Understanding the Dynamics of a Coastal Lagoon: Drivers, Exchanges, State of the Environment, Consequences and Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
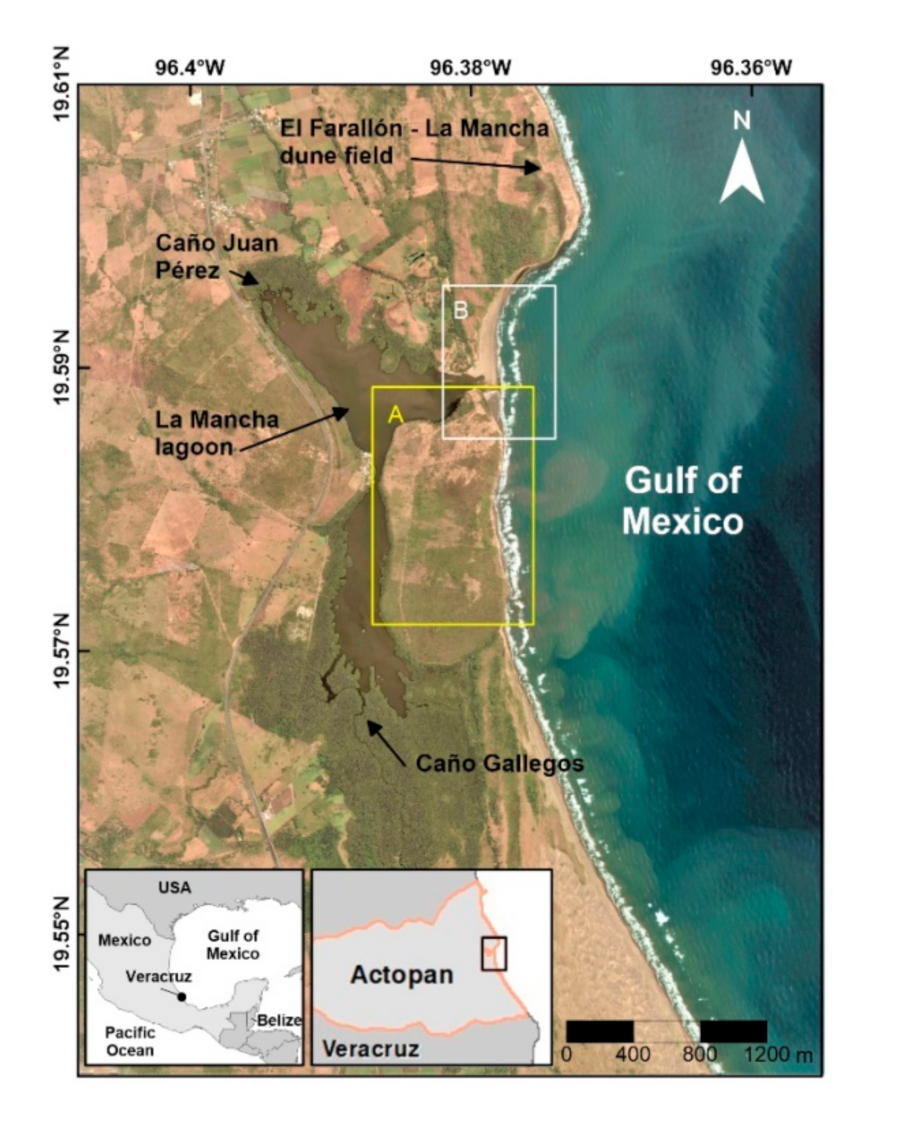
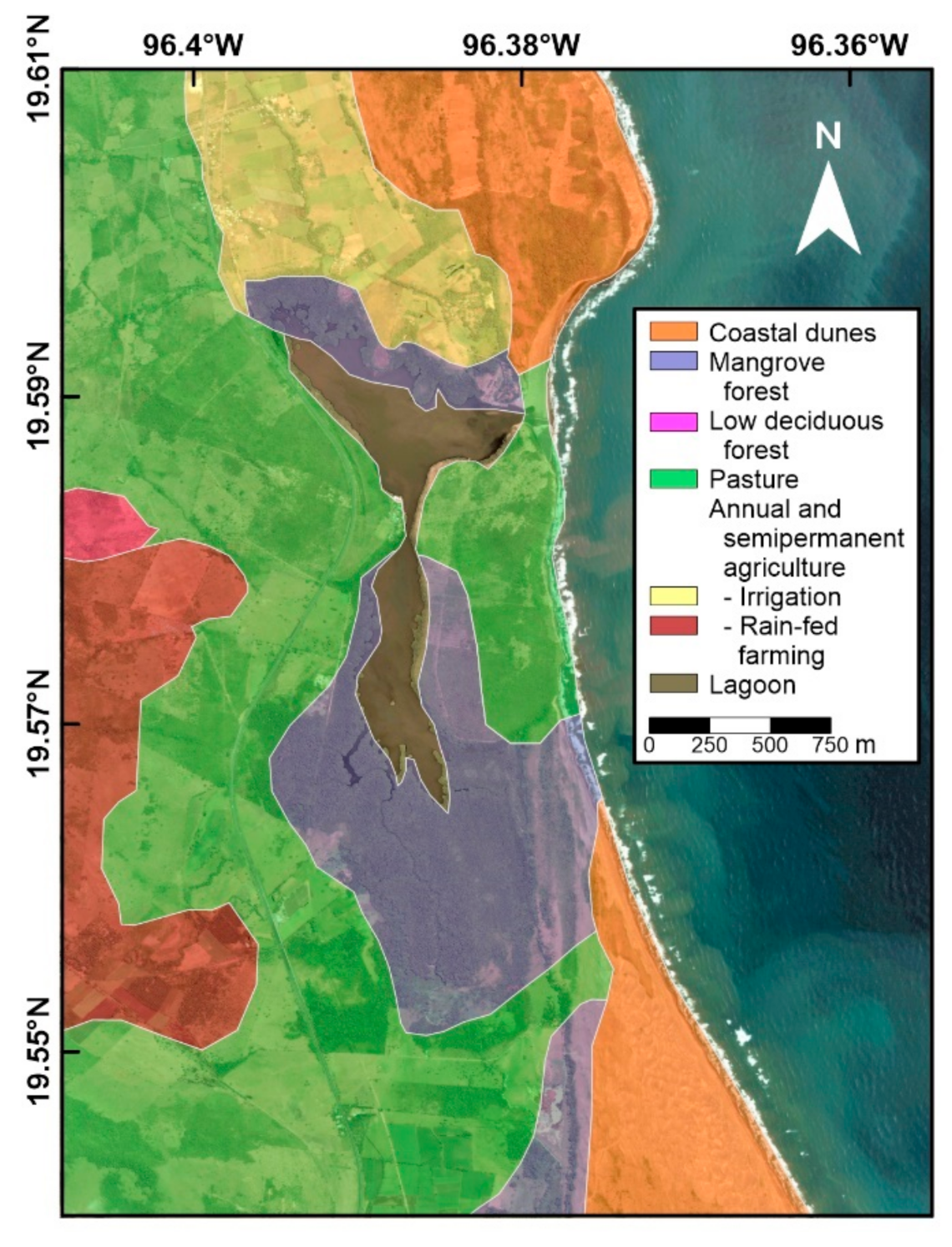
2.1. Study Area
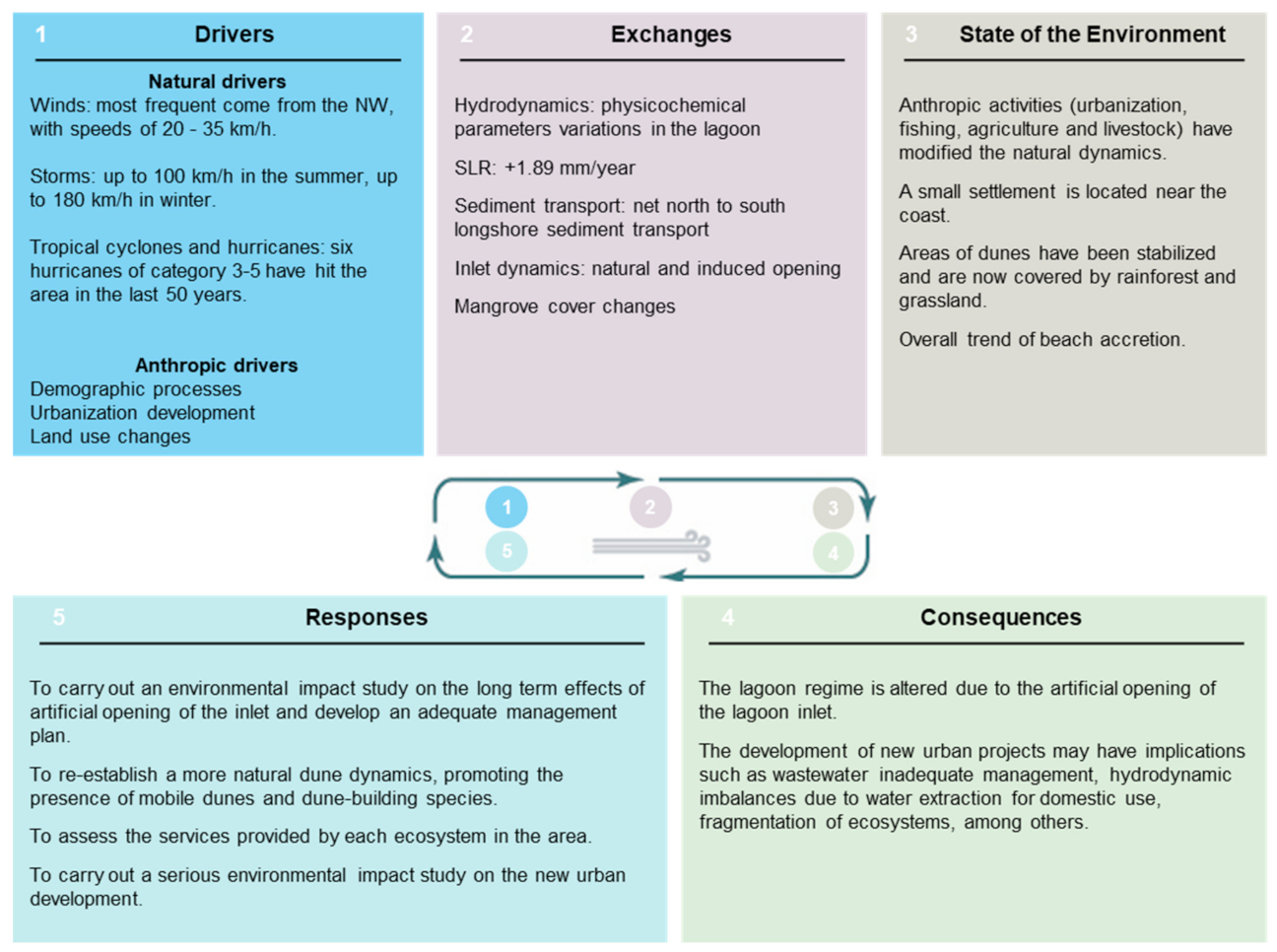
2.2. DESCR Framework
- Drivers, as the social, economic or environmental forces that put pressure on the environment, which are both natural (storms, hurricanes, etc.) and human (urbanization, pollution, etc.);
- Exchanges, which are the measure of how much the driving forces have produced changes in the system;
- The State of the Environment, where the current environmental conditions are defined after analyzing the pressures;
