Abstract
Seismic interferometry is often proposed as a cost-efficient technique for reservoir monitoring including CO2 sequestration due to its low cost and environmental advantages over active source imaging. Although many studies have demonstrated the ability of seismic interferometry to retrieve surface waves, body wave imaging remains challenging due to their generally lower amplitudes of body waves in seismic interferometry data. An optimum data acquisition strategy can help retrieve low amplitude body waves better, however, rare attempts have been made to evaluate various data acquisition strategies. In this study, we use numerical modeling to examine three different acquisition schemes to evaluate the retrievability of P waves from seismic interferometry data. From our numerical results, we observe that (1) positing receivers beneath the attenuated weathered layer improves the data quality and signal to noise ratio, but additional processing steps including predictive deconvolution and Radom transform filter are necessary to remove the downgoing surface multiples, artifacts that are generated from this data acquisition; (2) vertical seismic profiling (VSP) alongside with the conventional surface seismic acquisition improve the target zone detection; and (3) crosswell acquisition of seismic interferometry is an ineffective means to obtain reflection events due to the non-similarity of ray paths from the noise sources meaning that the required stationary phase theory is not fulfilled.
1. Introduction
Ambient noise seismic interferometry (ANSI) involves the cross-correlation of seismic noise recorded by pairs of receivers to extract information about the earth structure [1,2]. The noise can be generated by anthropic activities such as construction and traffic noise and also natural noise that is constantly occurring in the subsurface from teleseismic earthquakes, ocean tides, etc. Conceptually, the purpose of cross-correlation of the noise between receivers produces an approximation of Green’s function that describes the earth medium response to an impulse source and eventually lead to the construction of the virtual shot gathers along a seismic array. Following the pioneering work by Claerbout [3], Wapenaar fully developed the math and profs for the original equations using a power reciprocity theorem for an arbitrary 3D inhomogeneous lossless medium [4,5]. Over the past 20 years, ANSI became a rapidly evolving field of research in the application of retrieving surface wave and body wave responses. Since ANSI does not require expensive active sources, it is cost effective in the sense that an array of geophones can be left deployed to record seismic noise over a long period of time for a time-lapse study, particularly regarding the monitoring of CO2 sequestration and fracturing [6,7,8,9]. Due to the aforementioned convenience, the capability of the ambient noise seismic interferometry (ANSI) method for subsurface imaging has been widely investigated at scales ranging from global earth’s interior to local exploration seismology applications.
Surface wave tomography, which most researchers have focused on, is relatively well established [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. Unfortunately, the vertical resolution of the seismic profile retrieved from the surface wave seismic interferometry is relatively insufficient to extract information from deep layers for exploration purposes. On the other hand, some studies have also been conducted, though it has proven to be more challenging than it is for surface waves, to extract body wave reflections from the deep subsurface structures from the cross-correlation of ambient noise [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. The successful extraction of the body wave reflections from the seismic background noise demonstrates promise in applications of geophysical exploration and time-lapse monitoring of petroleum and geothermal reservoirs deep in the earth.
In order to enhance the accuracy and resolution of the body wave retrieval using ANSI, many efforts have been made over the last few years to investigate the dependence of the quality of the retrieved seismic reflections on various characteristics of noise sources, source distributions, and acquisition configurations and so on [25,26,27,28]. However, limited source coverage in most practice situations inevitably violates the theoretical assumption of a closed sources distribution for seismic interferometry resulting in errors in the retrieved Green’s function [2]. Snieder [11] proposed that rather than the uniformly distributed noise sources, sources that are located in the areas of stationary phase region dominantly contribute to the quality of the retrieved virtual shot gathers. Thorbecke and Draganov [29] investigated the effects of some parameters such as the number of sources, noise recording time, and source locations showing that the increasing time duration of source signals and number of noise signals improves the performance of ANSI. In addition, several strategies other than the cross-correlation method for SI have been evaluated including cross coherence, multidimensional deconvolution (MDD), and Marchenko method and so on [17,30,31,32,33,34,35]. While many processing techniques of ANSI have been proposed, little has been given to data acquisition strategy; for example, rare attempts have been made in borehole seismology such as vertical seismic profiling (VSP) and crosswell seismic acquisition. The additional information extracted from the VSP and crosswell data can assist in the quality control for the seismic well tie and synthetic seismogram, detailed interpretation therefore can be achieved.
The major objective of this study is to evaluate how the ambient noise data acquisition strategy will impact on the retrievability of the virtual reflection response. First, through forward modeling, we investigate the effect of surface wave noise sources and show their effectiveness at degrading ANSI quality by deploying receivers beneath the attenuating weathered layer. Then, taking advantage of the borehole seismic survey, crosswell and zero-offset VSP acquisition were evaluated by comparing the ANSI result with the conventional surface acquisition case for P waves reflection retrieval in terms of signal to noise ratio and repeatability.
