Abstract
The early Triassic (~250 Ma) hornblende gabbro from the Tengxian area of Yunkai Massif, South China, contains a mineral assemblage of clinopyroxene, hornblende, biotite, plagioclase, K-feldspar and quartz and accessory apatite, and zircon and ilmenite. Based on mineral association and crystallization sequence, two generations of the mineral assemblage have been identified: clinopyroxene + plagioclase + apatite (zircon) in Generation I and ilmenite + hornblende + biotite + K-feldspar + quartz in Generation II. The high crystallization temperature (T = 999–1069 °C) of clinopyroxene and its coexistence with labradorite (An = 52–58) indicate that Generation I crystallized in a basaltic magma, while the hornblende’s relatively low crystallization temperature (T = 780–820 °C) and coexistence with K-feldspar and quartz suggest that Generation II formed in an evolved alkaline melt. The mineralogical records are likely attributed to pulsed intrusion of the late-stage evolved magma into a crystal mush, like in Generation I. The bulk-rock geochemical data include a sub-alkaline affinity, arc-type trace element features, and highly enriched Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic compositions, consistent with the isotopic records from the accessory minerals, e.g., the very high δ18O values in both zircon and apatite and significantly negative εHf(t) in zircon. The combined mineral and bulk-rock geochemical data suggest that the primary magma for the Tengxian hornblende gabbro was derived from a mantle wedge that had been metasomatized by voluminous subducted terrigenous sediment-derived melts in response to subduction of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean.
1. Introduction
The South China Block (SCB) is located in East Asia and consists of the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks. The tectonic evolution of the SCB includes the subduction and closure of the Nanhua, Proto-Tethys, Paleo-Tethys, and Paleo-Pacific oceans, respectively [1,2,3,4]. The Yunkai Massif is located in the southwestern SCB, in which the late Paleozoic to early Mesozoic geology is characterized by extensive deformation, metamorphism, and magmatism [1,5,6,7]. While paleogeographic reconstruction suggests that the Yunkai Massif ever constituted a segment of the eastern margin of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean [8], a debate remains about whether there was a subduction zone of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean [9,10].
Mafic magmas formed in diverse tectonic settings are often associated with different crustal recycling processes, e.g., subducted sediments at subduction zones [11], delaminated lower crusts in intracontinental orogens [12], and recycled oceanic slab in plume-related rifts [13]. Hornblende gabbro is a typical lithology at subduction zones, commonly occurring in the newly accreted mafic arc crust either as a cumulate or differentiate of hydrous mantle-derived melt, and its origin has been extensively studied in the literature [14,15,16]. Late Permian to early Triassic mafic intrusions sporadically occur in the Yunkai Massif, including hornblende gabbro, norite, dolerite, and diorite [17]. Previous studies have revealed that these mafic igneous rocks show highly enriched Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic features [10,18,19]. Nevertheless, debate continues about the tectonic setting of these mafic igneous rocks, including an intracontinental orogeny, a subduction zone, and even the tectonothermal influence of the Emeishan plume’s activity [9,18,19,20]. One of the key issues has been focused on the origin of the highly enriched isotopic signatures, which could either result from the significant involvement of recycled crustal components in the mantle source or originate from the wall rocks during open-system magmatic evolution (e.g., crustal assimilation and magma mixing), or both [10,18,20]. This requires additional geochemical analyses of minerals, which can help to further understand the petrogenesis of these mafic igneous rocks.
In this paper, we report high-precision analytical results of major and accessory minerals, including U-Pb age, Hf-O isotopes of zircon, chemical compositions and O isotope of apatite, and major and trace element contents of clinopyroxene and hornblende, together with bulk-rock major and trace elements, and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic data of an early Triassic mafic intrusion that consists of hornblende gabbro in the Tengxian area of the Yunkai Massif, South China. The comprehensive geochemical data from both mineral and bulk-rock enable us to fully understand the petrogenesis and the mass recycling recorded in these igneous rocks and to explore the geodynamic setting related to the Paleo-Tethys Ocean.
2. Geological Setting and Petrology
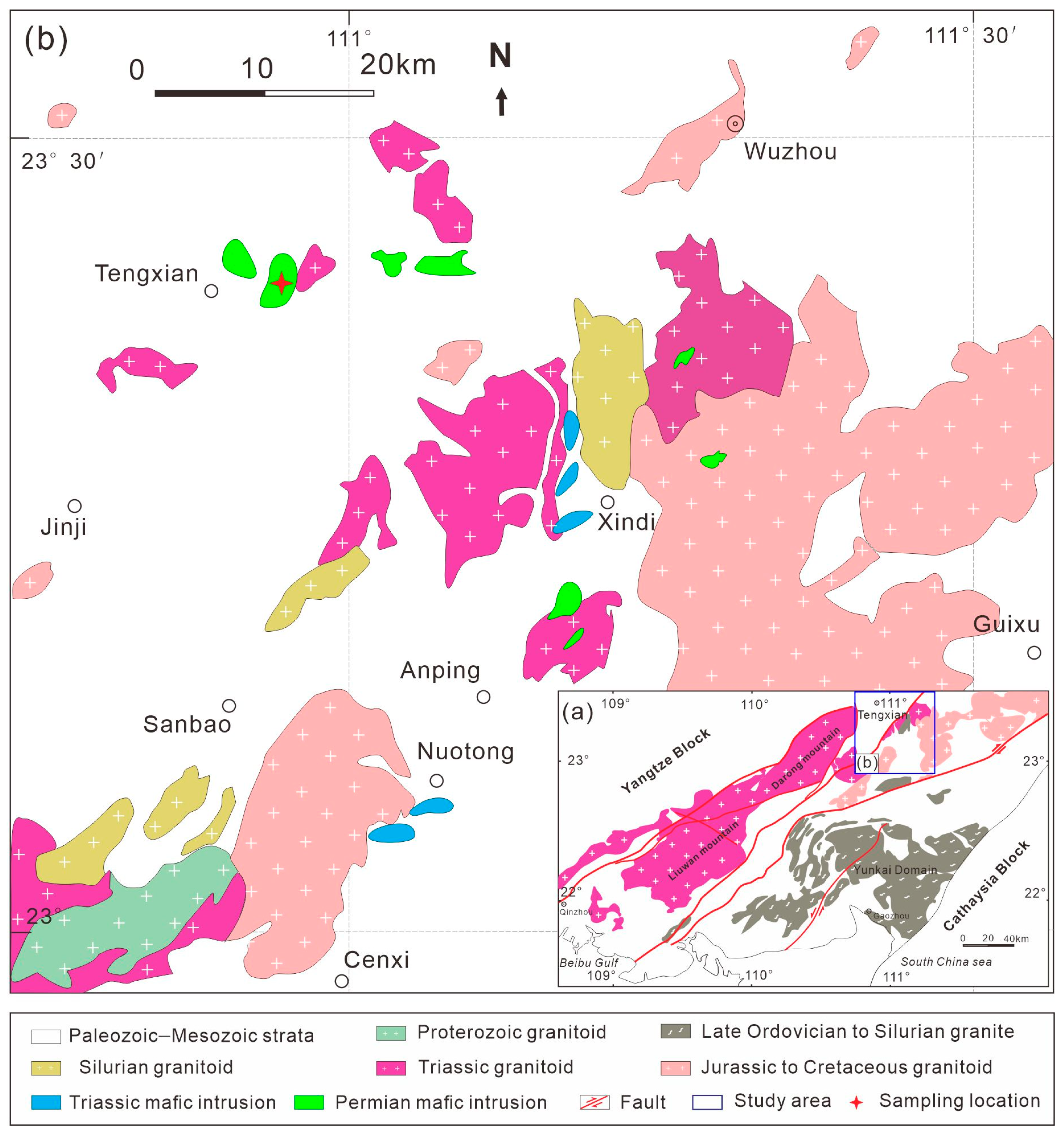
The Cathaysia Block consists of a Paleoproterozoic to early Neoproterozoic metamorphic basement which collided with the Yangtze Block to form the SCB during the Neoproterozoic era (Figure 1a). It has undergone complex tectonic–magmatic events since the early Paleozoic era, e.g., the Caledonian and Indosinian events have led to widespread lithospheric deformation, metamorphism, magmatism, and metallogeny [21,22]. The Yunkai Massif is located in the southwestern Cathaysia Block (Figure 1a), and it is also the southwestern segment of the Caledonian Wuyi-Yunkai orogen [23,24]. Three major tectonic events occurred in the early Paleozoic, early Mesozoic, and Jurassic–Cretaceous eras, respectively [3,25,26]. The early Paleozoic igneous rocks are widespread, including the anatectic granitoids, mafic volcanic lavas, and gabbroic intrusions [27,28]. The late Paleozoic–early Mesozoic (~265–231 Ma) mafic igneous rocks include basalts and intrusive rocks such as the diorite, norite, and gabbro in the Cenxi and Tengxian regions of the Yunkai Massif [10,18,19,20,29,30]. The Indosinian magmatism is widely distributed around the Yunkai Massif, including the peraluminous granitoids from Darongshan, Liuwandashan, Nali, and Napo [9,22,31,32,33].
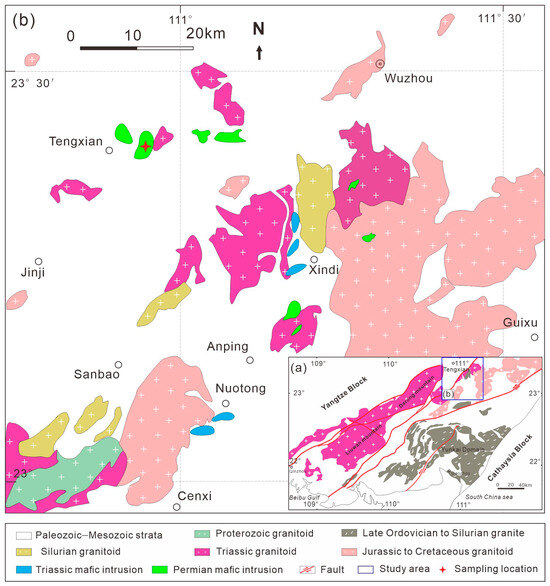
Figure 1.
(a) Geological map of Yunkai Massif showing (b) the distribution of Permian–Triassic Tengxian mafic intrusions. Modified after Zhao et al. [17].
The Tengxian area is located in the northern part of the Yunkai Massif and the gabbroic intrusion covers an area of >2 km2 (Figure 1b). It occurs as stock, intruding the early Paleozoic strata and locally overlain by the Jurassic–Cretaceous sedimentary rocks. The studied samples are hornblende gabbros, which were collected at a location of 23°21′0.31″ N and 110°54′50.70″ E (Figure 2a). They are relatively fresh and show a holocrystalline structure and massive texture. The major rock-forming mineral compositions are obtained through visual estimation, comprising clinopyroxene (10–15%), hornblende (20–25%), plagioclase (35–40%), K-feldspar (5–10%), biotite (5–10%), and quartz (2–5%) with accessory ilmenite, zircon, and apatite. The clinopyroxene (0.1–0.5 mm) is euhedral to subhedral with some showing a sieved texture, where it is surrounded by anhedral quartz and hornblende (Figure 2b–e). The hornblende (0.2–1.0 mm) is euhedral–subhedral in shape and contains inclusions of plagioclase, apatite (0.1–0.5 mm), and ilmenite (0.2–0.5 mm) (Figure 2b,c,f). The plagioclase (0.2–1.5 mm) and K-feldspar (0.2–1.0 mm) are euhedral–subhedral and coexist with clinopyroxene, hornblende, and anhedral biotite, demonstrating kaolinization at varying degrees (Figure 2b,c). The biotite (0.2–1.0 mm) occurs as anhedral crystal surrounded by plagioclase (Figure 2c,d). Quartz (0.1–0.5 mm) is anhedral in shape (Figure 2b,d). The contact boundary between quartz and plagioclase is relatively straight (Figure 2b). In this study, we have conducted bulk-rock geochemical analyses on four samples and carried out in situ chemical analyses on minerals from 19XZT-1 and 19XZT-2.

Figure 2.
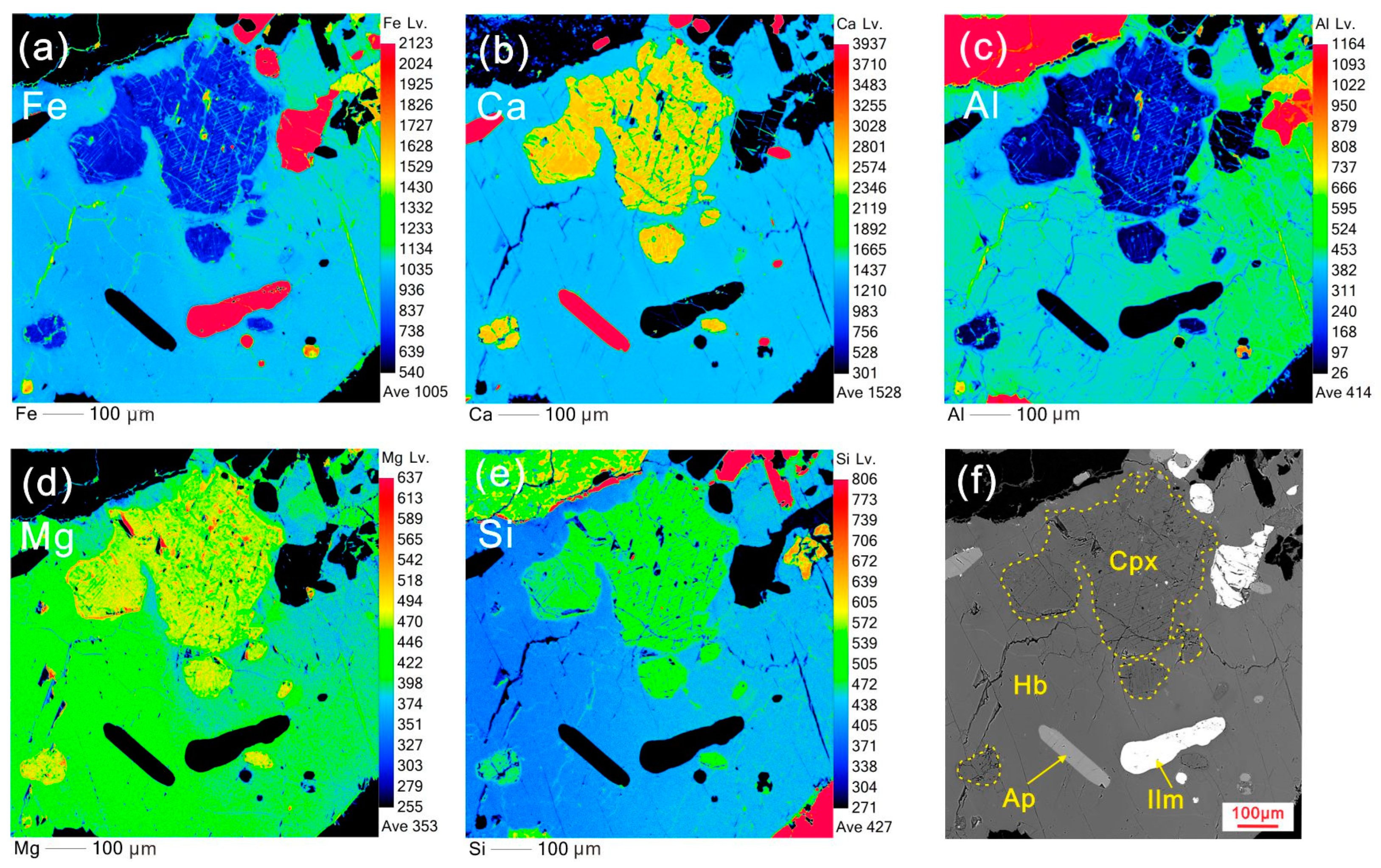
A photo of the sampling location in the field (a) and the mineral assemblage of hornblende gabbro (b–f). Photo (b) illustrates Pl inclusions in Hb and a subhedral Cpx surrounded by Kfs and Qz. Photo (c) shows Ap and Ilm inclusions in Hb. Photo (d) exhibits a mineral assemblage of Cpx (sieved), Hb, Pl, Bt, and Qz (anhedral). Photo (e) illustrates Ilm inclusions in Hb. Photo (f) shows the subhedral to euhedral Hb and the sieved Cpx. Mineral abbreviations: Cpx—clinopyroxene; Hb—hornblende; Pl—plagioclase; K-feldspar—Kfs; Bt—biotite; Qz—quartz; Ap—apatite; Ilm—ilmenite; G-I—Generation I; and G-II—Generation II. See details in the text. The red outlines in photos (b,c) indicate the fields for elemental mapping.
