Abstract
Mountain headwater streams are still somewhat on the boundary of interest regarding possible human impact on their morphology or geomorphic processes, which may be caused by our perception of mountains as islands of relatively preserved natural conditions. This paper summarizes the past and present human pressure on the headwater streams that drain the highest mountain ranges of the Outer Western Carpathians in Czechia. Anthropogenic pressure began in this region in the 16th century during a colonization of the mountains and continued by timber harvesting, timber floating, and construction of torrent control works until present. Each of these interventions produced a morphological response of the channels in relation to altered sediment or water fluxes at the whole catchment scale or within longitudinal stream profiles. Because it is highly unlikely to reach pre-settlement conditions of the channels, the management effort should be concentrated to achieve realistic restoration targets under the present socioeconomic circumstances by taking into consideration the morphodynamical specifics of mountain headwater streams.
1. Introduction
Practically all rural areas in Europe have been shaped or altered by humans and can be considered cultural landscapes [1]. Adjustments of channel geometry and morphology as a response to various human interventions have been frequently studied in the past decades in relatively wide gravel beds or meandering European rivers, primarily in the context of river degradation [2,3,4,5]. This led to the development of plenty of hydromorphological assessment protocols, which aim to follow the demands of the Water Framework Directive [6,7]. This awareness of the present low hydromorphological quality of river reaches stimulates a still increasing number of complex restoration projects in this part of the fluvial network [8]. However, mountain headwater streams of the first or second Strahler’s order are still rather on the boundary of interest regarding the possible human impact on their morphology or geomorphic processes. This may be caused by our general perception of mountains as islands of relatively preserved natural conditions in the context of European cultural landscapes. The second issue is usually the non-fish bearing character of these streams and thus, a lower motivation to sustain (or increase) their ecological quality. However, these relatively small streams constitute up to 80% of the total length of the drainage network and are responsible for the transfer of precipitation, sediments, organic matter, and nutrients from mountainous areas to downstream river reaches [9,10,11]. Moreover, we can expect a faster and larger morphological response from such small channels to alterations in sediment supply or hydrological regime when compared to large rivers, which underlines the vulnerability of headwater streams to changes of inner or outer boundary conditions (e.g., represented by decreased sediment production in the catchment area or construction of an in-channel structure) [11]. In this sense, it would be inconvenient to marginalize the possible impact of human activities on mountain headwater streams.
Human impact on fluvial systems can be perceived as indirect or direct [12]. The first group is represented by any human activity outside the river channel (i.e., in the whole catchment area), but with a potential to alter the fluxes of water, sediment, or organic matter (e.g., instream wood) to the channel. As a typical example, deforestation of the catchment may increase erosion and sediment supply to the channel, which subsequently leads to the channel aggradation and widening [13]. As for the second group, interventions in the channel such as construction of dams and weirs, straightening of the channel, or gravel extraction from the channel bed are among the common representatives of direct human impact. As a consequence, incision of the channel and sediment coarsening can be usually observed downstream of transverse structures impermeable for sediment transport, at the places of gravel extraction, and in the channels altered by artificial straightening and narrowing, whereas aggradation of sediments prevails upstream where the barriers for sediment transport [4,14,15]. In the context of mountain headwater streams, namely torrent control works are emblematic structures planned and built to control erosion processes and coarse sediment transport [16,17]. Indeed, individual agents often act simultaneously, which can amplify or reduce their impact on the resulting fluvial processes and the shaping of fluvial forms [18,19].
Based on the published materials and archival sources, this review article aims to summarize the past and present human pressure on mountain headwater streams that drain the highest mountain ranges of the Czech part of the Outer Western Carpathians under the concept of complex evolutionary trajectory. It attempts to demonstrate that although steep mountain headwater streams are generally perceived as “pristine streams” when compared relative to foothill or lowland rivers, various adjustments in geomorphological processes triggered by indirect and direct human activity can be expected in this part of a fluvial network. Finally, some implications for the processes of hydromorphological evaluation and restoration of mountain headwater streams are provided.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
This study primarily focuses on the headwater streams of the Moravskoslezské Beskydy Mountains (MSB), which represent the highest mountain range (up to 1328 m a.s.l.) of the Outer Western Carpathians in Czechia (Figure 1). Local temperate climate is one of the most humid in Central Europe, with an annual mean precipitation exceeding 1200 mm and the duration of snow cover exceeding 95 days annually [20]. Flood events are connected to long-term cyclonic precipitation or to convectional storms in the spring and summer months, whereas floods caused by snow melting are rare [21]. The highest flow during a common year usually occurs in spring owing to the combination of snow melting and rainfalls, but some channel reaches can indicate intermittent flow regime by their complete drying in July and August during relatively dry years [22]. The Mesozoic and Cenozoic flysch lithology predisposes the area to the frequent occurrence of various types of landslides [23,24]. Lack of in-channel boulders and the supply of relatively fine-sized material from adjacent hillslopes lead to frequent bedload transport in mountain streams [25,26]. This had led to the common occurrence of wandering river patterns in the foothills before extensive regulation works (e.g., channel straightening and narrowing, construction of grade-control structures, gravel extraction) in the 20th century, as was typical also for the Polish and Slovakian Carpathian foothills [27,28,29,30].
