Relative Sea-Level Changes During the Upper Holocene as Determined by Reference to Beachrock Formations Along the South Coastline of Cyprus and Their Correlation with the Archaeological Context of the Island
Abstract
1. Introduction
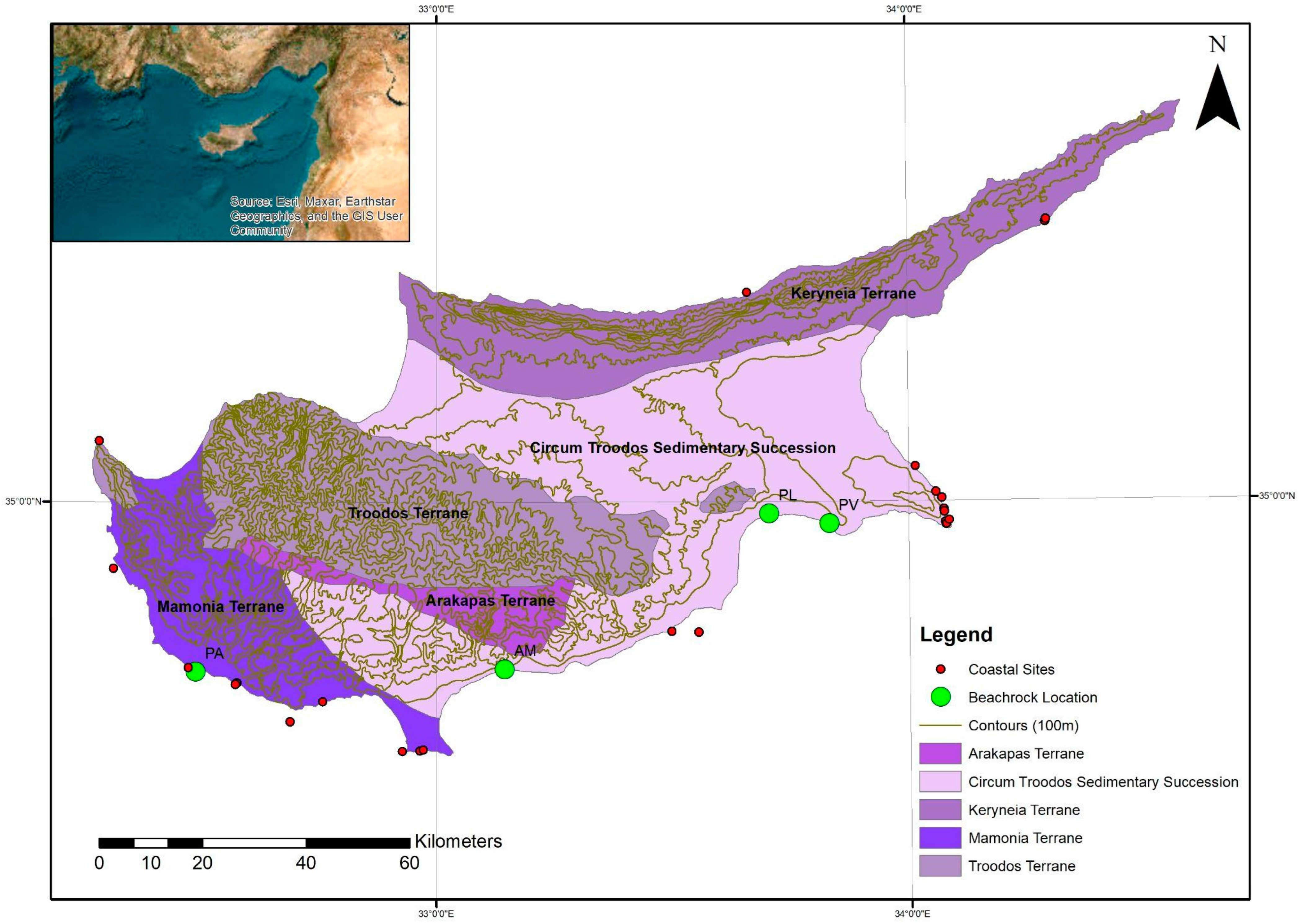
2. Study Area and Regional Tectonic Framework
3. Archaeological Context
4. Methodology
4.1. Fieldwork and Laboratory
4.2. Luminescence Dating
4.3. Reconstruction of the Relative Sea Level
5. Results
5.1. Beachrock Distribution
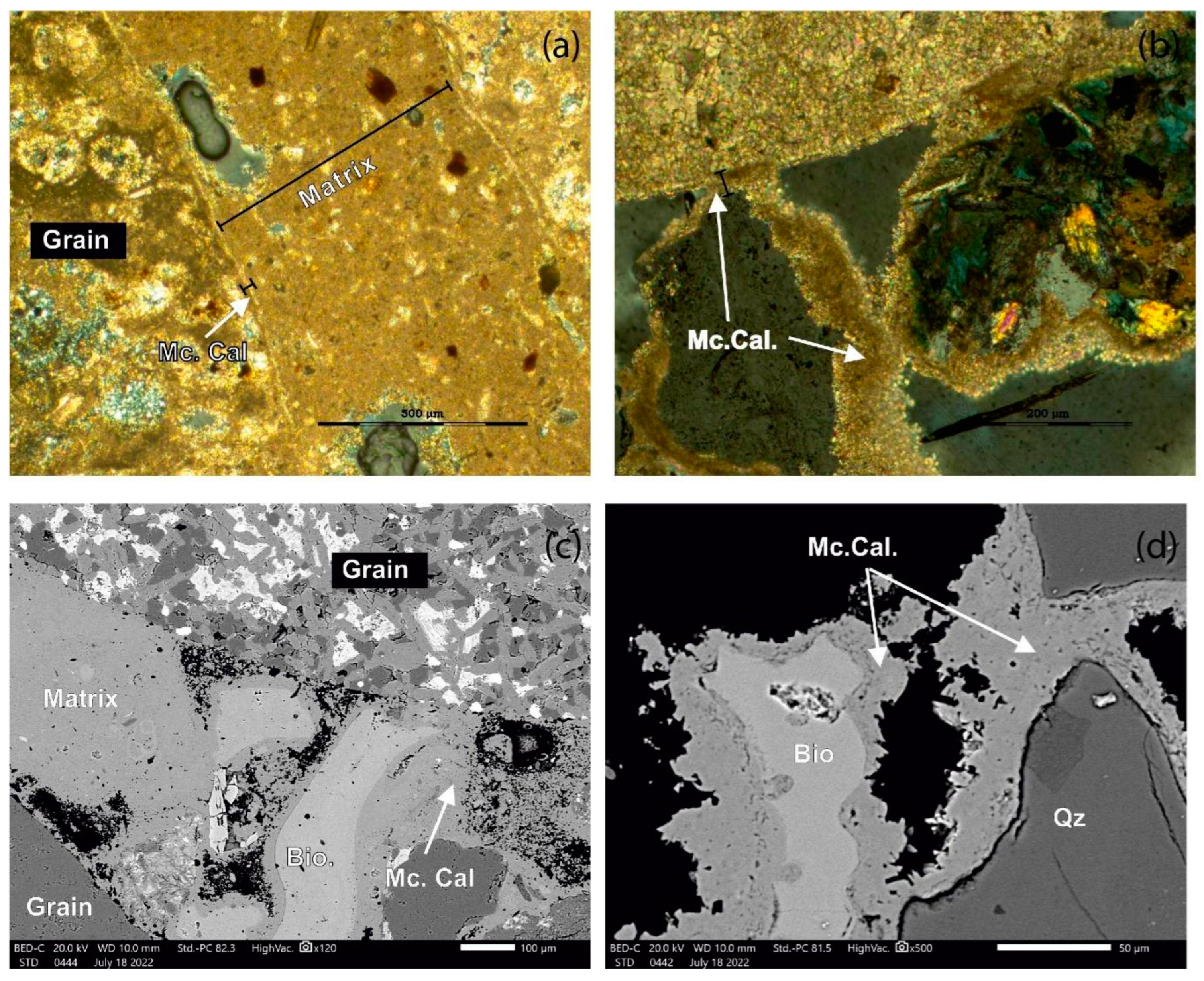
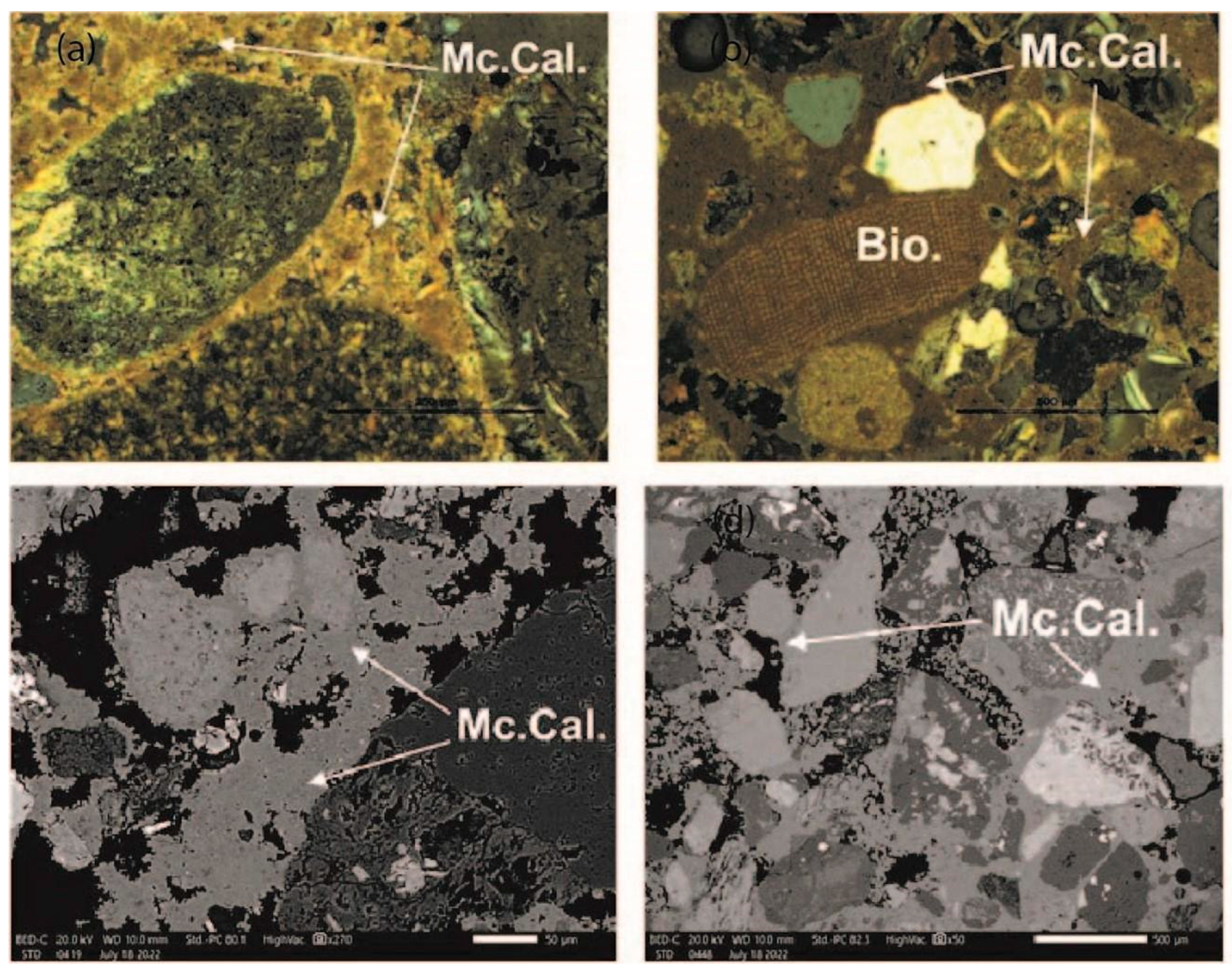
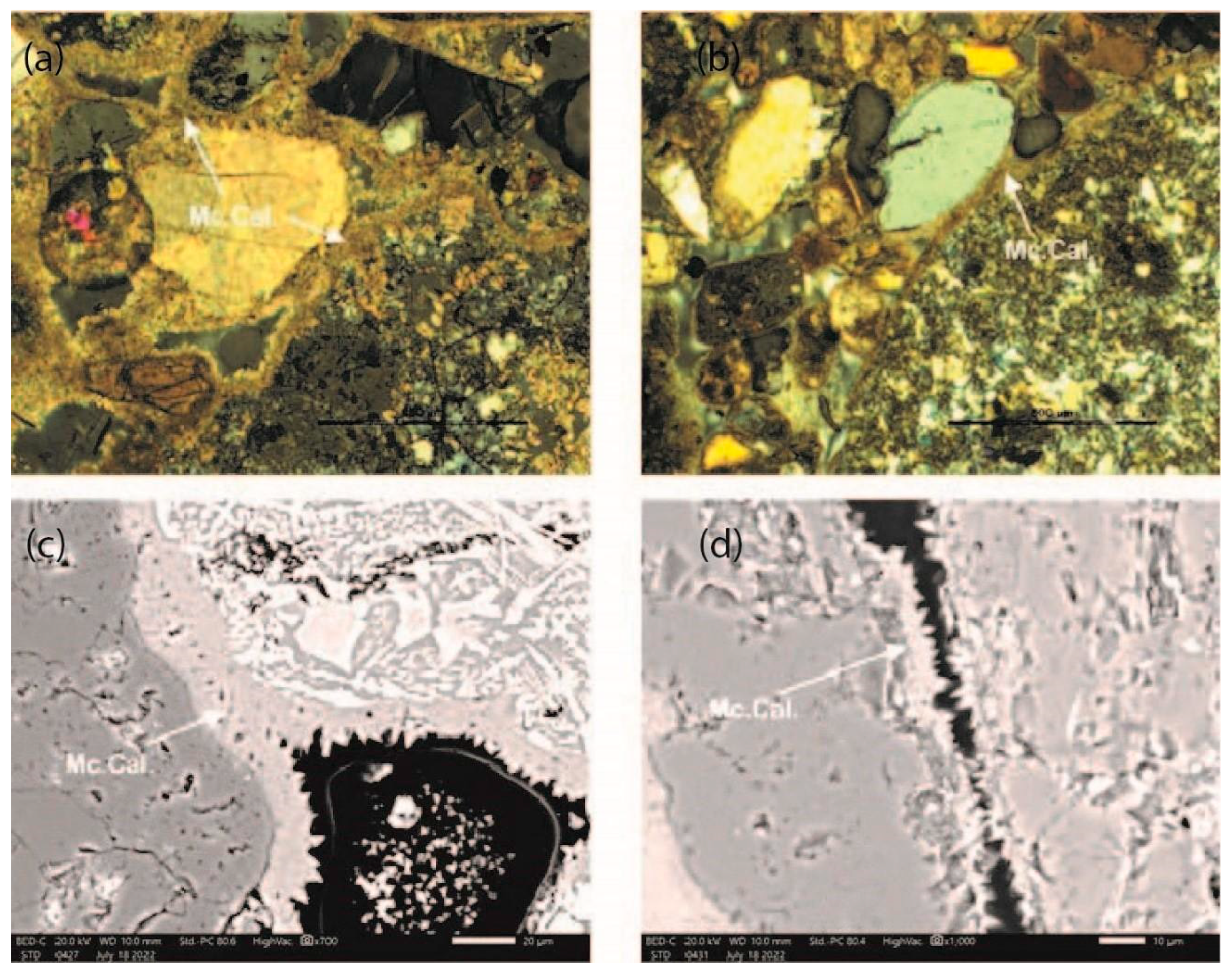
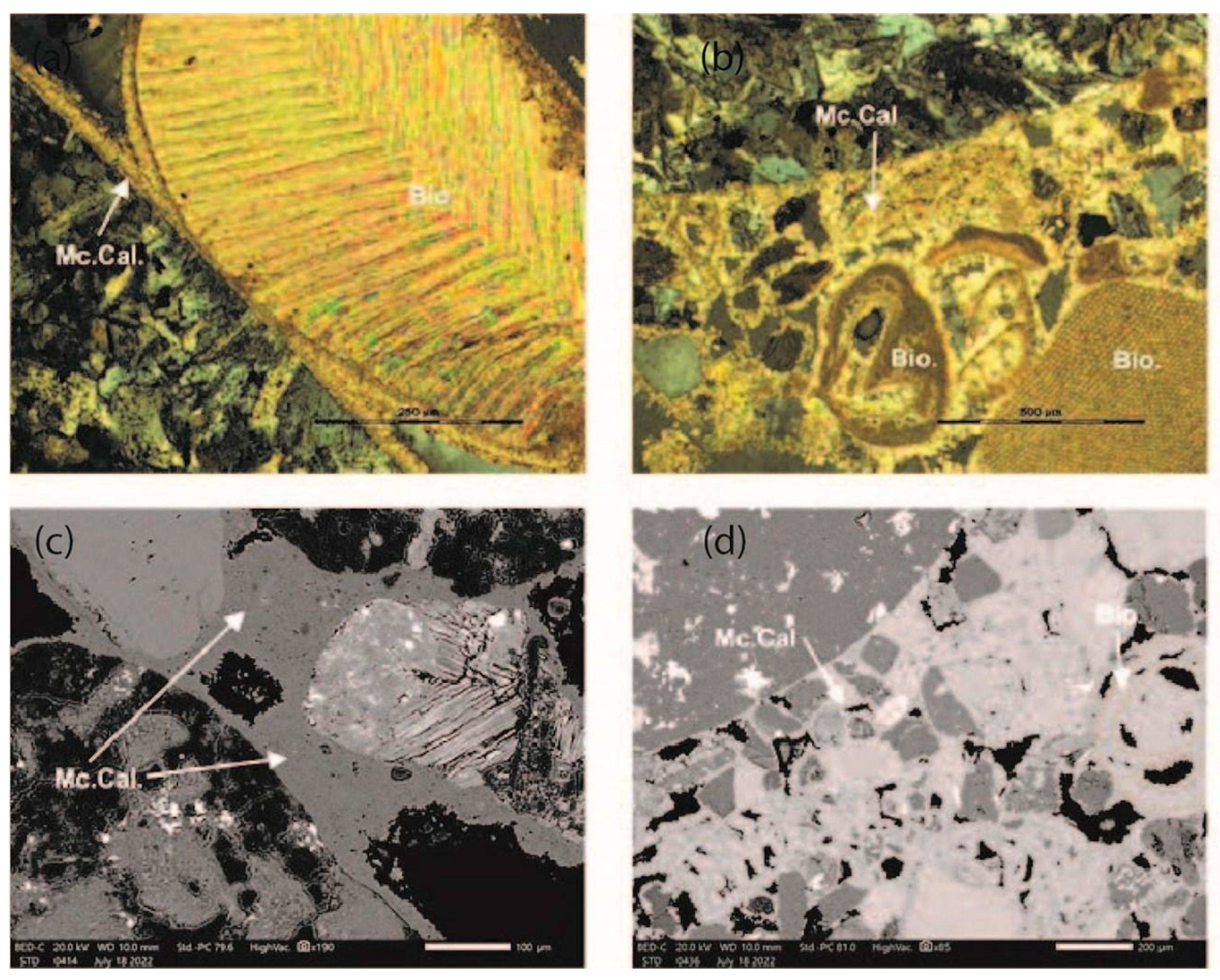
5.2. Cement Morphology
5.3. Mineralogy
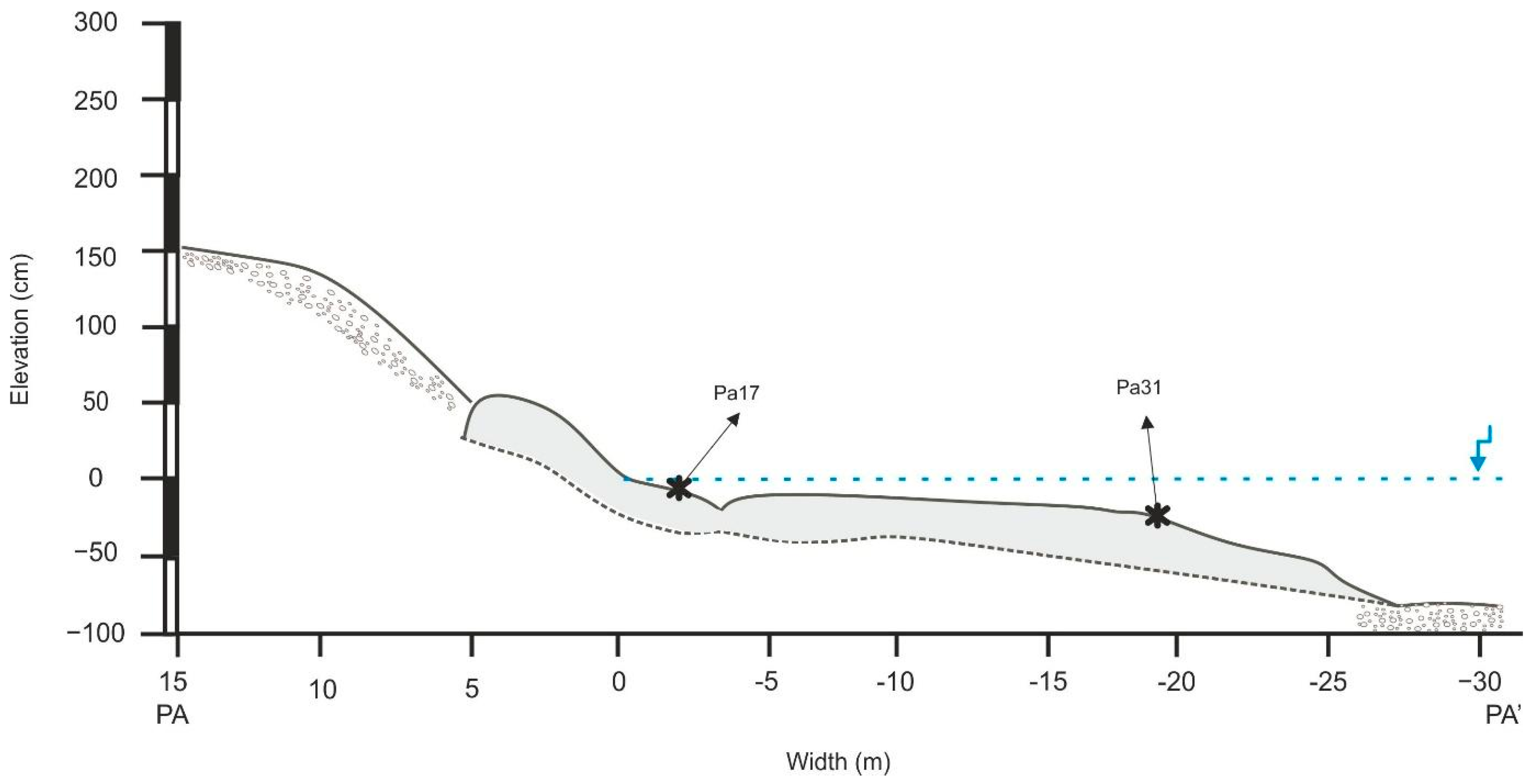
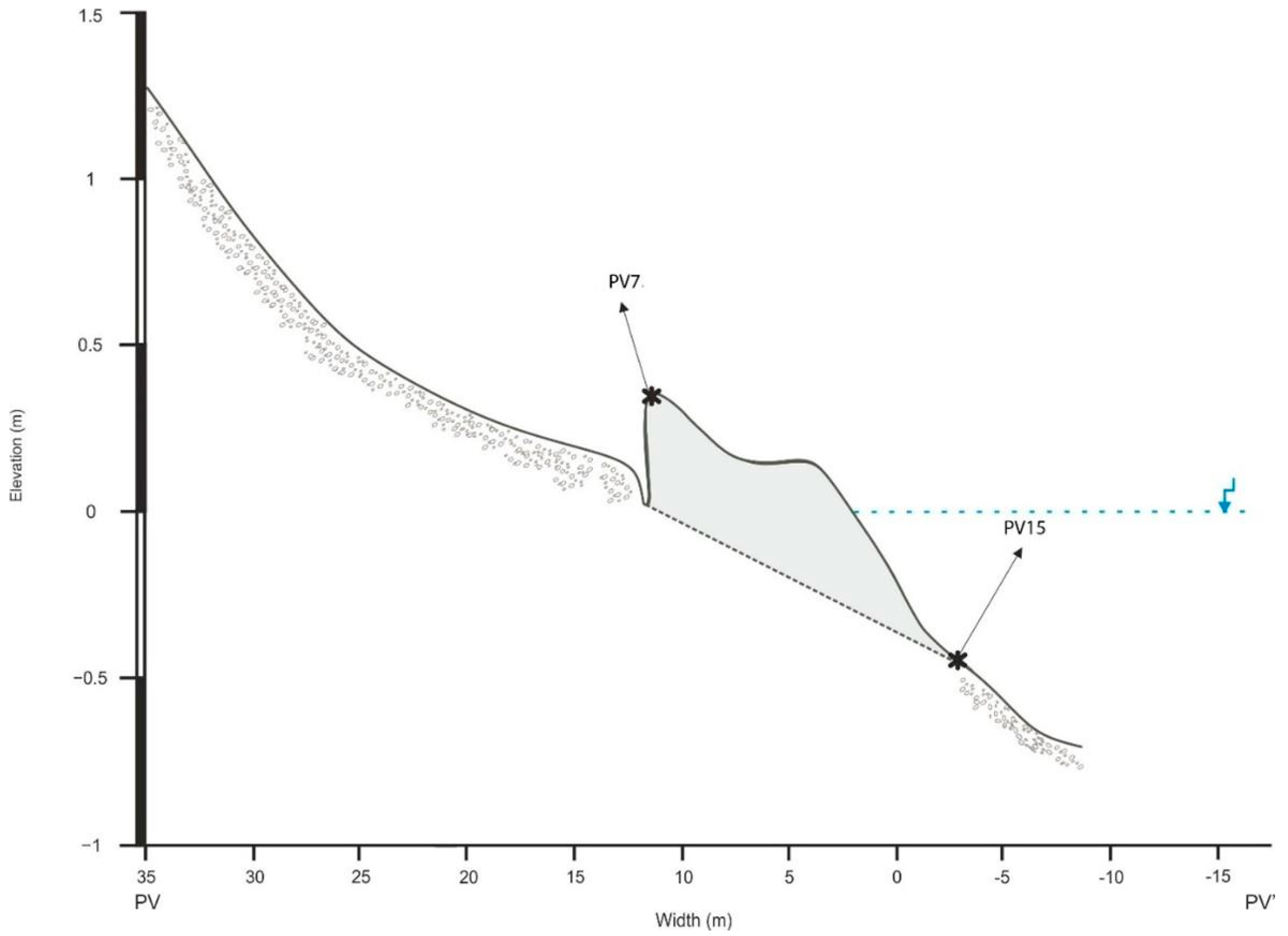
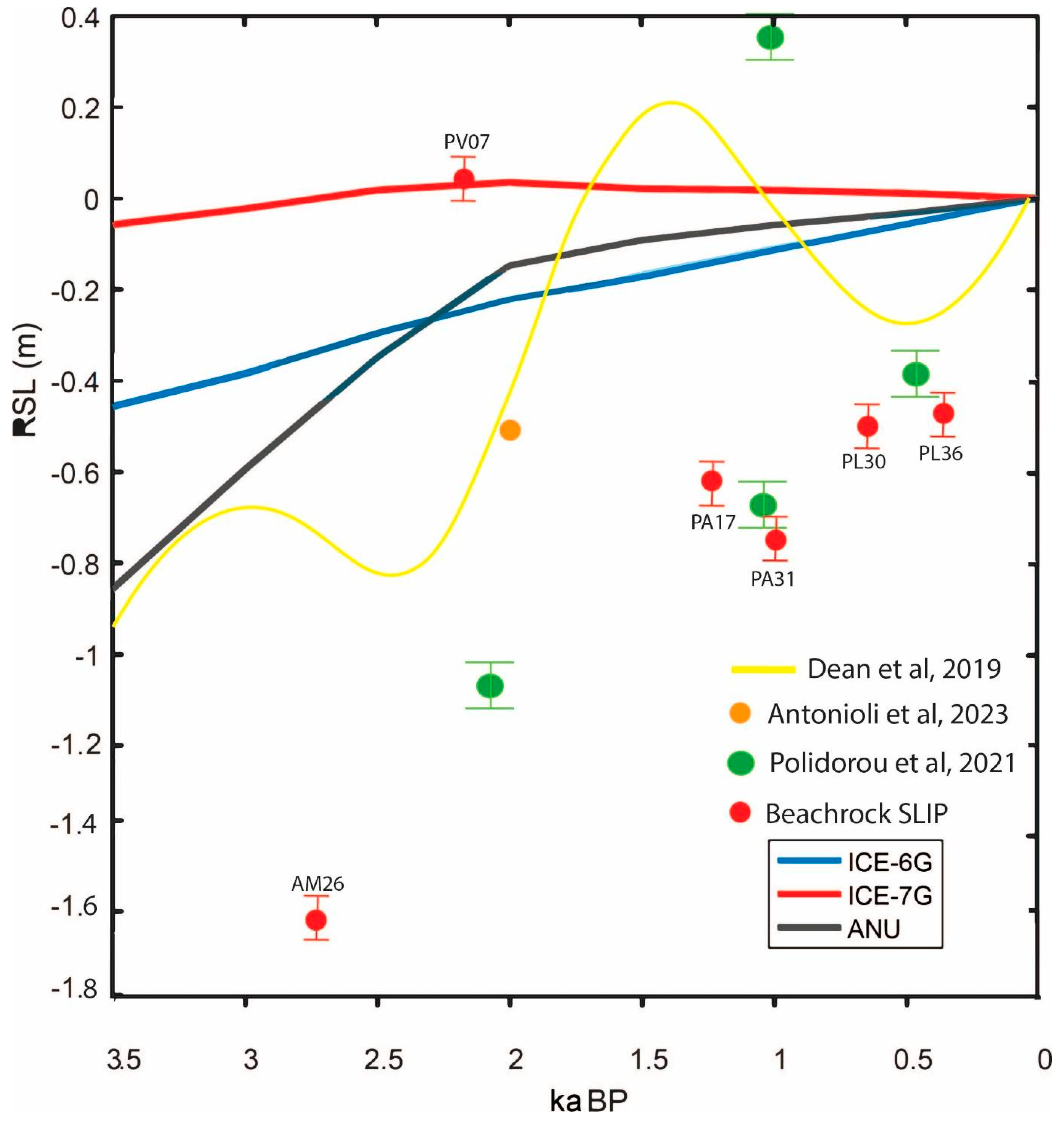
5.4. Relative Sea Level Calculations
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bar, A.; Bookman, R.; Galili, E.; Zviely, D. Beachrock Morphology along the Mediterranean Coast of Israel: Typological Classification of Erosion Features. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenroth, M.; Schneider, B.; Hoffmann, G. Beachrock as Sea-Level Indicator e A Case Study at the Coastline of Oman (Indian Ocean). Quat. Sci. Rev. 2019, 206, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romine, B.M.; Fletcher, C.H.; Frazer, L.N.; Anderson, T.R. Beach Erosion under Rising Sea-Level Modulated by Coastal Geomorphology and Sediment Availability on Carbonate Reef-Fringed Island Coasts. Sedimentology 2016, 63, 1321–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danjo, T.; Kawasaki, S. Characteristics of Beachrocks: A Review. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2014, 32, 215–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giresse, P.; Berné, S.; Certain, R.; Courp, T.; Hebert, B.; Raynal, O. Beachrocks and Lithified Barriers in the Gulf of Lions (Western Mediterranean Sea) as New Markers of the Last Sea-Level Rise. Sedimentology 2023, 70, 569–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastronuzzi, G.; De Giosa, F.; Quarta, G.; Pallara, M.; Scardino, G.; Scicchitano, G.; Peluso, C.; Antropoli, C.; Caporale, C.; Demarte, M. Holocene Sea Level Recorded by Beach Rocks at Ionian Coasts of Apulia (Italy). Geosciences 2023, 13, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.G.; Jones, M.C.; Osterman, L.E.; Passeri, D.L. Using Multiple Environmental Proxies and Hydrodynamic Modeling to Investigate Late Holocene Climate and Coastal Change within a Large Gulf of Mexico Estuarine System (Mobile Bay, Alabama, USA). Mar. Geol. 2020, 427, 106218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Yosef Mayer, D.E.; Kahanov, Y.; Roskin, J.; Gildor, H. Neolithic Voyages to Cyprus: Wind Patterns, Routes, and Mechanisms. J. Isl. Coast. Archaeol. 2015, 10, 412–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devillers, B.; Brown, M.; Morhange, C. Paleo-Environmental Evolution of the Larnaca Salt Lakes (Cyprus) and the Relationship to Second Millennium BC Settlement. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2015, 1, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morhange, C.; Goiran, J.P.; Bourcier, M.; Carbonel, P.; Le Campion, J.; Rouchy, J.M.; Yon, M. Recent Holocene Paleo-Environmental Evolution and Coastline Changes of Kition, Larnaca, Cyprus, Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Geol. 2000, 170, 205–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polidorou, M.; Saitis, G.; Evelpidou, N. Beachrock Development as an Indicator of Paleogeographic Evolution, the Case of Akrotiri Peninsula, Cyprus. Z. Für Geomorphol. 2021, 63, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, P.P.; Stephen, A.; Singh, P.; Prasad, S.; Anupama, K. Pollen Based Inference of Holocene Sea Level Changes, Depositional Environment and Climatic History of Cauvery Delta, Southern India. Catena 2021, 199, 105029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Fan, B.; Cao, Y.; You, H.; Wang, R.; Ge, Y.; Da, S.; She, Z.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Middle to Late Holocene Environmental Evolution and Sea Level Change on the West Coast of Bohai Bay. Quat. Int. 2023, 669, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.-Y.; Han, M.; Yoon, H.H.; Kim, J.C.; Choi, E.; Shin, W.-J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Jung, A.; Park, C.; Jun, C.-P. Holocene Relative Sea-Level Changes on the Southern East Coast of the Yellow Sea Holocene Relative Sea-Level Change GIA Model Levering Effect. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 2023, 629, 111779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galili, E.; Şevketoğlu, M.; Salamon, A.; Zviely, D.; Mienis, H.K.; Rosen, B.; Moshkovitz, S. Late Quaternary Beach Deposits and Archaeological Relicts on the Coasts of Cyprus, and the Possible Implications of Sea-Level Changes and Tectonics on the Early Populations. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2016, 411, 179–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattei, G.; Vacchi, M. The Geographic Variability of the Millennial Sea-Level Changes along the Coasts of Italy. Alp. Mediterr. Quat. 2023, 36, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacchi, M.; Ghilardi, M.; Melis, R.T.; Spada, G.; Giaime, M.; Marriner, N.; Lorscheid, T.; Morhange, C.; Burjachs, F.; Rovere, A. New Relative Sea-Level Insights into the Isostatic History of the Western Mediterranean. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2018, 201, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, S.; Horton, B.P.; Evelpidou, N.; Cahill, N.; Spada, G. Can We Detect Centennial Sea-Level Variations over the Last Three Thousand Years in Israeli Archaeological Records? Quat. Sci. Rev. 2019, 210, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkani, A.; Evelpidou, N.; Giaime, M.; Marriner, N.; Morhange, C.; Spada, G. Late Holocene Sea-Level Evolution of Paros Island (Cyclades, Greece). Quat. Int. 2019, 500, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evelpidou, N.; Kampolis, I.; Pirazzoli, P.A.; Vassilopoulos, A. Global Sea-Level Rise and the Disappearance of Tidal Notches. Glob. Planet. Change 2012, 92–93, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivan, D.; Wdowinski, S.; Lambeck, K.; Galili, E.; Raban, A. Holocene Sea-Level Changes along the Mediterranean Coast of Israel, Based on Archaeological Observations and Numerical Model. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 2001, 167, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirazzoli, P.A.; Thommeret, J.; Thommeret, Y.; Laborel, J.; Montag-Gioni, L.F. Crustal Block Movements from Holocene Shorelines: Crete and Antikythira (Greece). Tectonophysics 1982, 86, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, F.; De Falco, G.; Presti, V.L.; Moretti, L.; Scardino, G.; Anzidei, M.; Bonaldo, D.; Carniel, S.; Leoni, G.; Furlani, S.; et al. Relative Sea-Level Rise and Potential Submersion Risk for 2100 on 16 Coastal Plains of the Mediterranean Sea. Water 2020, 12, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danezis, C.; Nikolaidis, M.; Mettas, C.; Hadjimitsis, D.G.; Kokosis, G.; Kleanthous, C. Establishing an Integrated Permanent Sea-Level Monitoring Infrastructure towards the Implementation of Maritime Spatial Planning in Cyprus. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monioudi, I.N.; Velegrakis, A.F.; Chatzistratis, D.; Vousdoukas, M.I.; Savva, C.; Wang, D.; Bove, G.; Mentaschi, L.; Paprotny, D.; Morales-Ná Poles, O.; et al. Climate Change-Induced Hazards on Touristic Island Beaches: Cyprus, Eastern Mediterranean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1188896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitis, G.; Karkani, A.; Evelpidou, N.; Maroukian, H. Palaeogeographical Reconstruction of Ancient Diolkos Slipway by Using Beachrocks as Proxies, West Corinth Isthmus, Greece. Quaternary 2022, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, M.Z.; Erginal, A.E.; Kiyak, N.G.; Ozturk, T. Cement Fabrics and Optical Luminescence Ages of Beachrock, North Cyprus: Implications for Holocene Sea-Level Changes. Quat. Int. 2016, 401, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkani, A.; Evelpidou, N.; Vacchi, M.; Morhange, C.; Tsukamoto, S.; Frechen, M.; Maroukian, H. Tracking Shoreline Evolution in Central Cyclades (Greece) Using Beachrocks. Mar. Geol. 2017, 388, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauz, B.; Vacchi, M.; Green, A.; Hoffmann, G.; Cooper, A. Beachrock: A Tool for Reconstructing Relative Sea Level in the Far-Field. Mar. Geol. 2015, 362, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, A.J.; Robertson, A.H.F. Quaternary Uplift and Sea-Level Change at an Active Plate Boundary, Cyprus. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 1991, 148, 909–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, A.J.; Robertson, A.; Panayides, I.; Xenophontos, C.; Malpas, J. Quaternary Marine Terraces and Aeolianites in Coastal South and West Cyprus: Implications for Regional Uplift and Sea-Level Change. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on the Geology of the Eastern Mediterranean, Nicosia, Cyprus, 23–26 September 1998; proceedings 2000. pp. 105–123. [Google Scholar]