2. Seismic Interferometry Method
Seismic interferometry (SI), also known as Green’s function retrieval, obtains the seismic reflection response between two receivers through cross-correlating the observed signals. The Green’s function representation theorem for the cross-correlation type interferometry of an arbitrary inhomogeneous medium reads [36]
where xA, xB and xS represent the receiver locations at position A and B, and the source location, respectively. stands for the real part of the inter-receiver Green’s function extracted by integrating the cross-correlation of the observed wavefield. characterizes the empirical average of the random source time function and asterisk stands for convolution. The medium density is ρ and the acoustic wave velocity is c. Due to some theoretical approximations are made to Equation (1), the exact stationary phase condition is not completely satisfied leading to errors in seismic amplitude and artefact [36], but the phase information recovered are acceptable for SI. The observed wavefields at receiver A and B generated by all the uncorrelated noise sources within the boundary are written as:
Therefore, if the receivers are placed on the free surface, the boundary at the free surface can be relaxed. Figure 1 shows the concept described above simply. A wavefield emitted from an underground source is recorded by the geophone when the wavefield reaches the earth’s surface. Then, when the wave reflected from the earth’s surface to the underground is reflected in the earth’s surface by a scattered underground and an interface where the acoustic impedance changes are significant, this wave is recorded by another geophone. In these two figures, the path to the first geophone from underground is common. Two traces recorded by two geophones are cross-correlated, leading to the common path cancellation, while the reflection path from the first receiver to the second receiver remains. Thus, seismic reflection responses or Green’s function observed by the second geophone are obtained as if there was a source in the location of the first geophone. As a result, a virtual shot gather is obtained in a single geophone location.
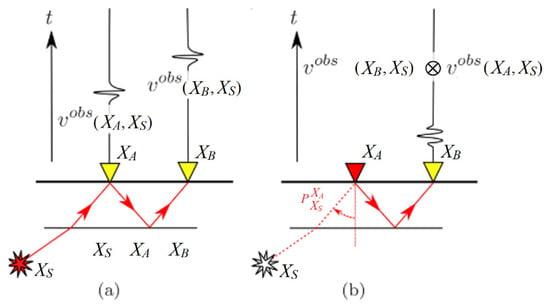
Figure 1.
The fundamental principle of reflected-wave interferometry. (a) The subsurface source is emitted a signal from underground to the surface and is recorded by two geophones. The second geophone receives the reflected signal by an underground scatterer. (b) The cross-correlation cancels the common path from the source XB to the first receiver X0, as if a source were located at receiver X0. The symbol ⊗ denotes cross-correlation.
The 2D finite difference wavefield modeling method was used to simulate the passive noise in the subsurface [5]. In this study, acoustic scheme was used to perform the following wavefield modeling, but visco-acoustic modeling was used to investigate the effect of the weathered layer effect on the ANSI. To suppress the numerical dispersion of the finite difference in the 2D wave equation, the space and time resolution used in these simulations are 2 m and 0.001 s, respectively. A Rikers wavelet activated at a random start time and source positions with maximum frequency of 24 Hz is used for the source time function to satisfy the noninterfering impulse sources required by SI. Additionally, the first 4 s of the total 120 s long noise signals recorded in P component for the acoustic and visco-acoustic schemes are demonstrated in Figure 2. Except of the earth arrivals, most of the source signals are interfered. To simplify the simulation, we use a global P wave Q factor 20 in the visco-acoustic scheme, from which we can see that the signal to noise ratio of the source signals from the near surface are improved.
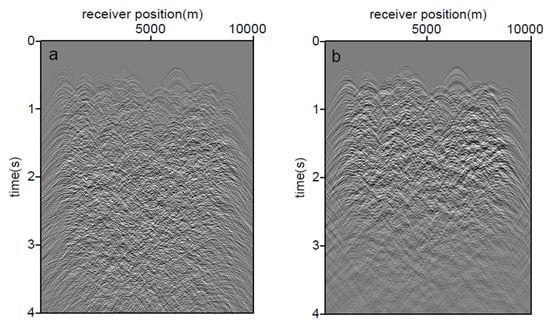
Figure 2.
Noise signals recorded from the acoustic (a) and visco-acoustic (b) simulations.
Data Processing
Table 1 presents the workflow for the retrieval of the virtual shot gathers and the seismic stacked sections from which the geological structures subsurface can be identified. Band-pass filter and fk filter are applied to the synthetic noise data to remove the ground roll. Following that, RMS normalization is performed to the synthetic noise. Then, one of the traces from the data is extracted as a master trace (every 5th trace) to cross-correlate against the other traces in each single gather. The location of the master trace is considered to be a virtual source for the resulting virtual “shot” gather. Cross-correlation results in causal and acausal response of Green’s function and summation over the causal and the time reversal part of the retrieved Green’s function can compensate for the incomplete illumination at two receivers [37]. After obtaining these virtual shot gathers, we conduct conventional processing steps, including sorting to CMP gathers, conducting velocity analysis, applying NMO correction, and stacking.

Table 1.
Processing flow of the ANSI to construct the virtual seismic reflections.
