Three-Dimensional Morphometric Analysis of the Columbretes Grande Turbidite Channel (Ebro Continental Margin, NW Mediterranean)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geomorphological Setting
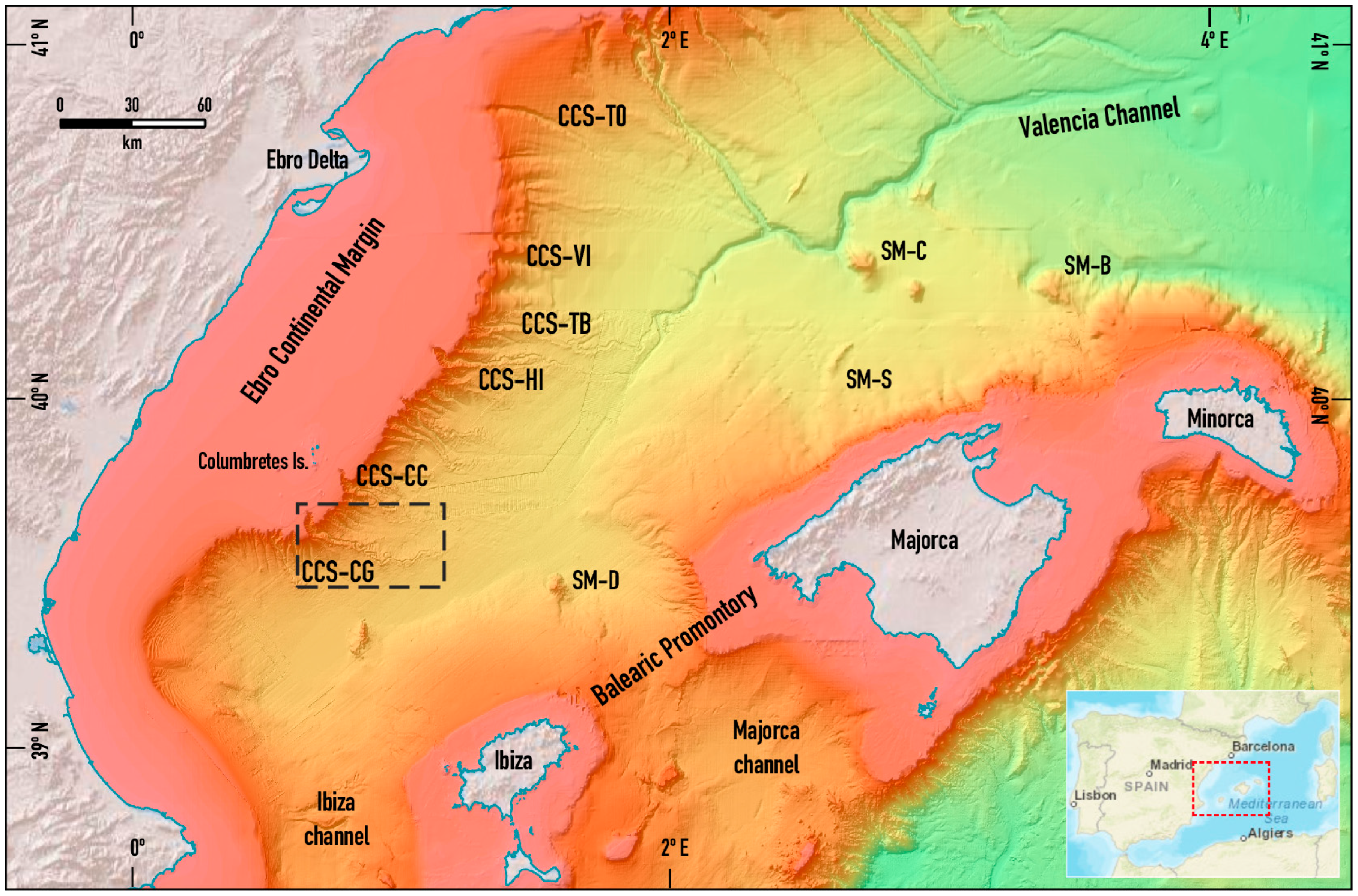
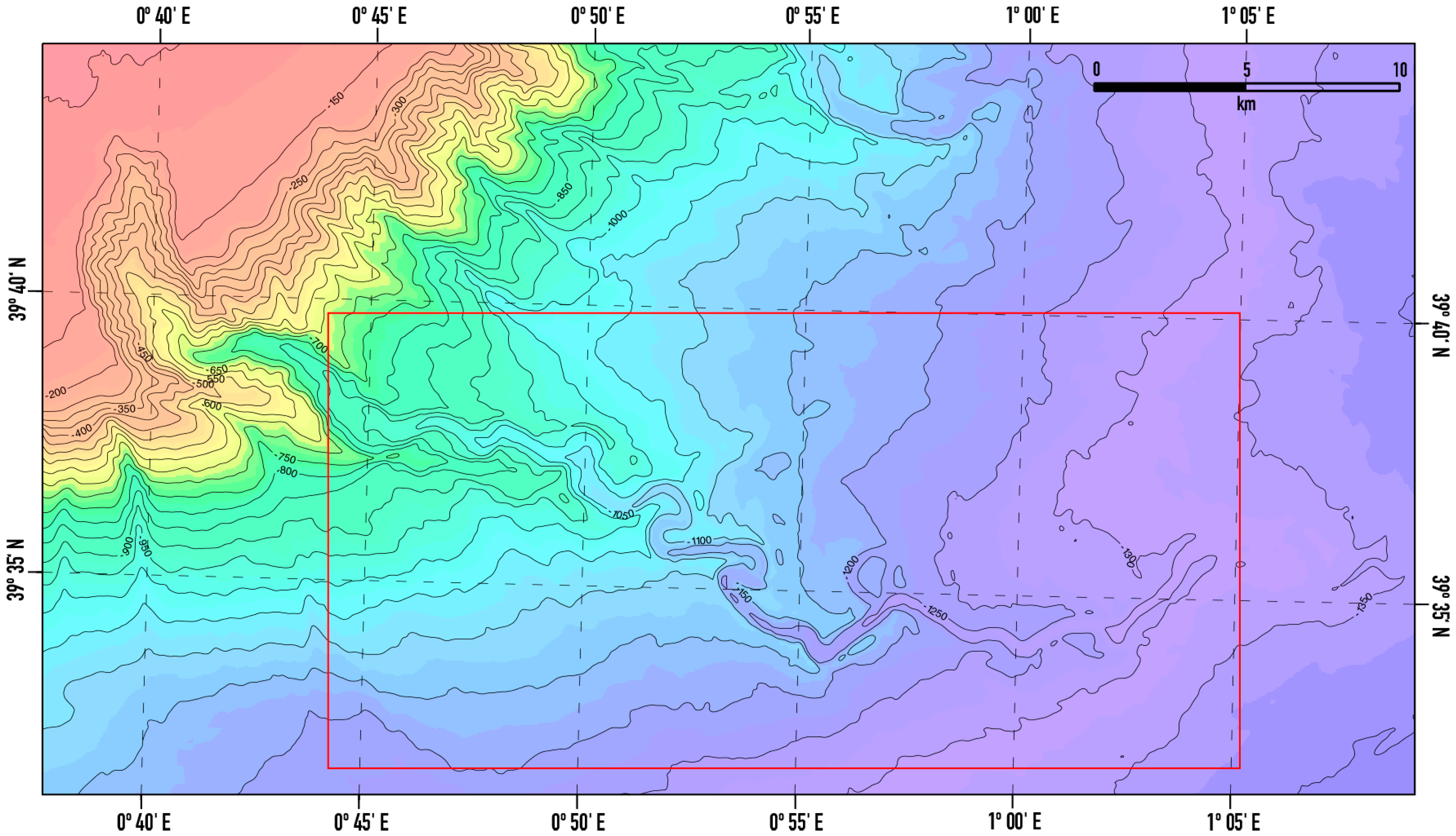
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data Acquisition and Preparation
3.2. Methodology
3.2.1. Software and Tools for 3D Morphometric Analysis
