Metallogeny and Genesis of Fault-Filling Barite-Sulfide Veins (Ougnat, Morocco): Petrography, Fluid Inclusion, and Sr-S Isotopic Constraints
Abstract
1. Introduction
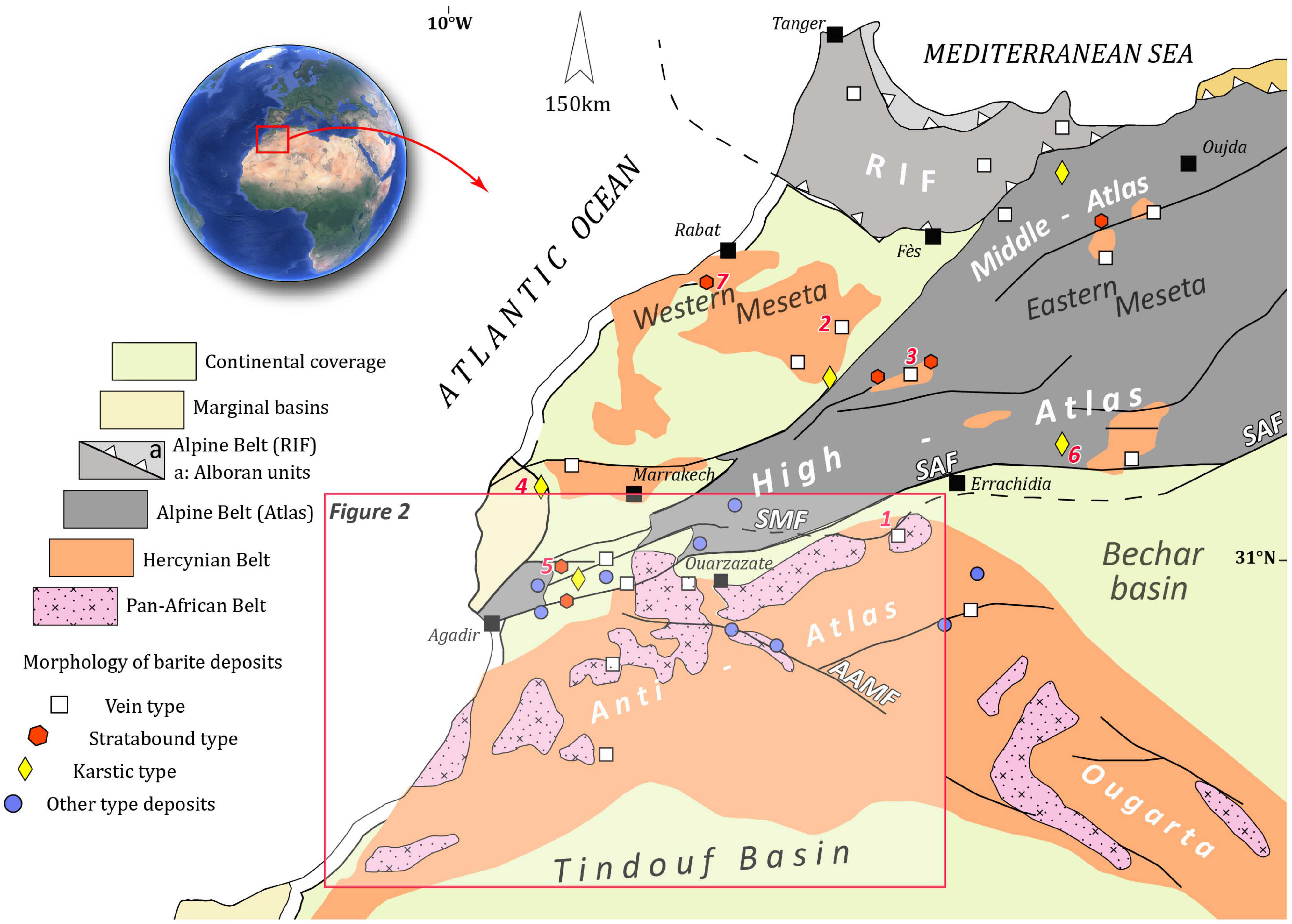
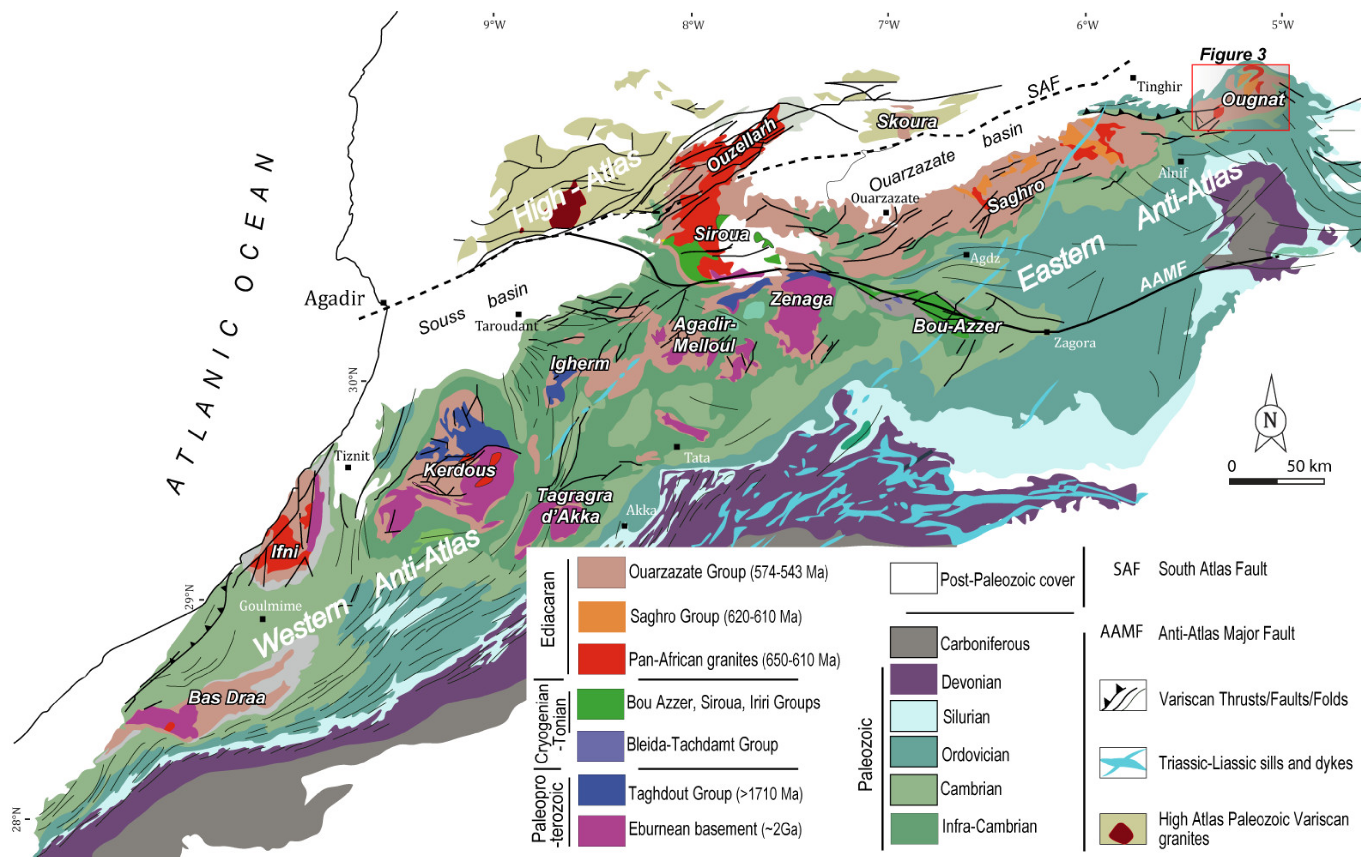
2. Geologic Setting

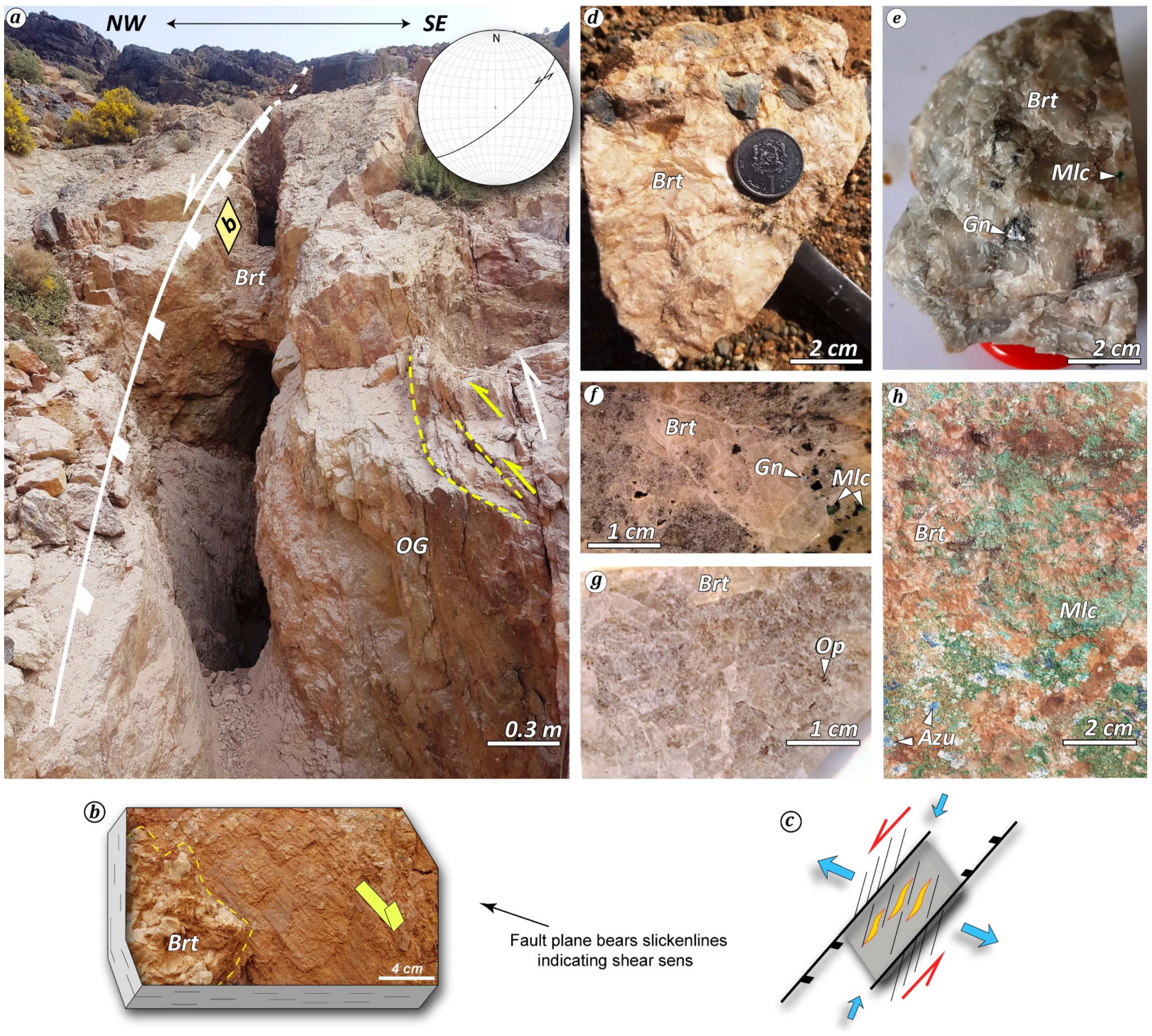
3. Deposit-Scale Barite Vein Description
4. Methodology
5. Results
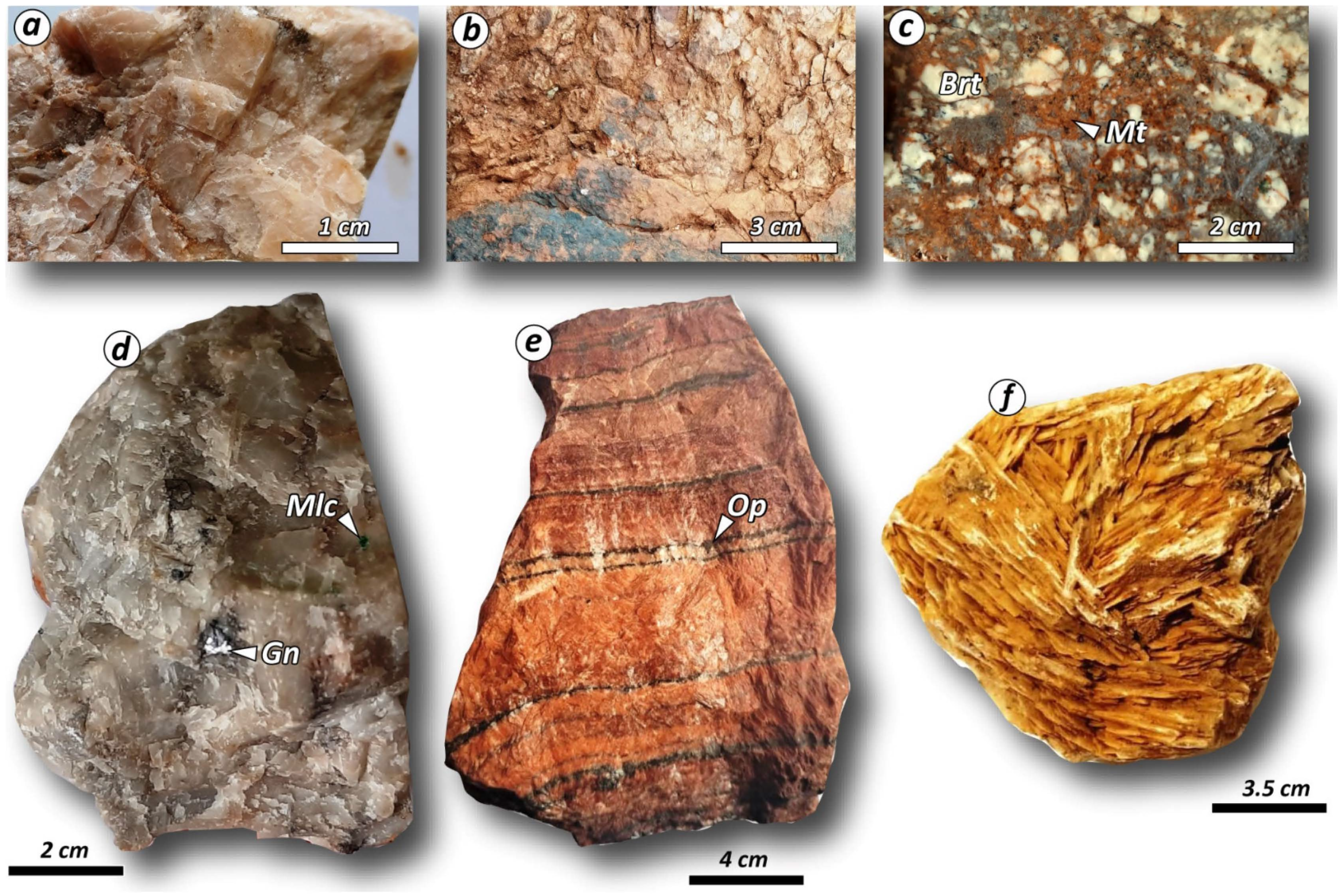
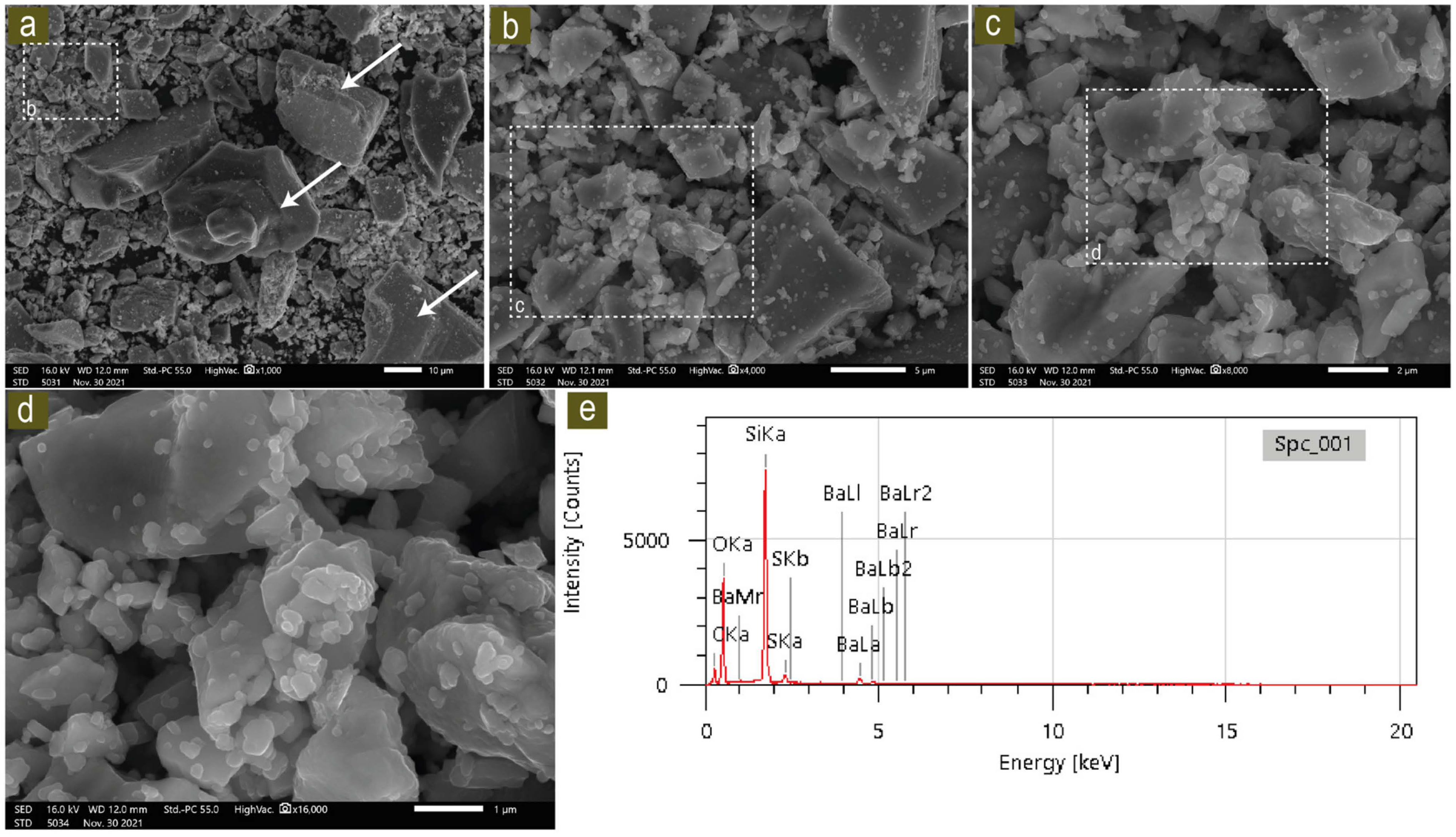
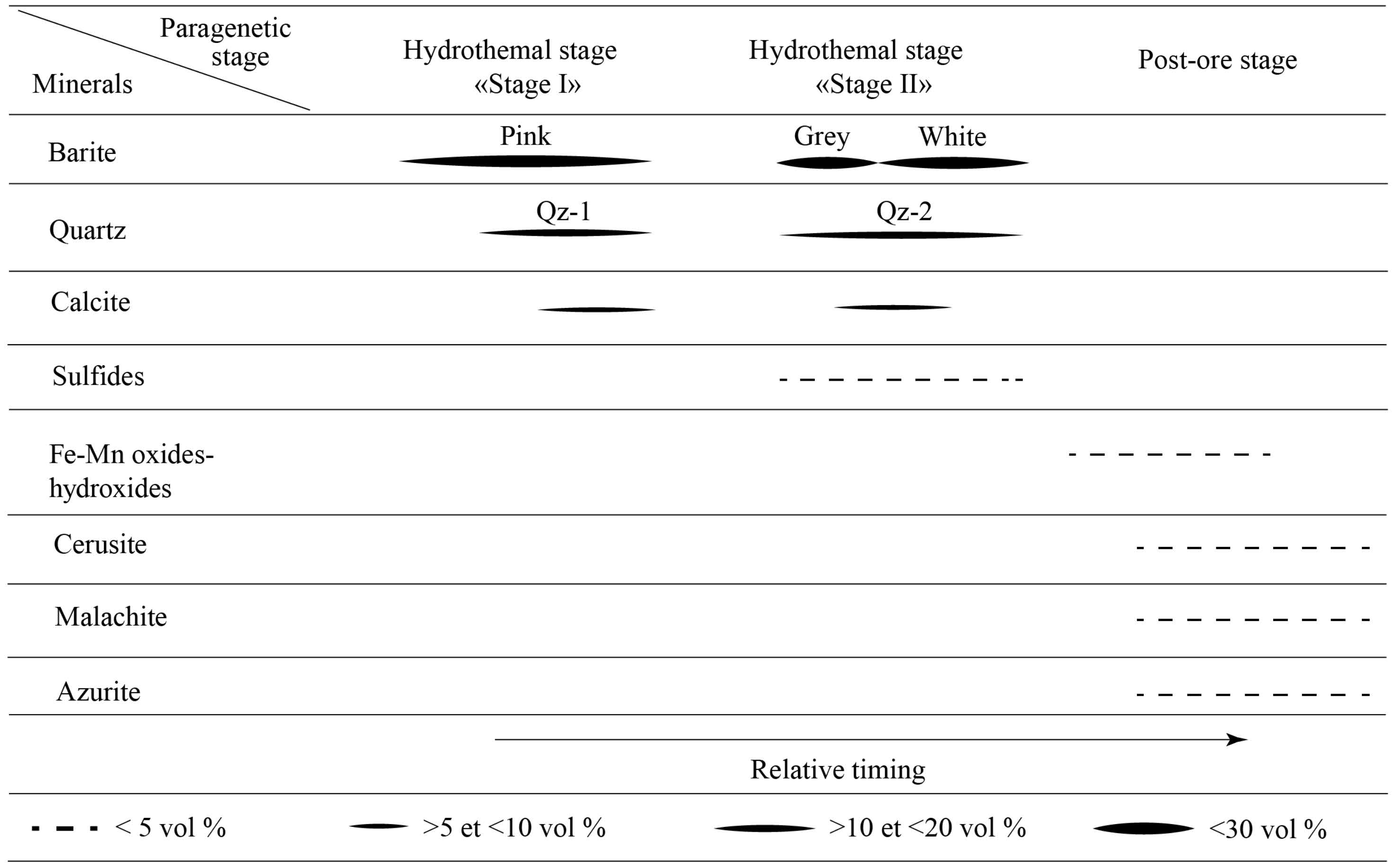
5.1. Barite Characterization: Textures, Petrography, Paragenesis, and SEM
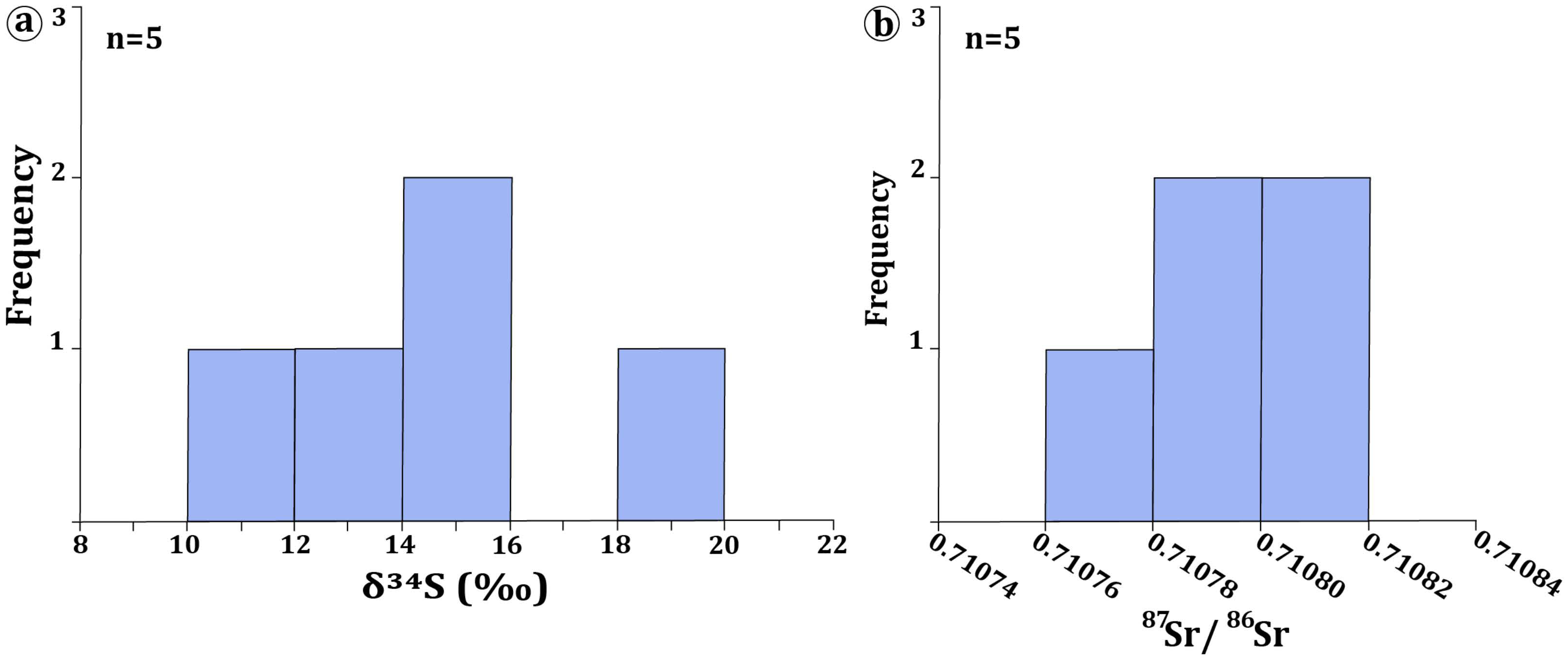
5.2. Sulfur Isotopes
5.3. Strontium Isotopes
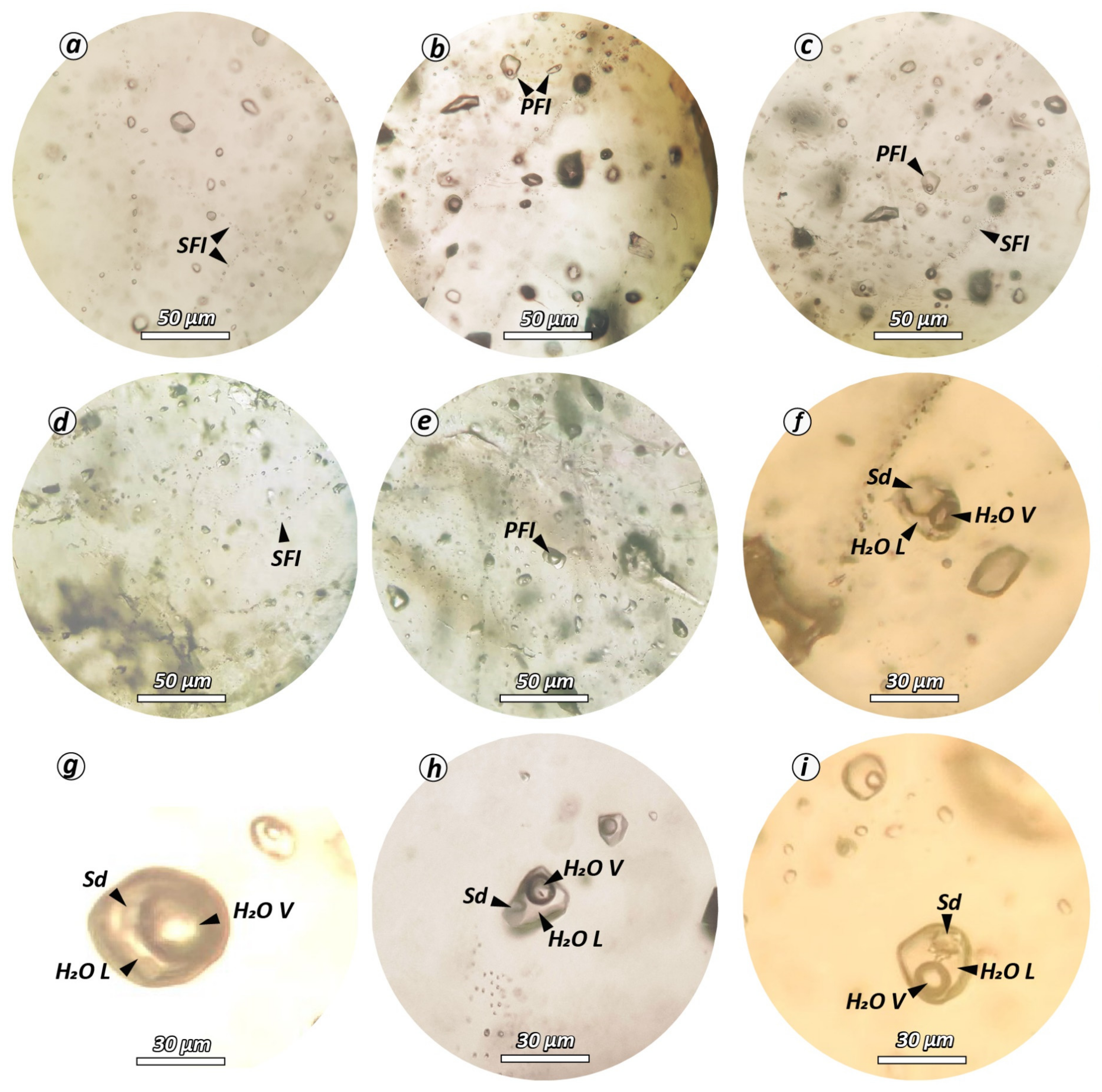
5.4. Fluid Inclusions
6. Discussion
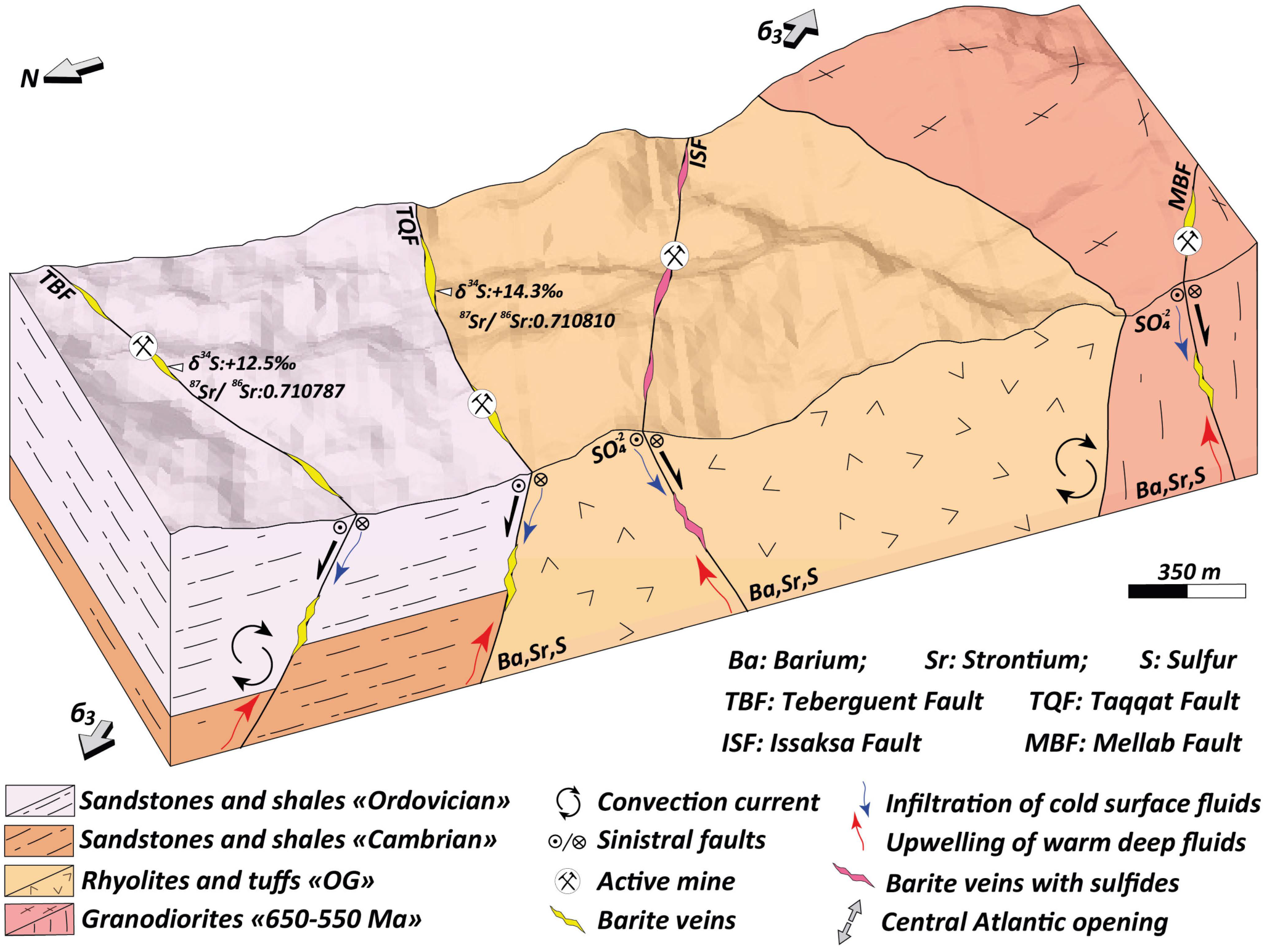
6.1. Sources of S, Sr, and Ba in the Barite Deposits
6.2. Fluid Mixing Model
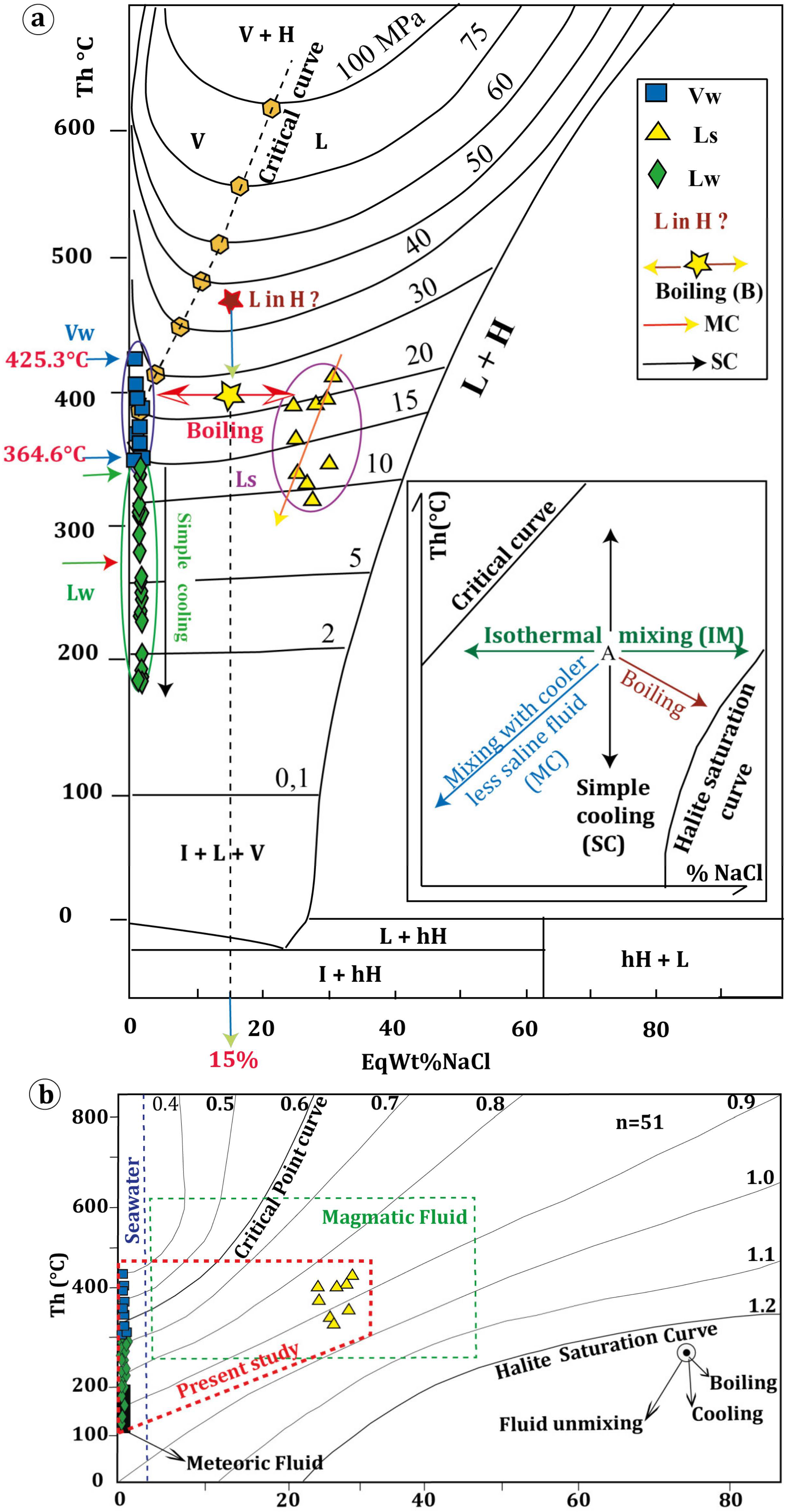
6.3. Barite Ore Genesis
6.4. Geodynamic Context
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clark, S.H.B.; Poole, F.G.; Wang, Z. Comparison of Some Sediment-Hosted, Stratiform Barite Deposits in China, the United States, and India. Ore Geol. Rev. 2004, 24, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.A.; Dumoulin, J.A.; Burruss, R.A.; Slack, J.F. Depositional Conditions for the Kuna Formation, Red Dog Zn-Pb-Ag-Barite District, Alaska, Inferred from Isotopic and Chemical Proxies. Econ. Geol. 2015, 110, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Y.; Yu, H.Y. Barite Deposit in China; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zou, H.; Said, N.; Liu, H. A New Classification of Barite Deposits in China. Ore Energy Resour. Geol. 2023, 14, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tas Ozdogan, A.; Uras, Y.; Oner, F. Geochemistry of the Barite Deposits near Adana-Feke Area (Eastern Taurides). Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2017, 58, 1349–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombros, S.F.; Seymour, K.S.; Williams-Jones, A.E.; Zhai, D.; Liu, J. Origin of a Barite-Sulfide Ore Deposit in the Mykonos Intrusion, Cyclades: Trace Element, Isotopic, Fluid Inclusion and Raman Spectroscopy Evidence. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 67, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, J.; Zhai, D. Factors Controlling Precipitation of Barite and Witherite and Genesis of the Ankang–Xunyang Barium Deposits, Shaanxi, China. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. Ed. 2015, 89, 836–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Lehmann, B.; Mao, J.; Zheng, W.; Ye, H.; Li, H. Strontium, Sulfur, Carbon, and Oxygen Isotope Geochemistry of the Early Cambrian Strata-Bound Barite and Witherite Deposits of the Qinling-Daba Region, Northern Margin of the Yangtze Craton, China. Econ. Geol. 2016, 111, 695–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Bao, H.; Peng, Y.; Yuan, X. Timing the Deposition of 17O-Depleted Barite at the Aftermath of Nantuo Glacial Meltdown in South China. Geology 2010, 38, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, S.T.; Zhang, Q. The Source of Fengjia and Langxi Barite–Fluorite Deposits in Southeastern Sichuan, China: Evidence from Rare Earth Elements and S, Sr, and Sm–Nd Isotopic Data. Geol. J. 2017, 52, 470–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Zhang, S.T.; Chen, A.-q.; Fang, Y.; Zeng, Z.F. Hydrothermal Fluid Sources of the Fengjia Barite–Fluorite Deposit in Southeast Sichuan, China: Evidence from Fluid Inclusions and Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes. Resour. Geol. 2016, 66, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azza, A.; Makkoudi, D. Cadre Structural Des Minéralisations Plombo-Barytiques de Tafilalet. Mines Géologie Et Énergie 1996, 55, 175–184. [Google Scholar]
- Bouabdellah, M.; Margoum, D. Geology, Fluid Inclusions, and Geochemistry of the Aouli Sulphide ± Fluorite ± Barite Vein Deposit (Upper Moulouya District, Morocco) and Its Relationships to Pangean Rifting and Opening of the Tethys and Central Atlantic Oceans. In Mineral Deposits of North Africa; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caia, J.; Huvelin, P. Géologie Des Gites Minéraux Marocains: Baryum et Strontium; Editions du Service Géologique du Maroc: Rabat, Morocco, 1980; Volume 276, pp. 271–308. [Google Scholar]
- El Hnot, H.; Mzahraoui, M. Origine et Mode de Mise En Place de La Barytine Du Gisement de Bou Ouzzal (Meseta Marocaine). Bull. De L’institut Sci. Rabat 2005, 27, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Marcoux, É.; Jébrak, M. Plumbotectonics of Moroccan Ore Deposits. BSGF Earth Sci. Bull. 2021, 192, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margoum, D.; Bouabdellah, M.; Klügel, A.; Banks, D.A.; Castorina, F.; Cuney, M.; Jébrak, M.; Bozkaya, G. Pangea Rifting and Onward Pre-Central Atlantic Opening as the Main Ore-Forming Processes for the Genesis of the Aouli REE-Rich Fluorite-Barite Vein System, Upper Moulouya District, Morocco. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 108, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaoui, S.; Aabi, A.; Nguidi, M.A.; Boushaba, A.; Belkasmi, M.; Baidder, L.; Bba, A.N.; Lamrani, O.; Taadid, M.; Zehni, A. Fault-Controlled Barite Veins of the Eastern Anti-Atlas (Ougnat, Morocco), a Far-Field Effect of the Central Atlantic Opening? Structural Analysis and Metallogenic Implications. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2023, 104970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenza, K.; Moritz, R.; Mouttaqi, A.; Fontignie, D.; Sharp, Z. Vein and Karst Barite Deposits in the Western Jebilet of Morocco: Fluid Inclusion and Isotope (S, O, Sr) Evidence for Regional Fluid Related to Central Atlantic Rifting. Econ. Geol. 2000, 95, 587–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wafik, A.; Essaifi, A.; Admou, H.; Mouttaqi, A. The Jbel Irhoud Barite Deposit (Western Jebilet). In Nouveaux Guides Géologiques et Miniers du Maroc; Editions du Service Géologique du Maroc: Rabat, Morocco, 2011; Volume 9, pp. 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Yaagoub, D.; Hinaje, S.; El Fartati, M.; Gharmane, Y. Analysis of Tectonic Fracturing in the Mibladen Ore Deposit (Upper Moulouya, Morocco) and Its Impact on the Pb–Ba Mineralization Emplacement. Rend. Lincei 2021, 32, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azza, A. Les Minéralisations Barytiques Du Maroc. Chron. De La Rech. Minière 1998, 531–532, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Castorina, F.; Masi, U.; Padalino, G.; Palomba, M. Trace-Element and Sr–Nd Isotopic Evidence for the Origin of the Sardinian Fluorite Mineralization (Italy). Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 2906–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherai, M.; Rddad, L.; Talbi, F.; Walter, B.F. Trace-Element Geochemistry and S–O Isotopes in the Fluorite-Barite Mineralization of Merguechoum, Moroccan Eastern Meseta: Insights into Ore Genesis to the Pangea Rifting. Acta Geochim. 2023, 42, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaillard, L.; Touray, J.-C.; Badra, L. Les Variations Verticales de La Teneur En Sr de Barytines Filoniennes Du Haut-Atlas Occidental, Maroc. Implications Pour La Prospection de Barytine de Qualité Chimique. C. R. Acad. Sci. 1989, 309, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Jaillard, L. Quelques Filons de Barytine En Decrochement et En Extension Dans Le Haut-Atlas Occidental (Maroc). Chronique de la Recherche Minière 1985, 481, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sizaret, S.; Marcoux, E.; Jébrak, M.; Touray, J.C. The Rossignol Fluorite Vein, Chaillac, France: Multiphase Hydrothermal Activity and Intravein Sedimentation. Econ. Geol. 2004, 99, 1107–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwinn, G.; Markl, G. REE Systematics in Hydrothermal Fluorite. Chem. Geol. 2005, 216, 225–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; Premo, W.R.; Courjault-Radé, P. Sm-Nd Dating of Fluorite from the Worldclass Montroc Fluorite Deposit, Southern Massif Central, France. Miner. Depos. Database 2005, 39, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piqué, À.; Canals, À.; Grandia, F.; Banks, D.A. Mesozoic Fluorite Veins in NE Spain Record Regional Base Metal-Rich Brine Circulation through Basin and Basement during Extensional Events. Chem. Geol. 2008, 257, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, V.; Vindel, E.; Martín-Crespo, T.; Corbella, M.; Cardellach, E.; Banks, D. Sources and Composition of Fluids Associated with Fluorite Deposits of Asturias (N Spain). Geofluids 2009, 9, 338–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, H.G.; Hansen, B.T.; Weber, B. REE Contents, REE Minerals and Sm/Nd Isotopes of Granite- and Unconformity-Related Fluorite Mineralization at the Western Edge of the Bohemian Massif: With Special Reference to the Nabburg-Wölsendorf District, SE Germany. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 40, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abia, E.H.; Nachit, H.; Marignac, C.; Ibhi, A.; Saadi, S.A. The Polymetallic Au-Ag-Bearing Veins of Bou Madine (Jbel Ougnat, Eastern Anti-Atlas, Morocco): Tectonic Control and Evolution of a Neoproterozoic Epithermal Deposit. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2003, 36, 251–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouabdellah, M.; Levresse, G. The Bou Madine Polymetallic Ore Deposit, Eastern Anti-Atlas, Morocco: Evolution from Massive Fe–As–Sn to Epithermal Au–Ag–Pb–Zn ± Cu Mineralization in a Neoproterozoic Resurgent Caldera Environment. In Mineral Deposits of North Africa; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakir, I.; Ahmed, B.; Habiba, A.; Abdessalam, O.; Youssef, A.B. Contribution of Geophysics to the Study of Barite Mineralization in the Paleozoic Formations of Asdaf Tinejdad (Eastern Anti Atlas Morocco). Econ. Environ. Geol. 2020, 53, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essalhi, A.; Essalhi, M.; Toummite, A. Environmental Impact of Mining Exploitation: A Case Study of Some Mines of Barite in the Eastern Anti-Atlas of Morocco. J. Environ. Prot. 2016, 07, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michard, A.; Soulaimani, A.; Hoepffner, C.; Ouanaimi, H.; Baidder, L.; Rjimati, E.C.; Saddiqi, O. The South-Western Branch of the Variscan Belt: Evidence from Morocco. Tectonophysics 2010, 492, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aabi, A.; Hejja, Y.; Nait Bba, A.; Boujamaoui, M.; Baidder, L.; El Azmi, M.; Maacha, L.; Hamzaoui, A. Tectonic Reactivation and Ore-Forming Fault Systems from the West African Craton Margin (Saghro, Anti Atlas, Morocco). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2024, 211, 105–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aabi, A.; Hejja, Y.; Bba, A.N.; Baidder, L.; Fekkak, A.; Bannari, A.; Maacha, L. Polyphase Tectonics, Fault Kinematics and Metallogenic Implications at the Fringe of a Craton (Anti-Atlas, Morocco). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2022, 196, 104731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aabi, A.; Baidder, L.; Hejja, Y.; El Azmi, M.; Bba, A.N.; Otmane, K. The Cu-Pb-Zn-Bearing Veins of the Bou Skour Deposit (Eastern Anti-Atlas, Morocco): Structural Control and Tectonic Evolution. C. R. Geosci. 2021, 353, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuduri, J.; Chauvet, A.; Barbanson, L.; Bourdier, J.L.; Labriki, M.; Ennaciri, A.; Badra, L.; Dubois, M.; Ennaciri-Leloix, C.; Sizaret, S.; et al. The Jbel Saghro Au(–Ag, Cu) and Ag–Hg Metallogenetic Province: Product of a Long-Lived Ediacaran Tectono-Magmatic Evolution in the Moroccan Anti-Atlas. Minerals 2018, 8, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouabdellah, M.; Sangster, D.F. Geology, Geochemistry, and Current Genetic Models for Major Mississippi Valley-Type Pb–Zn Deposits of Morocco. In Mineral Deposits of North Africa; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 463–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulaimani, A.; Michard, A.; Ouanaimi, H.; Baidder, L.; Raddi, Y.; Saddiqi, O.; Rjimati, E.C. Late Ediacaran–Cambrian Structures and Their Reactivation during the Variscan and Alpine Cycles in the Anti-Atlas (Morocco). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 98, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidder, L.; Michard, A.; Soulaimani, A.; Fekkak, A.; Eddebbi, A.; Rjimati, E.C.; Raddi, Y. Fold Interference Pattern in Thick-Skinned Tectonics; a Case Study from the External Variscan Belt of Eastern Anti-Atlas, Morocco. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 119, 204–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejja, Y.; Baidder, L.; Ibouh, H.; Bba, A.N.; Soulaimani, A.; Gaouzi, A.; Maacha, L. Fractures Distribution and Basement-Cover Interaction in a Polytectonic Domain: A Case Study from the Saghro Massif (Eastern Anti-Atlas, Morocco). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2020, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aabi, A.; Baidder, L.; Hejja, Y.; Bba, A.N.; El Azmi, M. Reply to Comment by El Ouardi et al. on The Cu-Pb-Zn-Bearing Veins of the Bou Skour Deposit (Eastern Anti-Atlas, Morocco): Structural Control and Tectonic Evolution. C. R. Geosci. 2022, 354, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lamotte, D.F.; Leturmy, P.; Missenard, Y.; Khomsi, S.; Ruiz, G.; Saddiqi, O.; Guillocheau, F.; Michard, A. Mesozoic and Cenozoic Vertical Movements in the Atlas System (Algeria, Morocco, Tunisia): An Overview. Tectonophysics 2009, 475, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hadi, H.; Simancas, J.F.; Martínez-Poyatos, D.; Azor, A.; Tahiri, A.; Montero, P.; Fanning, C.M.; Bea, F.; González-Lodeiro, F. Structural and Geochronological Constraints on the Evolution of the Bou Azzer Neoproterozoic Ophiolite (Anti-Atlas, Morocco). Precambrian Res. 2010, 182, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blein, O.; Baudin, T.; Soulaimani, A.; Cocherie, A.; Chèvremont, P.; Admou, H.; Ouanaimi, H.; Hafid, A.; Razin, P.; Bouabdelli, M.; et al. New Geochemical, Geochronological and Structural Constraints on the Ediacaran Evolution of the South Sirwa, Agadir-Melloul and Iguerda Inliers, Anti-Atlas, Morocco. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 98, 47–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, A.; Berger, J.; Baele, J.M.; Bruguier, O.; Diot, H.; Ennih, N.; Monnier, C.; Plissart, G.; Vandycke, S.; Watlet, A. Intra-Oceanic Arc Growth Driven by Magmatic and Tectonic Processes Recorded in the Neoproterozoic Bougmane Arc Complex (Anti-Atlas, Morocco). Precambrian Res. 2018, 304, 39–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, A.; Berger, J.; Baele, J.M.; Diot, H.; Ennih, N.; Plissart, G.; Monnier, C.; Watlet, A.; Bruguier, O.; Spagna, P.; et al. The Tachakoucht–Iriri–Tourtit Arc Complex (Moroccan Anti-Atlas): Neoproterozoic Records of Polyphased Subduction-Accretion Dynamics during the Pan-African Orogeny. J. Geodyn. 2016, 96, 81–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikenne, M.; Souhassou, M.; Cousens, B.; Montero, P.; Bea, F.; Askkour, F.; Haissen, F.; Beraaouz, E.H.; Ernst, R.E.; Bajddi, A.; et al. Zircon U–Pb Geochronology and Sm–Nd and Rb–Sr Isotope Systematics of Neoproterozoic Granitoïds from Bou Azzer (Anti-Atlas—Morocco): The Obduction Trigger of the Central Anti-Atlas Terrane. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2023, 202, 104900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekkak, A.; Pouclet, A.; Benharref, M. The Middle Neoproterozoic Sidi Flah Group (Anti-Atlas, Morocco): Synrift Deposition in a Pan-African Continent/Ocean Transition Zone. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2003, 37, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasquet, D.; Ennih, N.; Liégeois, J.P.; Soulaimani, A.; Michard, A. The Pan-African Belt. In Continental Evolution: The Geology of Morocco; Part of the Book Series: Lecture Notes in Earth Sciences (LNEARTH, Volume 116); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 33–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abati, J.; Aghzer, A.M.; Gerdes, A.; Ennih, N. Detrital Zircon Ages of Neoproterozoic Sequences of the Moroccan Anti-Atlas Belt. Precambrian Res. 2010, 181, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michard, A.; Soulaimani, A.; Ouanaimi, H.; Raddi, Y.; Aït Brahim, L.; Rjimati, E.C.; Baidder, L.; Saddiqi, O. Saghro Group in the Ougnat Massif (Morocco), an Evidence for a Continuous Cadomian Basin along the Northern West African Craton. In Proceedings of the Comptes Rendus—Geoscience; Elsevier Masson SAS: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 349, pp. 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Lécolle, M.; Derré, C.; Nerci, K. The Proterozoic Sulphide Alteration Pipe of Sidi Flah and Its Host Series. New Data for the Geotectonic Evolution of the Pan-African Belt in the Eastern Anti-Atlas (Morocco). Ore Geol. Rev. 1991, 6, 501–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lécolle, M.; Derré, C.; Hadri, M. Les Protolites Des Altérites à Pyrophyllite de l’Ougnat et Leurs Positions Dans l’histoire Du Protérozoïque: Mise à Jour Des Connaissances Géologiques Sur l’Anti-Atlas Oriental. Afr. Geosci. Rev. 2003, 10, 227–244. [Google Scholar]
- Raddi, Y.; Baidder, L.; Tahiri, M.; Michard, A. Variscan Deformation at the Northern Border of the West African Craton, Eastern Anti-Atlas, Morocco: Compression of a Mosaic of Tilted Blocks. Bulletin de la Société Géologique de France 2007, 178, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Baghdadi, M.; El-Boukhari, A.; Nadem, S.; Benyoucef, A.; Jouider, A. Typologie Du Zircon Dans Les Granitoïdes de La Boutonnière Précambrienne de Sidi Flah-Bouskour, Saghro, Anti Atlas, Maroc. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2001, 32, 635–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrini, Z.; Rafi, A.; Duthou, J.; Vidal, P. Chronologie Rb-Sr Des Granitoides Hercyniens Du Maroc; Consequences|Bulletin de La Société Géologique de France|GeoScienceWorld. Available online: https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/sgf/bsgf/article-abstract/163/3/281/122583/Chronologie-Rb-Sr-des-granitoides-hercyniens-du (accessed on 13 June 2023).
- Cheilletz, A.; Gilles, A.E.; Ae, L.; Gasquet, D.; Rachid, M.; Ae, A.-S.; Zyadi, R.; Archibald, D.A.; Farrar, A.E. The Giant Imiter Silver Deposit: Neoproterozoic Epithermal Mineralization in the Anti-Atlas, Morocco. Min. Miner Depos 2002, 37, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errami, E.; Bonin, B.; Laduron, D.; Lasri, L. Petrology and Geodynamic Significance of the Post-Collisional Pan-African Magmatism in the Eastern Saghro Area (Anti-Atlas, Morocco). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2009, 55, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youbi, N.; Kouyaté, D.; Söderlund, U.; Ernst, R.E.; Soulaimani, A.; Hafid, A.; Ikenne, M.; El Bahat, A.; Bertrand, H.; Rkha Chaham, K.; et al. The 1750 Ma Magmatic Event of the West African Craton (Anti-Atlas, Morocco). Precambrian Res. 2013, 236, 106–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidada, B.; Cousens, B.; Alansari, A.; Soulaimani, A.; Barbey, P.; Ilmen, S.; Ikenne, M. Geochemistry and Sm–Nd Isotopic Composition of the Imiter Pan-African Granitoids (Saghro Massif, Eastern Anti-Atlas, Morocco): Geotectonic Implications. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 127, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.J.; Chevallier, L.P.; Gresse, P.G.; Harmer, R.E.; Eglington, B.M.; Armstrong, R.A.; De Beer, C.H.; Martini, J.E.J.; De Kock, G.S.; Macey, P.H.; et al. Precambrian Evolution of the Sirwa Window, Anti-Atlas Orogen, Morocco. Precambrian Res. 2002, 118, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasquet, D.; Levresse, G.; Cheilletz, A.; Azizi-Samir, M.R.; Mouttaqi, A. Contribution to a Geodynamic Reconstruction of the Anti-Atlas (Morocco) during Pan-African Times with the Emphasis on Inversion Tectonics and Metallogenic Activity at the Precambrian–Cambrian Transition. Precambrian Res. 2005, 140, 157–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, G.J.; Benziane, F.; Aleinikoff, J.N.; Harrison, R.W.; Yazidi, A.; Burton, W.C.; Quick, J.E.; Saadane, A. Neoproterozoic Tectonic Evolution of the Jebel Saghro and Bou Azzer—El Graara Inliers, Eastern and Central Anti-Atlas, Morocco. Precambrian Res. 2012, 216–219, 23–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youbi, N.; Ernst, R.E.; Söderlund, U.; Boumehdi, M.A.; Lahna, A.A.; Gaeta Tassinari, C.; El Moume, W.; Bensalah, M.K. The Central Iapetus Magmatic Province: An Updated Review and Link with the ca. 580 Ma Gaskiers Glaciation. Spec. Pap. Geol. Soc. Am. 2020, 544, 35–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paile, Y. Etude Des Séries Volcaniques Du Précambrien III de l’Ougnat (Anti-Atlas Oriental, Maroc) et Des Minéralisations Plombo-Zincifères Complexes Associées (Gîte de Bou Madine). Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Paris XI-Orsay, Paris, France, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Raddi, Y.; Tahiri, M.; Derré, C.; Lécolle, M. Notice de La Carte Géologique d’Oukhit (Anti-Atlas, Maroc); Notes et Mémoires Service Géologique Maroc: Rabat, Morocco, 2006; 70p. [Google Scholar]
