Olfactory Generalization in Detector Dogs
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
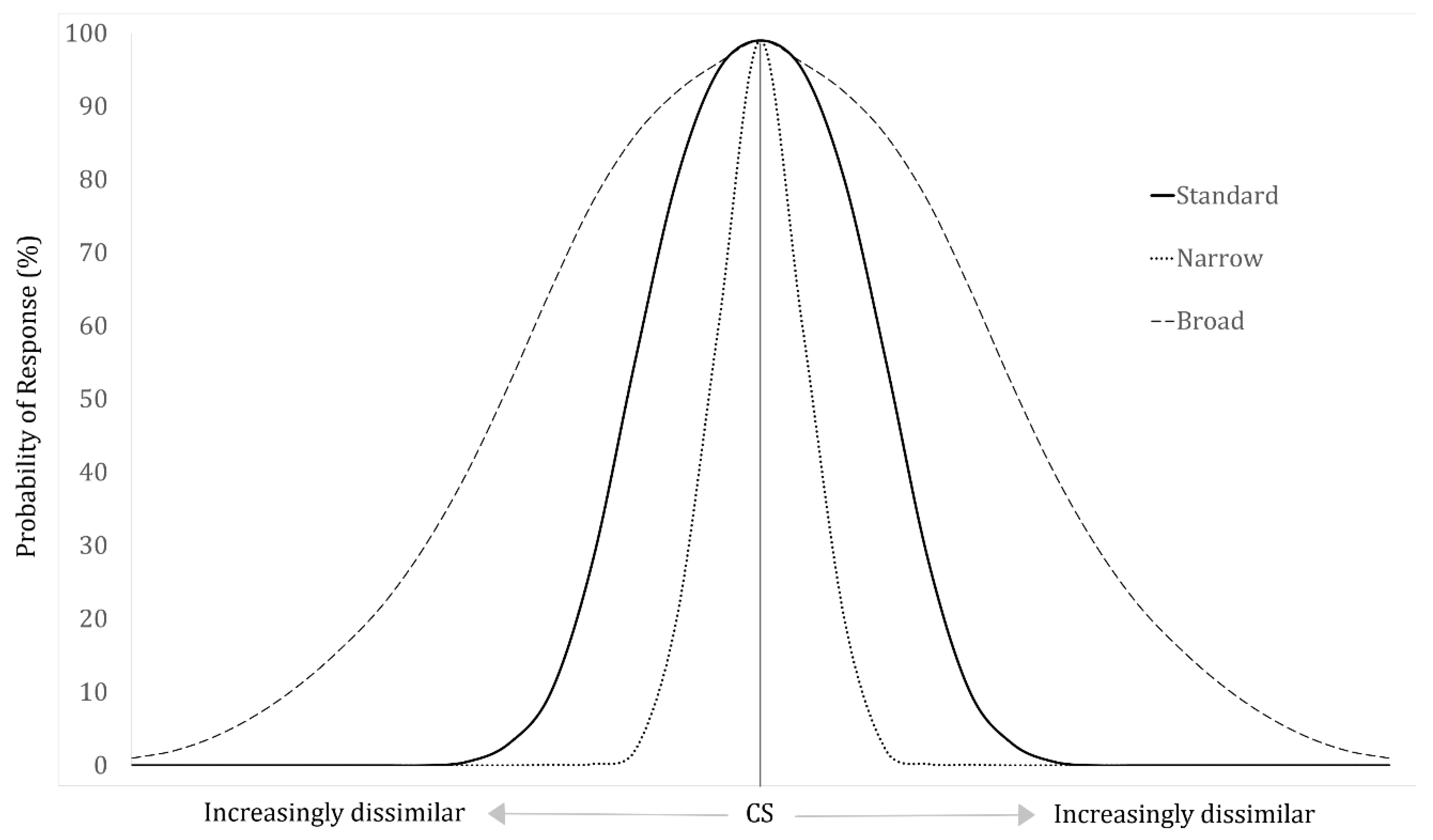
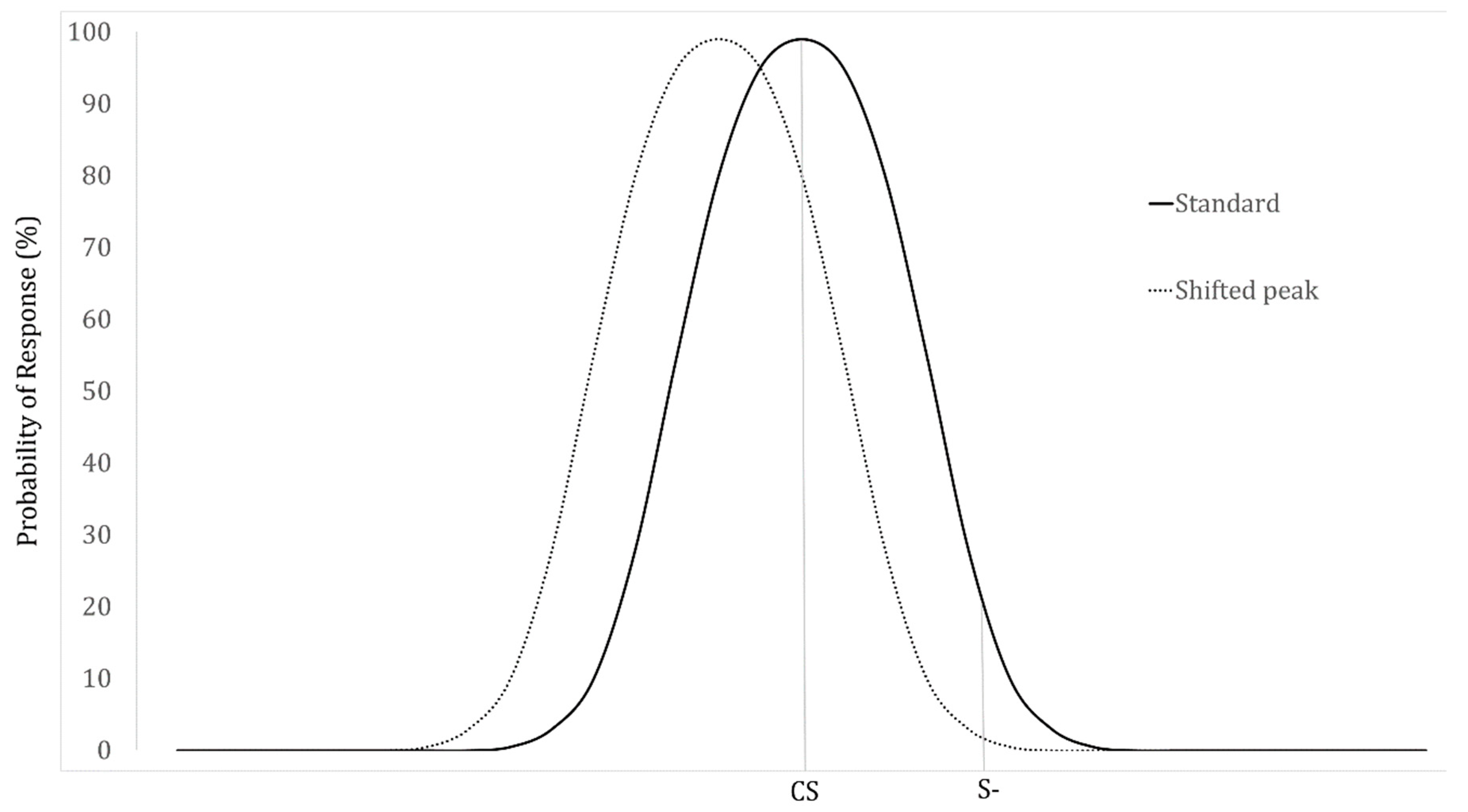
2. The Generalization Gradient
3. Generalization of Structurally-Similar Compounds
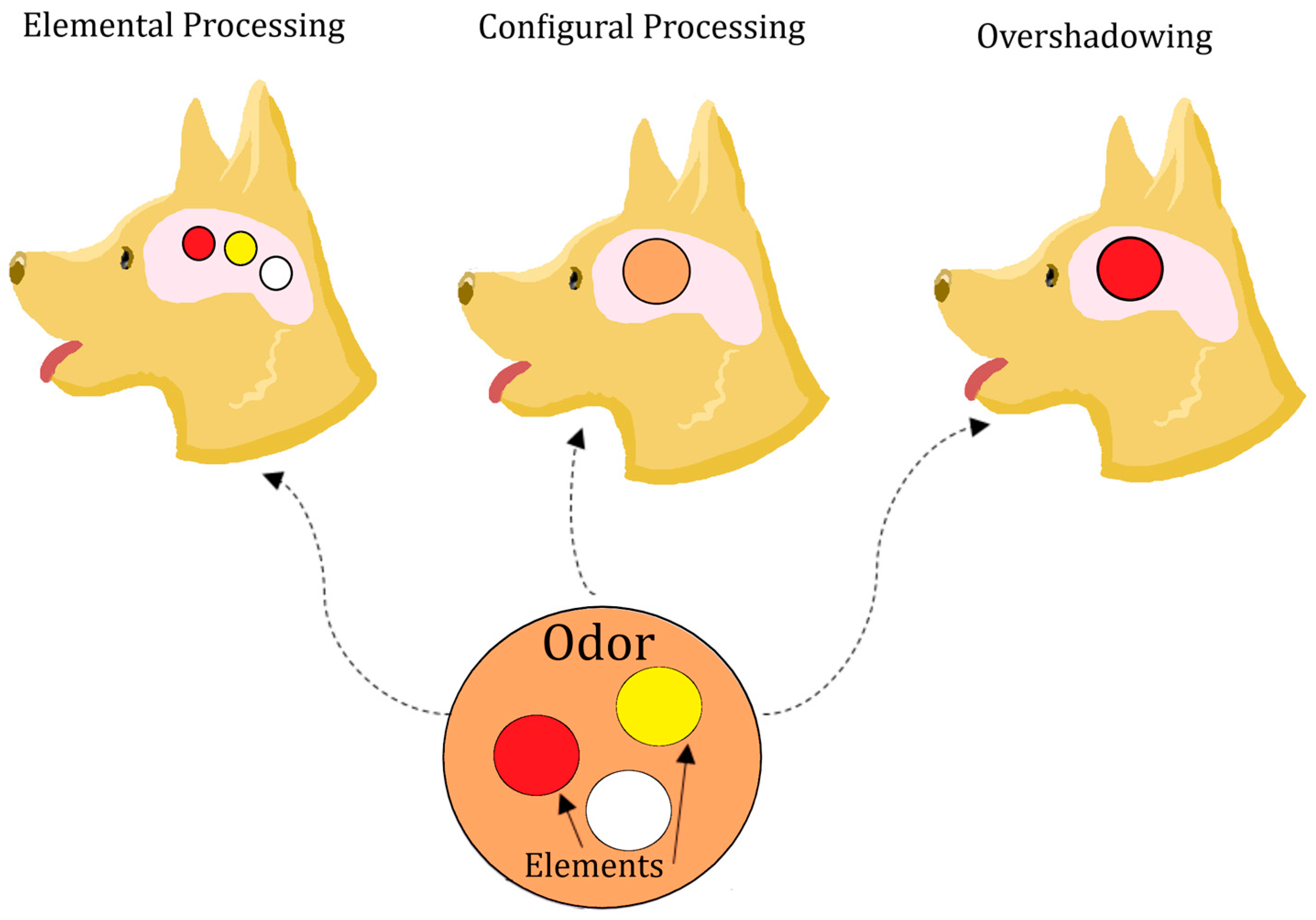
4. Generalization of Mixtures and Components
5. Generalization of Similar Complex Odors
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Furton, K.G.; Myers, L.J. The scientific foundation and efficacy of the use of canines as chemical detectors for explosives. Talanta 2001, 54, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, N.; Wan, T.; Harper, R.J.; Hsu, Y.L.; Chow, M.; Rose, S.; Furton, K.G. Laboratory and field experiments used to identify Canis lupus var. familiaris active odor signature chemicals from drugs, explosives, and humans. Anal. Bioanal Chem. 2003, 376, 1212–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greatbatch, I.; Gosling, R.J.; Allen, S. Quantifying Search Dog Effectiveness in a Terrestrial Search and Rescue Environment. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2015, 26, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, D.A.; Ralls, K.; Hurt, A.; Adams, B.; Parker, M.; Davenport, B.; Smith, M.C.; Maldonado, J.E. Detection and accuracy rates of dogs trained to find scats of San Joaquin kit foxes (Vulpes macrotis mutica). Anim. Conserv. 2003, 6, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lit, L. Evaluating Learning Tasks Commonly Applied in Detection Dog Training. In Canine Ergonomics: The Science of Working Dogs; Helton, W.S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 99–114. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlov, I.P. Conditioned Reflexes: An Investigation of the Physiological Activity of the Cerebral Cortex; Oxford Univ. Press: Oxford, UK, 1927. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, T.F.; Baer, D.M. An implicit technology of generalization. J. Appl. Behav. Anal. 1977, 10, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghirlanda, S.; Enquist, M. A century of generalization. Anim. Behav. 2003, 66, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guttman, N.; Kalish, H. Discriminability and Stimulus Generalizaiton. J. Exp. Psychol. 1956, 51, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerreta, M.M.; Furton, K.G. An assessment of detection canine alerts using flowers that release methyl benzoate, the cocaine odorant, and an evaluation of their behavior in terms of the VOCs produced. Forensic Sci. Int. 2015, 251, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, K.W. The differential response in animals to stimuli varying within a single dimension. Psychol. Rev. 1937, 44, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blough, P.M. Wavelength generalization and discrimination in the pigeon. Percept. Psychophys. 