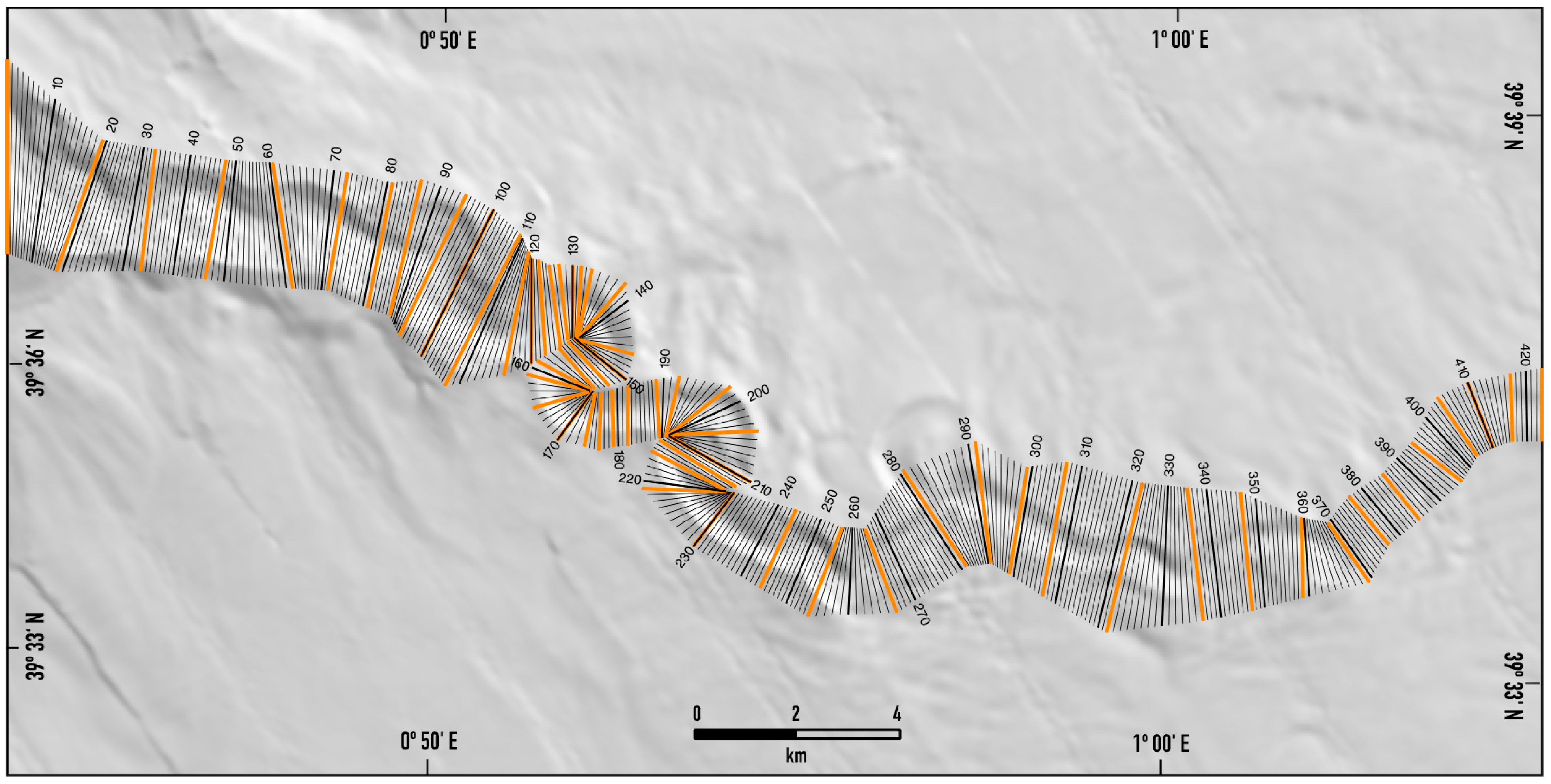
3.2.2. Borders and Channel Axis
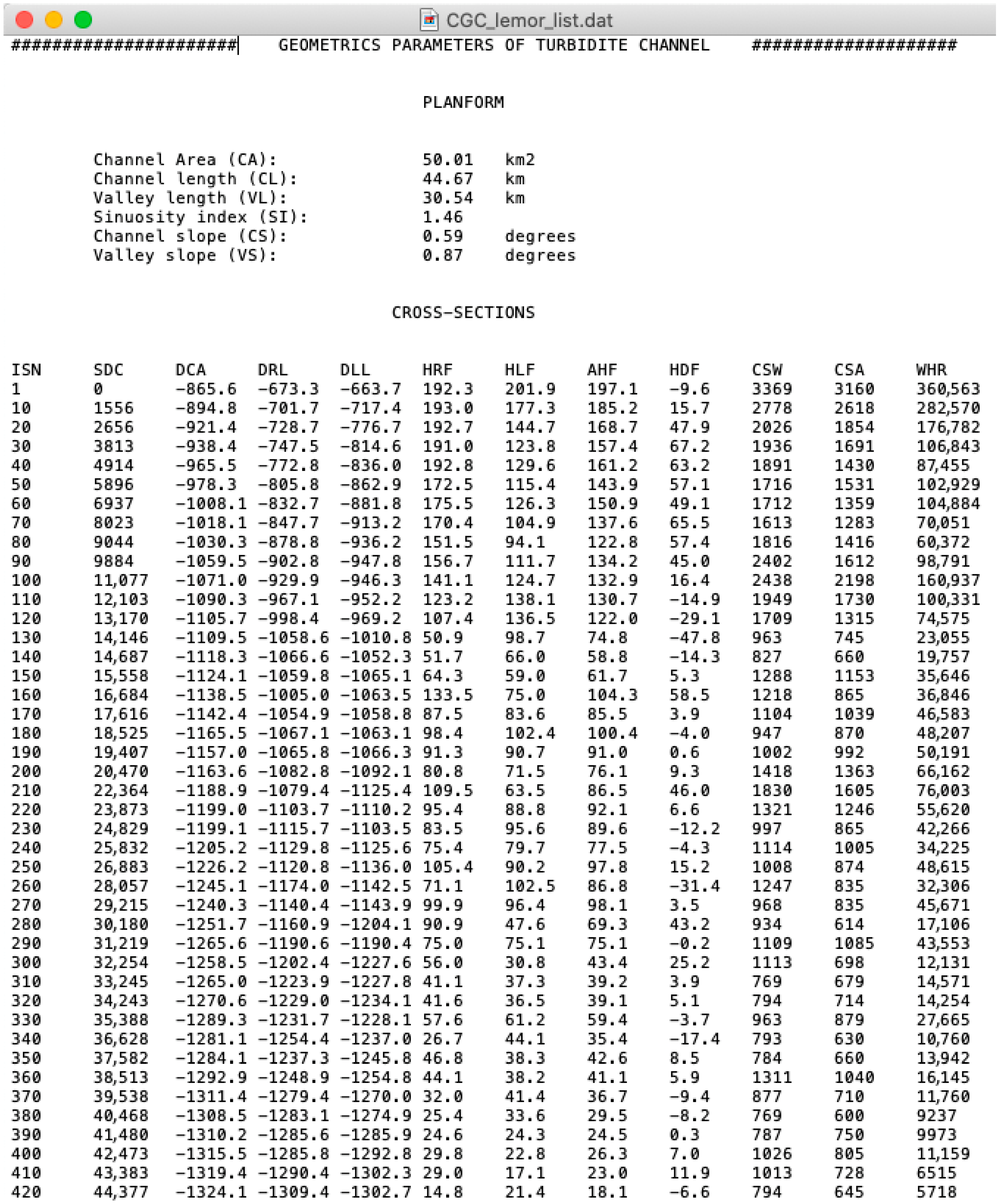
3.2.3. Determination of the Geometric Parameters of the Channel

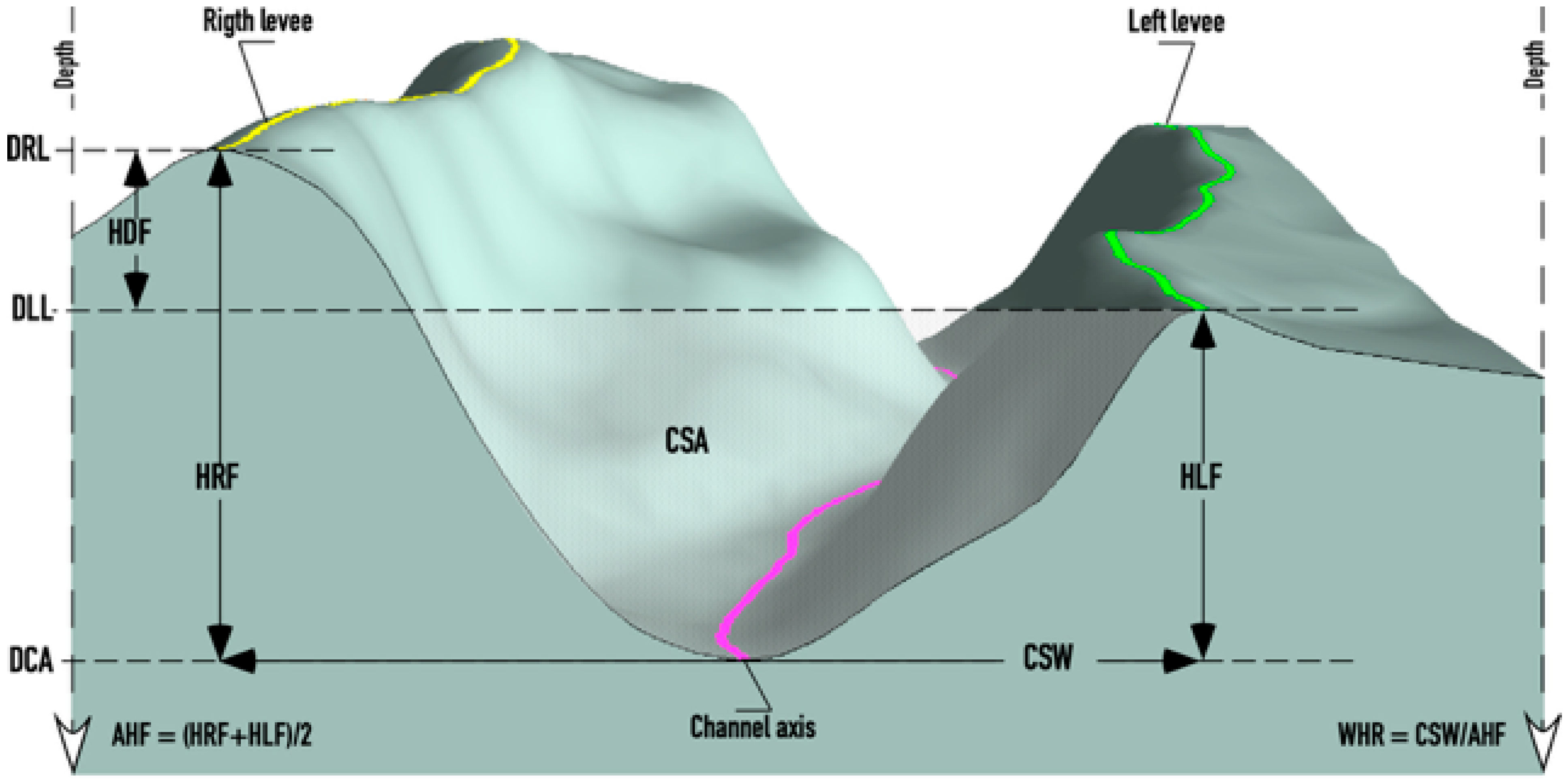
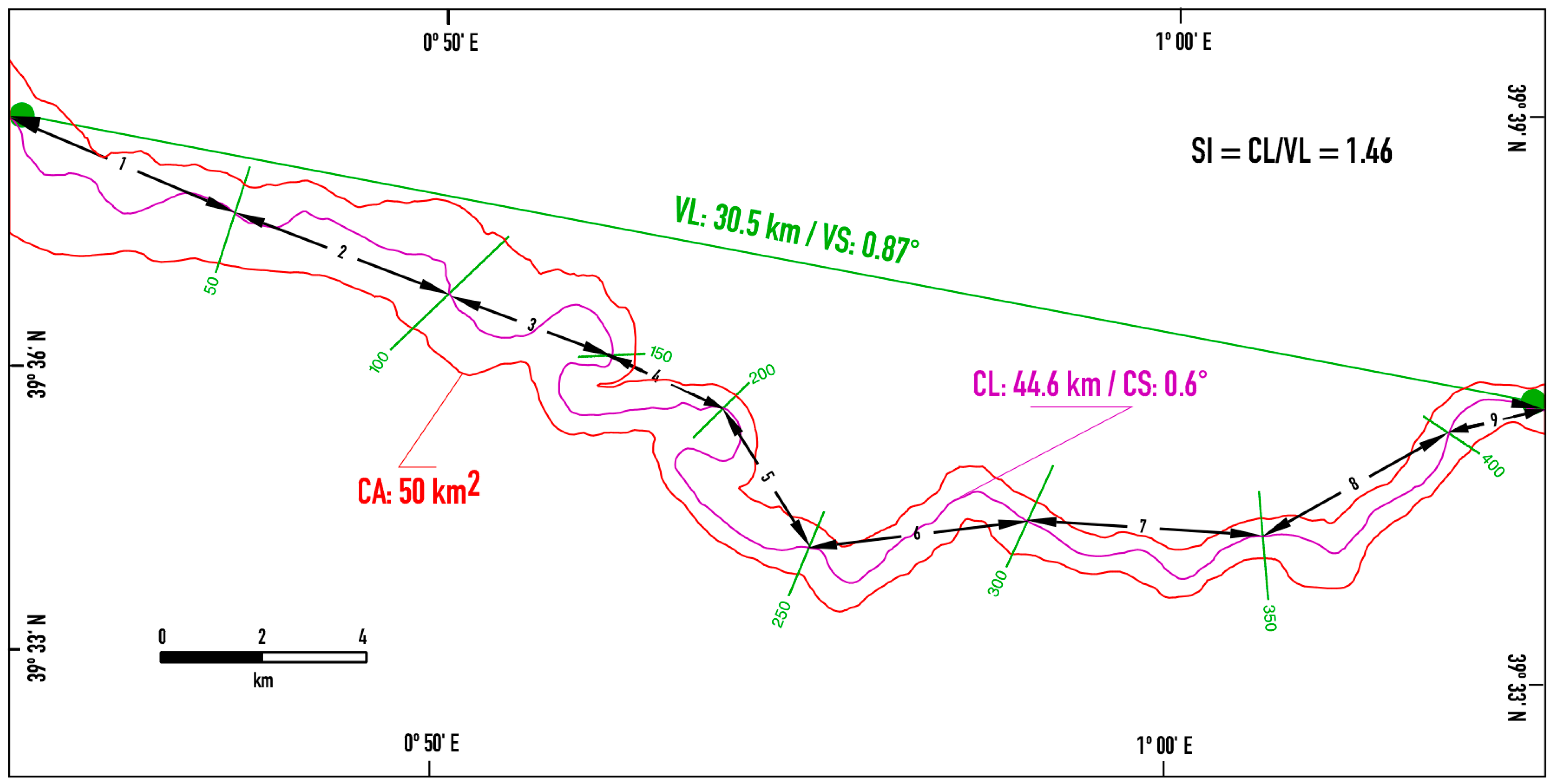
- Planform parameters
- Channel area (CA): It is the area of the polygon formed by the borders of the channel, between the first and last sections;
- Channel length (CL): It is the length of the channel along its axis;
- Valley length (VL): It is the length of a straight line that directly joins the first and last control sections of the channel;
- Sinuosity index (SI): It is the ratio between the length of the channel and the length of the valley;
- Channel slope (CS): It is the slope of the axis of the channel;
- Valley slope (VS): This is the slope of the valley according to VL.
