Simultaneous Magmatic and Hydrothermal Regimes in Alta–Little Cottonwood Stocks, Utah, USA, Recorded Using Multiphase U-Pb Petrochronology
Abstract
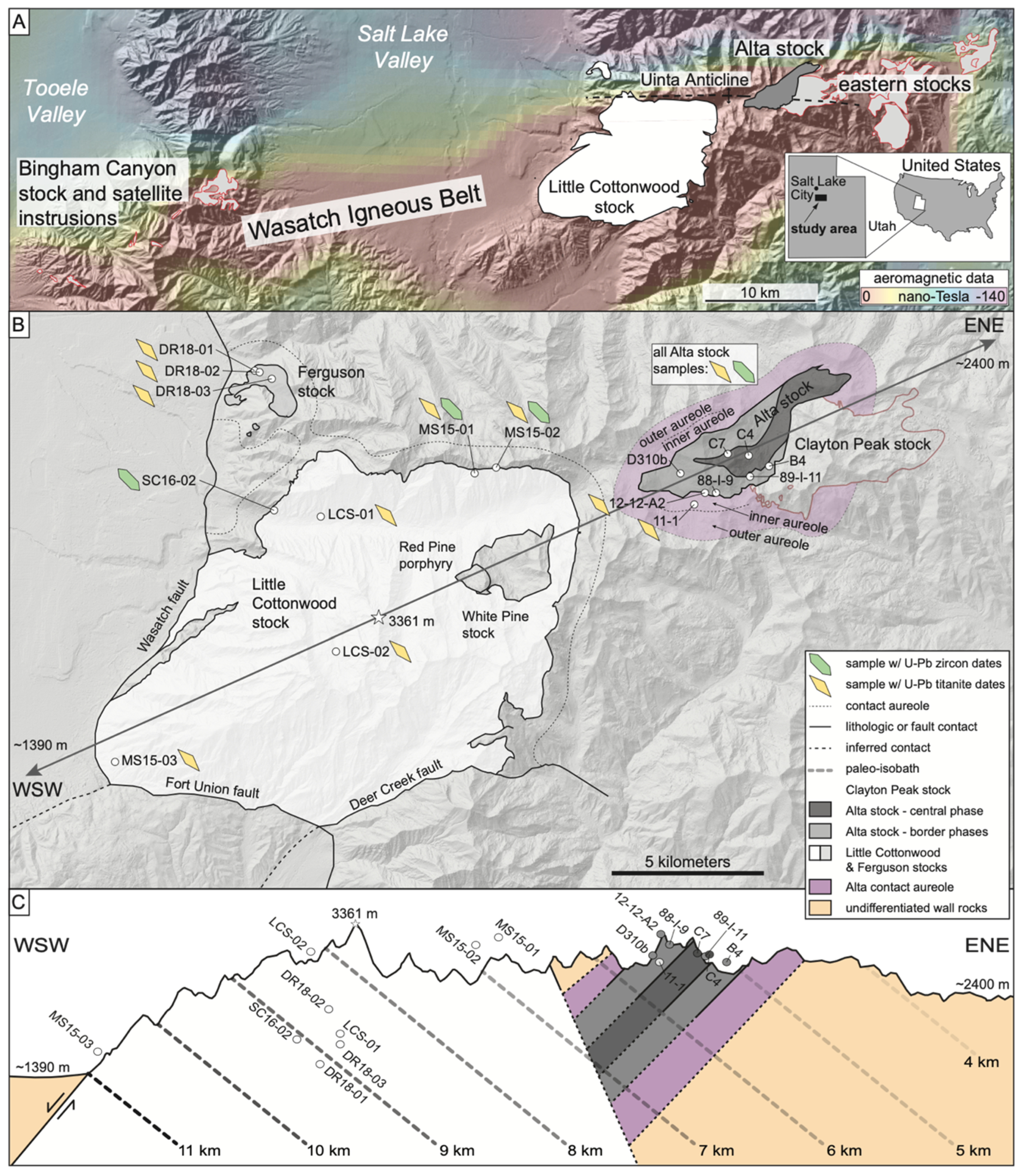
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
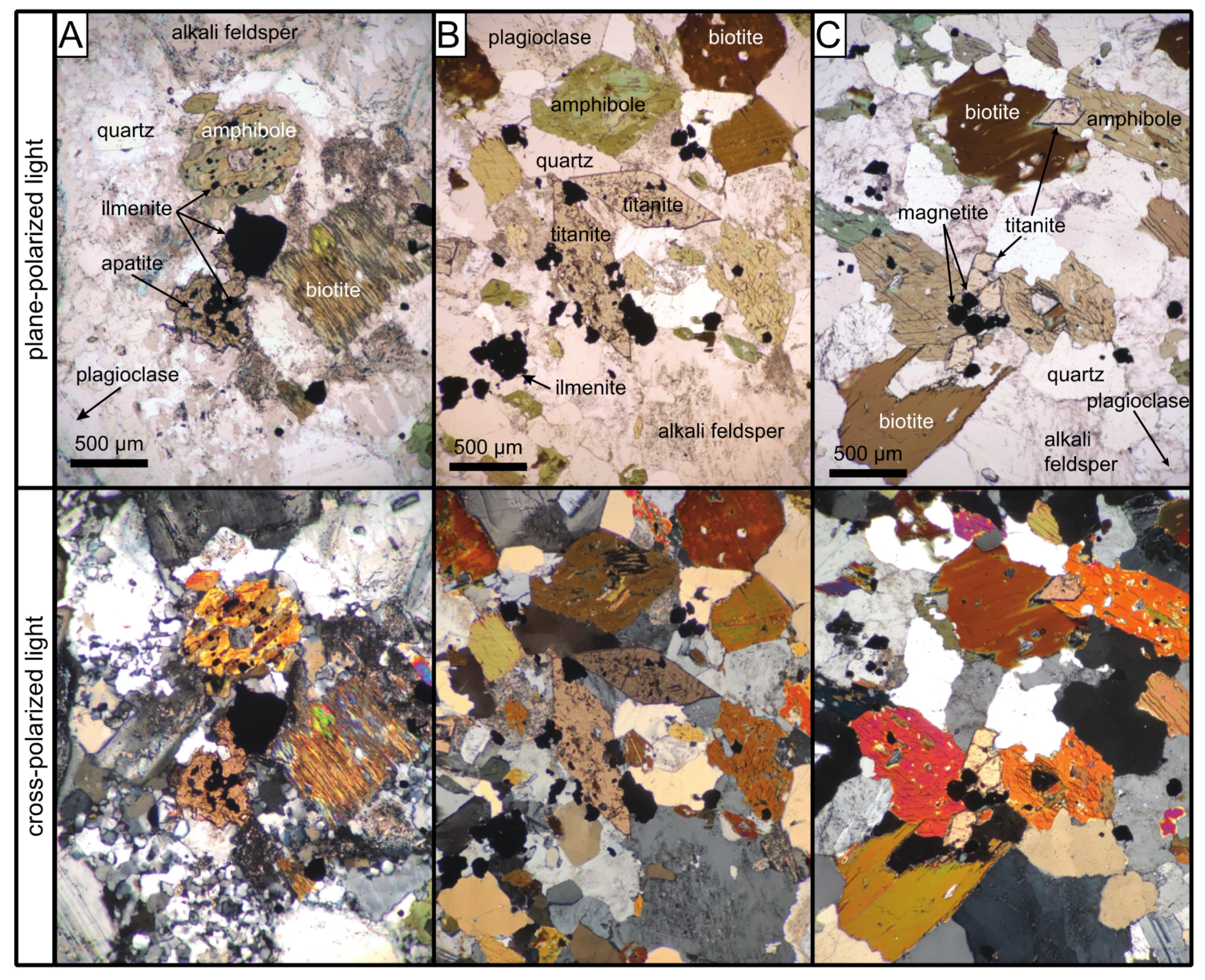
3.1. Petrologic Observations
3.2. Petrochronology
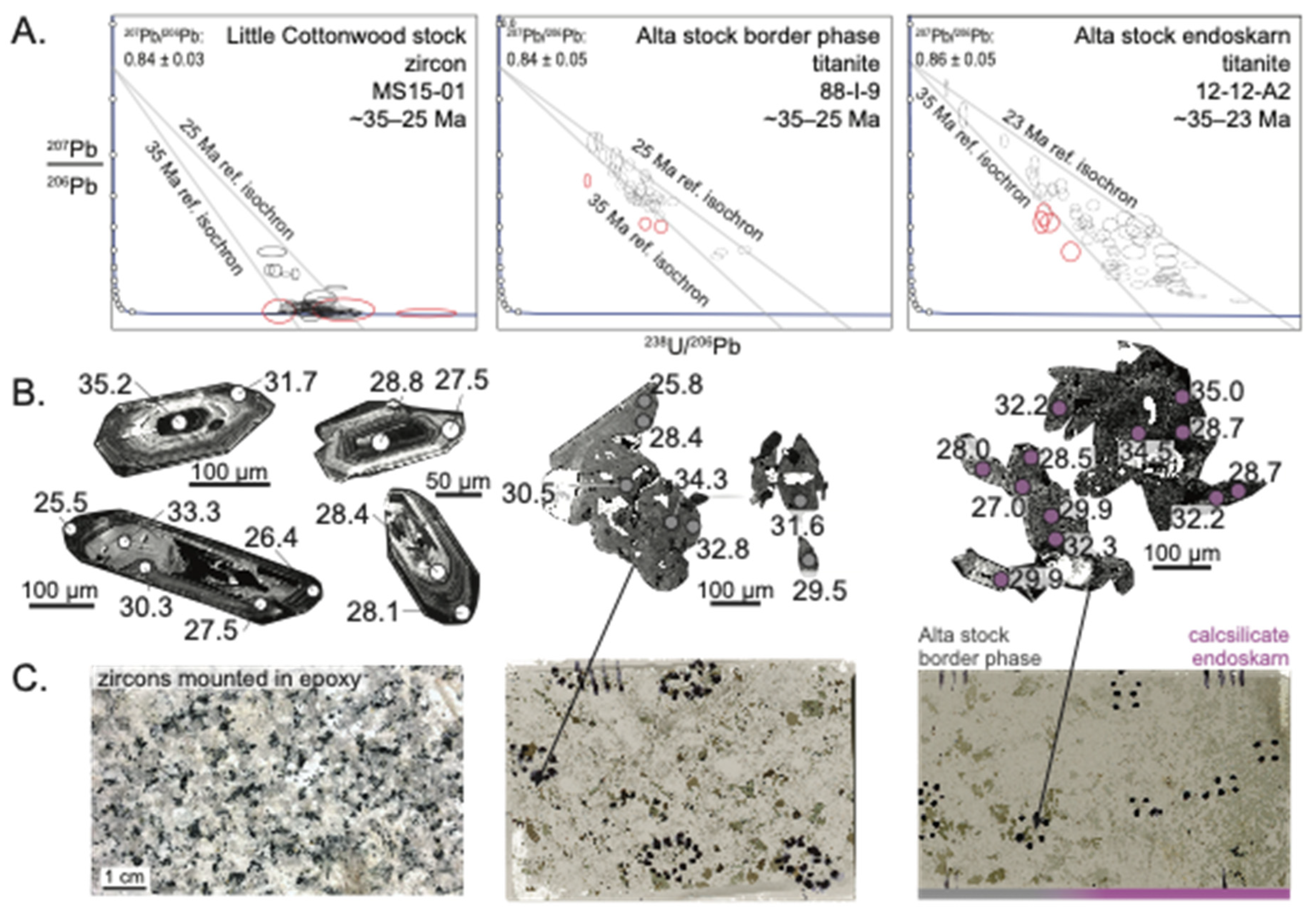
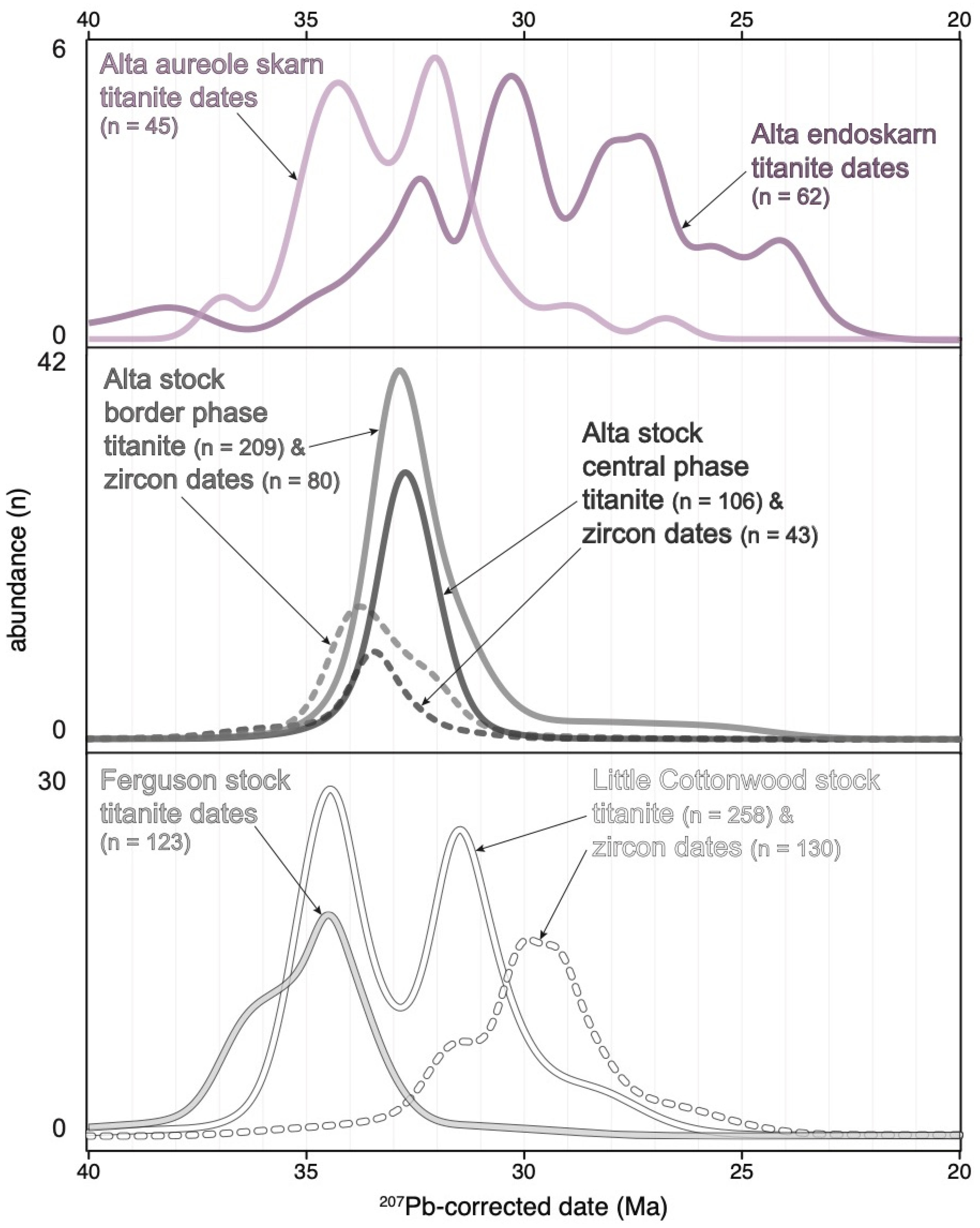
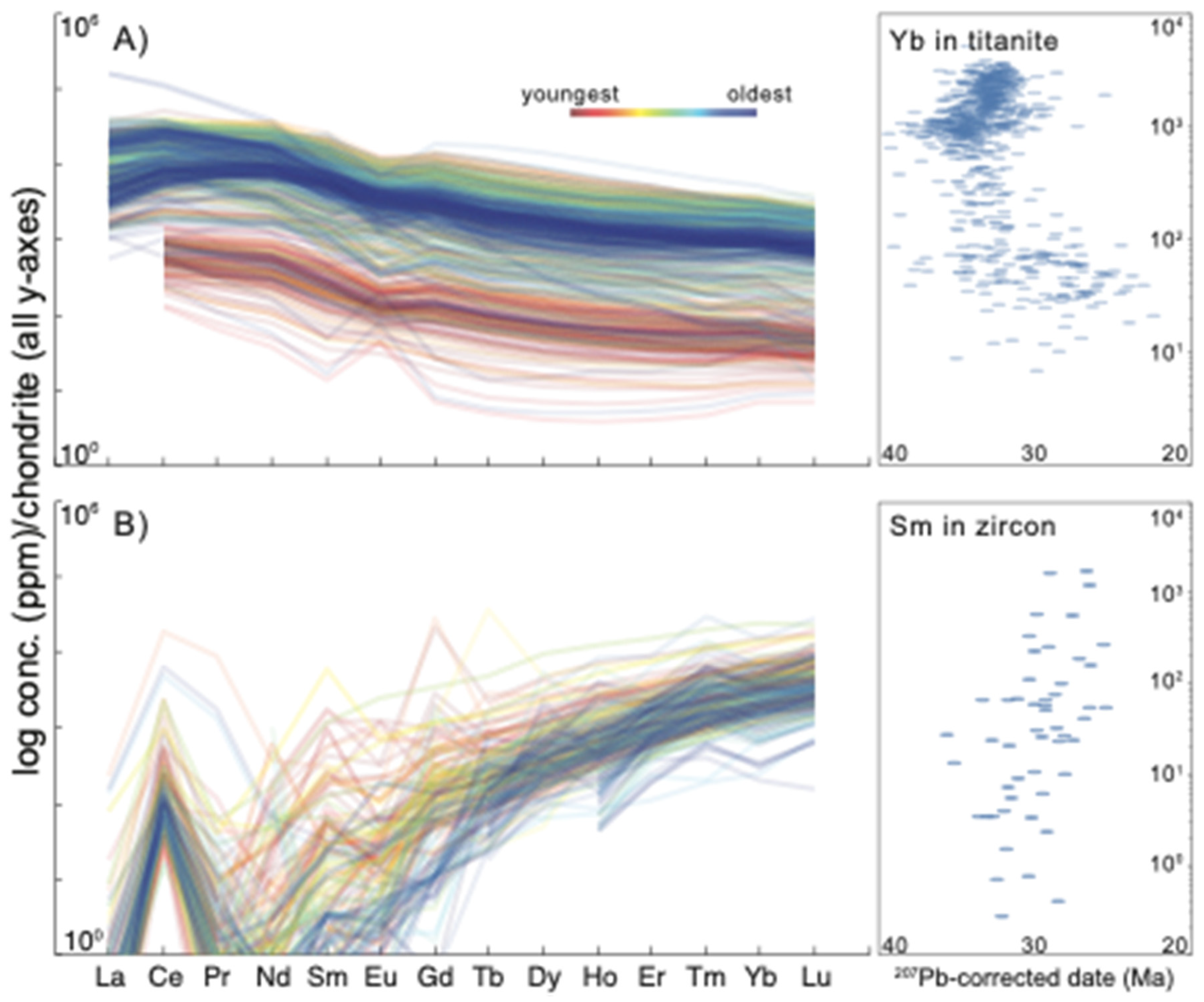
3.2.1. U-Pb Dates
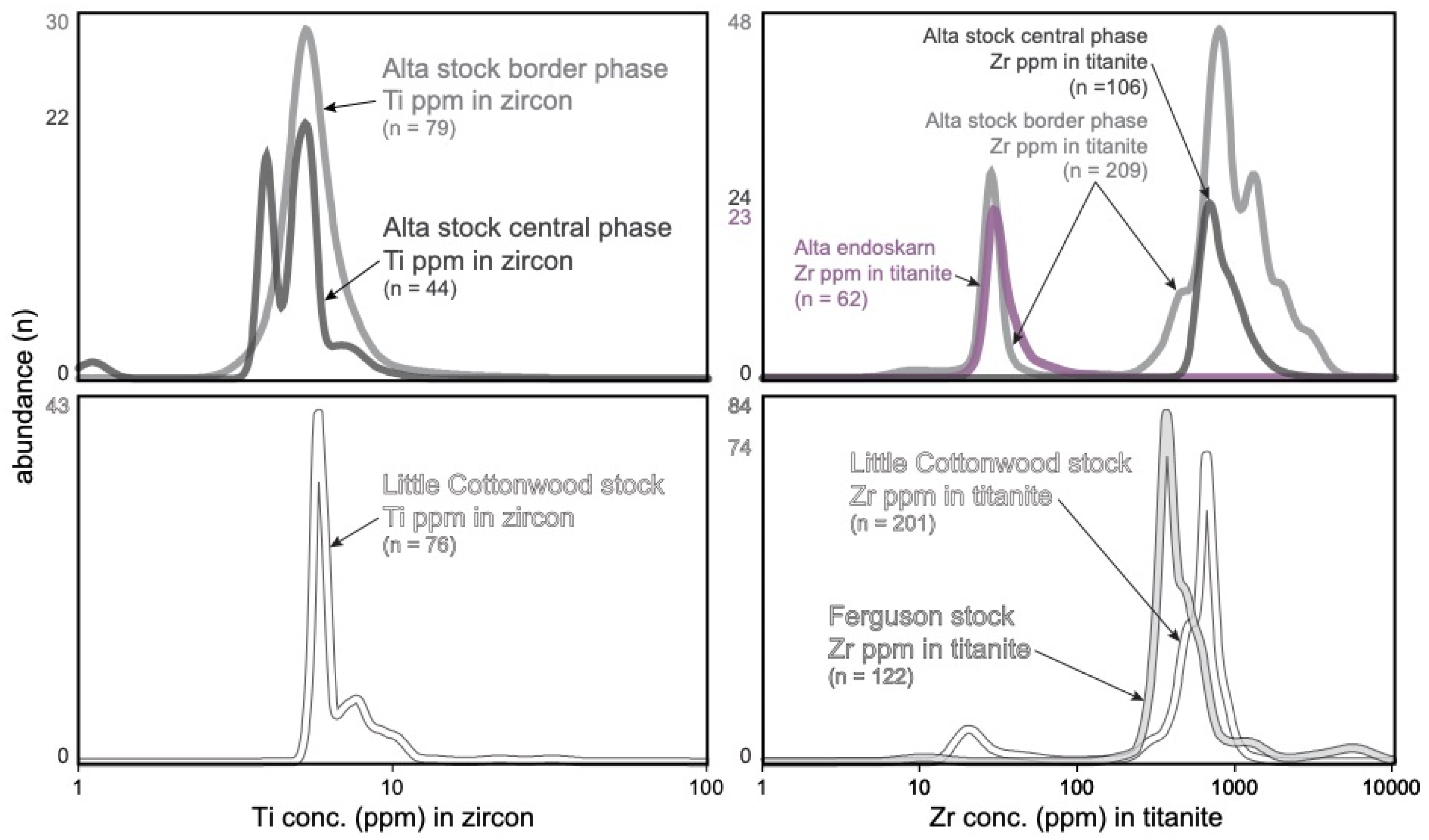
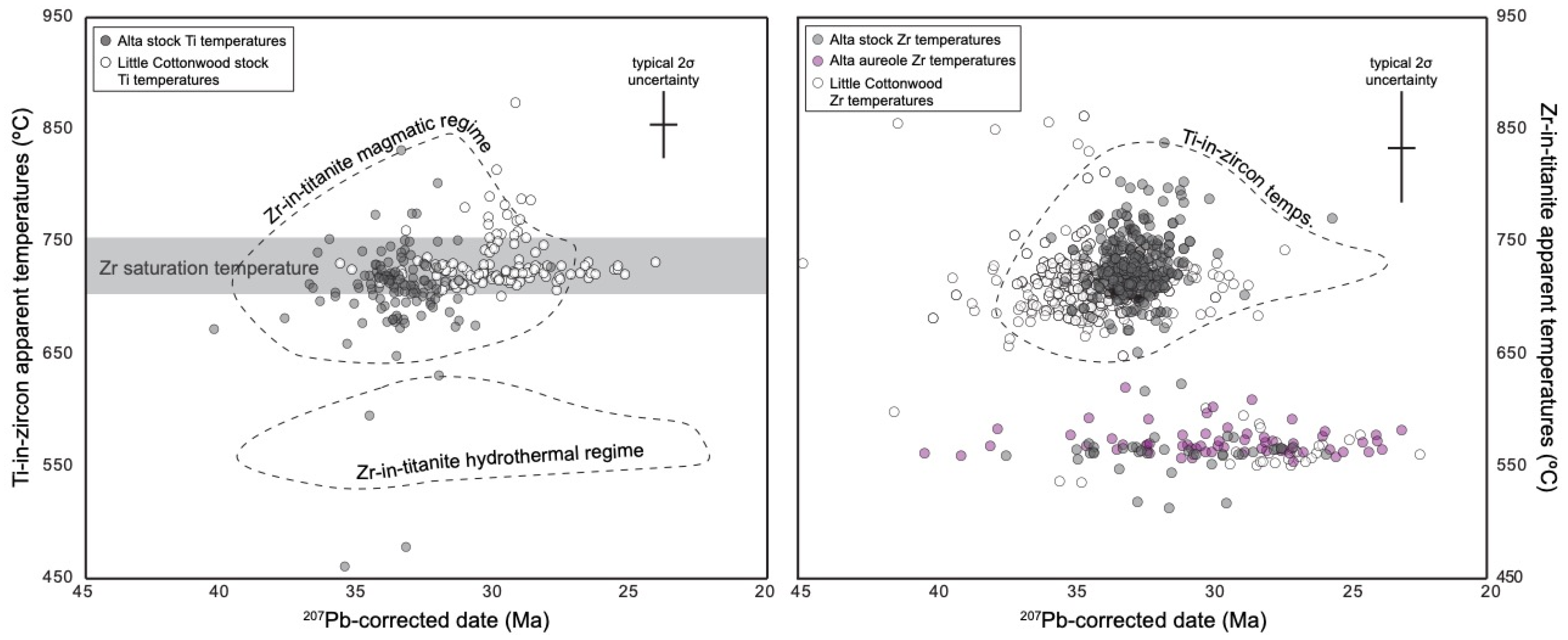
3.2.2. Trace Elements and Thermometry
4. Discussion
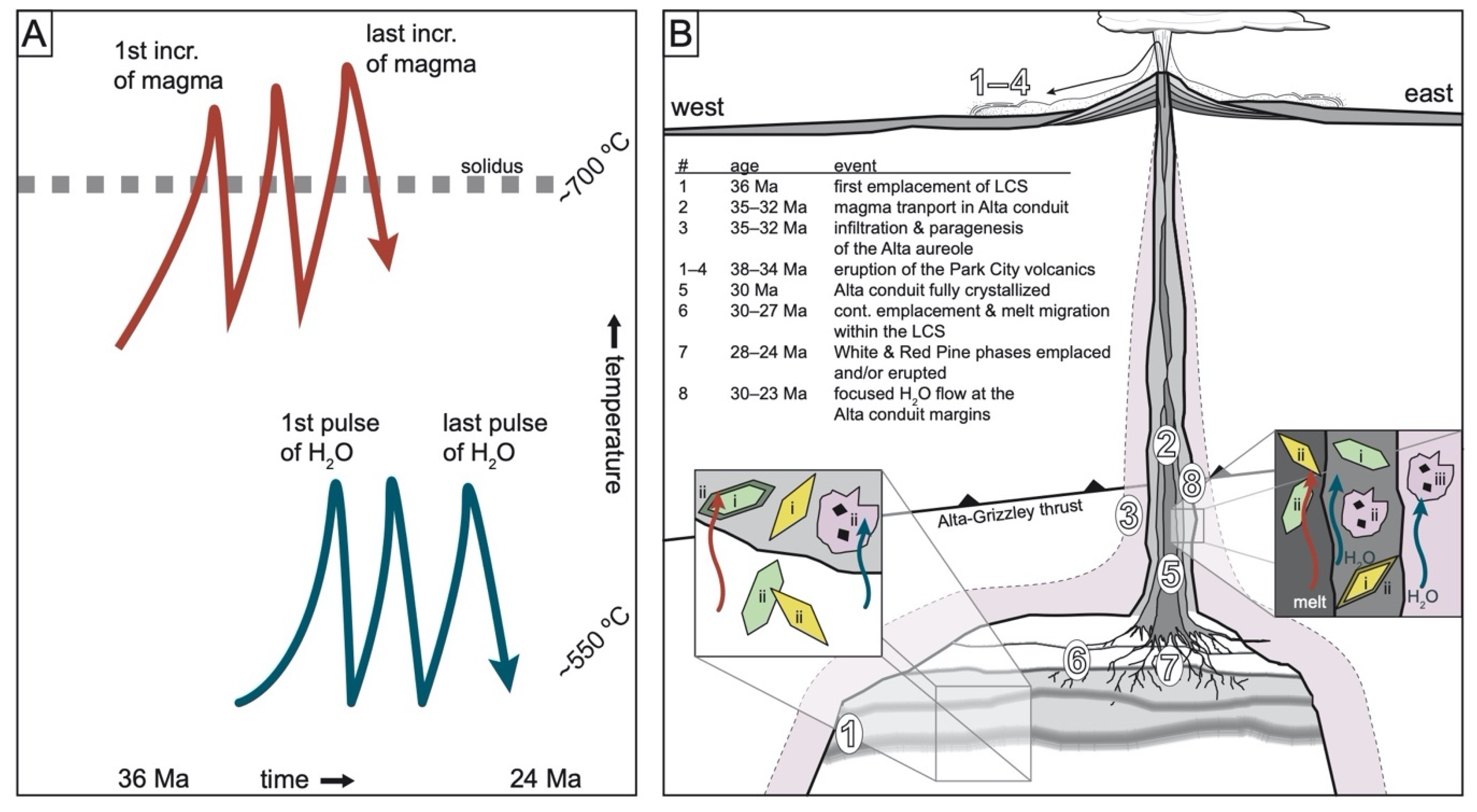
4.1. Thermal History
4.2. Hydrothermal Permeability Structure through Time
4.3. Magma Accumulation vs. Eruptive Discharge
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Annen, C. From Plutons to Magma Chambers: Thermal Constraints on the Accumulation of Eruptible Silicic Magma in the Upper Crust. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 284, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Koyaguchi, T.; Seno, T. Tectonic Stress Controls on Ascent and Emplacement of Magmas. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1999, 91, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Nabelek, P.I.; Liu, M. Heat and Fluid Flow in Contact Metamorphic Aureoles with Layered and Transient Permeability, with Application to the Notch Peak Aureole, Utah. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2001, 106, 6477–6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balashov, V.N.; Yardley, B.W.D. Modeling Metamorphic Fluid Flow with Reaction-Compaction-Permeability Feedbacks. Am. J. Sci. 1998, 298, 441–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annen, C. Factors Affecting the Thickness of Thermal Aureoles. Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverdatto, V.V.; Sharapov, V.N.; Melamed, V.G. The Controls and Selected Peculiarities of the Origin of Contact Metamorphic Zonation. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1970, 29, 310–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, S.R.; Ardill, K.; Vernon, R.; Žák, J. A Review of Mesoscopic Magmatic Structures and Their Potential for Evaluating the Hypersolidus Evolution of Intrusive Complexes. J. Struct. Geol. 2019, 125, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annen, C. Implications of Incremental Emplacement of Magma Bodies for Magma Differentiation, Thermal Aureole Dimensions and Plutonism-Volcanism Relationships. Tectonophysics 2011, 500, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floess, D.; Baumgartner, L.P. Constraining Magmatic Fluxes through Thermal Modelling of Contact Metamorphism. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2015, 422, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, W.T.; Bruhn, R.L. Fluid Inclusion Evidence for Minimum 11 Km Vertical Offset on the Wasatch Fault, Utah. Geology 1987, 15, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constenius, K.N. Late Paleogene Extensional Collapse of the Cordilleran Foreland Fold and Thrust Belt. Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. 