Collectively, two generations of a mineral assemblage can be identified with Generation I consisting of apatite (zircon) + clinopyroxene + plagioclase, whilst an assemblage of ilmenite + hornblende + biotite + K-feldspar + quartz comprises Generation II.
3. Analytical Techniques
3.1. Electron Probe Microanalyses (EPMA)
Elemental mapping for Fe, Ca, Al, and Mg were obtained by electron probe microanalysis (EPMA, JEOL JXA-iSP100 Electron Microprobe from Japan) at Guangzhou Tuoyan Analytical Technology Company Limited (GTATCL), Guangzhou, China. The operating conditions included an accelerating voltage of 20 kV and a beam current of 100 nA with a beam size of 1–2 µm. Mg, Si, and Al were analyzed using a TAP crystal. Fe and Ca were analyzed using a LIF and PETJ crystal, respectively.
Major element analysis of minerals and back-scattered electron (BSE) images were carried out using a JEOL JXA-iSP100 Electron Microprobe at GTATCL. The analytical conditions included an accelerating voltage of 15 kV and a beam current of 10 nA, and a 1–2 μm spot diameter. The analytical errors were within 2% based on standards. The standards used during element calibrations were apatite for Ca; albite for Na and Si; almandine for Al; orthoclase for K; and pyroxene for Mn, Fe, and Mg. The data reduction was performed via the atomic number absorption–fluorescence (ZAF) correction procedure.
Apatite grains were mounted in epoxy and polished to expose the internal texture. The major element contents of apatite were determined by a JOEL JXA-8100 electron microprobe from Japan at the Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry (GIG), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Guangzhou, China. The operating conditions were 15 kV accelerating voltage, 20 nA probe current, and 5 µm spot diameter. The detailed analytical procedure was reported by Zhang et al. [34].
3.2. LA-(MC)ICP-MS Analyses
3.2.1. Zircon U-Pb Age and Hf Isotope Analyses
Zircons were selected from the sample 19XZT-1 using conventional heavy-liquid and magnetic separation techniques and then handpicked under a binocular microscope, being mounted in epoxy resin disks together with zircon standards (Plesovice, Qinghu, and Penglai), and polished to around half their size for analysis. Cathodoluminescence (CL) images of the analyzed zircons were obtained using a JOEL JXA-8100 electron microprobe at GIGCAS, Guangzhou, China.
Zircons U-Pb dating and Hf isotope analyses were conducted at the Guilin University of Technology (GUT), China. Zircon U-Pb dating results and trace element contents were obtained using a laser ablation (LA) system coupled to an Agilent 7500a inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS). The running conditions included 80 mJ laser energy and a repetition rate of 6 Hz with a spot size of 32 μm and an ablation time of 50 s. The ablated aerosol was carried to the ICP source by helium via a Squid system to smooth the signals. The glass NIST610 [35] and zircon Plesovice (337 Ma) [36] were used as external calibration standards for age calculation and 29Si as the internal standard for concentration calculation [37,38]. The raw data calibration for zircon isotope ratios and trace elements was performed by ICPMSDataCal 12.0 [39]. Weighted mean calculations of zircon age and Concordia diagrams were made using the Isoplot program (version 3.0) [40]. Detailed analytical procedures were described by Guo et al. [11] and Tu et al. [41].
In situ zircon Lu-Hf isotope compositions were measured using a Neptune multicollector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (MC-ICP-MS) equipped with a 193 nm laser ablation system at the GUT. The operating conditions included an ablation time of 26 s, a repetition rate of 10 Hz, a laser beam energy density of 10 J/cm2, and an ablation spot diameter of 32 μm. Measured 176Hf/177Hf ratios were normalized to 179Hf/177Hf = 0.7325. The zircon U-Pb ages were used to calculate the εHf (t) values with the parameters including a 176Lu decay constant of λ = 1.867 × 10−11 year−1 [42] and chondritic values of 176Hf/177Hf = 0.282785 and 176Lu/177Hf = 0.0336 [43]. The analytical technique and calibration methods were described by Wu et al. [44] and Xu et al. [45].
3.2.2. Trace Element Analyses of Major Rock-Forming Minerals
In situ trace element analyses of clinopyroxene and hornblende were determined using an NWR 193 nm ArF Excimer laser ablation system coupled to an iCAP RQ (LA-ICP-MS) at the GTATCL. The ICP-MS was tuned using NIST 610 standard glass to yield low oxide production rates. An amount of 0.7 L/min He carrier gas was fed into the cup, and the aerosol was subsequently mixed with 0.89 L/min Ar make-up gas. The laser energy was 3 J/cm2, with a repetition rate of 6 Hz, a 30–50 μm spot size, and an analysis time of 45 s, followed by a 40 s background measurement. Trace element compositions of the samples were calibrated using various reference materials (NIST SRM 610 and BCR-2G) with Si content obtained by EPMA as the internal standard [39]. The glass standard BHVO-2G and BIR-1G were also determined to evaluate the data quality [46,47]. The raw isotope data were reduced using the 3D Trace Element data reduction scheme of IOLITE software (version 4.9.3) [48], in which user-defined time intervals were established for the baseline correction procedure to calculate session-wide, baseline-corrected values for each isotope. Detailed analytical techniques were described by Liu et al. [39] and Chu et al. [49].
3.3. SIMS Analyses of Zircon and Apatite O Isotopes
The oxygen isotope compositions of zircon and apatite were analyzed using a High- Resolution Secondary Ion Microprobe Spectrometer (Cameca HR-SIMS-1280) from France at GIGCAS, Guangzhou, China. Separated zircon and apatite grains and standards (Qinghu zircon and Durango apatite) were mounted in epoxy disks. Oxygen isotopes were measured in a multi-collector mode using two off-axis Faraday cups. During the analysis, the Cs+ primary ion beam was accelerated at 10 kV with an intensity of approximately 2 nA and a spot size of 20 × 30 μm. A normal incidence electron flood gun was used to compensate for the sample charge. The analytical procedures of apatite were similar to those used for the zircon oxygen isotope as described by Li et al. [50]. The instrumental mass fractionation factor (IMF) was obtained using the Durango fluorapatite and Penglai zircon as references, respectively, for apatite and zircon. The IMF was corrected using zircon standard 91500 with δ18OVSMOW = 9.9‰ [51]. The detailed analytical procedures and working conditions of zircon were reported by Xia et al. [52]. The analytical geochemical data for major minerals, accessory minerals including ilmenite, zircon, and apatite, and reference standards are listed in appended data tables (Supplementary Materials Tables S1–S6).
3.4. Bulk-Rock Major and Trace Element Analyses
Bulk-rock major and trace element contents were analyzed at Tongwei Analytical Technology Company Limited (TATCL), Guizhou, China. The fresh samples were powdered to less than 200 mesh. Around 0.5 g sample powder was mixed with 3.6 g Li2B4O7, 0.4 g LiF, 0.3 g NH4NO3, and minor LiBr in a platinum crucible. It was then melted in a furnace to form a glass disk for major element analysis. Major oxide element contents were measured by an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF). The analytical errors were within 2%. Trace element concentrations were determined by a Thermo Fisher (Dreieich, Germany) induced coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS) X2. Around 0.5 g sample powder was digested in 1 mL HNO3 + 0.5 mL HF in high-pressure Teflon bombs for two days. The analytical errors were within 5%, based on repetitive analyses of USGS standards W-2a (diabase) and BHVO-2 (basalt). More detailed analytical procedures were reported by Liu et al. [53].
3.5. Bulk-Rock Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf Isotope Analyses
The bulk-rock Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic compositions were also measured using a Neptune multicollector ICP-MS at the TATCL, Guizhou, China. Sample powders (~50 mg) were dissolved in distilled HNO3 + HF in screw-top PFA beakers at 120 °C for at least seven days. The Sr and REE were separated via cation columns. Nd was further separated by HDEHP-coated Kef columns. Hf was separated via a modified single-column separation procedure including ion exchange with Ln-specific resin. The procedural blanks were less than 200 pg for Sr and around 30 pg for Nd and around 50 pg for Hf. The measured values of 87Sr/86Sr, 143Nd/144Nd, and 176Hf/177Hf were separately normalized to 86Sr/88Sr = 0.1194, 146Nd/144Nd = 0.7219, and 179Hf/177Hf = 0.7325. The 87Sr/86Sr, 143Nd/144Nd, and 176Hf/177Hf ratios of the samples were corrected to NBS SRM 987 standard [87Sr/86Sr = 0.710248 ± 10, (2σ, n = 6)], JNdi-1 standard [143Nd/144Nd = 0.512114 ± 6 (2σ, n = 6)], and JMC-14374 standard [176Hf/177Hf = 0.282187 ± 5 (2σ, n = 6)], respectively. For Pb isotopic analyses, the sample powders were dissolved in concentrated HF at 180 °C for seven days. Pb was separated via a cation exchange technique with diluted HBr. The procedural blanks of Pb were within 50 pg. Pb isotopes were corrected using the international standard NBS 981 [54]. The results measured for NBS 981 are 204Pb/206Pb = 0.059015 (2σ, n = 6), 207Pb/206Pb = 0.914324 (2σ, n = 6), and 208Pb/206Pb = 2.164530 (2σ, n = 6), respectively. Detailed analytical procedures for Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes have been reported in the previous literature [55,56,57]. During the isotope analyses, analytical results of international standards of W-2a (diabase) and BHVO-2 (basalt), respectively, yield 87Sr/86Sr = 0.706995 ± 7 (2σ) and 87Sr/86Sr = 0.703479 ± 7 (2σ), 143Nd/144Nd = 0.512515 ± 6 (2σ) and 143Nd/144Nd = 0.512980 ± 6 (2σ), 176Hf/177Hf = 0.282726 ± 3 (2σ) and 0.283102 ± 4 (2σ), 206Pb/204Pb = 18.7588 ± 8 (σ) and 206Pb/204Pb = 18.6489 ± 4 (σ), 207Pb/204Pb = 15.6732 ± 10 (σ) and 207Pb/204Pb = 15.5371 ± 5 (σ), and 208Pb/204Pb = 38.6767 ± 32 (σ) and 208Pb/204Pb = 38.2499 ± 14 (σ).
4. Results
4.1. Zircon U-Pb Age and Hf-O Isotopes
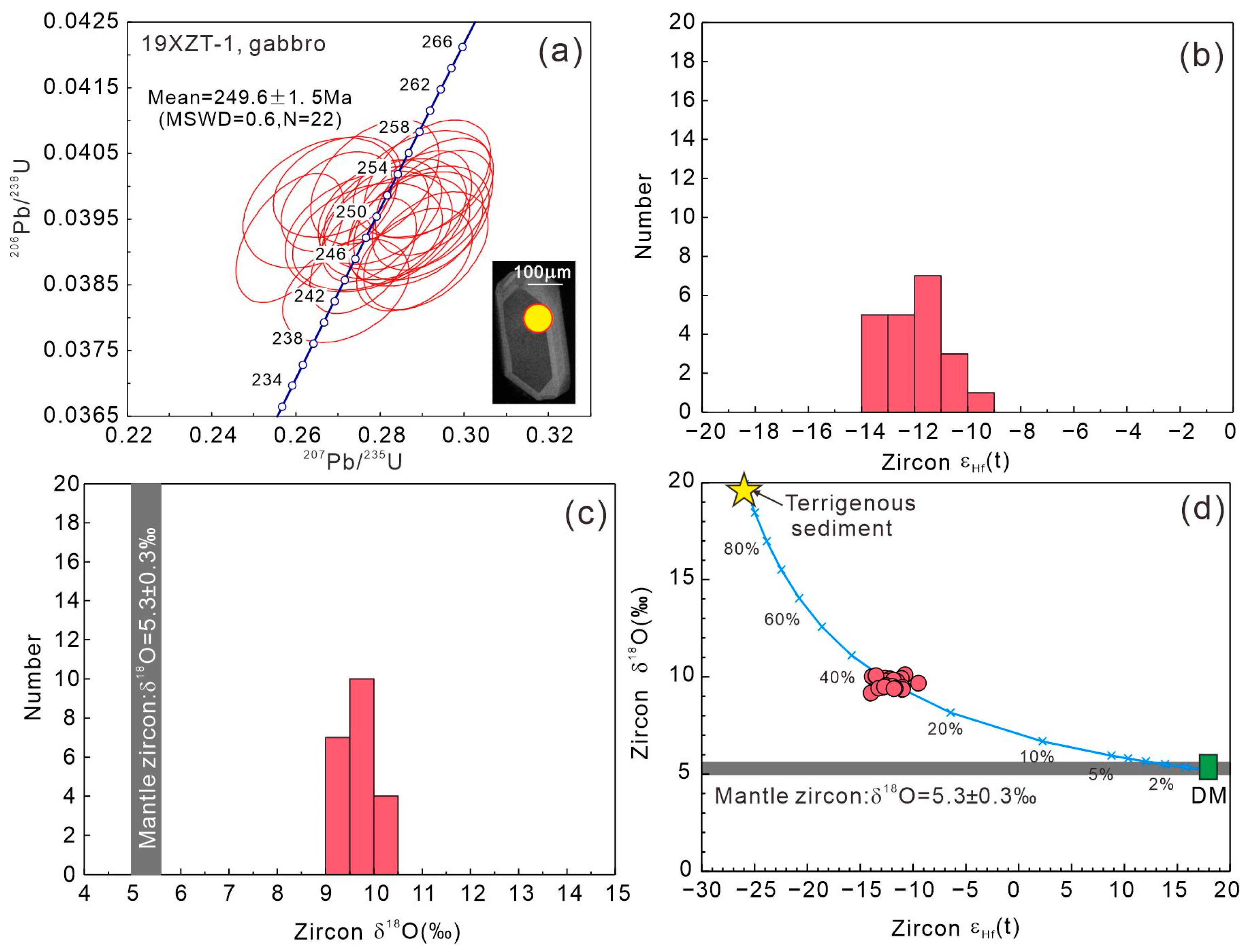
The zircons from the Tengxian hornblende gabbro (19XZT-1) are transparent crystals and have Th/U ratios ranging from 0.57 to 1.10, indicating a magmatic origin. The U-Pb dating of them yields a weighted mean 238U/206Pb age of 249.6 ± 1.5 Ma (MSWD = 0.6, n = 22, Figure 3a), confirming its emplacement during the early Triassic era. They have εHf(t) values from −14.0 to −9.5 (Figure 3b) and δ18O from 9.2 to 10.1‰, with an average of 9.7‰ (Figure 3c), much higher than the value of normal mantle zircons (δ18O = 5.3 ± 0.3‰) [58]. In an εHf(t) versus δ18O diagram (Figure 3d), the zircons plot around the mixing curve between the depleted mantle and a terrigenous sediment component [59,60,61,62], suggesting the involvement of recycled crust in their petrogenesis.