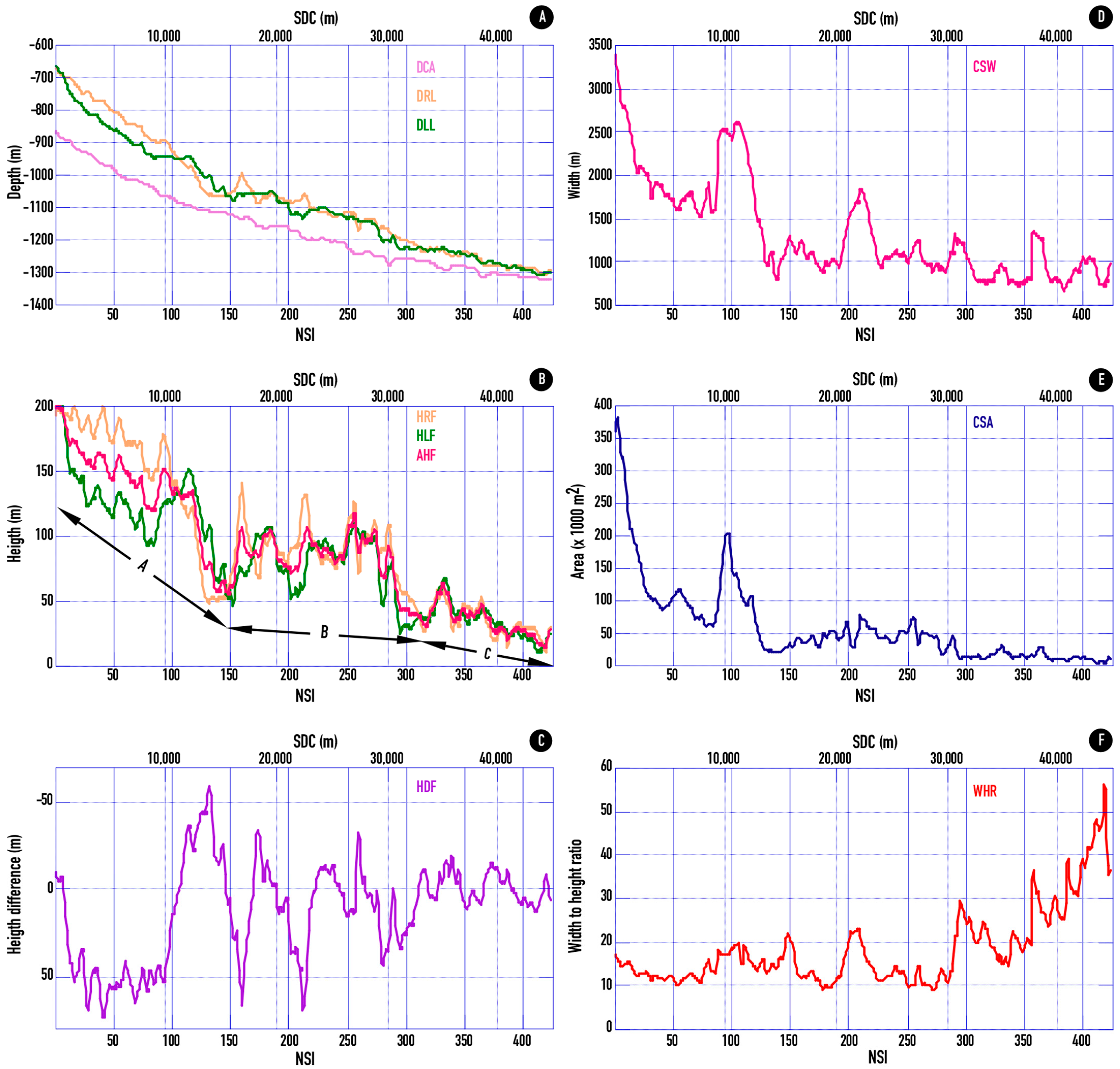
- Cross-sectional parameters.
- 7.
- Channel length to section (SDC): It is the length of the channel along its axis between the first section and the section considered;
- 8.
- Depth of the channel axis (DCA): It is the depth of the deepest point of the section;
- 9.
- Depth of the crest of the right levee (DRL). It corresponds to the depth of the highest point of the right levee;
- 10.
- Depth of the crest of the left levee (DLL): It corresponds to the depth of the highest point of the left levee;
- 11.
- Right flank height (HRF): It is measured with respect to the depth of the channel axis in the section;
- 12.
- Height of the left flank (HLF): It is measured with respect to the depth of the channel axis in the section;
- 13.
- 14.
- Height difference between flanks (HDF): It is the difference in height between the right and left flanks;
- 15.
- Channel width (CSW): It is the distance horizontally between the lines perpendicular to the crests of the levees;
- 16.
- Channel section area (CSA). Defined by the polygon resulting from the intersection between the line representing the width of the channel and the section of the channel itself;
- 17.
- Width-to-height ratio of the section (WHR). This parameter represents the ratio between the channel width and the average height of flanks.
