Evidence of Seismic-Related Liquefaction Processes within the Volcanic Record of the Campi Flegrei Caldera (Italy)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
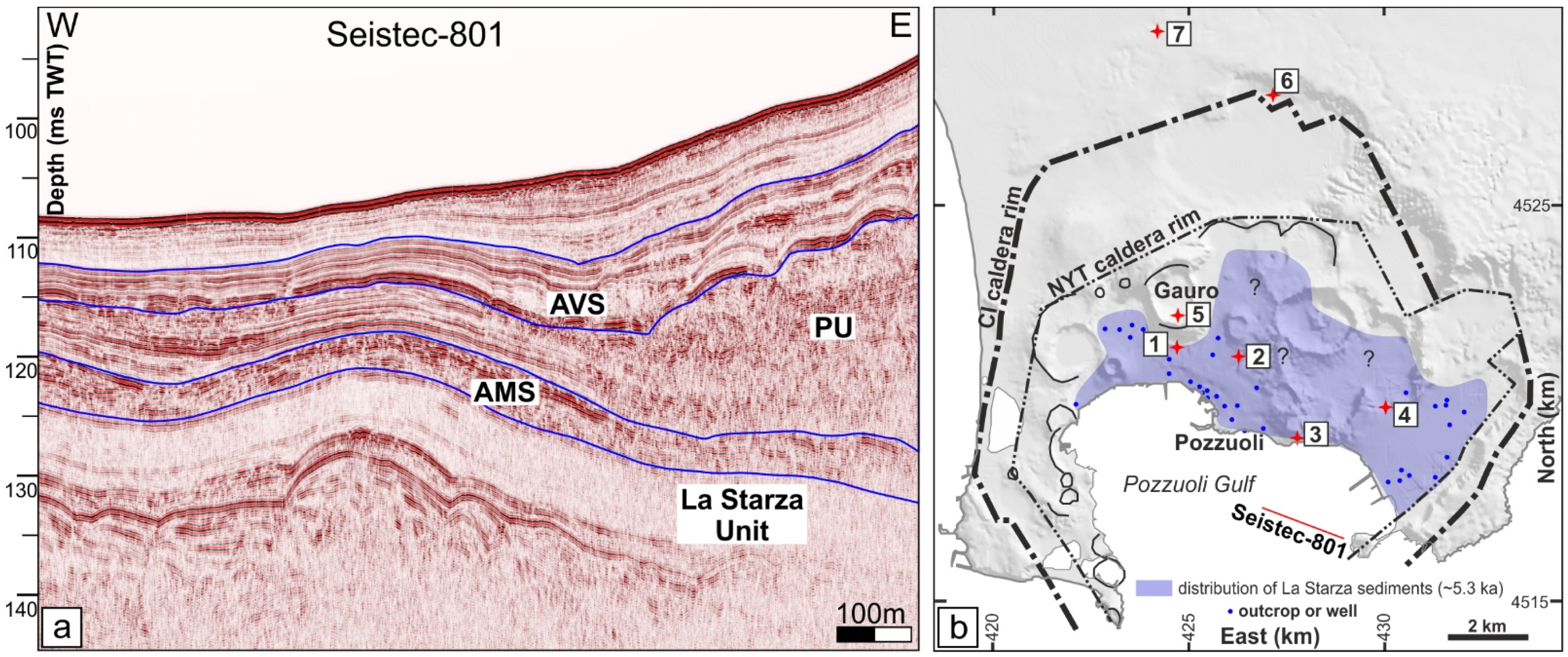
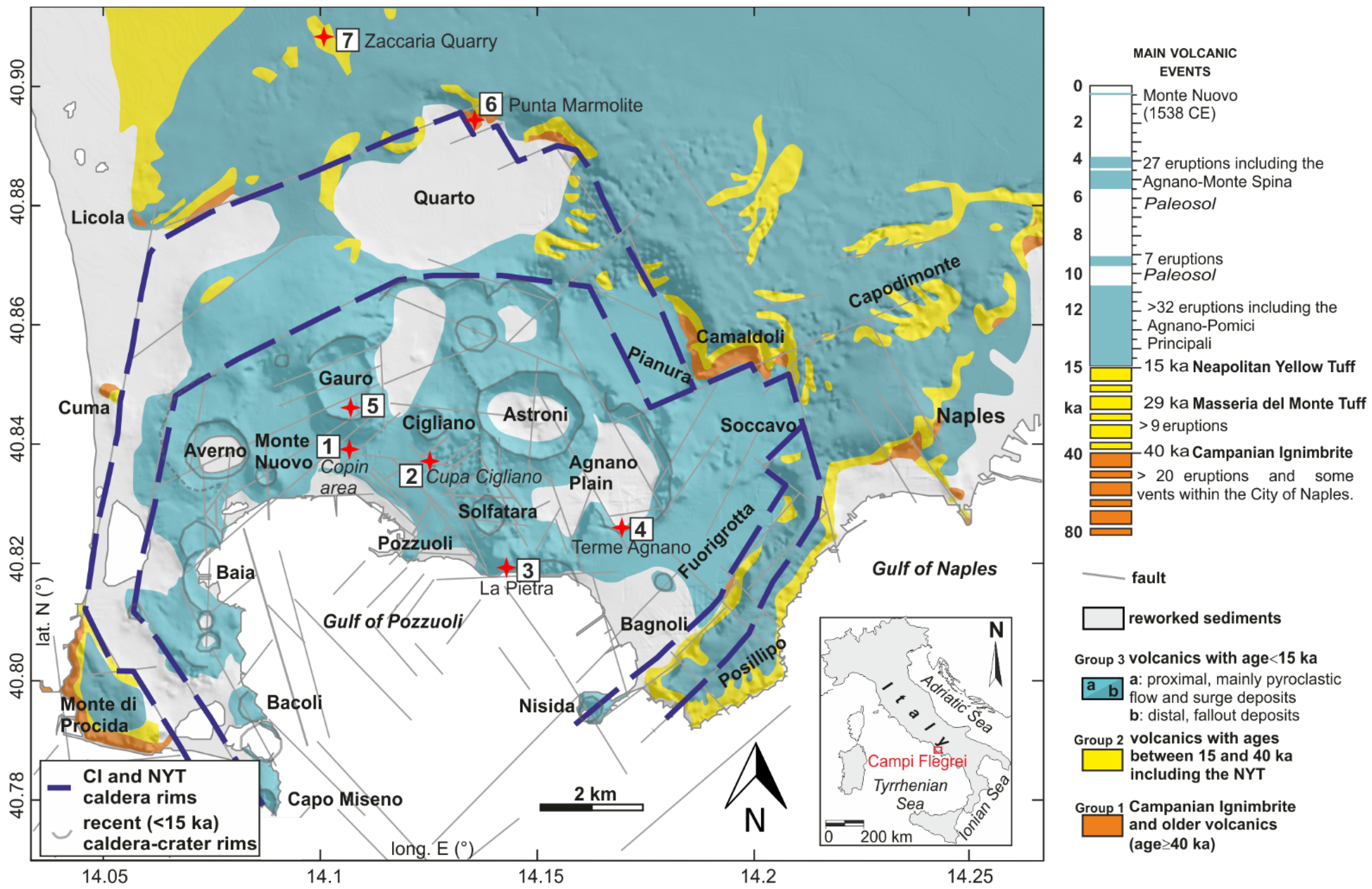
2. Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
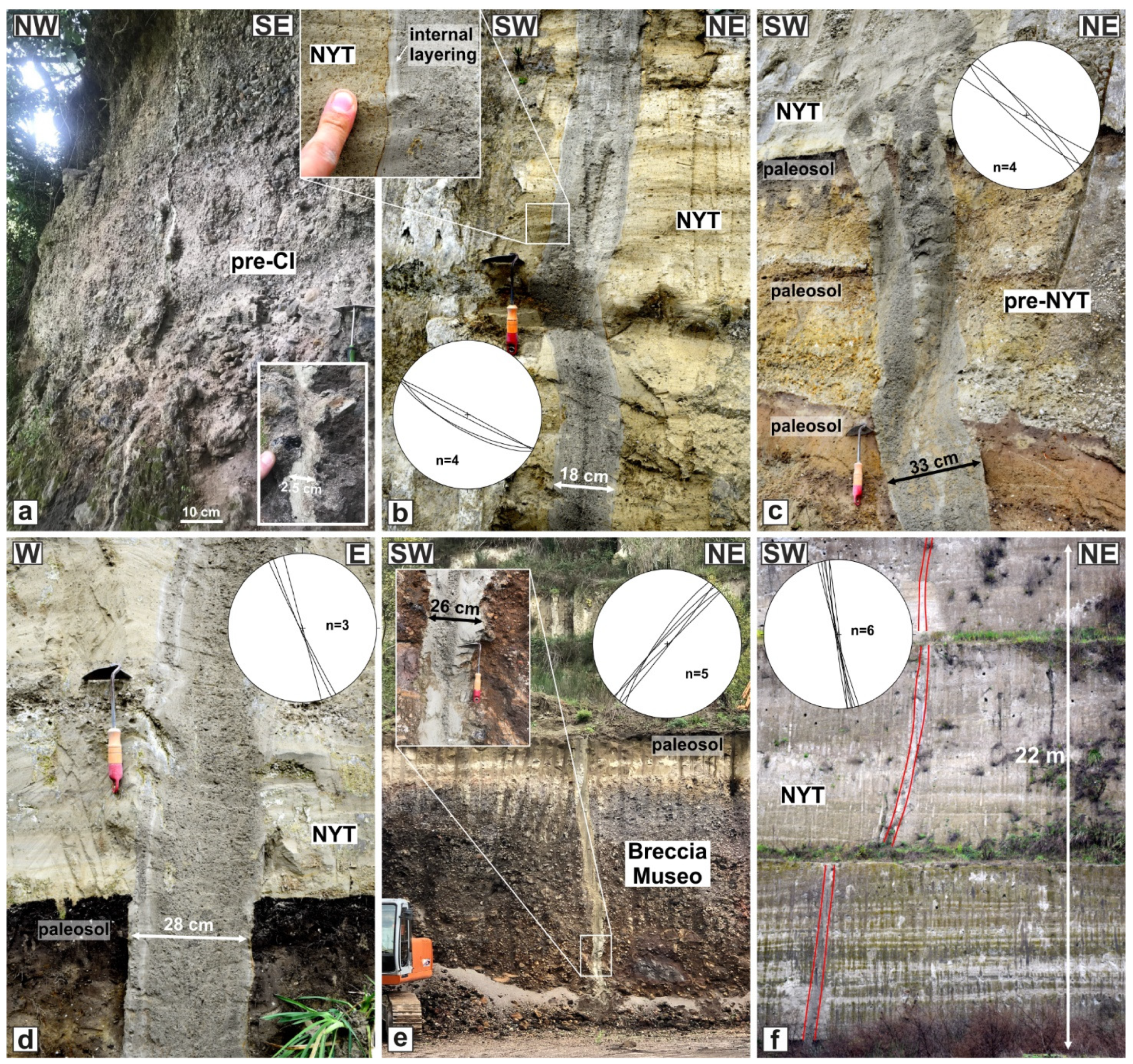
4. Results
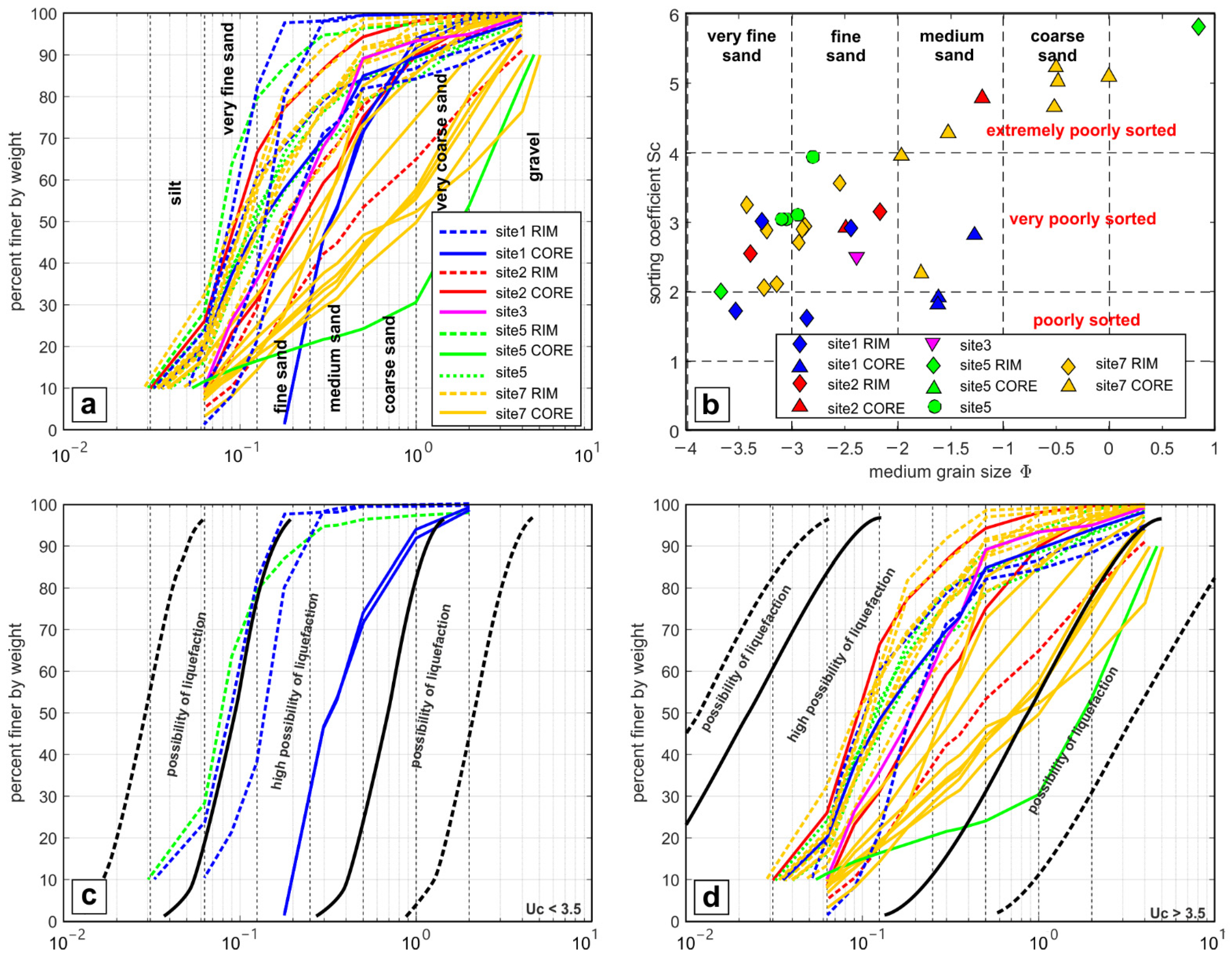
4.1. Grain Size Analysis
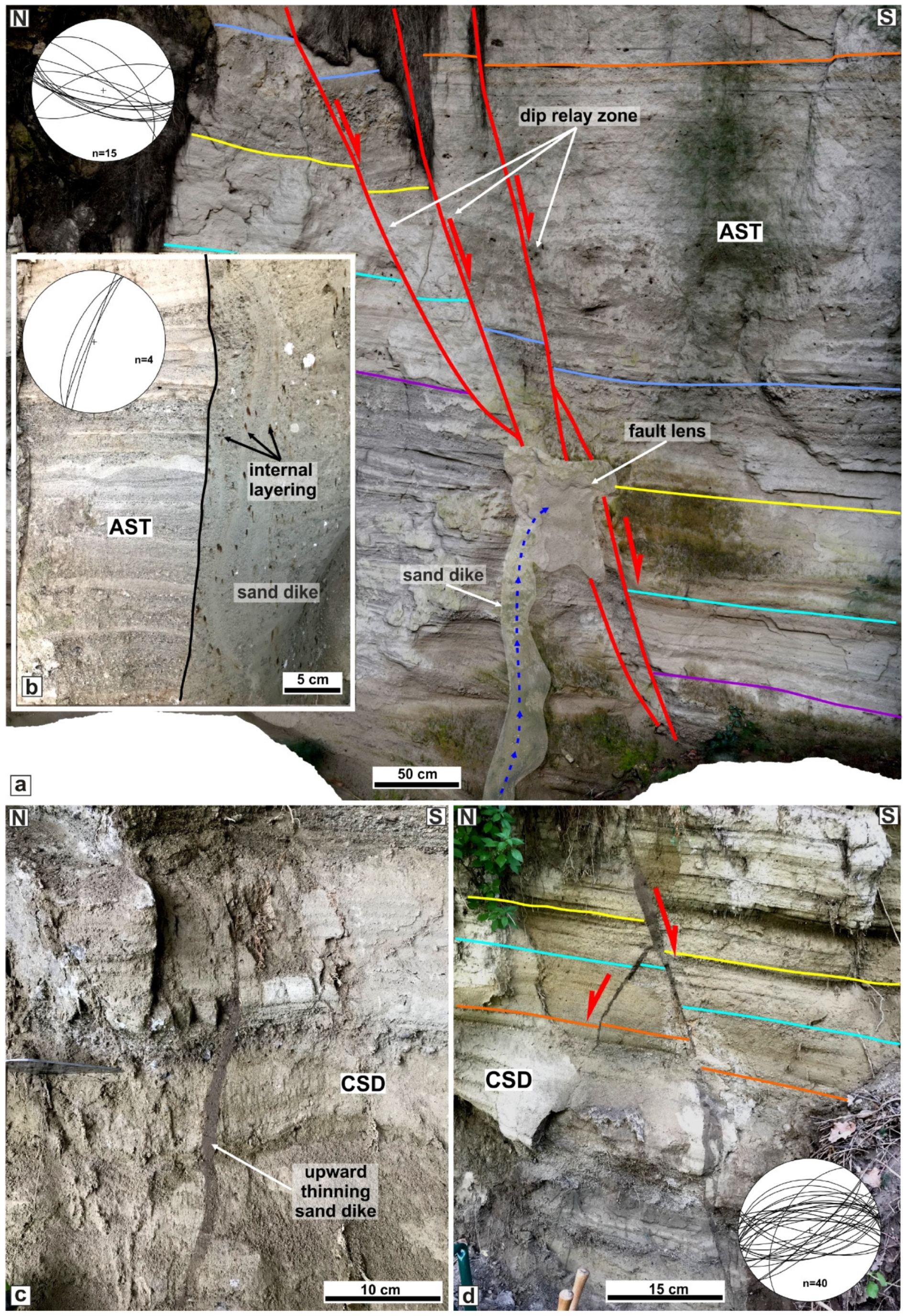
4.2. Structures
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ishihara, K. Liquefaction and Flow Failure during Earthquake. Géotechnique 1993, 43, 351–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yu, M. Review of soil liquefaction characteristics during major earthquakes of the twenty-first century. Nat. Hazards 2013, 65, 2375–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuribayashi, E.; Tatsuoka, F. Brief review of liquefaction during earthquakes in Japan. Soils. Found 1977, 15, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, J.R.L. Sedimentary Structures: Their Character and Physical Basis; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1982; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- Obermeier, S. Use of liquefaction-induced features for paleoseismic analysis—An overview of how seismic liquefaction features can be distinguished from other features and how their regional distribution and properties of source sediment can be used to infer the location and strength of Holocene paleo-earthquakes. Eng. Geol. 1996, 44, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, G. Experimental soft-sediment deformation: Structures formed by the liquefaction of unconsolidated sands and some ancient examples. Sedimentology 1996, 43, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, M.; Barstow, N. Liquefaction-related ground failure: A case study in the New Madrid seismic zone, central United States. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1996, 86, 636–645. [Google Scholar]
- Galli, P. New empirical relationships between magnitude and distance for Liquefaction. Tectonophysics 2000, 324, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenat, C.; Barrier, P.; Ott d’Estevou, P.; Hibsch, C. Seismites: An attempt at critical analysis and classification. Sediment. Geol. 2007, 196, 5–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y. Liquefaction beyond the near field. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2007, 78, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, R.; Poli, M.E.; Minarelli, L.; Rapti, D.; Sboras, S.; Stefani, M.; Zanferrari, A. Palaeoseismological evidence for the 1570 Ferrara earthquake, Italy. Tectonics 2016, 35, 1423–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, M.P.; Villamor, P.; Almond, P.; Bastin, S.; GionaBucci, M.; Langdridge, R.; Clark, K.; Hardwick, C. Liquefaction induced by the 2010–2011 Canterbury, New Zealand, Eartquake Sequence and Lessons Learned for the Study of Paleoliquefaction features. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2017, 88, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, A.; Capilleri, P.P.; Grasso, S. Site Characterization by Dynamic In Situ and Laboratory Tests for Liquefaction Potential Evaluation during Emilia Romagna Earthquake. Geosciences 2018, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, S.; Tsuchida, H.; Koizumi, K. A new criterion for assessing liquefaction potential using grain size accumulation curve and N-value. Rep. Port Harb. Res. Inst. 1986, 25, 125–234. [Google Scholar]
- Kameda, J.; Kamiya, H.; Masumoto, H.; Morisaki, T.; Hiratsuka, T.; Inaoi, C. Fluidized landslides triggered by the liquefaction of subsurface volcanic deposits during the 2018 Iburi–Tobu earthquake, Hokkaido. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogo, K.; Hazarika, H.; Kokusho, T.; Matsumoto, D.; Ishibashi, S.; Sumartini, W.O. Analysis of liquefaction of volcanic soil during the 2016 Kumamoto Earthquake based on boring data. Lowl. Technol. Int. 2018, 19, 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- McNutt, S.R. Seismic Monitoring and Eruption Forecasting of Volcanoes: A Review of the State-of-the-Art and Case Histories. In Monitoring and Mitigation of Volcano Hazards; Scarpa, R., Tilling, R.I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996; pp. 99–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, P.J.D.; Bornas, M.A.V.; Dominey-Howes, D.; Pidlaoan, A.C.; Magill, C.R.; Solidu, R.U., Jr. A synthesis and review of historical eruptions at Taal Volcano, Southern Luzon, Philippines. