Hydrological Impact of Ilisu Dam on Mosul Dam; the River Tigris
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. General
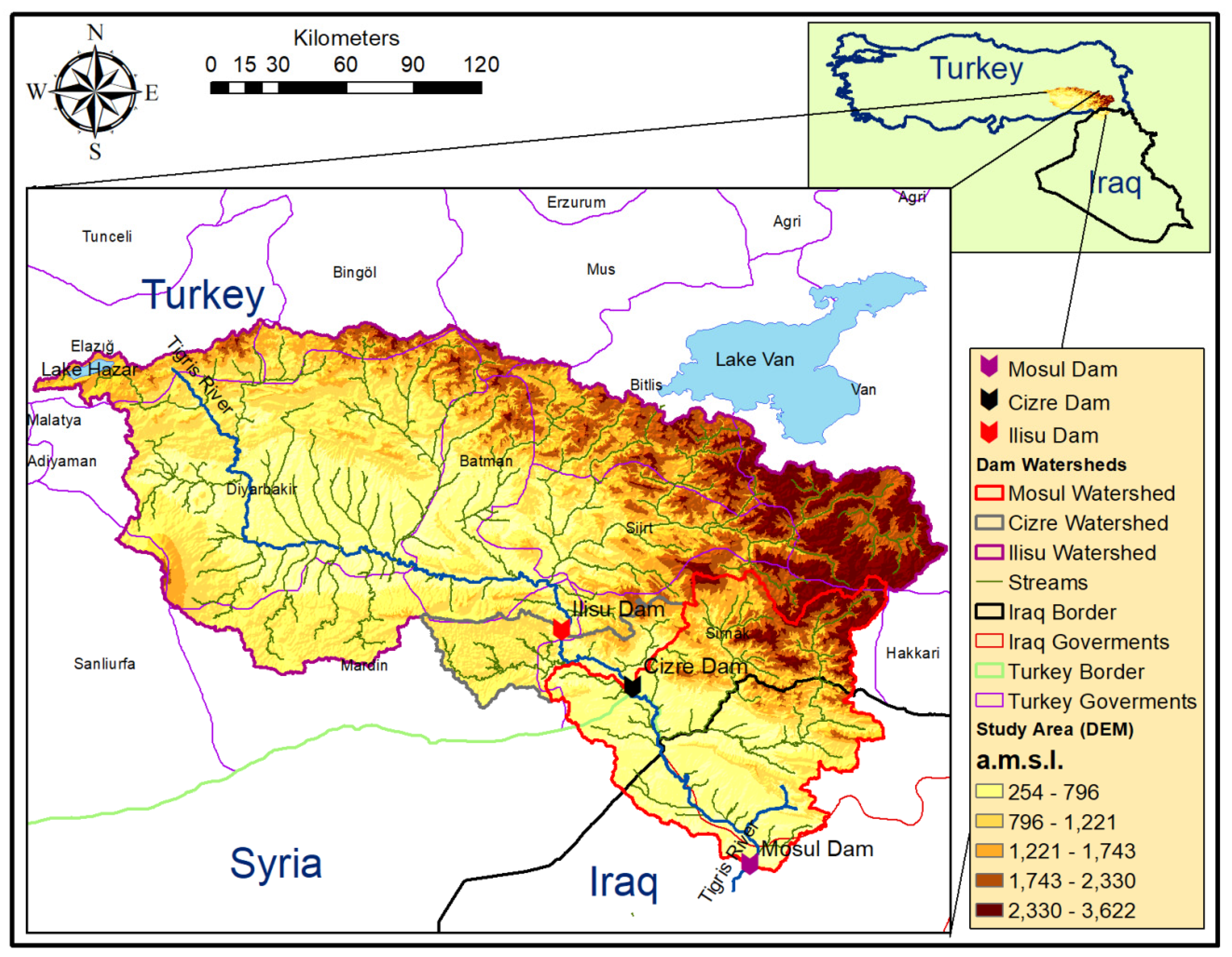
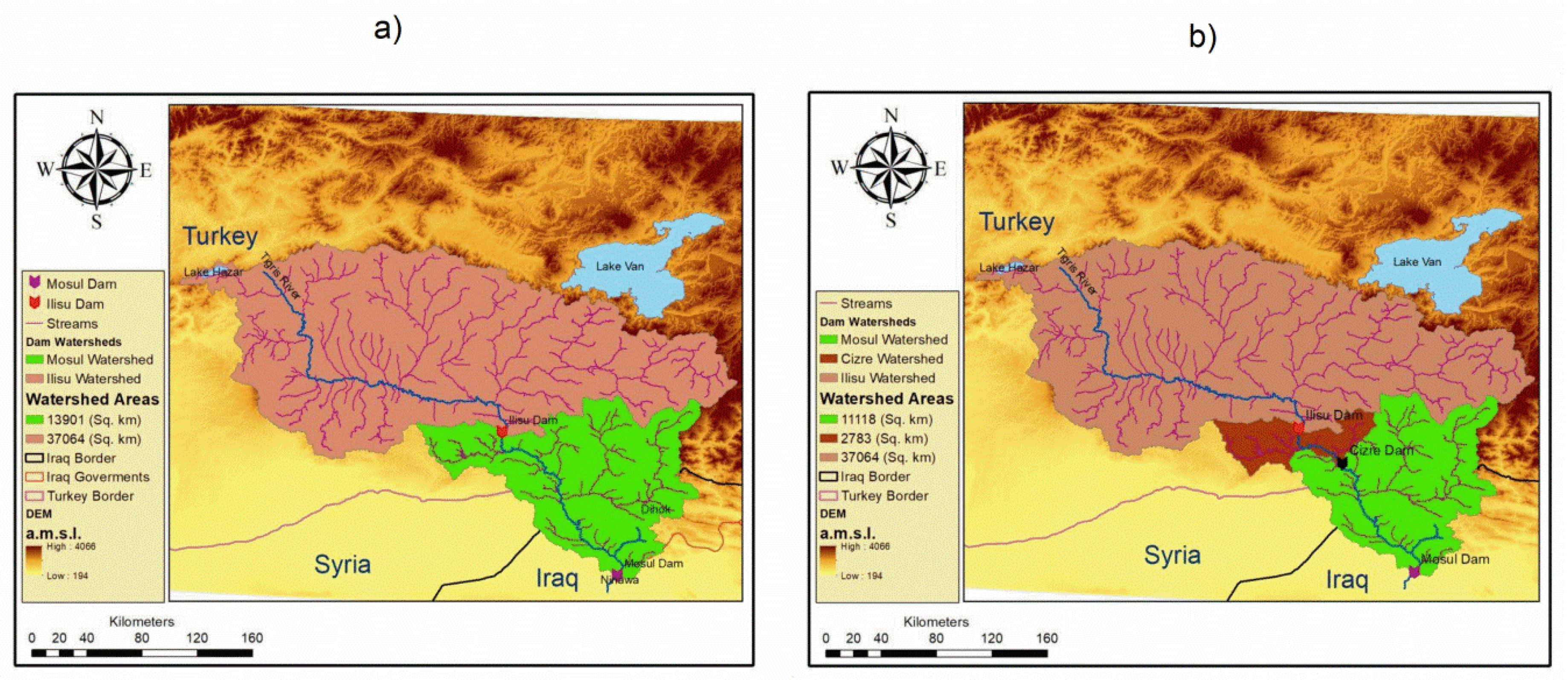
1.2. The Watershed of the Ilisu Dam
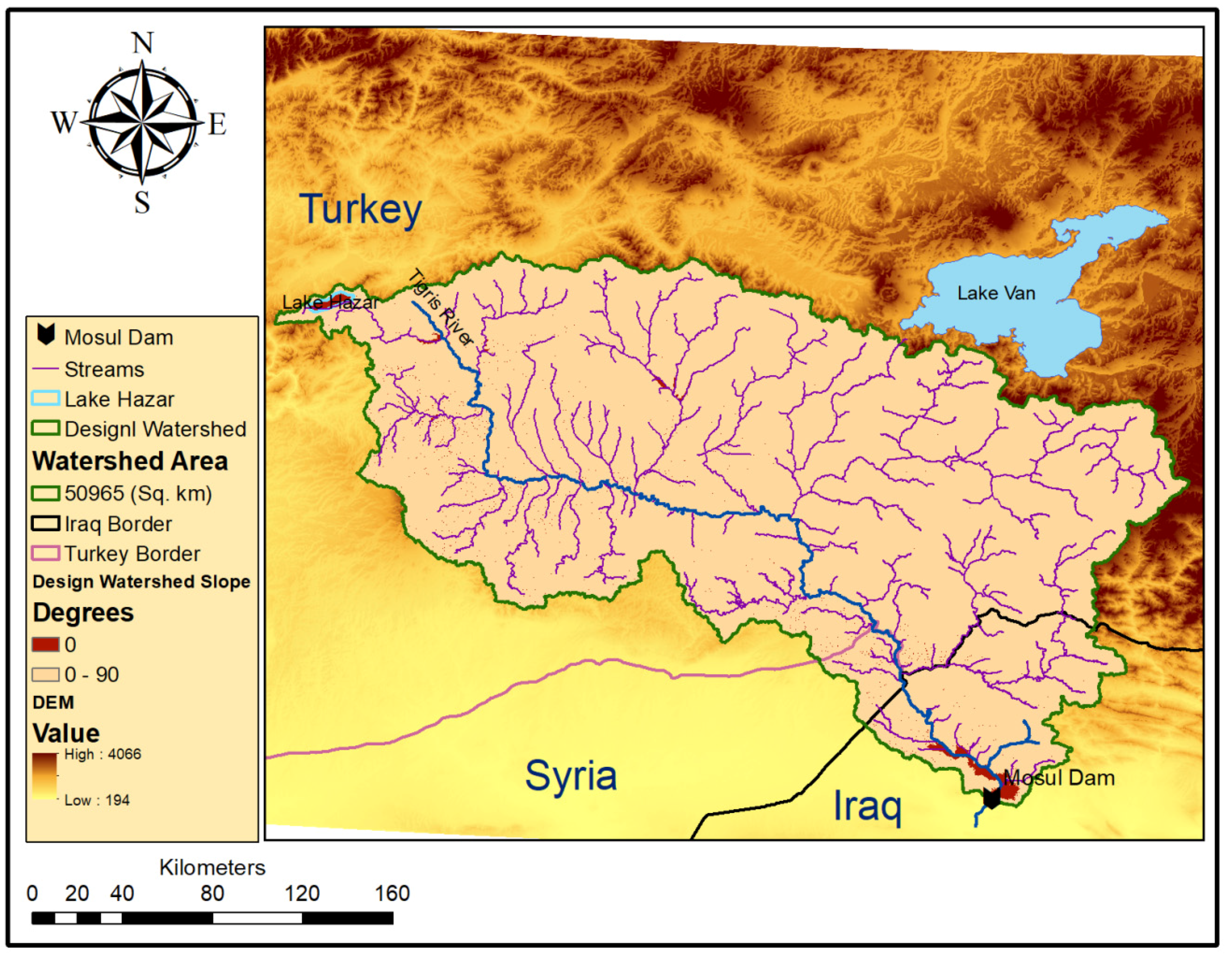
2. Study Area, Watershed Features and Methodology
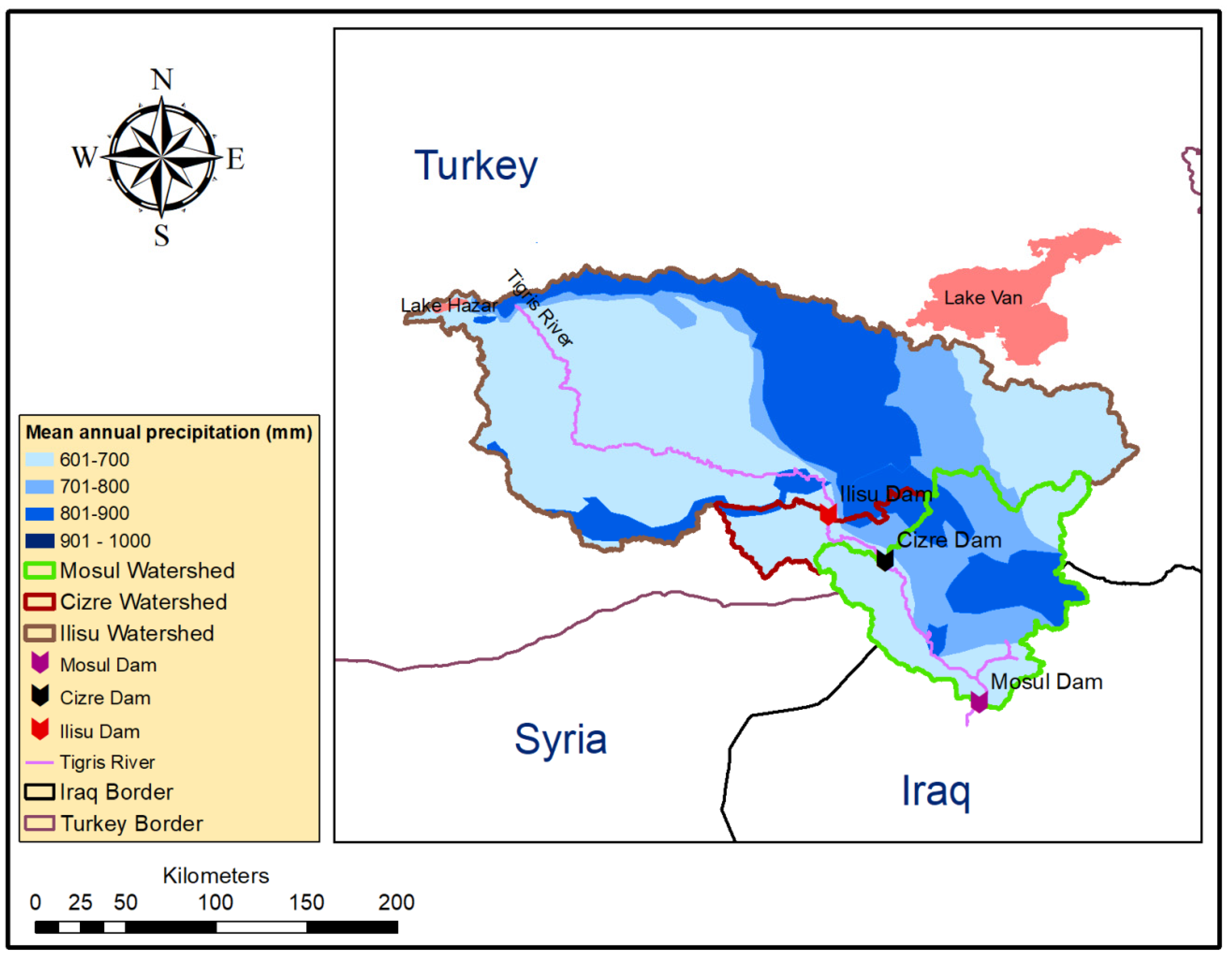
2.1. Study Area, Watershed Characteristics and Rainfall Distribution
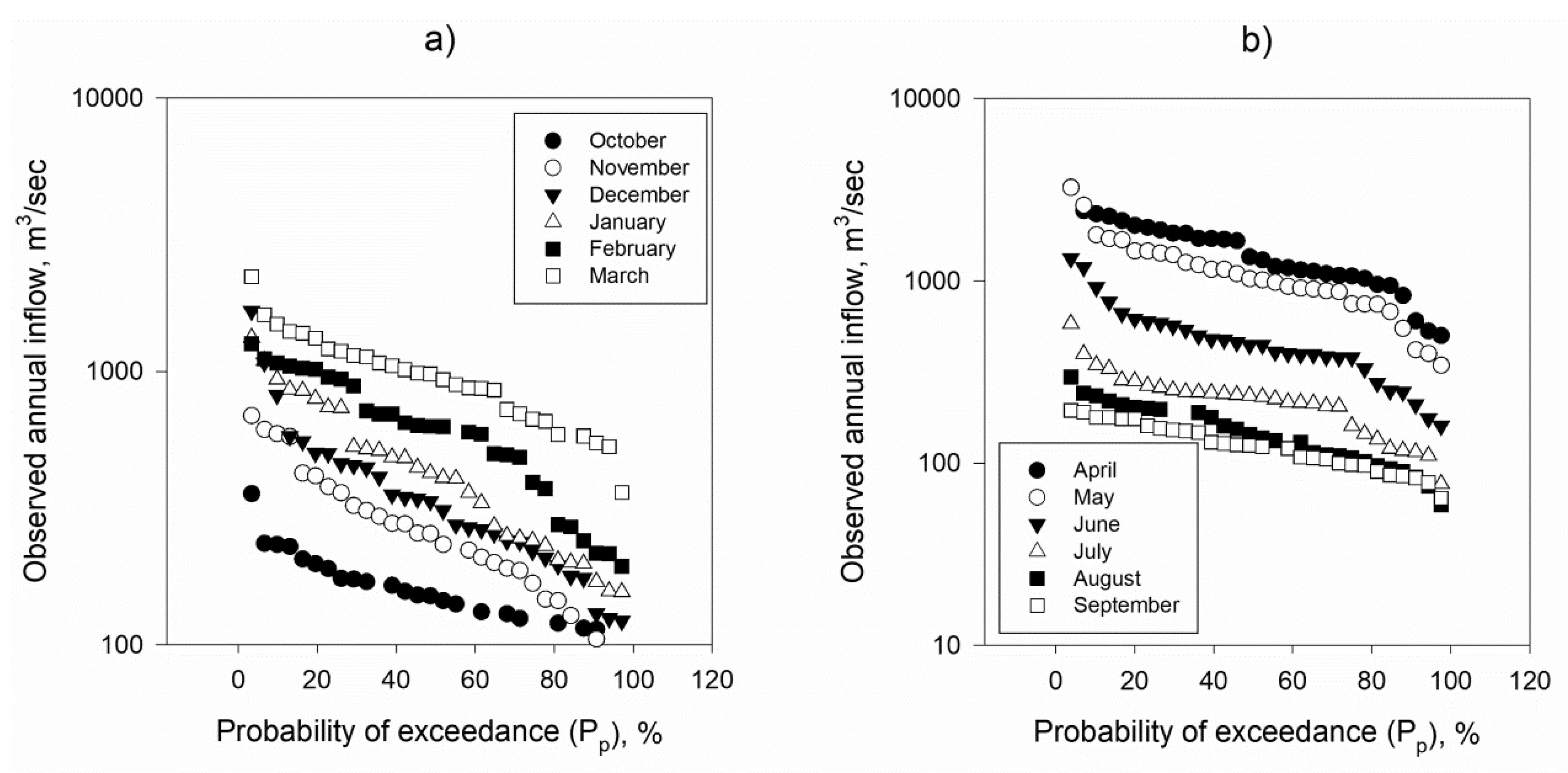
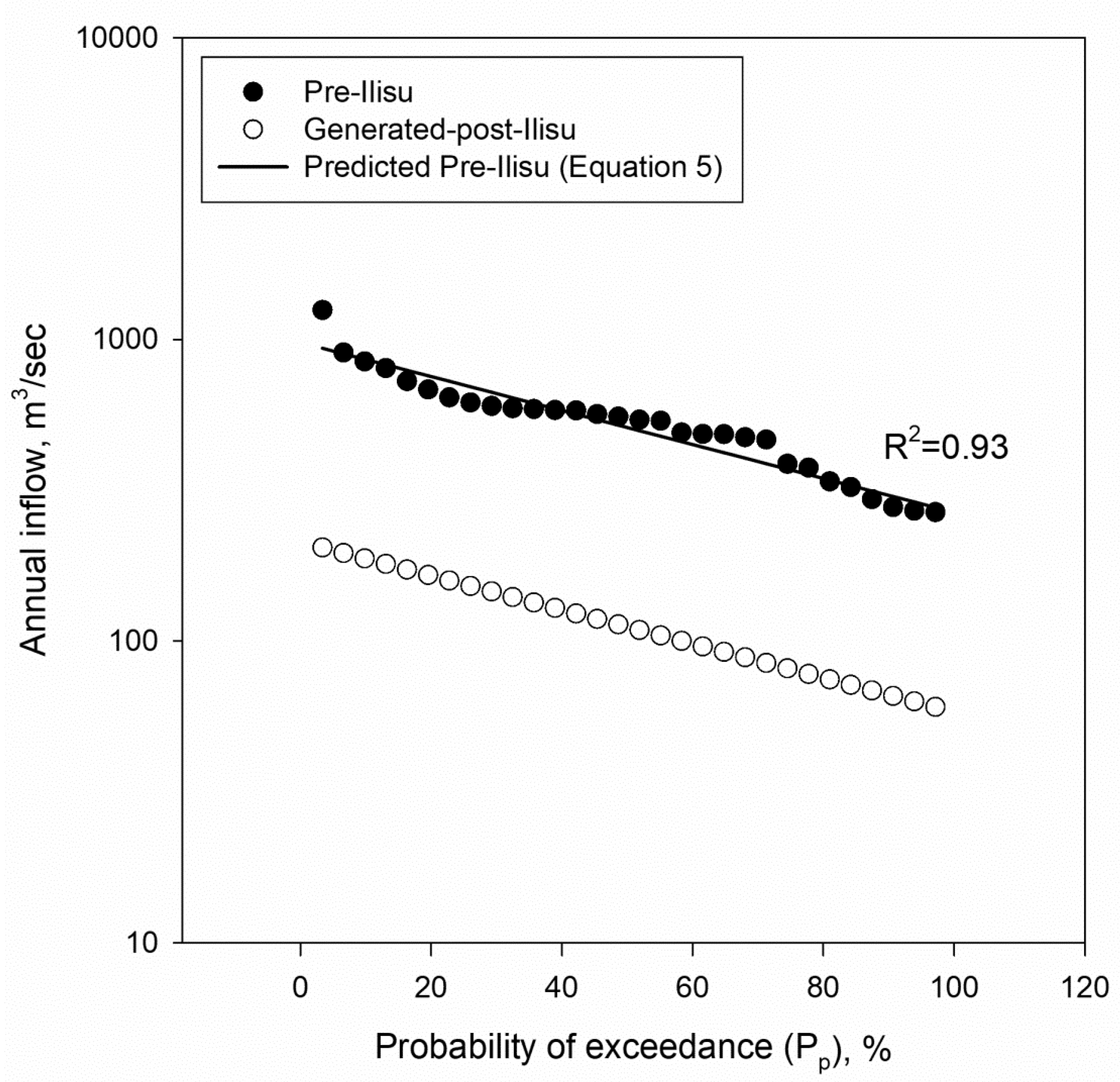
2.2. Inflow Calculations and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Watershed and Precipitation Distribution Analysis
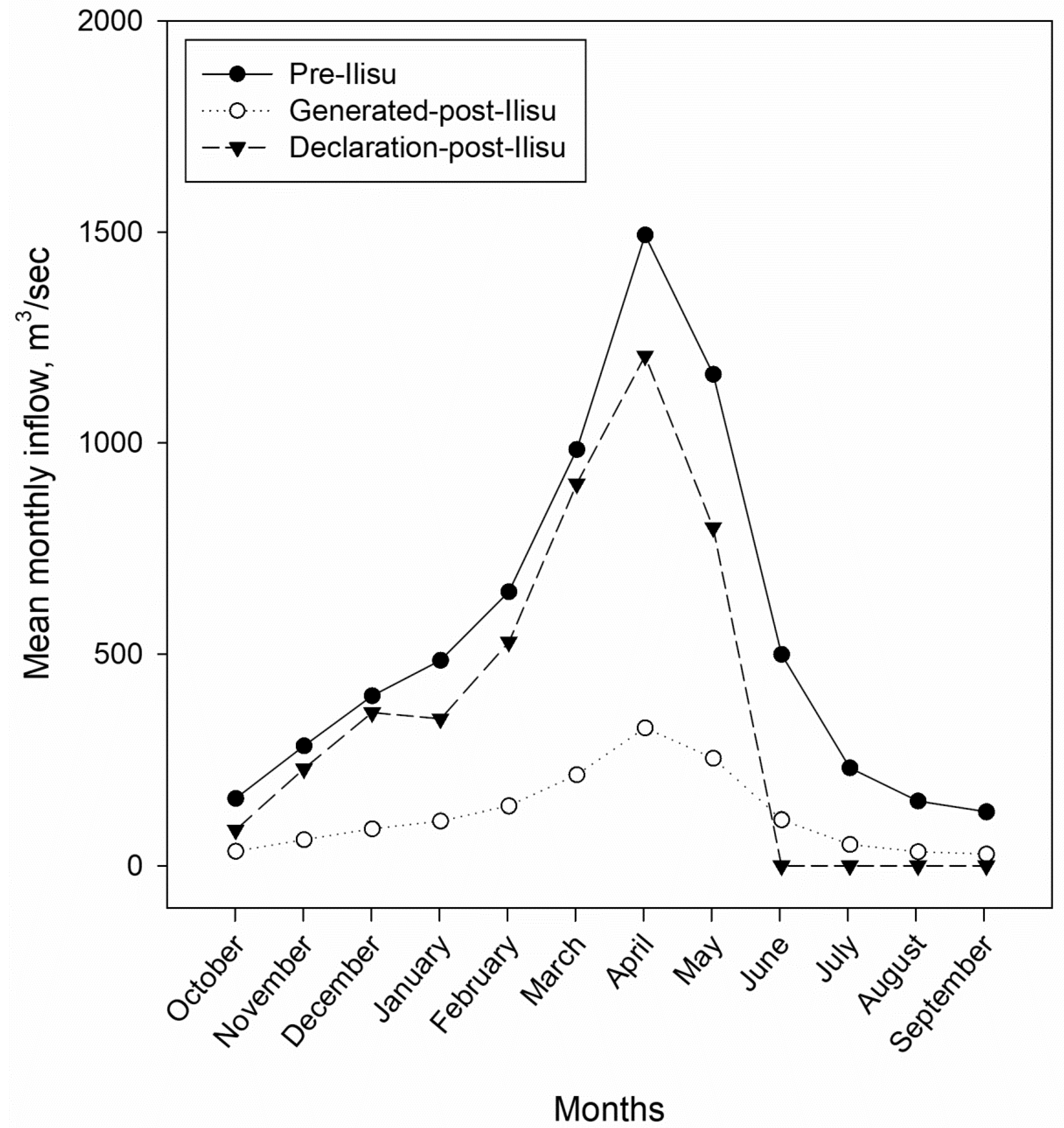
3.2. Inflow to the Mosul Dam