- Waters, J.V.; Jones, S.J.; Armstrong, H.A. Climatic Controls on Late Pleistocene Alluvial Fans, Cyprus. Geomorphology 2010, 115, 228–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massari, F.; Capraro, L.; Rio, D. Climatic Modulation of Timing of Sytems-Tract Development with Respect to Sea-Level Changes (Middle Pleistocene of Crotone, Calabria, Southern Italy). J. Sediment. Res. 2007, 77, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, M.C.; Sandiford, M.; Cupper, M.L. Distinguishing Tectonic from Climatic Controls on Range-Front Sedimentation. Basin Res. 2007, 19, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambeck, K.; Esat, T.M.; Potter, E.K. Links between Climate and Sea Levels for the Past Three Million Years. Nature 2002, 419, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Pichon, X.; Kreemer, C. The miocene-to-present kinematic evolution of the eastern mediterranean and middle east and its implications for dynamics. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2010, 38, 323–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, A.E.; Hall, J.; Yaltirak, C. Miocene to Recent tectonic evolution of the eastern Mediterranean: New pieces of the old Mediterranean puzzle. Mar. Geol. 2005, 221, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempler, D.; Garfunkel, Z. Structures and kinematics in the northeastern Mediterranean: A study of an irregular plate boundary. Tectonophysics 1994, 234, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brew, G.; Barazangi, M.; Al-Maleh, A.K.; Sawaf, T. Tectonic and Geologic Evolution of Syria. GeoArabia 2001, 6, 573–616. [Google Scholar]
- Montadert, L.; Nicolaides, S.; Semb, H.P. Lie Petroleum systems offshore Cyprus. In Petroleum Systems of the Tethyan Region; Marlow, L., Kendall, C., Yose, L., Eds.; AAPG Memoir: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2014; Volume 106, pp. 301–334. [Google Scholar]
- Bowman, S.A. Regional seismic interpretation of the hydrocarbon prospectivity of offshore Syria. GeoArabia 2011, 16, 95–124. [Google Scholar]
- Faccenna, C.; Bellier, O.; Martinod, J.; Piromallo, C.; Regard, V. Slab detachment beneath eastern Anatolia: A possible cause for the formation of the North Anatolian fault. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 242, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.H.F.; Parlak, O.; Ustaömer, T. Overview of the Palaeozoic–Neogene evolution of Neotethys in the Eastern Mediterranean region (southern Turkey, Cyprus, Syria). Pet. Geosci. 2012, 18, 381–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClusky, S.; Balassanian, S.; Barka, A.; Demir, C.; Ergintav, S.; Georgiev, I.; Gurkan, O.; Hamburger, M.; Hurst, K.; Kahle, H.; et al. Global Positioning System constraints on plate kinematics and dynamics in the eastern Mediterranean and Caucasus. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 5695–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilinger, R.; McClusky, S.; Vernant, P.; Lawrence, S.; Ergintav, S.; Cakmak, R.; Ozener, H.; Kadirov, F.; Guliev, I.; Stepanyan, R. GPS constraints on continental deformation in the Africa-Arabia-Eurasia continental collision zone and implications for the dynamics of plate interactions. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, B05411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, N.; Alvarez-Marrón, J.; Klaeschen, D. The structure of the Africa-Anatolia plate boundary in the eastern Mediterranean. Tectonics 2000, 19, 723–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, A.H. Whose Myth? Archaeological Data, Interpretations, and Implications for the Human Association with Extinct Pleistocene Fauna at Akrotiri Aetokremnos, Cyprus. J. Mediterr. Archaeol. 1996, 9, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, R.D.; Simmons, A.H. Akrotiri Aetokremnos, Cyprus. In Encyclopedia of Geoarchaeology; Gilbert, A.S., Ed.; Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, N.G. The Archaeology of Cyprus: From Earliest Prehistory through the Bronze Age. By A. Bernard Knapp. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2013. Pp. xx + 640 + 152 Figures + 5 Tables. $38.99 (Paperback). J. Near East. Stud. 2015, 74, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keswani, P.S.; Keswani, P.S. Hierarchies, Heterarchies, and Urbanization Processes: The View from Bronze Age Cyprus. J. Mediterr. Archaeol. 1997, 9, 211–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovou, M. The Early Iron Age Urban Forms of Cyprus, in Mediterranean Urbanization 800-600 B.C. In Proceedings of the British Academy 126; Osborne, R., Cunliffe, B., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 17–43. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/4152489/_Iacovou_M_2005_The_Early_Iron_Age_Urban_Forms_of_Cyprus_in_Mediterranean_Urbanization_800_600_B_C_Robin_Osborne_and_Barry_Cunliffe_eds_Proceedings_of_the_British_Academy_126_Oxford_Oxford_University_Press_17_43 (accessed on 6 March 2024).
- Iacovou, M. From the Late Cypriot Polities to the Iron Age “Kingdoms”: Understanding the Political Landscape of Cyprus from Within. Les. Roy. Chypr À L’épreuve L’histoire 2018, 60, 7–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoulou, T. Ναυτική Δραστηριότητα Και Λιμενικό Δίκτυο Στην Κλασική Κύπρο. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cyprus, Nicosia, Cyprus, 2007. Available online: https://www.ancientportsantiques.com/wp-content/uploads/Documents/PLACES/Crete-Cyprus/Cyprus-TheodoulouPhD2007.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2024).
- Satraki, A. Abnormal Functional Activation and Maturation of Fronto-Striato-Temporal and Cerebellar Regions During Sustained Attention in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 2010, 171, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekker-Nielsen, T. The Roads of Ancient Cyprus; Museum Tusculanum Press: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Leidwanger, J. Opportunistic Ports and Spaces of Exchange in Late Roman Cyprus. J. Marit. Archaeol. 2013, 8, 221–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayides, P.; Jacobs, I. Cyprus in the Long Late Antiquity. History and Archaeology Between the Sixth and Eighth Centuries; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Demesticha, S. Cutting a Long Story Short? Underwater and Maritime Archaeology in Cyprus. J. East. Mediterr. Archaeol. Herit. Stud. 2018, 6, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, J.R. American Archaeologists in Cypriot Waters: One Nation’s Contributions to the Underwater Exploration of Cyprus’ Past. Near East. Archaeol. 