Effects of Mining Activities on Gerbillus nanus in Saudi Arabia: A Biochemical and Histological Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
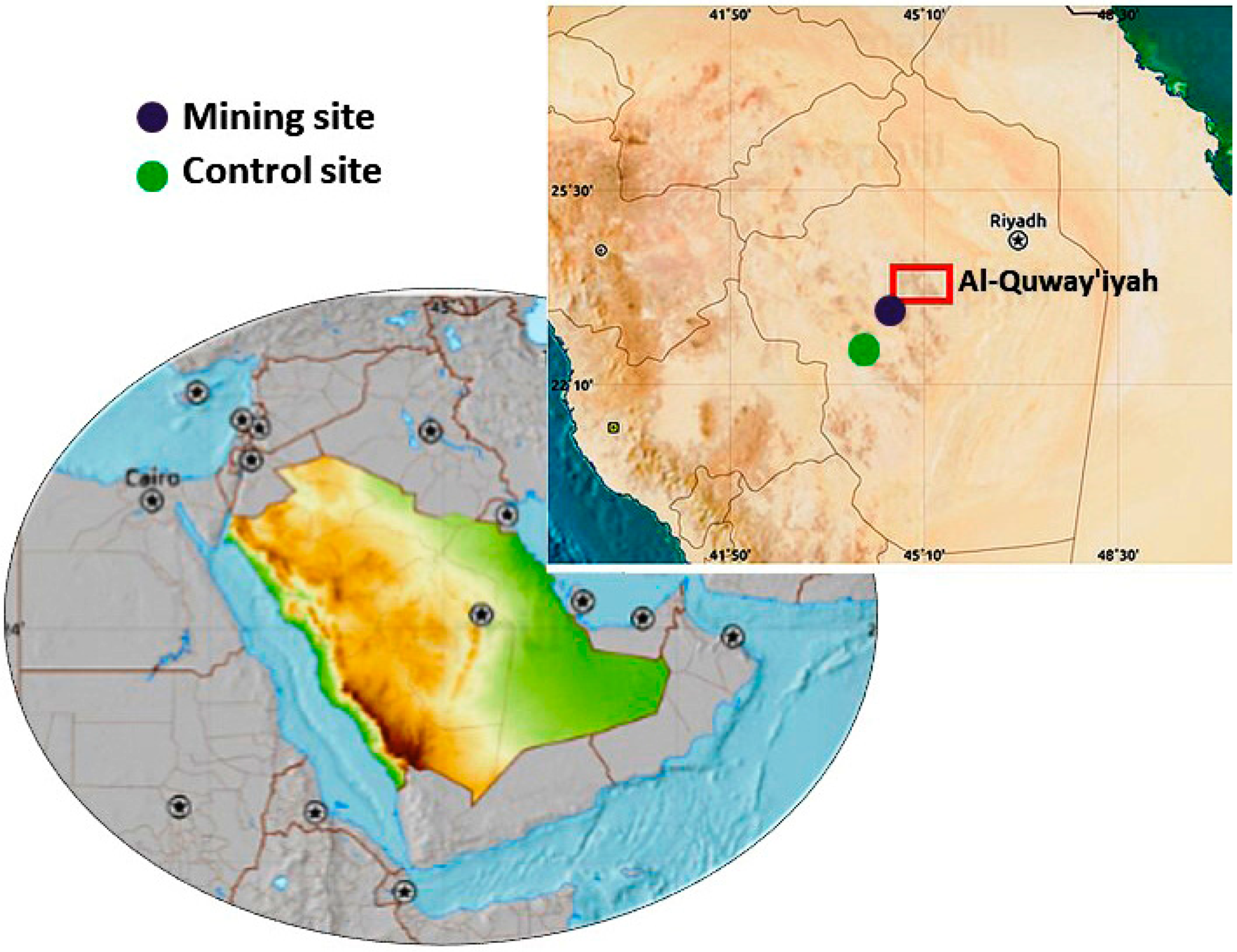
2.1. Study Site and Collection of Samples
- Site 1 (Mining): Located 500 m away from the gold mine, between E45° 05′ and N23° 47′.
- Site 2 (Control): Located 20,000 m away from the gold mine, between E45° 06′ and N23° 36′.
