Review of Impact Factors of the Velocity of Large Hailstones for Laboratory Hail Impact Testing Consideration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Hailstone Properties in Current Standard Testing Procedures
3. The Terminal Velocity of Hailstones
3.1. Density of Hailstones
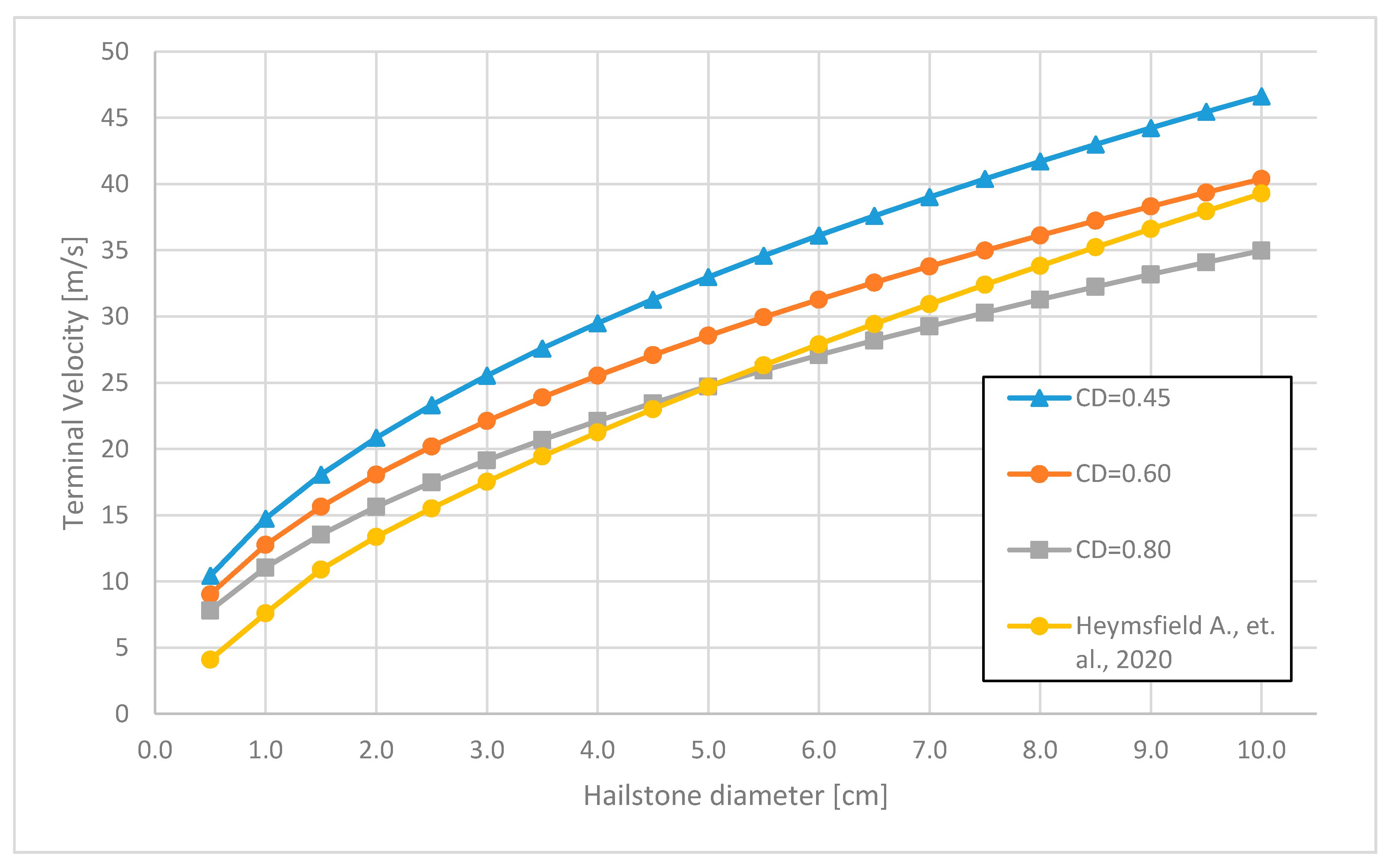
3.2. The Drag Coefficient and Reynolds Number
3.3. The Spherical Shape of Hailstones
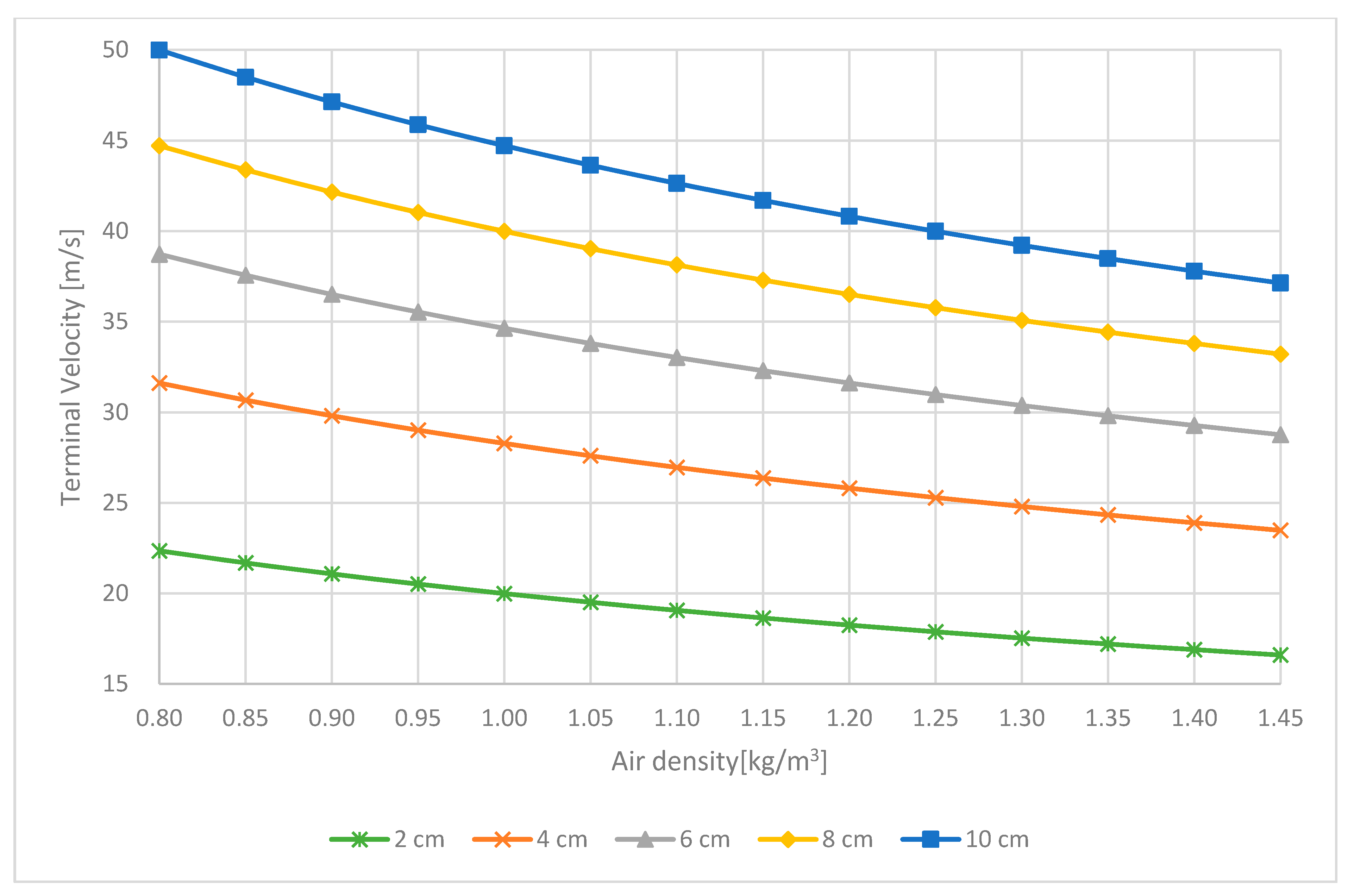
3.4. The Effect of Air Density
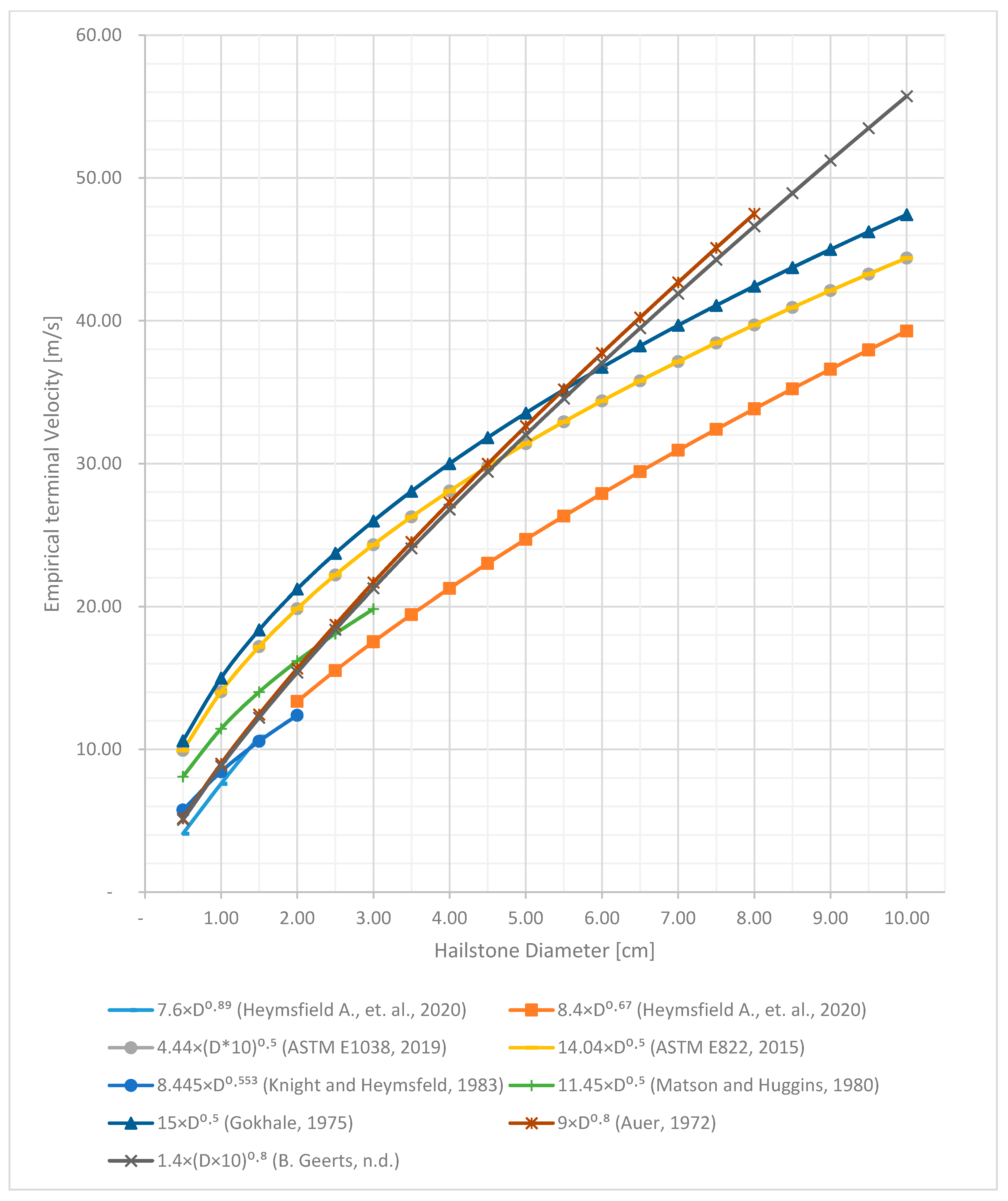
3.5. Empirical Models to Determine Terminal Velocity
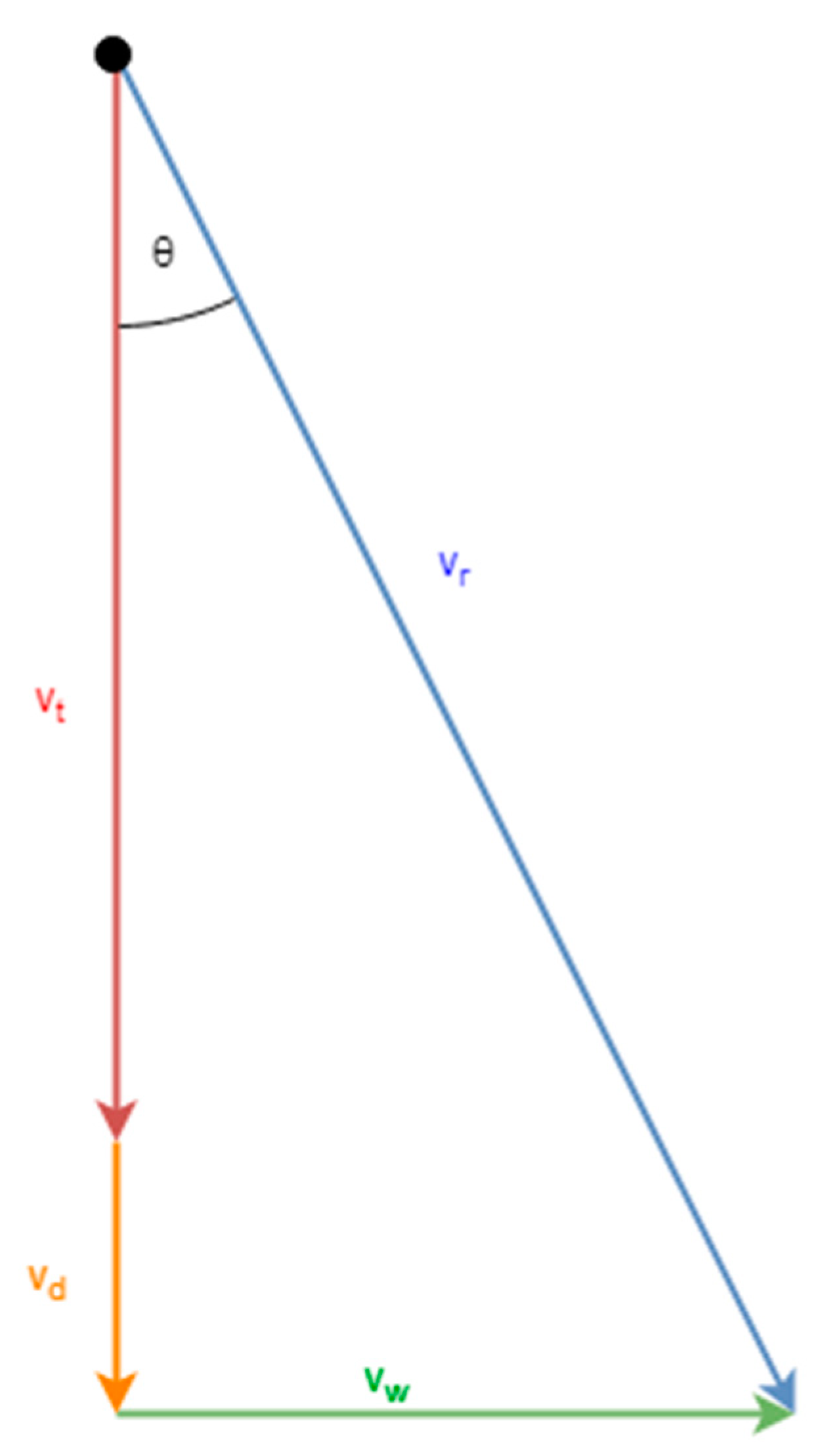
4. Hailstone Velocity in Combination with Wind
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fraile, R.; Berthet, C.; Dessens, J.; Sánchez, J.L. Return periods of severe hailfalls computed from hailpad data. Atmos. Res. 2003, 67–68, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinet, F. Climatology of hail in France. Atmos. Res. 2001, 56, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, J.; Elsom, D.M.; Reynolds, D.J. Climatology of severe hailstorms in Great Britain. Atmos. Res. 2001, 56, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozowski, E.P.; Strong, G.S. On the Calibration of Hailpads. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 1978, 17, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO). Technical Regulations: Volume II—Meteorological Service for International Air Navigation, 2018th ed.; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- National Weather Service. Severe Weather Definitions. n. d. Available online: https://www.weather.gov/bgm/severedefinitions (accessed on 3 August 2020).
- Kumjian, M.R.; Gutierrez, R.; Soderholm, J.S.; Nesbitt, S.W.; Maldonado, P.; Luna, L.M.; Marquis, J.; Bowley, K.A.; Imaz, M.A.; Salio, P. Gargantuan Hail in Argentina. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.S.; Blong, R.J.; Leigh, R.J.; McAneney, K.J. Characteristics of the 14 April 1999 Sydney hailstorm based on ground observations, weather radar, insurance data and emergency calls. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 5, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noon, R. Forensic Engineering Investigation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Greenfeld, S.H. Hail Resistance of Roofing Products; Building Research Division, US Institute for Applied Technology: Washington, DC, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Lucy, R.R.; Petty, S.E. Hail Damage Assessments to Low-Sloped Roof Systems. In Forensic Engineering: Damage Assessments for Residential and Commercial Structures; Petty, S.E., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 119–159. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, R.; Juntikka, R.; Asp, L.E. High Velocity Hail Impact on Composite Laminates—Modelling and Testing. In Dynamic Failure of Composite and Sandwich Structures; Abrate, S., Castanié, B., Rajapakse, Y.D.S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 393–426. [Google Scholar]
- E44 Committee. Practice for Determining Resistance of Solar Collector Covers to Hail by Impact with Propelled Ice Balls 2015; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- E44 Committee. Test Method for Determining Resistance of Photovoltaic Modules to Hail by Impact with Propelled Ice Balls 2019; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F07 Committee. Test Method for Hail Impact Resistance of Aerospace Transparent Enclosures; West ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FM Approvals. Specification Test Standard for Impact Resistance Testing of Rigid Roofing Materials by Impacting with Freezer Ice Balls July 2005; FM Approvals: West Gloucester, RI, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- UL Standard. Standard for Impact Resistance of Prepared Roof Covering Materials 1/25/2010. Available online: https://standardscatalog.ul.com/ProductDetail.aspx?productId=UL2218 (accessed on 10 December 2020).
