3D Gaussian Splatting in Geosciences: A Novel High-Fidelity Approach for Digitizing Geoheritage from Minerals to Immersive Virtual Tours
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition
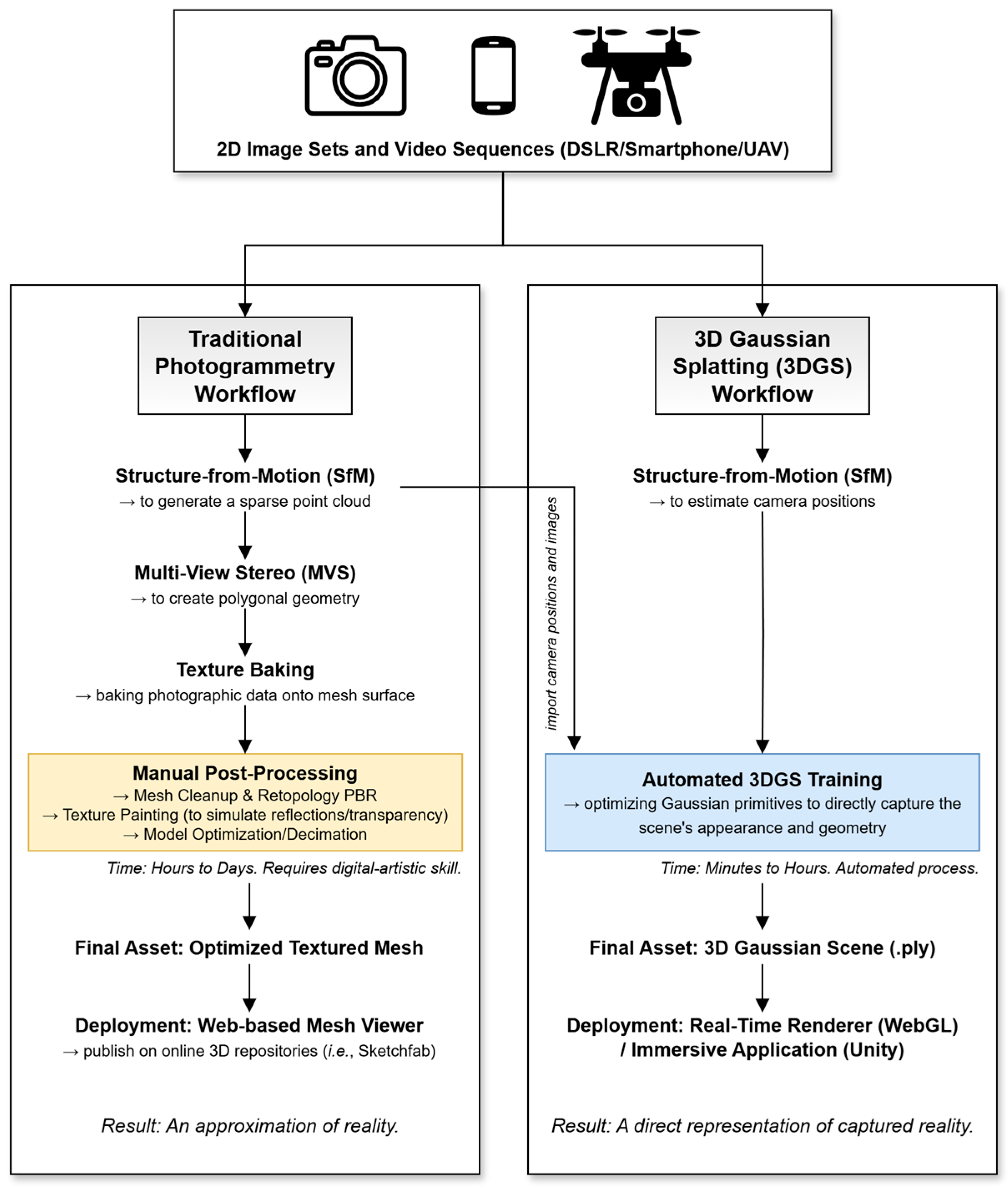
2.2. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction and Processing
2.2.1. Photogrammetry Workflow (Comparative Baseline)
2.2.2. Three-Dimensional Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) Workflow
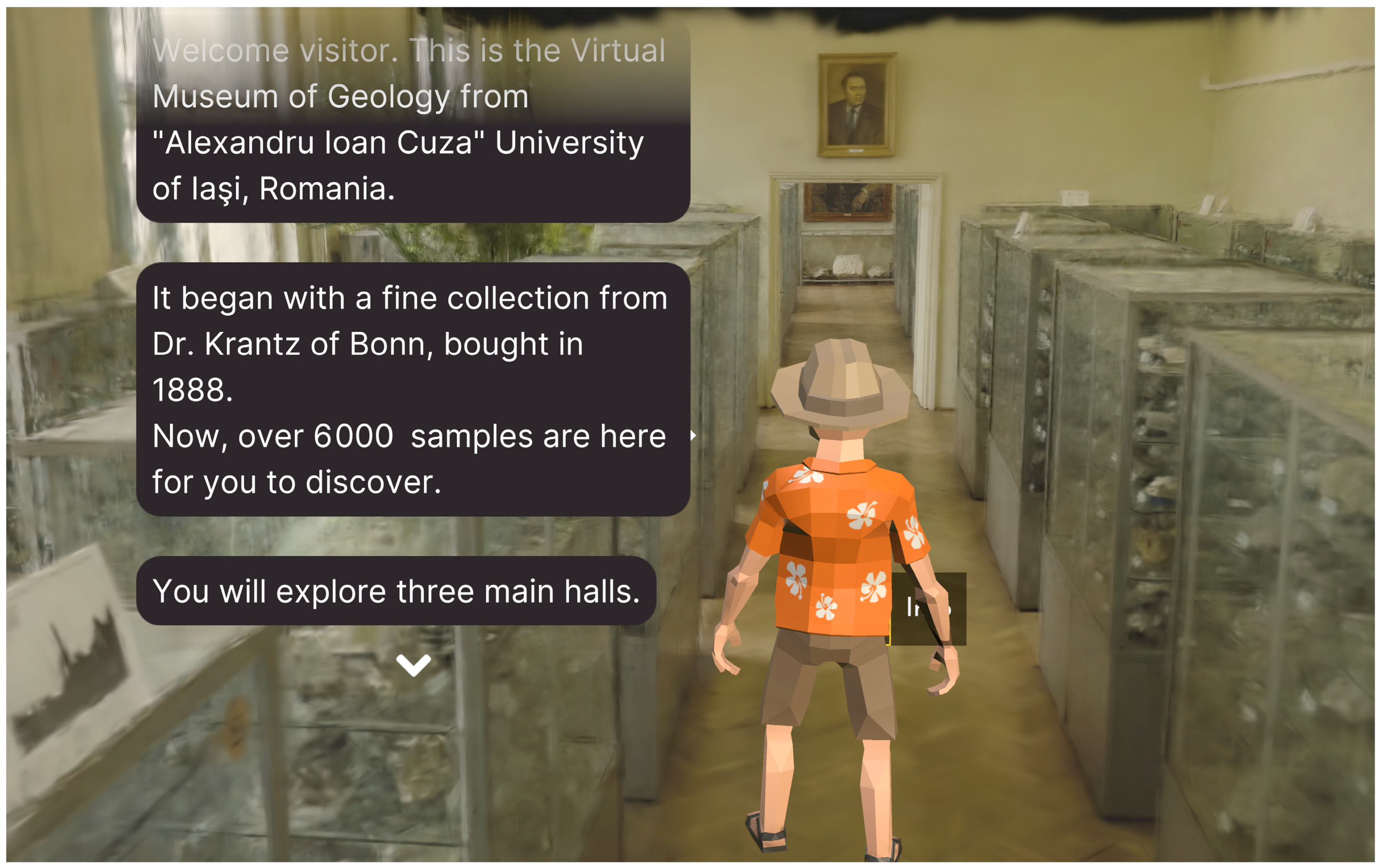
2.3. Digital Deployment and Visualization

3. Results
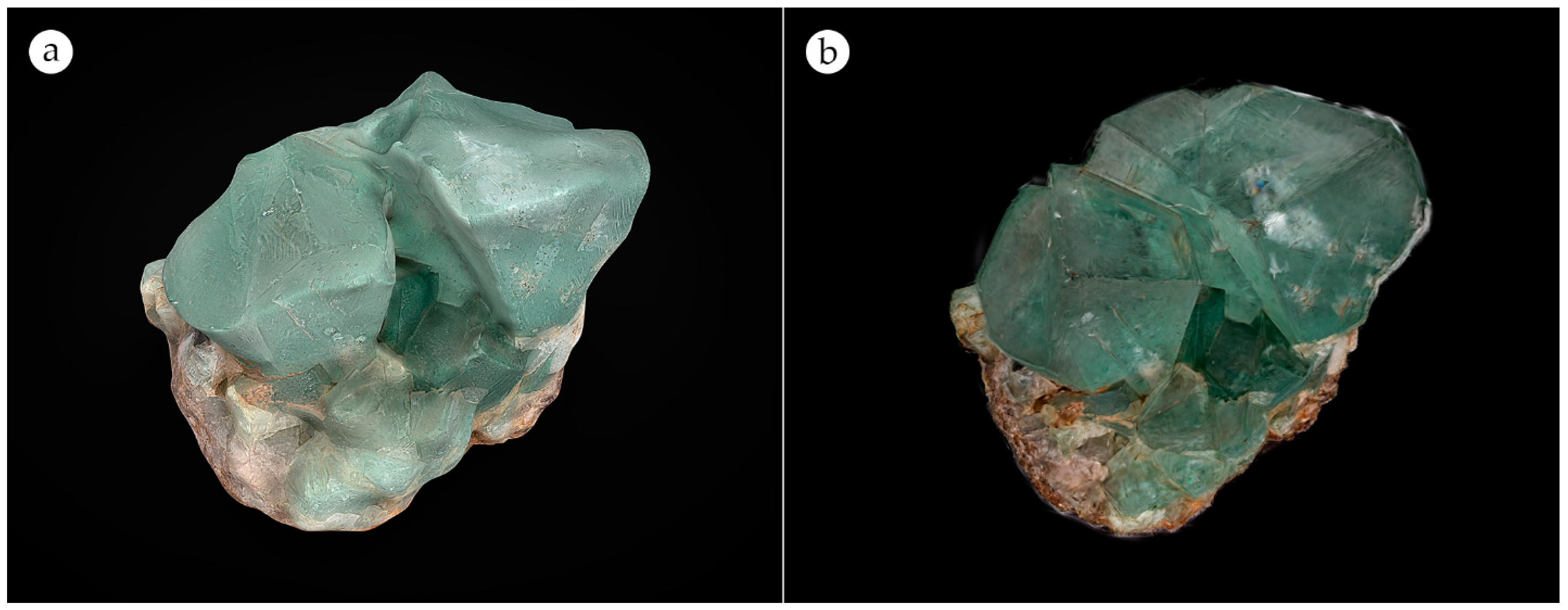
3.1. Qualitative Comparison of Specimen-Level Reconstructions
3.2. Versatility Across Multiple Scales
3.3. Quantitative Performance
4. Discussion
4.1. The Technological Leap: From Surface Approximation to Volumetric Representation
4.2. A Versatile, Multi-Scale Tool for Geoheritage
4.3. Enhancing Engagement in Geoeducation and Geotourism
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3D | Three-Dimensional |
| 3DGS | 3D Gaussian Splatting |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| LOG | Logarithmic (color profile) |
| LTS | Long-Term Support |
| MVS | Multi-View Stereo |
| NeRF | Neural Radiance Field |
| PBR | Physically Based Rendering |
| PLY | Polygon File Format |
| SfM | Structure-from-Motion |
| SH | Spherical Harmonics |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| VQ | Vector Quantization |
| WebGL | Web Graphics Library |
Appendix A
References
- Apopei, A.I. Towards Mineralogy 4.0? Atlas of 3D Rocks and Minerals: Digitally Archiving Interactive and Immersive 3D Data of Rocks and Minerals. Minerals 2024, 14, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, A.; Morrison, S.M.; Fox, P.; Ma, X.; Wong, M.L.; Williams, J.R.; McGuinness, K.N.; Krivovichev, S.V.; Lehnert, K.; Ralph, J. What is mineral informatics? Am. Mineral. 2023, 108, 1242–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apopei, A.I. Accessible Interface for Museum Geological Exhibitions: PETRA—A Gesture-Controlled Experience of Three-Dimensional Rocks and Minerals. Minerals 2025, 15, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondyli, A. The Museums of Geology and Paleontology as Geoeducational and Geoconservation Tools against Climate Change: A Case Study in Greece. Geoheritage 2024, 16, 64. [Google Scholar]