1996, 108, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, T.A.; Cambray, F.W.; Constenius, K.N. Origin and Emplacement of Igneous Rocks in the Central Wasatch Mountains, Utah. Rocky Mt. Geol. 2001, 36, 119–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCelles, P.G.; Coogan, J.C. Regional Structure and Kinematic History of the Sevier Fold-and-Thrust Belt, Central Utah. GSA Bull. 2006, 118, 841–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, P.; Currie, C.A.; Lawton, T.F.; Murphy, M.A. Location, Location, Location: The Variable Lifespan of the Laramide Orogeny. Geology 2017, 45, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, T.A.; Cambray, F.W.; Feher, L.; Constenius, K.N.; Group WIB Research. Petrochemistry and Emplacment History of the Wasatch Igneous Belt. In Society of Economics Geologists Guidebook 29, 2nd ed.; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 1998; pp. 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen, T.; Marshak, S. Origin of the Uinta Recess, Sevier Fold-Thrust Belt, Utah: Influence of Basin Architecture on Fold-Thrust Belt Geometry. Tectonophysics 1999, 312, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, P.A.; Taylor, A.R.; Ehlers, T.A. Is the Wasatch Fault Footwall (Utah, United States) Segmented over Million-Year Time Scales? Geology 2004, 32, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, W.; Wilson, P.N.; Bruhn, R. Pore-Fluid Chemistry and Chemical Reactions on the Wasatch Normal Fault, Utah. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, P.A.; Ehlers, T.A.; Chapman, D.S.; Farley, K.A.; Kamp, P.J.J. Exhumation of the Central Wasatch Mountains, Utah: 1. Patterns and Timing of Exhumation Deduced from Low-Temperature Thermochronology Data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, T.A.; Willett, S.D.; Armstrong, P.A.; Chapman, D.S. Exhumation of the Central Wasatch Mountains, Utah: 2. Thermokinematic Model of Exhumation, Erosion, and Thermochronometer Interpretation. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, A.M.; Wernicke, B.P.; Niemi, N.A.; Bennett, R.A.; Davis, J.L. Comparison of Geodetic and Geologic Data from the Wasatch Region, Utah, and Implications for the Spectral Character of Earth Deformation at Periods of 10 to 10 Million Years. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, D.A. Geologic Setting, Depths of Emplacement, and Regional Distribution of Fluid Inclusions in Intrusions of the Central Wasatch Mountains, Utah. Econ. Geol. 1989, 84, 386–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crittenden, M.D.; Stuckless, J.S.; Kistler, R.W.; Stern, T.W. Radiometric Dating of Intrusive Rocks in the Cottonwood Area, Utah. US Geol. Surv. J. Res. 1973, 1, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Bromfield, C.S.; Erickson, A.J.; Haddadin, M.A.; Mehnert, H.H. Potassium-Argon Ages of Intrusion, Extrusion, and Associated Ore Deposits, Park City Mining District, Utah. Econ. Geol. 1977, 72, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowallis, B.J.; Ferguson, J.; Jorgensen, G.J. Uplift along the Salt Lake Segment of the Wasatch Fault from Apatite and Zircon Fission Track Dating in the Little Cottonwood Stock. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part D Nucl. Tracks Radiat. Meas. 1990, 17, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wison, J.C. Geology of the Alta Stock, Utah. Ph.D. Thesis, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, W.M. A Stable Isotope and Fluid Inclusion Study of the Contact Al(Fe)-Ca-Mg-Si Skarns in the Alta Stock Aureole, Alta, Utah. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, A.A.; Calkins, F.C.; Crittenden, M.D.; Bromfield, C.S. Geologic Map of the Brighton Quadrangle, Utah. US Geol. Surv. Geol. Quad. Map GQ-534; 1966. Available online: https://www.sciencebase.gov/catalog/item/4f4e4b0be4b07f02db69d912 (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Moore, J.N.; Kerrick, D.M. Equilibria in Siliceous Dolomites of the Alta Aureole, Utah. Am. J. Sci. 1976, 276, 502–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.J.; Bowman, J.R. Contact Metamorphism Surrounding the Alta Stock: Thermal Constraints and Evidence of Advective Heat Transport from Calcite + Dolomite Geothermometry. Am. Mineral. 1994, 79, 513–525. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, S.J.; Bowman, J.R. Mineralogical Evidence for Fluid-Rock Interaction Accompanying Prograde Contact Metamorphism of Siliceous Dolomites: Alta Stock Aureole, Utah, USA. J. Petrol. 2000, 41, 739–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, J.R.; Willett, S.D.; Cook, S.J. Oxygen Isotopic Transport and Exchange during Fluid Flow; One-Dimensional Models and Applications. Am. J. Sci. 1994, 294, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.J.; Bowman, J.R.; Forster, C.B. Cook and Bowman 1997.Pdf. Am. J. Sci. 1997, 297, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchildon, N.; Dipple, G.M. Irregular Isograds, Reaction Instabilities, and the Evolution of Permeability during Metamorphism. Geology 1998, 26, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlers, A.; Baumgartner, L.P. Melt Infiltration into Quartzite during Partial Melting in the Little Cottonwood Contact Aureole (UT, USA): Implication for Xenocryst Formation. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2013, 31, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankey, V.; Cueves, A.; Daniels, D.; Finn, C.A.; Hernandez, I. Digital Data Grids for the Magnetic Anomaly Map of North America. US Geol. Surv. Open File Rep. 414; 2002. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2002/ofr-02-414/ (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Biek, R.F. Interim Geologic Map of the Park City East Quadrangle, Summit and Wasatch Counties, Utah. Utah Geol. Surv. Open File Rep. 677; 2017. Available online: https://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/ofr6924 (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Bartley, J.M.; Coleman, D.S.; Glazner, A.F. Incremental Pluton Emplacement by Magmatic Crack-Seal. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 2008, 97, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, S.L. Mineralogy, Petrology, Geochemistry and Crystal Size Distribution of Tertiary Plutons of the Central Wasatch Mountains, Utah; University of Utah: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, A.J.; Smith, R.K. The Oligocene Little Cottonwood Stock, Central Wasatch Mountains, Utah: An Example of Compositional Zoning by Side-Wall Fractional Crystallization of an Arc-Related Intrusion. Mt. Geol. 2005, 34, 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden, M.D. Geology of the Draper Quadrangle, Utah. US Geol. Surv. Geol. Quadrang. Map GQ-377 Scale 124,000; 1965. Available online: https://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/gq377 (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Johnson, B.R.; Glazner, A.F. Formation of K-Feldspar Megacrysts in Granodioritic Plutons by Thermal Cycling and Late-Stage Textural Coarsening. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2010, 159, 599–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundstrom, C.C. The Role of Thermal Migration and Low-Temperature Melt in Granitoid Formation: Can Granite Form without Rhyolitic Melt? Int. Geol. Rev. 2016, 58, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, J.A. The Origin of Granite: The Role and Source of Water in the Evolution of Granitic Magmas. Spec. Pap. Geol. Soc. Am. 1990, 253, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, M.D. Quantitative Petrological Evidence for the Origin of K-Feldspar Megacrysts in Dacites from Taapaca Volcano, Chile. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2011, 162, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazner, A.F.; Johnson, B.R. Late Crystallization of K-Feldspar and the Paradox of Megacrystic Granites. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2013, 166, 777–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.W. Oxygen Isotope, Cathodoluminescence, and Titanium in Quartz Geothermometry in the Alta Stock, UT: Geothermical Insights into Pluton Assembly and Early Cooling History; University of Utah: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ackerson, M.R.; Mysen, B.O.; Tailby, N.D.; Watson, E.B. Low-Temperature Crystallization of Granites and the Implications for Crustal Magmatism. Nature 2018, 559, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stearns, M.A.; Hacker, B.R.; Ratschbacher, L.; Rutte, D.; Kylander-Clark, A.R.C. Titanite Petrochronology of the Pamir Gneiss Domes: Implications for Middle to Deep Crust Exhumation and Titanite Closure to Pb and Zr Diffusion. Tectonics 2015, 34, 784–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, J.M.; Hacker, B.R.; Kylander-Clark, A.R.C.; Stearns, M.; Seward, G. Controls on Trace Element Uptake in Metamorphic Titanite: Implications for Petrochronology. J. Petrol. 2017, 58, 1031–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holder, R.M.; Hacker, B.R. Fluid-Driven Resetting of Titanite Following Ultrahigh-Temperature Metamorphism in Southern Madagascar. Chem. Geol. 2019, 504, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartley, J.M.; Glazner, A.F.; Coleman, D.S. Dike Intrusion and Deformation during Growth of the Half Dome Pluton, Yosemite National Park, California. Geosphere 2018, 14, 1283–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, S.Z. ScienceDirect the Fluid Regime of Crystallization of Water-Saturated Granitic and Pegmatitic Magmas: A Physicochemical Analysis. RGG 2016, 56, 1292–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylander-Clark, A.R.C.; Hacker, B.R.; Cottle, J.M. Laser-Ablation Split-Stream ICP Petrochronology. Chem. Geol. 2013, 345, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylander-Clark, A.R.C. Petrochronology by Laser-Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2017, 83, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, M.J. Titanite Petrochronology. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2017, 83, 419–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pupin, J.P. Zircon and Granite Petrology. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1980, 73, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, B.R.; Chamberlain, K.R.; Schumacher, J.C. Sphene (Titanite): Phase Relations and Role as a Geochronometer. Chem. Geol. 2001, 172, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, E.B.; Harrison, T.M. Zircon Saturation Revisited: Temperature and Composition Effects in a Variety of Crustal Magma Types. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1983, 64, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehnke, P.; Watson, E.B.; Trail, D.; Harrison, T.M.; Schmitt, A.K. Zircon Saturation Re-Revisited. Chem. Geol. 2013, 351, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.F.; McDowell, S.M.; Mapes, R.W. Hot and Cold Granites: Implications of Zircon Saturation Temperatures and Preservation of Inheritance. Geology 2003, 31, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaltegger, U.; Brack, P.; Ovtcharova, M.; Peytcheva, I.; Schoene, B.; Stracke, A.; Marocchi, M.; Bargossi, G.M. Zircon and Titanite Recording 1.5 Million Years of Magma Accretion, Crystallization and Initial Cooling in a Composite Pluton (Southern Adamello Batholith, Northern Italy). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 286, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troitzsch, U.; Ellis, D.J. Thermodynamic Properties and Stability of AlF-Bearing Titanite CaTiOSiO4–CaAlFSiO4. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2002, 142, 543–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemley, J.J.; Meyer, C.; Hodgson, C.J.; Thatcher, A.B. Sulfide Solubilities in Alteration-Controlled Systems. Science 1967, 158, 1580–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markl, G.; Piazolo, S. Stability of High-Al Titanite from Low-Pressure Calcsilicates in Light of Fluid and Host-Rock Composition. Am. Mineral. 1999, 84, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrov, S.M.; Troneva, M.A. Composition, Mineral Assemblages, and Genesis of Titanite and Malayaite in Skarns. Geochem. Int. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watters, W.A. Petrography and Genesis of a Wollastonite Body and Its Associated Rocks at Holyoake Valley, Nelson, New Zealand. N. Z. J. Geol. Geophys. 1995, 38, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.M.; Wing, B.A.; Rumble, D. Formation of Wollastonite by Chemically Reactive Fluid Flow during Contact Metamorphism, Mt. Morrison Pendant, Sierra Nevada, California, USA. J. Petrol. 2001, 42, 1705–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodford, D.T.; Sisson, V.B.; Leeman, W.P. Boron Metasomatism of the Alta Stock Contact Aureole, Utah: Evidence from Borates, Mineral Chemistry, and Geochemistry. Am. Mineral. 