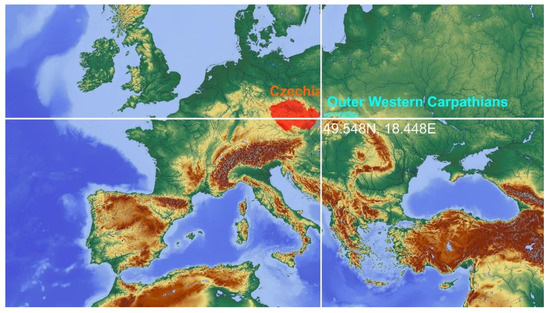
Figure 1.
Geographical position of the studied mountain range; the GPS coordinates correspond to the Lysá hora Mt., the highest peak (1328 m a.s.l.) of the Outer Western Carpathians in Czechia.
The first inhabitants came to the MBS during Wallachian colonization in 16–17th century, which led to intensive timber harvesting and spreading of pastures and meadows [31]. However, since the second half of the 19th century, this mountain range has been almost completely reforested [31,32]. The present forest canopy predominantly consists of monocultures of Norway spruce (Picea abies) and European beech (Fagus sylvatica) as a result of the rigid forest management. Although the MSB and surrounding mountain ranges are included in the Beskydy Protected landscape area (1160 km2) in the context of the Czech legislative, the areas without this strict forest management cover approximately only 320 km2 [33].
2.2. Data Sources
This review study summarizes and synthetizes the published material on fluvial geomorphic processes in the mountain catchments of this well-studied region and puts it into a broader context under the concept of the complex evolutionary trajectory. This concept emphasizes the fact that a river or stream represents a complex system which adjusts its morphology to variable boundary conditions over time, such as changes in flow and sediment fluxes [7,34]. To complete this inventory, the archival materials of the Czech Forests State Enterprise were studied with a primary focus on the construction of torrent control works during the 20th century to understand the extent and motivation of heavily managing a major part of the local fluvial network. Digitalized imprints of the Stable Cadastre (1826–1843; 1:2880 scale) and archival postcards mainly from the first half of the 20th century were among the additional sources of information about the historical evolution of land use and fluvial landscape (e.g., presence of instream wood or riparian vegetation).
3. Overview of Human Impact on Geomorphic Processes of Mountain Headwater Streams
3.1. Land Cover Changes
Historical changes of land cover produced alterations of the catchment-scale hydrologic processes and sediment supply into channels. The lowest terraces developed along some of the less steep headwater streams of the MSB are interpreted as legacy sediments due to slash-and-burn deforestation and intensive shepherd activity during the Wallachian colonization (16–17th century), which was supported by radiocarbon dating and pollen analysis of the terrace sediments [35,36]. Therefore, this colonization presents a beginning point of the human impact on the local headwater streams, although the aggradation tendencies might be accelerated by the effect of increased precipitation during the Little Ice Age [37]. Later, gradual reforestation after the abandonment of pastures and decreased demand for timber since the second half of the 19th century likely reduced the supply of sediments and related aggradation trends in the channels. For example, the forested area in the intramountain Slavíč catchment (18.4 km2) increased from 64% to 92% between the years of 1836 and 2006 [38], although extensive grazing activities persisted into the 20th century in some catchments, especially in the southern part of the MSB and neighboring mountain ranges (Figure 2a). As a result of the reforestation, nowadays we observe a gradual incision of the channels on the former floodplain, in some specific cases up to several meters [32,35]. However, there had been a lag response between the reforestation and decease of intensive bedload transport in the channels, and at least in the first half of the 20th century some of the streams were still quite overloaded by gravel- and cobble-sized sediments. These high bedload transport rates accompanied by large morphological changes in the active channels were likely the main motivation to plan and construct extensive torrent control works in the MSB during this time (Figure 2b,c). This is believed to be why many of these managed streams are nowadays incised down to the bedrock due to low sediment supply conditions in the present (for more details, see Section 3.3).
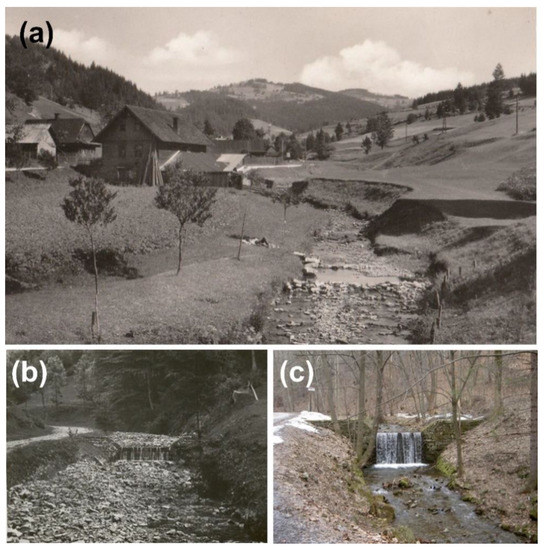

Figure 2.
