Hydrogeology of Reclaimed Floodplain in A Permafrost Area, Yakutsk, Russia
Abstract
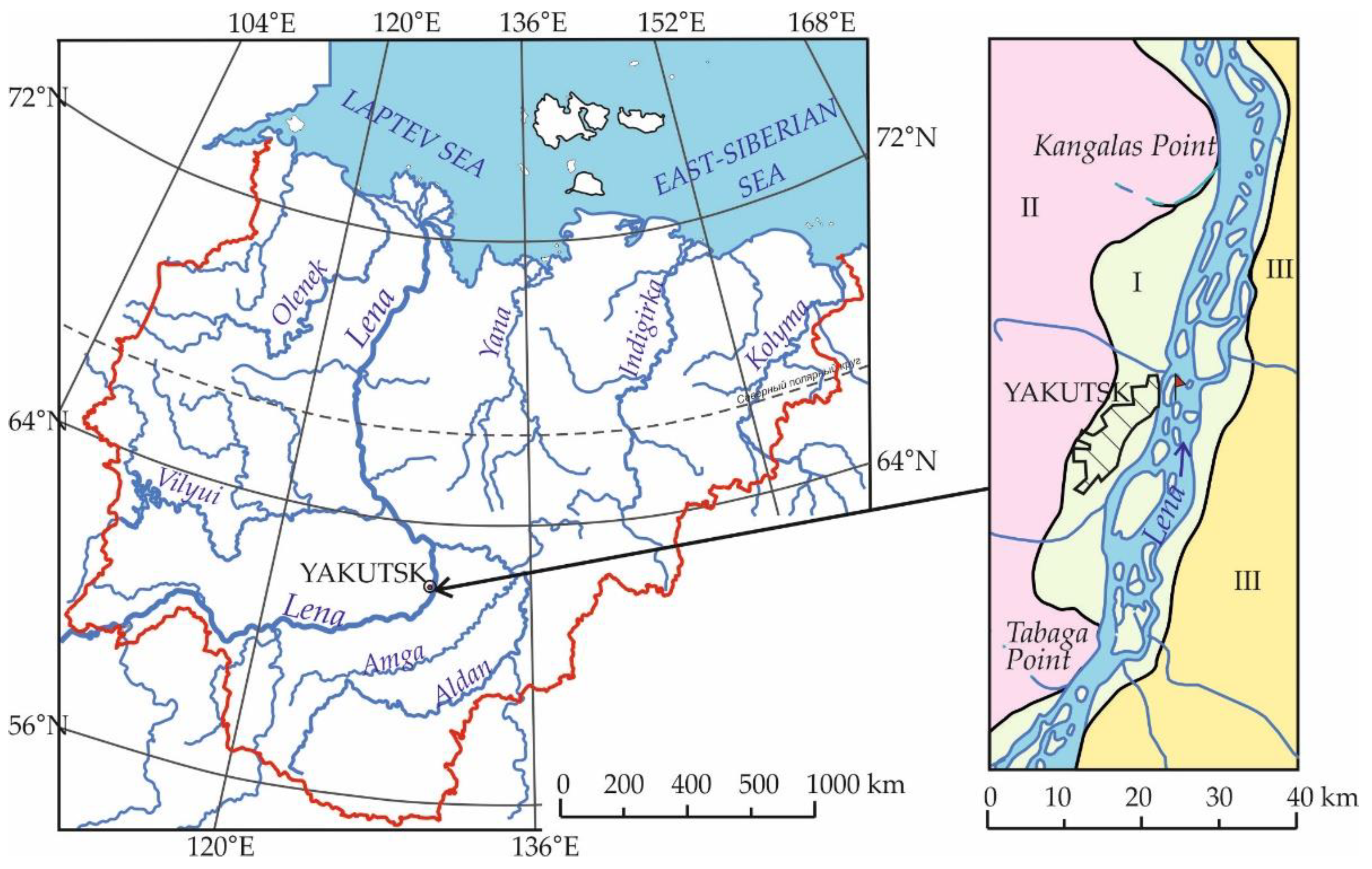
1. Introduction
2. Problem Statement
3. Methods
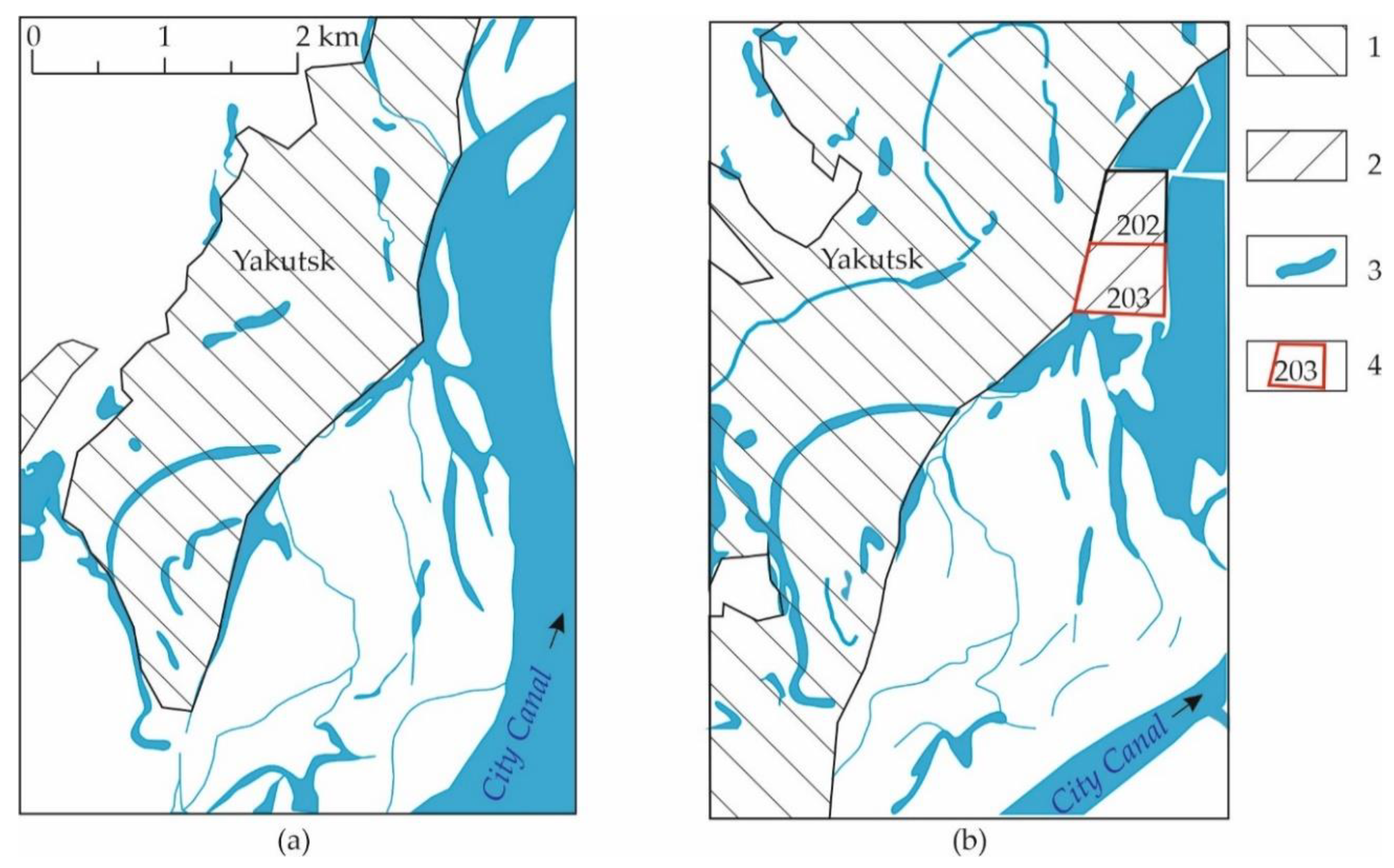
4. Natural and Modified Environmental Characteristics of the Floodplain Area
5. Results
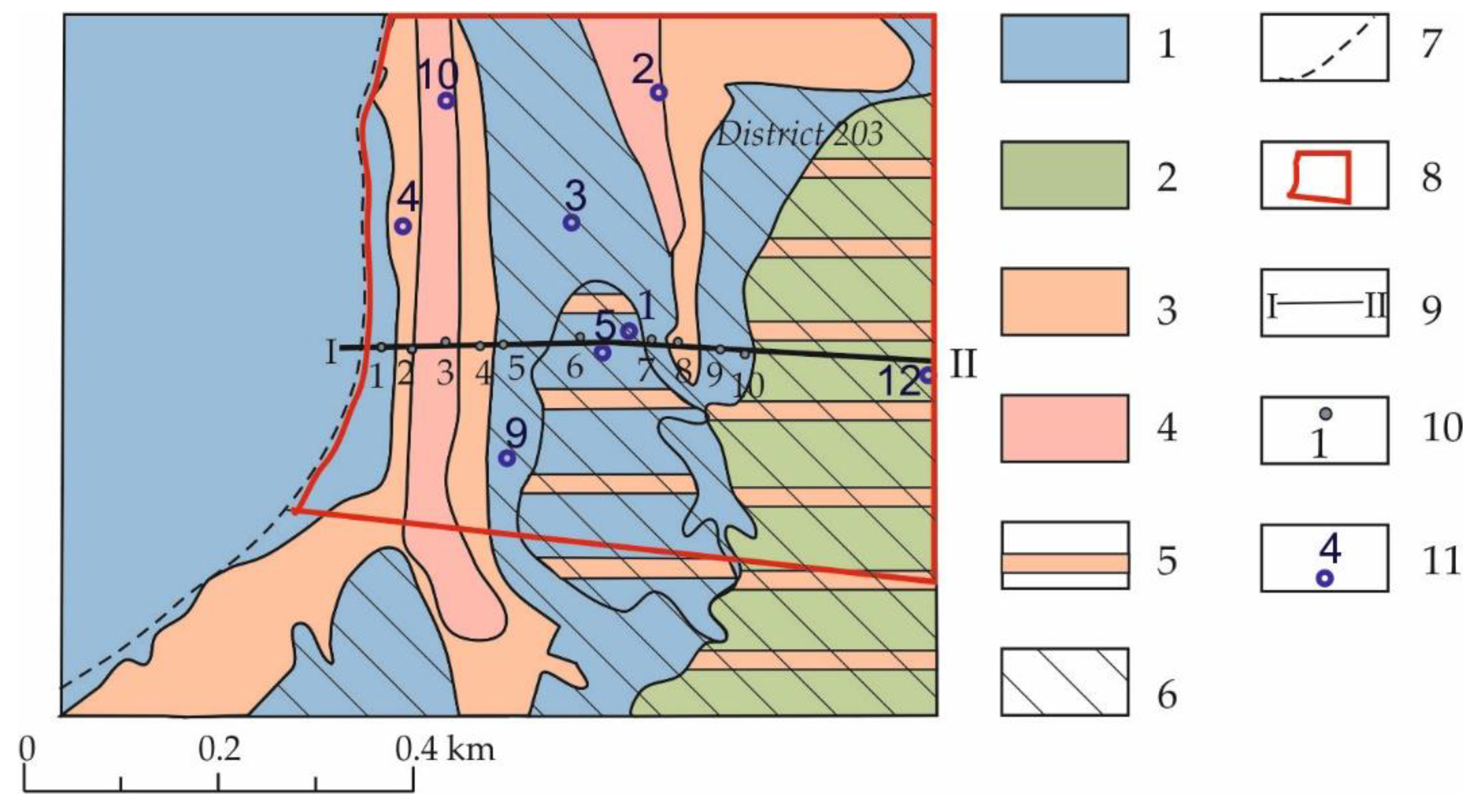
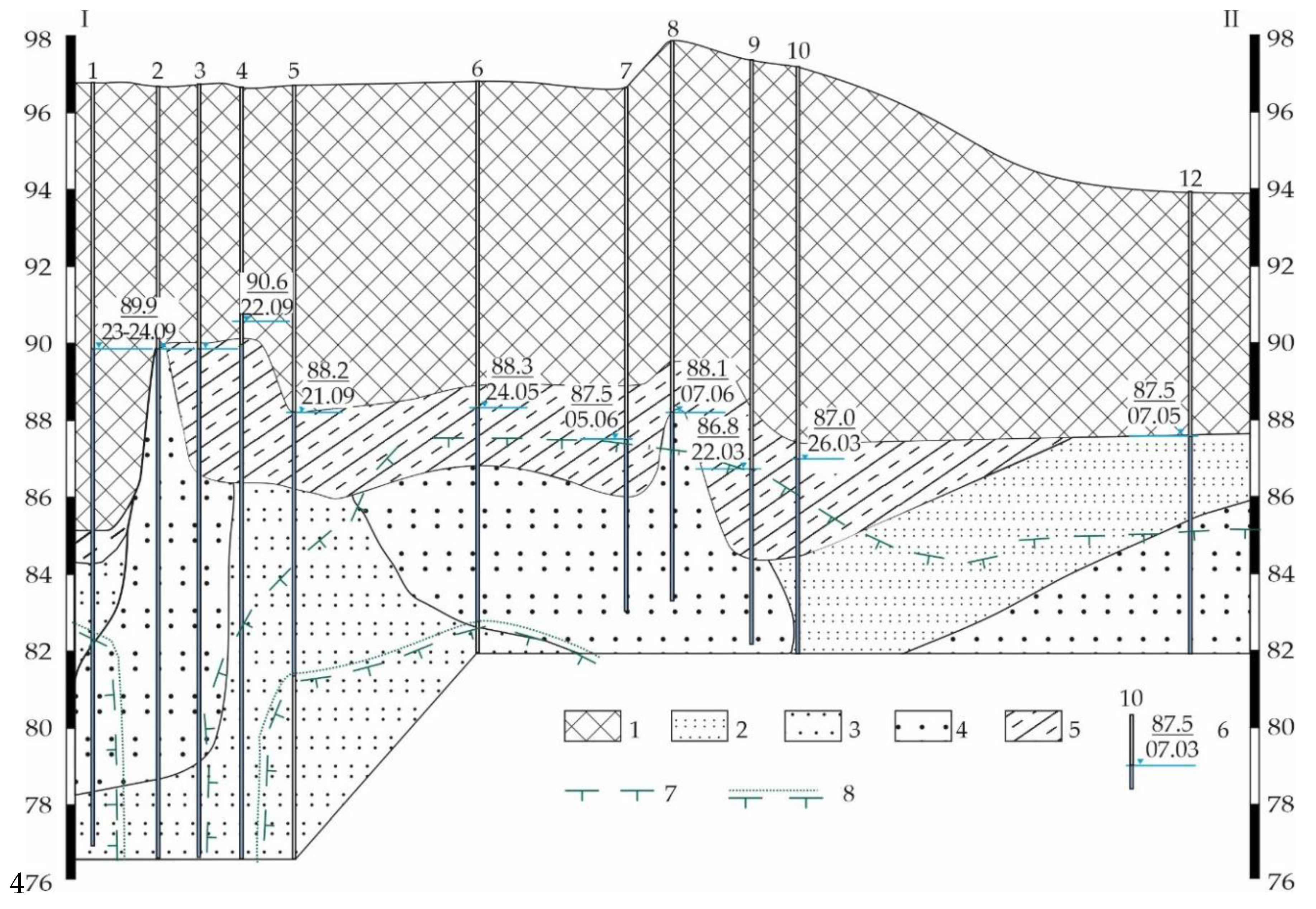
5.1. Permafrost Conditions
5.2. Groundwater Levels
5.3. Chemistry of Surface and Subsurface Waters
6. Discussion
6.1. The Reasons for Talik Preservation in the Reclaimed Floodplain
6.2. Soil Saturation Mechanisms
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoff, J.; Nooy van der Kolff, A. (Eds.) Hydraulic Fill Manual: For Dredging and Reclamation Works; CRC Press: London, UK, 2012; p. 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, D.; Chen, R.; Meadows, M.E.; Choi, Y.R.; Banerjee, A.; Zilong, X. Mapping Trajectories of Coastal Land Reclamation in Nine Deltaic Megacities using Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminskaya, V.I. The main features of designing and building the hydraulic-fill territories for the offshore passenger terminal in Saint Petersburg. Gornyi Informatsionno-Analiticheskii Bulleten 2009, 1, 444–451. [Google Scholar]
- Zharkova, N.I.; Cherniichuk, G.A.; Zharkov, I.Y.; Galeev, R.K. Artificial soils in Kazan: Features of composition formation, structure and properties. Uchenye Zapiski Kazanskogo Universiteta 2013, 155, 130–143. [Google Scholar]
- Preobrazhenskii, A.A.; Kanakov, G.V. The problems and prospects of construction in reclaimed floodplain in Nizhny Novgorod region. In Mezhvuzovskii Sbornik Statei Laureatov Konkursov, 12th ed.; Nizhny Novgorod State University of Architecture and Civil Engineering: Nizhny Novgorod, Russia, 2010; pp. 86–88. [Google Scholar]