- Consequences, which are the effects of the processes on the environment, e.g., sediment transport may lead to erosion/accretion processes, and loss of ecosystem services;
- Responses, which are the mitigation actions adopted by local authorities and stakeholders to solve environmental problems and/or improve the quality of the environment.
3. Results
3.1. Drivers in the DESCR Framework
3.1.1. Natural Drivers
- Winds;
- Waves;
- Storms, tropical cyclones and hurricanes.
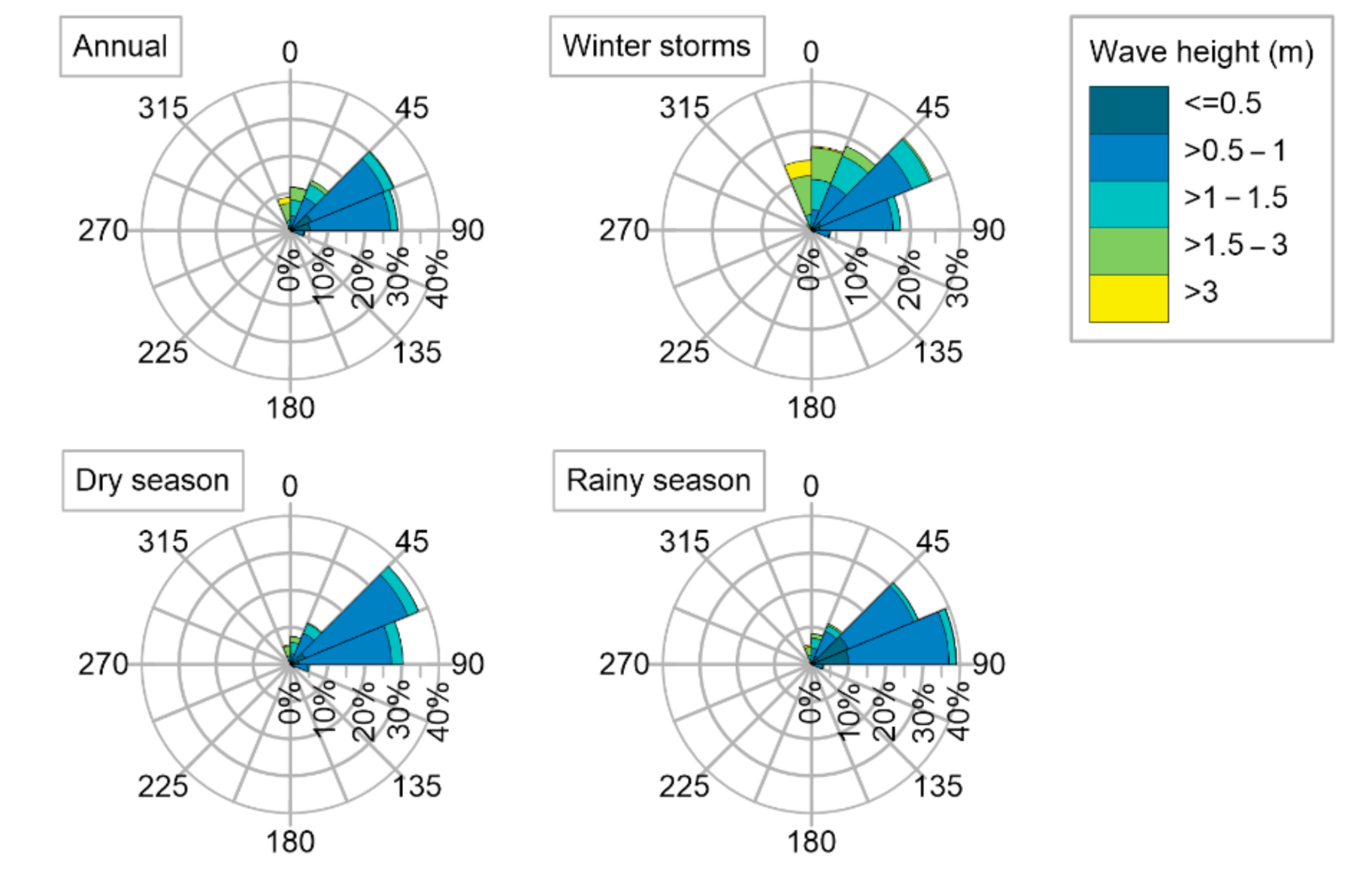
Winds
Waves
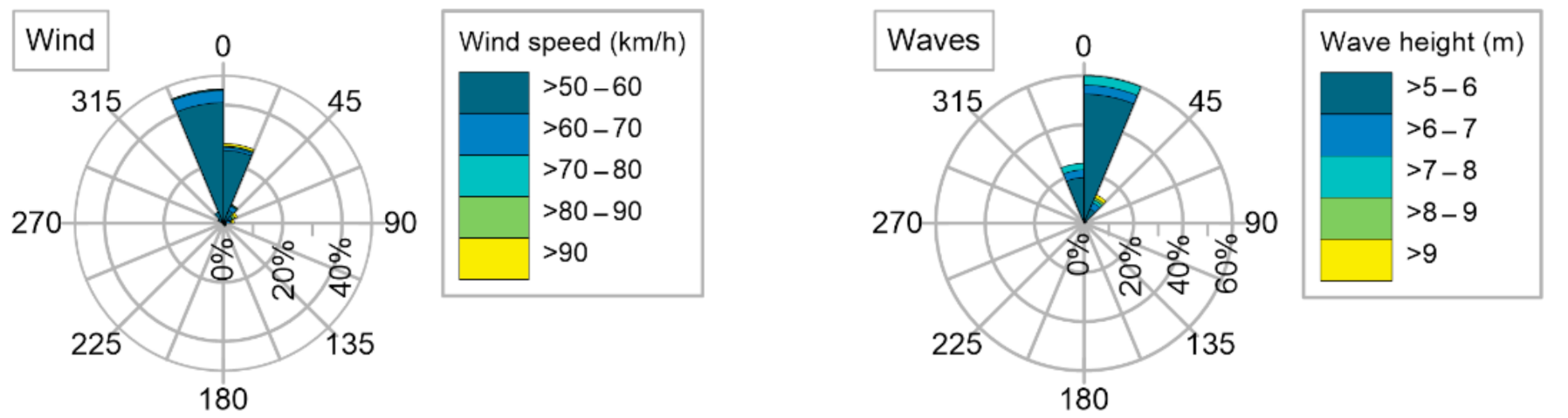
Storms, Tropical Cyclones and Hurricanes
Tides
3.1.2. Anthropic Drivers
- Tourism;
- Planed urban infrastructure.