3. Results
3.1. Land Acquisition below the Weathered Layer (Surface Wave Impact)
In seismic interferometry, the geophones are conventionally placed on surface. It is known that there are multiple kinds of surface noise such as traffic noise, human activities, natural sources (such as wind and stream wave), and industry vibrations that could have defective effects on retrieved reflections. Due to the close proximity of the surface noise sources and the receivers, compared with deep source signal sources relative to distant receivers, the surface noise often dominates the recorded signal in land acquisition. These surface noises, due to lack of attenuation in the path between them and the surface receivers, usually are used for passive surface wave imaging for shallow structures. This would contaminate the deep body waves ANSI [17]; therefore, elimination of surface noise-related artefacts is critical to improving the retrieval of reflected body waves from the deep earth structures.
In the conventional data acquisition where geophones are places on the surface, a weathered layer typically exhibiting high porosity and lock of cementation acts as an attenuator of meaningful seismic signal. Usually, the low velocity and attenuating effects of the weathered layer have negative impacts on data processing procedures; however, placing the receivers beneath the weathered layer may help. Therefore, the elimination of the defective effect or taking advantage of its low-quality factor is a valuable topic for study. In this case, a visco-acoustic scheme was used for modeling, which means during the wave propagation the mechanical energy will dissipate into heat energy, to investigate the effect of weathered layer on body wave ANSI quality.
Figure 3 shows the geological models where the geophones are placed on the free surface and below the weathered layer, respectively, for comparison of the ANSI result. The uppermost layer is intended to represent the weathered layer, below which 1000 noise sources represented by black dots are randomly distributed in each model (10,000 m in width and 4100 m in depth) and are activated randomly during a period of 120 s. We intend to simulate natural sources coming from deep formations; therefore, their maximum frequency was set to 24 Hz. The 1000 sources are randomly triggered. The values of P-wave velocities and densities for different layers, with their thicknesses and two-way travel times are given in Table 2. We choose every 5th geophone (e.g., 1, 6, 11, 16, 21…) as a master trace for cross-correlation with all other traces to generate virtual shot gathers, eventually creating 201 virtual shot gathers with a 50 m shot interval in total. Each shot gather is composed of 1000 traces with a 10 m receiver interval. Three virtual shot gathers at the position of trace 301, 501, and 701 are retrieved, from which clear reflections are observed (Figure 4). Because the third interface is curved, the peak of that hyperbola is not at the zero-offset position. After obtaining all the virtual shot gathers, further processing includes CDP sorting velocity analysis, normal moveout corrections (NMO), and the final stacked section before using geophones on free surface and beneath the attenuating weathered layers are shown in Figure 5. There is no AGC or time-dependent gain applied to this section. Because the geophones are buried, the primary reflections all arrive about 0.33 s earlier on this section than their counterparts on the surface-geophone section. Note that for buried receivers, it could be obviously observed that the continuity of events has been enhanced. However, the by-product of burying the geophone is also obvious—the top reflected multiples representing the downgoing reflections from the uppermost free surface appear, mixed with some of the primary reflections. Some of them even have a tuning effect with primary reflections, which may lead to mistakes in further interpretation.
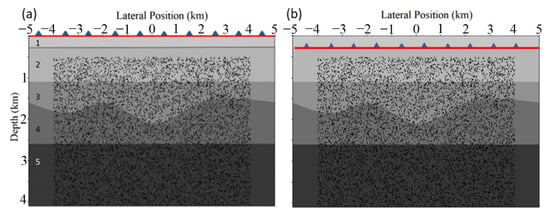
Figure 3.
The geological mode used in this study. The red line with blue triangles shows the location of receivers. The dots show 1000 noise sources locations from deeper layers. In (a,b) the red line shows the acquisition line above and below the weathered layer, respectively. The sources are randomly distributed below the depth 500 m and within the offset −4000 to 4000 m.

Table 2.
The P wave velocities and densities for the model in Figure 3.
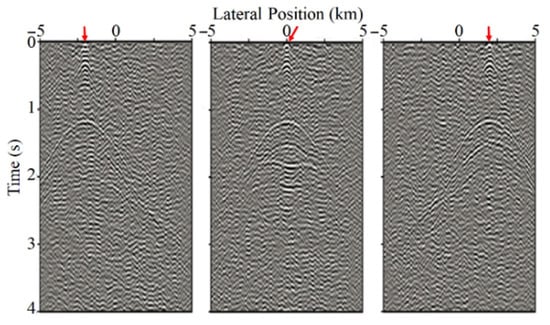
Figure 4.
Three virtual shot gathers example at three positions for geological model in Figure 3a. The red arrows show the location of the master trace.
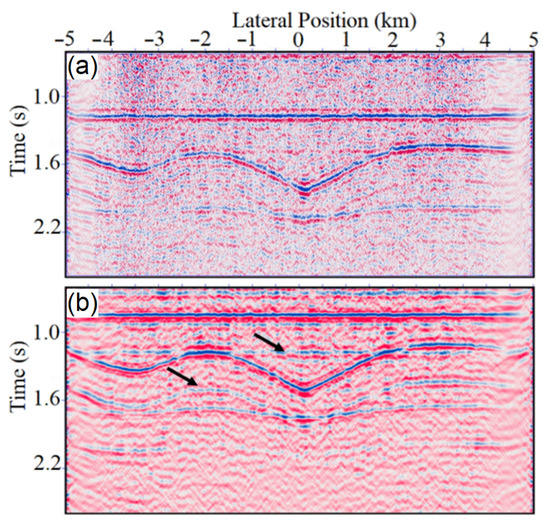
Figure 5.