1972, 12, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, R.N. Toward a Universal Law of Generalization for Psychological Science. Science 1987, 237, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wisniewski, M.G.; Church, B.A.; Mercado, E., 3rd. Learning-related shifts in generalization gradients for complex sounds. Learn. Behav. 2009, 37, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fay, R. Auditory frequency generalization in the goldfish (Carassius auratus). J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 1970, 14, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, R.H.; Gross, C.G. Maintained generalization gradlents in the monkeyl. Psychon. Sci. 1969, 14, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K. Shepard’s Universal Law Supported by Honeybees in Spatial Generalization. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 2000, 11, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baerends, G. The hering gull and its egg. Part II. The responsiveness to egg-features. Behaviour 1982, 82, 1–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, K.C.; Chandra, S.; Durtschi, M.L.; Smith, B.H. The generalization of an olfactory-based conditioned response reveals unique but overlapping odour representations in the moth Manduca sexta. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204, 3085–3095. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buss, A.H. Stimulus generalization and aggressive verbal stimuli. Exp. Psychol. 1961, 61, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FeldmanHall, O.; Dunsmoor, J.E.; Tompary, A.; Hunter, L.E.; Todorov, A.; Phelps, E.A. Stimulus generalization as a mechanism for learning to trust. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1690–E1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braun, J.J.; Marcus, J. Stimulus generalization among odorants by rats. Physiol. Behav. 1969, 4, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laska, M.; Teubner, P. Olfactory Discrimination Ability for Homologous Series of Aliphatic Alcohols and Aldehydes. Chem. Senses 1999, 24, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laska, M.; Galizia, C.G.; Giurfa, M.; Menzel, R. Olfactory Discrimination Ability and Odor Structure–Activity Relationships in Honeybees. Chem. Senses 1999, 24, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleland, T.A.; Morse, A.; Yue, E.L.; Linster, C. Behavioral models of odor similarity. Behav. Neurosci. 