Tourism in Coastal Areas and the Effects of Dune Trampling
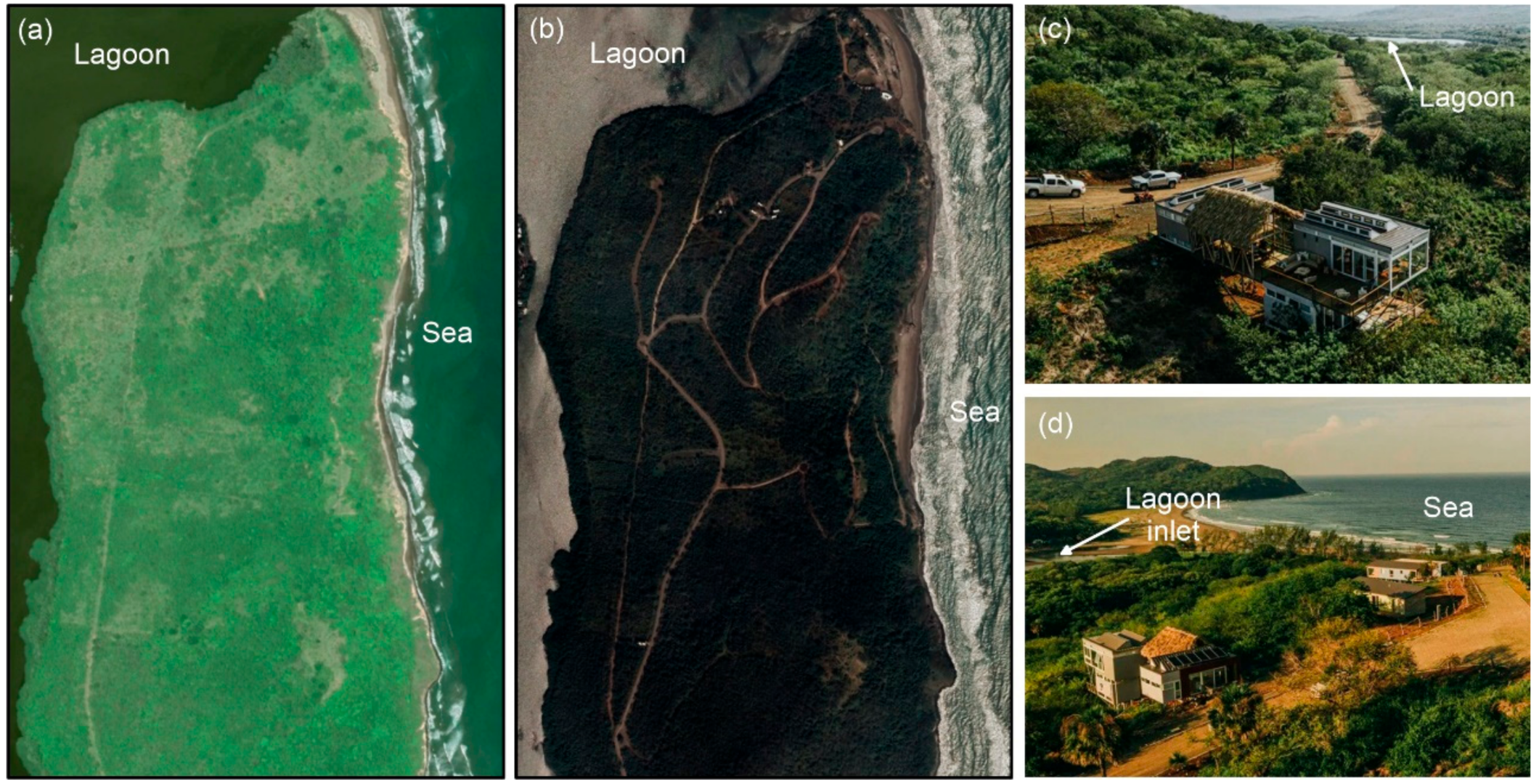
Planned Urban Infrastructure
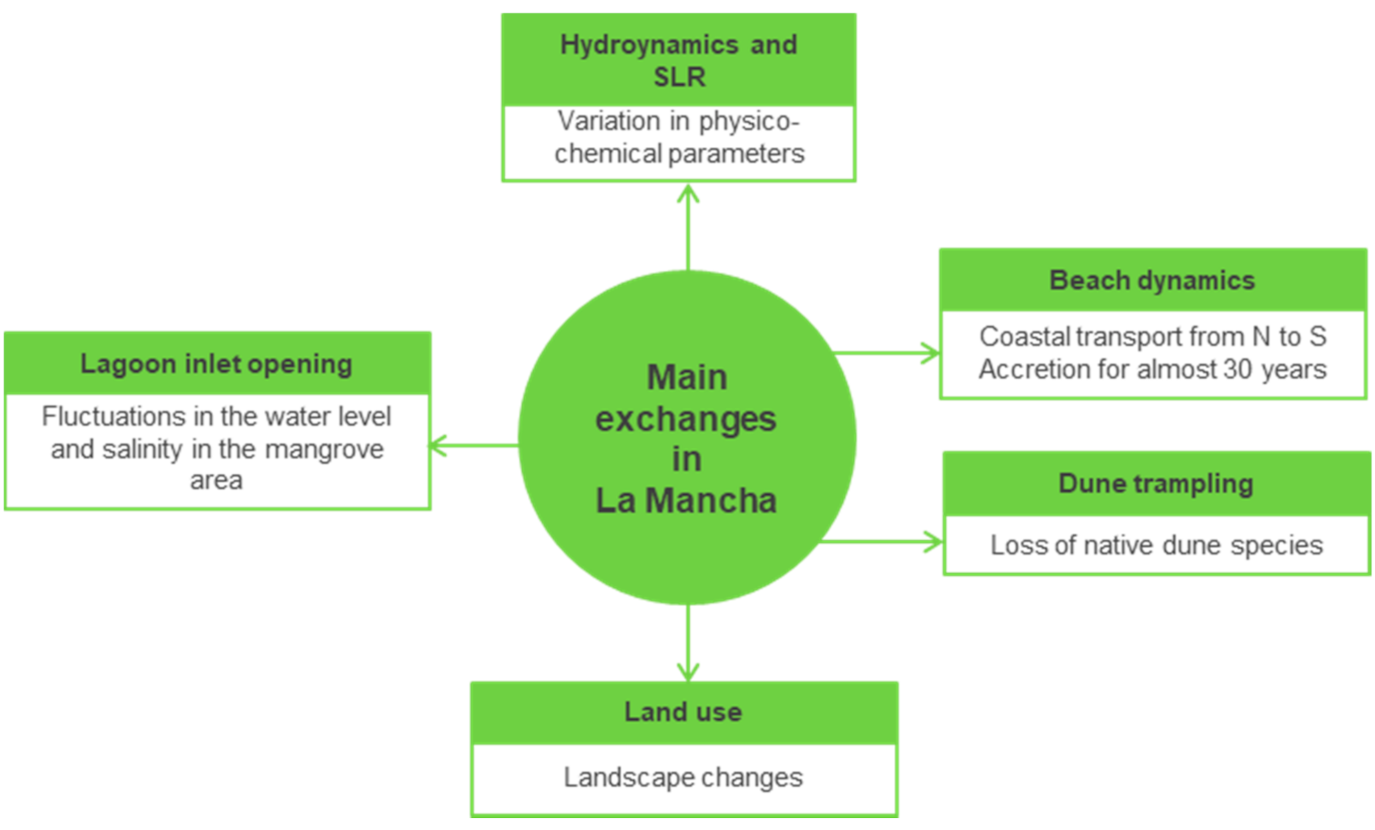
3.2. Exhanges in the DESCR Framework
3.2.1. Hydrodynamics and SLR
3.2.2. Problems Affecting the Vegetation and Fauna
3.3. State of the Environment in the DESCR Framework
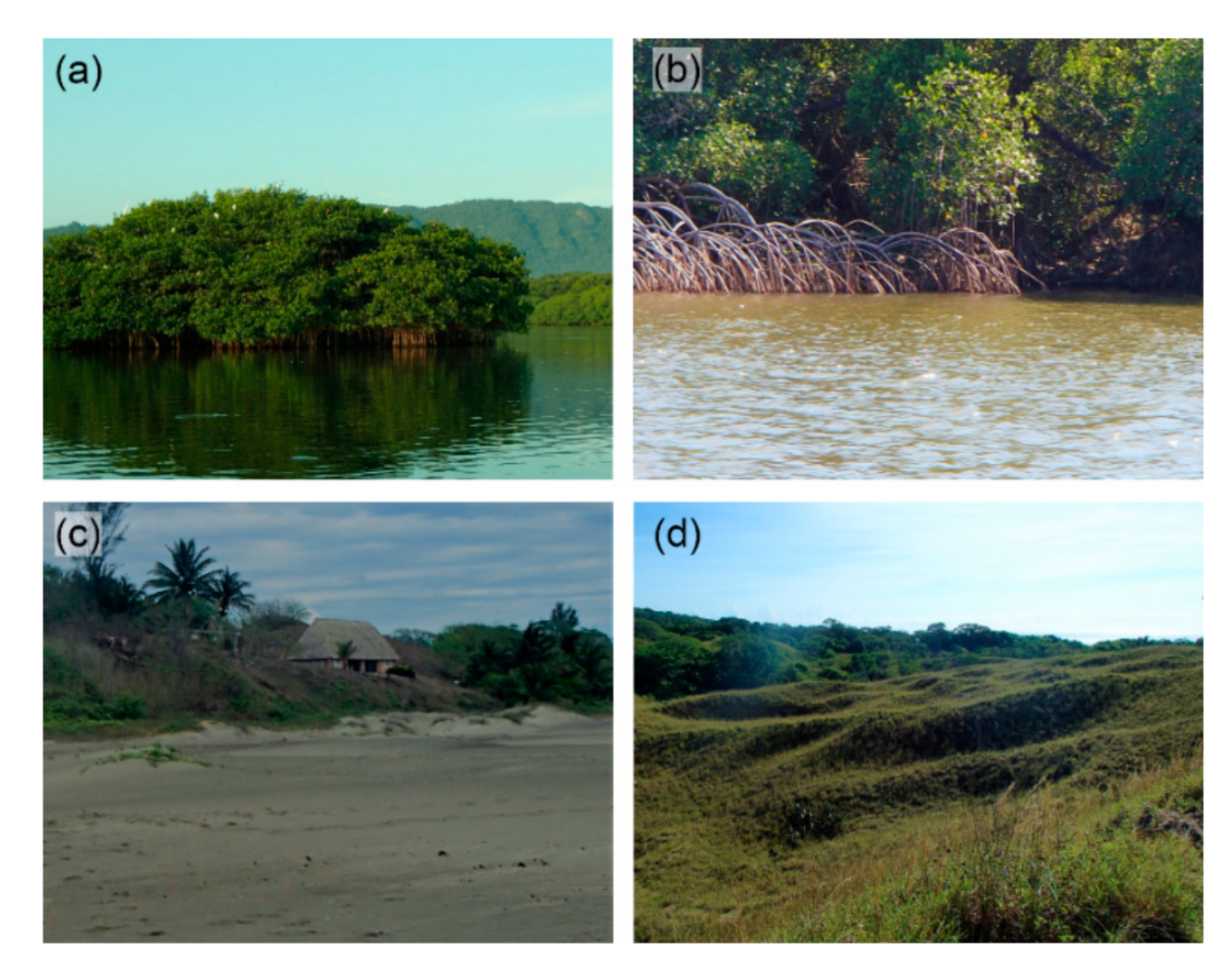
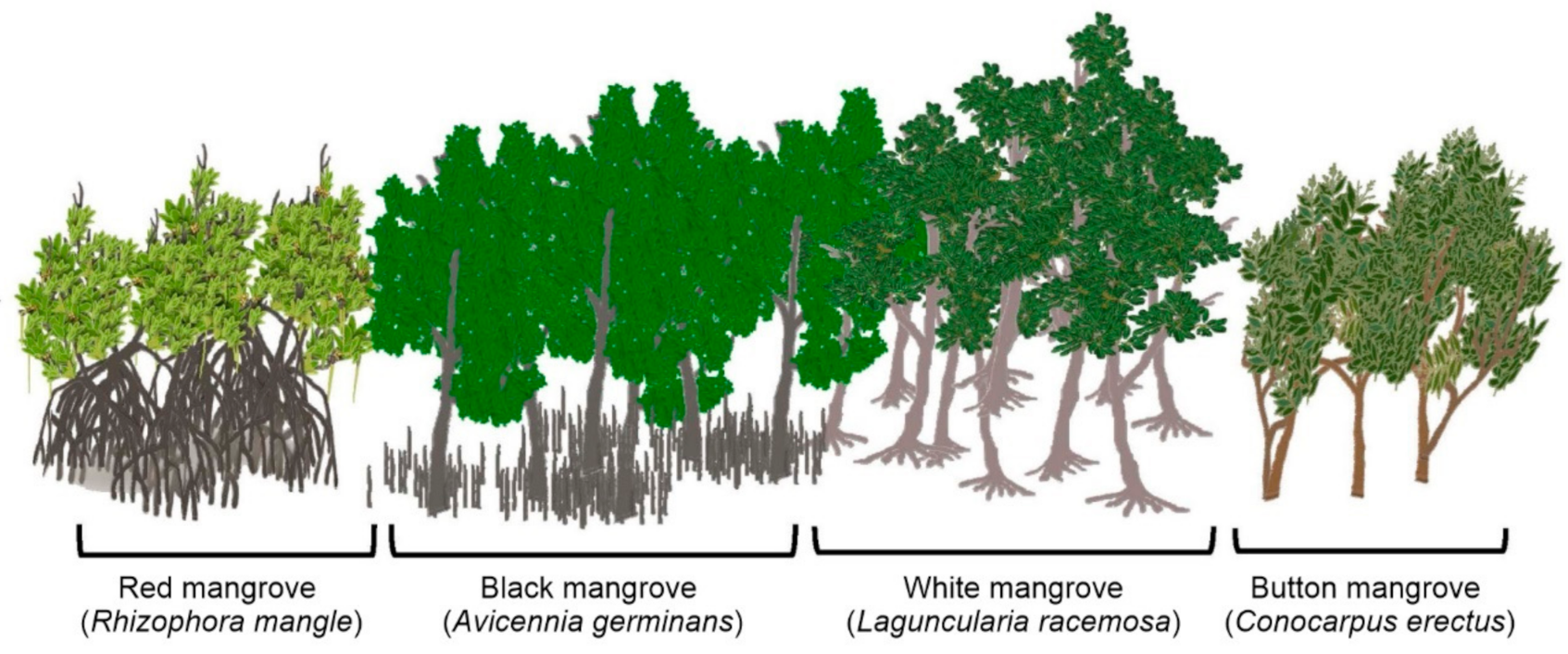
3.3.1. Lagoon Vegetation
3.3.2. Anthropic Impacts
3.4. Consequences in the DESCR Framework
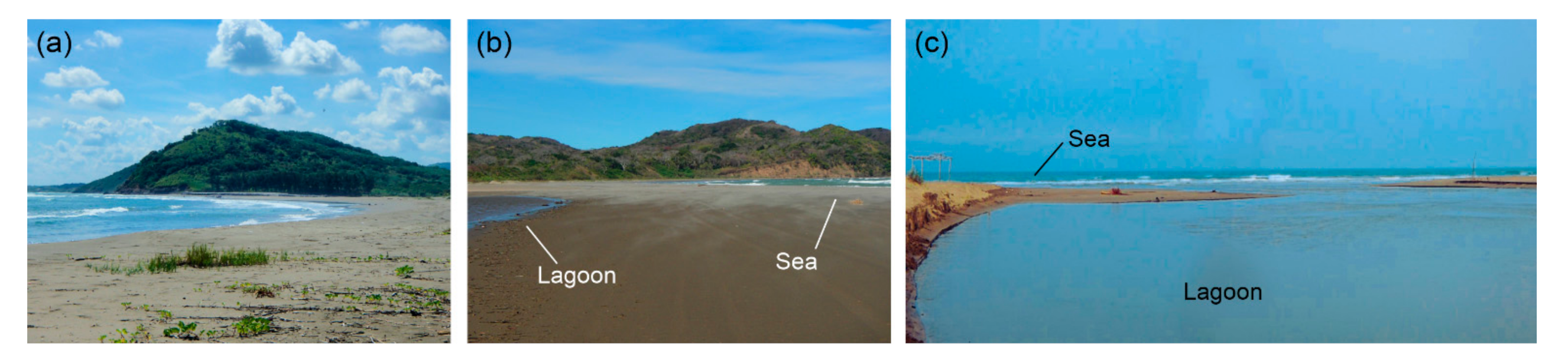
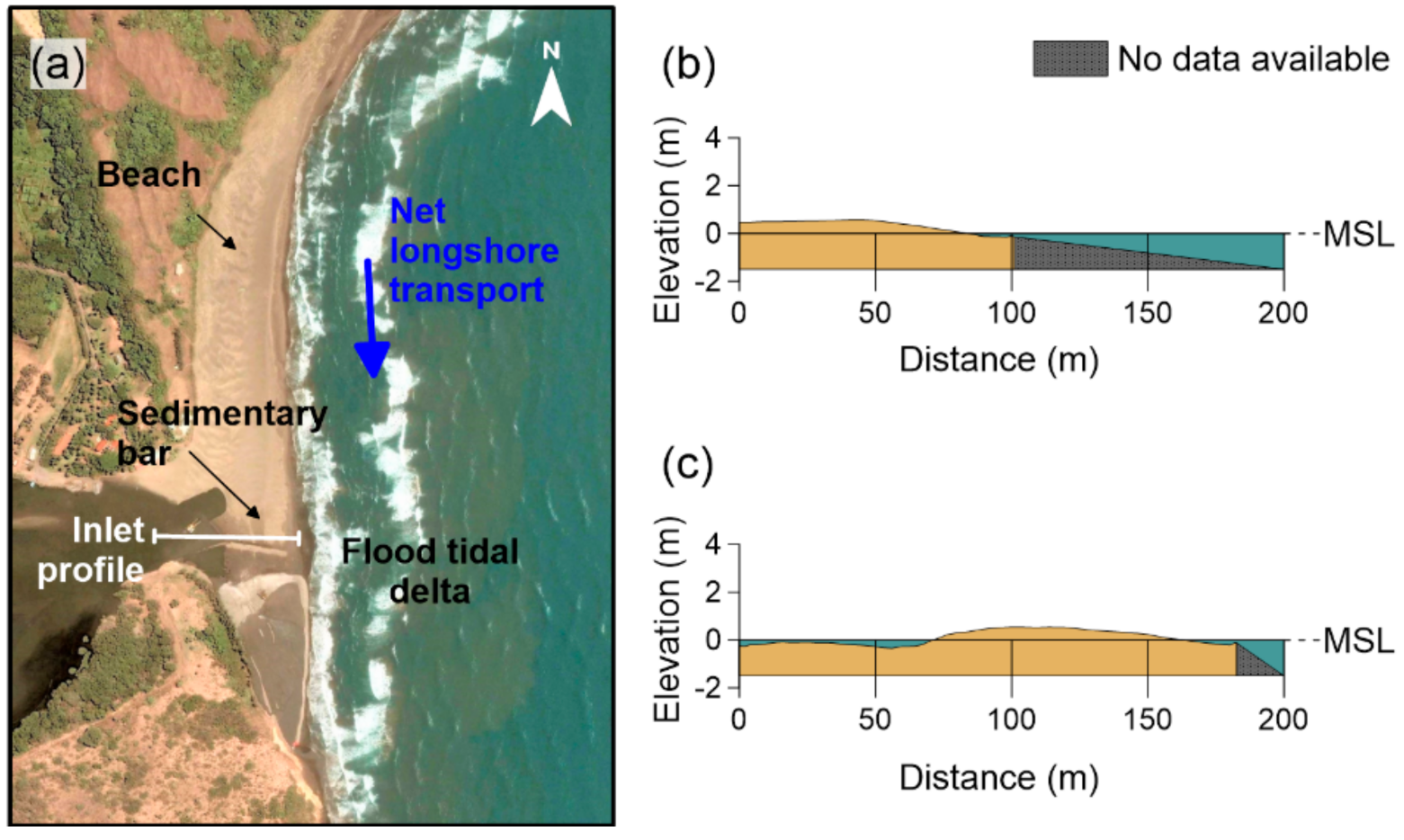
3.4.1. Beach and Dunes
3.4.2. Lagoon and Mangroves
3.5. Responses in the DESCR Framework
- Participation: representatives of the local, state and federal government; federation of fishermen; ecotourism organizations; academic institutions; grouping of fishing cooperatives with political interests; civil society [60].
