Statistical Analysis of Heavy Rains and Floods around the French Mediterranean Basin over One Half a Century of Observations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area, Data and Method
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Data of Mediterranean Episodes (1968–2020)
- Class (100–200 mm), class (200–300 mm), class (>300 mm)/24 h
- Class (300–400 mm), class > 400 mm/48 h
2.2.2. Data of Rainfall and Temperature (1973–2020)
2.2.3. Data of Flood
2.2.4. Other Data
- -
- The North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) data are obtained as a monthly time-series from: https://climexp.knmi.nl/selectdailyindex.cgi?id=someone@somewhere (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- -
- The Mediterranean Oscillation Indices (WeMOi), obtained from the normalized pressure difference between Padua and Cadiz, monthly. The monthly time-series are obtained from: https://crudata.uea.ac.uk/cru/data/moi/Web_WeMOi-2020.txt (accessed on 22 March 2022)
- -
- SST data (for the Mediterranean Sea) (time series of sea surface temperature anomalies) (°C), referring to the mean temperature between 1981 and 2010, in each of the European seas and in the Planetary Ocean). Data sources: SST data sets from Met Office (HadISST1, HadSST.4.0.0.0 și OSTIA), US National Ocean and Atmosphere Administration (ERSSTv5), ESA SST CCI analysis version 2.1. https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/figures/decadal-average-sea-surface-temperature-3/ (accessed on 22 March 2022).
3. Methodological Approach
- -
- To study the spatial distribution and the evolution of Mediterranean episodes, we use an observation frequency analysis.
- -
- The analysis of correlation between the index of climate “NOA”, “WMOI”, the temperature of the Mediterranean sea “SSTMED” and rainfall signal was computed by the coherence diagram (WCO) for different modes of variability.
4. Results
- -
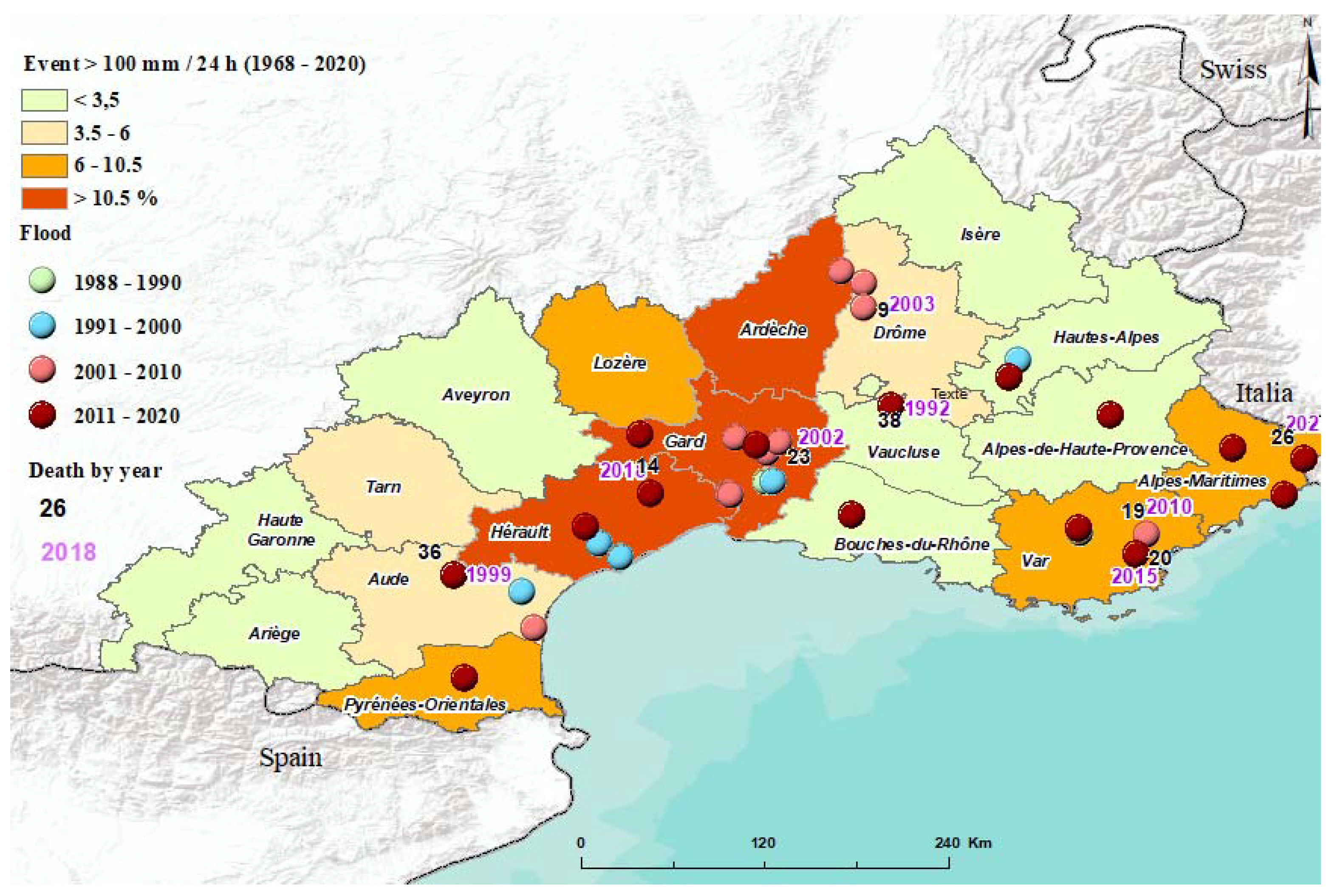
- Spatio-temporal variability of Mediterranean episodes
- -
- The largest number of deaths are recorded in the last decade (104 deaths in 2011–2020) (Table 1).
- -
- The largest number of episodes of heavy and torrential rains are to be observed in the same decade (14 episodes of heavy rains and 4 of torrential rains) (this proves what we have previously mentioned regarding the increase in extreme phenomena associated with climate changes).
- -
- Mediterranean episode trends in the 18 departments (1968–2018)
5. Discussion
5.1. The Link between the Increase of Intense Events and Global Warming
5.2. The Link with Regional Patterns of Climate Variability
5.2.1. Link with NAO
5.2.2. The Link with the Local Atmospheric Circulation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Météo—France. 2019. Available online: https://pluiesextremes.meteo.fr/ (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Boe, J. Changement Global et Cycle Hydrologique: Une Étude de Régionalisation sur la France. Ph.D. Thesis, Centre Européen de Recherche et de Formation Avancée en Calcul Scientifique (CERFACS), Université Paul Sabatier-Toulouse III, Toulouse, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Neppel, L.; Pujol, N.; Sabatier, R. A multivariate regional test for detection of trends in extreme rainfall: The case of extreme daily rainfall in the French Mediterranean area. Adv. Geosci. 2010, 23, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cantet, P.; Bacro, J.-N.; Arnaud, P. Using a rainfall stochastic generator to detect trends in extreme rainfall. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2011, 25, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, M.; Knutti, R.; Arblaster, J.; Dufresne, J.-L.; Fichefet, T.; Friedlingstein, P.; Gao, X.; Gutowski, W.J.; Johns, T.; Krinner, G.; et al. Long-term climate change: Projections, commitments and irreversibility. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Daligaux, J.; Paul Minvielle Stéphane Angles, S. Paysages de l’agriculture littorale dans le Var. Méditerranée Rev. Géographique Des Pays Méditerranéens/J. Mediterr. Geogr. 2013, 120, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubeyroux, J.M.; Neppel, L.; Veysseire, J.M.; Tramblay, Y.; Carreau, J.; Gouget, V. Evolution des précipitations extrêmes en France en contexte de changement climatique. La Houille Blanche 2015, 2015, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöschl, G.; Hall, J.; Parajka JRui, A.P. Changing climate shifts timing of European floods. Science 2017, 357, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groisman, P.Y.; Knight, R.W.; Zolina, O.G. Recent trends in regional and global intense precipitation patterns. Clim. Vulnerability 2013, 5, 25–55. [Google Scholar]
- Harader, E. L’impact du Changement Climatique sur les Événements Hydrologiques Extrêmes des Petits Bassins Versants Méditerranéens: Le Cas du Bassin Versant du Lez. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Toulouse, Université Toulouse III-Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ribes, A.; Thao, S.; Vautard, R.; Dubuisson, B.; Somot, S.; Colin, J.; Planton, S.; Soubeyroux, J.-M. Observed increase in extreme daily rainfall in the French Mediterranean. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 521, 1095–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramblay, Y.; Somot, S. Future evolution of extreme precipitation in the Mediterranean. Clim. Change 2018, 1512, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Zhang, X.; Adnan, M.; Badi, W.; Dereczynski, C.; di Luca, A.; Ghosh, S.; Iskandar, I.; Kossin, J.; Lewis, S.; et al. Weather and Climate Extreme Events in a Changing Climate. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1513–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, S.; Alexandridis, V.; Theodoridou, T. Flood Exposure of Residential Areas and Infrastructure in Greece. Hydrology 2022, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Y. Flood exposure of critical infrastructures in the United States. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 39, 101240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiki, K.; Finance, O. Exposition et Vulnérabilité Sociale des Villes Françaises au Risque Inondation: Une Analyse Spatiotemporelle à Fine Échelle (1999–2017). Cybergeo Eur. J. Geogr. 2022. Available online: https://journals.openedition.org/cybergeo/39179 (accessed on 3 March 2022). [CrossRef]
- Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED). CRED Crunch 66-Disasters Year in Review. 2021. Available online: https://cred.be/sites/default/files/CREDCrunch66N.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Petrucci, O.; Papagiannaki, K.; Aceto, L.; Boissier, L.; Kotroni, V.; Grimalt, M.; Llasat, M.; Llasat-Botija, M.; Rosselló, J.; Pasqua, A.; et al. MEFF: The database of MEditerranean flood fatalities (1980 to 2015). J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 122, e12461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papagiannaki, K.; Petrucci, O.; Diakakis, M.; Kotroni, V.; Aceto, L.; Bianchi, C.; Brázdil, R.; Gelabert, M.G.; Inbar, M.; Kahraman, A.; et al. Développer un ensemble de données à grande échelle sur les décès dus aux inondations pour les territoires de la région euro-méditerranéenne, FFEM-DB. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, L.; Zhang, X.; Peterson, T.C.; Caesar, J.; Gleason, B.; Tank, A.M.G.K.; Haylock, M.; Collins, D.; Trewin, B.; Rahimzadeh, F.; et al. Global observed changes in daily climate extremes of temperature and precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D05109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dieppois, B.; Durand, A.; Fournier, M.; Diedhiou, A.; Fontaine, B.; Masssei, N.; Nouaceur, Z.; Sebag, D. Low-frequency variability and zonal contrast in Sahel rainfall and Atlantic sea surface temperature teleconnections during the last century. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 121, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouacer, Z.; Murarescu, O. Rainfall Variability and Trend Analysis of Annual Rainfall in North Africa. Int. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 2016, 7230450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouaceur, Z. La reprise des pluies et la recrudescence des inondations en Afrique de l’Ouest sahélienne. Physio-Géo. Géographie Phys. Environ. 2020, 15, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nouaceur, Z.; Laignel, B.; Turki, I. Changements climatiques au Maghreb: Vers des conditions plus humides et plus chaudes sur le littoral algérien? PhysioGéo 2013, 7, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, B.; Roucou, P.; Camara, M.; Vigaud, N.; Konare, A.; Sanda, S.; Diedhiou, A.; Janicot, S. Variabilité pluviométrique, changement climatique et régionalisation en région de mousson africaine. Météorologie 2012, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Criado-Aldeanueva, F.; Soto-Navarro, F.J. The Mediterranean Oscillation Teleconnection Index: Station-Based versus Principal Component Paradigms. Adv. Meteorol. 2013, 2013, 738501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougrededoit, A. Le climat du basin méditerranéen. In Le Climat, l’eau et les Hommes, Ouvrages en l’honneur de Jean Mounier; Presses Universitaires de Rennes: Rennes, France, 1997; pp. 251–280. [Google Scholar]
- Xoplaki, E. Climate Variability over the Mediterranean. Ph.D. Thesis, Diss. Naturwiss. Bern. Literaturverz, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Boudevillain, B.; Argence, S.; Claud, C.; Ducrocq, V.; Joly, B.; Joly, A.; Lambert, D.; Nuissier, O.; Plu, M.; Ricard, D.; et al. Cyclogenèses et précipitations intenses en région méditerranéenne: Origines et caractéristiques Projet? Météorologie 2009, 8, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joly, D.; Brossard, T.; Cardot, H.; Cavailhes, J.; Hilal, M.; Wavresky, P. Les types de climats en France, une construction spatiale. Cybergeo Eur. J. Geogr. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelièvre, F.; Sala, S.; Ruget, F.; Volaire, F. Evolution Climatique du Sud de la France 1950–2009, Projet CLIMFOUREL PSDR-3, Régions L-R, M-P, R-A. Série Les Focus PSDR3; 2011; Available online: https://studylibfr.com/doc/8236342/evolution-du-climat-du-sud-de-la-france-1950-2009 (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Quezel, P. La région méditerranéenne française et ses essences forestières. Signification écologique dans le contexte circum-méditerranéen, forêts méditerranéenne. Méditerranéenne 1979, 1, 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, A. Analyse spatio-temporelle de la variabilité hydrologique du bassin versant du Mississippi: Rôles des fluctuations climatiques et déduction de l’impact des modifications du milieu physique. In Thèse de Géologie–Hydrologie; Université de Rouen: Rouen, France, 2010; p. 329. [Google Scholar]
- Zamrane, Z. Recherche d’indices de variabilité climatique dans des séries hydroclmatiques au Maroc: Identification. positionnement temporel. tendances et liens avec les fluctuations climatiques: Cas des grands bassins de la Moulouya. du Sebou et du Tensift. In Sciences de la Terre; Université Montpellier: Montpellier, France, 2016; p. 197. [Google Scholar]