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahi, K.A.; Al-Madhhachi, A.T.; Al-Hussaini, S.N. Assessment of surface water resources of eastern Iraq. Hydrology 2019, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Madhhachi, A.T.; Al-Mussawy, H.A.; Basheer, M.I.; Abdul-Sahib, A.A. Quantifying Tigris riverbanks stability of southeast Baghdad city using BSTEM. Int. J. Hydrol. Sci. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partow, H. The Mesopotamian Marshlands: Demise of an Ecosystem Early Warning and Assessment; Division of Early Warning and Assessment, United Nations Environment Program: Nairobi, Kenya, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Rahi, K.A.; Halihan, T. Changes in the salinity of the Euphrates River system in Iraq. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2010, 10, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgen, A. The Southeastern Anatolia Project (GAP) in Turkey: An alternative perspective on the major rationales of GAP. J. Balk. Near East. Stud. 2019, 21, 532–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolars, J. Problems of International River Management: The Case of the Euphrates, 2nd ed.; International waters of the Middle East—from Euphrates–Tigris to Nile; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1994; pp. 44–94. [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, M.; Ulu, A.; Karaduman, C. CFD Analysis of Ilısu Dam Sluice Outlet. Fırat Univ. Turk. J. Sci. Technol. 2018, 13, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, M.; Ulu, A.; Karaduman, C. Investigation of aeration performance of Ilısu Dam outlet using two-phase flow model. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, E.; Tigrek, S. Hydropower production without sacrificing environment: A case study of Ilisu Dam and Hasankeyf. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2016, 32, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, E.; Tigrek, S. The Tigris hydropower system operations: The need for an integrated approach. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2019, 35, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, W.H.; Ronayne, M. The Ilisu Dam Environmental Impact Assessment Report: Review and critique. Public Archaeol. 2002, 2, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahi, K.A.; Halihan, T. Salinity evolution of the Tigris River. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2018, 18, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declaration, B.; Williams, P.B.; Frucht, S.B. A Review of the Hydrologic and Geomorphic Impacts of the Proposed Ilisu Dam. Available online: http://www2.weed-online.org/uploads/PWA_Ilisu_Report.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2016).
- Al-Ansari, N.; Issa, I.E.; Sissakian, V.; Adamo, N.; Knutsson, S. Mystery of Mosul Dam the most dangerous dam in the world: The project. J. Earth Sci. Geotech. Eng. 2015, 5, 15–31. [Google Scholar]
- Rahi, K.A. Salinity management in the Shatt Al-Arab River. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosul, D. Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mosul_Dam (accessed on 28 February 2020).
- Al-Taiee, T.M.; Rasheed, A.M. Simulation Tigris River Flood Wave in Mosul City Due to a Hypothetical Mosul Dam Break. Damascus Univ. J. 2009, 25, 17–36. [Google Scholar]
- Mosul Dam Task Force Declares: Mission Complete, Departs Iraq. Mosul Dam Task Force Program Office. Available online: https://www.defensemedianetwork.com/stories/mosul-dam-task-force-declares-mission-complete-departs-iraq/ (accessed on 27 February 2020).