- Cocal-Smith, V.; Hinchliffe, G.; Petterson, M.G. Digital Tools for the Promotion of Geological and Mining Heritage: Case Study from the Thames Goldfield, Aotearoa, New Zealand. Geosciences 2023, 13, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S. Research on the application of digital media technology in museum exhibition design: A case study of the national museum of Singapore. In Proceedings of the ICDEBA 2023, Hangzhou, China, 19 November 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, G.D.M.; Labishak, G.; Brown, S.; Isom, S.L.; Pettus, H.D.; Byers, T. Teaching with Digital 3D Models of Minerals and Rocks. GSA Today 2020, 30, 42–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apopei, A.I.; Buzgar, N.; Buzatu, A.; Maftei, A.E.; Apostoae, L. Digital 3D Models of Minerals and Rocks in a Nutshell: Enhancing Scientific, Learning, and Cultural Heritage Environments in Geosciences by Using Cross-Polarized Light Photogrammetry. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 16, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramov, N.; Lankegowda, H.; Liu, S.; Barazzetti, L.; Beltracchi, C.; Ruttico, P. Implementing Immersive Worlds for Metaverse-Based Participatory Design through Photogrammetry and Blockchain. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Cui, J.; Liu, H.; Li, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, Y. GlassGaussian: 3D Gaussian Splatting for Glass-Like Materials. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2025, 13, 31517–31531. [Google Scholar]
- Do, T.L.P.; Choi, J.; Le, V.Q.; Gentet, P.; Hwang, L.; Lee, S. HoloGaussian Digital Twin: Reconstructing 3D Scenes with Gaussian Splatting for Tabletop Hologram Visualization of Real Environments. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Ding, T.; Huo, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Gao, Y.; Luo, J. 3D Gaussian Splatting: Survey, Technologies, Challenges, and Opportunities. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.17418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, W. A Survey on 3D Gaussian Splatting. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.07687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Yuan, Y.J.; Zhang, L.X.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.P.; Yan, L.Q.; Gao, L. Recent advances in 3D Gaussian splatting. Comput. Vis. Media 2024, 10, 613–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerbl, B.; Kopanas, G.; Leimkühler, T.; Drettakis, G. 3D Gaussian Splatting for Real-Time Radiance Field Rendering. ACM Trans. Graph. 