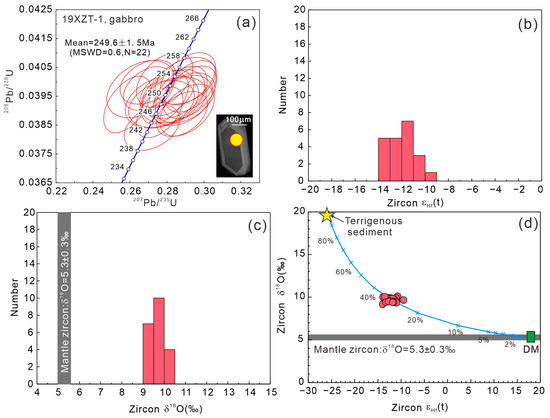
Figure 3.
Cathodoluminescence images and a U-Pb Concordia diagram of zircon from the Tengxian hornblende gabbro (a), histograms of εHf(t) values (b) and δ18O (c), and a δ18O versus εHf(t) diagram (d) for zircons from the Tengxian hornblende gabbro. Data sources: depleted mantle (DM) has Hf = 0.3 ppm and εHf(t) = +18 [59], and δ18O = 5.25 [58], terrigenous sediment has Hf = 10 ppm [60], εHf(t) = −26 [61], and δ18O = 20‰ [62].
4.2. Mineral Chemistry
4.2.1. Clinopyroxene
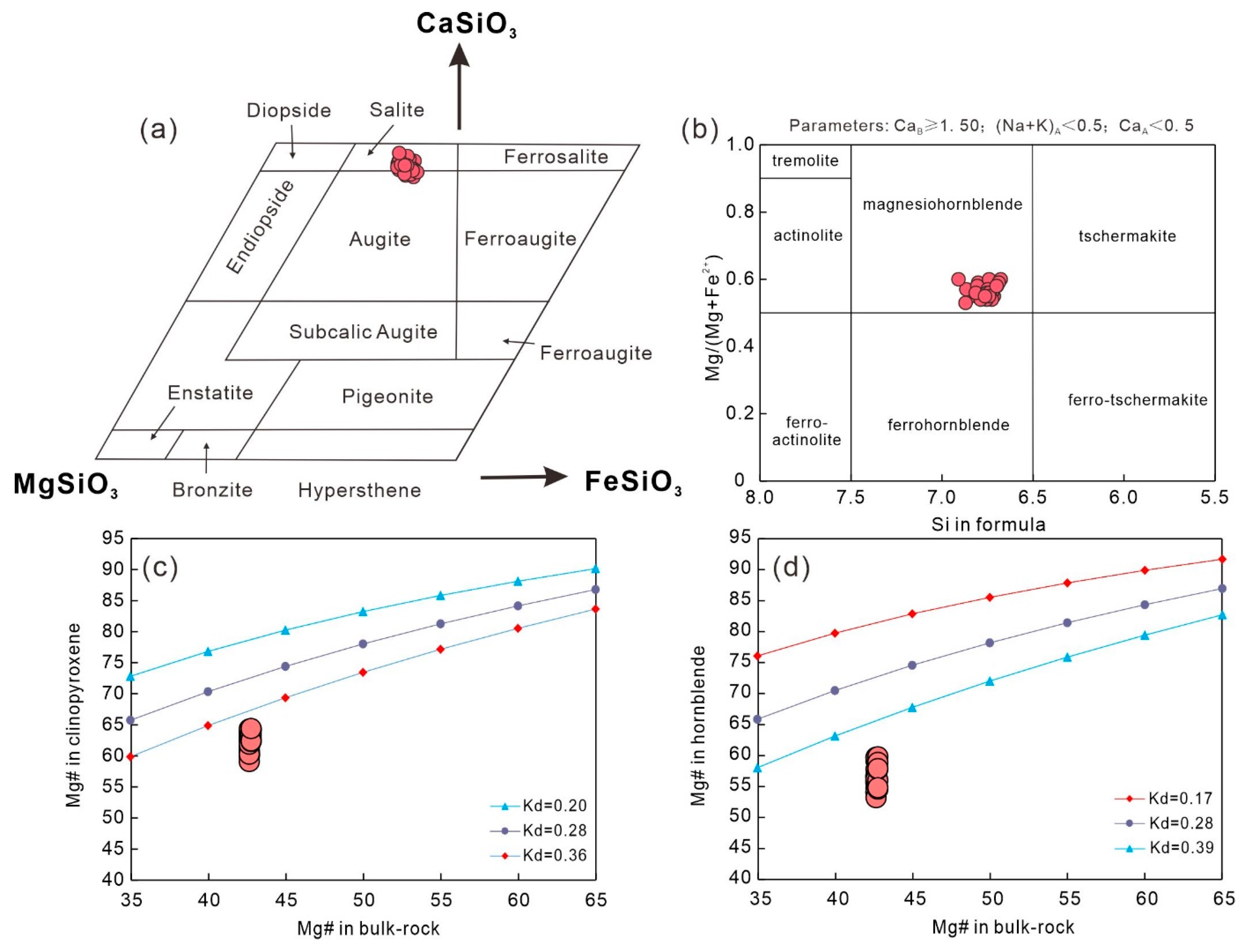
The clinopyroxene contains SiO2 (50.6–52.6 wt.%), CaO (21.4–23.0 wt.%), FeO (11.6–13.9 wt.%), MgO (11.13–12.05 wt.%), and Mg# (Mg# = 100 × Mg/(Mg + Fe2+) in its atomic ratio (59.1–64.4) (Table S2). It is classified as augite–salite with a formula of Wo44.2–47.9En32–35.0Fs18.5–22.5 (Figure 4a). We use the clinopyroxene thermobarometer from Putirka (2008) to calculate the P-T conditions of crystallization based on the clinopyroxene compositions [63]. The results suggest that the clinopyroxene crystallized under the conditions of T = 999–1069 °C and P = 192–846 MPa (Table S2).
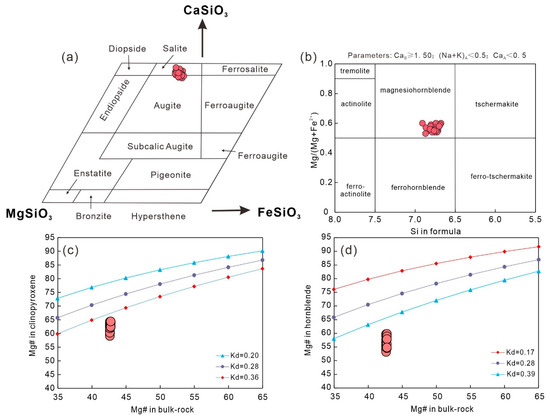
Figure 4.
(a) CaSiO3-MgSiO3-FeSiO3 classification diagram of clinopyroxene. (b) A Si in formula versus Mg/(Mg + Fe2+) classification diagram of hornblende. A comparison of Mg# between the bulk-rock and clinopyroxene (c) and hornblende (d) in the Tengxian hornblende gabbros. The Fe-Mg partition coefficient (Kd) values of clinopyroxene and hornblende are from [63,64].
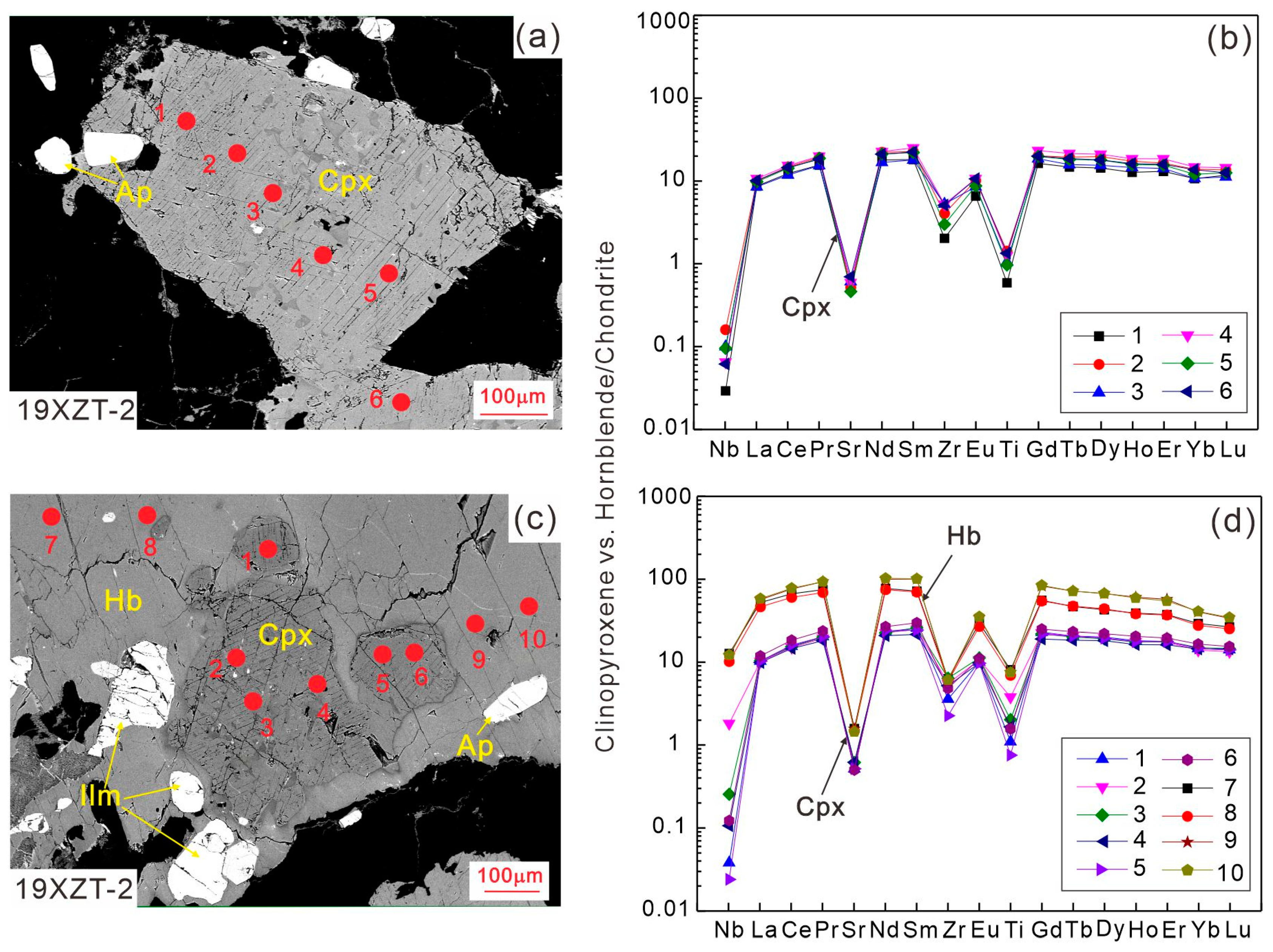
In the elemental mapping results, similar concentrations of Fe, Ca, Al, Mg, and Si are observed in both euhedral and sieved clinopyroxene (Figure 5 and Figure 6), indicating an identical origin. The apatite is entrapped in euhedral clinopyroxene, indicating its crystallization earlier than clinopyroxene (Figure 5). Furthermore, both euhedral and sieved clinopyroxene crystals show parabola-like curves with Nb, Sr, Zr, and Ti depletions relative to REE and significantly negative Eu anomalies (Eu/Eu* = 0.38–0.50) in primitive mantle (PM)-normalized trace element spidergrams (Figure 7a,b).
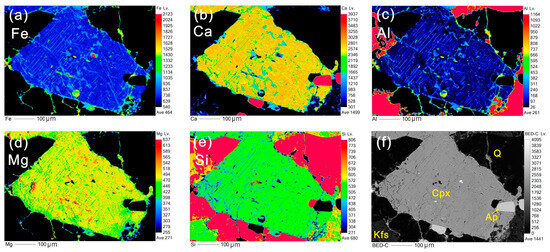
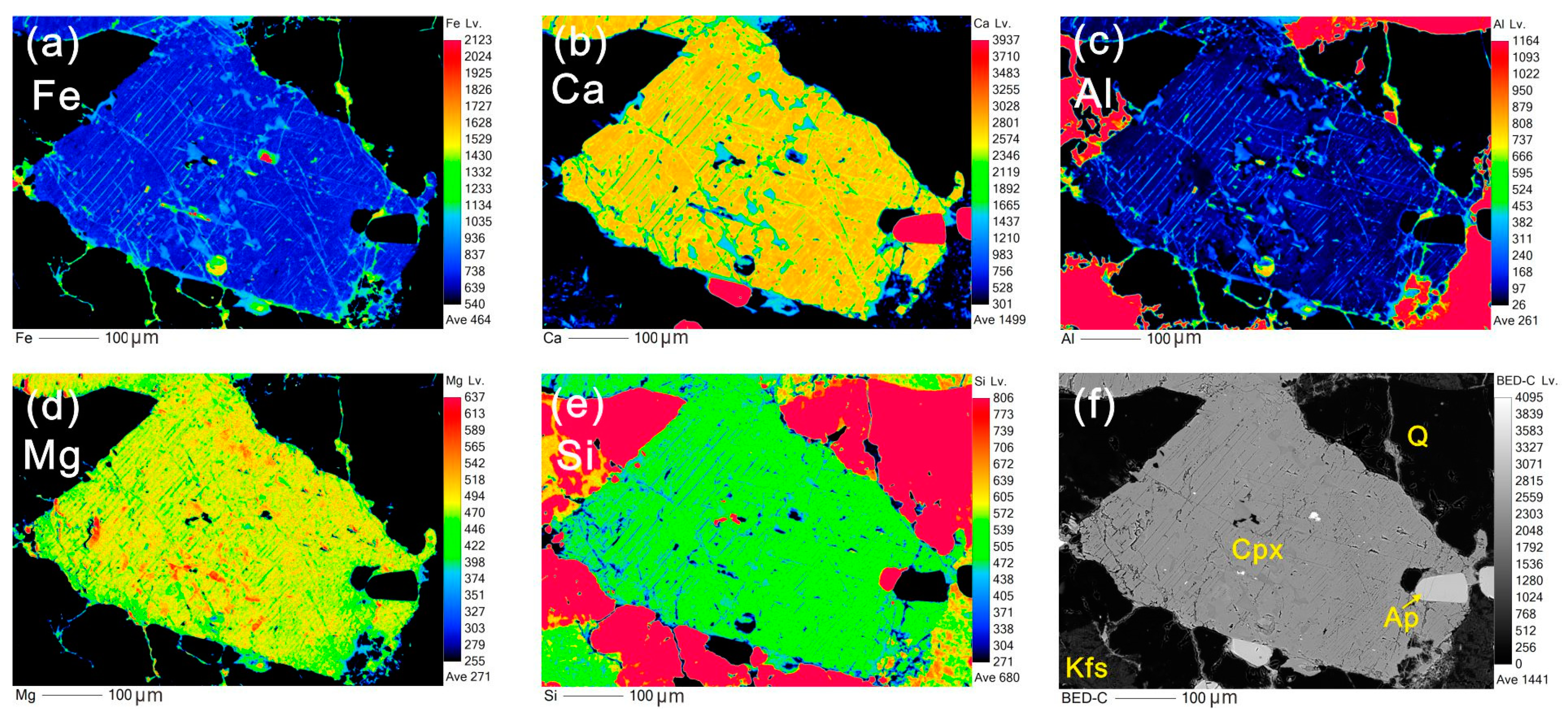
Figure 5.
Mapping results of euhedral clinopyroxene and its surrounding quartz (Sample 19XZT-2). (a) FeO, (b) CaO, (c) Al2O3, (d) MgO, (e) SiO2, and (f) BSE image of coexisting minerals, the mineral abbreviations are referenced in Figure 2.