2008, 71, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callot, O.; Fourrier, S.; Yon, M. Kition-Bamboula VIII: Le Port de Guerre de Kition. In Kition-Bamboula VIII; MOM Editions: Lyon, France, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moska, P.; Bluszcz, A.; Poreba, G.; Tudyka, K.; Adamiec, G.; Szymak, A.; Przybyła, A. Luminescence Dating Procedures at the Gliwice Luminescence Dating Laboratory. Geochronometria 2021, 48, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijma, M.P.; Engelhart, S.E.; Törnqvist, T.E.; Horton, B.P.; Hu, P.; Hill, D.F. A protocol for a geological sea-level database. In Handbook of Sea-Level Research; Shennan, I., Long, A.J., Horton, B.P., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.H.; Danjo, T.; Kawasaki, S. Artificial Beachrock Formation through Sand Solidification towards the Inhibit of Coastal Erosion in Bangladesh. Int. J. Geomate 2015, 9, 1528–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacchi, M.; Marriner, N.; Morhange, C.; Spada, G.; Fontana, A.; Rovere, A. Earth-Science Reviews Multiproxy Assessment of Holocene Relative Sea-Level Changes in the Western Mediterranean: Sea-Level Variability and Improvements in the de Fi Nition of the Isostatic Signal. Earth Sci. Rev. 2016, 155, 172–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattei, G.; Caporizzo, C.; Corrado, G.; Vacchi, M.; Stocchi, P.; Pappone, G.; Schiattarella, M.; Aucelli, P.P.C. On the Influence of Vertical Ground Movements on Late-Quaternary Sea-Level Records. A Comprehensive Assessment along the Mid-Tyrrhenian Coast of Italy (Mediterranean Sea). Quat. Sci. Rev. 2022, 279, 107384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Empereur, J.-Y.; Koželj, T.; Picard, O.; Wurch-Koželj, M. The Hellenistic Harbour of Amathus. Underwater Excavations, 1984–1986. Volume 1: Architecture and History; Peeters Publishers: Leuven, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnaird, T.C.; Robertson, A.H.F.; Morris, A. Timing of Uplift of the Troodos Massif (Cyprus) Constrained by Sedimentary and Magnetic Polarity Evidence. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 2011, 168, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, U.; Pantazides, H. The Uplift of the Troodos Massif, Cyprus. Tectonics 2019, 38, 3124–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, F.; Furlani, S.; Spada, G.; Melini, D.; Zomeni, Z. The Lambousa (Cyprus) Fishtank in a Quasi-Stable Coastal Area of the Eastern Mediterranean, a Notable Marker for Testing GIA Models. Geosciences 2023, 13, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argus, D.F.; Peltier, W.R.; Drummond, R.; Moore, A.W. The Antarctica Component of Postglacial Rebound Model ICE-6G_C (VM5a) Based on GPS Positioning, Exposure Age Dating of Ice Thicknesses, and Relative Sea Level Histories. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 198, 537–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltier, W.R.; Argus, D.F.; Drummond, R. Space Geodesy Constrains Ice Age Terminal Deglaciation: The Global ICE-6G_C (VM5a) Model. J. Geophys. Res. Solid. Earth 2015, 120, 450–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Peltier, W.R. Space-Geodetic and Water Level Gauge Constraints on Continental Uplift and Tilting over North America: Regional Convergence of the ICE-6G_C (VM5a/VM6) Models. Geophys. J. Int. 2017, 210, 1115–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Peltier, W.R. Glacial Isostatic Adjustment, Relative Sea Level History and Mantle Viscosity: Reconciling Relative Sea Level Model Predictions for the U.S. East Coast with Geological Constraints. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 201, 1156–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambeck, K.; Purcell, A. Sea-Level Change in the Mediterranean Sea since the LGM: Model Predictions for Tectonically Stable Areas. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2005, 24, 1969–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdkamp, P. Climate Change and the Productive Landscape in the Mediterranean Region in the Roman Period; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 411–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaritelli, G.; Cacho, I.; Català, A.; Barra, M.; Bellucci, L.G.; Lubritto, C.; Rettori, R.; Lirer, F. Persistent Warm Mediterranean Surface Waters during the Roman Period. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmkuhl, F.; Owen, L. Late Quaternary Glaciation of Tibet and the Bordering Mountains: A Review. Boreas 2005, 34, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, S. Terminal Moraine Formation Processes and Geomorphology of Glacier Forelands at the Selected Outlet Glaciers of Jostedalsbreen, South Norway. In Landscapes and Landforms of Norway; World Geomorphological Landscapes; Beylich, A.A., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalongeville, R.; Bernier, P.; Prieur, A.; Le Campion, T. Les Variations Récentes de La Ligne de Rivage Du Sud-Est de Chypre/The Early Changes of Southeastern Cyprus Shorelines. Géomorphologie: Relief, processus, environnement. Geomorphology 2000, 6, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Cement Type |
|---|---|
| PA17 | Quartz, Calcium Carbonate, Hornblende, Albite, Clinochlore, Clinopyroxene, Clinochrysotile |
| PA31 | Quartz, Calcium Carbonate, Manganocalcite, Albite, Clinochlore, Clinopyroxene |
| AM26 | Quartz, Calcium Carbonate, Magnesiohornblende, Albite, Clinochlore, Clinopyroxene, Dolomite |
| PL30 | Quartz, Calcium Carbonate, Magnesiohornblende, Albite, Clinochlore, Clinopyroxene, Aragonite |
| PV7 | Quartz, Calcium Carbonate, Magnesiohornblende, Albite, Clinochlore, Clinopyroxene |
| PV15 | Quartz, Calcium Carbonate, Magnesiohornblende, Albite, Clinochlore, Clinopyroxene, Epidote, Montmorillonite |
| Sample | Cement Type | Cement Thickness | SLIP | Indicative Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA17 | Thin isopachous micritic HMC. No matrix and no bioclasts | <10 μm | Intertidal, undifferentiated | MHW to MLW |
| PA31 | Thin isopachous bladed micritic HMC, brown coloured | <8 μm | Intertidal, undifferentiated | MHW to MLW |