Historical and present stages of headwater streams in relation to the sediment supply conditions: (a) pre-regulation state of the Pluskovec Stream without riparian vegetation as a result of shepherd activity (probably 1920s–1930s); contrast sediment loading of the headwater channel between (b) the 1920s and (c) the present (check dam in the Malý Lipový catchment).
The reforestation by monocultures (usually Norway spruce or European beech) has serious consequences for the recruitment and potential geomorphic function of instream wood. This rigid forest management leads to the lack of instream wood pieces in the channels as a result of timber harvesting activities, including riparian strips or removal of large wood from the channels, except some inaccessible steep valleys or nature reserves with a higher degree of protection. More than ten-fold lower volumes of instream wood were reported from the streams adjacent to managed forest when compared to those in unmanaged old-growth forests [39]. These small wood loads correlate with the low number of log steps as important morphologic features of instream wood in steep streams, which may otherwise stabilize stream longitudinal profiles and trap sediments (Figure 3). In the stream-draining managed forests, the mean log step frequency was 1.3 steps per 100 m channel length, whereas 3.0–5.6 steps per 100 m channel length were found in the streams located in old-growth forests located in nature reserves [40,41]. Moreover, the changed tree species composition led to different residence times of instream wood, while slower decay rates were expected for conifers [42].
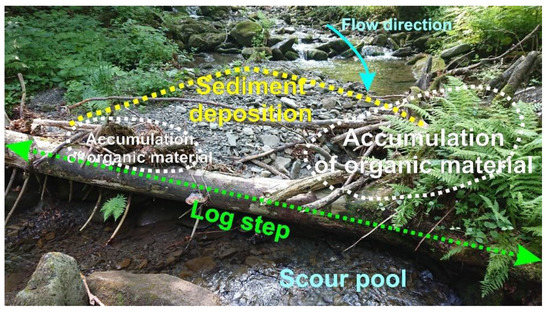
Figure 3.
Geomorphic impact of a log step in a stream surrounded by an unmanaged forest (the Satina catchment). Such log steps are rare in the streams surrounded by forests under intensive management.
3.2. Timber Floating
The first signs of direct human impact on the headwater streams can be related to timber floating, when the first splash dams were constructed at the turn of the 18th and 19th century (Figure 4a). A few of these dams allocated in the headwater segments were reconstructed in the past decades (Figure 4b), and now they serve as recreational facilities and refugia for amphibians, but many others are almost completely extinct. Timber was usually floated during snow melting (March or April) with additional supply of water from opened splash dams, which produced annual artificial flooding of many local channels until the Second World War [31]. Together with regulation works (removal of obstacles, cutting of riparian vegetation to increase access to the banks, or construction of stone embankments), such artificial floods likely produced accelerated erosion of the channels, and nowadays some local streams still indicate quite regular trapezoid cross-sectional profiles with low geomorphic heterogeneity of the channel bed.
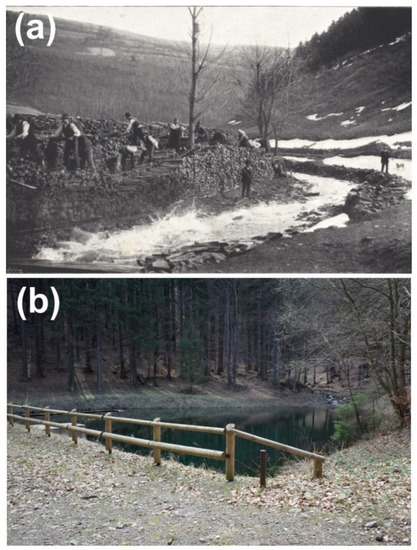

Figure 4.
Features connected with historical timber floating: (a) timber floating in Dolní Bečva in the 1890s, noting the lack of riparian vegetation on the stream banks (source: [43]), (b) splash dam Kyčerov, used for timber floating until the 1920s and completely reconstructed in the 2010s (reservoir capacity is 1500 m3).