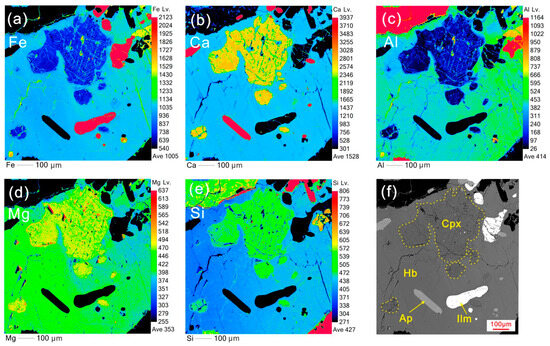
Figure 6.
Mapping results of a sieved Cpx crystal and its surrounding hornblende and accessory minerals, showing the compositional disequilibrium and reaction texture (Sample 19XZT-2). (a) FeO, (b) CaO, (c) Al2O3, (d) MgO, (e) SiO2, and (f) BSE image of the mineral association, the mineral abbreviations are referenced in Figure 2.
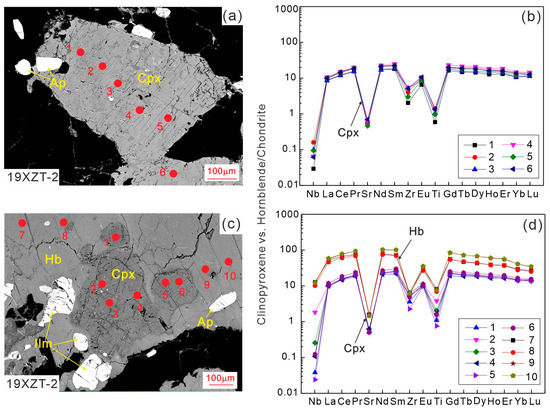
Figure 7.
Back-scattered electron images showing a euhedral clinopyroxene (a) and a sieved clinopyroxene with surrounding hornblende (c) (sample 19XZT-2). Red full circles and numbers indicate the locations and orders of LA-ICPMS analyses. Diagrams (b,d) show the PM-normalized trace element patterns of clinopyroxene and hornblende in (a) and (c), respectively. Normalized values of PM are from [65] hereafter.
4.2.2. Hornblende
The hornblende has 44.4–47.2 wt.% SiO2, 9.54–10.7 wt.% MgO, 18.0–19.5 wt.% FeO, 7.59–8.53 wt.% Al2O3, and 10.9–11.6 wt.% CaO, and Mg# (53.2–59.8) (Table S3) and is classified as magnesiohornblende (Figure 4b). The Mg# of clinopyroxene and hornblende show disequilibrium with the bulk-rock Mg# (Figure 4c,d), consistent with the accumulation of clinopyroxene and hornblende to some degree (Figure 2). The hornblende also shows quite similar trace element spidergrams [e.g., REE enrichments and Nb, Sr, Zr, and Ti depletions, and significant negative Eu anomalies (Eu/Eu* = 0.38–0.46)] to clinopyroxene. Relative to the clinopyroxene core, the surrounding hornblende has much higher trace element concentrations (Figure 7c,d).
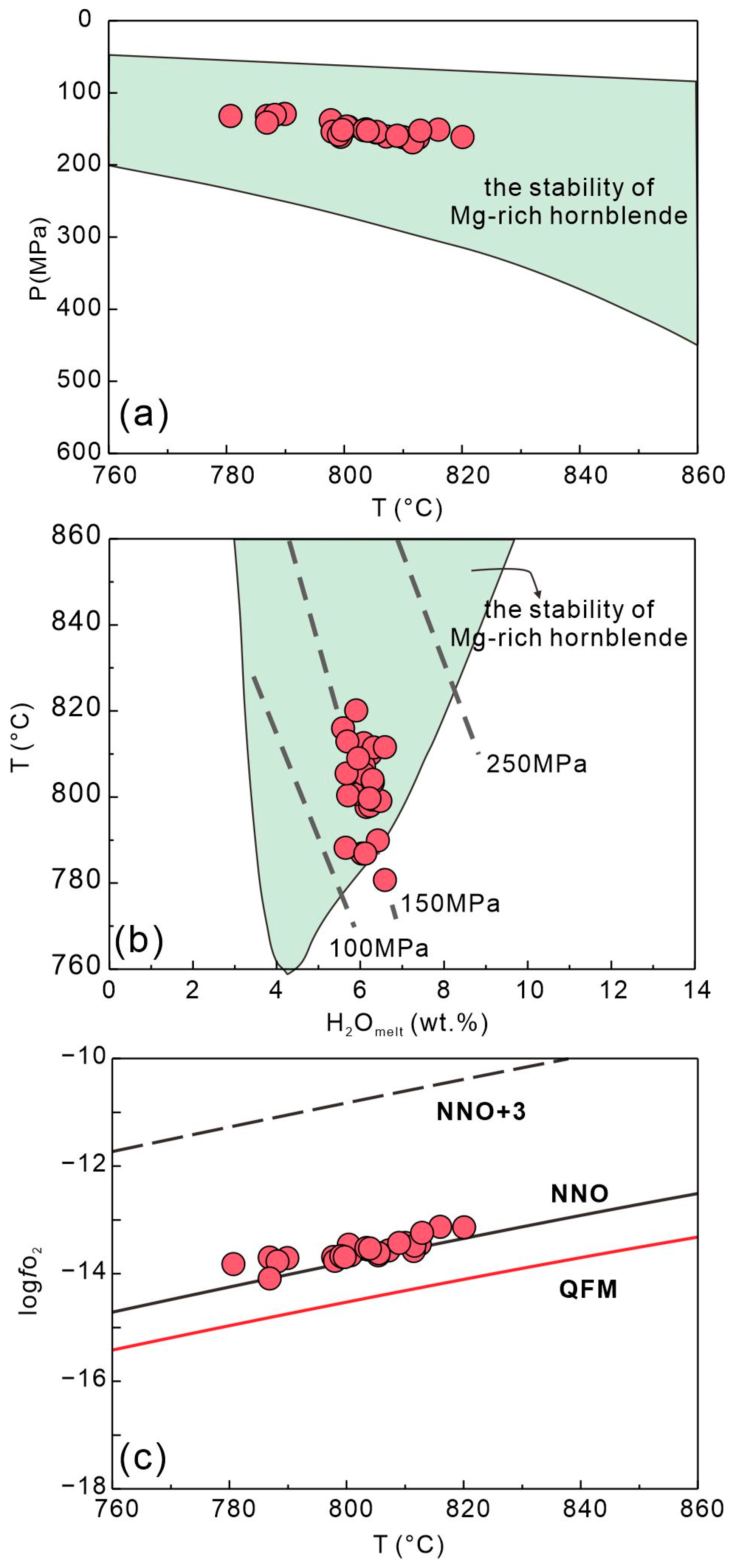
Based on the chemical compositions (Table S3), we use the thermobarometer to estimate the crystallization conditions of hornblende [66]. The results show that the hornblende crystallized under the conditions of T = 780–820 °C, P = 129–168 MPa, H2Omelt = 5.6–6.6 wt.%, and logfO2 = ΔNNO − ΔNNO + 0.45 (Figure 8). The crystallization temperature of hornblende is much lower than that of clinopyroxene, consistent with the petrographic observations that clinopyroxene crystallizes earlier than hornblende (Figure 2).
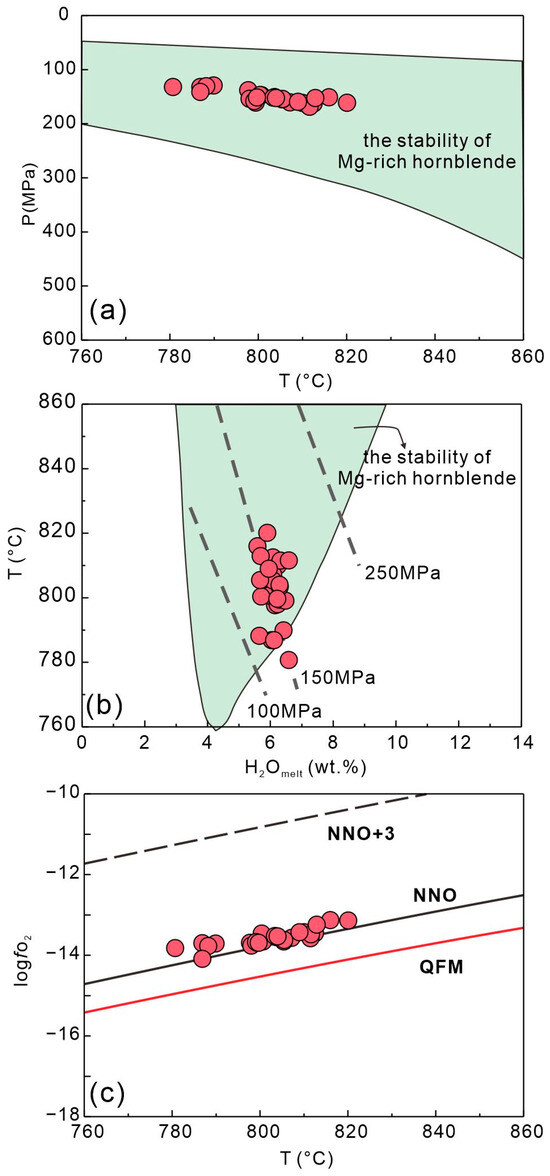
Figure 8.
(a) P (MPa) versus T (°C), (b) T versus H2Omelt, and (c) logfO2 versus T diagrams of hornblende in the Tengxian hornblende gabbro. The green field in (a,b) represents the stability fields of Mg-rich calcic hornblende crystallizing in normal magmatic conditions [67]. The dashed lines in (b) show isobars, whereas (c) reports the most common metal–metal oxide buffers according to Hirschmann et al. [68].
4.2.3. Plagioclase
The plagioclase contains SiO2 (54.0–55.5 wt.%), Al2O3 (28.2–28.9 wt.%), CaO (10.9–11.8 wt.%), Na2O (4.73–5.46 wt.%), and FeO (0.09–0.17 wt.%), classified as labradorite with anorthite (An) content ranging between 51.9 and 57.8 (Table S4), suggesting its crystallization from a basaltic magma. Also, the elemental mapping results help to identify the K-feldspar from plagioclase, which can hardly be distinguished due to surface alteration (Figure 2).
4.2.4. Fe-Ti Oxides
The Fe-Ti oxides in the Tengxian hornblende gabbro contain 48.2–51.58 wt.% TiO2, 46.10–49.49 wt.% FeO, 0.03–0.09 wt.% MgO, and 1.10–1.93 wt.% MnO and are classified as ilmenite (Table S5), indicating the reducing state.
4.2.5. Apatite
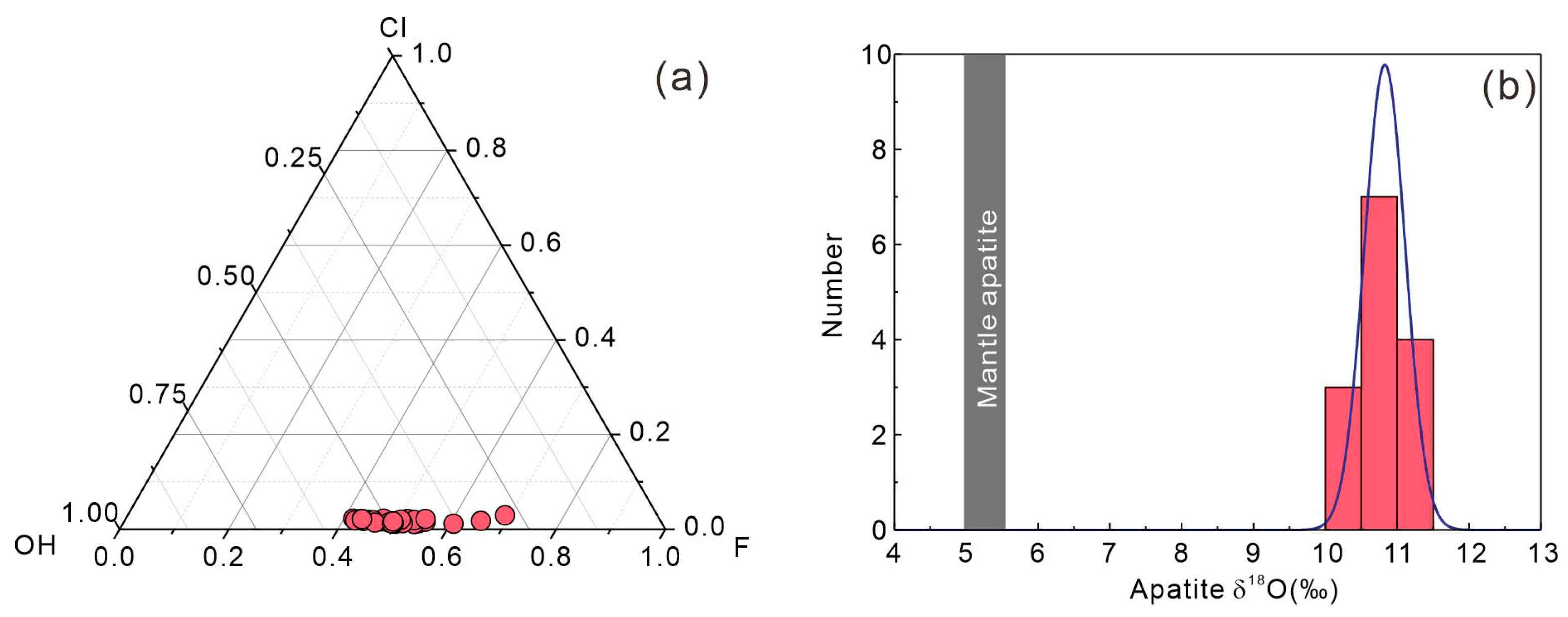
The apatite crystals from the Tengxian hornblende gabbro are mostly prismatic, with a grain size ranging from 50 to 100 µm (Figure 2c), and belong to hydroxyapatite (Figure 9a). They contain 40.9–43.6 wt.% P2O5, 55–57.6 wt.% CaO, 0.02–0.34 wt.% FeO, 0.01–0.24 wt.% MnO, 0.08–0.20 wt.% Cl, and 1.56–2.54 wt.% F (Table S6).
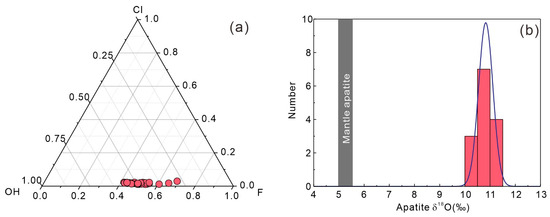
Figure 9.
Plot of F-Cl-OH triangle classification diagram of apatite (a) and histograms of δ18O (b) of apatite crystals from the Tengxian hornblende gabbro.
The analyzed apatites have crust-like O isotopic compositions, with δ18O ranging from 10.3‰ to 11.2‰ and a mean δ18O value of 10.8‰ (n = 14) (Figure 9b). Such high δ18O values in apatite are also consistent with the high-δ18O zircons when considering the oxygen isotope fractionation between the two accessory phases (the average ∆δ18O zircon-apatite = 0.4 ± 0.6‰, 1σ) [69].
In summary, the mineral associations of clinopyroxene and plagioclase in Generation I indicates their crystallization in a basaltic magma, while the presence of hornblende, K-feldspar, quartz, and ilmenite in Generation II suggests an evolved alkaline melt under reducing and hydrous conditions. More importantly, the very high δ18O values in both zircon and apatite and negative εHf(t) in zircon imply a significant involvement of recycled crust during their petrogenesis.