- Dimuhametov, M.S.; Dimuhametov, D.M. Physico-mechanical properties of the peaty soils of the Kama valley of Perm city and their changes as a result of loading action. Vestnik Permskogo Universiteta 2009, 11, 94–107. [Google Scholar]
- Chistobaev, A.I.; Visleneva, O.A. Is there land shortage for urban development in Russia? Regionalnaya Ekologiya 2013, 1–2, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kaminskaya, V.I. Design Optimization of Solutions and Technologies for the Construction of Hydraulic-Fill Structures; Stroyizdat North-West: Saint Petersburg, Russia, 2011; p. 163. [Google Scholar]
- Kovrov, O.S.; Prychyna, K.S. Slope stability assessment of hydraulic-fill soil dams and fill-up embankments. Naukovyi Visnyk Natsionalnoho Hirnychoho Universytetu 2017, 6, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Tezcan, S.O.; Bhatia, S.K.; Fiegle, S. Seismic Stability and Rehabilitation Analysis of a Hydraulic Fill Dam. In Proceedings of the International Conferences on Recent Advances in Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering and Soil Dynamics, San Diego, CA, USA, 26–31 March 2001; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- Ogorodnikova, E.N.; Nikolaeva, S.K. Geocological features of land reclaimed by hydraulic filling. In Proceedings Sergeevskie Chteniya. Engineering Geology and Environmental Geoscience. Fundamental Problems and Applied Task; RUDN Press: Moscow, Russia, 2016; Volume 18, pp. 331–335. [Google Scholar]
- Kitze, F.F.; Simoni, O.W. An Earth Fill Dam on Permafrost, Hess Creek Dam, Livengood, Alaska; Technical Report No. 196; U.S. Army Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory: Hanover, NH, USA, 1972; pp. 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, D.E.; McRae, T.E. Densification of Submarine Hydraulic Fills. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 6–9 May 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konovalov, P.A.; Kushnir, S.Y. Hydraulic Fill Ground as the Foundation of Structures; Nedra: Moscow, Russia, 1991; p. 256. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, L.T.; Tsernant, A.A.; Poleshchuk, V.L.; Tseeva, A.N.; Levanov, N.I. Construction on Hydraulic Fills on Permafrost; Publishing House Economics, Construction, Transport: Moscow, Russia, 2008; p. 323. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.V.; Kuzmin, G.P. Alluvial hydraulic engineering constructions in the permafrost area of Russia: Experience of construction, problems and possibilities of use of borehole hydroproduction. Nauka Obrazovanie 2015, 2, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Recommendations for Engineering and Geological Surveys and Design of Buildings and Structures Foundations on Hydraulic-Fill Tterritories; NIIOSP: Moscow, Russia, 1985; p. 38.
- Soil Bases and Foundations on Permafrost; SP 25.13330.2012; NIIOSP: Moscow, Russia, 2012; p. 236.
- Poleschuk, V.L. Creation of building sites on permafrost by hydraulic filling. In Proceedings, Workshop on Productive Forces Development in the Yakut ASSR; Yakutsk Book Publishing House: Yakutsk, Russia, 1981; pp. 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, L.T.; Poleschchuk, V.L.; Tseeva, A.N.; Ignatova, G.M.; Egorov, G.E. Securing reliability of building on silt soils in the permafrost zone (on the example of Yakutsk). Kriosfera Zemli 1998, 2, 72–81. [Google Scholar]
- Shesternev, D.M.; Zhang, R.V.; Kuzmin, G.P.; Shepelev, V.V.; Pavlova, N.A.; Popenko, F.E. Industrial and residential construction on hydraulic fill in permafrost regions; problems and prospects. J. Eng. Heilongjiang Univ. 2014, 5, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syromyatnikov, I.I.; Kunitsky, V.V. Features of the temperature regime of dredged sands in District 202. In Proceedings, VIII Russian Scientific and Practical Conference “Geology and Mineral. Resources of North.-East. Russia”; Melnikov Permafrost Institute SB RAS Press: Yakutsk, Russia, 2018; Volume 2, pp. 282–285. [Google Scholar]