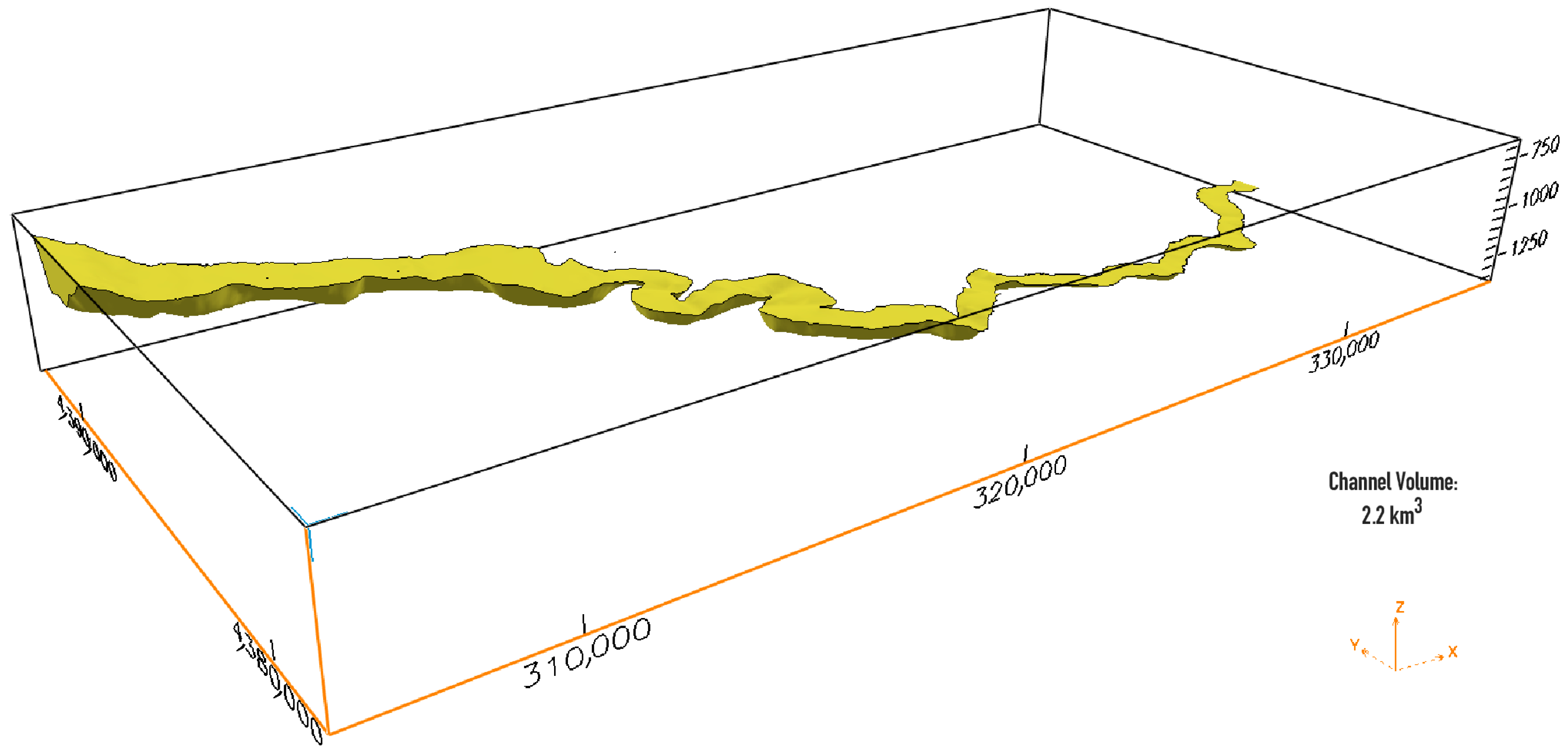
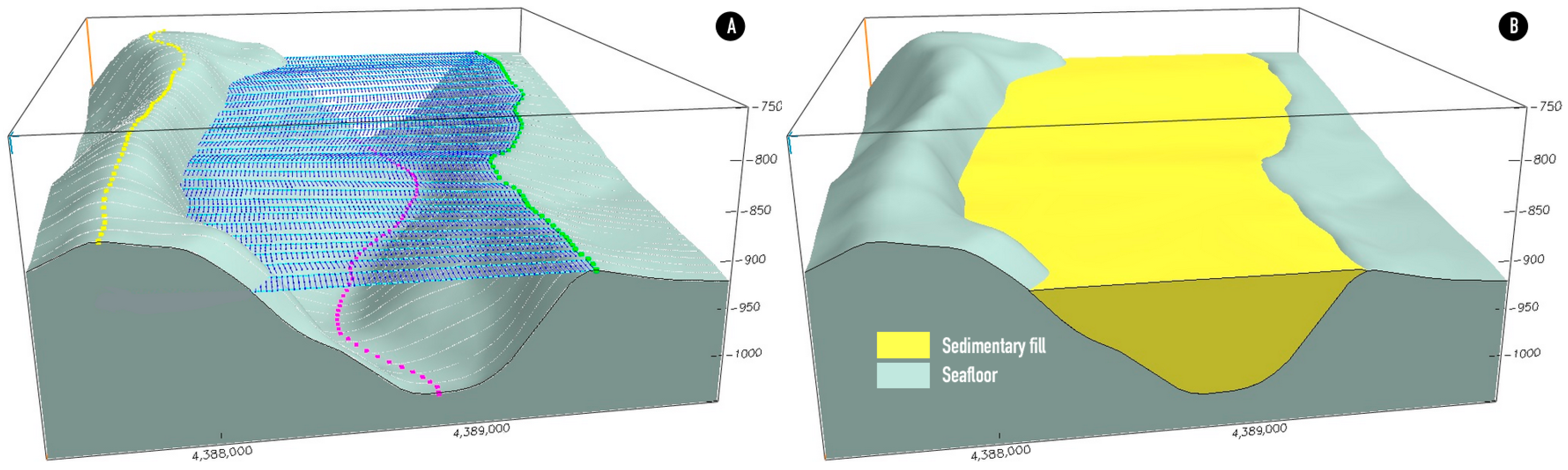
3.2.4. Three-Dimensional Visualization and Channel Volume Calculation
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. General Channel Morphology
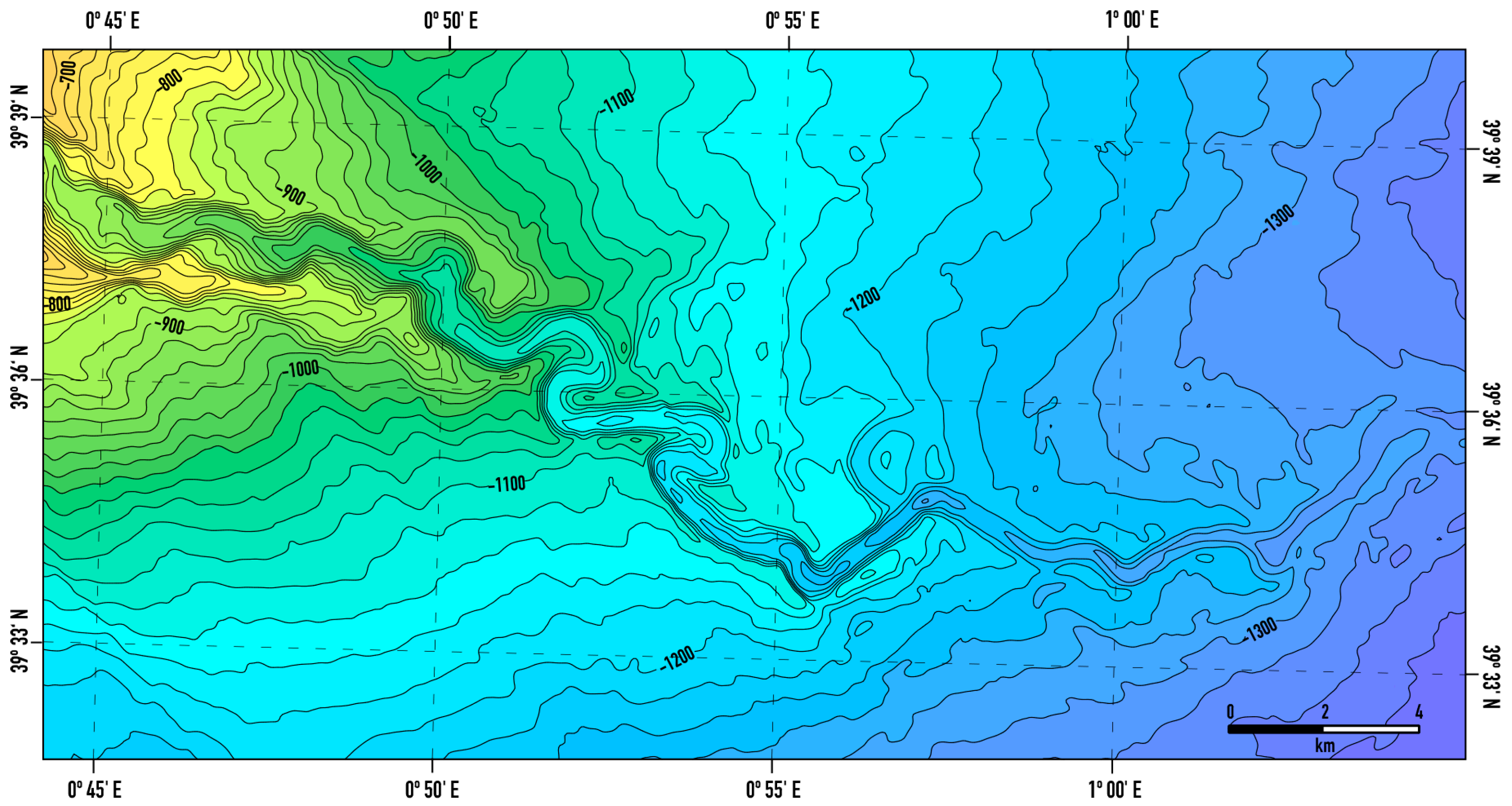



4.2. Quantitative Channel Analysis
4.2.1. Planform Geometry
- Area and length
- Slope
- Sinuosity
- Channel slope/sinuosity relationship

4.2.2. Cross-Sectional Geometry
- Depth of axis channel and levees
- Channel height
- Height difference between flanks
- Width
- Section area
- Width-to-height ratio
4.3. 3D Visualization and Channel Volume
4.4. Morphosedimentary Interpretation
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHF | Average Height of Flanks |
| CA | Channel Area |
| CCS | Canyon–Channel System |
| CGC | Columbretes Grande Channel |
| CL | Channel Length |
| CLS | Channel–Levee System |
| CS | Channel Slope |
| CSA | Channel Section Area |
| CSW | Channel Section Width |
| DCA | Depth of the Channel Axis |
| DLL | Depth of the crest of the Left Levee |
| DRL | Depth of the crest of the Right Levee |
| ECM | Ebro Continental Margin |
| HDF | Height Difference between Flanks |
| HLF | Height of the Left Flank |
| HRF | Height of the Right Flank |
| ISN | Interpolated Section Number |
| SDC | Section Distance since the beginning of the Channel |
| SI | Sinuosity Index |
| TC | Turbidite Channel |
| VL | Valley Length |
| VS | Valley Slope |
| WHR | Width-to-Height Ratio of the section |
Appendix A
References
- Babonneau, N.; Savoye, B.; Cremer, M.; Klein, B. Morphology and Architecture of the Present Canyon and Channel System of the Zaire Deep-Sea Fan. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2002, 19, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canals, M.; Casamor, J.L.; Lastras, G.; Monaco, A.; Acosta, J.; Berné, S.; Loubrieu, B.; Weaver, P.P.E.; Grehan, A.; Dennielou, B. The Role of Canyons in Strata Formation. Oceanography 2004, 17, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasenhündl, M.; Talling, P.J.; Pope, E.L.; Baker, M.L.; Heijnen, M.S.; Ruffell, S.C.; Da Silva Jacinto, R.; Gaillot, A.; Hage, S.; Simmons, S.M.; et al. Morphometric Fingerprints and Downslope Evolution in Bathymetric Surveys: Insights into Morphodynamics of the Congo Canyon-Channel. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 12, 1381019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skene, K.I.; Piper, D.J.W.; Hill, P.S. Quantitative Analysis of Variations in Depositional Sequence Thickness from Submarine Channel Levees. Sedimentology 2002, 49, 1411–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fildani, A. Submarine Canyons: A Brief Review Looking Forward. Geology 2017, 45, 383–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, C.M.G.; Ryan, W.B.F. Sedimentary Features Associated with Channel Overbank Flow: Examples from the Monterey Fan. Mar. Geol. 2000, 163, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.D.; Pickering, K.T. Submarine Channels: Processes and Architecture; Vallis Press: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wonham, J.P.; Jayr, S.; Mougamba, R.; Chuilon, P. 3D Sedimentary Evolution of a Canyon Fill (Lower Miocene-Age) from the Mandorove Formation, Offshore Gabon. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2000, 17, 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, J.; McCaffrey, B.; Kneller, B. A Process Model for the Evolution, Morphology, and Architecture of Sinuous Submarine Channels. J. Sediment. Res. 2000, 70, 434–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damuth, J.E.; Kowsmann, R.O.; Flood, R.D.; Belderson, R.H.; Gorini, M.A. Age Relationships of Distributary Channels on Amazon Deep-Sea Fan: Implications for Fan Growth Pattern. Geology 1983, 11, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deptuck, M.E.; Sylvester, Z. Submarine Fans and Their Channels, Levees, and Lobes. In Submarine Geomorphology; Micallef, A., Krastel, S., Savini, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 273–299. ISBN 978-3-319-57852-1. [Google Scholar]
- Flood, R.D.; Manley, P.L.; Kowsmann, R.O.; Appi, C.J.; Pirmez, C. Seismic Facies and Late Quaternary Growth of Amazon Submarine Fan. In Seismic Facies and Sedimentary Processes of Submarine Fans and Turbidite Systems; En, P.W., Link, M.H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 415–434. [Google Scholar]