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 177, 565–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, S.; Isaia, R.; Ciarcia, S.; Di Giuseppe, M.G.; Iannuzzi, E.; Prinzi, E.P.; Tramparulo, F.D.A.; Troiano, A. Seismically induced soft-sediment deformation phenomena during the volcano-tectonic activity of Campi Flegrei caldera (southern Italy) in the last 15 kyr. Tectonics 2019, 38, 1999–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acocella, V. Bridging the gap from caldera unrest to resurgence. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosi, M.; Sbrana, A. Phlegrean fields. Quad. Ric. Sci. 1987, 9, 171. [Google Scholar]
- Deino, A.L.; Orsi, G.; Piochi, M.; de Vita, S. The age of the Neapolitan Yellow Tuff caldera-forming eruption (Campi Flegrei caldera–Italy) assessed by 40Ar/39Ar dating method. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2004, 133, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaccio, B.; Hajdas, I.; Isaia, R.; Deino, A.; Nomade, S. High-Precision 14C and 40Ar/39Ar Dating of the Campanian Ignimbrite (Y-5) Reconciles the Time-Scales of Climatic-Cultural Processes at 40 Kyr BP. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Vito, M.A.; Isaia, R.; Orsi, G.; Southon, J.; de Vita, S.; D’Antonio, M.; Pappalardo, L.; Piochi, M. Volcanism and deformation in the past 12 ka at the Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1999, 91, 221–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, S.; Ciarcia, S. Tectono-stratigraphic setting of the Campania region (Southern Italy). J. Maps 2018, 14, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, S.; Prinzi, E.P.; Tramparulo, F.D.A.; De Paola, C.; Di Maio, R.; Piegari, E.; Sabbatino, M.; Natale, J.; Notaro, P.; Ciarcia, S. Late Miocene-early Pliocene out-of-sequence thrusting in the southern Apennines (Italy). Geosciences 2020, 10, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaia, R.; Vitale, S.; Di Giuseppe, M.G.; Iannuzzi, E.; Tramparulo, F.D.A.; Troiano, A. Stratigraphy, structure, and volcano-tectonic evolution of Solfatara maar-diatreme (Campi Flegrei, Italy). Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2015, 127, 1485–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isaia, R.; Vitale, S.; Marturano, A.; Aiello, G.; Barra, D.; Ciarcia, S.; Iannuzzi, E.; Tramparulo, F.D.A. High-resolution geological investigations to reconstruct the long-term ground movements in the last 15 kyr at Campi Flegrei caldera (southern Italy). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2019, 385, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacroce, R. Somma-Vesuvius. Quad. Ric. Sci. 1987, 8, 230. [Google Scholar]