Stacked seismic section using geophones on (a) free surface and (b) beneath the attenuating weathered layer (Q = 30) corresponding to the geological model in Figure 3a,b. Arrows show downgoing surface multiples with the late arrival time of around 0.33 s comparing to their primary reflections.
To remove the surface multiples from stacked seismic sections using buried receivers, we applied predictive deconvolution followed by a spiking deconvolution, and Hyperbolic Radon transform filter to the prestack data, yielding the section shown in Figure 6, from which we observe that the surface multiplies have been satisfactorily removed and temporal resolution is increased.
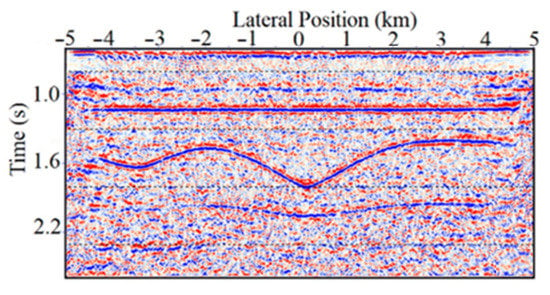
Figure 6.
Stacked buried-geophone section after applying predictive and spiking deconvolution, and Radon transform filter. We note that the Radon transform significantly removes the surface multiples that remained in Figure 5 indicated by the arrows.
3.2. Zero-Offset VSP Acquisition Scheme
VSP data provides the integrate information of the borehole measurements with the seismic survey. The VSP acquisition usually helps in a calibration of the surface seismic method. However, VSP data acquired using active source are costly in field. In this section, we propose the generation of the zero-offset VSP data using passive noise which reduces the budge significantly. An anticline synthetic model was used for the simulation, from which layer 3 was assigned as a coal layer with proper velocity and density values (the target area covered by yellow dashes, shown in Figure 7). This geological model containing a total of five layers and four interfaces with anticline structures has a lateral width of 10,000 m and a depth of 4000 m. The VSP tool is positioned on the x-axis (5000, 0) in the coordinate and has a vertical extension on the y-axis (0, 3000) with the 101 geophones positioned in the borehole from 1000 to 3000 m depth. The surface seismic and the VSP acquisition are simultaneously operated during the simulation and 500 noise sources were randomly distributed for a 120 s recording. Following the same processing steps as in the previous section, single virtual shot gathers retrieved at the position of the middle trace and the stacked section for the surface acquisition scenario are obtained (Figure 8).
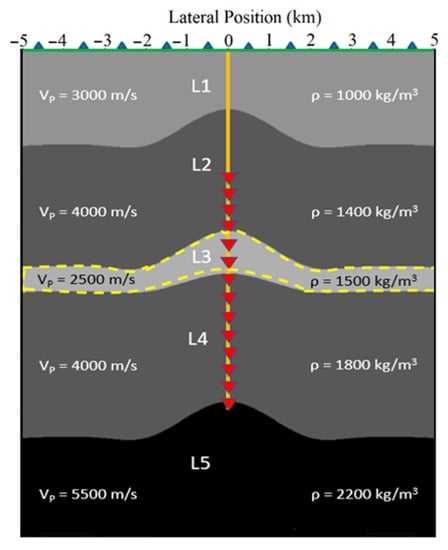
Figure 7.
An acoustic velocity model with anticlines that are combined surface seismic and zero-offset VSP geometry. Blue triangles correspond to 201 geophones that are placed on the free surface. L3 (covered by yellow-dashed area) corresponds to the coal layer. The red triangles in the vertical direction (101 geophones) show the array of the geophones for VSP acquisition.
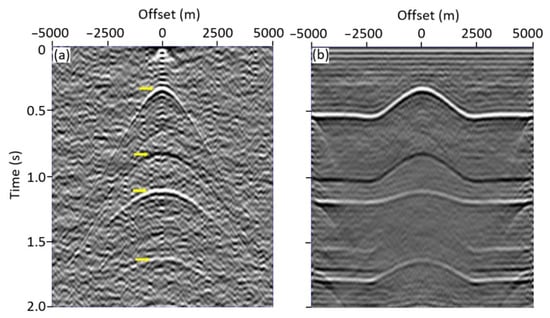
Figure 8.
(a) A virtual shot gather retrieved at position of receiver 101 and (b) the final stacked section retrieved from the surface acquisition scheme. The yellow arrows correspond to the reflections from four interface in Figure 7.