2002, 116, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoder, W.M.; Setlow, B.; Bizon, J.L.; Smith, D.W. Characterizing olfactory perceptual similarity using carbon chain discrimination in Fischer 344 rats. Chem. Senses 2014, 39, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, N.J.; Collada, A.; Smith, D.W.; Wynne, C.D.L. Performance of domestic dogs on an olfactory discrimination of a homologous series of alcohols. Applied Animal Behaviour Science 2016, 178, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.G.; DeGreeff, L.E.; Peranich, K.; Holness, H.; Furton, K.G. Canine Generalization to Molecularly Similar Odors and Odor Mixtures; Naval Research Laboratory: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Döving, K.B. An electrophysiological study of odour similarities of homologous substances. J. Physiol. 1966, 186, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linster, C.; Smith, B.H. Generalization Between Binary Odor Mixtures and Their Components in the Rat. Physiol. Behav. 1999, 66, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, E.J. Improvement in perceptual judgments as a function of controlled practice or training. Psychol. Bull. 1953, 50, 401–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleland, T.A.; Narla, V.A.; Boudadi, K. Multiple learning parameters differentially regulate olfactory generalization. Behav. Neurosci 2009, 123, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, H.M. Discrimination Training Effect on Stimulus Generalization Gradient for Spectrum Stimuli. Science 1957, 125, 888–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizo, L.A.; McMahon, C.V. Temporal generalization and peak shift in humans. Learn. Behav. 2007, 35, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perez, M.; Nowotny, T.; d’Ettorre, P.; Giurfa, M. Olfactory experience shapes the evaluation of odour similarity in ants: A behavioural and computational analysis. Proc. Biol. Sci 2016, 283, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purtle, R.B. Peak shift: A review. Psychol. Bull. 1973, 80, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewski, M.G.; Radell, M.L.; Guillette, L.M.; Sturdy, C.B.; Mercado, E., 3rd. Predicting shifts in generalization gradients with perceptrons. Learn. Behav. 2012, 40, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrace, H.S. Wavelength generalization after discrimination learning with and without errors. Science 1964, 144, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadbois, S.; Reeve, C. Canine Olfaction: Scent, Sign, and Situation. In Domestic Dog Cognition and Behavior; Horowitz, A., Ed.; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derby, C.D.; Hutson, M.; Livermore, B.A.; Lynn, W.H. Generalization among related complex odorant mixtures and their components: Analysis of olfactory perception in the Spiny Lobster. Physiol. Behav. 1996, 60, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linster, C.; Hasselmo, M.E. Behavioral Responses to Aliphatic Aldehydes Can Be Predicted From Known Electrophysiological Responses of Mitral Cells in the Olfactory Bulb. Physiol. Behav. 