- Canals, M.; Alonso, B.; Ercilla, G.; Farrán, M.; Sorribas, J.; Baraza, J.; Calafat, A.M.; Casamor, J.L.; Estrada, F.; Masson, D.; et al. Dinámica de los canales submarinos del talud y el glacis continentales del Ebro (Mediterráneo-noroccidental) a partir de imágenes acústicas de alta resolución. Geogaceta 1996, 20, 363–367. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, B.; Ercilla, G. Introducción: Sistemas turbidíticos y canales medio-oceánicos. In Valles Submarinos y Sistemas Turbidíticos Modernos; En, B.A., Ercilla, G., Eds.; CSIC: Barcelona, Spain, 2000; pp. 19–66. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam, G.; Moiola, R.J. Submarine Fans: Characteristics, Models, Classification, and Reservoir Potential. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1988, 24, 383–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nibbelink, K. Modeling Deepwater Reservoir Analogs through Analysis of Recent Sediments Using Coherence, Seismic Amplitude, and Bathymetry Data, Sigsbee Escarpment, Green Canyon, Gulf of Mexico. Lead. Edge 1999, 18, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimer, P.; Slatt, R.M. Turbidite Systems; Part I, Sequence and Seismic Stratigraphy. Lead. Edge 1999, 18, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonnesu, F. 3D Seismic Images of a Low-Sinuosity Slope Channel and Related Depositional Lobe (West Africa Deep-Offshore). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2003, 20, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, R.D.; Damuth, J.E. Quantitative Characteristics of Sinuous Distriburary Channels on the Amazon Deep-Sea Fan. GSA Bull. 1987, 98, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.D.; Kenyon, N.H.; Pickering, K.T. Quantitative Analysis of the Geometry of Submarine Channels: Implications for the Classification of Submarine Fans. Geology 1992, 20, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaucke, I.; Hesse, R.; Ryan, W.B.F. Flow Parameters of Turbidity Currents in a Low-Sinuosity Giant Deep-Sea Channel. Sedimentology 1997, 44, 1102–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, W.R.; Normark, W.R. Sedimentologic and Geometric Criteria for Comparing Modern and Ancient Sandy Turbidite Elements. In Proceedings of the GCSSEPM Foundation 20th Annual Research Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 3–6 December 2000; Deep-Water Reservoirs of the World. Volume 1, pp. 606–623. [Google Scholar]
- Stow, D.A.V.; Mayall, M. Deep-Water Sedimentary Systems: New Models for the 21st Century. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2000, 17, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.D.; Gardiner, A.R. Outcrop Analogues for Deep-Water Channel and Levee Genetic Units from the Grès d’Annot Turbidite System. In Proceedings of the GCSSEPM Foundation 20th Annual Research Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 3–6 December 2000; Deep-Water Reservoirs of the World. pp. 175–189. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, R. 3D Modeling of Stratigraphic Heterogeneity in Channelized Reservoirs, Methods and Applications in Seismic Attributes Facies Classification. Can. Soc. Explor. Geophys. (CSEG) Rec. 2004, 3, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada, F.; Ercilla, G.; Alonso, B. Quantitative Study of a Magdalena Submarine Channel (Caribbean Sea): Implications for Sedimentary Dynamics. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2005, 22, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amblas, D.; Canals, M.; Lastras, G.; Berne, S.; Loubrieu, S. Imaging the Seascapes of the Mediterranean. Oceanography 2004, 17, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, O.; Lastras, G.; Canals, M.; Olabarrieta, M.; González, M.; Aniel-Quiroga, Í.; Otero, L.; Durán, R.; Amblas, D.; Casamor, J.L.; et al. The BIG’95 Submarine Landslide-Generated Tsunami: A Numerical Simulation. J. Geol. 2012, 120, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.H. Estimated Post-Messinian Sediment Supply and Sedimentation Rates on the Ebro Continental Margin, Spain. Mar. Geol. 1990, 95, 395–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, J.; Canals, M.; López-Martínez, J.; Muñoz, A.; Herranz, P.; Urgeles, R.; Palomo, C.; Casamor, J.L. The Balearic Promontory Geomorphology (Western Mediterranean): Morphostructure and Active Processes. Geomorphology 2003, 49, 177–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, B.; Canals, M.; Palanques, A.; Rehault, J.-P. A Deep-Sea Channel in the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea: Morphology and Seismic Structure of the Valencia Channel and Its Surroundings. Mar. Geophys. Res. 1995, 17, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canals, M.; Casamor, J.L.; Urgeles, R.; Lastras, G.; Calafat, A.M.; Batist, M.; Masson, D.; Berné, S.; Alonso, B.; Hughes-Clarke, J.E. The Ebro Continental Margin, Western Mediterranean Sea: Interplay between Canyon-Channel Systems and Mass Wasting Processes. In Proceedings of the Deep-Water Reservoirs of the World, GCSSEPM Foundation 20th Annual Research Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 3–6 December 2000; CD edition. pp. 152–174. [Google Scholar]
- Maillard, A.; Mauffret, A. Structure and Volcanism of the Valencia Trough, North-Western Mediterranean. Bull. Soc. Geol. Fr. 1993, 164, 365–383. [Google Scholar]