3.3. Torrent Control Works
The first complex torrent control works were planned and built in the MSB at the beginning of the 20th century, when previous experiences coming from the Austrian Alps were fully adapted for local medium-high mountain settings [44]. These torrent control works consisted of (i) up to several meters-high retention check dams in the uppermost parts of steep streams or in deeply incised gullies, (ii) lower-grade control structures downstream, and (iii) bank reinforcement by ripraps. The spatial extend of these structures along the managed stream longitudinal profile depends on the channel slope and protection aims, while a closer spacing of check dams (up to 20 transversal structures per 1 km stream length) with artificial embankments frequently occurs at lower channel slopes about 2–3% [45]. Nowadays, these measures are widespread in mountain channels of the MSB and practically all catchments with ≥1–2 km2 area are managed by sediment and/or erosion control structures (see examples on Figure 5 and Figure 6). While (i) are used to decrease bedload transport rates by trapping sediments during flood events, (ii) and (iii) control vertical and lateral channel stability. Therefore, a different response to fluvial processes and resulting morphology is expected in the dependence of the structures, original channel geometry (mainly bed slope), and catchment-scale sediment supply [46]. Namely, the decreased bed sediment heterogeneity due to missing coarse fractions (trapped by retention structures) was measured in a steep stream (channel slope ±10%) with higher check dams, which was demonstrated by better sediment sorting in comparison with an unimpacted stream. Cross-sectional and longitudinal heterogeneity was degraded in a managed foothill stream with channel slope about 2% and presence of additional bank stabilizations, which corresponds to the geometric simplification of cross-sectional and longitudinal profiles [39]. This alteration of channel morphology accompanied by the loss of a mosaic of bedforms, and armoring processes of the channel bed produce an acceleration of downstream sediment transport due to low channel roughness and limited space for the development of bar deposits [47].
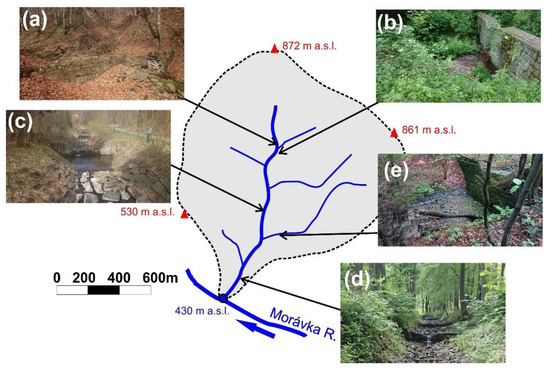
Figure 5.
Examples of the torrent control works in the Vysutý catchment (catchment area is 2.47 km2): (a) remnants of the old retention check dam, (b) ca. 2.5 m-tall new retention check dam built in 2011, (c) ca. 1.0–1.5 m-tall grade control structures, (d) low bed sills in the downstream part, (e) 3 m-tall retention check dam in the small recipient.
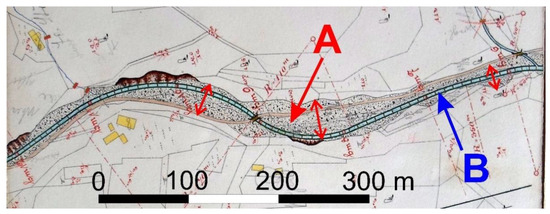
Figure 6.
The first construction plan of the torrent control works in the Vysutý from the beginning of the 20th century as an illustrative example of the morphological alteration of local mountain headwater streams. Original active channel with extensive gravel and cobble out-of-channel deposits ((A) the red arrows show the extend of the deposits) was replaced by a narrow (~5 m) channel stabilized by a dense sequence of grade control structures (B).
Furthermore, note that many torrent control works have recently been abandoned and at various stages of destruction, which is a similar trend across many European mountain ranges [16,48]. Therefore, the morphological response of the streams is also dependent on the present stage of torrent control works and their maintenance (e.g., Figure 5a). For example, a decrease of check dam height by erosion of its crest may increase bedload transport rates by increasing the bed slope upstream the crest or evacuation of stored sediments. Similarly, gradual destruction of artificial embankments leads to a gradual restoration of sediment connectivity between the channel and adjacent hillslope.
The specific interventions are crossings of streams by forest roads, which are usually realized by the construction of culverts. The local road density is relatively high (up to 3 km per 1 km2), which is related to the intensive forest management [44]. Recent observations documented a frequent underestimation of the culverts’ capacity during high flows, which causes their frequent clogging, sediment accumulation upstream, and propagation of channel incision several ten meters downstream from the crossings [49]. In the perspective of flood risk, these alterations produce overbank flows and occasional flooding of forest roads and damages of culverts by their undermining [50]. Moreover, erosion of unpaved forest roads has been recognized as an important source of suspended sediments for local streams during surface runoff events [51].