- Normative: General Law of Ecological Balance and Environmental Protection (LEGEEPA); National Water Law; Federal Law of the Sea; Sustainable Rural Development Law; Sustainable Forestry Development Law; General Wildlife Law; Fishing Law; Federal Law of Rights; General Law of Human Settlements; Mexican Official Standard NOM-059-SEMARNAT-200 (Environmental Protection-Mexican native species of wild flora and fauna); NOM-126-SEMARNAT-2000; Official Mexican Standard NOM-022-SEMARNAT-2003; Official Mexican Standard NOM-001-SEMARNAT-1996; Mexican Official Standard NOM-075-SEMARNAT-1994 [61].
- Institutions: Secretary of the Environment and Natural Resources (SEMARNAT); Secretariat of Agriculture, Livestock, Rural Development, Fisheries and Food (CONAPESCA) [62]; marine secretary; Ministry of Communications and Transportation; Secretary of Tourism; Secretariat of Health; Office of the Attorney General of the Republic; Secretariat of Management for Environmental Protection; General Directorate of the Federal Maritime Terrestrial Zone and Coastal Environments; National Water Commission; National Commission for Protected Natural Areas; Federal Attorney for Environmental Protection; National Institute of Ecology [61].
- Managers: administration of the Institute of the Ecology Sector of the Institute of Ecology; Secretariat of the Environment and Natural Resources (SEMARNAT); ZOFEMATAC Federal Maritime Terrestrial Zone, dependency of SEMARNAT; Municipality of Actopan; State Coordination of the Environment (SEDERE) [60]; La Mancha en Movimiento S.S.S. [63]; PROFEPA Social Participation Committee; state nuclear power plant Nucleoeléctrica Laguna Verde (Federal Electricity Commission); Directorate of Fisheries State Agency; National Water Commission [61].
- Information: Community and Sustainable Development Program and Management Plan for the Protection and Conservation of the La Mancha-El Llano Ramsar Site [64]; La Mancha-El Llano Community Management Plan. In Search of a Sustainable Coastal Development [51]; Strategy for Comprehensive Coastal Management-The Municipal Approach [60]; Environments of Veracruz. The coast of La Mancha [62]; government; general bibliography.
- Resources: no specific data.
- Instruments: La Mancha-El Llano Community Management Plan [51].
