Carvalho, A.; Ellis, J.; Parteli, E.; Sherman, D.; Sherman, D.; Swann, C. Measuring Aeolian Saltation Flux Profiles: Comparison of Methods [Data Set]. Zenodo 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Mctainsh, G.; Leys, J.; Raupach, M. Efficiencies of Sediment Samplers for Wind Erosion Measurement. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1993, 31, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.S.; Ni, J.R. Sampling Efficiency of Vertical Array Aeolian Sand Traps. Geomorphology 2003, 52, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lämmel, M.; Rings, D.; Kroy, K. A Two-Species Continuum Model for Aeolian Sand Transport. New J. Phys. 2012, 14, 093037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, O.; Claudin, P.; Andreotti, B. Direct Numerical Simulations of Aeolian Sand Ripples. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15665–15668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P. Calculating Error Statistics for Aeolian Flux Profiles Measurement (MATLAB). Zenodo 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namikas, S.L.; Bauer, B.O.; Edwards, B.L.; Hesp, P.A.; Zhu, Y. Measurements of Aeolian Mass Flux Distributions on a Fine-Grained Beach: Implications for Grain-Bed Collision Mechanics. J. Coast. Res. 2009, I, 337–341. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, F.; Zhao, A. Velocity Profile of a Sand Cloud Blowing over a Gravel Surface. Geomorphology 2002, 45, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.D.; Valance, A.; Dupont, P.; Ould El Moctar, A. Scaling Laws in Aeolian Sand Transport. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 094501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).