Evidence of Gas Emissions from Permafrost in the Russian Arctic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Gas Emissions in the Russian Arctic
2.1. Emission from Terrestrial Permafrost
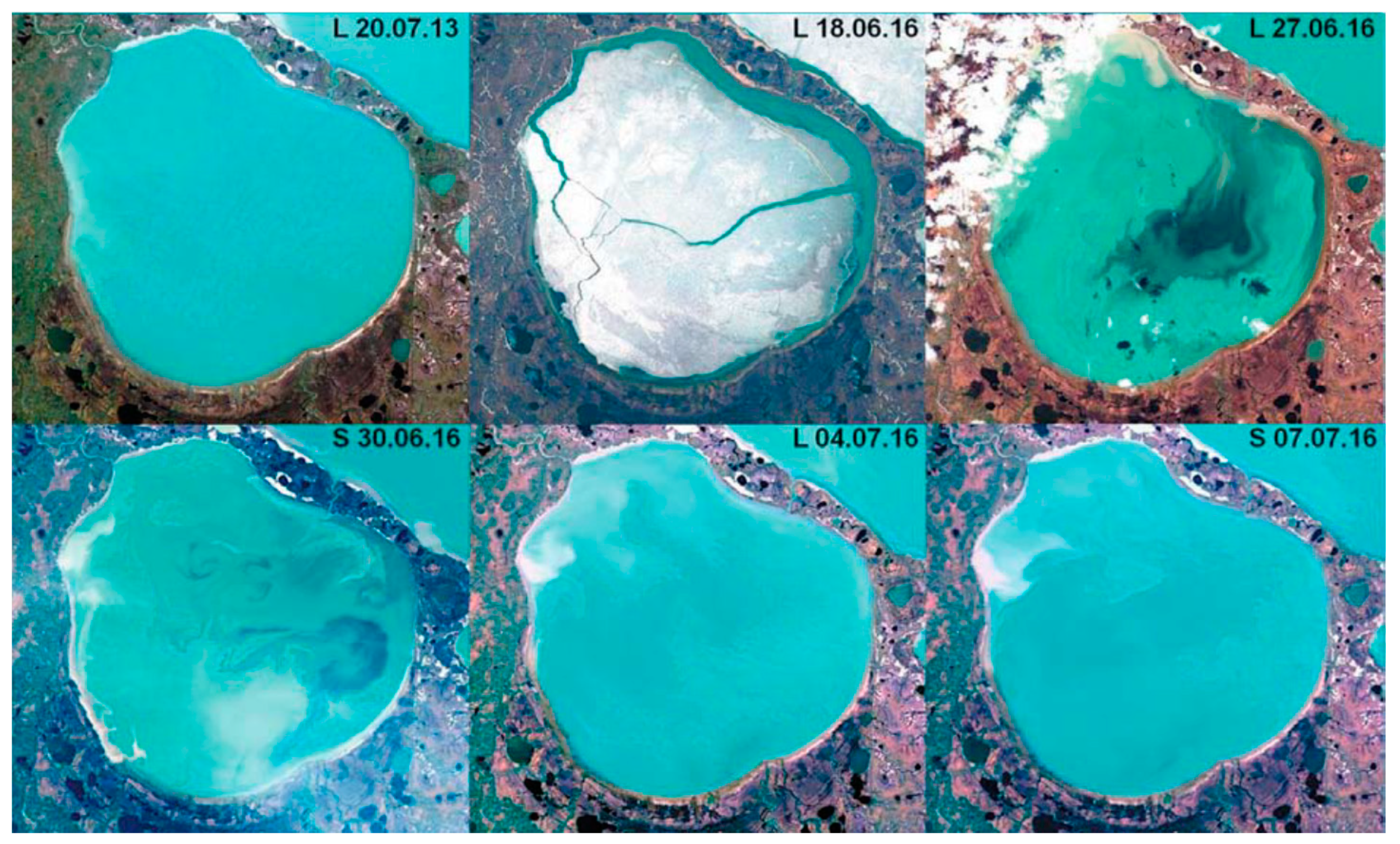
2.1.1. Gas Venting from Lakes
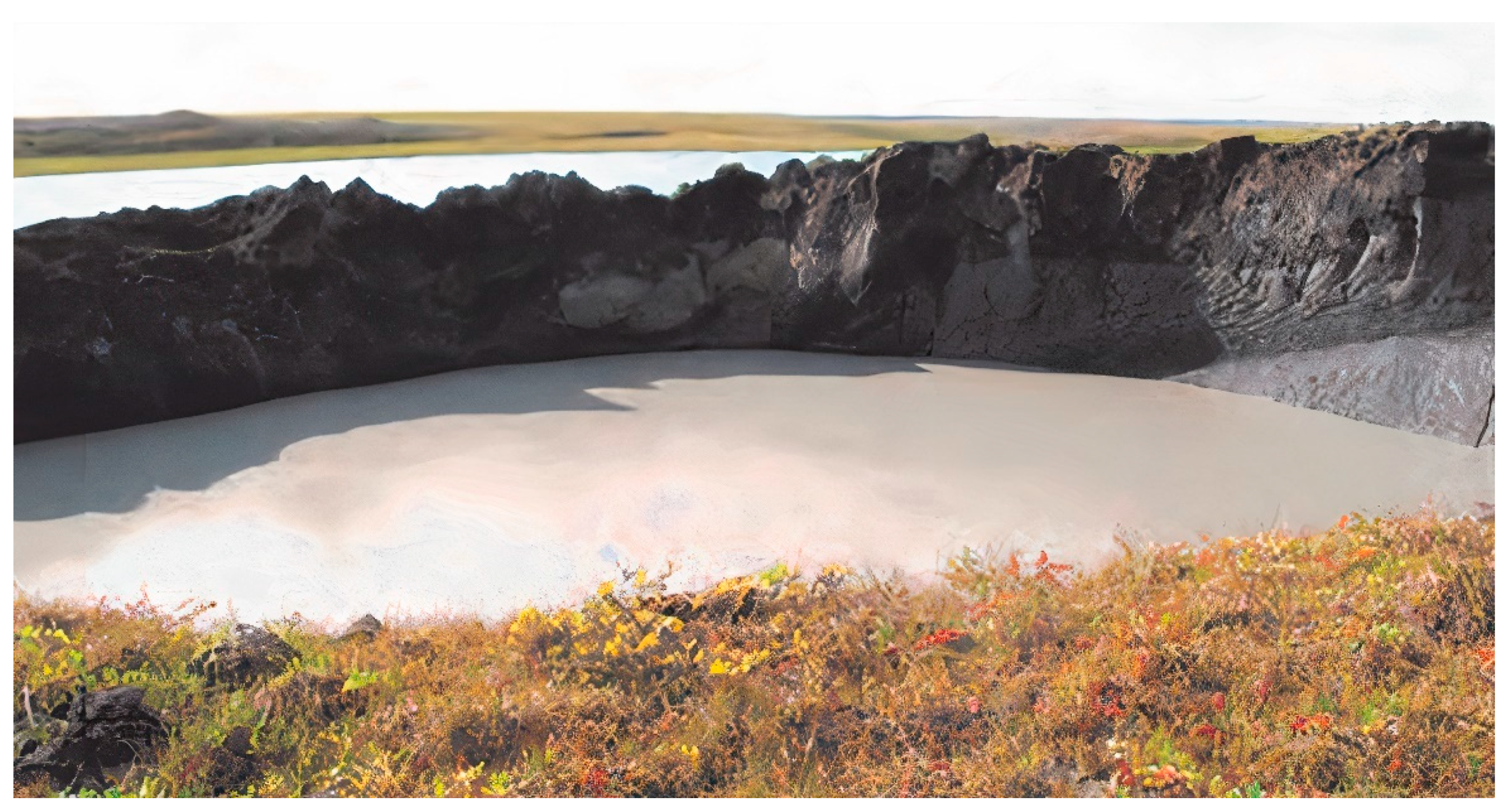
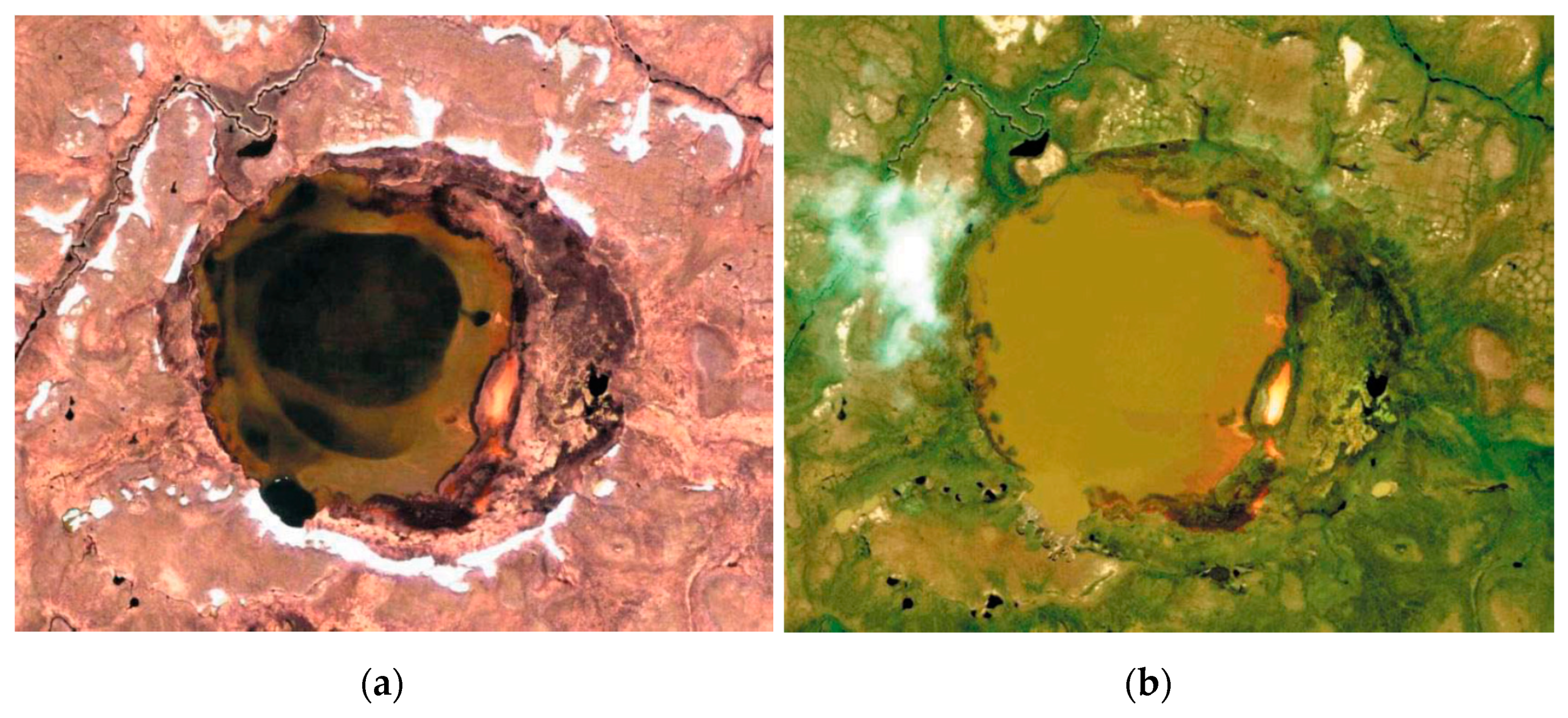
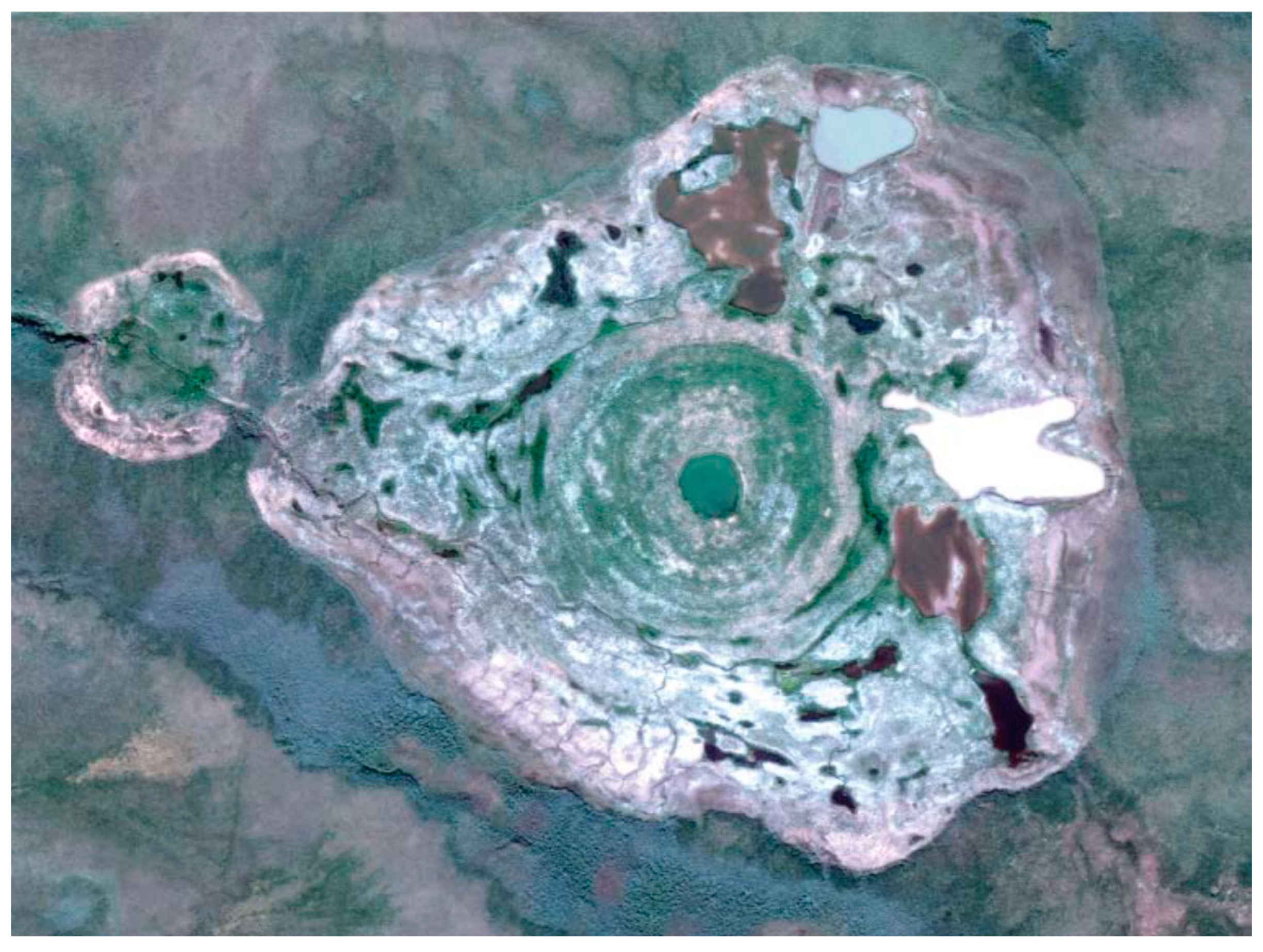
2.1.2. Gas Emission with the Formation of Craters