- Soulaimani, A.; Burkhard, M. The Anti-Atlas Chain (Morocco): The Southern Margin of the Variscan Belt along the Edge of the West African Craton. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2008, 297, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destombes, J.; Hollard, H. Carte Géologique Du Maroc Au 1/200 000, Feuille Tafilalt-Taouz. In Notes et Mémoires du Service Géologique du Maroc; Editions du Service Géologique du Maroc: Rabat, Morocco, 1986; Volume 244. [Google Scholar]
- Michard, A.; Hoepffner, C.; Soulaimani, A.; Baidder, L. The Variscan Belt. In Continental Evolution: The Geology of Morocco; Part of the Book Series: Lecture Notes in Earth Sciences (LNEARTH); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 116, pp. 65–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destombes, J.; Hollard, H.; Willefert, S. Lower Palaeozoic Rocks of Morocco. In Palaeoz. Rocks North-Western West-Central Africa; Holland, C.H., Ed.; John Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1985; pp. 91–336. [Google Scholar]
- Destombes, J.; Feist, R. Découverte Du Cambrien Supérieur En Afrique (Anti-Atlas Central, Maroc). C. R. Acad. Sci. 1987, 304, 719–724. [Google Scholar]
- Baidder, L.; Raddi, Y.; Tahiri, M.; Michard, A. Devonian Extension of the Pan-African Crust North of the West African Craton, and Its Bearing on the Variscan Forelanddeformation: Evidence from Eastern Anti-Atlas (Morocco). Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2008, 297, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raddi, Y.; Derré, C.; Lécolle, M. Notice de La Carte Géologique de Bou Adil (Anti-Atlas, Maroc). In Notes et Mémoires du Service Géologique du Maroc; Editions du Service Géologique du Maroc: Rabat, Morocco, 2012; 70p. [Google Scholar]
- Destombes, J.; Hollard, H. Carte Géologique Du Maroc Au 1:200 000. Feuille Todgha-Ma’der. In Notes et Mémoires du Service Géologique du Maroc; Editions du Service Géologique du Maroc: Rabat, Morocco, 1988; Volume 244. [Google Scholar]
- Tahiri, M.; Derré, C.; Lécolle, M.; Baidder, L. Carte Géologique Du Maroc Au 1/50 000, Feuille d’Oukhit (Anti-Atlas, Maroc). In Notes et Mémoires du Service Géologique du Maroc; Editions du Service Géologique du Maroc: Rabat, Morocco, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lalou, C.; Brichet, E.; Ku, T.L.; Jehanno, C. Radiochemical, Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and X-Ray Dispersive Energy (EDAX) Studies of a FAMOUS Hydrothermal Deposit. Mar. Geol. 1977, 24, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creaser, R.A.; Gütter, H.; Carlson, J.; Crawford, B. Macrocrystal Phlogopite Rb–Sr Dates for the Ekati Property Kimberlites, Slave Province, Canada: Evidence for Multiple Intrusive Episodes in the Paleocene and Eocene. Lithos 2004, 76, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmden, C.; Creaser, R.A.; Muehlenbachs, K. Paleosalinities in Ancient Brackish Water Systems Determined by 87Sr/86Sr Ratios in Carbonate Fossils: A Case Study from the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 2105–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poty, B.; Leroy, J.; Jachimowicz, L. Un Nouvel Appareil Pour La Mesure Des Températures Sous Le Microscope: L’installation de Microthermométrie Chaixmeca. Bull. Minér. 1976, 99, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, M.R.; Bodnar, R.J. Systematics of Stretching of Fluid Inclusions II: Barite at 1 Atm Confining Pressure. Econ. Geol. 1988, 83, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michard, A.-G. Sédiments-Temoins de La Transgression Mésozoïque Dans Le Tafilalt et Maïder; Conséquences Sur La Métallogénie Des Gisements Filoniens à Pn-Zn (Cu) de l’Anti-Atlas Marocian. Chronique de la Recherche Minière 1989, 495, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Kharis, A.-A.; Ilmen, S.; Aissa, M.; Baidada, B.; Moussaid, A.; Mezougane, H.; Fadili, A.; Houane, H.; Syad, S.; Maacha, L. Metallogenesis of the Cu-Ni Sulfide Type Mineralization in the Bounhas Vein Deposit (Eastern Anti-Atlas, Morocco): Insights from Ore Mineral Paragenesis and Fluid Phases. Sci. Afr. 2023, 21, e01767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claypool, G.E.; Holser, W.T.; Kaplan, I.R.; Sakai, H.; Zak, I. The Age Curves of Sulfur and Oxygen Isotopes in Marine Sulfate and Their Mutual Interpretation. Chem. Geol. 1980, 28, 199–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rddad, L.; Bouhlel, S. The Bou Dahar Jurassic Carbonate-Hosted Pb–Zn–Ba Deposits (Oriental High Atlas, Morocco): Fluid-Inclusion and C–O–S–Pb Isotope Studies. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 72, 1072–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumańska-Słowik, M.; Beata, N.; Toboła, T.; Powolny, T.; Huber, M.; Milovska, S.; Dobosz, N.; Guzik, K. Origin of Gem-Quality Barite at Jebel Ouichane District in Nador, Morocco: Implications from Integrated Fluid Inclusions, Stable Isotopes, and Geochemistry. Res. Artic. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jébrak, M.; El Wartiti, M.; Marcoux, E.; Zaharoui, M. The Bouznika Cambrian Barite Deposit (Morocco), an Early Mineralization on the Iapetus Margin. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2011, 60, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roedder, E. Fluid Inclusions: An Introduction to Studies of All Types of Fluid Inclusions, Gas, Liquid, or Melt, Trapped in Materials from Earth and Space, and Their Application to the Understanding of Geologic Processes; Mineralogical Society of America: Chantilly, VA, USA, 1984; Volume 12, p. 644. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, S.A.; Turner, J.A. Studies on Southern Australian Abalone (Genus Haliotis). VI. Habitat Preference, Abundance and Predators of Juveniles. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1985, 93, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, S.M.; Hall, D.L.; Bodnar, R.J. Synthetic Fluid Inclusions. V. Solubility Relations in the System NaCl-KCl-H2O under Vapor-Saturated Conditions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 989–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.J.; Jabbari, M.Y.; Chen, S.B. Convective Mass Transfer and Pressure Loss Characteristics of Staggered Short Pin-Fin Arrays. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1994, 37, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanor, J.S. Origin of Saline Fluids in Sedimentary Basins. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 1994, 78, 151–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.; Bellanca, A.; Neri, R.; Tolomeo, L. Use of Strontium Isotopes to Determine the Sources of Hydrothermal Fluorite and Barite from Northwestern Sicily (Italy). Chem. Geol. Isot. Geosci. Sect. 1987, 66, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H. External Sulphur in IOCG Mineralization: Implications on Definition and Classification of the IOCG Clan. Ore Geol. Rev. 2013, 51, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dora, M.L.; Roy, S.K.; Khan, M.; Randive, K.; Kanungo, D.R.; Barik, R.; Kaushik, C.S.; Bari, S.H.; Pattanayak, R.S.; Krishna, K.V.S.; et al. Rift-Induced Structurally Controlled Hydrothermal Barite Veins in 1.6 Ga Granite, Western Bastar Craton, Central India: Constraints from Fluid Inclusions, REE Geochemistry, Sulfur and Strontium Isotopes Studies. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesler, S.; Jones, L.; Ruiz, J. Strontium Isotopic Geochemistry of Mississippi Valley-Type Deposits, East Tennesse: Implications for Age and Source of Mineralizing Brines. Available online: https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsa/gsabulletin/article-abstract/100/8/1300/182201/Strontium-isotopic-geochemistry-of-Mississippi (accessed on 2 August 2023).
- Marchev, P.; Downes, H.; Thirlwall, M.F.; Moritz, R. Small-Scale Variations of 87Sr/86Sr Isotope Composition of Barite in the Madjarovo Low-Sulphidation Epithermal System, SE Bulgaria: Implications for Sources of Sr, Fluid Fluxes and Pathways of the Ore-Forming Fluids. Min. Miner. Depos. 2002, 37, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontak, D.J.; Kyser, K.; Gize, A.; Marshall, D. Structurally Controlled Vein Barite Mineralization in the Maritimes Basin of Eastern Canada: Geologic Setting, Stable Isotopes, and Fluid Inclusions. Econ. Geol. 2006, 101, 407–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staude, S.; Göb, S.; Pfaff, K.; Ströbele, F.; Premo, W.R.; Markl, G. Deciphering Fluid Sources of Hydrothermal Systems: A Combined Sr- and S-Isotope Study on Barite (Schwarzwald, SW Germany). Chem. Geol. 2011, 286, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.W.; Zhang, Z.C.; Yang, J.M.; Zuo, G.C.; Zhang, Z.H.; Ye, D.J.; Jiang, M. The Metallogenic Series and Prospecting Assessment of Copper, Gold, Iron and Tungsten Polymetallic Ore Deposits in the West Sector of the Northern Qilian Mountains; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2003; pp. 157–242. [Google Scholar]
- Lydon, J.W. Volcanogenic Massive Sulphide Deposits, Part 1 A Descriptive Model. Geosci. Can. 1984, 11, 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Groves, D.I.; Goldfarb, R.J.; Robert, F.; Hart, C.J.R. Gold Deposits in Metamorphic Belts: Overview of Current Understanding, Outstanding Problems, Future Research, and Exploration Significance. Econ. Geol. 2003, 98, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusnitsyn, A.I.; Sadykov, S.A.; Perova, E.N.; Vereshchagin, O.S. Genesis of Barite–Galena Ores at the Ushkatyn-III Deposit, Central Kazakhstan: Analysis of Geological, Mineralogical, and Isotopic (Δ34S, Δ13C, Δ18O) Data. Geol. Ore Depos. 2022, 64, 78–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outigua, A.; Essaifi, A.; Corsini, M.; Outhounjite, M.; Zouhair, M. Sidi m’barek: A Representative Example of the Moroccan Massive Sulfide Deposits. In Geological Society Special Publication; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2021; Volume 502, pp. 67–95. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, B.F.; Jensen, J.L.; Coutinho, P.; Laurent, O.; Markl, G.; Steele-MacInnis, M. Formation of Hydrothermal Fluorite-Hematite Veins by Mixing of Continental Basement Brine and Redbed-Derived Fluid: Schwarzwald Mining District, SW-Germany. J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Li, M.; Santosh, M.; Zheng, D.; Cao, H.-w.; Jiang, X.W.; Chen, H.F.; Li, Z. Fault-Controlled Carbonate-Hosted Barite-Fluorite Mineral Systems: The Shuanghe Deposit, Yangtze Block, South China. Gondwana Res. 2021, 101, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaminia, Z.; Tadayon, M.; Griffith, E.M.; Solé, J.; Corfu, F. Tectonic-Controlled Sediment-Hosted Fluorite-Barite Deposits of the Central Alpine-Himalayan Segment, Komsheche, NE Isfahan, Central Iran. Chem. Geol. 2021, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veizer, J.; Hoef, J.; Lowe, D.R.; Thurston, P.C. Geochemistry of Precambrian Carbonates: II. Archean Greenstone Belts and Archean Sea Water. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deb, M.; Hoefs, J.; Bauman, A. Isotopic Composition of Two Precambrian Stratiform Barite Deposits from the Indian Shield. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1991, 55, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, C.; Tornos, F.; Darbyshire, D.P.F.; Casquet, C. The Age and Origin of the Barite-Fluorite (Pb-Zn) Veins of the Sierra Del Guadarrama (Spanish Central System, Spain): A Radiogenic (Nd, Sr) and Stable Isotope Study. Chem. Geol. 1994, 112, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matter, A.; Peters, T.; Ramseyer, K. 87Sr/86Sr-Verhältnisse Und Sr-Gehalte von Tiefengrundwässern, Mineralien Sowie Gesteinen Aus Dem Kristallin Und Der Trias Der Nordschweiz. Eclogae Geol. Helv. 1987, 80, 579–592. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, R.; Baumann, A. Preliminary Report on the Sr Isotopic Composition of Hydrothermal Vein Barites in the Federal Republic of Germany. Min. Miner. Depos. 1984, 19, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, J.B.; Morton, J.; Valdes-Nodarse, E.L.; Diaz-Carmona, A. Sr Isotopes of Bedded Barites; Guide to Distinguishing Basins with Pb-Zn Mineralization. Econ. Geol. 1995, 90, 2058–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, S.; Clauer, N. Strontium Isotopic Compositions and Potassium and Rubidium Contents of Formation Waters in Sedimentary Basins: Clues to the Origin of the Solutes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauriohooho, K.; Barker, S.L.L.; Rae, A. Mapping Lithology and Hydrothermal Alteration in Geothermal Systems Using Portable X-Ray Fluorescence (PXRF): A Case Study from the Tauhara Geothermal System, Taupo Volcanic Zone. Geothermics 2016, 64, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNutt, R.H.; Frape, S.K.; Fritz, P.; Jones, M.G.; MacDonald, I.M. The 87Sr86Sr Values of Canadian Shield Brines and Fracture Minerals with Applications to Groundwater Mixing, Fracture History, and Geochronology. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedenquist, J.W.; Henley, R.W. The Importance of COs on Freezing Point Measurements of Fluid Inclusions: Evidence from Active Geothermal Systems and Implications for Epithermal Ore Deposition. Econ. Geol. 1985, 80, 1379–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, R.; Robert, W.; Brown, D. The Volumetric Properties of Aqueous Sodium Chloride Solutions from 0O to 500OC at Pressures up to 2000 Bars Based on a Regression of Available Data in the Literature. Geol. Surv. Bull. 1977, 1421, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, B.F.; Kortenbruck, P.; Scharrer, M.; Zeitvogel, C.; Wälle, M.; Mertz-Kraus, R.; Markl, G. Chemical Evolution of Ore-Forming Brines—Basement Leaching, Metal Provenance, and the Redox Link between Barren and Ore-Bearing Hydrothermal Veins. A Case Study from the Schwarzwald Mining District in SW-Germany. Chem. Geol. 2019, 506, 126–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre, P.; Stampfli, G.M. From Rifting to Passive Margin: The Examples of the Red Sea, Central Atlantic and Alpine Tethys. Tectonophysics 1992, 215, 69–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, K.O.; Uchupi, E. The SYN-RIFT Supersequence and Crustal Boundary. The Geology of the Atlantic Ocean; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 263–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardellach López, E.; Canals i Sabaté, À.; Tritlla i Cambra, J. Late and Post-Hercynian Low Temperature Veins in the Catalonian Coastal Ranges. Acta Geol. Hisp. 1990, 25, 0075–0081. [Google Scholar]
- Carignan, J.; Gariépy, C.; Hillaire-Marcel, C. Hydrothermal Fluids during Mesozoic Reactivation of the St. Lawrence Rift System, Canada: C, O, Sr and Pb Isotopic Characterization. Chem. Geol. 1997, 137, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornos, F.; Spiro, B.F. The Geology and Isotope Geochemistry of the Talc Deposits of Puebla de Lillo (Cantabrian Zone, Northern Spain). Econ. Geol. 2000, 95, 1277–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, M.; Muchez, P.; Schneider, J. Permo-Mesozoic Multiple Fluid Flow and Ore Deposits in Sardinia: A Comparison with Post-Variscan Mineralization of Western Europe. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2002, 204, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haschke, S.; Gutzmer, J.; Wohlgemuth-Ueberwasser, C.C.; Kraemer, D.; Burisch, M. The Niederschlag Fluorite-(Barite) Deposit, Erzgebirge/Germany—A Fluid Inclusion and Trace Element Study. Min. Miner. Depos. 2021, 56, 1071–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burisch, M.; Markl, G.; Gutzmer, J. Breakup with Benefits—Hydrothermal Mineral Systems Related to the Disintegration of a Supercontinent. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2022, 580, 117373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Particular Year | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 2800 | 3100 | 3200 | 2900 | 2500 | 2100 | 1900 |
| Kazakhstan | 482 | 500 | 620 | 620 | 600 | 450 | 500 |
| Turkey | 170 | 200 | 290 | 250 | 130 | 258 | 300 |
| India | 1050 | 1100 | 2000 | 2200 | 2000 | 1600 | 2600 |
| Iran | 480 | 500 | 550 | 490 | 200 | 224 | 220 |