- Schleusener, R.A.; Jennings, P.C. An Energy Method for Relative Estimates of Hail Intensity. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1960, 41, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, A.B.; Matson, R.J.; Crow, E.L. The Hailpad: Construction and Materials, Data Reduction, and Calibration; Citeseer: Boulder, CO, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Browning, K.A.; Ludlam, F.H.; Macklin, W.C. The density and structure of hailstones. Q. J. R. Met. Soc. 1963, 89, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittori, O.; di Caporiacco, G. The density of hailstones. Nubila 1959, 2, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Insurance Institute for Business & Home Safety. Impact Resistance Test Protocol for Asphalt Shingles. 2019. Available online: https://ibhs.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/ibhs-impact-resistance-test-protocol-for-asphalt-shingles.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2020).
- Laurie, J.A.P. Hail and Its Effects on Buildings; Council for Scientific and Industrial Research: Pretoria, South Africa, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Petty, S.E. Synthetic Storm Damage (Fraud) to Roof Surfaces. In Forensic Engineering: Damage Assessments for Residential and Commercial Structures; Petty, S.E., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 161–182. [Google Scholar]
- List, R. Zur Aerodynamik von Hagelkörnern. ZAMP 1959, 10, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, F.W.; Calvin, L.D. Hailfall of 10 September 1959 Near Medford, Oregon. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1961, 42, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilham, E.G.; Relf, E.F. The dynamics of large hailstones. Q. J. R. Met. Soc. 1937, 63, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, G.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, D.C.; Kumar, H. Comparative Analysis of Different Air Density Equations. MAPAN 2013, 28, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, H.P. A General Equation for the Terminal Fall Speed of Solid Hydrometeors. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 2419–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, R.J.; Huggins, A.W. The Direct Measurement of the Sizes, Shapes and Kinematics of Falling Hailstones. J. Atmos. Sci. 1980, 37, 1107–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, C.A.; Knight, N.C. Hailstorms. In Severe Convective Storms; Doswell, C.A., Ed.; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 223–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisner, C.; Orville, H.D.; Myers, C. A Numerical Model of a Hail-Bearing Cloud. J. Atmos. Sci. 1972, 29, 1160–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, R. Properties and Growth of Hailstones. In Thunderstorm Morphology and Dynamics; Kessler, E., Ed.; University of Oklahoma Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1982; pp. 409–445. [Google Scholar]
- Prodi, F. Measurements of Local Density in Artificial and Natural Hailstones. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1970, 9, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, A.J. A Technique for Investigating Graupel and Hail Development. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1983, 22, 1143–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, A.J. The Characteristics of Graupel Particles in Northeastern Colorado Cumulus Congestus Clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 1978, 35, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, R. Kennzeichen atmosphärischer Eispartikeln: 1. Teil. J. Appl. Math. Phys. (ZAMP) 1958, 9, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, R. Kennzeichen atmosphärischer Eispartikeln: 2. Teil. J. Appl. Math. Phys. (ZAMP) 1958, 9, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olovsson, I. Snow, Ice and Other Wonders of Water: A Tribute to the Hydrogen Bond; World Scientific: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, H.H. Properties of ice and supercooled water. In CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics: A Ready-Reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data, 95th ed.; Haynes, W.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Giammanco, I.M.; Maiden, B.R.; Estes, H.E.; Brown-Giammanco, T.M. Using 3D Laser Scanning Technology to Create Digital Models of Hailstones. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, C.A.; Schlatter, P.T.; Schlatter, T.W. An Unusual Hailstorm on 24 June 2006 in Boulder, Colorado. Part II: Low-Density Growth of Hail. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2008, 136, 2833–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giammanco, I.M.; Brown, T.M.; Grant, R.G.; Dewey, D.L.; Hodel, J.D.; Stumpf, R.A. Evaluating the Hardness Characteristics of Hail through Compressive Strength Measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battan, L.J.; Wilson, D.S. “Hail” on a Mountain in Arizona. J. Appl. Meteorol. (1962–1982) 1969, 8, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Knight, C.A.; Knight, N.C. Quenched, Spongy Hail. J. Atmos. Sci. 1973, 30, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Morgan, G.M.; Towery, N.G. On the Role of Strong Winds in Damage to Crops by Hail and Its Estimation with a Simple Instrument. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1976, 15, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torenbeek, E.; Wittenberg, H. Flight Physics: Essentials of Aeronautical Disciplines and techNology, with Historical Notes; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, F.F. Functional Dependence of Drag Coefficient of a Sphere on Reynolds Number. Phys. Fluids 1970, 13, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, A.; Szakáll, M.; Jost, A.; Giammanco, I.; Wright, R. A Comprehensive Observational Study of Graupel and Hail Terminal Velocity, Mass Flux, and Kinetic Energy. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 75, 3861–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magono, C. Thunderstorms; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Oxford, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Macklin, W.C.; Ludlam, F.H. The fallspeeds of hailstones. Q. J R. Met. Soc. 1961, 87, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, A.S. Weather Modification by Cloud Seeding; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Gokhale, N.R. Hailstorms and Hailstone Growth, 1st ed.; State University of New York Press: Albany, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Theis, A.; Borrmann, S.; Mitra, S.K.; Heymsfield, A.J.; Szakáll, M. A Wind Tunnel Investigation into the Aerodynamics of Lobed Hailstones. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.K.; Chueh, C.-C.; Wang, C.-K. A numerical study of flow fields of lobed hailstones falling in air. Atmos. Researc. 2015, 160, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.K.; Chueh, C.-C. A numerical study on the ventilation coefficients of falling lobed hailstones. Atmos. Res. 2020, 234, 104737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, A.; Wright, R. Graupel and Hail Terminal Velocities: Does a “Supercritical” Reynolds Number Apply? J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 3392–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, A.; Szakáll, M.; Jost, A.; Giammanco, I.; Wright, R.; Brimelow, J. Corrigendum. J. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 77, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, A.J.; Giammanco, I.M.; Wright, R. Terminal velocities and kinetic energies of natural hailstones. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 8666–8672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; English, M.; Wong, R. Hailstone Size Distributions and Their Relationship to Storm Thermodynamics. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1985, 24, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, A.; Crow, E.L.; Long, A.B. Errors in Hailpad Data Reduction. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1980, 19, 733–747. [Google Scholar]
- Koontz, J.D. What Are the Effects of Hail on Residential Roofing Products? Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/What-are-the-effects-of-hail-on-residential-roofing-Koontz/e4d3f6c1a57462efdd39f5aa1ec740bf2809208e (accessed on 10 December 2020).
- Morgan, G.M., Jr.; Summers, P.W. Hailfall and Hailstorm Characteristics. In Thunderstorm Morphology and Dynamics; Kessler, E., Ed.; University of Oklahoma Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1982; pp. 363–408. [Google Scholar]
- Gessler, S.E.; Petty, S.E. Hail Fundamentals and General Hail-Strike Damage Assessment Methodology. In Forensic Engineering: Damage Assessments for Residential and Commercial Structures; Petty, S.E., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 23–67. [Google Scholar]
- Knight, N.C. Hailstone Shape Factor and Its Relation to Radar Interpretation of Hail. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1986, 25, 1956–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Picard, A.; Davis, R.S.; Gläser, M.; Fujii, K. Revised formula for the density of moist air (CIPM-2007). Metrologia 2008, 45, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, E.W. Thermophysical Properties of Air. In CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics: A Ready-Reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data, 95th ed.; Haynes, W.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 6–15, 6–20. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, T. Earth Atmosphere Model. 2014. Available online: https://www.grc.nasa.gov/WWW/K-12/rocket/atmosmet.html (accessed on 29 May 2019).
- Salby, M.L. Fundamentals of Atmospheric Physics; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA; London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- DvS, R. A Giant Hailstone from Kansas in Free Fall. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1972, 11, 1008–1011. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Department of the Interior Geological Survey. Elevations and Distances in the United States; U.S. Department of the Interior Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 2001.
- Auer, A.H., Jr. Distribution of Graupel and Hail with Size. Mon. Weather Rev. 1972, 100, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruppacher, H.R.; Klett, J.D. Microphysics of Clouds and Precipitation; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Geerts, B. Fall Speed of Hydrometeors. Available online: http://www-das.uwyo.edu/~geerts/cwx/notes/chap09/hydrometeor.html (accessed on 10 May 2019).
