Unraveling the Drivers Controlling the Transient and Seasonal CO2 Dynamic in a Shallow Temperate Cave
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Studied Site
2.2. Cave and Weather Monitoring System
3. Results
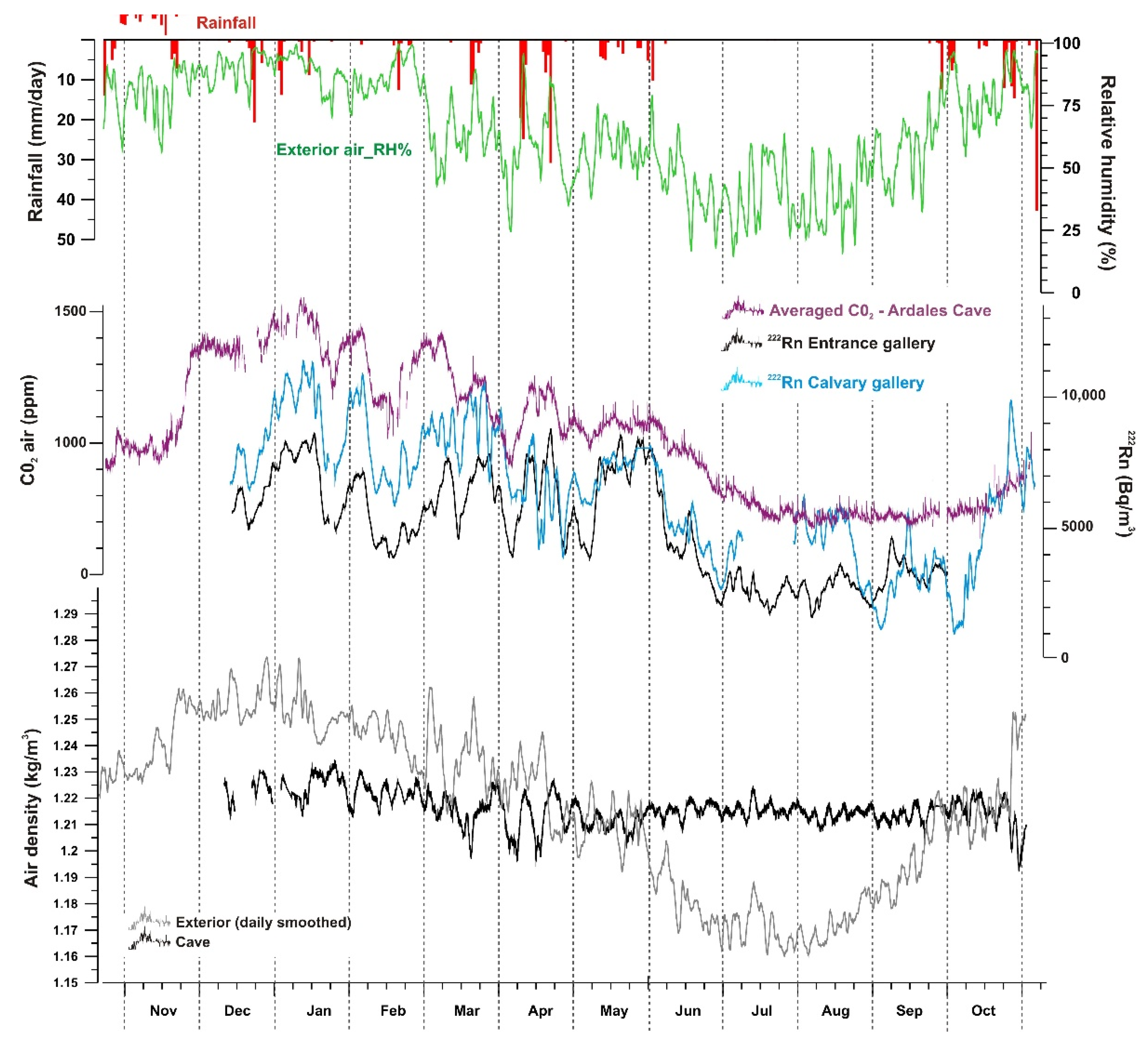
3.1. General Meteorological Conditions and Prevailing Temperature and Humidity in the Cave
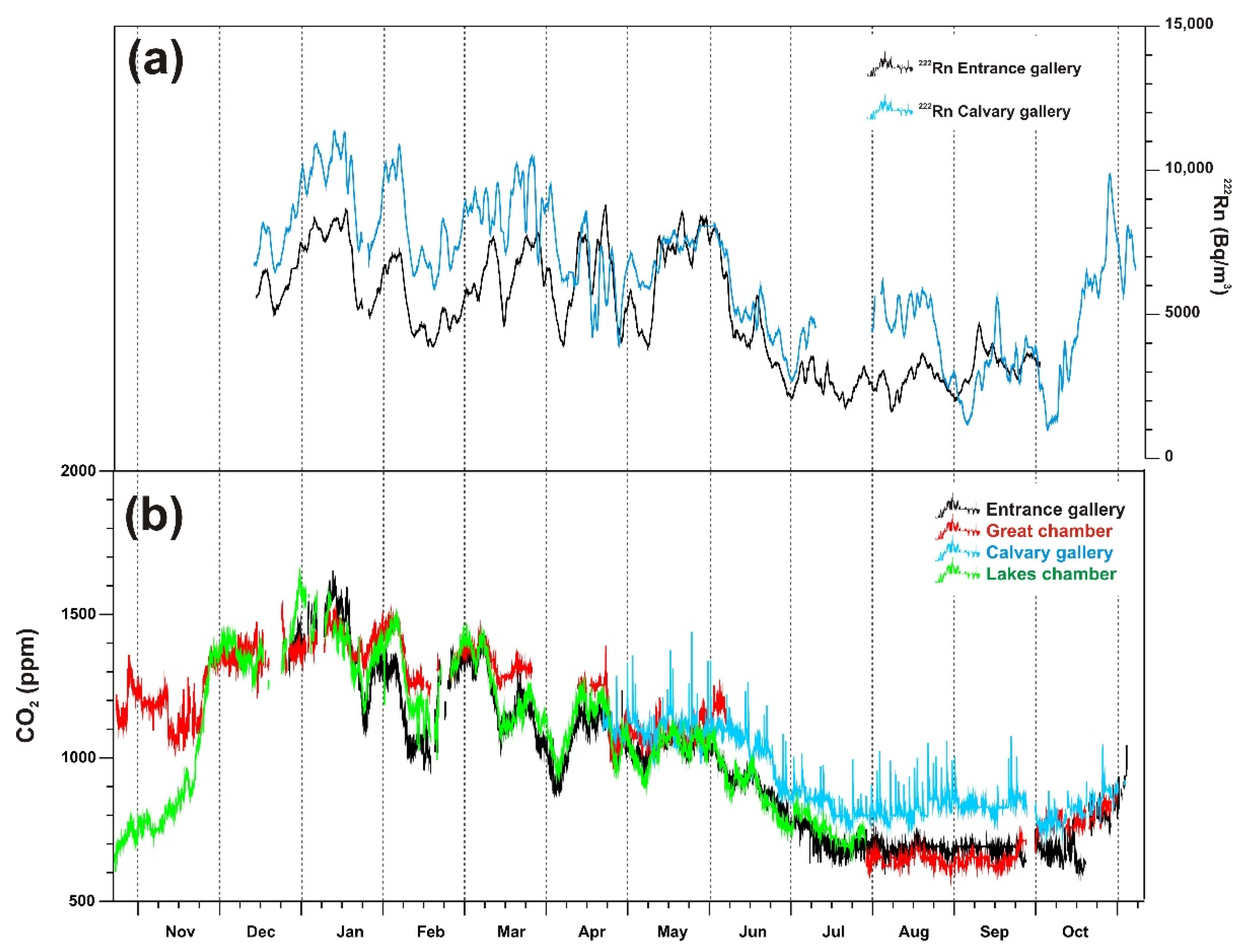
3.2. Gas Composition of the Cave Atmosphere: CO2 and 222Rn
4. Discussion
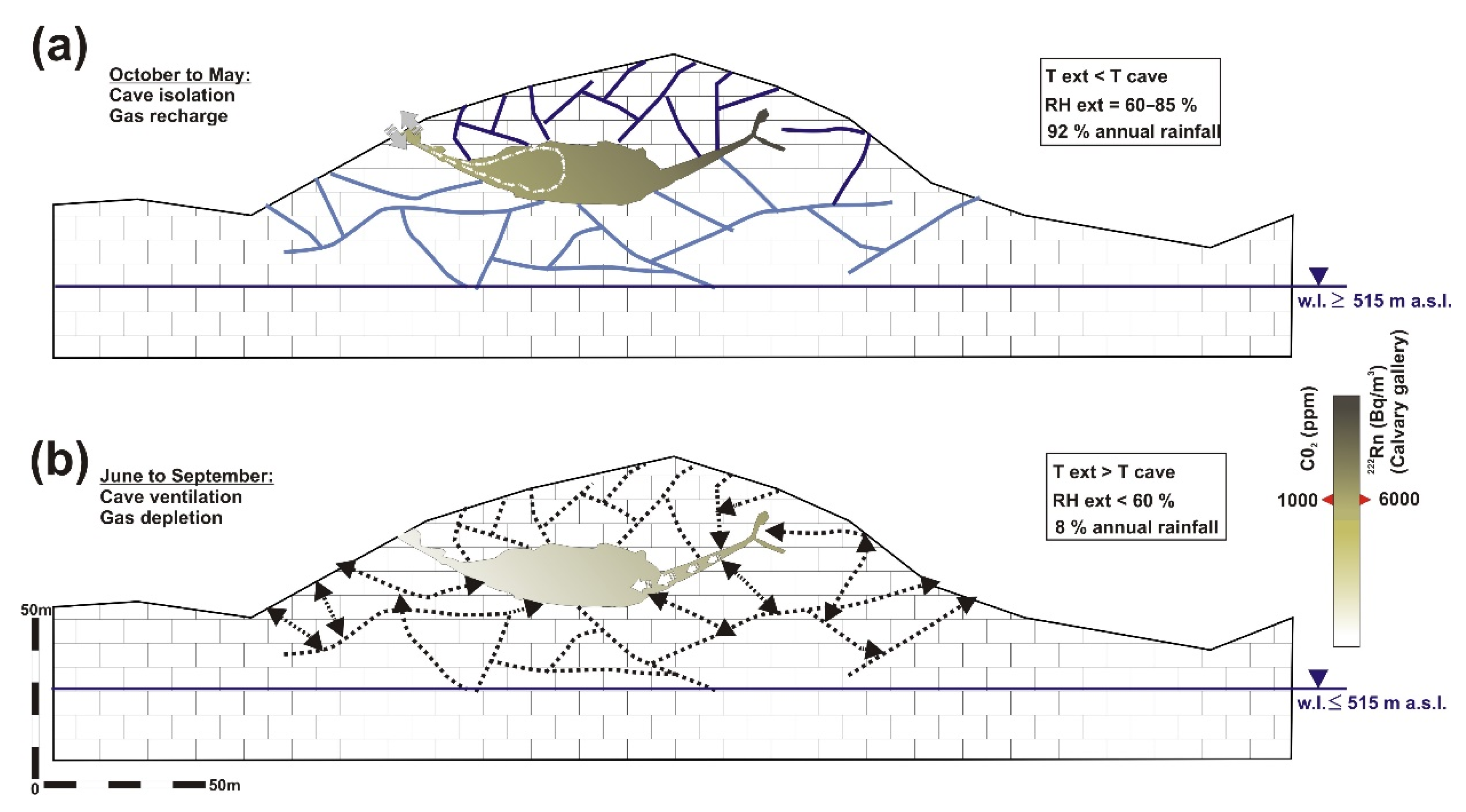
4.1. Drivers and Seasonal Pattern of Cave Gases
4.2. Cave Topographical and Geomorphological Features Controlling Gases Dynamic
4.3. The Motionless Atmosphere in the Calvary Gallery; an Example of Gas Trapping
4.4. Observations and Importance for Carbon Balance in Karst and Cave Conservation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gombert, P. Role of karstic dissolution in global carbon cycle. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2002, 33, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Dreybrodt, W.; Wang, H.J. A possible important CO2 sink by the global water cycle. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Ortiz, P.; Roland, M.; Sanchez-Moral, S.; Janssens, I.A.; Domingo, F.; Godderis, Y.; Kowalski, A.S. Hidden, abiotic CO2 flows and gaseous reservoirs in the terrestrial carbon cycle: Review and perspectives. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 2010, 150, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Cortes, A.; Cuezva, S.; Garcia-Anton, E.; Alvarez-Gallego, M.; Pla, C.; Benavente, D.; Cañaveras, J.C.; Calaforra, J.M.; Mattey, D.P.; Sanchez-Moral, S. Changes in the storage and sink of carbon dioxide in subsurface atmospheres controlled by climate-driven processes: The case of the Ojo Guareña karst system. Environ. Earth. Sci. 2015, 74, 7715–7730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, J.U.L.; Bertram, R.A.; Ridley, H.E. A first approximation of the Earth’s second largest reservoir of carbon dioxide gas. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmerich, E.W. Carbon dioxide fluxes in a semiarid environment with high carbonate soils. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 2003, 116, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielnick, P.; Dugas, W.A.; Mitchell, K.; Havstad, K. Long-term measurements of CO2 flux and evapotranspiration in a Chihuahuan desert grassland. J. Arid. Environ. 2005, 60, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, A.S.; Serrano-Ortiz, P.; Janssens, I.A.; Sanchez-Moral, S.; Cuezva, S.; Domingo, F.; Alados-Arboledas, L. Can flux tower research neglect geochemical CO2 exchange? Agric. Forest Meteorol. 2008, 148, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walvoord, M.A.; Striegl, R.G.; Prudic, D.E.; Stonestrom, D.A. CO2 dynamics in the Amargosa desert: Fluxes and isotopic speciation in a deep unsaturated zone. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, W02006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, W.W. Origin of caves and other solution openings in the unsaturated (vadose) zone of carbonate rocks: A model for CO2 generation. Geology 1985, 13, 822–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente, D.; Vadillo, I.; Carrasco, F.; Soler, A.; Linan, C.; Moral, F. Air carbon dioxide contents in the vadose zone of a Mediterranean karst. Vadose Zone J. 2010, 9, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuezva, S.; Fernandez-Cortes, A.; Benavente, D.; Serrano-Ortiz, P.; Kowalski, A.S.; Sanchez-Moral, S. Short-term CO2(g) exchange between a shallow karstic cavity and the external atmosphere during summer: Role of the surface soil layer. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrier, F.; Richon, P.; Gautam, U.; Tiwari, D.R.; Shrestha, P.; Sapkota, S.N. Seasonal variations of natural ventilation and radon-222 exhalation in a slightly rising dead-end tunnel. J. Environ. Radioact. 2007, 97, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisia, S.; Fairchild, I.J.; Fohlmeister, J.; Miorandi, R.; Spoetl, C.; Borsato, A. Carbon mass-balance modelling and carbon isotope exchange processes in dynamic caves. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 380–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattey, D.P.; Atkinson, T.C.; Barker, J.A.; Fisher, R.; Latin, P.; Durrell, R.; Ainsworth, M. Carbon dioxide, ground air and carbon cycling in Gibraltar karst. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 184, 88–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Anton, E.; Cuezva, S.; Fernandez-Cortes, A.; Alvarez-Gallego, M.; Pla, C.; Benavente, D.; Canaveras, J.C.; Sanchez-Moral, S. Abiotic and seasonal control of soil-produced CO2 efflux in karstic ecosystems located in Oceanic and Mediterranean climates. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 164, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Anton, E.; Cuezva, S.; Fernandez-Cortes, A.; Benavente, D.; Sanchez-Moral, S. Main drivers of diffusive and advective processes of CO2-gas exchange between a shallow vadose zone and the atmosphere. Int. J. Greenh. Gas. Con. 2014, 21, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourges, F.; Genthon, P.; Mangin, A.; d’Hulst, D. Microclimates of l’Aven d’Orgnac and other French limestone caves (Chauvet, Esparros, Marsoulas). Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 1651–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Cortes, A.; Sanchez-Moral, S.; Cuezva, S.; Benavente, D.; Abella, R. Characterization of trace gases’ fluctuations on a low energy cave (Castañar de Ibor, Spain) using techniques of entropy of curves. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Cortes, A.; Sanchez-Moral, S.; Cuezva, S.; Cañaveras, J.C.; Abella, R. Annual and transient signatures of gas exchange and transport in the Castañar de Ibor cave (Spain). Int. J. Speleol. 2009, 38, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Milanolo, S.; Gabrovsek, F. Analysis of carbon dioxide variations in the atmosphere of Srednja Bijambarska Cave, Bosnia and Herzegovina. Bound. Layer Meteor. 2009, 131, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczk, A.J.; Froelich, P.N. Cave air ventilation and CO2 outgassing by radon-222 modeling: How fast do caves breathe? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 289, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, D.D.; Markewitz, D. How deep is soil? Soil, the zone of the earth’s crust that is biologically active, is much deeper than has been thought by many ecologists. BioScience 1995, 45, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morner, N.A.; Etiope, G. Carbon degassing from the lithosphere. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2002, 33, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisbrod, N.; Dragila, M.I.; Nachshon, U.; Pillersdorf, M. Falling through the cracks: The role of fractures in Earth–atmosphere gas exchange. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L02401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Algarra, A.; Mazzoli, S.; Perrone, V.; Rodríguez-Cañero, R.; Navas-Parejo, P. Variscan Tectonics in the Malaguide Complex (Betic Cordillera, Southern Spain): Stratigraphic and structural Alpine versus Pre-Alpine constraints from the Ardales Area (Province of Malaga). I. Stratigraphy. J. Geol. 2009, 117, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, A.P.; Zilhão, J.; d’Errico, F.; Cantalejo-Duarte, P.; Dominguez-Bella, S.; Fullola, J.M.; Weniger, G.C.; Ramos-Muñoz, J. The symbolic role of the underground world among Middle Paleolithic Neanderthals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2021495118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, D.L.; Standish, C.D.; Garcia-Diez, M.; Pettitt, P.B.; Milton, J.A.; Zilhão, J.; Alcolea-Gonzalez, J.J.; Cantalejo-Duarte, P.; Collado, H.; de Balbin, R.; et al. U-Th dating of carbonate crusts reveals Neandertal origin of Iberian cave art. Science 2018, 359, 912–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuezva, S. Dinámica Microambiental de un Medio Kárstico Somero (Cueva de Altamira, Cantabria): Microclima, Geomicrobiología y Mecanismos de Interacción Cavidad-Exterior. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Madrid, Spain, May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rivas-Martínez, S.; Rivas-Sáenz, S.; Penas-Merino, A. Worldwide bioclimatic classification system. Glob. Geobot. 2011, 1, 1–638. [Google Scholar]