3.4. The Complex Evolutionary Trajectory of Mountain Headwater Streams
Of the documented examples of geomorphologically effective human alterations of mountain headwater catchments and based on this list, it can be inferred that even small steep catchments in Central Europe cannot be perceived as completely pristine landscapes in view of fluvial processes and resulting channel morphologies. Figure 7 aims to summarize the main human-induced driving factors on the morphology of the studied streams based on the concept of the complex evolutionary trajectory, but the specific response in the individual catchment (i.e., the intensity or duration of the aggradation and degradation trends in the channel) will differ in relation to the timing and intensity of these interventions and the position of the reach within the fluvial continuum (i.e., greater aggradation can be expected in the less confined valleys). This implies recent general degradation of headwater channel reaches as the consequence of management practices, which alter catchment-scale sediment fluxes and limit recruitment of large wood. The list of alterations does not include some representatives of a rather wider regional indirect human impact such as the occurrence of acid rains produced by industrial complexes (iron works, power plants), which caused decease of forest in some ridge parts of the MSB and other mountains in Czechia in the 1970s and 1980s or a bark beetle calamity, which led to the contemporary collapse of local spruce monocultures in the last few years. Indeed, both forest disturbances may produce increased sediment supply in some catchments by temporary loss of vegetation cover. Moreover, global climate change driven by human-induced emissions of greenhouse gases impacts the precipitation regime and evapotranspiration, which, among other things, alters flood magnitudes as drivers of sediment transport and morphological changes [52].
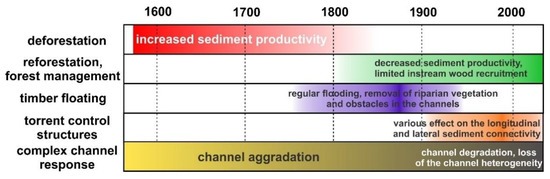
Figure 7.
General response of mountain headwater channels in the studied region to the main human interventions.
Intensive anthropogenic pressure on headwater streams in the MSB began in the 16th century during a colonization of the mountains, which was quite late in the context of other small European catchments affected by ancient or medieval deforestation [53,54] or mining activities [55]. However, a similarity of the main driving factors can be found across the European mountains, where the phase of general deforestation with timber exploitation (sometimes connected also with timber floating) and agricultural practices was replaced by depopulation of mountainous areas and spontaneous reforestation [53,55,56,57,58]. These variations in land cover and land use were reflected in the sediment fluxes and morphodynamics of headwater streams by the gradual transition from rich sediment supply conditions to a decrease in sediment productivity. Some European mountain ranges (e.g., Italian Alps, French Prealps, or White Mountains in Crete, Greece) have undergone repeated cycles of deforestation and reforestation in relation to the historic fluctuations in demographic, political, and cultural aspects [53,57,59]. Moreover, many of the small mountain catchments have recently been impacted by the presence of check dams and additional in-channel structures to control downstream sediment transport rates and channel morphodynamics [16,58,60], although not all of these structures are nowadays regularly maintained. Note that the morphological response of the channels can be of different intensity across Europe, which is dictated by various hydrological regimes (e.g., rather semiarid conditions of Southern Europe vs. the mild wet climate of Central Europe) and the resistance of lithology (e.g., unconsolidated sediments or soft flysch vs. resistant crystalline rocks). Moreover, some other unmentioned human activities (e.g., prescribed fires) occur in specific or spatially limited areas, but they may influence the hydrological or sediment regimes of mountain catchments as well [61].
3.5. Implications for of Hydromorphological Assessment and Restoration of Mountain Headwater Streams
Fast and simultaneously extensive responses to the change of boundary conditions and missing floodplain segments in the case of strictly confined valleys belong to the main specifics of mountain headwater streams in the context of their hydromorphological quality and evaluation [35,62]. In addition, one should consider large variations in channel-reach morphologies of headwater streams, which arises from the (dis)balance between the sediment supply (i.e., frequency, magnitude, and grain size) and the transport capacity (frequency and magnitude of transport events such as floods or debris flows) with the additional impact of vegetation (primarily the presence of instream wood) [63,64,65]. For example, the occurrence of plane beds with prominently low channel heterogeneity can correspond to unaltered natural conditions of the balanced sediment supply and transport capacity as well as to the degradation of the channel reach between subsequent consolidation check dams [47,64,66]. Therefore, hydromorphological assessments of mountain headwater streams have to precisely focus on the cause-response links at the catchment scale, when detailed fluvial geomorphic mapping and analysis of historical sources (e.g., old maps and aerial photos to assess land cover changes, documentation about flood events) is necessary to put the present ‘snapshot’ of the evaluated channel reach into wider spatial and temporal context. Such a procedure does not substantially differ from the modern process-based hydromorphological assessment protocols, which are generally based on the evaluation of temporal morphological variability to delimit current morphological conditions or to determine future channel evolution [6,7].
With particular reference to the land cover of mountain catchments, it is highly unlikely that the planting of trees will be stopped in the future and thus, that we will reach pre-settlement, old-growth forest conditions. Similarly, some degree of protection against large morphological changes or intensive bedload transport during extraordinary flood pulses is often necessary in inhabited mountain valleys. It implies that the management effort should be concentrated to achieve realistic restoration targets under the present socioeconomic circumstances. Nevertheless, there are still several ways how we can significantly improve the hydromorphological quality of mountain headwater streams by (at least partially) restoration of fluvial processes, for example:
- Restoration of downstream sediment connectivity as much as possible by removal of longitudinal barriers (check dams, unfitted culverts) or artificial embankments, but with careful evaluation of possible flood risk in the inhabited valleys and alluvial cones;
- protection of riparian tree buffers and thus, improvement of the potential for instream wood recruitment and its consequent geomorphic function in the channels;
- complex restoration of managed and/or degraded channel reaches by addition of instream wood elements or close-to-natural-grade control structures that mimic natural step-pool morphology [67,68].