4.3. Bulk-Rock Geochemistry
4.3.1. Major and Trace Element Geochemistry
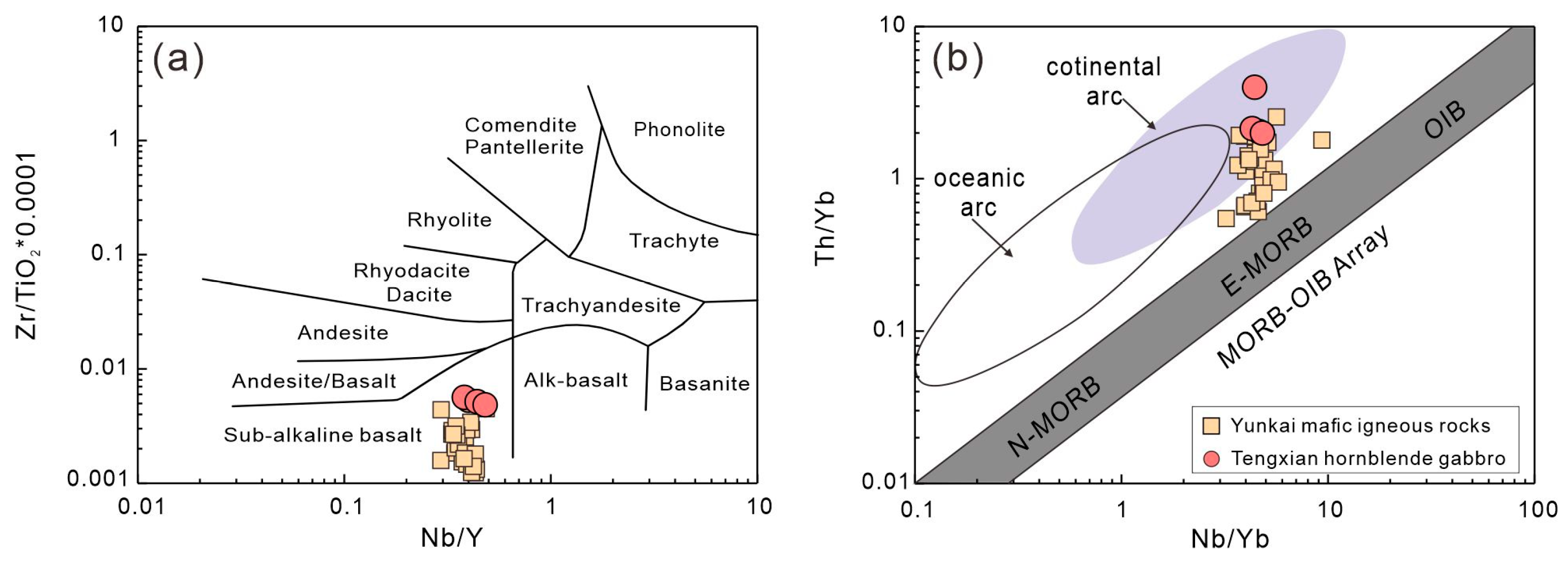
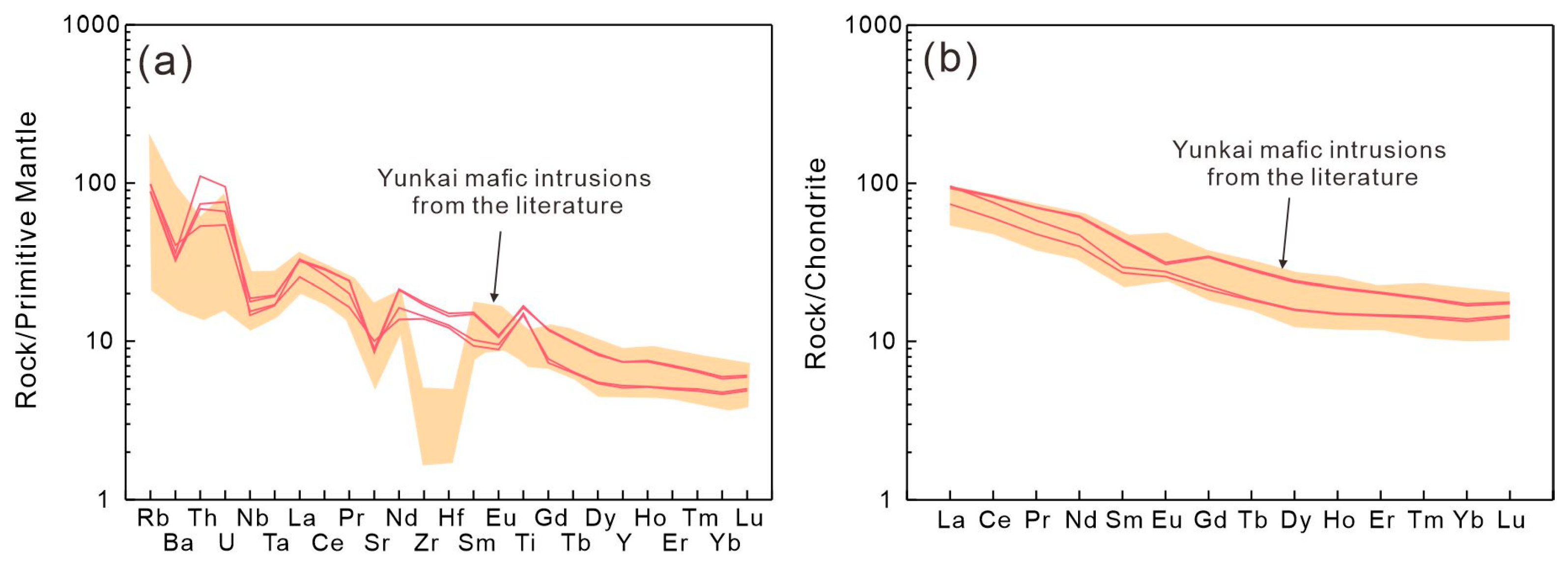
The Tengxian hornblende gabbros have 44.0–50.4 wt.% SiO2, 4.99–5.2 wt.% MgO, 12.4–14.7 wt.% FeO, 13.82–15.35 wt.% Al2O3, and 6.16–6.88 wt.% CaO. They plot in the range of sub-alkaline basalt on a Nb/Y-Zr/TiO2 diagram (Figure 10a) and fall into the field of continental arc magmas on a Th/Yb versus Nb/Yb diagram (Figure 10b). In the PM-normalized trace element spidergrams (Figure 11a), these rocks show enrichments in large-ion lithophile elements (LILEs) and light rare earth elements (LREEs) but depletions in Sr and Nb-Ta. They also show sub-parallel chondrite-normalized REE patterns (Figure 11b) characterized by obvious LREE enrichment relative to HREE and variable Eu anomalies (Table S7).
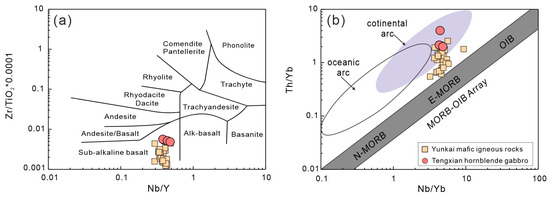
Figure 10.
Plots of 10–4 × Zr/TiO2 versus Nb/Y (a) and Th/Yb versus Nb/Yb (b) [70] of the Tengxian hornblende gabbro. Comparative data of late Permian to early Triassic mafic intrusions in the Yunkai Massif are from t he literature [18,20].
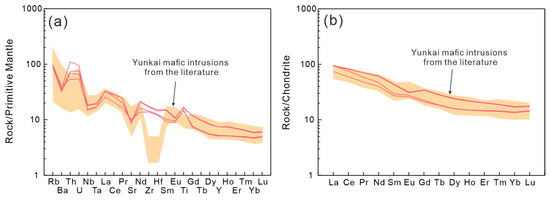
Figure 11.
PM-normalized trace element spidergrams (a) and chondrite-normalized REE patterns (b) of the Tengxian hornblende gabbro. Data sources are the same as in Figure 10.
4.3.2. Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf Isotope Geochemistry
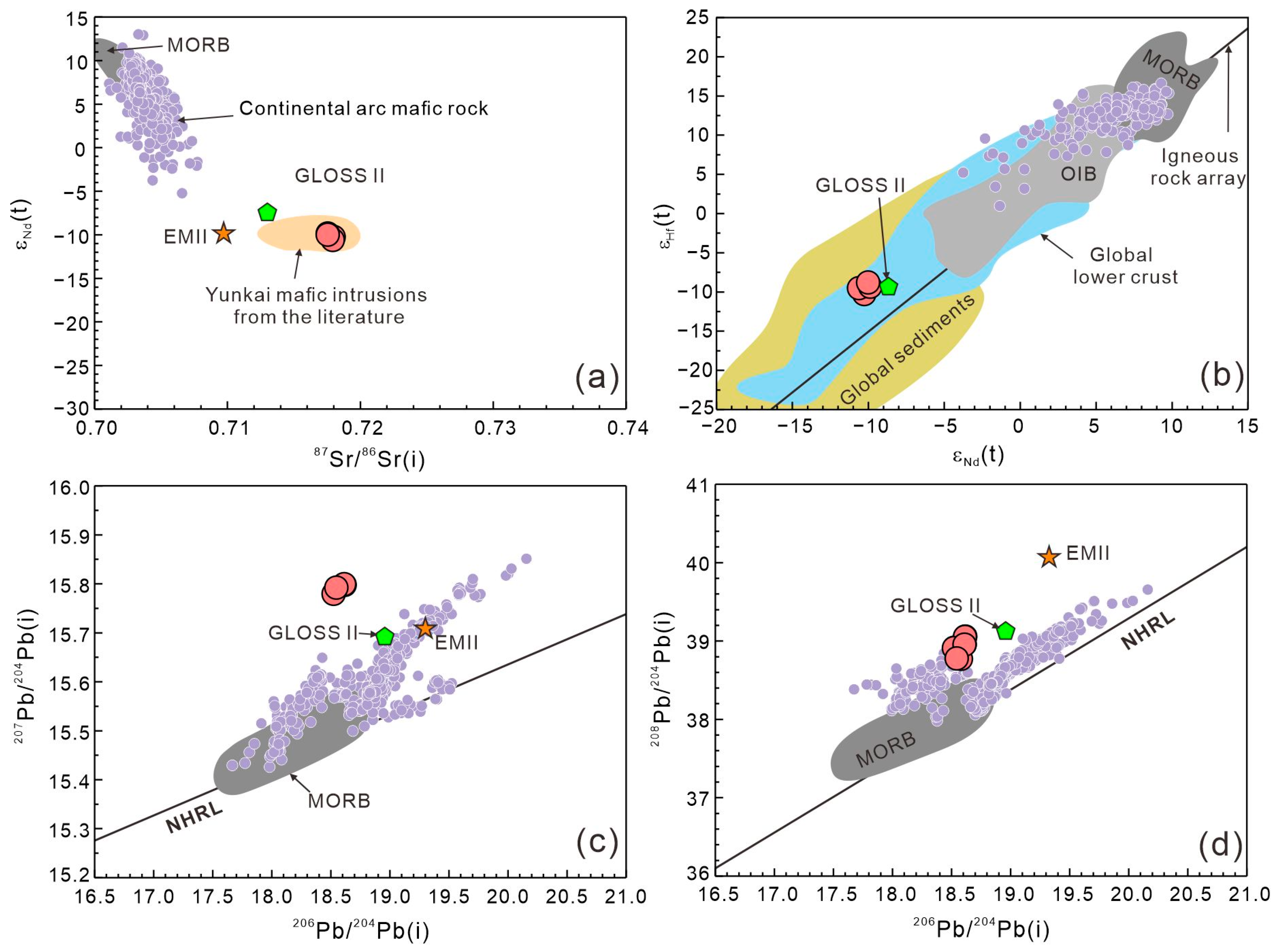
The Tengxian hornblende gabbros show narrow Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic variations (Table S8), with 87Sr/86Sr(i) = 0.7175–0.7180, εNd(t) = −10.6~−9.9, εHf(t) = −10.3~−9.4, 206Pb/204Pb(i) = 18.52–18.62, 207Pb/204Pb(i) = 15.78–15.80, and 208Pb/204Pb(i) = 38.91–39.05. They have similar Sr-Nd isotopic characteristics to the late Paleozoic to early Triassic mafic igneous rocks across the Yunkai Massif (Figure 12a). Compared to modern continental arc mafic rocks, the Tengxian hornblende gabbros have more radiogenic Sr and Pb (in particular, the 207Pb/204Pb(i) ratio) but less radiogenic Nd and Hf isotopic compositions (Figure 12). The Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotope compositions of Tengxian hornblende gabbros generally resemble those of GLOSS-II, which represents the average of global subducted sediments [71].
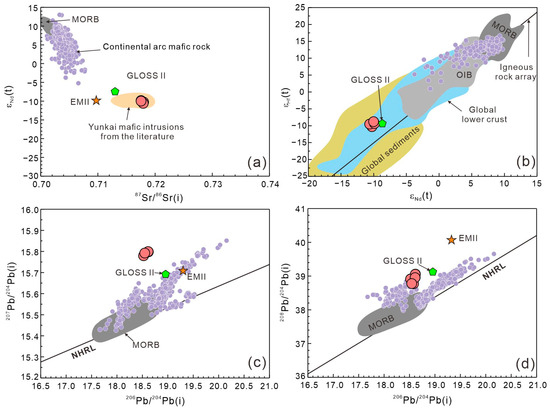
Figure 12.
Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotope compositions of the Tengxian hornblende gabbro. Data sources: continental arc mafic rocks (Georoc Database: http://georoc.mpch-mainz.gwdg.de/georoc/ (accessed on 17 January 2024)); late Permian to early Triassic Yunkai mafic intrusions are from [10,18,20].
As a whole, the bulk-rock geochemical data such as the arc-type trace element features and highly enriched Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic compositions suggest a significant involvement of recycled crustal components either in the mantle source or inherited from the wall rocks during the magmatic evolution, or both.
5. Discussion
5.1. Magmatic Evolution
The Tengxian hornblende gabbros have low MgO and Mg#, indicating the significant role of fractional crystallization. The extremely low Cr (11–24.3 ppm) and Ni (7.4–20.6 ppm) contents further imply the role of ferromagnesian fractionation such as olivine and pyroxene. In addition, some samples show negative Eu anomalies in the chondrite-normalized REE patterns (Figure 11b), suggesting the effect of plagioclase fractionation.
The modal abundance and Mg# disequilibrium between clinopyroxene and bulk-rock suggest the role of clinopyroxene accumulation, at least in some domains (Figure 2 and Figure 4c). However, both the euhedral and sieved clinopyroxene crystals show significantly negative Eu and Ti anomalies, and accumulation of clinopyroxene would lower the Ti and Eu concentrations, in contrast with the bulk-rocks, which even show positive Ti and variable Eu anomalies (Figure 10). This means a minor effect of clinopyroxene accumulation on the bulk-rock compositions. Instead, the bulk-rock positive Ti anomalies may be ascribed to the presence Fe-Ti oxides during the late stage of magmatic evolution, consistent with the thermodynamic calculation results of hornblende that suggest a reducing hydrous environment (Figure 8b,c).