3.6. Summary of the DESCR Framework
- Alteration in the natural patterns of the physicochemical parameters (e.g., salinity and pH) due to the forced opening of the inlet;
- Sea level rise;
- Sediment deficit;
- Sediment availability reduction;
- Changes in native species coverage;
- Land use changes, including development of urbanization.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Author, Year | Title | Main Contributions |
|---|---|---|
| Moreno-Casasola et al., 2006 [51] | Plan de manejo comunitario La Mancha-El Llano. En busca de un desarrollo costero sustentable. Estrategias para el manejo integral de la zona costera: un enfoque municipal | A management strategy based on the environmental protection and the experiences of the Latin American Forum of Environmental Sciences. |
| Moreno-Casasola, 2006 [62] | Entornos Veracruzanos. La costa de La Mancha | This book describes the main characteristics, physical, ecological, social and cultural, in great detail. |
| Moreno-Casasola et al., 2007 [52] | Los conflictos de la conservación: el caso de La Mancha. Hacia una cultura de conservación de la diversidad biológica | A view of the experiences of the social sectors of La Mancha and the conflicts of interests between them and the government regarding the introduction of the La Mancha-El Llano Community Management Plan. |
| Moreno-Casasola and Salinas Pulido, 2007 [64] | Programa de desarrollo comunitario sustentable y plan de manejo para la protección y conservación del Sitio Ramsar La Mancha-El Llano | An environmental conservation and community project for La Mancha, Veracruz, based on the sustainable management models of three groups of people from the local community. |
| Hesp and Martínez, 2008 [16] | Transverse dune trailing ridges and vegetation succession | A description of features, such as evolution and vegetation, of the Farallon dunes located in La Mancha, Veracruz. |
| Utrera-López and Moreno-Casasola, 2008 [20] | Mangrove litter dynamics in La Mancha Lagoon, Veracruz, Mexico | A description of litter dynamics among mangrove types in La Mancha, to help understand functional heterogeneity within this coastal ecosystem. |
| Psuty et al., 2009 [15] | Interaction of alongshore sediment transport and habitat conditions at Laguna La Mancha, Veracruz, Mexico | An overview of the hydrological regime, the dynamic of sediments and the ecological features in La Mancha. |
| Mata et al., 2011 [71] | Floristic composition and soil characteristics of tropical freshwater forested wetlands of Veracruz on the coastal plain of the Gulf of Mexico | Analysis of the geomorphological setting, influence and soil properties on the structure of vegetation of five coastal lagoons in Veracruz, one being La Mancha. |
| Martínez et al., 2014 [9] | Land use changes and sea level rise may induce a “coastal squeeze” on the coasts of Veracruz, Mexico | Analysis of the coastal line geodynamics and geodynamic trends to model niches under SLR scenarios. |
| Ruiz and López-Portillo, 2014 [72] | Variación espacio-temporal de la comunidad de macroinvertebrados epibiontes en las raíces del mangle rojo Rhizophora mangle (Rhizophoraceae) en la laguna costera de La Mancha, Veracruz, México | An analysis of spatiotemporal variations of epibiont macroinvertebrates in red mangrove roots (Rhizophoraceae), based on the hydrological dynamics of the system. |
| Ramírez Méndez et al., 2015 [73] | Estudio de la dinámica y calidad de agua en la laguna de La Mancha, Veracruz | A study of the dynamics of hydrodynamic, morphodynamic and hydrological conditions and physicochemical parameters of La Mancha and its littoral cell. |
| Chávez et al., 2017 [12] | Impact of Inlet Management on the Resilience of a Coastal Lagoon: La Mancha, Veracruz, Mexico | A study on features of La Mancha lagoon, such as ecosystem vulnerability, physical processes, such as erosion and accretion of the beach, inlet dynamics, and hydrodynamics of circulation patterns in the lagoon. |
| Rivera et al., 2019 [36] | Modelling the effects of the artificial opening of an inlet: Salinity distribution in a coastal lagoon | Numerical results are used to analyze and describe changes in the salinity distribution in La Mancha lagoon, showing results which would be useful in developing an adequate management plan. |
| Gómez Ramírez, 2020 [53] | El estudio de los ciclones tropicales se minimizó, en la manifestación del impacto ambiental para el Proyecto Diada La Mancha, en la costa del municipio de Actopan, Estado de Veracruz | A review of the problems caused by the lack of a serious environmental impact study prior to the development of the La Mancha-Diada project. |
| Author, Year | Title | Main Contributions |
|---|---|---|
| Cortés López, 2017 [44] | Desarrollo de un Índice de Riesgo sobre la ocurrencia de Opresión Costera en el centro-norte del Estado de Veracruz Master Thesis | Development of a risk index, based on the occurrence of coastal oppression, considering the evolution of the coastline and of the sediments in 14 beaches, one being La Mancha. |
| Chávez, 2018 [46] | Balance Hidrodinámico en Humedales Costeros y su valor como elemento de protección litoral PhD Thesis | Analysis and characterization of the physical protection against floods provided by wetlands, based on the monitoring of the main physical processes and the determination of their balances. |
| Ramírez Méndez, 2018 [18] | Rumbo a un Plan de Manejo Integral de la laguna de La Mancha, Veracruz Master Thesis | Study of physical, ecological and social parameters of La Mancha, Veracruz, in order to extend a management plan for this zone. |
References
- Silva, R.; Oumeraci, H.; Martínez, M.L.; Chávez, V.; Lithgow, D.; van Tussenbroek, B.I.; van Rijswick, H.F.; Bouma, T.J. Ten commandments for sustainable, safe, and w/healthy sandy coasts facing global change. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.L.; Landgrave, R.; Silva, R.; Hesp, P. Shoreline Dynamics and Coastal Dune Stabilization in Response to Changes in Infrastructure and Climate. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 92, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez, V.; Lithgow, D.; Losada, M.; Silva-Casarín, R. Coastal green infrastructure to mitigate coastal squeeze. J. Infrastruct. Preserv. Resil. 2021, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Martínez, M.L.; van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Guzmán-Rodríguez, L.O.; Mendoza, E.; López-Portillo, J. A Framework to Manage Coastal Squeeze. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, E.; Weterings, R. Environmental Indicators: Typology and Overview; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1999; pp. 6–15. [Google Scholar]
- Patrício, J.; Elliott, M.; Mazik, K.; Papadopoulou, K.-N.; Smith, C.J. DPSIR—Two decades of trying to develop a unifying framework for marine environmental management? Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Chávez, V.; Bouma, T.J.; van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Arkema, K.K.; Martínez, M.L.; Oumeraci, H.; Heymans, J.J.; Osorio, A.F.; Mendoza, E. The incorporation of biophysical and social components in coastal management. Estuaries Coasts 2019, 42, 1695–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Martínez, M.L.; Hesp, P.A.; Catalán, P.; Osorio, A.F.; Martell, R.; Fossati, M.; Miot da Silva, G.; Mariño-Tapia, I.; Pereira, P. Present and future challenges of coastal erosion in Latin America. J. Coast. Res. 2014, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.L.; Mendoza-González, G.; Silva-Casarín, R.; Mendoza-Baldwin, E. Land use changes and sea level rise may induce a “coastal squeeze” on the coasts of Veracruz, Mexico. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 29, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno Casasola, P.; Galaviz Rojas, J.L.; Lomelí Zárate, D.; Pérez Ortiz, M.A.; Domínguez Lara, A.L.; Vázquez Saavedra, T. Diagnóstico de los manglares de Veracruz: Distribución, vínculo con los recursos pesqueros y su problemática. Madera Bosques 2002, 8, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsar Sites Information Service-La Mancha y El Llano. Available online: https://rsis.ramsar.org/ris/1336 (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Chávez, V.; Mendoza, E.; Ramírez, E.; Silva, R. Impact of inlet management on the resilience of a coastal lagoon: La Mancha, Veracruz, Mexico. J. Coast. Res. 2017, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Mancha, E.M. Ecoturismo La Mancha en Movimiento. Available online: https://www.ecoturismolamancha.com/ (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Digital Globe. Available online: https://www.digitalglobe.com (accessed on 12 June 2012).