- Zamrane, Z.; Mahé, G.; Laftouhi, N.-E. Wavelet Analysis of Rainfall and Runoff Multidecadal Time Series on Large River Basins in Western North Africa. Water 2021, 13, 3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labat, D. Recent Advances in Wavelet Analyses: Part 1. A Review of Concepts. J. Hydrol. 2005, 314, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraun, D. What Can We Learn from Climate Data? Methods for Fluctuation. Time/Scale and Phase Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Potsdam, Potsdam, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Maraun, D.; Kurths, J. Cross wavelet analysis: Significance testing and pitfalls. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2004, 11, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, A.; Morlet, J. Decomposition of Hardy Functions into Square Integrable Wavelets of Constant Shape. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 1984, 15, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacob, D.; Petersen, J.; Eggert, B.; Alias, A.; Christensen, O.B.; Bouwer, L.M.; Braun, A.; Colette, A.; Déqué, M.; Georgievski, G. EURO-CORDEX: New high-resolution climate change projections for European impact research. Reg. Environ. Change 2014, 14, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenot, O.; Bouin, M.-N.; Ducrocq, V.; Brossier, C.L.; Nuissier, O.; Pianezze, J.; Duffourg, F. Influence of the sea state on Mediterranean heavy precipitation: A case-study from HyMeX SOP1. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowell David, P. The Impact of Mediterranean SSTs on the Sahelian Rainfall Season. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrille, P.; Lafore, J.P. An idealized two-dimensional framework to study the West African monsoon. Part II: Large-scale advection and the diurnal cycle. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 64, 2783–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somot, S.; Sevault, F.; Déqué, M.; Crépon, M. 21st century climate change scenario for the Mediterranean using a coupled atmosphere–ocean regional climate model. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 63, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kharin, V.; Zwiers, F.; Zhang, X.; Wehner, M. Changes in temperature and precipitation extremes in the CMIP5 ensemble. Clim. Change 2013, 119, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman, P.A. Precipitation extremes under climate change. Curr. Clim. Change Rep. 2015, 1, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madakumbura, G.D.; Thackeray, C.W.; Norris, J.; Goldenson, N.; Hall, A. Anthropogenic influence on extreme precipitation over global land areas seen in multiple observational datasets. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folland, C.; Palmer, T.; Parker, D. Sahel rainfall and worldwide sea temperatures, 1901–1985. Nature 1986, 320, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, A.; Saravanan, R.; Chang, P. Oceanic forcing of Sahel rainfall on interannual to interdecadal time scales. Sciente 2003, 302, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Held, I.M.; Delworth, T.L.; Lu, J.; Findell, K.L.; Knutson, T.R. Simulation of Sahel drought in the 20th and 21st centuries. PNAS 2005, 102, 17891–17896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biasutti, M.; Gianini, A. Robust Sahel drying in response to late 20th century forcings. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caminade, C.; Terray, L. Twentieth Century Sahel Rainfall Variability as Simulated by the ARPEGE AGCM, and Future Changes. Clim. Dyn. 2010, 35, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasutti, M. Forced Sahel rainfall trends in the CMIP5 archive. JGR Atmos. 2013, 111, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Delworth Thomas, L. Impact of Atlantic multidecadal oscillations on India/Sahel rainfall and Atlantic hurricanes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L17712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin-Vide, J.; Lopez-Bustins, J.A. The Western Mediterranean Oscillation and Iberian Peninsula Rainfall. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 1455–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, C. Statistical Disclosure Risk: Separating Potential and Harm. Int. Stat. Rev. 2012, 80, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, M.; Giuffrida, A.; Tedesco, S. The Mediterranean Oscillation, impact on precipitation and hydrology in Italy. In Conference on Climate Water; Publications of the Academy of Finland: Helsinki, Finland, 1989; pp. 121–137. [Google Scholar]