1999, 66, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas-Danguin, T.; Sinding, C.; Romagny, S.; El Mountassir, F.; Atanasova, B.; Le Berre, E.; Le Bon, A.M.; Coureaud, G. The perception of odor objects in everyday life: A review on the processing of odor mixtures. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjellanger, R.; Andersen, E.K.; McLean, I.G. A Training Program for Filter-Search Mine Detection Dogs. Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2002, 15, 277–286. [Google Scholar]
- Domjan, M.P. The Principles of Learning and Behavior: Active Learning Edition; Cengage Learning: North Ryde, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, J.M. A model for stimulus generalization in pavlovian conditioning. Psychol. Rev. 1987, 94, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, L.M.; Crk, T.; Thorngate, J. A redefinition of odor mixture quality. Behav. Neurosci 2005, 119, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, N.J.; Wynne, C.D.L. Odor mixture training enhances dogs’ olfactory detection of Home-Made Explosive precursors. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livermore, A.; Hutson, M.; Ngo, V.; Hadjisimos, R.; Derby, C.D. Elemental and Configural Learning and the Perception of Odorant Mixtures by the Spiny Lobster Panulirus argus. Physiol. Behav. 1997, 62, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarowski, L.; Foster, M.L.; Gruen, M.E.; Sherman, B.L.; Fish, R.E.; Milgram, N.W.; Dorman, D.C. Olfactory discrimination and generalization of ammonium nitrate and structurally related odorants in Labrador retrievers. Anim. Cogn. 2015, 18, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeGreeff, L.E.; Peranich, K.; Simon, A.G. Detection of Ammonium Nitrate Variants by Canine: A Study of Generalization between Like Substances; Naval Research Laboratory: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarowski, L.; Dorman, D.C. Explosives detection by military working dogs: Olfactory generalization from components to mixtures. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2014, 151, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokni, D.; Hemmelder, V.; Kapoor, V.; Murthy, V.N. An olfactory cocktail party: Figure-ground segregation of odorants in rodents. Nat. Neurosci 2014, 17, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer-Tenhagen, C.; Johnen, D.; Heuwieser, W.; Becker, R.; Schallschmidt, K.; Nehls, I. Odor Perception by Dogs: Evaluating Two Training Approaches for Odor Learning of Sniffer Dogs. Chem. Senses 2017, 42, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranz, W.; Kitts, K.; Strange, N.; Cummins, J.; Lotspeich, E.; Goodpaster, J. On the smell of Composition C-4. Forensic Sci. Int. 2014, 236, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papet, L.E. Narcotic and explosive odors: Volatile organic compounds as training aids for olfactory detection. In Canine Olfaction Science and Law; Jezierski, T., Ensminger, J., Papet, L.E., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 265–278. [Google Scholar]