2001, 86, 513–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stearns, M.A.; Cottle, J.M.; Hacker, B.R.; Kylander-Clark, A.R.C. Extracting Thermal Histories from the Near-Rim Zoning in Titanite Using Coupled U-Pb and Trace-Element Depth Profiles by Single-Shot Laser-Ablation Split Stream (SS-LASS) ICP-MS. Chem. Geol. 2016, 422, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggins, S.M.; Kinsley, L.P.J.; Shelley, J.M.G. Deposition and Element Fractionation Processes during Atmospheric Pressure Laser Sampling for Analysis by ICP-MS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1998, 127, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleinikoff, J.N.; Wintsch, R.P.; Fanning, C.M.; Dorais, M.J. U–Pb Geochronology of Zircon and Polygenetic Titanite from the Glastonbury Complex, Connecticut, USA: An Integrated SEM, EMPA, TIMS, and SHRIMP Study. Chem. Geol. 2002, 188, 125–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenbeck, M.; Allé, P.; Corfu, F.; Griffin, W.L.; Meier, M.; Oberli, F.; von Quadt, A.; Roddick, J.C.; Spiegel, W. Three Natural Zircon Standards for U-Th-Pb, Lu-Hf, Trace Element and REE Analyses. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 1995, 19, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenbeck, M.; Hanchar, J.M.; Peck, W.H.; Sylvester, P.; Valley, J.; Whitehouse, M.; Kronz, A.; Morishita, Y.; Nasdala, L.; Fiebig, J.; et al. Further Characterisation of the 91,500 Zircon Crystal. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2004, 28, 9–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazdab, F.K. Characterization of Flux-Grown Trace-Element-Doped Titanite Using the High-Mass-Resolution Ion Microprobe (SHRIMP-RG). Can. Mineral. 2009, 47, 813–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Spandler, C.; Hammerli, J.; Sha, P.; Hilbert-Wolf, H.; Hu, Y.; Roberts, E.; Schmitz, M. MKED1: A New Titanite Standard for in Situ Analysis of Sm-Nd Isotopes and U-Pb Geochronology. Chem. Geol. 2016, 425, 110–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sláma, J.; Košler, J.; Condon, D.J.; Crowley, J.L.; Gerdes, A.; Hanchar, J.M.; Horstwood, M.S.A.; Morris, G.A.; Nasdala, L.; Norberg, N.; et al. Plešovice Zircon–A New Natural Reference Material for U-Pb and Hf Isotopic Microanalysis. Chem. Geol. 2008, 249, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrus, J.A.; Kamber, B.S. VizualAge: A Novel Approach to Laser Ablation ICP-MS U-Pb Geochronology Data Reduction. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2012, 36, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, C.; Hellstrom, J.; Paul, B.; Woodhead, J.; Hergt, J. Iolite: Freeware for the Visualisation and Processing of Mass Spectrometric Data. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2011, 26, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.R. Isoplot/Ex: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronol. Cent. Spec. Publ. 2001, 1a, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeesch, P. Geoscience Frontiers IsoplotR: A Free and Open Toolbox for Geochronology. Geosci. Front. 2018, 9, 1479–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.R. On the Treatment of Concordant Uranium-Lead Ages. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.M.; Watson, E.B. New Thermodynamic Models and Revised Calibrations for the Ti-in-Zircon and Zr-in-Rutile Thermometers. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2007, 154, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, L.A.; Watson, E.B.; Wark, D.A. A Thermobarometer for Sphene (Titanite). Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2008, 155, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiorso, M.S.; Sack, O. Fe-Ti Oxide Geothermometry: Thermodynamic Formulation and the Estimation of Intensive Variables in Silicic Magmas. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1991, 108, 485–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualda, G.A.R.; Ghiorso, M.S.; Lemons, R.V.; Carley, T.L. Rhyolite-MELTS: A Modified Calibration of MELTS Optimized for Silica-Rich, Fluid-Bearing Magmatic Systems. J. Petrol. 2012, 53, 875–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferriss, E.D.A.; Essene, E.J.; Becker, U. Computational Study of the Effect of Pressure on the Ti-in-Zircon Geothermometer. Eur. J. Mineral. 2008, 20, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, I.; Carl, C. The Statistical Distribution of the Mean Squared Weighted Deviation. Chem. Geol. Isot. Geosci. Sect. 1991, 86, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, C.D.; Jeffries, T.E.; Smith, M. Common Lead-Corrected Laser Ablation ICP–MS U–Pb Systematics and Geochronology of Titanite. Chem. Geol. 2006, 227, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trail, D.; Bruce Watson, E.; Tailby, N.D. Ce and Eu Anomalies in Zircon as Proxies for the Oxidation State of Magmas. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 97, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Seltmann, R.; Qu, H.; Song, Y. Characterization of the Zircon Ce Anomaly for Estimation of Oxidation State of Magmas: A Revised Ce/Ce* Method. Mineral. Petrol. 2019, 113, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, P.; Candela, P.; Rivers, M. Interpreting Magmatic Processes from Accessory Phases: Titanite—A Small-Scale Recorder of Large-Scale Processes. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 2000, 91, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtukenberg, A.G.; Punin, Y.O.; Artamonova, O.I. Effect of Crystal Composition and Growth Rate on Sector Zoning in Solid Solutions Grown from Aqueous Solutions. Mineral. Mag. 2009, 73, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwinskii, A.J. Experimental Studies of Igneous Rock Series Central Sierra Nevada Batholith, California. J. Geol. 1968, 76, 548–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naney, M.T. Phase Equilibria of Rock-Forming Ferromagnesian Silicates in Granitic Systems. Am. J. Sci. 1983, 283, 993–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Page, F.Z.; Cavosie, A.J.; Fournelle, J.; Kita, N.T.; Lackey, J.S.; Wilde, S.A.; Valley, J.W. Ti-in-Zircon Thermometry: Applications and Limitations. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2008, 156, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, D.; Finger, F. Application of Ti-in-zircon thermometry to granite studies: Problems and possible solutions. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2019, 174, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdes, M.L.; Baumgartner, L.P.; Person, M.; Rumble, D. One-and Two-Dimensional Models of Fluid Flow and Stable Isotope Exchange at an Outcrop in the Adamello Contact Aureole, Southern Alps, Italy. Am. Mineral. 1995, 80, 1004–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, D.A. Evolution of Hydrothermal Fluids in the Alta Stock, Central Wasatch Mountains, Utah; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1991; Volume 1977.