- Ogonerov, V.V.; Pavlova, N.A.; Danzanova, M.V. Hydrogeology of Reclaimed Floodplains in Permafrost Areas: A Case Study of Yakutsk. In Proceedings, International Youth Scientific Conference “Environmental Problems of Nature and Subsoil Use”, 2nd ed.; Kurylenko, V.V., Ed.; St. Petersburg State University: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2019; Volume 19, pp. 264–268. [Google Scholar]
- Spektor, V.V.; Bakulina, N.T.; Spektor, V.B. Landforms and age of alluvium in the Lena valley in “Yakutsky Razboi”. Geomorfologiya 2008, 1, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Balobaev, V.T.; Ivanova, L.D.; Nikitina, N.M.; Shepelev, V.V.; Lomovtseva, N.S.; Skutin, V.I. Ground Water in Central Yakutia and Its Prospective Use; SB RAS Press, Geo Branch: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2003; p. 137. [Google Scholar]
- Syromyatnikov, I.I.; Fedorov, A.N.; Kunitsky, V.V.; Dorofeev, I.V. Permafrost rocks in Yakutsk. In Applied Ecological Problems in Yakutsk; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2017; pp. 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Shepelev, V.V. Suprapermafrost Waters in the Cryolithozone; Academic Publishing House “Geo”: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2011; p. 167. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlova, N.A.; Danzanova, M.V.; Serikov, S.I. Assessment of anthropogenic effect on surface ponding and hydrochemical conditions in the city of Yakutsk. Geoekologiya 2014, 3, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Bochever, F.M.; Garmonov, I.V.; Lebedev, A.V.; Shestkov, V.M. Fundamentals of Hydrogeological Analyses; Nedra: Moscow, Russia, 1969; p. 368. [Google Scholar]
- Surface Water Resources in the USSR. Lena-Indigirka Basin; Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1972; Volume 17, p. 562.