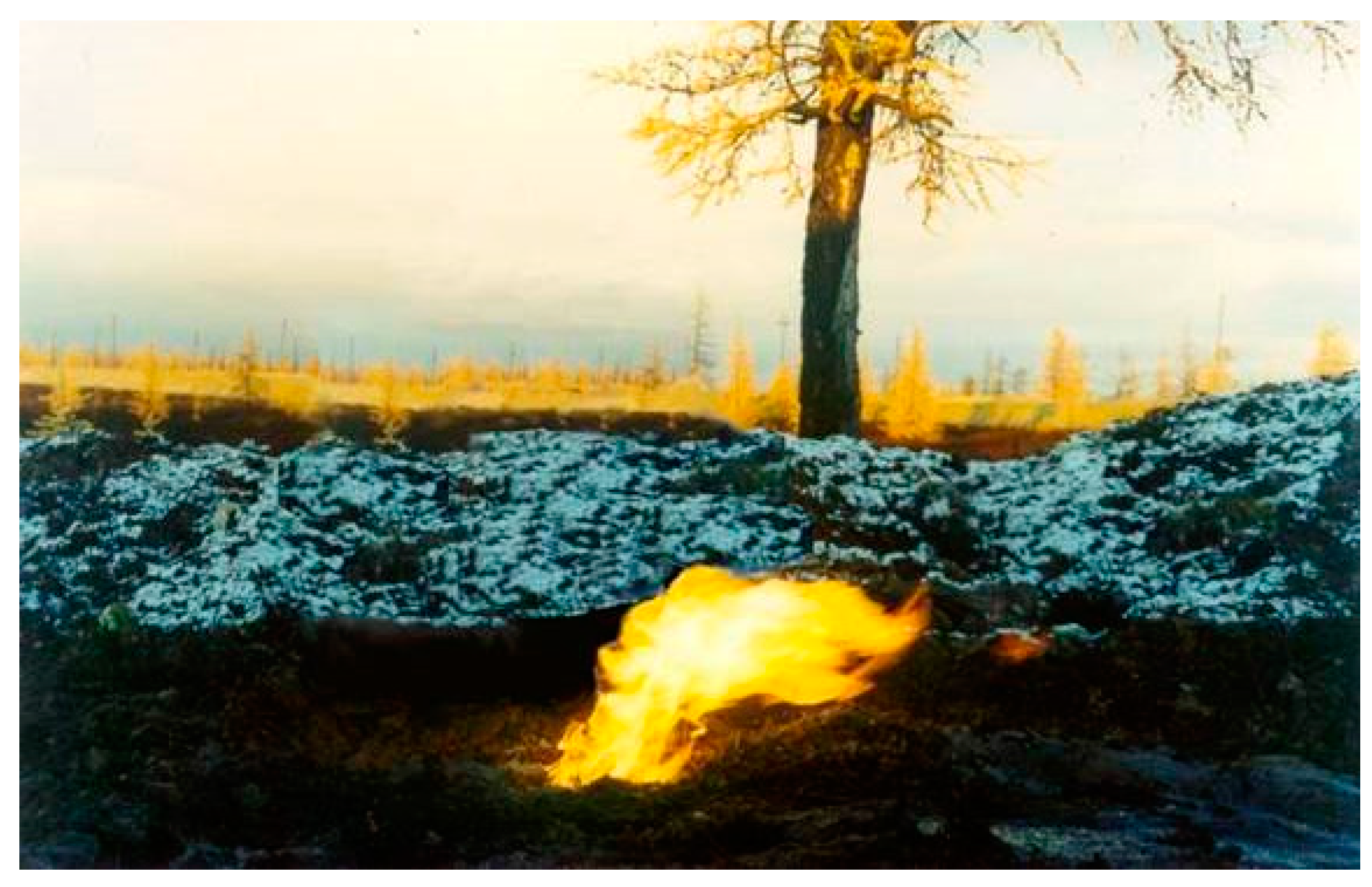
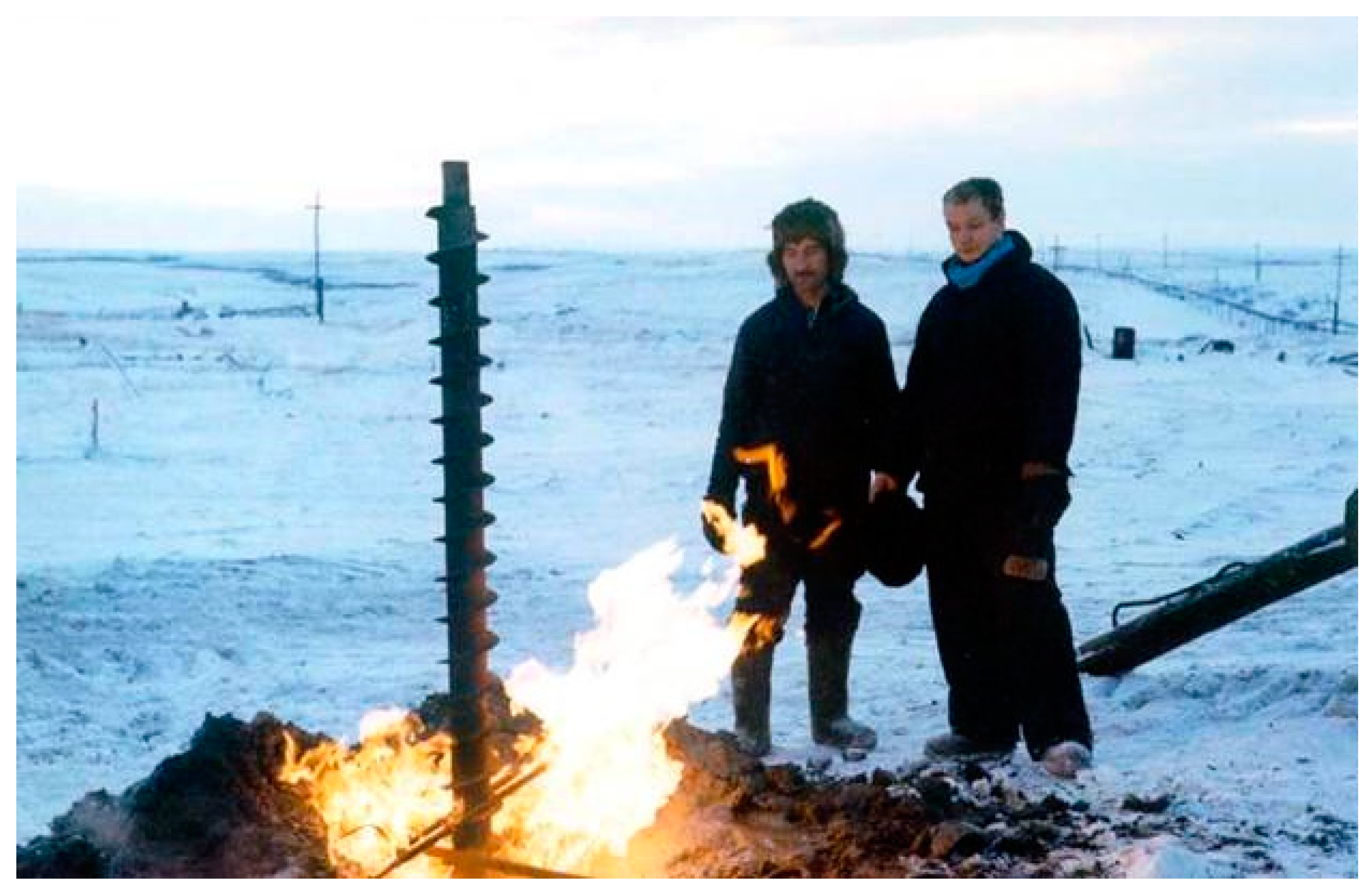
2.1.3. Gas Emission Observed During Drilling in Permafrost
2.2. Gas Emissions in the Arctic Shelf
2.2.1. Natural Gas Emission
2.2.2. Man-Induced Gas Emission
3. Discussion
- −
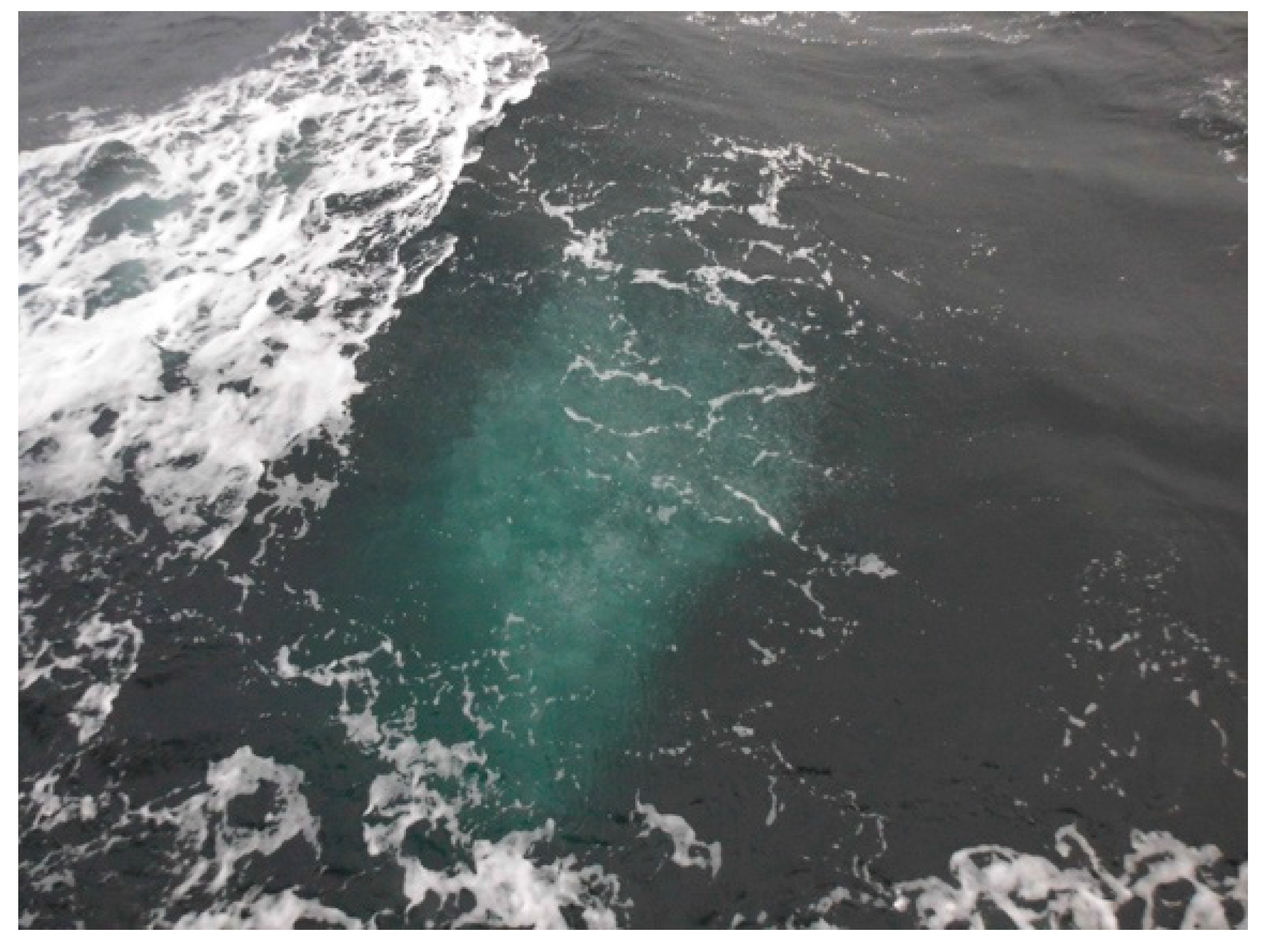
- Greenish-blue transparent water, often with a visible lake bottom;
- −
- Craters and similar features on the lake bottom;
- −
- More or less strongly eroded parapet or rock fragments around craters as evidence of explosive emission;
- −
- Mudflows in clear water associated with the release of a gas-water mixture through muddy bottom sediments;
- −
- Ebullition;
- −
- Bubbles of various shapes entrapped in ice;
- −
- Ice holes persistent over the winter season, through which gas fluids vent to the air.