- Furton, K.G.; Hong, Y.C.; Hsu, Y.L.; Luo, T.; Rose, S.; Walton, J. Identification of Odor Signature Chemicals in Cocaine Using Solid-Phase Microextraction– Gas Chromatography and Detector-Dog Response to Isolated Compounds Spiked on U.S. Paper Currency. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2002, 40, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, R.J.; Almirall, J.R.; Furton, K.G. Identification of dominant odor chemicals emanating from explosives for use in developing optimal training aid combinations and mimics for canine detection. Talanta 2005, 67, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furton, K.G.; Hsu, C.Y.; Luo, T.; Alvarez, N.; Lagos, P. Novel sample preparation methods and field testing procedures used to determine the chemical basis of cocaine detection by canines. In Proceedings of the Forensic Evidence Analysis and Crime Scene Investigation, Boston, MA, USA, 10 February 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Sinding, C.; Thomas-Danguin, T.; Chambault, A.; Beno, N.; Dosne, T.; Chabanet, C.; Schaal, B.; Coureaud, G. Rabbit neonates and human adults perceive a blending 6-component odor mixture in a comparable manner. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laing, D.G.; Francis, G.W. The Capacity of Humans to Identify Odors in Mixtures. Physiol. Behav. 1989, 46, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiltrout, C.; Dogra, S.; Linster, C. Configurational and nonconfigurational interactions between odorants in binary mixtures. Behav. Neurosci. 2003, 117, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, G.S. Attention in the pigeon. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 1961, 4, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takiguchi, N.; Okuhara, K.; Kuroda, A.; Kato, J.; Ohtake, H. Performance of mice in discrimination of liquor odors: Behavioral evidence for olfactory attention. Chem. Senses 2008, 33, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Černá, K.; Pinc, L.; Pachman, J. Ability of explosives detector dogs to generalize odor of TNT. In Proceedings of the New Trends in Research of Energetic Materials, Pardubice, Czech Republic, 13–15 April 2011; pp. 542–549. [Google Scholar]