- Bosshard, P.; Declaration, B. Ilisu–a Test Case of International Policy Coherence. Available online: https://www.rivernet.org/turquie/ilisu.htm (accessed on 5 May 2019).
- Yihdego, Y.; Webb, J.A. An empirical water budget model as a tool to identify the impact of land-use change in stream flow in southeastern Australia. Water Resour. Manag. J. 2013, 27, 4941–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yihdego, Y.; Webb, J.A. Assessment of wetland hydrological dynamics in a modified catchment basin: Case of Lake Buninjon, Victoria, Australia. Water Resour. Manag. J. 2017, 89, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yihdego, Y.; Khalil, A.; Salem, S.H. Nile River’s Basin Dispute: Perspectives of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD). Glob. J. Hum. Soc. Sci. 2017, 17, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Yihdego, Y.; Reta, G.; Becht, R. Human impact assessment through a transient numerical modelling on The UNESCO World Heritage Site, Lake Navaisha, Kenya. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worst-Case. The Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary, Merriam-Webster Inc. Available online: https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/worst-case (accessed on 19 January 2020).
- United States Geological Survey, Earth Explorer (USGS-EE), 2018. Available online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 5 January 2019).
- Saleh, D.K. Stream Gage Descriptions and Streamflow Statistics for Sites in the Tigris River and Euphrates River Basins, Iraq; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2010.