- −
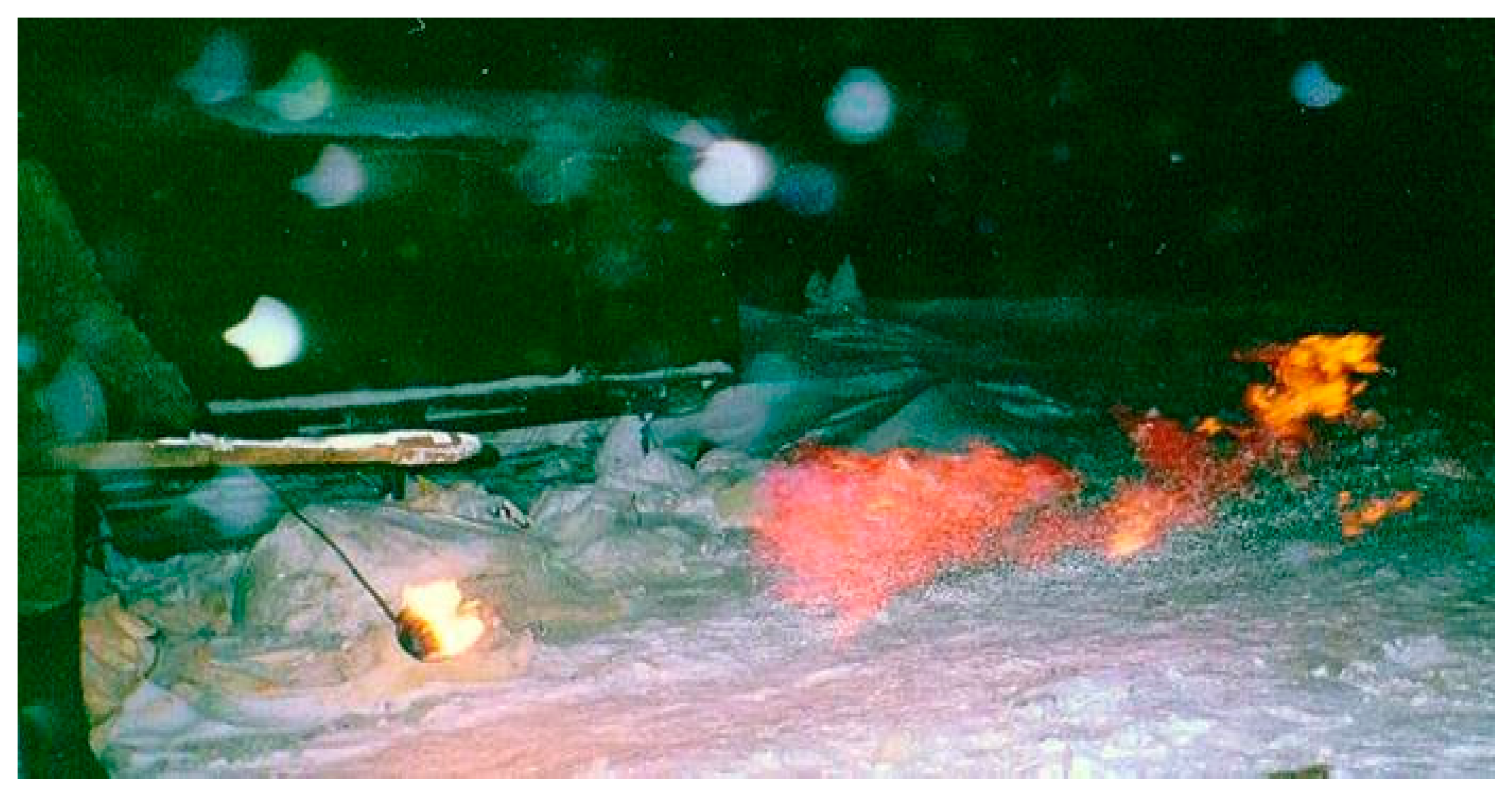
- In the witnessed cases, gas release was accompanied by explosions and fire;
- −
- All gas analyses showed the presence of methane;
- −
- Many of the gas-emission events were preceded by heaving that produced meters high mounds;
- −
- All discovered craters were round in shape but differed in size and depth, up to tens of m;
- −
- In all cases, rocks around the craters contained ground or pore ice evident in the crater walls or in the ejected fragments;
- −
- Most of the craters were encircled by parapets of ejected rock and soil; rock fragments were dispersed to distances of 100 m or farther around;
- −
- Most of the craters became filled with water and transformed into lakes in two or three years after the emission event.
- −
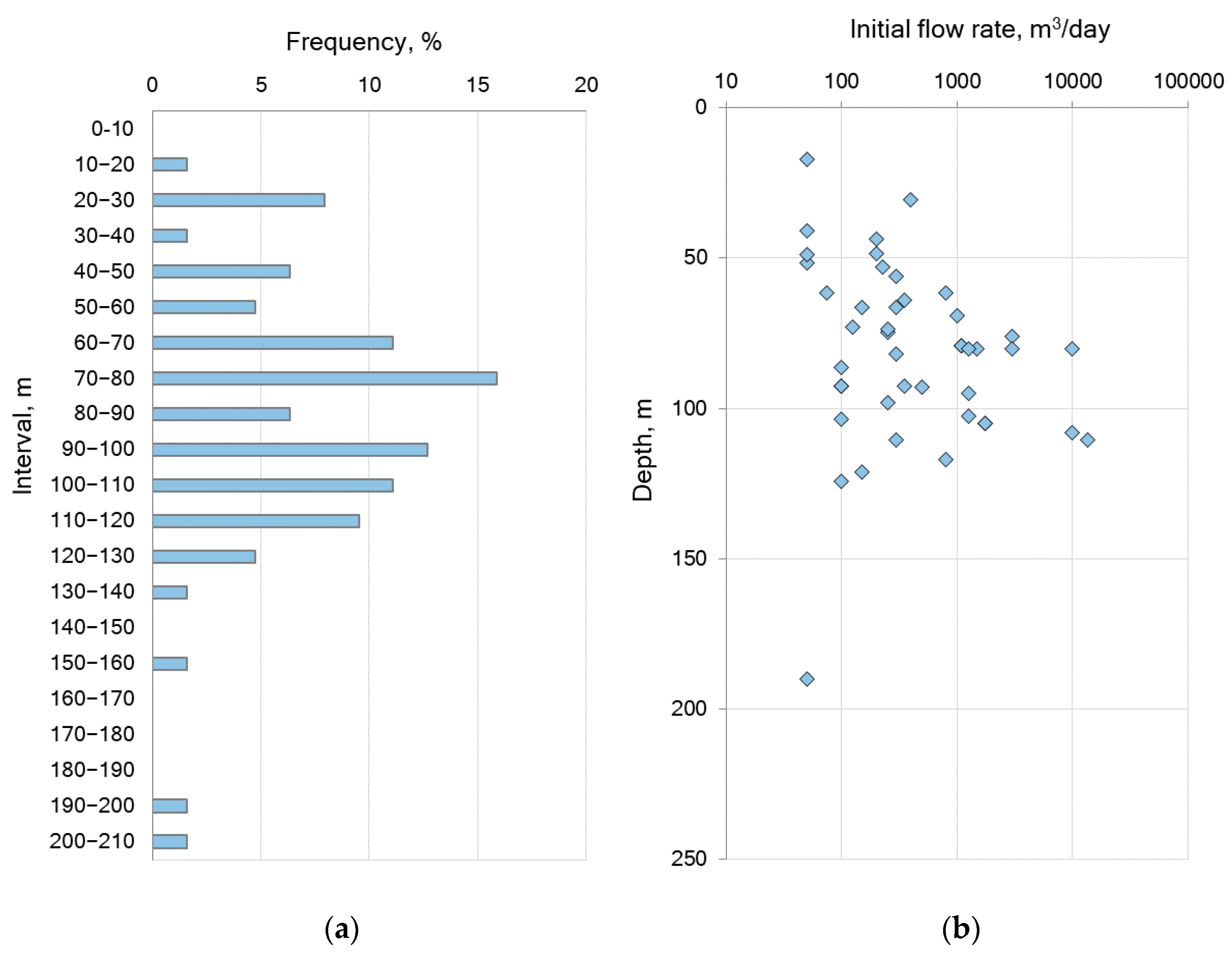
- Gas most often releases from shallow permafrost at depths from 10–20 m to 150 m;
- −
- Gas flux ranges from seeping to explosions at rates of hundreds to thousands of m3/d;
- −
- Gas emission can last from a few minutes to a month or longer;
- −
- Most of the emission events are known from oil and gas fields in northern West Siberia (Yamal, Taz, and Gydan Peninsulas);
- −
- Gas released from rocks of different lithologies, but most often from sandy-loam and sandy horizons with low salinity;
- −
- Gas emission occurs from ice-rich permafrost;
- −
- Gas mostly consists of methane and smaller amounts of nitrogen and carbon dioxide;
- −
- The carbon isotope composition of gas indicates its biogenic origin (−65 to −75‰ PDB δ13C);
- −
- Intrapermafrost gas can exist in a free or hydrate form; the presence of free gas is limited by the amount of pore ice while gas hydrates can remain stable within a certain range of pressures and temperatures (hydrate stability zone); metastable relict hydrates that formed under favorable conditions in the past can survive due to self-preservation [33,85,101,102].