- Elliker, K.R.; Sommerville, B.A.; Broom, D.M.; Neal, D.E.; Armstrong, S.; Williams, H.C. Key considerations for the experimental training and evaluation of cancer odour detection dogs: Lessons learnt from a double-blind, controlled trial of prostate cancer detection. BMC Urology 2014, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, H.F.; Wilkinson, A.; Croxton, R.S.; Graham, D.K.; Harding, R.C.; Hodkinson, H.L.; Keep, B.; Cracknell, N.R.; Zulch, H.E. Animals can assign novel odours to a known category. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer-Tenhagen, C.; Wetterholm, L.; Tenhagen, B.-A.; Heuwieser, W. Training dogs on a scent platform for oestrus detection in cows. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2011, 131, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, A.; Woollett, D.A.; Parker, M. Training considerations in wildlife detection. In Canine Olfaction Science and Law; Jezierski, T., Ensminger, J., Papet, L.E., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vynne, C.; Skalski, J.R.; Machado, R.B.; MGroom, M.J.; Jacamo, A.T.; Marinho-Filho, J.; Ramos Neto, M.B.; Pomilla, C.; Silveira, L.; Smith, H.; et al. Effectiveness of Scat-Detection Dogs in Determining Species Presence in a Tropical Savanna Landscape. Conserv. Biol. 2011, 25, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, C.; Schoon, A.; Heitkönig, I.M.A. Wildlife detection dog training: A case study on achieving generalization between target odor variations while retaining specificity. J. Vet. Behav. Clin. Appl. Res. 2016, 13, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxley, J.; Waggoner, L. Detection of Explosives by Dogs. In Aspects of Explosives Detection; Marshall, M., Oxley, J.C., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-M.; Chi, W.-L.; Lin, C.-C.; Tseng, Y.-C.; Chen, W.-T.; Kung, Y.-L.; Lien, Y.-Y.; Chen, Y.-Y. Fire Ant-Detecting Canines: A Complementary Method in Detecting Red Imported Fire Ants. J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, J.; O’Connor, S.; Park, K.J.; Goulson, D. Testing a detection dog to locate bumblebee colonies and estimate nest density. Apidologie 2011, 42, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tipple, C.A.; Caldwell, P.T.; Kile, B.M.; Beussman, D.J.; Rushing, B.; Mitchell, N.J.; Whitchurch, C.J.; Grime, M.; Stockham, R.; Eckenrode, B.A. Comprehensive characterization of commercially available canine training aids. Forensic Sci. Int. 2014, 242, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Browne, C. The Use of Dogs to Detect New Zealand Reptile Scents. Master’s Thesis, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealnad, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cablk, M.E.; Heaton, J.S. Accuracy and Reliability of Dogs in Surveying for Desert Tortoise (Gopherus agassizii). Ecol. Appl. 2006, 16, 1926–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosconi, F.; Campanaro, A.; Carpaneto, G.M.; Chiari, S.; Hardersen, S.; Mancini, E.; Maurizi, E.; Sabatelli, S.; Zauli, A.; Mason, F.; et al. Training of a dog for the monitoring of Osmoderma eremita. Nat. Conserv. 