- Tramparulo, F.D.A.; Vitale, S.; Isaia, R.; Tadini, A.; Bisson, M.; Prinzi, E.P. Relation between alternating open/closed-conduit conditions and deformation patterns: An example from the Somma-Vesuvius volcano (southern Italy). J. Struct. Geol. 2018, 112, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbrana, A.; Marianelli, P.; Pasquini, G. Volcanology of Ischia (Italy). J. Maps 2018, 14, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, L.; Civetta, L.; D’Antonio, M.; Deino, A.; Di Vito, M.; Orsi, G.; Carandente, A.; De Vita, S.; Isaia, R.; Piochi, M. Chemical and Sr-isotopic evolution of the Phlegrean magmatic system before the Campanian Ignimbrite and the Neapolitan Yellow Tuff eruptions. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1999, 91, 141–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpati, C.; Perrotta, A.; Lepore, S.; Calvert, A. Eruptive history of Neapolitan volcanoes: Constraints from 40Ar-39Ar dating. Geol. Mag. 2013, 150, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orsi, G.; De Vita, S.; Di Vito, M. The restless, resurgent Campi Flegrei nested caldera (Italy): Constraints on its evolution andu configuration. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1996, 74, 179–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silleni, A.; Giordano, G.; Isaia, R.; Ort, M.H. The magnitude of the 39.8 ka campanian ignimbrite eruption, Italy: Method, uncertainties and errors. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 543399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acocella, V. Activating and reactivating pairs of nested collapses during caldera-forming eruptions: Campi Flegrei (Italy). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L17304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, S.; Isaia, R. Fractures and faults in volcanic rocks (Campi Flegrei, southern Italy): Insight into volcano-tectonic processes. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2014, 103, 801–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosino, P.; Arienzo, I.; Mazzeo, F.C.; Natale, J.; Petrelli, M.; Milia, A.; Perugini, D.; D′Antonio, M. The San Gregorio Magno lacustrine basin (Campania, southern Italy): Improved characterization of the tephrostratigraphic markers based on trace elements and isotopic data. J. Quat. Sci. 2019, 34, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi, G.; Civetta, L.; Del Gaudio, C.; De Vita, S.; Di Vito, M.A.; Isaia, R.; Petrazzuoli, S.M.; Ricciardi, G.P.; Ricco, C. Short-term ground deformations and seismicity in the nested Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1999, 91, 415–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, A.; Isaia, R.; Neri, A.; Vitale, S.; Aspinall, W.P.; Bisson, M.; Bisson, M.; Flandoli, F.; Baxter, P.J.; Bertagnini, A.; et al. Quantifying volcanic hazard at Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy) with uncertainty assessment: I. Vent opening maps. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth 2015, 120, 2309–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bevilacqua, A.; Neri, A.; Bisson, M.; Esposti Ongaro, T.; Flandoli, F.; Isaia, R.; Rosi, M.; Vitale, S. The effects of vent location, event scale and time forecasts on pyroclastic density current hazard maps at Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy). Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 5, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.C.; Isaia, R.; Pearce, N.J.C. Tephrostratigraphy and glass compositions of post-15 kyr Campi Flegrei eruptions: Implications for eruption history and chronostratigraphic markers. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2011, 30, 3638–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, A.; Flandoli, F.; Neri, A.; Isaia, R.; Vitale, S. Temporal models for the episodic volcanism of Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy) with uncertainty quantification. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth 2016, 121, 7821–7845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaia, R.; Marianelli, P.; Sbrana, A. Caldera unrest prior to intense volcanism in Campi Flegrei (Italy) at 4.0 ka B.P.: Implications for caldera dynamics and future eruptive scenarios. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L21303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, A.; Neri, A.; De Martino, P.; Isaia, R.; Novellino, A.; Tramparulo, F.D.A.; Vitale, S. Radial interpolation of GPS and leveling data of ground deformation in a resurgent caldera: Application to Campi Flegrei (Italy). J. Geod. 2020, 94, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sacchi, M.; Caccavale, M.; Corradino, M.; Esposito, G.; Ferranti, L.; Hámori, Z.; Horvath, F.; Insinga, D.; Marino, C.; Matano, F.; et al. The use and beauty of ultra-high-Resolution seismic reflection imaging in Late Quaternary marine volcaniclastic settings, Napoli Bay, Italy. Földt. Közlöny 2019, 149, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Natale, J.; Ferranti, L.; Isaia, R.; Marino, C.; Sacchi, M.; Spiess, V.; Steinmann, L.; Vitale, S. Integrated on-land-offshore stratigraphy of the Campi Flegrei caldera: New insights into the volcano-tectonic evolution in the last 15 kyr. Basin Res. 2022, 34, 855–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, J.; Ferranti, L.; Marino, C.; Sacchi, M. Resurgent dome faults in the offshore of the Campi Flegrei caldera (Pozzuoli Bay, Campania): Preliminary results from high-resolution seismic reflection profiles. Boll. Geofis. Teor. Ed. Appl. 2020, 61, 333–342. [Google Scholar]
- Lambeck, K.; Antonioli, F.; Anzidei, M.; Ferranti, L.; Leoni, G.; Scicchitano, G.; Silenzi, S. Sea level change along the Italian coast during the Holocene and projections for the future. Quat. Int. 2011, 232, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidoboni, E.; Ciuccarelli, C. The Campi Flegrei caldera: Historical revision and new data on seismic crises, bradyseisms, the Monte Nuovo eruption and ensuing earthquakes (twelfth century 1582 ad). Bull. Volcanol. 2011, 73, 655–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INGV. Monitoring Bullettin. 2022. Available online: https://www.ov.ingv.it (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Troiano, A.; Isaia, R.; Di Giuseppe, M.G.; Tramparulo, F.D.A.; Vitale, S. Deep Electrical Resistivity Tomography for a 3D picture of the most active sector of Campi Flegrei caldera. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamburello, G.; Caliro, S.; Chiodini, G.; De Martino, P.; Avino, R.; Minopoli, C.; Carandente, A.; Rouwet, D.; Aiuppa, A.; Costa, A.; et al. Escalating CO2 degassing at the Pisciarelli fumarolic system, and implications for the ongoing Campi Flegrei unrest. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2019, 384, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaia, R.; Di Giuseppe, M.G.; Natale, J.; Troiano, A.; Tramparulo, F.D.A.; Vitale, S. Volcano-tectonic setting of the Pisciarelli Fumarole Field, Campi Flegrei caldera, southern Italy: Insights into fluid circulation patterns and hazard scenarios. Tectonics 2021, 40, e2020TC006227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.L.; Ward, W.C. Brazos River bar, a study in the significance of grain size parameters. J. Sediment. Petrol. 1957, 27, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, T.C.; McPherson, J.G. Grain-size and textural classification of coarse sedimentary particles. J. Sediment. Res. 1999, 69, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaia, R.; D’Antonio, M.; Dell’Erba, F.; Di Vito, M.; Orsi, G. The Astroni volcano: The only example of closely spaced eruptions in the same vent area during the recent history of the Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2004, 133, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camanni, G.; Roche, V.; Childs, C.; Manzocchi, T.; Walsh, J.; Conneally, J.; Delogkos, E. The three-dimensional geometry of relay zones within segmented normal faults. J. Struct. Geol. 2019, 129, 103895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Pascua, M.A.; Silva, P.G.; Perez-Lopez, R.; Giner-Robles, J.L.; Martín-Gonzalez, F.; Del Moral, B. Polygenetic sand volcanoes: On the features of liquefaction processes generated by a single event (2012 Emilia Romagna 5.9 Mw earthquake, Italy). Quat. Int. 2015, 357, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vita, S.; Orsi, G.; Civetta, L.; Carandente, A.; D’Antonio, M.; Deino, A.; di Cesare, T.; Di Vito, M.A.; Fisher, R.V.; Isaia, R.; et al. The Agnano-Monte Spina eruption (4100 years BP) in the restless Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1999, 91, 269–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, S.F.; Youd, T.L. Empirical Analysis of Horizontal Ground Displacement Generated by Liquefaction-Induced Lateral Spread. Ph.D. Dissertation, Brigham Young University, Provo, UT, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Araujo, W.; Ledezma, C. Factors That Affect Liquefaction-Induced Lateral Spreading in Large Subduction Earthquakes. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, S.; Manzella, I.; Cole, P.; Roverato, M. Grain size distribution and sedimentology in volcanic mass-wasting flows: Implications for propagation and mobility. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2020, 109, 2679–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Pascua, M.A.; Garduño-Monroy, V.H.; Israde-Alcantara, I.; Perez-Lopez, R. Estimation of the paleoepicentral area from the spatial gradient of deformationin lacustrine seismites (Tierras Blancas Basin, Mexico). Quat. Int. 2010, 219, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, D.; Amoroso, S.; Minarelli, L.; Stefani, M. Sand liquefaction induced by a blast test: New insights on source layer and grainsize segregation mechanisms (late Quaternary, Emilia, Italy). J. Sediment. Res. 2019, 89, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diggs, T.N. An outcrop study of clastic injection structures in the Carboniferous Tesnus Formation, Marathon Basin, Trans-Pecos Texas. In Sand Injectites: Implications for Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production; Hurst, A., Cartwright, J., Eds.; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2007; Volume 87, pp. 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, J.A.; Peakall, J.; Keevil, G.M. An integrated model of extrusive sand injectites in cohesionless sediments. Sedimentology 2011, 58, 1693–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vitale, S.; Natale, J.; Isaia, R.; Tramparulo, F.D.; Ciarcia, S. Evidence of Seismic-Related Liquefaction Processes within the Volcanic Record of the Campi Flegrei Caldera (Italy). Geosciences 2022, 12, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12060241
Vitale S, Natale J, Isaia R, Tramparulo FD, Ciarcia S. Evidence of Seismic-Related Liquefaction Processes within the Volcanic Record of the Campi Flegrei Caldera (Italy). Geosciences. 2022; 12(6):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12060241
Chicago/Turabian StyleVitale, Stefano, Jacopo Natale, Roberto Isaia, Francesco D’Assisi Tramparulo, and Sabatino Ciarcia. 2022. "Evidence of Seismic-Related Liquefaction Processes within the Volcanic Record of the Campi Flegrei Caldera (Italy)" Geosciences 12, no. 6: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12060241
APA StyleVitale, S., Natale, J., Isaia, R., Tramparulo, F. D., & Ciarcia, S. (2022). Evidence of Seismic-Related Liquefaction Processes within the Volcanic Record of the Campi Flegrei Caldera (Italy). Geosciences, 12(6), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12060241