- −
- −
- Methane in most of the gas seeps is of deep-seated (thermogenic) origin;
- −
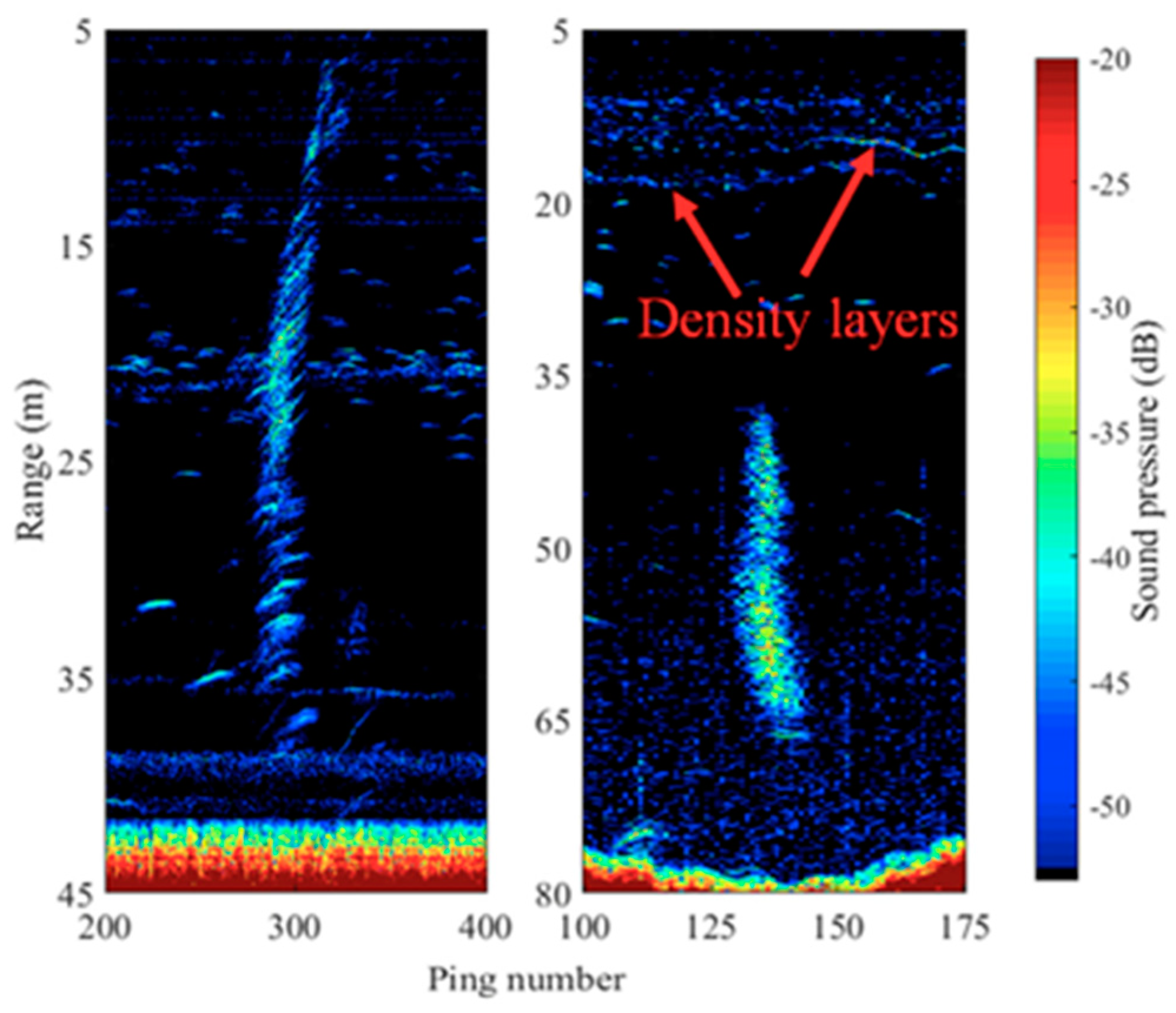
- Water column transfer of methane occurs by diffusive and ebullition mechanisms; gas migration in bubbles produces seeps and plumes; gas vents to the atmosphere if bubbles reach sizes at least 3–4 mm;
- −
- Gas emission can arise when drilling strips intra- or subpermafrost gas accumulations or can result from the destabilization of gas hydrates;
- −
- Pockmarks or plow marks are implicit indicators of gas venting on the Arctic shelf.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shakhova, N.; Semiletov, I.; Chuvilin, E. Understanding the permafrost-hydrate system and associated methane releases in the East Siberian Arctic Shelf. Geosciences 2019, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sergienko, V.I.; Lobkovskii, L.I.; Semiletov, I.P.; Dudarev, O.V.; Dmitrievskii, N.N.; Shakhova, N.E.; Romanovskii, N.N.; Kosmach, D.A.; Nikol’skii, D.N.; Nikiforov, S.L.; et al. The Degradation of Submarine Permafrost and the Destruction of Hydrates on the Shelf of East Arctic Seas as a Potential Cause of the Methane Catastrophe: Some Results of Integrated Studies in 2011. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2012, 446, 1132–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanovskii, N.N.; Hubberten, H.-W.; Gavrilov, A.V.; Eliseeva, A.A.; Tipenko, G.S. Offshore Permafrost and Gas Hydrate Stability Zone on the Shelf of East Siberian Seas. Geo-Marine Lett. 2005, 25, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dean, J.F.; Middelburg, J.J.; Röckmann, T.; Aerts, R.; Blauw, L.G.; Egger, M.; Jetten, M.S.M.; de Jong, A.E.E.; Meisel, O.H.; Rasigraf, O.; et al. Methane feedbacks to the global climate system in a warmer world. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 207–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, P.; Portnov, A.; Krylov, A.; Egorov, A.; Vanshtein, B. Geochemical Evidence for Seabed Fluid Flow Linked to the Subsea Permafrost Outer Border in the South Kara Sea. Chemie Erde 2019, 125509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serov, P.; Portnov, A.; Mienert, J.; Semenov, P.; Ilatovskaya, P. Methane Release from Pingo-like Features across the South Kara Sea Shelf, an Area of Thawing Offshore Permafrost. J. Geophys. Res. F Earth Surf. 2015, 120, 1515–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuzin, I.L.; Lyubina, Y.N.; Reinin, I.V. Gas production in West Siberian lakes and its relation to oil and gas fields. In Tectonic Criteria for Petroleum Exploration (Remote-Sensing Evidence); VNIGRI: Leningrad, Russia, 1990; pp. 117–127. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Glotov, V.E.; Glotova, L.P. Natural sources of atmospheric methane in Circumpacific region of cryolithozone (North-East of Russia). Bull. Samara Sci. Center Russ. Acad. Sci. 2015, 17, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Sizov, O.V. Remote sensing of gas emission consequences in northern West Siberia. Geomatika 2015, 1, 53–68. [Google Scholar]
- Bogoyavlensky, V.I.; Sizov, O.S.; Mazharov, A.V.; Bogoyavlensky, I.V.; Nikonov, R.A. Remote sensing of terrestrial gas emission in the Arctic: Yamal Peninsula. Arkt. Ekol. Ekon. 2016, 3, 4–15. [Google Scholar]
- Streletskaya, I.D.; Vasiliev, A.A.; Oblogov, G.E.; Streletskiy, D.A. Methane content in ground ice and sediments of the Kara Sea coast. Geosciences 2018, 8, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuzin, I.L. On the priority in the studies of land gas shows in Western Siberia. Sov. Geol. Geophys. 1990, 31, 142–144. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzin, I.L. On the nature of anomalous lakes: Indicators of hydrocarbons in deep sediments. In Assessment of Reservoir Petroleum Potential in West Siberia; VNIGRI: St. Petersburg, Russia, 1992; pp. 129–137. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kuzin, I.L. The extent of natural gas emission in West Siberia. Izvestiya RGO 1999, 131, 24–35. [Google Scholar]
- Rivkin, F.M. Gas contents in shallow permafrost. In Geocryological Conditions of the Kharasavey and Krusenstern Gas Condensate Fields (Yamal Peninsula); VNIIEgeosystem: Moscow, Russia, 2003; pp. 133–146. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Desyatkin, A.R.; Fedorov, P.P.; Nikolaev, A.N.; Borisov, B.Z.; Desyatkin, R.V. Methane emission during floods in thermokarst lakes of Central Yakutia. Vestnik NEFU 2016, 2, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Badu, Y.B. Gas shows and the nature of cryolithogenesis in marine sediments of the Yamal Peninsula. Earth Cryosphere 2017, XXI, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savichev, A.; Leibman, M.; Kadnikov, V.; Kallistova, A.; Pimenov, N.; Ravin, N.; Dvornikov, Y.; Khomutov, A. Microbiological study of Yamal lakes: A key to understanding the evolution of gas emission craters. Geosciences 2018, 8, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dvornikov, Y.A.; Leibman, M.O.; Khomutov, A.V.; Kizyakov, A.I.; Semenov, P.B.; Bussmann, I.; Babkin, E.M.; Heim, B.; Portnov, A.; Babkina, E.A.; et al. Gas—Emission craters of the Yamal and Gydan peninsulas: A proposed mechanism for lake genesis and development of permafrost landscapes. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2019, 30, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vlasov, A.N.; Khimenkov, A.N.; Volkov-Bogorodskiy, D.B.; Levin, Y.K. Natural explosive processes in permafrost. Dostizheniya Nauki Tekhniki 2017, 3, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizyakov, A.; Khomutov, A.; Zimin, M.; Khairullin, R.; Babkina, E.; Dvornikov, Y.; Leibman, M. Microrelief associated with gas emission craters: Remote-sensing and field-based study. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buldovicz, S.N.; Khilimonyuk, V.Z.; Bychkov, A.Y.; Ospennikov, E.N.; Vorobyev, S.A.; Gunar, A.Y.; Gorshkov, E.I.; Chuvilin, E.M.; Cherbunina, M.Y.; Kotov, P.I.; et al. Cryovolcanism on the earth: Origin of a spectacular crater in the Yamal Peninsula (Russia). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, S.; Bychkov, A.; Khilimonyuk, V.; Buldovicz, S.; Ospennikov, E.; Chuvilin, E. Formation of the Yamal crater in northern West Siberia: Evidence from geochemistry. Geosciences 2019, 9, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bogoyavlensky, V.I.; Bogoyavlensky, I.V.; Sizov, O.S.; Nikonov, R.A.; Kargina, T.N. Earth degassing in the Arctic: Comprehensive studies of the distribution of frost mounds and thermokarst lakes with gas blowout craters on the Yamal peninsula. Arct. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 4, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khimenkov, A.N.; Sergeev, D.O.; Vlasov, A.N.; Volkov-Bogorodsky, D.B. Explosive processes in the permafrost zone as a new type of geocryological hazard. Geoecology. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. Geocryol. 2019, 6, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuvilin, E.; Stanilovskaya, J.; Titovsky, A.; Sinitsky, A.; Sokolova, N.; Bukhanov, B.; Spasennykh, M.; Cheremisin, A.; Grebenkin, S.; Davletshina, D.; et al. A Gas-Emission Crater in the Erkuta River Valley, Yamal Peninsula: Characteristics and Potential Formation Model. Geosciences 2020, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuvilin, E.M.; Yakushev, V.S.; Perlova, E.V.; Kondakov, V.V. Gas component of permafrost within the Bovanenkovo gas condensate field (Yamal Peninsula). Doklady Earth Sci. 1999, 369, 522–524. [Google Scholar]