- Lastras, G.; Canals, M.; Urgeles, R.; De Batist, M.; Calafat, A.M.; Casamor, J.L. Characterisation of the Recent BIG’95 Debris Flow Deposit on the Ebro Margin, Western Mediterranean Sea, after a Variety of Seismic Reflection Data. Mar. Geol. 2004, 213, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, S.; Ryan, W.B.F.; Normark, W.R. Modes of Development of Slope Canyons and Their Relation to Channel and Levee Features on the Ebro Sediment Apron, off-Shore Northeastern Spain. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1987, 4, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.H.; Maldonado, A. Factors Controlling Depositional Patterns of Ebro Turbidity Systems, Mediterranean Sea. AAPG Bull. 1988, 72, 698–716. [Google Scholar]
- Danobeitia, J.J.; Alonso, B.; Maldonado, A. Geological Framework of the Ebro Continental Margin and Surrounding Areas. Mar. Geol. 1990, 95, 265–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, B.; Canals, M.; Got, H.; Maldonado, A. Sea Valleys and Related Depositional Systems in the Gulf of Lions and Ebro Continental Margins. AAPG Bull. 1991, 75, 1195–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, B. El sistema turbidítico del Ebro: Evolución morfo-sedimentaria durante el Plio-Cuaternario. In Valles Submarinos y Sistemas Turbidíticos Modernos; En, B.A., Ercilla, G., Eds.; CSIC: Barcelona, Spain, 2000; pp. 91–112. [Google Scholar]
- Medialdea, T.; Somoza, L.; Leon, R.; Lobato, A. Mapa Geomorfológico. In Mar Balear; Geological and Mining Institute: Madrid, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Amblas, D.; Gerber, T.P.; Canals, M.; Pratson, L.F.; Urgeles, R.; Lastras, G.; Calafat, A.M. Transient Erosion in the Valencia Trough Turbidite Systems, NW Mediterranean Basin. Geomorphology 2011, 130, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casamor, J.L. Introducción al 3-D Con El Programa earthVision; Universitat de Barcelona: Barcelona, Spain, 2013; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Guglielmo, G.; Jackson, M.P.A.; Vendeville, B.C. Three-Dimensional Visualization of Salt Walls and Associated Fault Systems. AAPG Bull. 1997, 81, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casamor, J.L. Modelización y Visualización 3-D En Geociencias Marinas. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Nordfjord, S.; Goff, J.A.; Austin, J.A.; Sommerfield, C.K. Seismic Geomorphology of Buried Channel Systems on the New Jersey Outer Shelf: Assessing Past Environmental Conditions. Mar. Geol. 2005, 214, 339–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibling, M.R. Width and Thickness of Fluvial Channel Bodies and Valley Fills in the Geological Record: A Literature Compilation and Classification. J. Sediment. Res. 2006, 76, 731–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, K.M.; Mohrig, D. Quantifying the Morphology and Growth of Levees in Aggrading Submarine Channels. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, 2007JF000896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balic, N.; Koch, B. Canscan—An Algorithm for Automatic Extraction of Canyons. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHargue, T.; Pyrcz, M.J.; Sullivan, M.D.; Clark, J.D.; Fildani, A.; Romans, B.W.; Covault, J.A.; Levy, M.; Posamentier, H.W.; Drinkwater, N.J. Architecture of Turbidite Channel Systems on the Continental Slope: Patterns and Predictions. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2011, 28, 728–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrillo-Escoriza, J.; Lobo, F.J.; Puga-Bernabéu; Bárcenas, P.; Mendes, I.; Pérez-Asensio, J.N.; Durán, R.; Andersen, T.J.; Carrión-Torrente; García, M.; et al. Variable Downcanyon Morphology Controlling the Recent Activity of Shelf-Incised Submarine Canyons (Alboran Sea, Western Mediterranean). Geomorphology 2024, 453, 109127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, G.; Lin, C.; Liu, W.; Li, Q.; Feng, Z.; Ning, S. Quantitative Morphometric Analysis of a Deep-Water Channel in the Taranaki Basin, New Zealand. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2023, 42, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirmez, C.; Imran, J. Reconstruction of Turbidity Currents in Amazon Channel. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2003, 20, 823–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossu, R.; Wells, M.G. The Evolution of Submarine Channels under the Influence of Coriolis Forces: Experimental Observations of Flow Structures. Terra Nova 2013, 25, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.; Peakall, J.; Hodgson, D.M.; Bradbury, W.; Booth, A.D. Latitudinal Changes in Submarine Channel-Levee System Evolution, Architecture and Flow Processes. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 976852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Satoh, M.; Okamura, Y. Channel-Levee Complexes, Terminal Deep-Sea Fan and Sediment Wave Fields Associated with the Toyama Deep-Sea Channel System in the Japan Sea. Mar. Geol. 1998, 147, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.B.; Pantin, H.M. Channel-Axis, Overbank and Drift Sediment Waves in the Southern Hikurangi Trough, New Zealand. Mar. Geol. 2002, 192, 123–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posamentier, H.W. Depositional Elements Associated with a Basin Floor Channel-Levee System: Case Study from the Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2003, 20, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumm, S.A. Sinuosity of Alluvial Rivers on the Great Plains. GSA Bull. 1963, 74, 1089–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumm, S.A.; Khan, H.R. Experimental Study of Channel Patterns. GSA Bull. 1972, 83, 1755–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, Z.; Pirmez, C. Latitudinal Changes in the Morphology of Submarine Channels: Reevaluating the Evidence for the Influence of the Coriolis Force. In Latitudinal Controls on Stratigraphic Models and Sedimentary Concepts; Fraticelli, C.M., Ed.; SEPM (Society for Sedimentary Geology): Claremore, OK, USA, 2019; pp. 82–92. ISBN 978-1-56576-346-3. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, J.D.; Pickering, K.T. Architectural Elements of Submarine Channels, Growth Patterns and Application to Hydrocarbon Exploration. AAPG Bull. 1996, 80, 194–221. [Google Scholar]
- Pettinga, L.; Jobe, Z.; Shumaker, L.; Howes, N. Morphometric Scaling Relationships in Submarine Channel–Lobe Systems. Geology 2018, 46, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatt, R.M.; Weimer, P. Turbidite Systems; Part 2, Subseismic-Scale Reservoir Characteristics. Lead. Edge 1999, 18, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirmez, C.; Beaubouef, R.T.; Friedmann, S.J.; Mohrig, D.C. Equilibrium Profile and Baselevel in Submarine Channels: Examples from Late Pleistocene Systems and Implications for the Architecture of Deepwater Reservoirs. In Proceedings of the Deep-water Reservoirs of the World, GCSSEPM Foundation 20th Annual Research Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 3–6 December 2000; pp. 782–804. [Google Scholar]
- Schumm, S.A. Evolution and Response of the Fluvial System: Sedimentologic Implications. Soc. Econ. Paleon. Mineral. Spec. Pub 1981, 31, 19–29. [Google Scholar]
- Mayall, M.; Jones, E.; Casey, M. Turbidite Channel Reservoirs—Key Elements in Facies Prediction and Effective Development. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2006, 23, 821–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, I.; Carr, D.; Cirilli, P.; Drinkwater, N.; McCormick, D.; Tilke, P.; Thurmond, J. Use of 3D Digital Analogues as Templates in Reservoir Modelling. Pet. Geosci. 2000, 6, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittori, J.; Morash, A.; Savoye, B.; Marsset, T.; Lopez, M.; Batist, M.; Droz, L.; Cremer, L. The Quaternary Congo Deep-Sea Fan: Preliminary Results on Reservoir Complexity in Turbiditic Systems Using 2D High Resolution Seismic and Multibeam Data. In Proceedings of the Deep-water Reservoirs of the World, GCSSEPM Foundation 20th Annual Research Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 3–6 December 2000; CD edition. pp. 1045–1058. [Google Scholar]

| Reach | CL (m) | VL (m) | SI | CS (°) | VS (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5896 | 4840 | 1.22 | 1.10 | 1.33 |
| 2 | 5181 | 4607 | 1.12 | 0.99 | 1.15 |
| 3 | 4481 | 3228 | 1.39 | 0.68 | 0.94 |
| 4 | 4912 | 2431 | 2.02 | 0.43 | 0.93 |
| 5 | 6413 | 3229 | 1.99 | 0.51 | 1.11 |
| 6 | 5371 | 4247 | 1.26 | 0.28 | 0.44 |
| 7 | 5328 | 4559 | 1.17 | 0.28 | 0.32 |
| 8 | 4891 | 4098 | 1.19 | 0.36 | 0.44 |
| 9 | 2198 | 2001 | 1.10 | 0.32 | 0.61 |
| All channel | 44,671 | 30,540 | 1.46 | 0.59 | 0.87 |
| Cross-Sections | DCA (m) | DRL (m) | DLL (m) | HRF (m) | HLF (m) | AHF (m) | HDF (m) | CSW (m) | CSA (m2) | WHR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maxim value | −865.6 | −673.3 | −663.7 | 198.9 | 202.0 | 200.1 | 73.9 | 3369 | 379,058 | 55.91 |
| Mean value | −1165.0 | −1069.9 | −1082.8 | 95.1 | 82.2 | 88.7 | 12.9 | 1326 | 58,547 | 17.97 |
| Minim value | −1327.8 | −1311.8 | −1309.7 | 10.4 | 11.5 | 13.2 | −58.1 | 659 | 3455 | 8.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Casamor, J.L. Three-Dimensional Morphometric Analysis of the Columbretes Grande Turbidite Channel (Ebro Continental Margin, NW Mediterranean). Geosciences 2025, 15, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15080318
Casamor JL. Three-Dimensional Morphometric Analysis of the Columbretes Grande Turbidite Channel (Ebro Continental Margin, NW Mediterranean). Geosciences. 2025; 15(8):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15080318
Chicago/Turabian StyleCasamor, José Luis. 2025. "Three-Dimensional Morphometric Analysis of the Columbretes Grande Turbidite Channel (Ebro Continental Margin, NW Mediterranean)" Geosciences 15, no. 8: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15080318
APA StyleCasamor, J. L. (2025). Three-Dimensional Morphometric Analysis of the Columbretes Grande Turbidite Channel (Ebro Continental Margin, NW Mediterranean). Geosciences, 15(8), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15080318