- Psuty, N.P.; Martínez, M.L.; López-Portillo, J.; Silveira, T.M.; García-Franco, J.G.; Rodríguez, N.A. Interaction of alongshore sediment transport and habitat conditions at Laguna La Mancha, Veracruz, Mexico. J. Coast. Conserv. 2009, 13, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hesp, P.A.; Martínez, M.L.M. Transverse dune trailing ridges and vegetation succession. Geomorphology 2008, 99, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Trejo, H.; Priego-Santander, A.; López-Portillo, J.; Isunza-Vera, E. Los paisajes Físico-Geográficos de los manglares de la laguna de La Mancha, Veracruz, México. Interciencia 2006, 31, 211–219. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez Méndez, E. Rumbo a un Plan de Manejo Integral de la Laguna de La Mancha, Veracruz. Master Thesis, Univesidad Nacional Autónoma de Mexico, Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez Landa, I.; Galaviz-Villa, I.; Garay Marín, J. Incremento en el nivel de mar en la zona costera de Veracruz. In Temas Selectos de Vulnerabilidad Costera en el Estado de Veracruz; Lango-Reynoso, F.B., Alfonso, V., Castañeda-Chávez, M.R., Eds.; Universidad Autónoma de Campeche, Instituto de Ecología, Pesquerías y Oceanografía del Golfo de México (EPOMEX): Campeche, México, 2019; pp. 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Utrera-López, M.E.; Moreno-Casasola, P. Mangrove Litter Dynamics in la Mancha Lagoon, Veracruz, Mexico. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 16, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordstrom, K.F.; Jackson, N.L. Removing shore protection structures to facilitate migration of landforms and habitats on the bayside of a barrier spit. Geomorphology 2013, 199, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Nicholls, R.J. A global analysis of human settlement in coastal zones. J. Coast. Res. 2003, 19, 584–599. [Google Scholar]
- Reanalysis, C. Available online: https://climate.copernicus.eu/climate-reanalysis (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- Martínez, M.L.; Silva, R.; Lithgow, D.; Mendoza, E.; Flores, P.; Martínez, R.; Cruz, C. Human impact on coastal resilience along the coast of Veracruz, Mexico. J. Coast. Res. 2017, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jáuregui, E.; Zitácuaro, I. El impacto de los ciclones tropicales del Golfo de México, en el estado de Veracruz. Cienc. Hombre 1995, 623, 75–119. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, R.; Ruiz, G.; Posada, G.; Pérez, D.; Rivillas, G.; Espinal, J.; Mendoza, E. Atlas de Clima Marítimo de la Vertiente Atlántica Mexicana; Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México: Mexico City, Mexico, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Martínez, G.; Silva-Casarín, R.; Pérez-Romero, D.M.; Posada-Vanegas, G.; Bautista-Godínez, E.G. Modelo híbrido para la caracterización del oleaje. Ing. Hidráulica México 2009, 24, 5–22. [Google Scholar]
- Estación Mareográfica de Tuxpan, Veracruz. Available online: https://oceanografia.semar.gob.mx/Templates/grafnum_tuxpan.html (accessed on 14 July 2021).
- Estación Mareográfica de Veracruz, Veracruz. Available online: https://oceanografia.semar.gob.mx/Templates/grafnum_veracruz.html (accessed on 14 July 2021).
- Estaciones de Campo INECOL. Available online: https://www.inecol.mx/inecol/index.php/es/ct-menu-item-1/estaciones-de-campo (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Hesp, P.; Schmutz, P.; Martínez, M.M.; Driskell, L.; Orgera, R.; Renken, K.; Revelo, N.A.R.; Orocio, O.A.J. The effect on coastal vegetation of trampling on a parabolic dune. Aeolian Res. 2010, 2, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E-consulta. Inicia Construcción de Fraccionamiento de 800 Casas en la Mancha. Available online: http://www.e-veracruz.mx/nota/2018-01-19/ecologia/inicia-construccion-de-fraccionamiento-de-800-casas-en-la-mancha (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- Veracruz, L.J. Destrucción en Sitio Ramsar de La Mancha. Available online: http://www.jornadaveracruz.com.mx/Post.aspx?id=180120_115217_446 (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- Diada-Ecommunity. Diada-Desarrollos- La Mancha-5. Available online: https://i2.wp.com/www.diada.mx/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/DIADA-Desarrollos-La-Mancha-5.jpg (accessed on 29 April 2021).
- Diada-Ecommunity. Diada-Desarrollos- La Mancha-8. Available online: https://i0.wp.com/www.diada.mx/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/DIADA-Desarrollos-La-Mancha-8.jpg (accessed on 29 April 2021).
- Rivera, J.; Chávez, V.; Silva, R.; Mendoza, E. Modelling the effects of the artificial opening of an inlet: Salinity distribution in a coastal lagoon. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 92, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Ibar, V.F.; Rivera-Monroy, V.H. Coastal lagoons and estuaries in Mexico: Processes and vulnerability. Estuaries Coasts 2014, 37, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Moreno, P.; Martínez, M.L.; Mendoza, E.; López-Portillo, J.; Lithgow, D.; Vázquez, G.; Martínez, R.; Ibarra, R. La Zona Costera del Estado de Veracruz: Clima Marítimo, Medio Físico y Medio Biótico; Instituto de Ecología, A.C.: Xalapa, Mexico, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- De la Lanza Espino, G.; Pérez, M.A.O.; Pérez, J.L.C. Diferenciación hidrogeomorfológica de los ambientes costeros del Pacífico, del Golfo de México y del Mar Caribe. Investig. Geográficas Boletín Inst. Geogr. 2013, 2013, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aguayo-Camargo, J. Neotectónica y facies sedimentarias cuaternarias en el suroeste del Golfo de México, dentro del marco tectono-estratigráfico regional evolutivo del Sur de México. Ing. Investig. Tecnol. 2005, 6, 19–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, N.; Sutherland, W.J.; Khan, M.N.I.; Berger, U.; Schmitz, N.; Dahdouh-Guebas, F.; Koedam, N. Using expert knowledge and modeling to define mangrove composition, functioning, and threats and estimate time frame for recovery. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 2247–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Casasola, P.; Cejudo-Espinosa, E.; Capistrán-Barradas, A.; Infante-Mata, D.; López-Rosas, H.; Castillo-Campos, G.; Pale-Pale, J.; Campos-Cascaredo, A. Composición florística, diversidad y ecología de humedales herbáceos emergentes en la planicie costera central de Veracruz, México. Bol. Soc. Bot. Méx 2010, 87, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portillo, J.L.; Ezcurra, E. Los manglares de México: Una revisión. Madera Bosques 2002, 8, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés López, L. Desarrollo de un Índice de Riesgo Sobre Opresión Costera en el Centro-Norte del Estado de Veracruz. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Masselink, G.; Short, A.D. The effect of tide range on beach morphodynamics and morphology: A conceptual beach model. J. Coast. Res. 1993, 9, 785–800. [Google Scholar]
- Chávez, V. Balance Hidrodinámico en Humedales Costeros y su Valor Como Elemento de Protección Litoral; Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México: Mexico City, Mexico, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Conjunto de Datos Vectoriales de Uso del Suelo y Vegetación E14-3 (Veracruz) escala 1:250 000 serie V (Conjunto Nacional). Ver. Available online: https://datos.gob.mx/busca/dataset/mapas-de-uso-del-suelo-y-vegetacion-escala-1-250-000-serie-v-veracruz-de-ignacio-de-la-llave/resource/6ecb85a1-3f86-46fd-b37b-dd19f2cb5429?inner_span=True (accessed on 29 April 2021).