2017, 20, 237–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stadler, S.; Stefanuto, P.H.; Byer, J.D.; Brokl, M.; Forbes, S.; Focant, J.F. Analysis of synthetic canine training aids by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1255, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfiester, M.; Koehler, P.G.; Pereira, R.M. Ability of Bed Bug-Detecting Canines to Locate Live Bed Bugs and Viable Bed Bug Eggs. J. Econ. Entomol. 2008, 101, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.G.; Mills, D.K.; Furton, K.G. Chemical and canine analysis as complimentary techniques for the identification of active odors of the invasive fungus, Raffaelea lauricola. Talanta 2017, 168, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, E. The Influence of Training Procedures on Generalization Performance in Scent-Detection Rats. Ph.D. Thesis, Western Michigan University, Michigan, MI, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Goldblatt, A.; Gazit, I.; Terkel, J. Olfaction and explosives detector dogs. In Canine Ergonomics: The Science of Working Dogs; Helton, W.S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 99–114. [Google Scholar]
- Lotfizadeh, A.D.; Redner, R.; Edwards, T.L.; Quisenberry, A.J.; Baker, L.E.; Poling, A. Effects of altering motivation for food in rats trained with food reinforcement to discriminate between d-amphetamine and saline injections. Pharm. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 103, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.; Symonds, M.; Hall, G.; de Brugada, I. Flattening of a generalization gradient following a retention interval: Evidence for differential forgetting of stimulus features. Behav. Process. 2017, 145, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, A.; Kalish, H.I. Prediction of Discrimination from Generalization after Variations in Schedule of Reinforcement. Science 1963, 142, 412–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kueh, D.; Baker, L.E. Reinforcement schedule effects in rats trained to discriminate 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) or cocaine. Psychopharmacol. 2007, 189, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moser, A.Y.; Bizo, L.; Brown, W.Y. Olfactory Generalization in Detector Dogs. Animals 2019, 9, 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9090702
Moser AY, Bizo L, Brown WY. Olfactory Generalization in Detector Dogs. Animals. 2019; 9(9):702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9090702
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoser, Ariella Y., Lewis Bizo, and Wendy Y. Brown. 2019. "Olfactory Generalization in Detector Dogs" Animals 9, no. 9: 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9090702
APA StyleMoser, A. Y., Bizo, L., & Brown, W. Y. (2019). Olfactory Generalization in Detector Dogs. Animals, 9(9), 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9090702