| AM1 | Micritic HMC as pore filling. Brown-coloured well-developed crystals | 20 μm | Intertidal, undifferentiated | MHW to MLW |
| AM26 | Isopachous micritic HMC as pore filling, meniscus, brown coloured. 10% bioclast contribution | 50–100 μm | Intertidal, undifferentiated | MHW to MLW |
| PL30 | Bladed isopachous micritic HMC, brown coloured. | 10–20 μm | Intertidal, undifferentiated | MHW to MLW |
| PL37 | Bladed isopachous micritic HMC, matrix infilling and pellet concentrations | 10–20 μm | Intertidal, undifferentiated | MHW to MLW |
| PV7 | Isopachous micritic HMC, brown bio-micritic cement. Pellet concentrations | 10–20 μm | Intertidal, undifferentiated | MHW to MLW |
| PV15 | Isopachous bladed micritic and sparitic HMC. 20% bioclast contribution | ≈40 μm | Not qualified | --------------- |
| Beachrock ID | Height (m) | Age (ka) | Tidal Range (m) | Measurement Error (m) | Indicative Meaning (m) | RWL (m) | RSL (m) | Error (cm) | Uplift (mm/y) | Total Uplift Per Site (mm) | SL (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL37 | −0.22 | 0.36 | 0.41 | 0.05 | 0.42 | 0.21 | −0.43 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 39.6 | −0.4696 |
| PL30 | −0.19 | 0.66 | 0.41 | 0.05 | 0.42 | 0.21 | −0.4 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 72.6 | −0.4726 |
| PA31 | −0.18 | 1.03 | 0.41 | 0.05 | 0.42 | 0.21 | −0.39 | 0.13 | 0.35 | 360.5 | −0.7505 |
| PA17 | 0.02 | 1.26 | 0.41 | 0.05 | 0.42 | 0.21 | −0.19 | 0.13 | 0.35 | 441 | −0.631 |
| PV7 | 0.36 | 2.18 | 0.41 | 0.05 | 0.42 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.1 | 218 | 0.068 |
| AM26 | −1.01 | 2.79 | 0.41 | 0.05 | 0.42 | 0.21 | −1.22 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 418.5 | −1.6385 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Polidorou, M.; Saitis, G.; Karkani, A.; Gatt, J. Relative Sea-Level Changes During the Upper Holocene as Determined by Reference to Beachrock Formations Along the South Coastline of Cyprus and Their Correlation with the Archaeological Context of the Island. Geosciences 2025, 15, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15040137
Polidorou M, Saitis G, Karkani A, Gatt J. Relative Sea-Level Changes During the Upper Holocene as Determined by Reference to Beachrock Formations Along the South Coastline of Cyprus and Their Correlation with the Archaeological Context of the Island. Geosciences. 2025; 15(4):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15040137
Chicago/Turabian StylePolidorou, Miltiadis, Giannis Saitis, Anna Karkani, and Judith Gatt. 2025. "Relative Sea-Level Changes During the Upper Holocene as Determined by Reference to Beachrock Formations Along the South Coastline of Cyprus and Their Correlation with the Archaeological Context of the Island" Geosciences 15, no. 4: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15040137
APA StylePolidorou, M., Saitis, G., Karkani, A., & Gatt, J. (2025). Relative Sea-Level Changes During the Upper Holocene as Determined by Reference to Beachrock Formations Along the South Coastline of Cyprus and Their Correlation with the Archaeological Context of the Island. Geosciences, 15(4), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15040137