2023, 42, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, B.; Xu, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, W.; He, Y. 3D Gaussian Splatting as a New Era: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2015, 31, 4429–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, V.; Li, R.; Kerr, J.; Turkulainen, M.; Yi, B.; Pan, Z.; Seiskari, O.; Ye, J.; Hu, J.; Tancik, M. gsplat: An Open-Source Library for Gaussian Splatting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2025, 26, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Prosvetov, A.; Prokhorenko, A.; Guryeva, E.; Starinskiy, V. Illuminating the Moon: A comparative study of photogrammetry, Neural Radiance Fields, and Gaussian Splatting for lunar surface reconstruction under varying illumination. Astron. Comput. 2025, 52, 100953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, W.; Cai, G.; Guo, Q. Large-scale 3D terrain reconstruction using 3D Gaussian Splatting. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.13329. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, K. Towards Urban Digital Twins with Gaussian Splatting: Challenges and Opportunities in Large Scale 3D Mapping and Beyond. Master’s Thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, K.; Lu, D.; Li, L.; Chen, N.; He, H.; Xu, L.; Li, J. Enhanced 3-D Urban Scene View Synthesis and Geometry Extraction Using Gaussian Splatting: A Case Study from Google Earth. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 4701714. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhou, C.; Wang, W.; Sun, H.; Zhan, K.; Peng, S. Street Gaussians: Modeling Dynamic Urban Scenes with Gaussian Splatting. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2024, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, B.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B. RSGaussian: 3D gaussian splatting with LiDAR for aerial remote sensing novel view synthesis. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.18380. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Y. DroneSplat: 3D Gaussian Splatting for Drone Photography. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.07767. [Google Scholar]