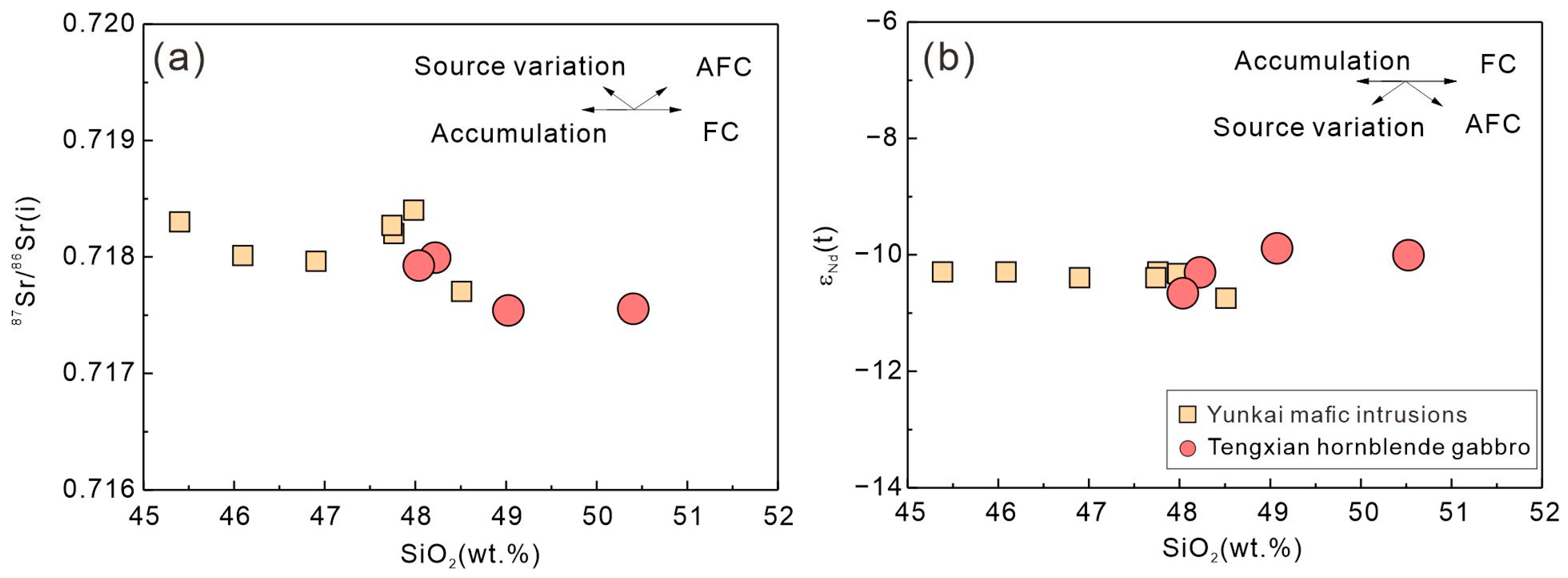
Crustal contamination/assimilation may lead to Sr and Nd isotopic variations, e.g., an increase in the bulk-rock 87Sr/86Sr(i) and a decrease in εNd(t) with the magmatic differentiation. As illustrated in Figure 13, there lacks any linear relationship between SiO2 and the bulk-rock 87Sr/86Sr(i) and εNd(t) in the Tengxian hornblende gabbros, precluding a significant effect of such open-system processes [10,20].
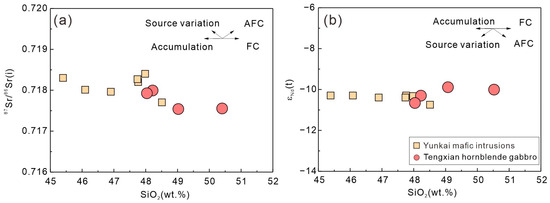
Figure 13.
Plots of SiO2 versus 87Sr/86Sr(i) (a) and εNd(t) (b) of the Tengxian hornblende gabbro. Data sources are the same as in Figure 12.
5.2. Magma–Mineral Interaction
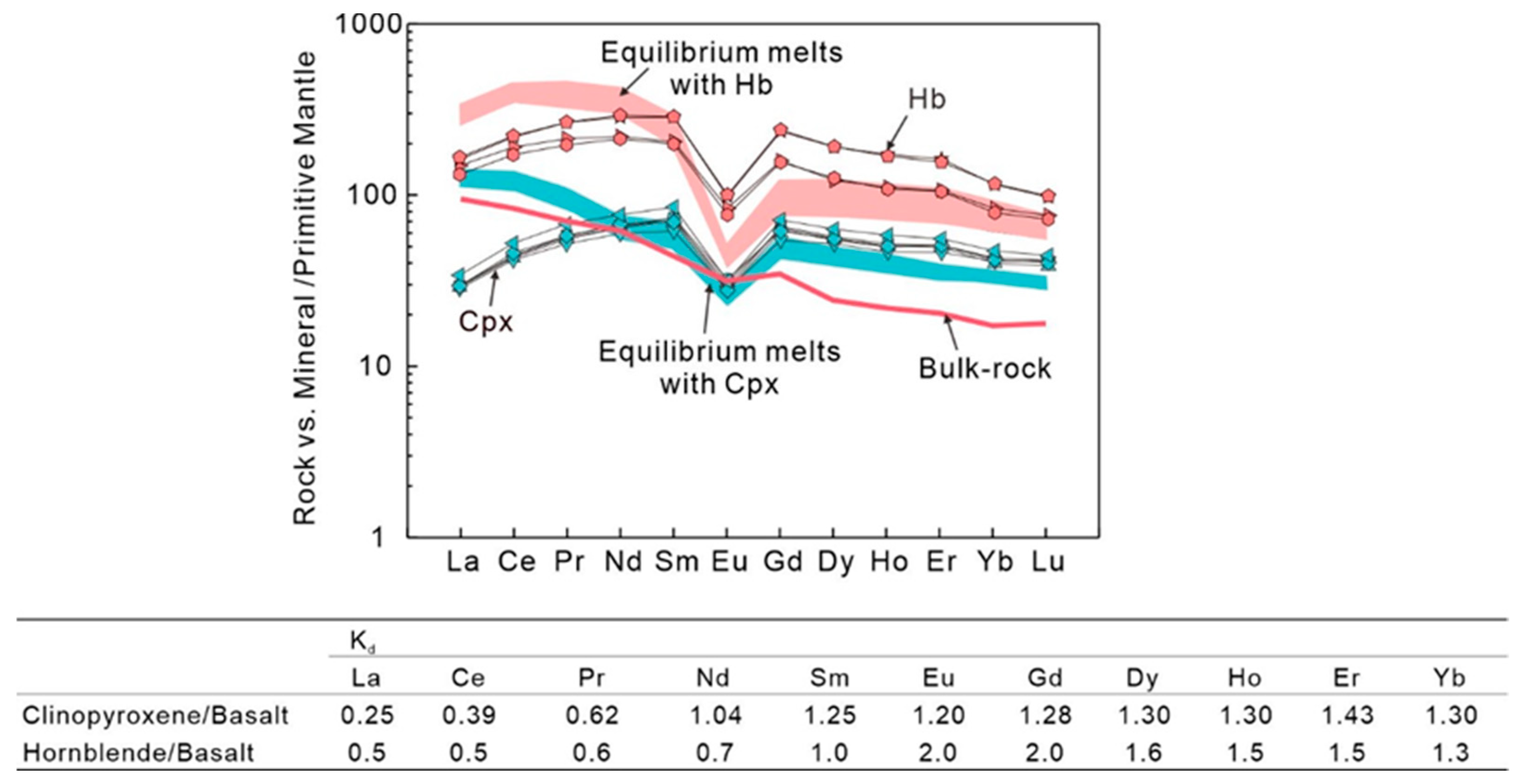
The Tengxian hornblende gabbros show variable accumulation of clinopyroxene, in which the surrounding hornblende occurs as small-sized anhedral or veined crystals (Figure 2), suggesting a possible effect of the crystallization of intercumulus liquid [72]. In most cases, however, the hornblende occurs as coarse-grained euhedral to subhedral crystals and represents the later-stage crystallizing phase (Figure 2b,f). Even if the hornblende had crystallized from the intercumulus liquid, which should have also been in equilibrium with the clinopyroxene, the estimated composition of the interstitial melts, respectively, equilibrating with clinopyroxene and hornblende should be similar. However, as illustrated in Figure 14, the calculated melt in equilibrium with clinopyroxene has REE concentrations three to four times lower than that in equilibrium with hornblende. We therefore conclude that most of the hornblende could not have formed through crystallization of the assumed intercumulus liquid.
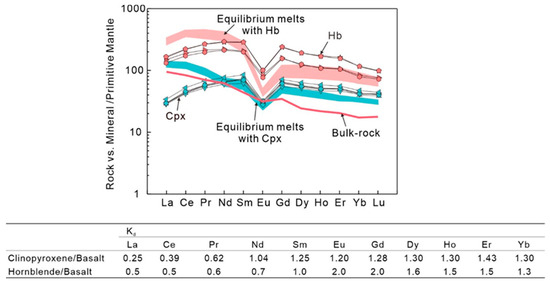
Figure 14.
Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of clinopyroxene and hornblende and the calculated magma compositions in the Tengxian hornblende gabbros. During the calculation, we adopt the Kd values between clinopyroxene and hornblende and basalt from the website: https://earthref.org/GERM/ (accessed on 5 January 2024).
Regardless of their crystallization sequence, the trace element similarities between the clinopyroxene in Generation I and the hornblende in Generation II (Figure 7) suggest a cogenetic origin. Clinopyroxene and hornblende have similar enrichments in MREE relative to LREE and HREE but marked depletion in Sr and Ti, implying that both phases crystallized from similar parental melts. The results of calculating parental melts, respectively, in equilibrium with clinopyroxene and hornblende also show quite consistent REE patterns with LREE enrichments and Eu depletion (Figure 14). In combination with the presence of negative Sr and Eu anomalies in both euhedral and sieved clinopyroxene (Figure 7), these results suggest either significant crystallization of plagioclase or inheritance from a parental magma showing Sr and Eu depletions, or both. Such clinopyroxene with relatively low Mg#, Na2O and high FeO has been ever interpreted as Fe-rich clinopyroxene crystallizing in a crust-derived felsic magma [73]. However, this hypothesis is unsuitable to explain the formation of clinopyroxene in the Tengxian hornblende gabbros.
(1) Although the assemblage of clinopyroxene and quartz has been occasionally discovered in granitoids derived from metaigneous protoliths [74], the clinopyroxene is typically present in alkaline granite in the form of aegirine or nepheline [75], instead of augite-salite as observed in the Tengxian gabbro (Figure 7a).
(2) The quartz in the hornblende gabbro is anhedral and occurs along the cracks or pits (Figure 2), so it probably represents a late-stage crystallizing phase instead of coexistence with the clinopyroxene antecrystal.
(3) The mineral association of clinopyroxene and labradorite in Generation I indicates a basaltic parental magma instead of an alkaline felsic melt (Figure 2).
Nevertheless, the high-δ18O apatite, which even crystallized prior to clinopyroxene, indicates an 18O-enriched mantle source. Regardless of its association with plagioclase, the clinopyroxene most likely crystallized in a Sr-Eu-depleted parental magma. Both the euhedral and sieved clinopyroxene have almost identical compositions (Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7), suggesting that the intrusion of late-stage evolved magma exerted a minor effect on the clinopyroxene composition. The sieved texture of clinopyroxene is prevalent during magma–mineral interaction as a result of hornblende overgrowth and clinopyroxene consumption (Figure 5). The occurrence of K-feldspar and biotite is likely attributed to the intrusion of late-stage alkaline melt into the magma chamber (Figure 2b,c).
We therefore consider that the mineral assemblage of apatite (zircon) + clinopyroxene + plagioclase in Generation I represents the earlier crystallizing product from a basaltic magma, whereas the mineral assemblage of hornblende + K-feldspar + biotite + quartz in Generation II crystallized in a late-stage evolved alkaline melt. Pulsed intrusion of the evolved magma into the early crystallized mush led to the erosion and metasomatism of the early-stage minerals such as clinopyroxene.
5.3. Source Characteristics
The early Triassic hornblende gabbros in the Yunkai Massif are characterized by highly enriched Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic signatures, implying the remarkable contribution of recycled crustal components to the melting source (Figure 12). In particular, the exceptionally high 207Pb/204Pb(i) ratios in the Tengxian hornblende gabbros are typical of continental upper crust (Figure 12c,d) [76], which is consistent with the very high δ18O values in both zircon and apatite and the remarkably negative εHf(t) of zircon. Such enriched Hf-O isotopic compositions also resemble the Indosinian S-type granites, which are widely distributed in the Yunkai Massif and have been interpreted as originating from the metasedimentary protoliths [17]. Previous studies demonstrated that both terrigenous sediment and continental upper crust have enriched zircon Hf-O isotope signatures [77]. In the bulk-rock εNd(t) vs. εHf(t) diagram (Figure 12b), the Tengxian samples plot above the terrestrial line in a Hf-Nd isotope array (igneous rock array), suggesting the role of the ‘zircon effect’ in response to addition of high-Nd/Hf slab fluid/melt into the mantle source [78]. The enriched mantle source will exhibit more radiogenic Hf than Nd, as observed in the Tengxian hornblende gabbro.
The combined mineral and bulk-rock geochemical data require the contribution of both the terrigenous sediment and mantle components to the formation of Tengxian hornblende gabbros. There are three ways of introducing the sedimentary component into the mantle: (1) bulk mixing; (2) sediment-derived fluid metasomatism, and (3) sediment-derived melt metasomatism.
Since the terrigenous sediment is much easier to fuse than mantle lithologies like peridotite and pyroxenite, the derived melt from such a mixed source should be felsic instead of mafic in composition, as observed in the Tengxian hornblende gabbro. A bulk source mixing thus seems unlikely in interpreting the petrogenesis of the Tengxian hornblende gabbro. During the metasomatism, the involvement of sediment-derived melt typically results in a low ratio of fluid-mobile elements (e.g., Rb, Ba, and Sr) to fluid-immobile elements (such as LREE, Th, and HFSE), in contrast with the presence of the sediment-released fluid with a high ratio of Ba/La and Ba/Nb [79].
The Tengxian hornblende gabbros are characterized by Ba and Rb depletions relative to Th and U (Figure 11a) and have low Ba/La (10.2–16.1) and Rb/Th (6.7–13.7) (Table S7), indicating a minor role of sediment-derived fluid metasomatism. In contrast, these rocks have very high Th/Yb (2–4) ratios, a typical feature of magma derived from an enriched mantle metasomatized by terrigenous sediment-derived melt.
Hydrous melting of the recycled terrigenous sediment is feasible as hydrous minerals can release water at relatively shallow depths [80]. Since the possible effect of crustal assimilation/contamination during magmatic evolution is precluded, we conclude that the terrigenous sediment-derived melts dominated to enrich the mantle source for the Tengxian hornblende gabbro. This is consistent with the zircon Hf-O isotopic array that yields a trend of mixing between a juvenile component with mantle-like δ18O and MORB-like εHf(t), and a recycled crustal component composed mainly of terrigenous sediments with extremely high δ18O and negative εHf(t) values. The modeling results suggest that the addition of 30% terrigenous sediment-derived melt could produce the Hf-O isotopic compositions observed in the Tengxian hornblende gabbros (Figure 3d). Collectively, the comprehensive mineral and bulk-rock geochemical data suggest that the addition of voluminous terrigenous sediments into the mantle, through a predominant melt-mediated metasomatism, formed the enriched source for the Tengxian hornblende gabbro [80,81].
5.4. Implications for Subduction of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean
The formation of the early Triassic (~250 Ma) Tengxian hornblende gabbro requires significant recycling of terrigenous sediments (HFSE depletion and highly enriched isotopic signatures) into the mantle, even though debate continues about the tectonic background of the Yunkai Massif. Obviously, the significant involvement of a recycled oceanic slab, which is characterized by HSFE enrichment and depleted isotopic signatures as observed in plume-related rifts [13,82], can be precluded. This suggests a minor influence of contemporaneous Emeishan plume activity on the tectonic evolution of the Yunkai Massif [20].