| United States | 240 | NA | 480 | 390 | NA | NA | NA |
| Morocco | 107 | 140 | 1000 | 1100 | 800 | 1100 | 1300 |
| Mexico | 197 | 140 | 400 | 400 | 280 | 321 | 320 |
| Pakistan | 107 | 140 | 110 | 110 | 110 | - | - |
| Thailand | 223 | 148 | 150 | NA | NA | - | |
| Russia | 434 | 430 | 220 | 160 | 160 | - | - |
| Other | 470 | 470 | 460 | 900 | 340 | 528 | 580 |
| Global | 7320 | 7700 | 9480 | 9520 | 7500 | 6730 | 7900 |
| Sl. No | Sample No | Latitude (N) | Longitude (W) | Mineral | δ34S (‰ vs. CDT) | 87Sr/86Sr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MO-3 | 31°21′10.63″ | 5°5′28.57″ | White barite | 12.5 | 0.710787 |
| 2 | MO-7 | 31°22′11.98″ | 5°2′19.11″ | Grey barite | 14.3 | 0.710810 |
| 3 | MO-9 | 31°29′14.08″ | 4°58′13.10″ | Grey barite | 15 | 0.710772 |
| 4 | MO-13 | 31°33′33.92″ | 4°50′30.84″ | Pink barite | 10.8 | 0.710816 |
| 5 | MO-15 | 31°31′30.14″ | 4°39′21.10″ | White barite | 19.5 | 0.710793 |
| Measurement No. | Barite Studied | FI Type | RV% | Te | Tm_Ice | Tm_Solid | Th | % NaCl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8/3. | Lw | 10% | −21.6 | −0.1 | 208.3 | 0.18 | |
| 2 | 6/4. | Lw | 10% | −21.5 | 0 | 216.2 | 0 | |
| 3 | 1/1. | Lw | 10% | −22.1 | −0.1 | 180.1 | 0.18 | |
| 4 | 2/2. | Lw | 20% | −22.1 | 0 | 183.2 | 0 | |
| 5 | 7/4. | Lw | 10% | −22.1 | 0 | 183.2 | 0 | |
| 6 | 8/1. | Lw | 15% | −21.8 | 0 | 185.3 | 0 | |
| 7 | 14/2. | Lw | 10% | −22.3 | −0.3 | 188.6 | 0.35 | |
| 8 | 10/2. | Lw | 10% | −24.5 | 0 | 200.4 | 0 | |
| 9 | 12/3. | Lw | 10% | −22.4 | 0 | 201.7 | 0 | |
| 10 | 13/4. | Lw | 10% | −22.6 | −0.1 | 227.6 | 0.18 | |
| 11 | 1/2. | Lw | 12% | −21.1 | 0 | 229.3 | 0 | |
| 12 | 10/3. | Lw | 10% | −22.8 | 0 | 234.1 | 0 | |
| 13 | 12/4. | Lw | 20% | −23.1 | −1.4 | 244.6 | 0.7 | |
| 14 | 7/2. | Lw | 12% | −21.9 | 0 | 245.2 | 0 | |
| 15 | 13/3. | Lw | 15% | −22.2 | −0.1 | 246.3 | 0.18 | |
| 16 | 16/5. | Lw | 15% | −22.1 | 0 | 246.3 | 0 | |
| 17 | 6/3. | Lw | 10% | −21.1 | −0.1 | 255.4 | 0.18 | |
| 18 | 16/4. | Lw | 15% | −21.3 | −0.3 | 263.2 | 0.35 | |
| 19 | 16/6. | Lw | 15% | −22.1 | 0 | 263.2 | 0 | |
| 20 | 5/1. | Lw | 15% | −22.2 | −0.1 | 285.3 | 0.18 | |
| 21 | 8/4. | Lw | 10% | −22.2 | −0.9 | 286.3 | 0.7 | |
| 22 | 16/3. | Lw | 10% | −24.6 | 0 | 296.9 | 0 | |
| 23 | 7/3. | Lw | 10% | −22 | 0 | 321.4 | 0 | |
| 24 | 7/1. | Lw | 10% | −21.1 | 0 | 329.3 | 0 | |
| 25 | 6/5. | Lw | 10% | −21.5 | 0 | 328.9 | 0 | |
| 26 | 2/1. | Lw | 15% | −21.4 | −0.2 | 331.2 | 0.35 | |
| 27 | 11/1. | Lw | 15% | −21.3 | 0 | 335.5 | 0 | |
| 27 | 11/1. | Lw | 15% | −21.3 | 0 | 335.5 | 0 | |
| 28 | 6/7. | Lw | 10% | −22.1 | −0.2 | 347.8 | 0.35 | |
| 29 | 8/2. | Lw | 15% | −21.9 | 0 | 347.8 | 0 | |
| 30 | 11/2. | Lw | 10% | −21.5 | 0 | 348.7 | 0 | |
| 31 | 2/3. | Lw | 10% | −21.3 | 0 | 352.3 | 0 | |
| 32 | 16/2. | Lw | 12% | −24.6 | −0.1 | 355.4 | 0.18 | |
| 33 | 6/6. | Lw | 10% | −22.1 | −0.1 | 359.7 | 0.18 | |
| 34 | 8/5. | Vw | 75% | −24.6 | −0.2 | 389.8 | 0.35 | |
| 35 | 8/6. | Vw | 70% | −21.5 | −0.3 | 364.6 | 0.35 | |
| 36 | 8/7. | Vw | 65% | −26.4 | −0.4 | 375.3 | 0 | |
| 37 | 11/3. | Vw | 70% | −25.2 | 0 | 368.1 | 0 | |
| 38 | 11/4. | Vw | 60% | −24.8 | 0 | 425.3 | 0 | |
| 39 | 12/1. | Vw | 70% | −28.3 | −0.2 | 372.3 | 0.35 | |
| 40 | 12/2. | Vw | 65% | −26.4 | −0.1 | 405.6 | 0.18 | |
| 41 | 14/1. | Vw | 80% | −25.3 | −0.1 | 364.8 | 0.18 | |
| 42 | 6/1. | Ls | 10% | −26.5 | −12.6 | 256.5 | 392.5 | 29.5 |
| 43 | 6/2. | Ls | 10% | −24.2 | −10.5 | 238.5 | 368.4 | 27.5 |
| 44 | 7/5. | Ls | 12% | −22.6 | −16.2 | 285.2 | 412.9 | 30.5 |
| 45 | 10/5. | Ls | 12% | −25.1 | −14.4 | 280.1 | 345.2 | 30 |
| 46 | 10/6. | Ls | 10% | −23.8 | −6.2 | 228.6 | 336.3 | 25.3 |
| 47 | 13/1. | Ls | 15% | −39.1 | −14.5 | 251.8 | 328.8 | 29.2 |
| 48 | 13/2. | Ls | 20% | −27.7 | −13.6 | 202.5 | 329.5 | 27 |
| 49 | 16/1. | Ls | 15% | −28.2 | −5.6 | 293.6 | 358.6 | 31.2 |
| 50 | 16/7. | Ls | 15% | −21.6 | −17.3 | 288.7 | 388.2 | 30.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samaoui, S.; Aabi, A.; Boushaba, A.; Mohammed, B.; Nait Bba, A.; Essaifi, A.; Baidder, L.; Lamrani, O. Metallogeny and Genesis of Fault-Filling Barite-Sulfide Veins (Ougnat, Morocco): Petrography, Fluid Inclusion, and Sr-S Isotopic Constraints. Geosciences 2024, 14, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences14030083
Samaoui S, Aabi A, Boushaba A, Mohammed B, Nait Bba A, Essaifi A, Baidder L, Lamrani O. Metallogeny and Genesis of Fault-Filling Barite-Sulfide Veins (Ougnat, Morocco): Petrography, Fluid Inclusion, and Sr-S Isotopic Constraints. Geosciences. 2024; 14(3):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences14030083
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamaoui, Samir, Ayoub Aabi, Abdellah Boushaba, Belkasmi Mohammed, Abdellah Nait Bba, Abderrahim Essaifi, Lahssen Baidder, and Othmane Lamrani. 2024. "Metallogeny and Genesis of Fault-Filling Barite-Sulfide Veins (Ougnat, Morocco): Petrography, Fluid Inclusion, and Sr-S Isotopic Constraints" Geosciences 14, no. 3: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences14030083
APA StyleSamaoui, S., Aabi, A., Boushaba, A., Mohammed, B., Nait Bba, A., Essaifi, A., Baidder, L., & Lamrani, O. (2024). Metallogeny and Genesis of Fault-Filling Barite-Sulfide Veins (Ougnat, Morocco): Petrography, Fluid Inclusion, and Sr-S Isotopic Constraints. Geosciences, 14(3), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences14030083