2.2. Determination of HMs
2.3. Assay of Liver and Kidney Function Markers
2.4. Assay of Oxidative Stress Markers and Antioxidants
2.5. Histological Study
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
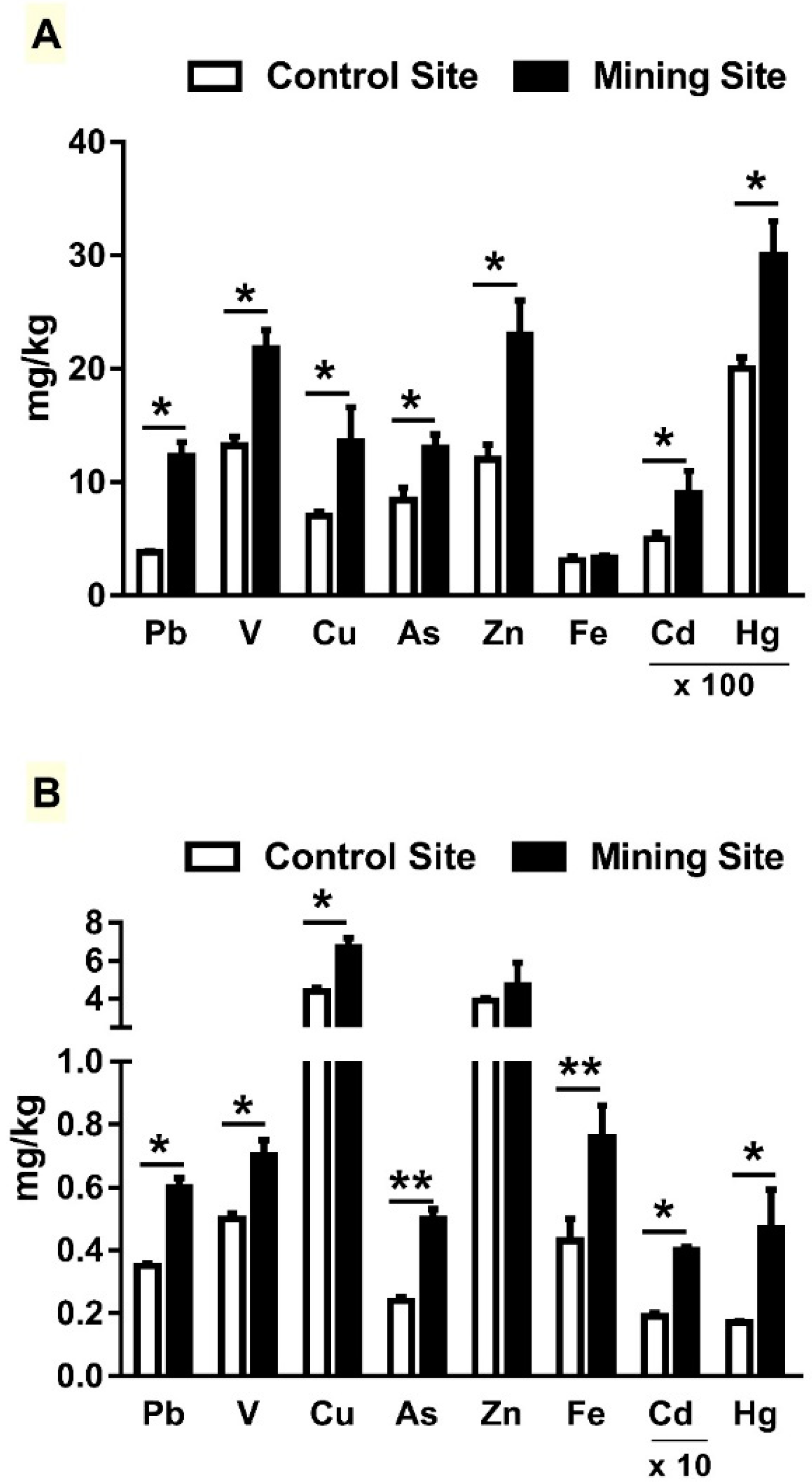
3.1. HM Concentration in Soil and L. shawii Samples
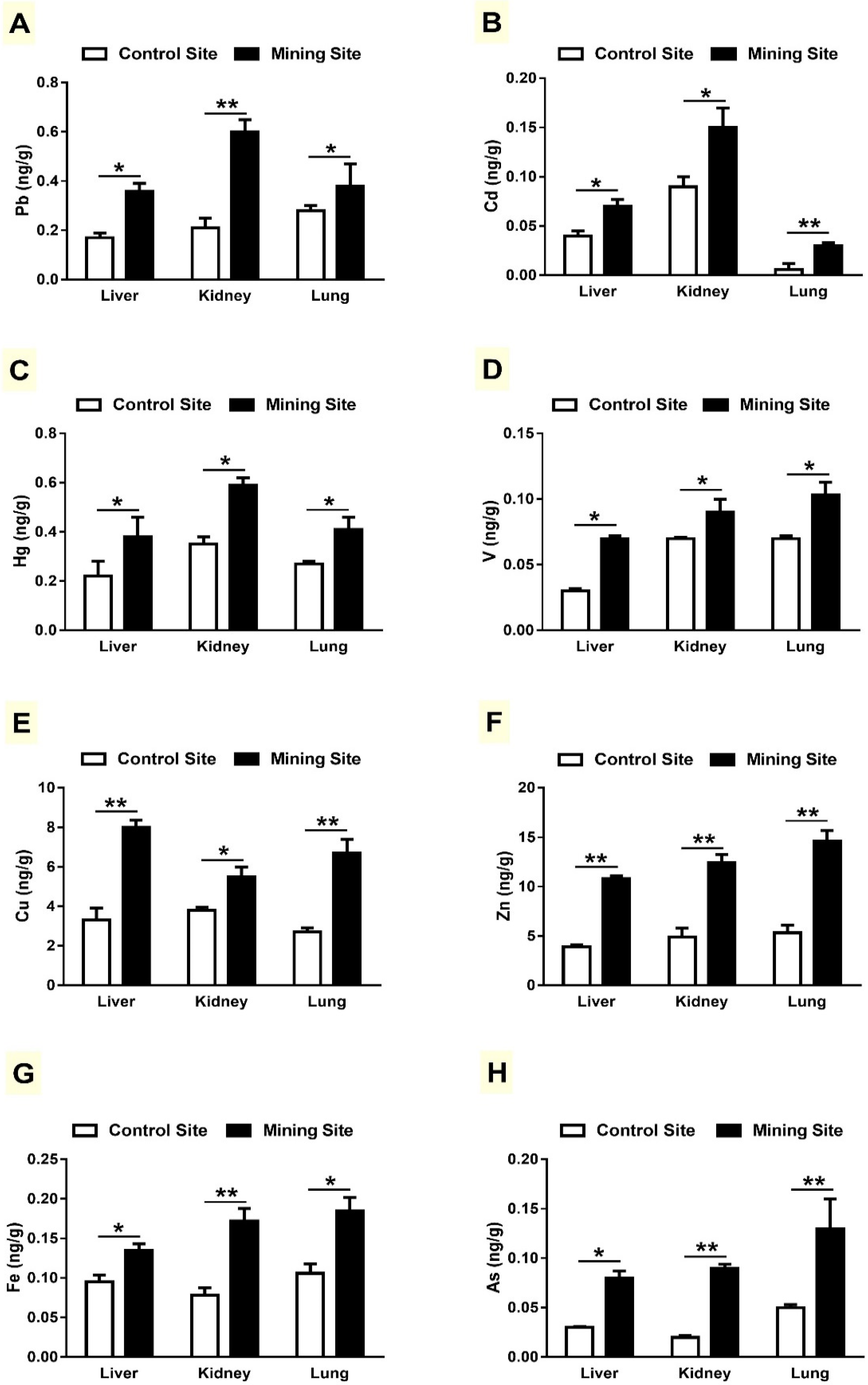
3.2. Concentration of HMs in Liver, Kidneys and Lungs of G. nanus
3.3. Effect of Mining on Liver Function and Histology in G. nanus
3.4. Effect of Mining on Kidney Function and Histology in G. nanus
3.5. Effect of Mining on the Lung of G. nanus
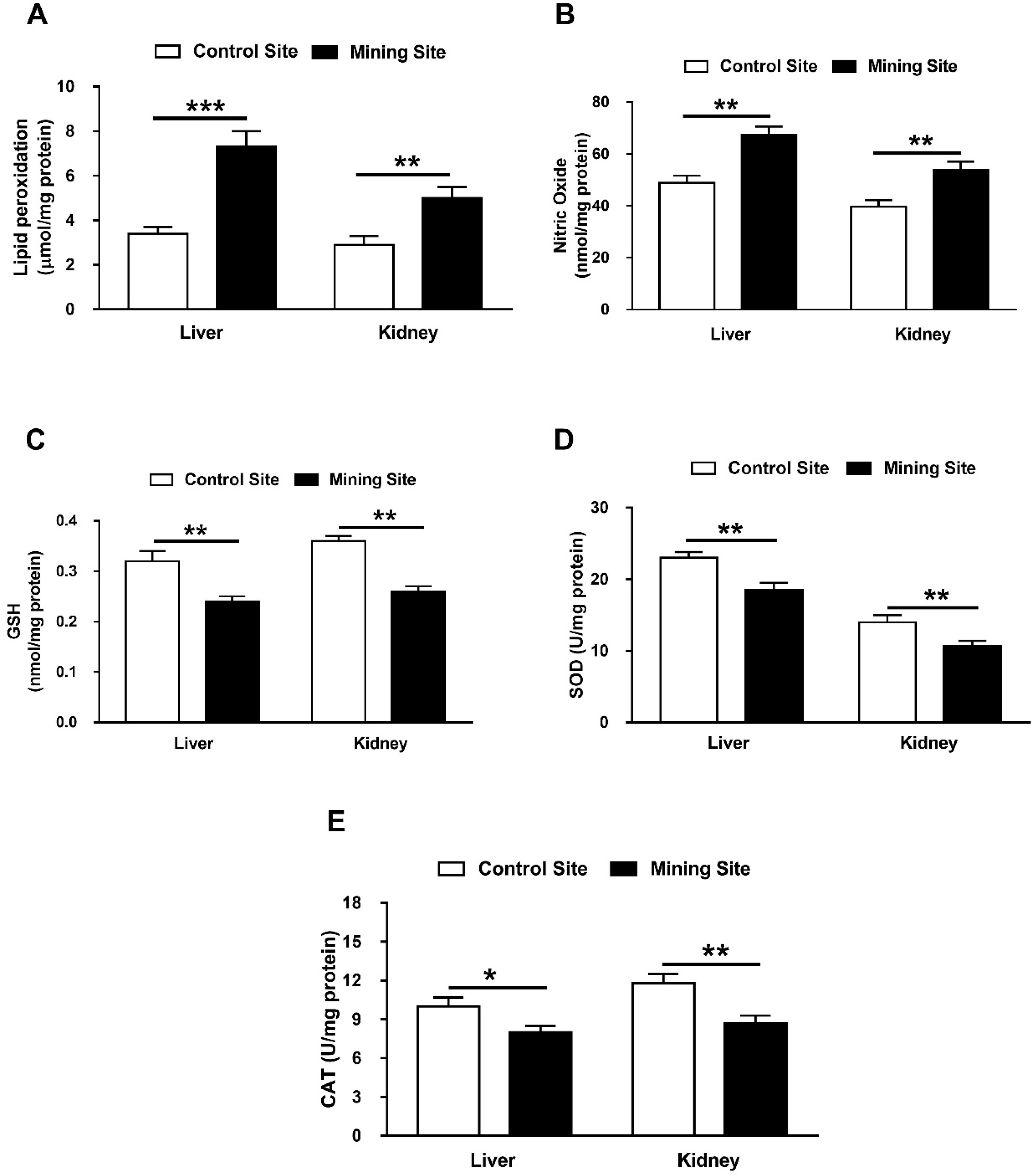
3.6. Effect of Mining on Hepatic and Renal Redox Balance in G. nanus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krook, J.; Svensson, N.; Eklund, M. Landfill mining: A critical review of two decades of research. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loayza, N.; Rigolini, J. The local impact of mining on poverty and inequality: Evidence from the commodity boom in Peru. World Dev. 