- Rozhdestvenskii, A.V.; Buzin, V.A.; Shalashina, T.L. Conditions of maximum water level formation of the Lena River near Yakutsk. Meteorol. Gigrologiya 2010, 10, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Gautier, E.; Dépret, T.; Virmoux, C.; Grancher, D.; Brunstein, D.; Costard, F.; Fedorov, A.; Konstantinov, P. Going with the flow: Hydrologic response of middle Lena River (Siberia) to the climate variability and change. J. Hydrol. 2018, 557, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalov, R.S.; Zavadsky, A.S.; Ruleva, S.N.; Kirik, O.M.; Prokop’yev, V.P.; Androsov, I.M.; Sakharov, A.I. Morphology, deformations and temporary modifications of the Lena River channel and its influence on the Yakutsk economic infrastructure. Geomorfologiya 2016, 3, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tananaev, N. Hydrological and sedimentary controls over fluvial thermal erosion, the Lena river, Central Yakutia. Geomorphology 2016, 253, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimova, N.P.; Pavlova, N.A. Hydrogeochemical Studies of Permafrost in Central Yakutia; Academic Publishing House “Geo”: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2014; p. 189. [Google Scholar]
- Romanovsky, N.N. Groundwater in Permafrost; Moscow State University Press: Moscow, Russia, 1983; p. 231. [Google Scholar]
- Anisimova, N.P.; Pavlova, N.A.; Stambovskaya, Y.V. Chemical composition of talik waters in the middle Lena River. Nauka Obrazovanie 2005, 4, 118–124. [Google Scholar]
- Gavriliev, R.I. Thermal Properties of Rocks and Soil Cover in Permafrost; SB RAS Publishing House: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1998; p. 280. [Google Scholar]
- Boitsov, A.V.; Shepelev, V.V. Permafrost-hydrogeological conditions of the mass of eolian sands of Makhatta (Central Yakutia). In Hydrogeological Studies of the Cryolithozone; Melnikov Permafrost Institute SB RAS Press: Yakutsk, Russia, 1976; pp. 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ershov, E.D. Ceneral Geocryology: Manual for High; Moscow University Press: Moscow, Russia, 2002; p. 682. [Google Scholar]
- Garagulya, L.S.; Kudryavtsev, V.A.; Kondratieva, K.A. Fundamentals of Permafrost Forecast in Engineering and Geological Research; MSU Publishing House: Moscow, Russia, 1974; p. 432. [Google Scholar]
- Skachkov, Y.B. Trends in extreme air temperatures in Yakutsk. Nauka Obrazovanie 2012, 2, 39–41. [Google Scholar]
- Varlamov, S.P.; Skryabin, P.N.; Skachkov, Y.B. Ground temperature monitoring in the Tuimaada valley. In Proceedings, Solutions to Key Development Problems in Yakutsk City: Theoretical Background; Sfera: Yakutsk, Russia, 2010; pp. 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Iijima, Y.; Park, H.; Suzuki, K.; Yabuki, H.; Ohata, T.; Fedorov, A.N.; Maximov, T.C. Abrupt Increases in Soil Temperatures Following Increased Precipitation in a Permafrost Region, Central Lena River Basin, Russia. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2010, 2, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