- Brooks Hanson, R. The Hydrodynamics of Contact Metamorphism. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1995, 107, 595–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintze, L.F. Geologic Map of Utah. Utah Geol. Mineral. Surv. Map A-1 Scale 1,500,000. 1980. Available online: https://mrdata.usgs.gov/geology/state/state.php?state=UT (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Davis, J.W.J.W.; Coleman, D.S.D.S.; Gracely, J.T.J.T.; Gaschnig, R.; Stearns, M.A. Magma Accumulation Rates and Thermal Histories of Plutons of the Sierra Nevada Batholith, CA. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2012, 163, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.M.; Crisp, J.A.; Spera, F.J. Long-Term Volumetric Eruption Rates and Magma Budgets. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2006, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöpa, A.; Annen, C. The Effects of Magma Flux Variations on the Formation and Lifetime of Large Silicic Magma Chambers. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2013, 118, 926–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.E. Age and Stratigraphic Relations of the Fowkes Formation, Eocene, of Southwestern Wyoming and Northeastern Utah. Rocky Mt. Geol. 1973, 12, 27–31. [Google Scholar]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stearns, M.A.; Bartley, J.M.; Bowman, J.R.; Forster, C.W.; Beno, C.J.; Riddle, D.D.; Callis, S.J.; Udy, N.D. Simultaneous Magmatic and Hydrothermal Regimes in Alta–Little Cottonwood Stocks, Utah, USA, Recorded Using Multiphase U-Pb Petrochronology. Geosciences 2020, 10, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10040129
Stearns MA, Bartley JM, Bowman JR, Forster CW, Beno CJ, Riddle DD, Callis SJ, Udy ND. Simultaneous Magmatic and Hydrothermal Regimes in Alta–Little Cottonwood Stocks, Utah, USA, Recorded Using Multiphase U-Pb Petrochronology. Geosciences. 2020; 10(4):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10040129
Chicago/Turabian StyleStearns, Michael A., John M. Bartley, John R. Bowman, Clayton W. Forster, Carl J. Beno, Daniel D. Riddle, Samuel J. Callis, and Nicholas D. Udy. 2020. "Simultaneous Magmatic and Hydrothermal Regimes in Alta–Little Cottonwood Stocks, Utah, USA, Recorded Using Multiphase U-Pb Petrochronology" Geosciences 10, no. 4: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10040129
APA StyleStearns, M. A., Bartley, J. M., Bowman, J. R., Forster, C. W., Beno, C. J., Riddle, D. D., Callis, S. J., & Udy, N. D. (2020). Simultaneous Magmatic and Hydrothermal Regimes in Alta–Little Cottonwood Stocks, Utah, USA, Recorded Using Multiphase U-Pb Petrochronology. Geosciences, 10(4), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10040129