While the surface geophone measures only the upgoing waves, the VSP acquisition in the borehole records both upgoing and downgoing wavefields. After cross-correlation of the recorded noise, the time–depth conversion is applied to obtain the virtual VSP shot gather (Figure 9). The primary downgoing wave or first arrival curve are picked along the red solid line, from which we see the changes in slope on this line indicate changes in velocity in the subsurface. Since the VSP data contain the downgoing wavefield and the upgoing wavefield interfering with each other, these wavefields must be decomposed. For the separation of the wavefields, frequency-wavenumber filtering is used to convert the time domain data to the frequency domain by 2D Fourier Transform. From the f-k spectra in Figure 10, the downgoing wavefield has a negative slope and is located in the positive quadrant, while the upgoing wavefield is in the right side in the panel with an opposite slope. After filtering the downgoing wavefield, both wavefields are successfully obtained with a time-depth relation (Figure 11). In the next step, static correction is carried out. All traces in the VSP data are shifted using the first arrival time. Therefore, upgoing events reduced to the time they can be recorded. Thereby, all traces in the upgoing wavefield are aligned and flattened (Figure 12). Thus, one-way time is transformed into two-way travel time (TWT). At last, the flattened upgoing wavefield is used for building corridor stacks, which can be used to compare the surface seismic acquisition result. The traces are stacked using the outside corridor stack because of it is multiple-free and has only primary events.
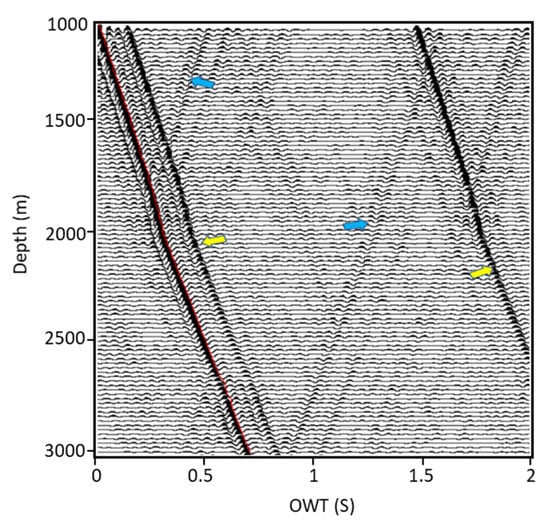
Figure 9.
The retrieved VSP data from ANSI. The red line shows downgoing first arrival, the yellow arrows show downgoing multiples, and the blue arrows are pointing at upgoing waves or reflections.
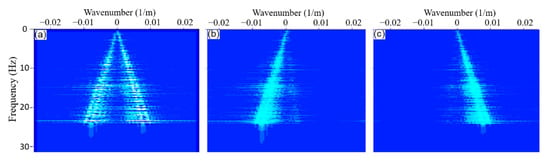
Figure 10.
Separation of the downgoing wavefield and the upgoing wavefield; (a) before frequency-wavenumber filtering, (b) the downgoing wavefield positioned in the positive quadrant, and (c) the upgoing wavefield positioned in the negative quadrant.
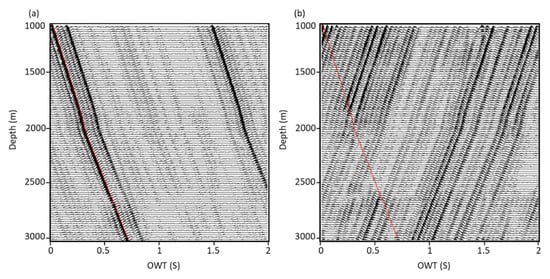
Figure 11.
The separated (a) downgoing and (b) upgoing wavefield. The red line shows the P-wave downgoing primary trend in Figure 9.
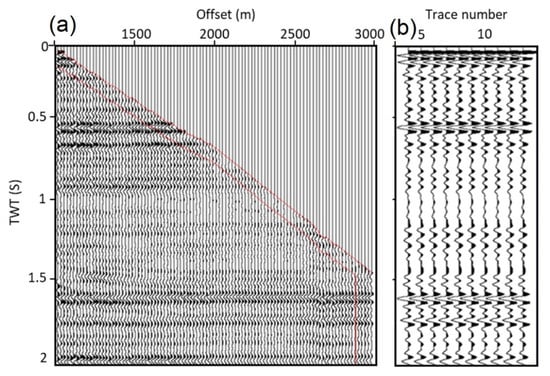
Figure 12.
(a) The flattened upgoing wavefield. The red narrow corridor corresponds to the outside corridor stack, containing 10 traces. The receivers on the VSP in the borehole are starting from 1000 m to 3000 m. (b) The corridor stack that consists of 10 traces corresponding to the red narrow corridor.
3.3. Crosswell Seismic Acquisition Geometry
Crosswell survey, where the source points are location in one borehole and the receiver array is located in a second borehole, can be referred as a special case of the VSP survey (Figure 13). The term crosswell comes from the transverse ray paths that arise when measurements are made between two boreholes. In the ANSI application from the crosswell survey, the sources are positioned at different depths and gradually detonated. This creates a good ray overlap between the drilling holes. With the crosswell measurements, the area between two boreholes can therefore be investigated. Typically, tomographic methods that are used here to evaluate the travel times between the sources are receivers so that the two-dimensional distribution of the propagation velocity can be determined.