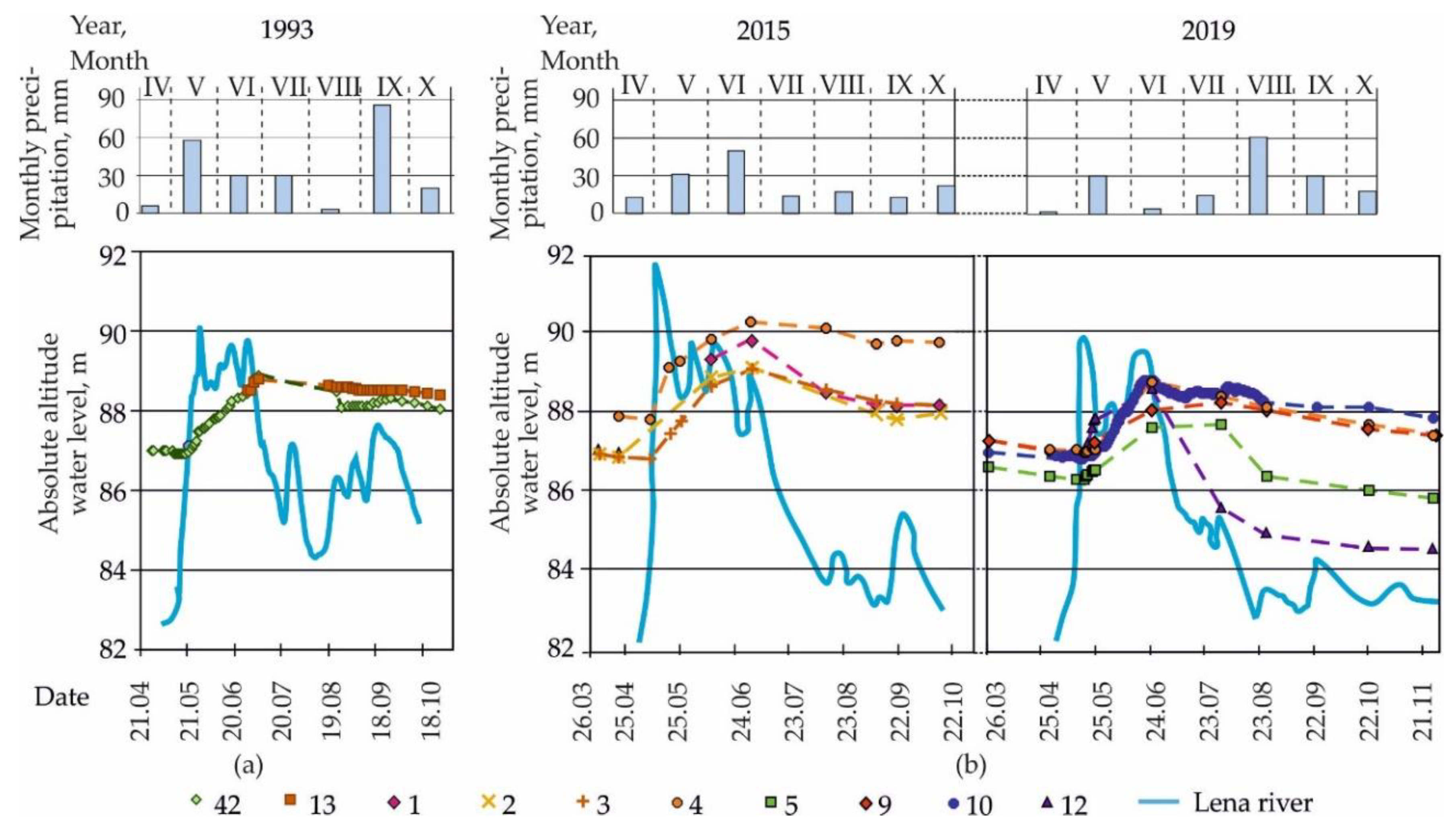

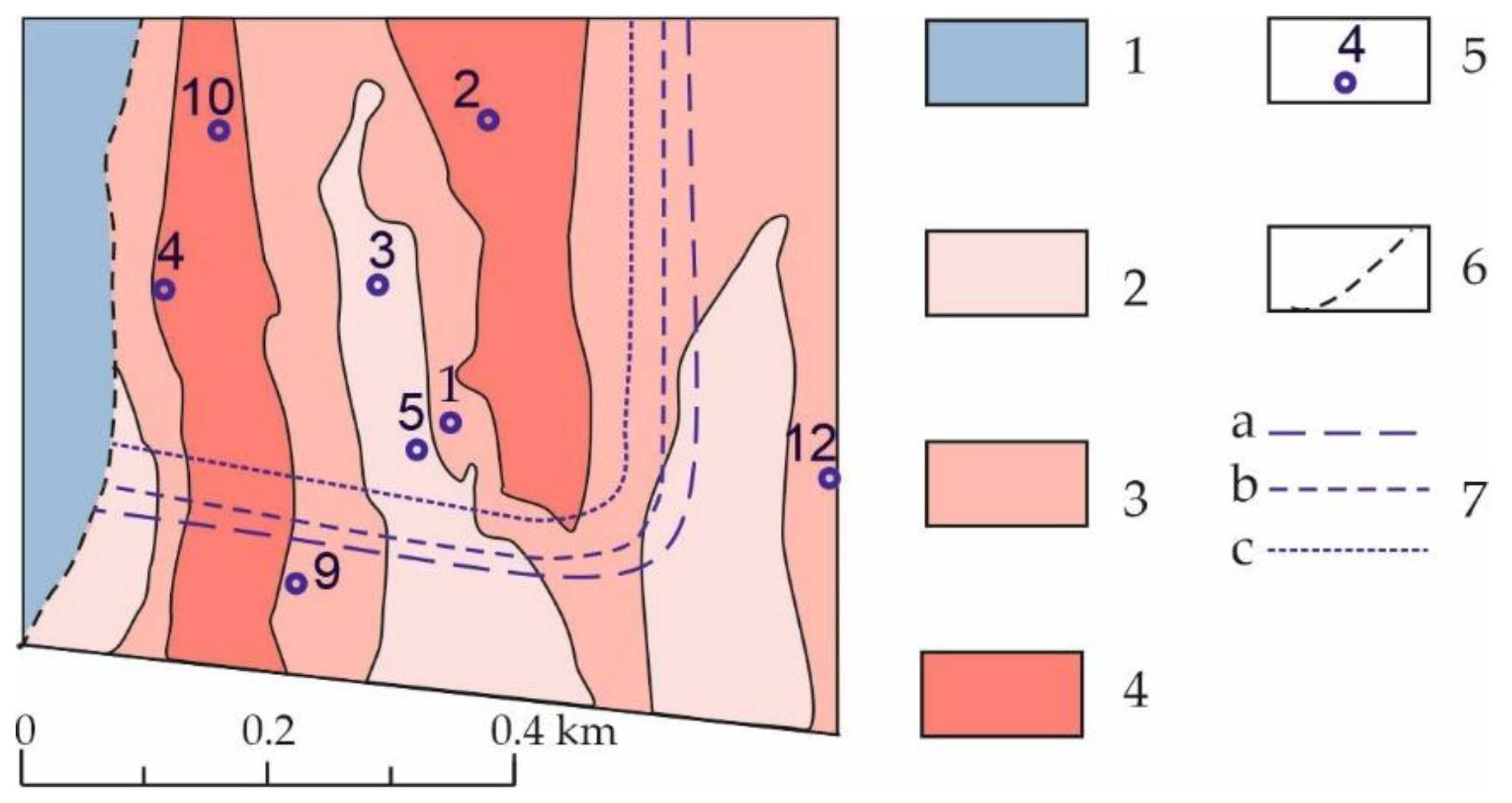
| Year of Observation | Total Precipitation (May-Sept.), mm | Water Level on Breakup Onset (Date) | Duration of Water Level above 87 m, Days | Seasonal Extremes of Water Level | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring (Mar.–May) | Summer (Jun–Aug.) | Autumn (Sept.–Nov.) | |||||||
| Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | ||||
| 1992 | 104 | 84.2 (17.05) | 73 | 92.1 | 82.0 | 88.4 | 84.9 | 87.4 | 84.0 |
| 1993 | 207 | 87.1 (22.05) | 127 | 90.1 | 83.0 | 89.7 | 84.3 | 87.6 | 85.0 |
| 1994 | 199 | 89.1 (22.05) | 60 | 90.5 | 82.0 | 91.6 | 84.1 | 87.3 | 84.0 |
| 1995 | 110 | 86.7 (24.05) | 150 | 91.6 | 83.0 | 91.2 | 84.4 | 85.7 | 84.0 |
| 2014 | 170 | 88.5 (8.05) | 36 | 89.5 | 81.9 | 88.3 | 84.08 | 88.0 | 82.9 |
| 2015 | 125 | 89.3 (12.05) | 61 | 91.6 | 81.9 | 89.6 | 83.7 | 85,3 | 83.1 |
| 2016 | 164 | 86.3 (15.05) | 64 | 88.9 | 81.7 | 90.6 | 85.4 | 86.2 | 82.5 |
| 2017 | 153 | 88.6 (17.05) | 70 | 90.4 | 81.7 | 90.4 | 84.4 | 88.1 | 82.6 |
| 2018 | 154 | 89.9 (14.05) | 77 | 92.1 | 82.2 | 90.6 | 86.2 | 86.7 | 83.2 |
| 2019 | 140 | 85.6 (15.05) | 46 | 89.9 | 82.1 | 89.5 | 82.8 | 84.7 | 82.6 |
| Date | pH | Unit | Cations | Anions | Minerali-Zation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | K+ | HCO3− | SO42− | Cl− | ||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| Borehole No 3 (aquifer is in the depth range between 8.0 and 13.5 m) | ||||||||||
| 21.04.15 | 6.5 | mg/L | 61.3 | 25.6 | 46.0 | 5.0 | 268.7 | 76.6 | 59.1 | 411.9 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 3.06 | 2.11 | 2.00 | 0.13 | 4.40 | 1.59 | 1.67 | |||
| 19.05.15 | 6.5 | mg/L | 58.6 | 30.2 | 74.0 | 13.0 | 422.4 | 10.0 | 101.6 | 508.1 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 2.92 | 2.48 | 3.22 | 0.33 | 6.92 | 0.21 | 2.87 | |||
| 30.05.15 | 6.6 | mg/L | 54.2 | 30.9 | 53.0 | 4.7 | 372.6 | 6.0 | 81.1 | 424.9 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 2.71 | 2.54 | 2.30 | 0.12 | 6.11 | 0.12 | 2.29 | |||
| 22.06.15 | 6.7 | mg/L | 49.6 | 28.7 | 60.0 | 4.4 | 340.7 | 10.3 | 63.7 | 407.9 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 2.473 | 2.36 | 2.61 | 0.11 | 5.584 | 0.2 | 1.797 | |||
| 03.07.15 | 6.5 | mg/L | 64.7 | 28.5 | 61.0 | 6.0 | 352.0 | 5.8 | 108.7 | 458.1 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 3.23 | 2.35 | 2.65 | 0.15 | 5.77 | 0.12 | 3.07 | |||
| 13.08.15 | 6.6 | mg/L | 63.5 | 24.5 | 66.0 | 7.5 | 281.6 | 18.1 | 104.0 | 441.9 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 3.17 | 2.02 | 2.87 | 0.19 | 4.62 | 0.38 | 2.93 | |||