Subduction and delamination are two kinds of geodynamic processes to introduce the terrigenous sediments into the mantle and even to the much deeper Earth [80,83]. Lithospheric shortening and thickening in the course of intracontinental orogeny can result in the eclogitization of lower continental crust and subsequent delamination of the thickened lithosphere [12], with a characteristic rock type of adakite or intermediate–felsic intrusion with adakitic trace element features [84,85]. In the Yunkai Massif, the lack of such a lithological assemblage rules out the possibility of lithospheric delamination as a mechanism for the recycling of terrigenous sediments [86,87].
Arc magmas with enriched isotopic features often form during the late stage of slab subduction, such as amphibole-rich cumulate xenoliths in the Gangdese arc and appinites from the Liaodong Peninsula, NE China [88,89,90]. The subduction of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean has been widely acknowledged as a likely driving force for the tectono-magmatic activities in the SCB during the late Paleozoic to early Mesozoic eras [9,18]. Previous studies have even proposed that the impact of Paleo-Tethys Ocean subduction across the SCB region could be traced back to ~245 Ma [8,91]. Nevertheless, robust petrological evidence for the late Paleozoic to early Mesozoic subduction of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean beneath the Yunkai Massif is lacking. Some previous studies even considered the influence of the initial subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Ocean during this period [10]. Up to now, arc mafic counterparts with such highly enriched isotopic features as observed in the Tengxian hornblende gabbro have not been discovered across the eastern Cathaysia Block [92], where the subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Ocean was initiated [93]. It is therefore unlikely that the formation of Tengxian gabbro can be attributed to the initial subduction of Paleo-Pacific Ocean.
Alternatively, the enriched Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic features of the early Triassic Tengxian hornblende gabbro might have been inherited from an ancient enriched lithospheric mantle. Melts derived from such an enriched lithospheric mantle are generally SiO2-undersaturated like carbonatite, kimberlite, lamprophyre, and peralkaline igneous rocks [94,95], distinct from the Tengxian hornblende gabbros that are SiO2-saturated with the occurrence of quartz. In addition, the early-stage crystallizing phases like zircon and apatite have very high δ18O values (Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 9), indicating that the high-δ18O nature has been inherited from the enriched mantle source. At mantle temperature, diffusion-driven oxygen isotope fractionation is quite fast and the enriched O isotopic signatures cannot be preserved over a long timescale under the perturbance of the underlying asthenosphere [62]. This means that the enrichment of the mantle source was just or nearly contemporaneous with the formation of the hornblende gabbro, during which the terrigenous sediments were subducted beneath the mantle wedge. Indeed, the results reconstructed from paleogeography and paleo-plate tectonics also indicate that the Yunkai Massif was surrounded by a shallow sea or epicontinental sea during the Carboniferous to early Triassic period, with the sedimentary rocks consisting mainly of carbonates and terrigenous clastic rocks [96].
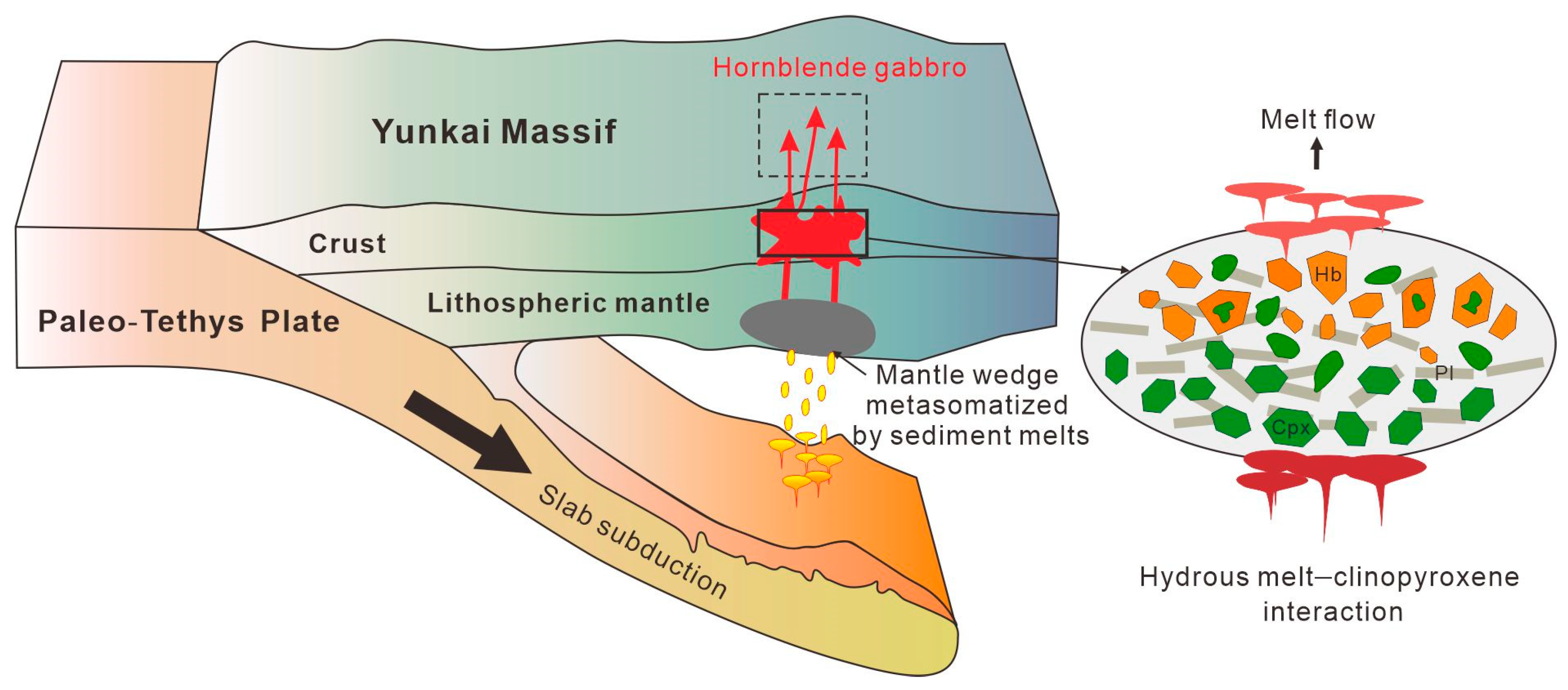
Collectively, the early Triassic hornblende gabbro in the Yunkai Massif was formed under the subduction of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean, during which substantial terrigenous sediments were introduced and fused to enrich the metasomatized magma wedge (Figure 15). Considering the tectonic evolution of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean and the sediment flux during different stages of slab subduction, the early Triassic hornblende gabbro in the Yunkai Massif likely formed during the late-stage subduction of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean [11].
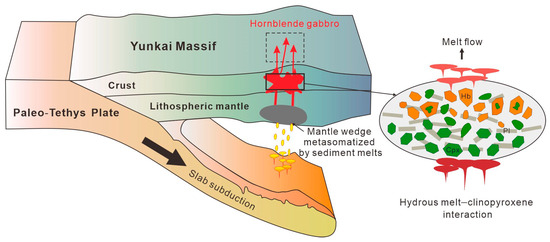
Figure 15.
A cartoon diagram depicting the origin of hornblende gabbro in the Yunkai Massif.
6. Conclusions
The comprehensive study including detailed in situ mineral and bulk-rock geochemical analyses indicates that the early Triassic hornblende gabbro in the Tengxian area provide a robust petrological record for the subduction of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean beneath the Yunkai Massif, South China. The following conclusions can be summarized.
(1) The zircon U-Pb dating shows that the hornblende gabbro was formed in the early Triassic (~250 Ma).
(2) Two generations of mineral assemblages have been identified: the earlier mineral assemblage is composed of apatite (zircon) + clinopyroxene + plagioclase and the later mineral assemblage consists of ilmenite + hornblende + K-feldspar + biotite + quartz. Pulsed intrusion of the evolved magma into the early crystallized mush formed the mineral associations.
(3) The parental magma of the early Triassic hornblende gabbro was hydrous and calc-alkaline and originated from an enriched mantle wedge metasomatized by voluminous subducted terrigenous sediment-derived melts.
The combined bulk-rock and mineral geochemistry from the hornblende gabbro in the Yunkai Massif provides an example for identifying the mineral generations and melt–mineral interaction during the magmatic evolution of mafic intrusions, and demonstrates how to distinguish the recycled crustal components among the diverse tectonic settings including the subduction zones, intracontinental orogens, and plume-related rifts.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/geosciences14060147/s1, Table S1: U-Pb-Hf-O isotopic compositions of zircons from the Tengxian intrusive rocks and international zircon standards; Table S2: Representative analyses of; clinopyroxene in the Tengxian Fe-rich intrusion; Table S3: Representative analyses of hornblende in the Tengxian Fe-rich intrusion; Table S4: Representative analyses of ilmenite in the Tengxian Fe-rich intrusion; Table S5: Representative analyses of ilmenite in the Tengxian Fe-rich intrusion; Table S6: LA-ICP-MS trace element analysis of apatites from the Tengxian intrusive rocks and international apatite standards; Table S7: Major and trace element contents of the Late Permian intrusive rocks in the Tengxian and the analyzed values of international standards; Table S8: Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotope compositions of the Late Permian intrusive rocks in the Tengxian and the analyzed values of international standards.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W. and F.G.; methodology, Y.W., F.G. and L.Z.; investigation, Y.W.; data curation, Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.W.; writing—review and editing, Y.W., F.G. and L.Z.; visualization, Y.W.; supervision, Y.W., F.G. and L.Z.; project administration, F.G.; funding acquisition, F.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grants number 42021002, 42073032 and 41525006.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We thank Linli Chen, Weikang Chen, Xiaobin Zhang, Feng Zhang, Zhenglin Li, Hongxia Yu, and Zexian Cui for their technical assistance during the mineral analyses. Reviews and comments from three anonymous referees are greatly appreciated, which helped to improve the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Shu, L.S.; Yao, J.L.; Wang, B.; Faure, M.; Charvet, J.; Chen, Y. Neoproterozoic plate tectonic process and Phanerozoic geodynamic evolution of the South China Block. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 216, 103596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawood, P.A.; Zhao, G.C.; Yao, J.L.; Wang, W.; Xu, Y.J.; Wang, Y.J. Reconstructing South China in Phanerozoic and Precambrian supercontinents. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 186, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, M.; Shu, L.S.; Wang, B.; Charvet, J.; Choulet, F.; Monie, P. Intracontinental subduction: A possible mechanism for the Early Palaeozoic Orogen of SE China. Terra Nova 2009, 21, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Wu, Y.M.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.B.; Zhao, L.; Liao, J. Magmatic responses to Cretaceous subduction and tearing of the paleo-Pacific Plate in SE China: An overview. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 212, 103448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Fan, W.M.; Zhao, G.C.; Ji, S.C.; Peng, T.P. Zircon U–Pb geochronology of gneissic rocks in the Yunkai massif and its implications on the Caledonian event in the South China Block. Gondwana Res. 2007, 12, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, A.M.; Fan, W.M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.Z. Origin of paleosubduction-modified mantle for Silurian gabbro in the Cathaysia Block: Geochronological and geochemical evidence. Lithos 2013, 160–161, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.S.; Wang, B.; Cawood, P.A.; Santosh, M.; Xu, Z.Q. Early Paleozoic and Early Mesozoic intraplate tectonic and magmatic events in the Cathaysia Block, South China. Tectonics 2015, 34, 1600–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, K.J.; Maloney, K.T.; Zahirovic, S.; Williams, S.E.; Seton, M.; Müller, R.D. Global plate boundary evolution and kinematics since the late Paleozoic. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 146, 226–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, L.; Jiang, Y.H.; Du, F.G. Geodynamics of Late Paleozoic to Early Mesozoic Magmatism in South China: Insights from the Genesis of the Late Permian S-type Granites in the Yunkai Massif. J. Geol. 2020, 128, 275–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.C.; Luo, B.J.; Xu, Y.J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Q. Geochronology, geochemistry, and petrogenesis of late Permian to early Triassic mafic rocks from Darongshan, South China: Implications for ultrahigh-temperature metamorphism and S-type granite generation. Lithos 2018, 308–309, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Li, H.X.; Fan, W.M.; Li, J.Y.; Zhao, L.; Huang, M.W. Variable sediment flux in generation of Permian subduction-related mafic intrusions from the Yanbian region, NE China. Lithos 2016, 261, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, R.; Kay, S.M. Delamination and delamination magmatism. Tectonophysics 1993, 219, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.G.; He, B.; Chung, S.L.; Menzies, M.A.; Frey, F.A. Geologic, geochemical, and geophysical consequences of plume involvement in the Emeishan flood-basalt province. Geology 2004, 32, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.; Ray, A.; Debnath, M.; Paul, S.P. Petrology, geochemistry of hornblende gabbro and associated dolerite dyke of Paharpur, Puruliya, West Bengal: Implication for petrogenetic process and tectonic setting. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 121, 793–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, J.S. Characteristic mineralogy of arc-related cumulate gabbros: Implications for the tectonic setting of gabbroic plutons and for andesite genesis. Geology 1986, 14, 848–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey-Vargas, R.; Abdollahi, M.J.; Parada, M.A.; López-Escobar, L.; Frey, F.A. Crustal xenoliths from Calbuco Volcano, Andean Southern Volcanic Zone: Implications for crustal composition and magma-crust interaction. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1995, 119, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Guo, F.; Fan, W.M.; Li, C.W.; Qin, X.F.; Li, H.X. Origin of the granulite enclaves in Indo-Sinian peraluminous granites, South China and its implication for crustal anatexis. Lithos 2012, 150, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.Y.; Qin, X.F.; Wang, Z.Q.; Gong, J.H.; Yang, W.; Zhu, A.H.; Shi, H.; Zhan, J.Y. Geochronology, geochemistry and geological significance of gabbros from Xindi-Anping area, southeastern Guangxi. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 2016, 35, 791–803, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Ke, X.Z.; Wang, X.D.; Wang, L.; Wang, J. Geochronology, Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of Late Permian Fe-Ti-P-Rich Ultramafic Rocks in Yunkai Terrane, South China. Earth Sci. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2021, 46, 1295–1310, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.X.; Kang, Z.Q.; Liu, D.; Chen, H.; Cao, Y.; Wei, N.S.; Wei, T.W.; Wang, R.; Liu, D.M.; Zhou, T.; et al. Geochronological, Geochemical and Geological Significance of Huilong Gabbroic Pluton in Southeastern Guangxi. Geoscience 2020, 34, 1015–1027, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.H.; Hsieh, P.S.; Lee, C.Y.; Zhou, H.W. Two episodes of the Indosinian thermal event on the South China Block: Constraints from LA-ICPMS U–Pb zircon and electron microprobe monazite ages of the Darongshan S-type granitic suite. Gondwana Res. 2011, 19, 1008–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Wei, J.H.; Santosh, M.; Tan, J.; Fu, L.B.; Zhao, S.Q. Geochronology and petrogenesis of Middle Permian S-type granitoid in southeastern Guangxi Province, South China: Implications for closure of the eastern Paleo-Tethys. Tectonophysics 2016, 682, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charvet, J.; Shu, L.S.; Faure, M.; Choulet, F.; Wang, B.; Lu, H.F.; Breton, N.L. Structural development of the Lower Paleozoic belt of South China: Genesis of an intracontinental orogen. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2010, 39, 309–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Li, X.H.; Wartho, J.A.; Clark, C.; Li, W.X.; Zhang, C.L.; Bao, C.M. Magmatic and metamorphic events during the early Paleozoic Wuyi-Yunkai orogeny, southeastern South China: New age constraints and pressure-temperature conditions. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2010, 122, 772–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Wang, Q.C.; Chen, K. Phanerozoic tectonics of south China block: New insights from the polyphase deformation in the Yunkai massif. Tectonics 2008, 27, TC6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.F.; Peng, S.B.; Kusky, T.; Polat, A.; Han, Q.S. Origin and tectonic implications of an Early Paleozoic (460–440 Ma) subduction-accretion shear zone in the northwestern Yunkai Domain, South China. Lithos 2018, 322, 104–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Xu, X.S.; Zou, H.B.; Liu, L. Early Paleozoic crust–mantle interaction and lithosphere delamination in South China Block: Evidence from geochronology, geochemistry, and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopes of granites. Lithos 2014, 184–187, 416–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Huang, X.L.; He, P.L.; Li, J. I-type granitoids associated with the early Paleozoic intracontinental orogenic collapse along pre-existing block boundary in South China. Lithos 2016, 248–251, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Huang, B.C.; Ni, Z.X.; Han, S.P.; Pan, Y.W.; Huang, Y. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb ages, petrogeochemistry and tectonic significance of the Indosinian basic intrusive rocks in the Tengxian region, southeastern Guangxi. Sediment. Geol. Tethyan Geol. 2015, 35, 76–87, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Zhang, H.X.; Zhao, Z.H.; Shi, M.Q.; Yang, S.F.; Chen, H.L. Permian island-arc basalt in West Guangdong and East Guangxi tectonic belt, South China: Implications for the Paleotethys. J. Nanjing Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2003, 39, 46–54, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, S.J.; Li, X.H.; Huang, H.Q.; Deng, X.G. Metasedimentary melting in the formation of charnockite: Petrological and zircon U-Pb-Hf-O isotope evidence from the Darongshan S-type granitic complex in southern China. Lithos 2015, 239, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.F.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.L.; Pan, L.Z.; Hu, G.A.; Zhou, F.S. Geochemistry of Permian Mafic Igneous Rocks from the Napo-Qinzhou Tectonic Belt in Southwest Guangxi, Southwest China: Implications for Arc-Back Arc Basin Magmatic Evolution. Acta Geol. Sin. 2012, 86, 1182–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zheng, Y.F.; Zhao, Z.F. Triassic granites in South China: A geochemical perspective on their characteristics, petrogenesis, and tectonic significance. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 266–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Guo, F.; Zhang, X.B.; Zhao, L. Magmatic degassing and fluid metasomatism promote compositional variation from I-type to peralkaline A-type granite in late Cretaceous Fuzhou felsic complex, SE China. Am. Mineral. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, M.D.; Pearson, N.J.; Sharma, A.; Griffin, W.L. Quantitative analysis of trace elements in geological materials by laser ablation ICPMS: Instrumental operating conditions and calibration values of NIST glasses. Geostand. Newsl. 1996, 20, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sláma, J.; Košler, J.; Condon, D.J.; Crowley, J.L.; Gerdes, A.; Hanchar, J.M.; Horstwood, M.S.A.; Morris, G.A.; Nasdala, L.; Norberg, N.; et al. Plešovice zircon—A new natural reference material for U–Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis. Chem. Geol. 2008, 249, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, N.J.G.; Perkins, W.T.; Westgate, J.A.; Gorton, M.P.; Jackson, S.E.; Neal, C.R.; Chenery, S.P. A Compilation of New and Published Major and Trace Element Data for NIST SRM 610 and NIST SRM 612 Glass Reference Materials. Geostand. Newsl. 1997, 21, 115–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Liu, X.M.; Yuan, H.L.; Hattendorf, B.; Günther, D.; Chen, L.; Hu, S.H. Determination of Forty Two Major and Trace Elements in USGS and NIST SRM Glasses by Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry. Geostand. Newsl. 2002, 26, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Hu, Z.C.; Gao, S.; Günther, D.; Xu, J.; Gao, C.G.; Chen, H.H. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chem. Geol. 2008, 257, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.R. ISOPLOT 3.0: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel; Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication; Berkeley Geochronology Center: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, X.L.; Zhang, H.; Deng, W.F.; Ling, M.X.; Liang, H.Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, W.D. Application of resolution in-situ laser ablation ICP-MS in trace element analyses. Geochimica 2011, 40, 83–98, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Söderlund, U.; Patchett, P.J.; Vervoort, J.D.; Isachsen, C.E. The 176Lu decay constant determined by Lu–Hf and U–Pb isotope systematics of Precambrian mafic intrusions. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 219, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvier, A.; Vervoort, J.D.; Patchett, P.J. The Lu–Hf and Sm–Nd isotopic composition of CHUR: Constraints from unequilibrated chondrites and implications for the bulk composition of terrestrial planets. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 273, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Xie, L.W.; Yang, J.H.; Xu, P. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U–Pb geochronology. Chem. Geol. 2006, 234, 105–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Wu, F.Y.; Xie, L.W.; Yang, Y.H. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons for U-Pb dating. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2004, 49, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochum, K.P.; Weis, U.; Stoll, B.; Kuzmin, D.; Yang, Q.; Raczek, I.; Jacob, D.E.; Stracke, A.; Birbaum, K.; Frick, D.A.; et al. Determination of Reference Values for NIST SRM 610–617 Glasses Following ISO Guidelines. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2011, 35, 397–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wörner, G.; Jochum, K.P.; Stoll, B.; Simon, K.; Kronz, A. The Preparation and Preliminary Characterisation of Three Synthetic Andesite Reference Glass Materials (ARM-1, ARM-2, ARM-3) for In Situ Microanalysis. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2019, 43, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, C.; Hellstrom, J.; Paul, B.; Woodhead, J.; Hergt, J.; Paton, C. Iolite: Freeware for the visualisation and processing of mass spectrometric data. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2011, 26, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, G.B.; Chen, H.Y.; Zhang, S.T.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.M. Geochemistry and geochronology of multi-generation garnet: New insights on the genesis and fluid evolution of prograde skarn formation. Geosci. Front. 2023, 14, 101495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Li, W.X.; Li, Q.L.; Wang, X.C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.H. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of the ~850 Ma Gangbian alkaline complex in South China: Evidence from in situ zircon U–Pb dating, Hf–O isotopes and whole-rock geochemistry. Lithos 2010, 114, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenbeck, M.; Hanchar, J.M.; Peck, W.H.; Sylvester, P.; Valley, J.; Whitehouse, M.; Kronz, A.; Morishita, Y.; Nasdala, L.; Fiebig, J.; et al. Further Characterisation of the 91500 Zircon Crystal. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2004, 28, 9–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.P.; Cui, Z.X.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.F.; Yang, Q.; Hui, H.; Lai, C.K. Zircon water content: Reference material development and simultaneous measurement of oxygen isotopes by SIMS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2019, 34, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, H.C.; Li, X.H. Simultaneous and precise determination of 40 trace element elements using ICP-MS. Geochimica 1996, 25, 552–558, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- White, W.M.; Albarède, F.; Télouk, P. High-precision analysis of Pb isotope ratios by multi-collector ICP-MS. Chem. Geol. 2000, 167, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.J.; Liang, X.R.; Li, X.H.; Liu, Y. Precise measurement of Sr isotopic composition of liquid and solid base using (LP) MC-ICPMS. Geochimica 2002, 31, 295–299, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.R.; Wei, G.J.; Li, X.H.; Liu, Y. Precise measurement of 143Nd/144Nd and Sm/Nd ratios using multiple-collectors inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer (MC-ICPMS). Geochimica 2003, 32, 91–96, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.H.; Li, Z.X.; Wingate, M.T.D.; Chung, S.L.; Liu, Y.; Lin, G.C.; Li, W.X. Geochemistry of the 755 Ma Mundine Well dyke swarm, northwestern Australia: Part of a Neoproterozoic mantle superplume beneath Rodinia? Precambrian Res. 2006, 146, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valley, J.W. Oxygen Isotopes in Zircon. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2003, 53, 343–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Fan, W.M.; Li, C.W.; Miao, L.C.; Zhao, L. Early Paleozoic subduction of the Paleo-Asian Ocean: Geochronological and geochemical evidence from the Dashizhai basalts, Inner Mongolia. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2009, 52, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzanti, E.; Bayon, G.; Vermeesch, P.; Barbarano, M.; Pastore, G.; Resentini, A.; Dennielou, B.; Jouet, G. The Zambezi deep-sea fan: Mineralogical, REE, Zr/Hf, Nd-isotope, and zircon-age variability in feldspar-rich passive-margin turbidites. J. Sediment. Res. 2022, 92, 1022–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Zhang, K.X.; Lin, S.F.; He, W.H.; Kou, X.H.; Zhou, X.H. Turbidite record of a middle Neoproterozoic active continental margin in the West Cathaysia terrane, South China: Implications for the relationships between the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks and their positions in Rodinia. Precambrian Res. 2020, 337, 105457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindeman, I. Oxygen Isotopes in Mantle and Crustal Magmas as Revealed by Single Crystal Analysis. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2008, 69, 445–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putirka, K.D. Thermometers and Barometers for Volcanic Systems. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2008, 69, 61–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putirka, K. Amphibole thermometers and barometers for igneous systems and some implications for eruption mechanisms of felsic magmas at arc volcanoes. Am. Mineral. 2016, 101, 841–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridolfi, F.; Renzulli, A.; Puerini, M. Stability and chemical equilibrium of amphibole in calc-alkaline magmas: An overview, new thermobarometric formulations and application to subduction-related volcanoes. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2009, 160, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridolfi, F. Amp-TB2: An Updated Model for Calcic Amphibole Thermobarometry. Minerals 2021, 11, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschmann, M.M.; Ghiorso, M.S.; Davis, F.A.; Gordon, S.M.; Mukherjee, S.; Grove, T.L.; Krawczynski, M.; Medard, E.; Till, C.B. Library of Experimental Phase Relations (LEPR): A database and Web portal for experimental magmatic phase equilibria data. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2008, 9, Q03011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruand, E.; Storey, C.; Fowler, M.; Heilimo, E. Oxygen isotopes in titanite and apatite, and their potential for crustal evolution research. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 255, 144–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.A. Immobile Element Fingerprinting of Ophiolites. Elements 2014, 10, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, T. The Chemical Composition of Subducting Sediments. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 4, pp. 607–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latypov, R.M.; Chistyakova, S.Y.; Namur, O.; Barnes, S. Dynamics of evolving magma chambers: Textural and chemical evolution of cumulates at the arrival of new liquidus phases. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 210, 103388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Nakamura, E.; Fan, W.M.; Kobayashi, K.; Li, C.W. Generation of Palaeocene Adakitic Andesites by Magma Mixing; Yanji Area, NE China. J. Petrol. 2007, 48, 661–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, H.; Tsujimori, T.; Kon, Y.; Aoki, S.; Aoki, K. Nature and timing of anatectic event of the Hida Belt (Japan): Constraints from titanite geochemistry and U-Pb age of clinopyroxene-bearing leucogranite. Lithos 2021, 398–399, 106256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, M. Quantification of Magmatic and Hydrothermal Processes in a Peralkaline Syenite-Alkali Granite Complex Based on Textures, Phase Equilibria, and Stable and Radiogenic Isotopes. J. Petrol. 2003, 44, 1247–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zartman, R.E.; Doe, B.R. Plumbotectonics—The model. Tectonophysics 1981, 75, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkesworth, C.J.; Kemp, A.I.S. Using hafnium and oxygen isotopes in zircons to unravel the record of crustal evolution. Chem. Geol. 2006, 226, 144–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervoort, J.D.; Plank, T.; Prytulak, J. The Hf–Nd isotopic composition of marine sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 5903–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Guo, F.; Fan, W.M.; Huang, M.W. Roles of Subducted Pelagic and Terrigenous Sediments in Early Jurassic Mafic Magmatism in NE China: Constraints on the Architecture of Paleo-Pacific Subduction Zone. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2019, 124, 2525–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, T.; Cooper, L.B.; Manning, C.E. Emerging geothermometers for estimating slab surface temperatures. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, R.; Hawkesworth, C.J.; Heath, E. The Lesser Antilles volcanic chain: A study in arc magmatism. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2000, 49, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanyu, T.; Tatsumi, Y.; Nakai, S.I.; Chang, Q.; Miyazaki, T.; Sato, K.; Tani, K.; Shibata, T.; Yoshida, T. Contribution of slab melting and slab dehydration to magmatism in the NE Japan arc for the last 25 Myr: Constraints from geochemistry. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2006, 7, Q08002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Fan, W.M.; Wang, Y.J.; Li, C.W. When Did the Emeishan Mantle Plume Activity Start? Geochronological and Geochemical Evidence from Ultramafic-Mafic Dikes in Southwestern China. Int. Geol. Rev. 2004, 46, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducea, M.N. Fingerprinting orogenic delamination. Geology 2011, 39, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsli, O.; Dokuz, A.; Uysal, İ.; Aydin, F.; Kandemir, R.; Wijbrans, J. Generation of the Early Cenozoic adakitic volcanism by partial melting of mafic lower crust, Eastern Turkey: Implications for crustal thickening to delamination. Lithos 2010, 114, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Abart, R.; Sayyed, M.I.; Hauzenberger, C.A.; Sami, M. Petrogenesis of the Wadi El-Faliq Gabbroic Intrusion in the Central Eastern Desert of Egypt: Implications for Neoproterozoic Post-Collisional Magmatism Associated with the Najd Fault System. Minerals 2023, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.G.; Hu, P.Y.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.M.; Wang, W. Early Jurassic lithospheric delamination in the Amdo microcontinent, central Tibet: Inferred from coeval OIB- and MORB-like gabbros. Lithos 2023, 456–457, 107314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.Y.; Yang, D.B.; Xu, W.L.; Yang, H.T.; Mu, M.S.; Wang, A.Q.; Quan, Y.K.; Hao, L.R. Modification of the lithospheric mantle induced by recycled crustal components: Insights from Early Cretaceous appinites from the Liaodong Peninsula, NE China. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2022, 135, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhu, D.C.; Wang, Q.; Weinberg, R.F.; Wang, R.; Li, S.M.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhao, Z.-D. Cumulate Mush Hybridization by Melt Invasion: Evidence from Compositionally Diverse Amphiboles in Ultramafic–Mafic Arc Cumulates within the Eastern Gangdese Batholith, Southern Tibet. J. Petrol. 2021, 62, egab073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.S.; Yang, Z.S.; Hou, Z.Q.; Wang, Q. Amphibole-rich cumulate xenoliths in the Zhazhalong intrusive suite, Gangdese arc: Implications for the role of amphibole fractionation during magma evolution. Am. Mineral. 2020, 105, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Tran, M.D.; Tang, Y.; Nguyen, Q.L.; Tran, T.H.; Wu, W.B.; Chen, J.F.; Zhang, Z.C.; Zhao, Z.D. Permo-Triassic granitoids in the northern part of the Truong Son belt, NW Vietnam: Geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic implications. Gondwana Res. 2012, 22, 628–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Guo, F.; Zhang, X.B.; Wu, Y.M.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhao, L. Early Cretaceous subduction of Paleo-Pacific Ocean in the coastal region of SE China: Petrological and geochemical constraints from the mafic intrusions. Lithos 2019, 334–335, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Li, Z.X.; He, B.; Li, W.X.; Li, Q.L.; Gao, Y.Y.; Wang, X.C. The Early Permian active continental margin and crustal growth of the Cathaysia Block: In situ U–Pb, Lu–Hf and O isotope analyses of detrital zircons. Chem. Geol. 2012, 328, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.M.; Jiang, S.Y.; Zhang, D.Y.; Wu, X.K. Partial Melting of Subducted Sediments Produced Early Mesozoic Calc-alkaline Lamprophyres from Northern Guangxi Province, South China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovin, A.V.; Sharygin, I.S.; Kamenetsky, V.S.; Korsakov, A.V.; Yaxley, G.M. Alkali-carbonate melts from the base of cratonic lithospheric mantle: Links to kimberlites. Chem. Geol. 2018, 483, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.X.; Zhang, K.J. A new model for the Indochina and South China collision during the Late Permian to the Middle Triassic. Tectonophysics 2009, 467, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).