- Doody, J.P. Sand Dune Conservation, Management and Restoration; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany; Department of Geosciences, Florida Atlantic University: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, M.L.; Silva, R.; López-Portillo, J.; Feagin, R.A.; Martínez, E. Coastal Ecosystems as an Ecological Membrane. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 95, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.L.; Vázquez, G.; Sánchez Colón, S. Spatial and temporal variability during primary succession on tropical coastal sand dunes. J. Veg. Sci. 2001, 12, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Casasola, P.; Salinas, M.; Amador, L.E.; Cruz, H.; Juárez, A.; Ruelas, L. Plan de manejo comunitario La Mancha-El Llano. En busca de un desarrollo costero sustentable. In Estrategias Para el Manejo INTEGRAl de la Zona Costera: Un Enfoque Municipal; Moreno-Casasola, P., Peresbarbosa, E., Travieso-Bello, A.C., Eds.; Instituto de Ecología A.C.—Comisión Nacional de Áreas Naturales Protegidas (SEMARNAT)—Gobierno del Estado de Veracruz: Veracruz, Mexico, 2008; Volume 1, pp. 121–149. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Casasola, P.; Paradowska, K.; Sada, S.G.; Salinas, G. Los conflictos de la conservación: El caso de La Mancha. In Hacia una Cultura de Conservación de la Diversidad Biológica; Halffter, G., Guevara, S., Melci, A., Eds.; Monografías Tercer Mileno: Zaragoza, España, 2007; Volume 6, pp. 225–236. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez Ramírez, M. El estudio de los ciclones tropicales se minimizó, en la manifestación del impacto ambiental para el proyecto Diada La Mancha, en la costa del municipio de Actopan, Estado de Veracruz. DELOS 2020, 12, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza-González, G.; Martínez, M.L.; Lithgow, D.; Pérez-Maqueo, O.; Simonin, P. Land use change and its effects on the value of ecosystem services along the coast of the Gulf of Mexico. Ecol. Econ. 2012, 82, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviedes, V.; Arenas-Granados, P.; Barragán-Muñoz, J.M. Regional public policy for Integrated Coastal Zone Management in Central America. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2020, 186, 105114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragán Muñoz, J.M. Manejo Costero Integrado en Iberoamérica: Diagnóstico y Propuestas Para una Nueva Política Pública; Red IBEMAR (CYTED): Cádiz, España, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuerdo Mediante el Cual se Expide la Política Nacional de Mares y Costas de México. Available online: https://www.dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5545511&fecha=30/11/2018 (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- Diputados, H.C.D. Plan Nacional de Desarrollo 2019–2024. Available online: http://www.diputados.gob.mx/LeyesBiblio/compila/pnd.htm (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- Programa Nacional Forestal 2020–2024. Available online: https://www.dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5609275&fecha=31/12/2020 (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- Moreno-Casasola, P.; Rojas, E.P.; Travieso-Bello, A.C. Estrategia Para el Manejo Costero Integral: Secc. IV–V; Instituto de Ecología: Xalapa, Mexico, 2006; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera Arriaga, E.; Villalobos, G.; Azuz Adeath, I.; Rosado May, F. (Eds.) El Manejo Costero en México; Universidad Autónoma de Campeche, SEMARNAT, CETYS-Universidad, Universidad de Quintana Roo: Campeche, Mexico, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno Casasola, P. Entornos Veracruzanos. La costa de La Mancha; Instituto de Ecología: Xalapa, Mexico, 2006; ISBN 9707090677. [Google Scholar]
- La Mancha en Movimiento: Capacitación. Available online: https://www.ecoturismolamancha.com/capacitaci%C3%B3n (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- Moreno-Casasola, P.; Salinas, G. Programa de desarrollo comunitario sustentable y plan de manejo para la protección y conservación del Sitio Ramsar La Mancha-El Llano. In Hacia una Cultura de Conservación de la Diversidad Biológica; Halffter, G., Guevara, S., Melci, A., Eds.; Monografías Tercer Mileno: Zaragoza, España, 2007; Volume 6, pp. 173–185. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Casasola, P.; Maarel, S.E.; Castillo, M.L.H.; Pisanty, I. Ecología de la vegetación de dunas costeras: Estructura y composición en el Morro de La Mancha. Biotica 1982, 7, 491–526. [Google Scholar]
- Barreiro-Güemes, T.; Balderas-Cortés, J. Evaluación de algunas comunidades de productores primarios de la Laguna de la Mancha, Veracruz. An. Inst. Cienc. del Mar y Limnol. Univ. Nal. Autón. México 1991, 2, 229–245. [Google Scholar]
- Barreiro-Güemes, M.; Matus, J. Diagnóstico ecológico y de uso de recursos de la laguna de La Mancha, Veracruz: Propuesta para su manejo. In Proceedings of the V Congreso Latinoamericano de Ciencias del Mar, La Paz, Mexico, 27 September–1 October 1993; p. 186. [Google Scholar]
- Villalobos, F.; Ortiz-Pulido, R.; Moreno, C.; Pavón-Hernández, N.; Hernández-Trejo, H.; Bello, J.; Montiel, S. Patrones de la macrofauna edáfica en un cultivo de Zea maiz durante la fase postcosecha en” La Mancha”, Veracruz, México. Acta Zool. Mex. 2000, 80, 167–183. [Google Scholar]
- Cázares Hernández, E. Monitoreo de Poblaciones de Tortugas Dulceacuícolas Como Parte del Proceso de Restauración de un Humedal del Sitio Ramsar la Mancha y el Llano; Universidad Veracruzana, Facultad de Ingeniería Química, Región Xalapa: Xalapa, México, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Botello, A. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from coastal lagoons of Veracruz State, Gulf of Mexico. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 67, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, D.I.; Moreno-Casasola, P.; Madero-Vega, C.; Castillo-Campos, G.; Warner, B.G. Floristic composition and soil characteristics of tropical freshwater forested wetlands of Veracruz on the coastal plain of the Gulf of Mexico. For. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 262, 1514–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.; López-Portillo, J. Variación espacio-temporal de la comunidad de macroinvertebrados epibiontes en las raíces del mangle rojo Rhizophora mangle (Rhizophoraceae) en la laguna costera de La Mancha, Veracruz, México. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2014, 62, 1309–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Méndez, E.; Mendoza, E.; Silva-Casarín, R. Estudio de la dinámica y calidad del agua en Laguna la Mancha Veracruz. In Proceedings of the IX Congreso “Los Puertos Mexicanos y su Conectividad, Veracruz, Mexico, 15–17 April 2015. [Google Scholar]




| Tidal Level | Tuxpan | La Mancha 1 | Veracruz |
|---|---|---|---|
| HAT (Highest Astronomical Tide) (m) | 1.040 | 1.087 | 1.100 |
| MHHW (Mean Higher High Water) (m) | 0.496 | 0.500 | 0.501 |
| MHW (Mean High Water) (m) | 0.410 | 0.415 | 0.417 |
| MSL (Mean Sea Level) (m) | 0.284 | 0.286 | 0.287 |
| MLW (Mean Low Water) (m) | 0.220 | 0.230 | 0.233 |
| MLLW (Mean Lower Low Water) (m) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| LAT (Lowest Astronomical Tide) (m) | −0.470 | −0.493 | −0.500 |
| Storm Surge | Return Period (Years) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 100 | |
| Atmospheric pressure gradient storm surge (m) | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.26 | 0.28 | 0.32 |
| Wind storm surge (m) | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.42 | 0.45 | 0.50 | 0.54 | 0.68 |
| Wave storm surge (m) | 1.27 | 1.40 | 1.47 | 1.51 | 1.54 | 1.58 | 1.62 | 1.66 | 1.70 | 1.80 |
| Pressure + wind + wave storm surge (m) | 1.36 | 1.67 | 1.90 | 2.04 | 2.14 | 2.23 | 2.31 | 2.42 | 2.52 | 2.80 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chacón Abarca, S.; Chávez, V.; Silva, R.; Martínez, M.L.; Anfuso, G. Understanding the Dynamics of a Coastal Lagoon: Drivers, Exchanges, State of the Environment, Consequences and Responses. Geosciences 2021, 11, 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11080301
Chacón Abarca S, Chávez V, Silva R, Martínez ML, Anfuso G. Understanding the Dynamics of a Coastal Lagoon: Drivers, Exchanges, State of the Environment, Consequences and Responses. Geosciences. 2021; 11(8):301. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11080301
Chicago/Turabian StyleChacón Abarca, Samantha, Valeria Chávez, Rodolfo Silva, M. Luisa Martínez, and Giorgio Anfuso. 2021. "Understanding the Dynamics of a Coastal Lagoon: Drivers, Exchanges, State of the Environment, Consequences and Responses" Geosciences 11, no. 8: 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11080301
APA StyleChacón Abarca, S., Chávez, V., Silva, R., Martínez, M. L., & Anfuso, G. (2021). Understanding the Dynamics of a Coastal Lagoon: Drivers, Exchanges, State of the Environment, Consequences and Responses. Geosciences, 11(8), 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11080301