| 21.09.15 | 6.7 | mg/L | 54.3 | 25.2 | 40.0 | 4.0 | 305.0 | 23.1 | 59.1 | 358.1 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 2.71 | 2.07 | 1.74 | 0.10 | 5.00 | 0.48 | 1.67 | |||
| 16.10.15 | 6.6 | mg/L | 62.6 | 29.4 | 44.0 | 4.0 | 328.5 | 30.9 | 68.0 | 407.6 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 3.12 | 2.42 | 1.91 | 0.10 | 5.38 | 0.64 | 1.92 | |||
| 15.01.16 | 7.2 | mg/L | 62.0 | 39.4 | 50.0 | 4.1 | 351.3 | 90.5 | 40.5 | 470.6 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 3.10 | 3.24 | 2.17 | 0.10 | 5.76 | 1.89 | 1.14 | |||
| 25.02.16 | 6.6 | mg/L | 66.4 | 25.4 | 54.0 | 4.0 | 319.4 | 88.5 | 40.5 | 449.9 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 3.31 | 2.09 | 2.35 | 0.10 | 5.24 | 1.84 | 1.14 | |||
| 30.03.16 | 6.7 | mg/L | 58.5 | 39.5 | 50.0 | 4.0 | 351.3 | 60.1 | 49.8 | 441.0 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 2.92 | 3.24 | 2.18 | 0.10 | 5.76 | 1.25 | 1.41 | |||
| Borehole No 4 (aquifer is in the depth interval between 8.0 and >20 m) | ||||||||||
| 21.04.15 | 6.9 | mg/L | 55.9 | 30.2 | 103 | 27.0 | 460.6 | 5.8 | 118.2 | 577.5 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 2.79 | 2.48 | 4.48 | 0.69 | 7.55 | 0.12 | 3.33 | |||
| 19.05.15 | 7.1 | mg/L | 47.7 | 25.2 | 125 | 33.0 | 470.2 | 4.1 | 126.5 | 606.5 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 2.38 | 2.07 | 5.44 | 0.84 | 7.71 | 0.09 | 3.57 | |||
| 30.05.15 | 6.9 | mg/L | 56.9 | 37.1 | 117 | 21.0 | 574.9 | 5.1 | 107.2 | 641.3 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 2.84 | 3.05 | 5.09 | 0.54 | 9.42 | 0.11 | 3.02 | |||
| 22.06.15 | 6.9 | mg/L | 56.6 | 35.1 | 110 | 21.0 | 500.4 | 0.8 | 115.9 | 596.0 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 2.82 | 2.89 | 4.78 | 0.54 | 8.20 | 0.02 | 3.27 | |||
| 03.07.15 | 6.9 | mg/L | 51.1 | 31.0 | 97.0 | 23.0 | 469.3 | 1.6 | 99.9 | 545.6 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 2.55 | 2.55 | 4.22 | 0.59 | 7.69 | 0.03 | 2.82 | |||
| 13.08.15 | 6.9 | mg/L | 64.6 | 23.1 | 91.0 | 21.0 | 422.4 | 1.8 | 115.8 | 536.5 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 3.23 | 1.90 | 3.96 | 0.54 | 6.92 | 0.04 | 3.27 | |||
| 21.09.15 | 6.7 | mg/L | 55.4 | 37.1 | 80.0 | 15.0 | 459.9 | 11.0 | 94.6 | 336.1 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 2.76 | 3.05 | 3.48 | 0.38 | 7.54 | 0.23 | 2.67 | |||
| 16.10.15 | 6.7 | mg/L | 63.5 | 36.8 | 82.0 | 17.0 | 486.9 | 1.9 | 94.6 | 545.4 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 3.17 | 3.02 | 3.57 | 0.43 | 7.98 | 0.04 | 2.67 | |||
| 14.12.15 | 6.8 | mg/L | 65.8 | 40.6 | 100 | 22.0 | 574.9 | 5.5 | 69.5 | 614.1 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 3.28 | 3.34 | 4.35 | 0.56 | 9.42 | 0.11 | 1.96 | |||
| 15.01.16 | 7.0 | mg/L | 73.9 | 46.2 | 120 | 23.0 | 638.8 | 4.9 | 115.9 | 713.7 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 3.69 | 3.80 | 5.22 | 0.59 | 10.47 | 0.10 | 3.27 | |||