4. Conclusions
On the example of the highest parts of the Outer Western Carpathians in Czechia, this review demonstrated that even headwater mountain streams cannot be considered as really unaltered by human impact in the context of the European cultural landscape. Moreover, there is usually more than a single alteration, which implies the complex morphological response of these small streams. Mountain headwater streams are key, but sometimes undervalued elements of the fluvial continuum and more conservation efforts should be put on this part of the fluvial network. Although it is practically impossible to restore pristine pre-settlement conditions in European mountains, there still exists the potential to substantially improve the hydromorphological state of small mountain streams by the implementation of complex restoration measures, which take into consideration the present socioeconomic circumstances and requirements of targeted aquatic species for their habitats. Crucially, any process-based restoration efforts should take into account the natural morphodynamics of mountain streams, namely, their fast and extensive morphological response to the changes of boundary conditions or individual disturbances.
Funding
This research was funded by the Grant competition of the University of Ostrava, grant number 10/PrF/2021.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank four anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments which significantly helped to improve the initial version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Tieskens, K.; Schulp, C.J.; Levers, C.; Lieskovský, J.; Kuemmerle, T.; Plieninger, T.; Verburg, P. Characterizing European cultural landscapes: Accounting for structure, management intensity and value of agricultural and forest landscapes. Land Use Policy 2017, 62, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurnell, A.; Surian, N.; Zanoni, L. Multi-thread river channels: A perspective on changing European alpine river systems. Aquat. Sci. 2009, 71, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollero, A. Channel changes and floodplain management in the meandering middle Ebro River, Spain. Geomorphology 2010, 117, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdukiewicz, H.; Wyżga, B.; Zawiejska, J. Twentieth-century hydromorphological degradation of Polish Carpathian rivers. Quat. Int. 2019, 504, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Blanka, V. River channel response to climate- and human-induced hydrological changes: Case study on the meandering Hernád River, Hungary. Geomorphology 2012, 175, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belletti, B.; Rinaldi, M.; Buijse, A.D.; Gurnell, A.M.; Mosselman, E. A review of assessment methods for river hydromorphology. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 73, 2079–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, M.; Surian, N.; Comiti, F.; Bussettini, M. A methodological framework for hydromorphological assessment, analysis and monitoring (IDRAIM) aimed at promoting integrated river management. Geomorphology 2015, 251, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhar, S.; Januschke, K.; Kail, J.; Poppe, M.; Schmutz, S.; Hering, D.; Buijse, A.D. Evaluating good-practice cases for river restoration across Europe: Context, methodological framework, selected results and recommendations. Hydrobiologia 2016, 769, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benda, L.; Hassan, M.A.; Church, M.; May, C.L. Geomorphology of Steepland Headwaters: The Transition from Hillslopes to Channels. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2005, 41, 835–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wipfli, M.S.; Richardson, J.; Naiman, R.J. Ecological Linkages Between Headwaters and Downstream Ecosystems: Transport of Organic Matter, Invertebrates, and Wood Down Headwater Channels. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohl, E. The significance of small streams. Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 11, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohl, E. Human impacts to mountain streams. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 217–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, M. Channel processes following land use changes in a degrading steep headwater stream in North Island, New Zealand. Geomorphology 2006, 81, 421–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M. PROFILE: Hungry Water: Effects of Dams and Gravel Mining on River Channels. Environ. Manag. 1997, 21, 533–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liro, M.; Ruiz-Villanueva, V.; Mikuś, P.; Wyżga, B.; Castellet, E.B. Changes in the hydrodynamics of a mountain river induced by dam reservoir backwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piton, G.; Carladous, S.; Recking, A.; Tacnet, J.M.; Liébault, F.; Kuss, D.; Quefféléan, Y.; Marco, O. Why do we build check dams in Alpine streams? An historical perspective from the French experience. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2016, 42, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombino, G.; Gurnell, A.; Tamburino, V.; Zema, D.; Zimbone, S.M. Sediment size variation in torrents with check dams: Effects on riparian vegetation. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 32, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpak, J. Assessment of Changes in Channel Morphology in a Mountain River Regulated Using Grade Control Structures. J. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 21, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortugno, D.; Boix-Fayos, C.; Bombino, G.; Denisi, P.; Rubio, J.M.Q.; Tamburino, V.; Zema, D.A. Adjustments in channel morphology due to land-use changes and check dam installation in mountain torrents of Calabria (southern Italy). Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 2469–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolasz, R.; Miková, T.; Valeriánová, A.; Voženílek, V. Climate Atlas of Czechia; Czech Hydrometeorological Institute and Palacký University in Olomouc: Olomouc, Czechia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Šilhán, K. Frequency, predisposition, and triggers of floods in flysch Carpathians: Regional study using dendrogeomorphic methods. Geomorphology 2015, 234, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bíba, M.; Oceánská, Z.; Vícha, Z.; Jařabáč, M. Lesnicko-hydrologický výzkum v Beskydských experimentálních povodích. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2006, 54, 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- Břežný, M.; Pánek, T. Deep-seated landslides affecting monoclinal flysch morphostructure: Evaluation of LiDAR-derived topography of the highest range of the Czech Carpathians. Geomorphology 2017, 285, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šilhán, K.; Tichavský, R.; Fabiánová, A.; Chalupa, V.; Chalupová, O.; Škarpich, V.; Tolasz, R. Understanding complex slope deformation through tree-ring analyses. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galia, T.; Škarpich, V. Do the coarsest bed fractions and stream power record contemporary trends in steep headwater channels? Geomorphology 2016, 272, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galia, T.; Škarpich, V.; Hradecký, J. Connectivity of the coarsest fraction in headwater channels: Imprints of fluvial processes and debris-flow activity. Geogr. Ann. Ser. A Phys. Geogr. 2015, 97, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyżga, B.; Zawiejska, J.; Hajdukiewicz, H. Multi-thread rivers in the Polish Carpathians: Occurrence, decline and possibilities of restoration. Quat. Int. 2016, 415, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidová, A.; Radecki-Pawlik, A.; Rusnák, M.; Plesiński, K. Hydromorphological evaluation of the river training impact on a multi-thread river system (Belá River, Carpathians, Slovakia). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Škarpich, V.; Galia, T.; Hradecký, J. Channel Bed Adjustment to Over Bankfull Discharge Magnitudes of the Flysch Gravel-Bed Stream—Case Study from the Channelized Reach of the Olše River (Czech Republic). Z. Geomorphol. 2016, 60, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škarpich, V.; Kašpárek, Z.; Galia, T.; Hradecký, J. Antropogenní impakt a jeho odezva v morfologii koryt beskydských štěrkonosných toků: Příkladová studie řeky Ostravice, Česko. Geografie 2016, 121, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polášek, J. Tradice Výroby a Zpracování železa v Beskydech a Pobeskydí: Plavení Dřeva a Zaniklé výrobní Objekty v Oblasti Moravskoslezských a Slezských Beskyd; Muzeum Beskyd: Frýdek-Místek, Czech Republic, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Škarpich, V.; Hradecký, J.; Tábořík, P. Structure and genesis of the quaternary filling of the Slavíč River valley (Moravskoslezské Beskydy Mts., Czech Republic). Morav. Geogr. Rep. 2011, 19, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Nature Conservation Agency of the Czech Republic. Available online: https://beskydy.ochranaprirody.cz/ (accessed on 15 May 2021).
- Brierley, G.J.; Fryirs, K.A. The Use of Evolutionary Trajectories to Guide ‘Moving Targets’ in the Management of River Futures. River Res. Appl. 2015, 32, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlapáková, L.; Pánek, T.; Horáčková, Š. Holocene fluvial terraces reveal landscape changes in the headwater streams of the Moravskoslezské Beskydy Mountains, Czechia. Geomorphology 2021, 377, 107589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wistuba, M.; Sady, A.; Poręba, G. The impact of Wallachian settlement on relief and alluvia composition in small valleys of the Carpathian Mts. (Czech Republic). Catena 2018, 160, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galia, T.; Škarpich, V. Morfologická odezva bystřinných koryt na dlouhodobé zásahy člověka v horských povodích na příkladu Moravskoslezských Beskyd (Česko). Geogr. CGS 2017, 122, 213–235. [Google Scholar]
- Voznicová, T. Changes in the Land Use in the Cadastral Territory of Morávka; University of Ostrava: Ostrava, Czech, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Galia, T.; Škarpich, V.; Ruman, S.; Macurová, T. Check dams decrease the channel complexity of intermediate reaches in the Western Carpathians (Czech Republic). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galia, T. Controls on log step occurrence in steep headwater streams draining Carpathian managed forests. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 120, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galia, T.; Ruiz-Villanueva, V.; Tichavský, R.; Šilhán, K.; Horacek, M.; Stoffel, M. Characteristics and abundance of large and small instream wood in a Carpathian mixed-forest headwater basin. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 424, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galia, T.; Šilhán, K.; Ruiz-Villanueva, V.; Tichavský, R.; Stoffel, M. Temporal dynamics of instream wood in headwater streams draining mixed Carpathian forests. Geomorphology 2017, 292, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Album Valašska; Odbor Klubu Českých Turistů: Štramberk, Czech Republic, 1898.