- James, E.W.; Banner, J.L.; Hardt, B. A global model for cave ventilation and seasonal bias in speleothem paleoclimate records. Geochim. Geophys. Geosys. 2015, 16, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pla, C.; Cuezva, S.; Martinez-Martinez, J.; Fernandez-Cortes, A.; Garcia-Anton, E.; Fusi, N.; Crosta, G.B.; Cuevas-Gonzalez, J.; Canaveras, J.C.; Sanchez-Moral, S.; et al. Role of soil pore structure in water infiltration and CO2 exchange between the atmosphere and underground air in the vadose zone: A combined laboratory and field approach. Catena 2017, 149, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourges, F.; Genty, D.; Perrier, F.; Lartiges, B.; Régnier, E.; François, A.; Leplat, J.; Touron, S.; Bousta, F.; Massault, M.; et al. Hydrogeological control on carbon dioxide input into the atmosphere of the Chauvet-Pont d’Arc cave. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 136844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukuljan, L.; Gabrovšek, F.; Covington, M.D.; Johnston, V.E. CO2 dynamics and heterogeneity in a cave atmosphere: Role of ventilation patterns and airfow pathways. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 146, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyraube, N.; Lastennet, R.; Denis, A.; Malaurent, P.; Houillon, N.; Villanueva, J.D. Determination and quantification of major climatic parameters influencing the CO2 of Lascaux Cave. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 133, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covington, M.D. The importance of advection for CO2 dynamics in the karst critical zone: An approach from dimensional analysis. Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Pap. 2016, 516, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajnc, B.; Ferlan, M.; Ogrinc, N. Soil CO2 sources above a subterranean cave-Pisani rov (Postojna Cave, Slovenia). J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 1883–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Lei, J.; He, Q.; Zeng, Z.; Lü, X.; Jiang, Y. Rainfall-driven and hydrologically-controlled variations in cave CO2 sources and dynamics: Evidence from monitoring soil CO2, stream flow and cave CO2. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 126060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Cortes, A.; Benavante, D.; Cuezva, S.; Cañaveras, J.C.; Alvarez-Gallego, M.; Garcia-Anton, E.; Soler, V.; Sanchez-Moral, S. Effect of water vapour condensation on the radon content in subsurface air in a hypogeal inactive-volcanic environment in Galdar cave, Spain. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 75, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Cortes, A.; Cuezva, S.; Sanchez-Moral, S.; Cañaveras, J.C.; Porca, E.; Jurado, V.; Martin-Sanchez, P.M.; Saiz-Jimenez, C. Detection of human-induced environmental disturbances in a show cave. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandez-Cortes, A.; Martin-Pozas, T.; Cuezva, S.; Cañaveras, J.C.; Saiz-Jimenez, C.; Sanchez-Moral, S. Unraveling the Drivers Controlling the Transient and Seasonal CO2 Dynamic in a Shallow Temperate Cave. Geosciences 2022, 12, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12090335
Fernandez-Cortes A, Martin-Pozas T, Cuezva S, Cañaveras JC, Saiz-Jimenez C, Sanchez-Moral S. Unraveling the Drivers Controlling the Transient and Seasonal CO2 Dynamic in a Shallow Temperate Cave. Geosciences. 2022; 12(9):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12090335
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandez-Cortes, Angel, Tamara Martin-Pozas, Soledad Cuezva, Juan Carlos Cañaveras, Cesareo Saiz-Jimenez, and Sergio Sanchez-Moral. 2022. "Unraveling the Drivers Controlling the Transient and Seasonal CO2 Dynamic in a Shallow Temperate Cave" Geosciences 12, no. 9: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12090335
APA StyleFernandez-Cortes, A., Martin-Pozas, T., Cuezva, S., Cañaveras, J. C., Saiz-Jimenez, C., & Sanchez-Moral, S. (2022). Unraveling the Drivers Controlling the Transient and Seasonal CO2 Dynamic in a Shallow Temperate Cave. Geosciences, 12(9), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12090335