- Yakushev, V.S.; Chuvilin, E.M. Natural gas and gas hydrate accumulations within permafrost in Russia. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2000, 31, 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- Bondarev, V.L.; Mirotvorskiy, M.Y.; Zvereva, V.B.; Oblekov, G.I.; Shaydullin, R.M.; Gudzenko, V.T. Above-Cenomanian sediments in the Yamal Peninsula: Gas contents and chemical compositions (a case study of the Bovanenkovo oil-and-gas-condensate field). Geol. Geofiz. Razrab. Neftyanykh Gazov. Mestorozhdenii 2008, 5, 22–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yakushev, V.S. Natural Gas and Gas Hydrates in Permafrost; VNIIGAZ: Moscow, Russia, 2009; 192p, ISBN 978-5-89754-048-8. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kraev, G.; Schulze, E.-D.; Kholodov, A.; Chuvilin, E.; Rivkina, E. Cryogenic displacement and accumulation of biogenic methane in frozen soils. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kraev, G.; Rivkina, E.; Vishnivetskaya, T.; Belonosov, A.; van Huissteden, J.; Kholodov, A.; Smirnov, A.; Kudryavtsev, A.; Tshebaeva, K.; Zamolodchikov, D. Methane in gas shows from boreholes in epigenetic permafrost of Siberian Arctic. Geosciences 2019, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chuvilin, E.; Bukhanov, B.; Davletshina, D.; Grebenkin, S.; Istomin, V. Dissociation and self-preservation of gas hydrates in permafrost. Geosciences 2018, 8, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obzhirov, A.; Shakirov, R.; Salyuk, A.; Suess, E.; Biebow, N.; Salomatin, A. relations between methane venting, geological structure and seismo-tectonics in the Okhotsk sea. Geo-Marine Lett. 2004, 24, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakhova, N.; Semiletov, I.; Leifer, I.; Salyuk, A.; Rekant, P.; Kosmach, D. Geochemical and geophysical evidence of methane release over the East Siberian Arctic Shelf. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2010, 115, C08007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakhova, N.; Semiletov, I.; Salyuk, A.; Yusupov, V.; Kosmach, D.; Gustafsson, Ö. Extensive methane venting to the atmosphere from sediments of the East Siberian Arctic Shelf. Science 2010, 327, 1246–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burwicz, E.; Rüpke, L.; Wallmann, K. Estimation of the global amount of submarine gas hydrates formed via microbial methane formation based on numerical reaction-transport modeling and a novel parameterization of Holocene sedimentation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 4562–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romanovskii, N.N.; Eliseeva, A.A.; Gavrilov, A.V.; Tipenko, G.S.; Hubberten, Х. The long-term dynamics of the permafrost and gas hydrate stability zone on rifts of the East Siberian Arctic shelf ((Report 2). Kriosf. Zemli 2006, 10, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Anisimov, O.A.; Borzenkova, I.I.; Lavrov, S.A.; Strelchenko, Y.G. The current dynamics of the submarine permafrost and methane emission on the shelf of the eastern arctic seas. Ice Snow 2012, 52, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimov, O.A.; Zaboikina, Y.G.; Kokorev, V.A.; Yurganov, L.N. Possible causes of methane release from the East Arctic seas shelf. Ice Snow 2014, 54, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-G.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.-H.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, S.-G.; Jin, Y.K. Occurrence of Active Gas Hydrate Mounds in the Southwestern Slope of the Chukchi Plateau, Arctic Ocean. Episodes 2020, 43, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paull, C.K.; Ussler, W.; Dallimore, S.R.; Blasco, S.M.; Lorenson, T.D.; Melling, H.; McLaughlin, F.A. Origin of pingo-like features on the Beaufort Sea shelf and their possible relationship to decomposing methane gas hydrates. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajan, A.; Mienert, J.; Bünz, S. Acoustic evidence for a gas migration and release system in Arctic glaciated continental margins offshore NW-Svalbard. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2012, 32, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bogoyavlensky, V.I. Oil and gas shows on land and offshore areas of the Arctic and the world ocean. Bureniye i Neft’ 2015, 6, 4–10. Available online: https://burneft.ru/archive/issues/2015-06/4 (accessed on 22 September 2020).
- Bogoyavlensky, V.I.; Erokhin, G.N.; Nikonov, R.A.; Bogoyavlensky, I.V.; Bryksin, V.M. Study of catastrophic gas blowout zones in the Arctic based on passive microseismic monitoring (on the example of Lake Otkrytiye). Arctic Ecol. Econ. 2020, 1, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibman, M.O.; Plekhanov, A.V. Yamal gas emission crater: Results of preliminary survey. KholodOk 2014, 2, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Leibman, M.O.; Kizyakov, A.I.; Plekhanov, A.V.; Streletskaya, I.D. New permafrost feature—Deep crater in Central Yamal, West Siberia, Russia, as a response to local climate fluctuations. Geogr. Environ. Sustain. 2014, 7, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizyakov, А.I.; Sonyushkin, A.V.; Leibman, М.О.; Zimin, M.V. Geomorphological conditions of the gas-emission crater and its dynamics in central Yamal. Earth’s Cryosphere 2015, 19, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Olenchenko, V.V.; Sinitsky, A.I.; Antonov, E.Y.; Eltsov, I.N.; Kushnarenko, O.N.; Plotnikov, A.E.; Potapov, V.V.; Epov, M.I. Results of geophysical researches of the area of new geological formation “Yamal crater”. Earth’s Cryosphere 2015, 19, 94–106. [Google Scholar]
- Kizyakov, A.I.; Zimin, M.V.; Sonyushkin, A.V.; Dvornikov, Y.A.; Khomutov, A.V.; Leibman, M.O. Comparison of gas emission crater geomorphodynamics on Yamal and Gydan peninsulas (Russia), based on repeat very--high--resolution stereopairs. Remote Sens. (Basel) 2017, 9, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalinko, M.K. Geological History and Petroleum Potential of the Khataigekoy Basin; Gostoptekhizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1959; 358p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mamzelev, А.Р.; Are, F.E. Geological-engineering conditions of Yamal peninsula along designing railroad. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Permafrost, Beijing, China, 5–9 July 1993; South China University of Technology Press: Guangzhou China, 1993; Volume 1, pp. 436–442. [Google Scholar]
- Are, F.E. Emission of deep gas into the atmosphere. Kriosfera Zemli 1998, II, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Melnikov, P.I.; Melnikov, V.P.; Tsarev, V.P.; Degtiarev, B.V.; Mizulina, N.B.; Popov, A.P.; Berezniakov, A.I.; Svetchnikov, A.M. Generation of hydrocarbons in the permafrost. Izv. AN SSSR Ser. Geol. 1989, 2, 118–128. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Badu, Y.B. The cryolithic structure of the ground. In The Cryosphere of Petroleum Fields, Yamal Peninsula: In 3 volumes. Vol. 1. The Kharasavey Field; Nedra: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2006; pp. 85–111. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chuvilin, E.M.; Perlova, E.V.; Baranov, Y.B.; Kondakov, V.V.; Osokin, A.B.; Yakushev, V.S. Structure and Properties of Permafrost in the Southern Bovanenkovo Gas-Condensate Field; GEOS: Moscow, Russia, 2007; 137p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kondakov, V.V.; Kusova, O.F.; Kondakov, M.V. Geocryological conditions of the northeastern Yamal Peninsula. In Proceedings of the IV Conference of Russian Permafrost Scientists, Moscow, Russia, 7–9 June 2011; University Book: Moscow, Russia, 2011; pp. 89–94. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Bolshakov, Y.Y.; Kultikov, A.M. Analysis of gas emission while drilling in the Bovanenkovo and Kharasavey fields. In Transactions, Institute of North Development Problems, Siberian Branch of the USSR Academy of Sciences; Institute of North Development Problems: Tyumen, Russia, 1989; 74p, N2 16-88. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kondakov, V.V.; Galyavich, A.S. Comprehensive studies of permafrost sediments with an assessment of their water and gas saturation. In Proceedings of the Problems of Cryology of the Earth: Abstracts. Conf., Pushchino, Russia, 20–24 April 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Chuvilin, E.M.; Yakushev, V.S.; Perlova, E.V. Gas and gas hydrates in the permafrost of Bovanenkovo gas field, Yamal Peninsula, West Siberia. Polarforschung 2000, 68, 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, M.S. Modern permafrost coastal Deltaic sediments of the Yana basin. Voprosy Geografii Yakutii 1969, 5, 138–147. [Google Scholar]