- Winiwarter, L.; Urban, S.; Holst, L.; Jutzi, B. Assessing the Potential of NeRF and 3D Gaussian Splatting for Change Detection from Terrestrial Image Sequences. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Kashiwa, Japan, 26–29 May 2025; pp. 441–448. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Wang, X.; Ni, H.; Xin, Y.; Shi, P. Water-Adapted 3D Gaussian Splatting for precise underwater scene reconstruction. Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 12, 1573612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancik, M.; Weber, E.; Ng, E.; Li, R.; Yi, B.; Wang, T.; Kristoffersen, A.; Austin, J.; Salahi, K.; Ahuja, A. Nerfstudio: A modular framework for neural radiance field development. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH 2023 Conference Proceedings, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 12–15 December 2023; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Brussee, A. Brush. Available online: https://github.com/ArthurBrussee/brush (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Boutsi, A.; Kourtis, A.; Tsiolakis, T.; Ioannidis, C. Interactive Online Visualization of Complex 3D Geo-Archaeological Models. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Enschede, The Netherlands, 10–14 June 2019; pp. 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Zhong, R.; Wang, K.; Xie, D. Li-GS: A fast 3D Gaussian reconstruction method assisted by LiDAR point clouds. Big Earth Data 2025, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildenhall, B.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Tancik, M.; Barron, J.T.; Ramamoorthi, R.; Ng, R. NeRF: Representing scenes as Neural Radiance Fields for view synthesis. Commun. ACM 2021, 65, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, D. A new era of indoor scene reconstrucion: A survey. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 110160–110192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietroni, E.; Ferdani, D. Virtual Restoration and Virtual Reconstruction in Cultural Heritage: Terminology, Methodologies, Visual Representation Techniques and Cognitive Models. Information 2021, 12, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Wang, Q.; He, H.; Wang, Z.; Gao, K. C3DGS: A COLMAP-free 3D Gaussian Splatting method with geometric consistency. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.12752. [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri, L.; Bruno, F.; Muzzupappa, M. Virtual museum system evaluation through user studies. J. Cult. Herit. 