- Knight, N.C.; Heymsfield, A.J. Measurement and Interpretation of Hailstone Density and Terminal Velocity. J. Atmos. Sci. 1983, 40, 1510–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jenkins, D.R.; Mathey, R.G. Hail Impact Testing Procedure for Solar Collector Cover. STIN 1982, 83, 22841. [Google Scholar]
- Changnon, S.A. Hail sensing and small-scale variability of windblown hail. J. Weather Modif. 1973, 5, 30–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sioutas, M.; Meaden, T.; Webb, J.D. Hail frequency, distribution and intensity in Northern Greece. Atmos. Res. 2009, 93, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, K.A. The Structure and Mechanisms of Hailstorms. In Hail: A Review of Hail Science and Hail Suppression; Foote, G.B., Foote, G.B., Knight, C.A., Eds.; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1977; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Strauch, R.G.; Merrem, F.H. Structure of an Evolving Hailstorm, Part III: Internal Structure from Doppler. Radar. Mon. Weather Rev. 1976, 104, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.T. The Downburst: Microburst and Macroburst; The University of Chicago: Chicago, IL, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.W.; Wakimoto, R.M. The Discovery of the Downburst: T. T. Fujita’s Contribution. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 82, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microburst. In An Illustrated Dictionary of Aviation, 1st ed.; Kumar, B., de Remer, D., Marshall, D.M., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, E.; Boldi, B.; Matlin, A.; Weber, M.; Hodanish, S.; Sharp, D.; Goodman, S.; Raghavan, R.; Buechler, D. The behavior of total lightning activity in severe Florida thunderstorms. Atmos. Res. 1999, 51, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savory, E.; Parke, G.A.; Zeinoddini, M.; Toy, N.; Disney, P. Modelling of tornado and microburst-induced wind loading and failure of a lattice transmission tower. Eng. Struct. 2001, 23, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encyclopædia Britannica. Microburst. 2019. Available online: https://academic-eb-com.lib-e2.lib.ttu.edu/levels/collegiate/article/microburst/52495 (accessed on 15 June 2019).
- Holmes, J.; Oliver, S. An empirical model of a downburst. Eng. Struct. 2000, 22, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Hangan, H. Numerical simulations of impinging jets with application to downbursts. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2007, 95, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, M.S.; Wood, G.S.; Fletcher, D.F. Numerical simulation of downburst winds. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2009, 97, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunter, W.S.; Schroeder, J.L. High-resolution full-scale measurements of thunderstorm outflow winds. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2015, 138, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.C.; Hidayat, F.A. Gust factors for thunderstorm and non-thunderstorm winds. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2002, 90, 1683–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, F.T.; Smith, D.A.; Schroeder, J.L.; Mehta, K.C. Thunderstorm characteristics of importance to wind engineering. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2014, 125, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
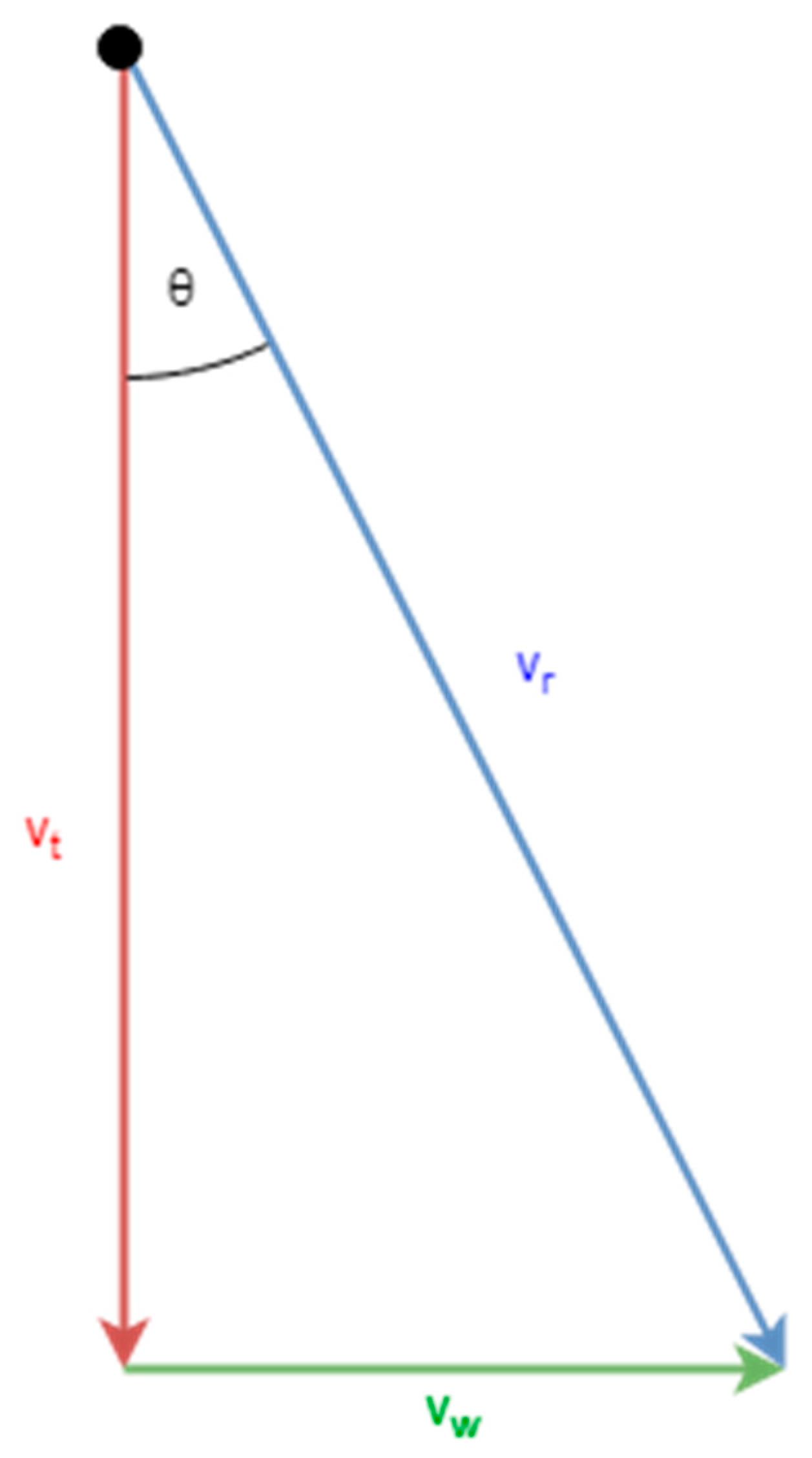
| Hailstone Diameter (cm) | Vertical Wind Speed (m/s) | Horizontal Wind Speed (m/s) | Resulting Hailstone Velocity (m/s) | Increase Compared to Terminal Velocity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 18.07 | 0 |
| 15 | 23.48 | 30 | ||
| 20 | 26.95 | 49 | ||
| 30 | 35.02 | 94 | ||
| 5 | 0 | 23.07 | 28 | |
| 15 | 27.51 | 52 | ||
| 20 | 30.53 | 69 | ||
| 30 | 37.84 | 109 | ||
| 10 | 0 | 28.07 | 55 | |
| 15 | 31.82 | 76 | ||
| 20 | 34.46 | 91 | ||
| 30 | 41.08 | 127 | ||
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 31.29 | 0 |
| 15 | 34.70 | 11 | ||
| 20 | 37.14 | 19 | ||
| 30 | 43.35 | 39 | ||
| 5 | 0 | 36.29 | 16 | |
| 15 | 39.27 | 25 | ||
| 20 | 41.44 | 32 | ||
| 30 | 47.09 | 50 | ||
| 10 | 0 | 41.29 | 32 | |
| 15 | 43.93 | 40 | ||
| 20 | 45.88 | 47 | ||
| 30 | 51.04 | 63 | ||
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 40.40 | 0 |
| 15 | 43.09 | 7 | ||
| 20 | 45.08 | 12 | ||
| 30 | 50.32 | 25 | ||
| 5 | 0 | 45.40 | 12 | |
| 15 | 47.81 | 18 | ||
| 20 | 49.61 | 23 | ||
| 30 | 54.41 | 35 | ||
| 10 | 0 | 50.40 | 25 | |
| 15 | 52.58 | 30 | ||
| 20 | 54.22 | 34 | ||
| 30 | 58.65 | 45 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dieling, C.; Smith, M.; Beruvides, M. Review of Impact Factors of the Velocity of Large Hailstones for Laboratory Hail Impact Testing Consideration. Geosciences 2020, 10, 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10120500
Dieling C, Smith M, Beruvides M. Review of Impact Factors of the Velocity of Large Hailstones for Laboratory Hail Impact Testing Consideration. Geosciences. 2020; 10(12):500. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10120500
Chicago/Turabian StyleDieling, Christian, Milton Smith, and Mario Beruvides. 2020. "Review of Impact Factors of the Velocity of Large Hailstones for Laboratory Hail Impact Testing Consideration" Geosciences 10, no. 12: 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10120500
APA StyleDieling, C., Smith, M., & Beruvides, M. (2020). Review of Impact Factors of the Velocity of Large Hailstones for Laboratory Hail Impact Testing Consideration. Geosciences, 10(12), 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10120500