- United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia (UN-ESCWA) and Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe (BGR). Chapter 3: Tigris River Basin. In Inventory of Shared Water Resources in Western Asia; UN-ESCWA: Beirut, Lebanon, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Barnard, R.W.; Perera, C.; Surles, J.G.; Trindade, A.A. The linearly decreasing stress Weibull (LDSWeibull): A new Weibull-like distribution. J. Balk. Near East. Stud. 2019, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, M.E.; Thomas, W.O.; Riggs, H.C. Nationwide summary of U.S. In Geological Survey Regional Regression Equations for Estimating Magnitude and Frequency of Floods for Ungaged SITES; USGS Water-Resources Investigations Report: Washington, VA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, M.N.; Al-Madhhachi, A.T.; Esmael, S.A. Quantifying soil erodibility parameters due to wastewater chemicals. Int. J. Hydrol. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 550–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Husseini, T.R.; Al-Madhhachi, A.T.; Hasan, M.B. Laboratory experiments and numerical model of local scour around submerged sharp crested weir. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 2020, 32, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Madhhachi, A.T.; Mutter, G.M.; Hasan, M.B. Predicting Mechanistic Detachment Model due to Lead-Contaminated Soil Treated with Iraqi Stabilizers. KSCE J. Civil Eng. 2019, 23, 2898–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Digital Elevation Model (DEM), m (AMSL) | Area of the Original Watershed, km2 | Total Catchment Area, km2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mosul Watershed | Cizre and Ilisu Watersheds | ||
| 254–796 | 14980 | 4816 | 10164 |
| 797–1221 | 16779 | 1986 | 14793 |
| 1222–1743 | 8679 | 2213 | 6466 |
| 1744–2330 | 6249 | 1210 | 5039 |
| 2331–3622 | 4278 | 893 | 3385 |
| Total km2 | 50965 | 11118 | 39847 |
| Average DEM, m (AMSL) | 1239 | 1164 | 1260 |
| Annual Precipitation Isolated, mm | |||
| 601–700 | 28363 | 4411 | 23952 |
| 701–800 | 8547 | 3718 | 4829 |
| 801–900 | 11487 | 2989 | 8498 |
| 901–1000 | 2569 | 0 | 2569 |
| Total km2 | 50965 | 11118 | 39847 |
| Average precipitation, mm | 727 | 737 | 724 |
| Statistical Description | Oct | Nov. | Dec. | Jan. | Feb. | March | April | May | June | July | Aug. | Sept. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (m3/sec) | 159 | 283 | 402 | 486 | 648 | 985 | 1493 | 1163 | 499 | 231 | 153 | 128 |
| Std. Dev. | 55 | 162 | 316 | 305 | 306 | 392 | 638 | 619 | 268 | 99 | 58 | 37 |
| Maximum (m3/sec) | 357 | 690 | 1665 | 1330 | 1265 | 2222 | 3275 | 3260 | 1329 | 584 | 298 | 195 |
| Minimum (m3/sec) | 78 | 95 | 122 | 156 | 194 | 360 | 502 | 345 | 160 | 77 | 59 | 64 |
| Median (m3/sec) | 148 | 244 | 323 | 417 | 629 | 956 | 1332 | 1023 | 445 | 233 | 141 | 124 |
| 25% | 120 | 163 | 217 | 238 | 388 | 665 | 1058 | 749 | 368 | 156 | 106 | 98 |
| 75% | 179 | 365 | 470 | 736 | 944 | 1191 | 1924 | 1433 | 590 | 262 | 198 | 156 |
| Regression Analysis | ||||||||||||
| a | 0.005 | 0.013 | 0.018 | 0.023 | 0.028 | 0.035 | 0.058 | 0.047 | 0.02 | 0.008 | 0.005 | 0.004 |
| b | 0.011 | 0.019 | 0.021 | 0.022 | 0.019 | 0.014 | 0.016 | 0.017 | 0.017 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.010 |
| Coefficient of determination, R2 | 0.90 | 0.97 | 0.92 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.87 | 0.97 | 0.98 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Madhhachi, A.-S.T.; Rahi, K.A.; Leabi, W.K. Hydrological Impact of Ilisu Dam on Mosul Dam; the River Tigris. Geosciences 2020, 10, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10040120
Al-Madhhachi A-ST, Rahi KA, Leabi WK. Hydrological Impact of Ilisu Dam on Mosul Dam; the River Tigris. Geosciences. 2020; 10(4):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10040120
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Madhhachi, Abdul-Sahib T., Khayyun A. Rahi, and Wafa K. Leabi. 2020. "Hydrological Impact of Ilisu Dam on Mosul Dam; the River Tigris" Geosciences 10, no. 4: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10040120
APA StyleAl-Madhhachi, A.-S. T., Rahi, K. A., & Leabi, W. K. (2020). Hydrological Impact of Ilisu Dam on Mosul Dam; the River Tigris. Geosciences, 10(4), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10040120