2017, 26, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopardi, A.; Ceccacci, S.; Mengoni, M.; Naspetti, S.; Gambelli, D.; Ozturk, E.; Zanoli, R. X-reality technologies for museums: A comparative evaluation based on presence and visitors experience through user studies. J. Cult. Herit. 2021, 47, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, D.A.L.; Morita, M.M.; Bilmes, G.M. Virtual museums. Captured reality and 3D modeling. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 45, 234–239. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J.; Jeong, S.C.; Kim, S.H. Comparative Analysis of Product Information Provision Methods: Traditional E-Commerce vs. 3D VR Shopping. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clini, P.; Angeloni, R.; D’Alessio, M.; Quarchioni, R. Enhancing onsite and online museum experience through digital reconstruction and reproduction: The Raphael and Angelo Colocci temporary exhibition. SCIRES-IT Sci. Res. Inf. Technol. 2023, 13, 71–84. [Google Scholar]
- Clini, P.; Nespeca, R.; Ferretti, U.; Galazzi, F.; Bernacchia, M. Inclusive Museum Engagement: Multisensory Storytelling of Cagli Warriors’ Journey and the Via Flaminia Landscape Through Interactive Tactile Experiences and Digital Replicas. Heritage 2025, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, C.; Gillikin Schoueri, K.; Schreibman, S. And Now What? Three-Dimensional Scholarship and Infrastructures in the Post-Sketchfab Era. Heritage 2025, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaneet, K.; Meibodi, K.P.; Koohpayegani, S.A.; Pirsiavash, H. Compact3d: Compressing gaussian splat radiance field models with vector quantization. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.18159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Type/Scale | Specific Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Limpedea Pillars | Landscape | Columnar-jointed andesite |
| Geology Museum | Architectural-scale | 60 cabinets with ~6500 minerals and rocks, area of 200 square meters |
| Cabinet of rocks and minerals | Object-scale | Cabinet with 50 samples of rocks and minerals |
| Bust of Grigore Cobălcescu | Object-scale | Bust made of plaster mixture by Dimitrie Tronescu around 1893 |
| Fedorov stage | Object-scale | Fedorov 5-axis Universal Stage for polarizing microscope made in the Soviet Union; highly reflective material; complex geometry |
| Gold pan | Object-scale | Wooden-made; used in the Apuseni Mountains (Romania) for decades to wash auriferous sands |
| Pyrite | Mineral | Luster |
| Fluorite | Mineral | Transparency |