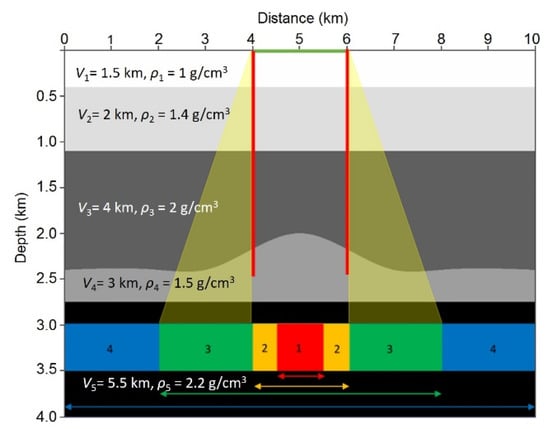
Figure 13.
The geological model used in this study. Noise boundary 1 (red) laterally extends from 4500 to 5500 m; noise boundary 2 (yellow) extends from 3000 to 6000 m; noise boundary 3 (green) extends from 2000 to 8000 m; and noise boundary 4 has the same lateral extent as the model. The yellow triangles show the ideal range for the surface geometry that is between 0° and 33° (between noise boundaries 2 and 3).
In this section, a simple layered model with a buried mound was created with the geometry and parameters shown in Figure 13 with the additional information concerning the representation of the four different noise boundaries. Two wells (vertical red lines) were placed on the flanks of the mound to be used for crosswell data acquisition. The green line in Figure 13 represents the location of a surface array. We adopt noise boundary models proposed by [7]. This model contains 1000-point sources of noise that occur pseudo-randomly in space and time within a specified spatial boundary.
For the crosswell acquisition, the top geophone in the left-side array is selected as the master trace, and cross-correlated will all of the geophones in the right-side array, one at a time, indexing down the virtual well. In this way, a crosswell common-source gather is produced. The geophone selected for the master trace is then indexed one location down in the left side well and used for cross-correlation with all of the geophones in the right side well, indexing down the well. This process continues until every geophone in the left side array was used as a master trace for a virtual shot gather. Although the validity of the process of cross-correlation in a surface setting has been demonstrated in others, the process fails when it is applied to crosswell data.
This can be seen in Figure 14, where the difference gathers are larger amplitude than either the base or repeat surveys themselves, representing essentially no similarity between the two surveys, even though the models were identical. There are no obvious reflectors visible in either the base or repeat surveys, and the differential between them yields a strong and seemingly arbitrary set of events. In this instance, cross-correlation does not stack a coherent image from random points of ambient noise in the subsurface. It has been shown elsewhere that SI can be utilized for a crosswell acquisition for an active source at the surface, but it was postulated that the use of random noise in the subsurface would create too complex a geometrical problem, as the source times and locations are unknown [38].
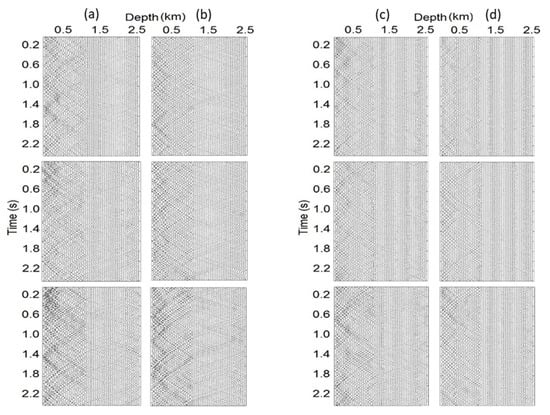
Figure 14.
Virtual shot gathers created from the crosswell survey for noise generated within boundaries 1, 2, 3 and 4, in columns (a–d), respectively. The top images represent base surveys, the middle images repeat surveys, and the bottom images the difference between base and repeat surveys.
The major problem for crosswell applications of SI using buried noise sources appears to result from an inability to stack the reflector information in a coherent way. For example, cross-correlation works well with a surface array geometry because the geophones used for cross-correlation are near to each other and at nearly the same distance from the (distant) noise volume. Therefore, upon cross-correlation, the traces are quite similar to each other, and the reflector responses stack nicely. In the crosswell case, where a geophone at the surface is being cross-correlated with geophones that are very near the noise source, or vice versa, the traces are highly dissimilar. This complicates cross-correlation, which depends on the bulk travel of raypaths being similar from the source to the geophone pair. The response from a given reflector will be significantly different at geophones in different layers in both amplitude and time, thereby making cross-correlation inappropriate.