| 25.02.16 | 7.0 | mg/L | 57.7 | 40.3 | 110 | 22.0 | 532.3 | 1.2 | 115.9 | 631.1 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 2.88 | 3.31 | 4.78 | 0.56 | 8.73 | 0.03 | 3.27 | |||
| 30.03.16 | 7.0 | mg/L | 71.6 | 33.6 | 102 | 21.0 | 517.4 | 1.1 | 115.9 | 610.5 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 3.57 | 2.76 | 4.44 | 0.54 | 8.48 | 0.02 | 3.27 | |||
| The Lena River | ||||||||||
| 25.03. 15 | 7.0 | mg/L | 31.2 | 24.1 | 78 | 1.5 | 129.8 | 65.9 | 140.9 | 407.7 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 1.56 | 1.98 | 3.4 | 0.04 | 2.13 | 1.37 | 3.97 | |||
| 31.05.15 | 6.9 | mg/L | 13.2 | 3.3 | 7.5 | 0.7 | 42.6 | 9.9 | 11.6 | 67.9 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 0.66 | 0.27 | 0.3 | 0.02 | 0.70 | 0.21 | 0.33 | |||
| 25.06.15 | 7.0 | mg/L | 12.4 | 4.7 | 10 | 0.9 | 46.3 | 9.9 | 14.3 | 76.6 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 0.62 | 0.39 | 0.4 | 0.02 | 0.76 | 0.21 | 0.40 | |||
| 02.07.15 | 6.3 | mg/L | 13.5 | 4.0 | 10 | 1.4 | 58.4 | 11.5 | 17.0 | 89.3 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 0.67 | 0.33 | 0.4 | 0.04 | 0.96 | 0.24 | 0.48 | |||
| 21.10.15 | 7.2 | mg/L | 26.5 | 9.9 | 23 | 0.8 | 89.2 | 26.0 | 47.3 | 178.4 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 1.32 | 0.82 | 1.0 | 0.02 | 1.46 | 0.54 | 1.33 | |||
| 27.11.15 | 7.3 | mg/L | 42.0 | 12.7 | 38 | 1.5 | 152.6 | 33.0 | 63.8 | 267.8 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 2.09 | 1.05 | 1.6 | 0.04 | 2.50 | 0.69 | 1.80 | |||
| 23.12.15 | 7.2 | mg/L | 46.6 | 17.0 | 39 | 1.3 | 190.2 | 30.0 | 61.2 | 290.3 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 2.33 | 1.40 | 1.7 | 0.03 | 3.12 | 0.62 | 1.73 | |||
| 28.01.16 | 7.1 | mg/L | 44.7 | 11.3 | 38 | 1.4 | 156.4 | 36.0 | 58.2 | 268.9 |
| Mg-equiv/L | 2.23 | 0.93 | 1.6 | 0.04 | 2.56 | 0.75 | 1.64 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pavlova, N.; Ogonerov, V.; Danzanova, M.; Popov, V. Hydrogeology of Reclaimed Floodplain in A Permafrost Area, Yakutsk, Russia. Geosciences 2020, 10, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10050192
Pavlova N, Ogonerov V, Danzanova M, Popov V. Hydrogeology of Reclaimed Floodplain in A Permafrost Area, Yakutsk, Russia. Geosciences. 2020; 10(5):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10050192
Chicago/Turabian StylePavlova, Nadezhda, Vasily Ogonerov, Marina Danzanova, and Vladimir Popov. 2020. "Hydrogeology of Reclaimed Floodplain in A Permafrost Area, Yakutsk, Russia" Geosciences 10, no. 5: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10050192
APA StylePavlova, N., Ogonerov, V., Danzanova, M., & Popov, V. (2020). Hydrogeology of Reclaimed Floodplain in A Permafrost Area, Yakutsk, Russia. Geosciences, 10(5), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10050192