| Stibnite | Mineral | Luster |
| Jasper | Mineral | Luster |
| Topaz | Mineral | Transparency |
| Sulfur | Mineral | Homogenous surface color |
| Calcite | Mineral | Crystal habit |
| Anthophyllite | Mineral | Crystal habit |
| Smoky Quartz | Mineral | Transparency |
| Quartz | Mineral | Crystal habit |
| Amethyst | Mineral | Crystal habit, Transparency |
| Labradorite | Mineral | Iridescence |
| Opal | Mineral | Opalescence |
| Vanadinite | Mineral | Crystal habit, Luster |
| Galena and Chalcopyrite | Mineral | Luster |
| Model Scale | Example | Input Data | Training Time (in Minutes) | Number of Gaussians | File Size (in MB) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | Low | |||||
| Mineral | Pyrite | 252 images | 35 | 743,272 | 171 | 17 |
| Object | Cabinet | 2 min 44 s of video | 44 | 981,165 | 226 | 23 |
| Architectural | Geology Museum | 10 min 25 s of video | 90 | 2,658,468 | 612 | 62 |
| Metric | Photogrammetry | 3D Gaussian Splatting |
|---|---|---|
| Input Data | ~350 still images | ~350 still images or video(s) up to 10 min |
| Processing Time | 2–4 h | 30–90 min (training) |
| Manual Post-Processing | 1–3 h (cleanup & PBR texturing) | ~10 min (outlier cleaning) |
| Final File Size | 10 to 100 MB (.obj + 4K textures) | 20 to 600 MB (.ply) |
| Compressed File Size | N/A | 2 to 60 MB (.splat) |
| Loading time 1 | ~3–5 s | ~3–12 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Apopei, A.I. 3D Gaussian Splatting in Geosciences: A Novel High-Fidelity Approach for Digitizing Geoheritage from Minerals to Immersive Virtual Tours. Geosciences 2025, 15, 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15100373
Apopei AI. 3D Gaussian Splatting in Geosciences: A Novel High-Fidelity Approach for Digitizing Geoheritage from Minerals to Immersive Virtual Tours. Geosciences. 2025; 15(10):373. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15100373
Chicago/Turabian StyleApopei, Andrei Ionuţ. 2025. "3D Gaussian Splatting in Geosciences: A Novel High-Fidelity Approach for Digitizing Geoheritage from Minerals to Immersive Virtual Tours" Geosciences 15, no. 10: 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15100373
APA StyleApopei, A. I. (2025). 3D Gaussian Splatting in Geosciences: A Novel High-Fidelity Approach for Digitizing Geoheritage from Minerals to Immersive Virtual Tours. Geosciences, 15(10), 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15100373