4. Discussions
We used acoustic modeling to assess different data acquisition scenarios for better retrieval of body waves from ANSI. In general, acoustic modeling can provide some approximate behavior of seismic data in particular for body wave simulations as it is the main theme of the present research. Acoustic modeling can provide reasonable results in the case of short-offset data acquisitions, or in other words, the incident angle of seismic waves is close to the right angle. Therein lies the reason why acoustic modeling for the simulation of body wave data has been used by many researchers, e.g., [4,17,27]. However, in reality, body waves are not simply P-waves but includes S-waves and reflected/transmitted/converted P/S S/P waves. In particular, in long offset P-wave data acquisitions where the incident angles of P-waves vary from 0° to 90°, in addition to the reflected and transmitted P-waves, two converted reflected and transmitted S-waves are generated. Moreover, in the case of surface conditions, we should expect the generation of surface waves, i.e., ground rolls and Love wave. Therefore, a more robust evaluation of different seismic data acquisition scenarios should be achieved via a visco-elastic modeling (considering Vp, Vs, Qp, Qs, and ρ parameters) instead of visco-acoustic modeling, which is incapable of modeling converted or surface waves. Providing that we consider the visco-elastic modeling, we can better evaluate the performance of various data acquisition methods. For instance, in our simulations pertinent to land acquisition below the weathered layer, the visco-elastic modeling will more effectively show the advantage of placing receivers below the weathered layer because the surface ambient noises are mostly dominated by surface waves that dramatically decay with depth (note that in acoustic modeling they are modeled as body waves that are not significantly attenuated with depth). We also should expect that for crosswell seismic acquisition geometry, the visco-elastic modeling will present further disadvantage of this data acquisition configuration for the retrieval of P-wave from ANSI since in this wide-angle data acquisition, a fraction of P-wave energy is converted to S-waves. Therefore, the retrieved P-waves will be much weaker than what we obtained through our acoustic modeling. On the other hand, for the zero-offset VSP acquisition scheme, we do not anticipate a significant difference in acoustic and visco-elastic modeling because of narrow angle (short offset) of data acquisition. In this case, no strong converted P-wave is generated, and therefore, acoustic and visco-elastic modeling will provide the same results.
Furthermore, it is well known that the ambient noise is dominated by surface waves and it should imply a complete wavefield modeling. Incidentally, we did not consider surface waves given the frequency range that we process the data in this study (e.g., 6–24 Hz).
5. Conclusions
We investigated three potential applications of the body wave extraction using seismic interferometry with different acquisition configurations, including:
- (1)
- In a weathered layer: We found when the area is contaminated by ambient noise (e.g., from anthropologic activities, winds, traffics), putting the geophones below the weathered layer can significantly improve the results although surface multiples are generated.
- (2)
- In a borehole crosswell: We created a target (coal layer) zone and tried to determine under which conditions the surface seismic method or zero-offset VSP method can detect the coal layer more successfully by using a few numbers of sources. In addition, VSP can give complementary information to that of surface data acquisition in particular when the geology is complex. In real conditions, noise distribution is not wide (limited), and we would not have many sources, therefore, VSP survey for ANSI is preferred.
- (3)
- In VSP application: We showed that for crosswell data, the application of cross-correlation to seismic traces is an ineffective means to obtain reflection events due to the non-similarity of ray paths from the noise sources to the (virtual) source and receiver locations, and the narrow stationary-phase region for those reflections are insufficiently sampled.
Author Contributions
Investigation, E.A., G.C. and B.W.; writing—original draft preparation, H.C.; editing, K.G.; writing—review and editing, R.A.; supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data can be accessible through the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank to J. Thorbecke for providing his finite-difference wavefield modeling and the Center for Wave Phenomena, Department of Geophysics, Colorado School of Mines for sharing the Seismic Un*x software.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Schuster, G.T.; Yu, J.; Sheng, J.; Rickett, J. Interferometric/daylight seismic imaging. Geophys. J. Int. 2004, 157, 838–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wapenaar, K.; Fokkema, J. Green’s function representations for seismic interferometry. Geophysics 2006, 71, SI33–SI46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claerbout, J.F. Synthesis of a layered medium from its acoustic transmission response. Geophysics 1968, 33, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wapenaar, K. Retrieving the elastodynamic Green’s function of an arbitrary inhomogeneous medium by cross correlation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 254301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wapenaar, K.; van der Neut, J.; Ruigrok, E. Passive seismic interferometry by multidimensional deconvolution. Geophysics 2008, 73, A51–A56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Paap, B.; Verdel, A.; Meekes, S.; Steeghs, P.; Vandeweijer, V.; Neele, F. Four Years of Experience with a Permanent Seismic Monitoring Array at the Ketzin CO2 Storage Pilot Site. Energy Procedia 2014, 63, 4043–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boullenger, B.; Verdel, A.; Paap, B.; Thorbecke, J.; Draganov, D. Studying CO2 storage with ambient-noise seismic interferometry: A combined numerical feasibility study and field-data example for Ketzin, Germany. Geophysics 2015, 80, Q1–Q13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Juhlin, C.; Gudmundsson, O.; Zhang, F.; Yang, C.; Kashubin, A.; Lüth, S. Reconstruction of subsurface structure from ambient seismic noise: An example from Ketzin, Germany. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 189, 1085–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghi, S.; White, D.J.; Draganov, D.; Bellefleur, G.; Craven, J.A.; Roberts, B. Passive seismic reflection interferometry: A case study from the Aquistore CO2 storage site, Saskatchewan, Canada. Geophysics 2017, 82, B79–B93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, R.L.; Lobkis, O.I. Ultrasonics without a source: Thermal fluctuation correlations at MHz frequencies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 134301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snieder, R. Extracting the Green’s function from the correlation of coda waves: A derivation based on stationary phase. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 046610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, N.M.; Campillo, M.; Stehly, L.; Ritzwoller, M.H. High-Resolution Surface-Wave Tomography from Ambient Seismic Noise. Science 2005, 307, 1615–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabra, K.G.; Gerstoft, P.; Roux, P.; Kuperman, W.A.; Fehler, M.C. Surface wave tomography from microseisms in Southern California. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L14311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, N.; Boué, P.; Brenguier, F.; Roux, P.; Ferrazzini, V.; Campillo, M. Body and surface wave reconstruction from seismic noise correlations between arrays at Piton de la Fournaise volcano. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; He, Y.; Du, Y.; Luo, Y. Inversion of vehicle-induced signals based on seismic interferometry and recurrent neural networks. Geophysics 2021, 86, Q37–Q45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.E.; Ku, T. Soil/rock interface profiling using a new passive seismic survey: Autocorrelation seismic interferometry. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 115, 104045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, N.; Snieder, R.; Tsuji, T.; Larner, K.; Matsuoka, T. Shear wave imaging from traffic noise using seismic interferometry by cross-coherence. Geophysics 2011, 76, SA97–SA106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, P.; Sabra, K.G.; Gerstoft, P.; Kuperman, W.A.; Fehler, M.C. P-waves from cross-correlation of seismic noise. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L19303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draganov, D.; Campman, X.; Thorbecke, J.; Verdel, A.; Wapenaar, K. Reflection images from ambient seismic noise. Geophysics 2009, 74, A63–A67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, P.; Campillo, M.; Pedersen, H.; LAPNET Working Group. Body-wave imaging of Earth’s mantle discontinuities from ambient seismic noise. Science 2012, 338, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, K. Global propagation of body waves revealed by cross-correlation analysis of seismic hum. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1691–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panea, I.; Draganov, D.; Vidal, C.A.; Mocanu, V. Retrieval of reflections from ambient noise recorded in the Mizil area, Romania. Geophysics 2014, 79, Q31–Q42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polychronopoulou, K.; Lois, A.; Draganov, D. Body-wave passive seismic interferometry revisited: Mining exploration using the body waves of local microearthquakes. Geophys. Prospect. 2020, 68, 232–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangwal, D.; Behm, M. Interferometric body-wave retrieval from ambient noise after polarization filtering: Application to shallow reflectivity imaging. Geophysics 2021, 86, Q47–Q58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, D.; Curtis, A. Seismic interferometry, surface waves and source distribution. Geophys. J. Int. 2008, 175, 1067–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletto, F.; Farina, B. Synthesis of a seismic virtual reflector. Geophys. Prospect. 2010, 58, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Mikesell, T.D.; Xia, J.; Cheng, F. A comprehensive comparison between the refraction microtremor and seismic interferometry methods for phase-velocity estimation. Geophysics 2017, 82, EN99–EN108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomas, A.; Singh, S.; Curtis, A. Imaging vertical structures using Marchenko methods with vertical seismic-profile data. Geophys. 2020, 85, S103–S113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorbecke, J.; Draganov, D. Finite-difference modeling experiments for seismic interferometry. Geophysics 2011, 76, H1–H18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, I.; Snieder, R. Interferometry by deconvolution: Part 2—Theory for elastic waves and application to drill-bit seismic imaging. Geophysics 2008, 73, S129–S141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snieder, R.; Miyazawa, M.; Slob, E.; Vasconcelos, I.; Wapenaar, K. A Comparison of Strategies for Seismic Interferometry. Surv. Geophys. 2009, 30, 503–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishitsuji, Y.; Rowe, C.A.; Wapenaar, K.; Draganov, D. Reflection imaging of the Moon’s interior using deep-moonquake seismic interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2016, 121, 695–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Askari, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, R.; Guo, R.; Feng, D. Comparison of seismic interferometry techniques for the retrieval of seismic body waves in CO2 sequestration monitoring. J. Geophys. Eng. 2019, 16, 1094–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Green’s function retrieval with Marchenko and inter-source seismic interferometry method for drill-bit seismic while drilling. J. Geophys. Eng. 2018, 15, 2047–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghadeh, D.H.; Bean, C.J.; Brenguier, F.; Smith, P.J. Retrieving reflection arrivals from passive seismic data using Radon correlation. J. Geophys. Eng. 2021, 18, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draganov, D.; Campman, X.; Thorbecke, J.; Verdel, A.; Wapenaar, K. Seismic exploration-scale velocities and structure from ambient seismic noise (>1 Hz). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2013, 118, 4345–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draganov, D.; Wapenaar, K.; Mulder, W.; Singer, J.; Verdel, A. Retrieval of reflections from seismic background-noise measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L04305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minato, S.; Matsuoka, T.; Tsuji, T.; Draganov, D.; Hunziker, J.; Wapenaar, K. Seismic interferometry using multidimensional deconvolution and crosscorrelation for crosswell seismic reflection data without borehole sources. Geophysics 2011, 76, SA19–SA34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).