- Törnros, T. On the relationship between the Mediterranean Oscillation and winter precipitation in the Southern Levant. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2013, 14, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakalli, A. Sea surface temperature change in the mediterranean sea under climate change: A linear model for simulation of the sea surface temperature up to 2100. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2017, 15, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, R.; Arakawa, O.; Ose, T.; Kusunoki, S.; Endo, H.; Kitoh, A. Classification of CMIP5 future climate responses by the tropical sea surface temperature changes. SOLA 2014, 10, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pastor, F.; Valiente, J.A.; Estrela, M.J. Sea surface temperature and torrential rains in the Valencia region: Modelling the role of recharge areas. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 1677–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pastor, F.; Valiente, J.A.; Palau, J.L. Sea Surface Temperature in the Mediterranean: Trends and Spatial Patterns (1982–2016)Pure Appl. Geophys. 2018, 175, 4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Period | Number of Floods | Deaths | Number of Episodes Heavy Rain | Number of Torrential Rain Events |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011–2020 | 16 | 104 | 14 | 4 |
| 2001–2010 | 10 | 62 | 7 | 3 |
| 1991–2000 | 6 | 87 | 5 | 1 |
| Total | 32 | 253 | 20 | 8 |
| Decade | T | Tx | Tn | Decade | T difference | Tx Difference | Tn Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 15.79 | 21.64 | 9.97 | A-B | 0.50 | 0.82 | 0.20 |
| B | 15.29 | 20.82 | 9.76 | B-C | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| C | 15.28 | 20.80 | 9.76 | C-D | 0.62 | 0.82 | 0.42 |
| D | 14.66 | 19.98 | 9.34 |
| Period | TX | NAO | WMOI | SSTMED |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period before 1991 | Ten-year and multi-decennial 8–12 and 12–16 years | Interannual scale 4–8 years | Decadal and multi-decadal scale 16–24 and 16–32 years | |
| Period 1991–2000 | connection | Interannual scale 2–4 years and 4–8 years | Interannual and ten-year 2–4 years and 8–16 years | Interannual scale 1.5 to 3 years |
| Period 2011–2020 | Evidence connection | Ten-year scale 10–16 years | Decadal and multi-decadal scale 8–16 and 16–24 years | Interannual scale 1.5 to 3 years |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nouaceur, Z.; Murarescu, O.; Muratoreanu, G. Statistical Analysis of Heavy Rains and Floods around the French Mediterranean Basin over One Half a Century of Observations. Geosciences 2022, 12, 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12120447
Nouaceur Z, Murarescu O, Muratoreanu G. Statistical Analysis of Heavy Rains and Floods around the French Mediterranean Basin over One Half a Century of Observations. Geosciences. 2022; 12(12):447. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12120447
Chicago/Turabian StyleNouaceur, Zeineddine, Ovidiu Murarescu, and George Muratoreanu. 2022. "Statistical Analysis of Heavy Rains and Floods around the French Mediterranean Basin over One Half a Century of Observations" Geosciences 12, no. 12: 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12120447
APA StyleNouaceur, Z., Murarescu, O., & Muratoreanu, G. (2022). Statistical Analysis of Heavy Rains and Floods around the French Mediterranean Basin over One Half a Century of Observations. Geosciences, 12(12), 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12120447