- Masurenkov, Y.P.; Slezin, Y.B.; Sobisevich, A.L. Gas plumes near the Bennett island. Izvestiya RAN Sr. Geogr. 2015, 3, 86–95. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rekant, P.V.; Tumskaya, V.E.; Gusev, E.A.; Schwenk, T.; Spiess, F.; Cherkashev, G.A.; Kassens, H. Distribution and features of subsea permafrost in the Semenovskaya and Vasilievskaya banks (Laptev Sea), from seismoacoustic profiling data. In Laptev Sea and Adjacent Arctic Seas: Current State and History; Moscow State University: Moscow, Russia, 2009; pp. 292–308. ISBN 9785211057166. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Shakhova, N.E.; Semiletov, I.P.; Salyuk, A.N.; Belcheva, N.N.; Kosmach, D.A. Methane anomalies in the near-water atmospheric layer above the shelf of the East Siberian Arctic Sea. Doklady Earth Sci. 2007, 415, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakhova, N.; Semiletov, I.; Leifer, I.; Sergienko, V.; Salyuk, A.; Kosmach, D.; Chernykh, D.; Stubbs, C.; Nicolsky, D.; Tumskoy, V.; et al. Ebullition and storm-induced methane release from the East Siberian Arctic Shelf. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakhova, N.; Semiletov, I.; Sergienko, V.; Lobkovsky, L.; Yusupov, V.; Salyuk, A.; Salomatin, A.; Chernykh, D.; Kosmach, D.; Panteleev, G.; et al. The East Siberian Arctic Shelf: Towards further assessment of permafrost-related methane fluxes and role of sea ice. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. 2015, 373, 2014045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakhova, N.E.; Sergienko, V.I.; Semiletov, I.P. The contribution of the East Siberian Shelf to the modern methane cycle. Her. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2009, 79, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranov, B.; Galkin, S.; Vedenin, A.; Dozorova, K.; Gebruk, A.; Flint, M. Methane seeps on the outer shelf of the Laptev Sea: Characteristic features, structural control, and benthic fauna. Geo-Marine Lett. 2020, 40, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarkin, V.; Semiletov, I.P.; Finke, N.; Shakhova, N.E.; Joye, S.B. Methane carbon stable isotope signatures in waters and sediments of the Laptev Sea Shelf. In Proceedings of the American Geophysical Union Fall Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–7 December 2012; p. B21D-0411. [Google Scholar]
- Weidner, E.; Weber, T.C.; Mayer, L.; Jakobsson, M.; Chernykh, D.; Semiletov, I. A wideband acoustic method for direct assessment of bubble-mediated methane flux. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 173, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matveeva, T.; Savvichev, A.S.; Semenova, A.; Logvina, E.; Kolesnik, A.N.; Bosin, A.A. Source, Origin, and Spatial Distribution of Shallow Sediment Methane in the Chukchi Sea. Oceanography 2015, 28, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveeva, T.V.; Semenova, A.A.; Shchur, N.A.; Logvina, E.A.; Nazarova, O.V. Prospects of Gas Hydrate Presence in the Chukchi Sea. J. Min. Inst. 2017, 226, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portnov, A.; Smith, A.J.; Mienert, J.; Cherkashov, G.; Rekant, P.; Semenov, P.; Serov, P.; Vanshtein, B. Offshore Permafrost Decay and Massive Seabed Methane Escape in Water Depths >20 m at the South Kara Sea Shelf. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 3962–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Firsov, Y.G.; Ivanov, M.V.; Koloskov, E.N. A new stage in bathymetric studies of the Russian Arctic waters: A case study of the Kara Sea. Bull. Admiral Makarov State Univ. Mar. River Fleet 2014, 6, 115–124. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Koloskov, E.N.; Firsov, Y.G. The use of modern hydrographic technologies for the study of bottom topography and gas occurrence in the Russian Arctic seas. Bull. Admiral Makarov State Univ. Mar. River Fleet 2015, 3, 54–62. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bondarev, V.N.; Rokos, S.I.; Kostin, D.A.; Dlugach, A.G.; Polyakova, N.A. Underpermafrost accumulations of gas in the upper part of the sedimentary cover of the Pechora Sea. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2002, 43, 545–556. [Google Scholar]
- Rokos, S.I. Engineering-geological features of shallow overpressure zones in reservoirs of the Pechora and southern Kara shelf. Inzhenernaya Geol. 2008, 4, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Bogoyavlensky, V.I. Natural and technogenic threats in fossil fuels production in the Earth’s cryolithosphere. Russ. Min. Ind. 2020, 1, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grigoriev, M.N. Permafrost degradation East Siberian Arctic seas: Evidence from field campaigns of 2014–2016. Probl. Arktiki Antarkt. 2018, 1, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Safronov, A.F.; Shits, E.Y.; Grigor’ev, M.N.; Semenov, M.E. Formation of gas hydrate deposits in the Siberian Arctic Shelf. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2010, 51, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruglikov, N.M.; Kuzin, I.L. Deep gas shows in the Urengoy gas field. Trans. ZapSibNIGNI 1973, 37, 96–106. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kuzin, I.L. Blue lakes in humid areas. Izvestiya RGO 2001, 133, 44–57. [Google Scholar]
- Bogoyavlensky, V.I.; Bogoyavlensky, I.V.; Nikonov, R.A. Results of aerial, space and field invetigations of large gas blowouts near Bovanenkovo field on Yamal Peninsula. Arctic Ecol. Econ. 2017, 3, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherskiy, N.V.; Tsarev, V.P. Prospects for petroleum development. In Improvement of Subsoil Use in the Northern and Eastern USSR, Part 1; Cherskiy, N.V., Ed.; YaB SB AS USSR: Yakutsk, Russia, 1973; pp. 54–60. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Yakushev, V.S.; Perlova, E.V.; Makhonina, N.A.; Chuvilin, E.M.; Kozlova, E.V. Gas hydrates in deposits on continents and islands. Ross. Khimicheskiy Zhurnal 2003, 3, 80–90. [Google Scholar]
- Yakushev, V.S.; Istomin, V.A. Gas-hydrates self-preservation effect. In Physics and Chemistry of Ice; Maeno, N., Hondoh, T., Eds.; Hokkaido University Press: Sapporo, Japan, 1992; pp. 136–139. [Google Scholar]
- Yakutseni, V.P. Unconventional resources of natural hydrocarbons—An additional raw material reserve of the national economy of the USSR. In Resources of Unconventional Gas Raw Materials and Problems of Its Development, Proceedings of the VNIGRI; Yakutseni, V.P., Ed.; VINIGRI: Leningrad, Russia, 1990; 261p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Avetov, N.P.; Krasnova, E.A.; Yakushev, V.S. Possible causes and nature of gas emission around gas and gas condensate boreholes in the Yamburg oil and gas condensate field. Vesti Gazovoy Nauki 2018, 1, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Makhonina, N.A.; Perlova, E.V.; Yakushev, V.S.; Akhmedsafin, S.K. Permafrost gas accumulations in the Zapolyarnoye oil-gas-condensate field. Nauka Tekhnika Gazov. Promyshlennosti 2004, 1–2, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Skorobogatov, V.A.; Yakushev, V.S.; Chuvilin, E.M. Sources of natural gas within permafrost north-west Siberia. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Permafrost. Collection Nordicana, N57, Yellowknife, NT, Canada, 23–27 June 1998; pp. 1001–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Yusupov, V.I.; Salyuk, A.N.; Karnaukh, V.N.; Semiletov, I.P.; Shakhova, N.E. Detection of methane ebullition in shelf waters of the Laptev sea in the Eastern Arctic region. Doklady Earth Sci. 2010, 430, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondur, V.G.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Vorobyev, V.E.; Zamshin, V.V. Remote sensing detection of gas shows (gas seeps) on the Russian shelf. Georesursy Geoenergiya Geopolit. 2014, 1, 1–23. Available online: http://oilgasjournal.ru/vol_9/bondur.html (accessed on 22 September 2020).
- Luhn, A. Russian Scientists Find “Most Powerful” Ever Methane Seep in Arctic Ocean; The Telegraph: Moscow, Russia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nikiforov, S. Scientists Have Discovered Extremely Large Methane Emission in the East Siberian Sea; Bull. Tomsk Polytechnical University: Tomsk, Russia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, G.I. Methodology and Results of Ecogeochemical Investigations of Barents Sea; VNIIOkeangeologiya: Saint Petersburg, Russia, 2002; p. 153. ISBN 5-88994-059-7. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, L.A.; Brumley, K.; Andronikov, A.; Chayes, D.N.; Armstrong, A.A.; Calder, B.; Hall, J.K.; Clyde, W.C.; Bothner, W.A.; Gardner, J.V. Recent Mapping and Sampling on Chukchi Borderland and the Alpha/Mendeleev Ridge Complex. In Proceedings of the American Geophysical Union Fall Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–19 December 2008; p. C11C-0516. [Google Scholar]