- Jařabáč, M.; Bělský, J. The protection against floods becomes effective in the Beskydy Mts. using forest hydrology. Časopis Beskydy 2008, 1, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Galia, T.; Škarpich, V. Response of Bed Sediments on the Grade-Control Structure Management of a Small Piedmont Stream. River Res. Appl. 2016, 33, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, L.; Comiti, F.; Crema, S.; Cavalli, M. Channel control works and sediment connectivity in the European Alps. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galia, T.; Škarpich, V.; Ruman, S. Impact of check dam series on coarse sediment connectivity. Geomorphology 2021, 377, 107595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zema, D.A.; Bombino, G.; Denisi, P.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Zimbone, S.M. Evaluating the effects of check dams on channel geometry, bed sediment size and riparian vegetation in Mediterranean mountain torrents. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galia, T.; Šilhán, K.; Škarpich, V. The geomorphic impacts of culverts at paved forest roads: Examples from Carpathian headwater channels, Czech Republic. Catena 2017, 157, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galia, T.; Hradecký, J.; Škarpich, V. Sediment Transport in Headwater Streams of the Carpathian Flysch Belt: Its Nature and Recent Effects of Human Interventions. In Sediment Matters; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 13–26. ISBN 9783319146966. [Google Scholar]
- Buzek, L. Plaveninový režim jako ukazatel intenzity vodní eroze v horských zalesněných povodích (na příkladu Moravskoslezských Beskyd). J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2004, 52, 24–40. [Google Scholar]
- Blöschl, G.; Hall, J.; Viglione, A.; Perdigão, R.A.P.; Parajka, J.; Merz, B.; Lun, D.; Arheimer, B.; Aronica, G.T.; Bilibashi, A.; et al. Changing climate both increases and decreases European river floods. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 573, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comiti, F. How natural are Alpine mountain rivers? Evidence from the Italian Alps. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2011, 37, 693–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A. Coupling between hillslopes and channels in upland fluvial systems: Implications for landscape sensitivity, illustrated from the Howgill Fells, northwest England. Catena 2001, 42, 225–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek, K.; Latocha, A. Response of small mid-mountain rivers to human impact with particular reference to the last 200 years; Eastern Sudetes, Central Europe. Geomorphology 2007, 92, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucała, A. The impact of human activities on land use and land cover changes and environmental processes in the Gorce Mountains (Western Polish Carpathians) in the past 50 years. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 138, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liébault, F.; Gomez, B.; Page, M.; Marden, M.; Peacock, D.; Richard, D.; Trotter, C.M. Land-use change, sediment production and channel response in upland regions. River Res. Appl. 2005, 21, 739–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preciso, E.; Salemi, E.; Billi, P. Land use changes, torrent control works and sediment mining: Effects on channel morphology and sediment flux, case study of the Reno River (Northern Italy). Hydrol. Process. 2011, 26, 1134–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherden, M.A.; Hall, J.A. Human impact on vegetation in the White Mountains of Crete since AD 500. Holocene 1999, 9, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombino, G.; Gurnell, A.M.; Tamburino, V.; Zema, D.A.; Zimbone, S.M. Adjustments in channel form, sediment calibre and vegetation around check-dams in the headwater reaches of mountain torrents, Calabria, Italy. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimas, K.; Hiesl, P.; Hagan, D.; Park, D. Prescribed fire effects on sediment and nutrient exports in forested environments: A review. J. Environ. Qual. 2020, 49, 793–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, M.; Surian, N.; Comiti, F.; Bussettini, M.; Belletti, B.; Nardi, L.; Lastoria, B.; Golfieri, B. Guidebook for the Evaluation of Stream Morphological Conditions by the Morphological Quality Index (MQI), Deliverable 6.2, Part. 3, of REFORM (REstoring Rivers FOR Effective Catchment Management), a Collaborative Project (Large-Scale Integrating Project) Funded by the European Commission within the 7th Framework Programme under Grant Agreement 282656, European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2015.
- Galia, T.; Hradecký, J. Channel-reach morphology controls of headwater streams based in flysch geologic structures: An example from the Outer Western Carpathians, Czech Republic. Geomorphology 2014, 216, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.R.; Buffington, J.M. Channel-reach morphology in mountain drainage basins. GSA Bull. 1997, 109, 596–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palucis, M.C.; Lamb, M.P. What controls channel form in steep mountain streams? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 7245–7255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comiti, F.; Mao, L.; Lenzi, M.A.; Siligardi, M. Artificial steps to stabilize mountain rivers: A post-project ecological assessment. River Res. Appl. 2009, 25, 639–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.-A.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Zhang, K.; Duan, X.; Chang, T.-C. Restoration of an incised mountain stream using artificial step-pool system. J. Hydraul. Res. 2010, 48, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzi, M.A. Stream bed stabilization using boulder check dams that mimic step-pool morphology features in Northern Italy. Geomorphology 2002, 45, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).