- Judd, A.; Hovland, M. Seabed Fluid Flow: The Impact on Geology, Biology, and the Marine Environment; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 1–475. ISBN 9780511535918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastochkin, A.N.; Naryshkin, G.D. New understanding of the Arctic sea bottom topography. Okeanologiya 1989, 29, 968–973. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov, V.A.; Gusev, E.A.; Lopatin, B.G. Age and structure of sediments in the Eastern Russian Arctic shelf. Geol. -Geofizicheskiye Kharakteristiki Lithosfery Arkticheskogo Regiona 2004, 5, 202–212. [Google Scholar]
- Bogoyavlensky, V.I. Prospects and problems of petroleum production in the Arctic Shelf. Bureniye i Neft’ 2012, 11, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yershov, E.D.; Lebedenko, Y.P.; Chuvilin, E.M.; Istomin, V.A.; Yakushev, V.S. Features of gas hydrate occurrence in permafrost. Dokl. USSR Acad. Sci. 1991, 321, 788–791. [Google Scholar]
- Dallimore, S.R.; Chuvilin, E.M.; Yakushev, V.S. Field and laboratory characterization of intrapermafrost gas hydrates, Mackenzie Delta, N.W.T., Canada. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Natural Gas Hydrates, Toulouse, France, 24–29 June 1996; pp. 525–531. [Google Scholar]
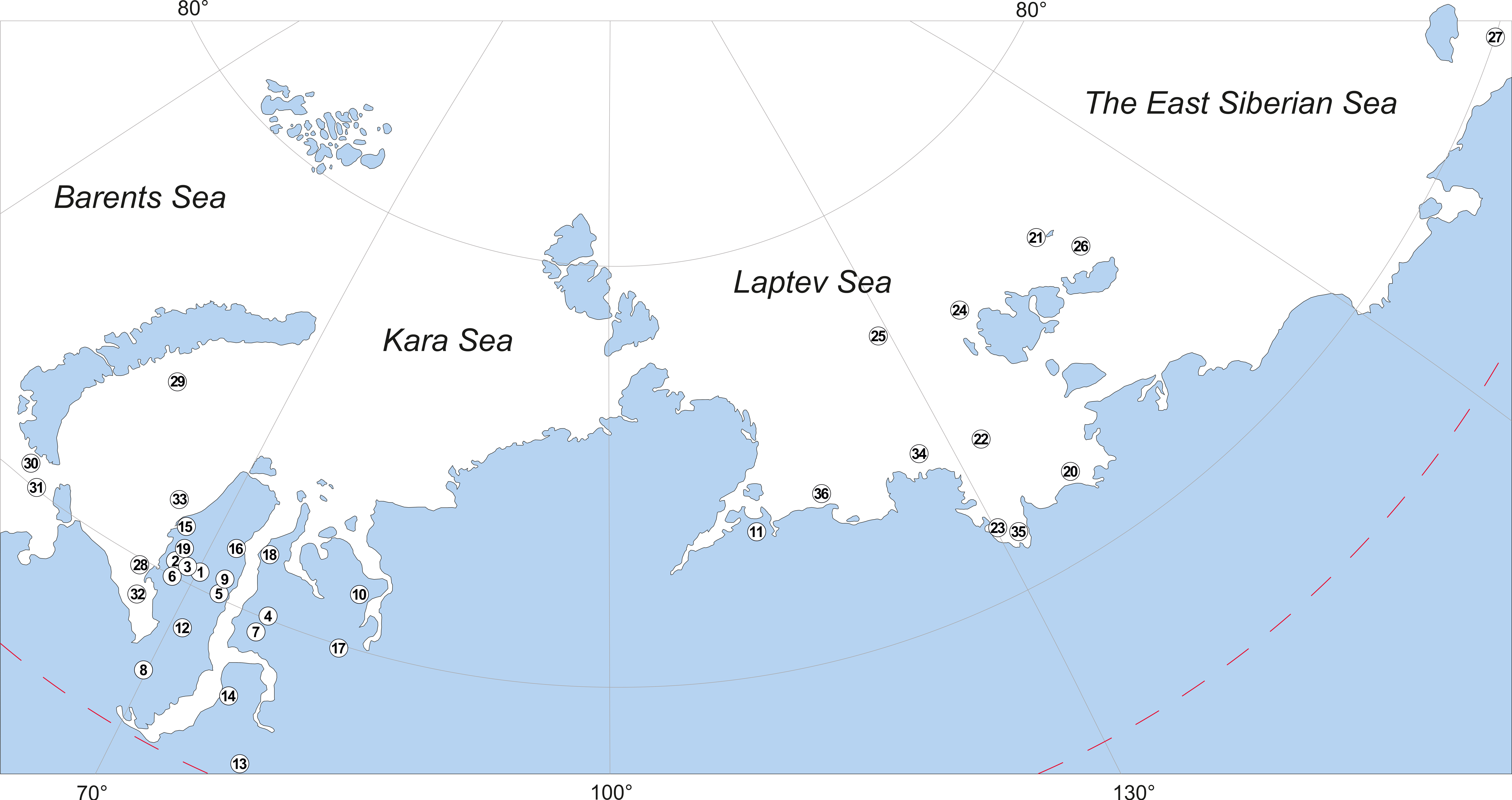





| No. in Map | Type | Location | Signatures | Possible Gas Sources | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Onshore | Natural | 1 | Lakes | Yamal Peninsula, Lake Neyto | Gas plumes on water surface, mudflows, holes in ice | Deep gas from Neyto field | [10] |
| 2 | Yamal Peninsula, Сrater Lake | Craters and parapets on lake bottom, mudflows | Possibly, deep gas-water fluids | [10,44] | |||
| 3 | Yamal Peninsula, group of lakes south of Bovanenkovo field | Blue water, holes in ice, mudflows | Active emission, possibly, deep gas | [9] | |||
| 4 | Gydan Peninsula, a lake 4 km from Merkuto lake on the left bank of Yuribey River | A crater encircled by a parapet | Prolonged ascending flow, possibly, deep gas | [9] | |||
| 5 | Yamal Peninsula, 54 km northeast of Arctic field, Otkrytie Lake | Large craters (up to 40 m in diameter on lake bottom) | Deep gas, possibly, from Cenomanian gas reservoirs | [45] | |||
| 6 | Craters | Yamal Peninsula, 30 km south of Bovanenkovo field | A large crater (up to 40 m in diameter and ~70 m deep), encircled with a well-pronounced parapet; ground dispersed to a distance of 120 m | Possibly, intrapermafrost gas | [22,44,46,47,48,49] | ||
| 7 | Gydan Peninsula, 100 km northwest of Antipayuta Village | A crater, 10–13 m in diameter and ~15 m deep; no parapet | Possibly, intrapermafrost gas | [50] | |||
| 8 | Yamal Peninsula, floodplain of Erkuta-Yakha River | A crater, 10–12 m in diameter and ~20 m deep, with a preserved fragment of a 2–3 m high mound and ground dispersed to a distance of 100 m | Biogenic gas in a talik and deep gas | [26] | |||
| 9 | Yamal Peninsula, 33 km northwest of Seyakha, Myudriyakha River | Fire gas explosion that produced a 50 m deep 50 × 70 m crater in a river, with dispersed blocks of permafrost and ice-rich soil, up to 150 m3 | Possibly, deep gas | [24,45] | |||
| 10 | Gydan Peninsula, north of Deryabino field, bank of Mongoche River | Fire gas explosion that produced a 20 m deep crater, with dispersed large fragments of rock | Possibly, deep gas | [9,25] | |||
| Man-caused | 11 | Drilling in permafrost | North Yakutia, Anabar-Khatanga interfluve | Gas shows at depths of 70–120 m | Intrapermafrost gas | [51] | |
| 12 | Yamal Peninsula, Yuribey River | Gas shows at depths of 10–50 m | Intrapermafrost gas | [52,53] | |||
| 13 | Taz Peninsula, Zapolyarny field | Gas shows at depths of 50–120 m | Intrapermafrost gas, possibly relict gas hydrates | [30] | |||
| 14 | Taz Peninsula, Yamburg field | Gas shows at depths of 45–55 m | Intrapermafrost gas, possibly relict gas hydrates | [30,54] | |||
| 15 | Yamal Peninsula, Kharasavey field | Gas shows at depths of 10–210 m | Intrapermafrost gas, possibly relict gas hydrates | [55,56] | |||
| 16 | Yamal Peninsula, South-Tambey field | Gas shows at depths of 40–60 m | Intrapermafrost gas, possibly relict gas hydrates | [57] | |||
| 17 | Gydan Peninsula, Pelyatka field | Gas shows at depths of 20–30 m | Intrapermafrost gas | [30] | |||
| 18 | Gydan Peninsula, Salman (Utrenneye) field | Gas shows at depths of 50–150 m | Intrapermafrost gas, possibly relict gas hydrates | [33] | |||
| 19 | Yamal Peninsula, Bovanenkovo field | Gas shows at depths of 20–130 m | Intrapermafrost gas, possibly relict gas hydrates | [28,56,58,59,60] | |||
| Offshore | Natural | 20 | Ascending flows and seeps | Laptev Sea, Yana Delta | Ebullition | Deep gas | [30,61] |
| 21 | East Siberian Sea, Bennett Island | Gas plumes, up to 1000 km long | Possibly, deep gas | [61,62] | |||
| 22 | Laptev Sea, between Semyonovsky Island and Lena Delta | Gas seeps | Possibly, deep gas | [63] | |||
| 23 | Laptev Sea, Ivashkina Lagoon | About 20 gas seeps; high concentration of methane in air | Deep gas | [64,65,66] | |||
| 24 | Laptev Sea, Kotelny Island | Gas seeps | Possibly, deep gas | [67] | |||
| 25 | Laptev Sea shelf, New Siberian Islands | A cluster of gas seeps at 50–90 m sea depths | Possibly, deep gas | [68] | |||
| 26 | Laptev Sea (between 76.5° and 77.5° N; 121–132° E) | More than 700 gas seeps, up to 1.3 km in diameter | Possibly, deep gas | [66,69] | |||
| 27 | Chukchi Sea, Herald Canyon and Wrangel Island | About 90 gas seeps at 50–95 m sea depths | Deep gas | [70,71,72] | |||
| 28 | Kara Sea, near Marre-Salle polar station | Gas seep at 6 m sea depths: 2 m in height and 15 m in width | Biogenic gas | [73] | |||
| 29 | Kara Sea, Universitetskaya structure | Gas seeps from a depth of 80 m and pingo-like features | Deep gas | [74,75] | |||
| Man made | 30 | Drilling in subsea permafrost | Pechora Sea, Kara Gates | 10 m high gas fountain from a borehole at sub-bottom depth 50 m | Deep gas | [53,54] | |
| 31 | Pechora Sea, Vaygach Island | 10 m high gas fountain from a borehole at sub-bottom depth 50 m, with an ebullition zone up to 200 m in diameter on the sea surface | Gas from subsea permafrost | [76,77] | |||
| 32 | Kara Sea, Baydaratskaya Bay | Gas show from sub-bottom depth 10–50 m | Possibly, deep gas | [78] | |||
| 33 | Kara Sea, Leningrad field | Gas show from a 200 m deep borehole | Possibly, deep gas | [78] | |||
| 34 | Laptev Sea, Lena Delta | Gas show from a borehole at 9 m depth | Gas from permafrost | [79] | |||
| 35 | Laptev Sea, Buor-Khaya Gulf | Gas show from a 13–16 m deep borehole | Gas from permafrost | [79] | |||
| 36 | Laptev Sea, Mamontov Klyk Cape | Gas show from boreholes up to 80 m deep | Gas from permafrost | [80] | |||
| Borehole No. | Gas Components, % | δ13C,‰ PDB | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | CO2 | N2 | ||
| 110.1 | 67.89 | 3.88 | 28.23 | −69.92 |
| 110.2 | 64.63 | 5.91 | 29.46 | −69.67 |
| 110.3 | 59.10 | 3.89 | 37.01 | −73.01 |
| 110.4 | 41.40 | 10.45 | 48.15 | −67.97 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chuvilin, E.; Ekimova, V.; Davletshina, D.; Sokolova, N.; Bukhanov, B. Evidence of Gas Emissions from Permafrost in the Russian Arctic. Geosciences 2020, 10, 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10100383
Chuvilin E, Ekimova V, Davletshina D, Sokolova N, Bukhanov B. Evidence of Gas Emissions from Permafrost in the Russian Arctic. Geosciences. 2020; 10(10):383. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10100383
Chicago/Turabian StyleChuvilin, Evgeny, Valentina Ekimova, Dinara Davletshina, Natalia Sokolova, and Boris Bukhanov. 2020. "Evidence of Gas Emissions from Permafrost in the Russian Arctic" Geosciences 10, no. 10: 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10100383
APA StyleChuvilin, E., Ekimova, V., Davletshina, D., Sokolova, N., & Bukhanov, B. (2020). Evidence of Gas Emissions from Permafrost in the Russian Arctic. Geosciences, 10(10), 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10100383