2016, 84, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, A.Y.; Jerry, C.S.; Dzigbodi, D.A. Review of environmental and health impacts of mining in Ghana. J. Health Pollut. 2018, 8, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudka, S.; Adriano, D.C. Environmental impacts of metal ore mining and processing: A review. J. Environ. Qual. 1997, 26, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warhate, S.R.; Yenkie, M.K.; Chaudhari, M.D.; Pokale, W.K. Impacts of mining activities on water and soil. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2006, 48, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Nowrouzi-Kia, B.; Gohar, B.; Casole, J.; Chidu, C.; Dumond, J.; McDougall, A.; Nowrouzi-Kia, B. A systematic review of lost-time injuries in the global mining industry. Work (Read. Mass.) 2018, 60, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fashola, M.O.; Ngole-Jeme, V.M.; Babalola, O.O. Heavy metal pollution from gold mines: Environmental effects and bacterial strategies for resistance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Gautam, N.; Mishra, A.; Gupta, R. Heavy metals and living systems: An overview. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2011, 43, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarup, L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br. Med Bull. 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rzymski, P.; Niedzielski, P.; Klimaszyk, P.; Poniedzialek, B. Bioaccumulation of selected metals in bivalves (Unionidae) and Phragmites australis inhabiting a municipal water reservoir. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 3199–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kok, T.M.; Hogervorst, J.G.; Briede, J.J.; van Herwijnen, M.H.; Maas, L.M.; Moonen, E.J.; Driece, H.A.; Kleinjans, J.C. Genotoxicity and physicochemical characteristics of traffic-related ambient particulate matter. Environ. Mol. Mutagenesis 2005, 46, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markiewicz-Górka, I.; Januszewska, L.; Michalak, A.; Prokopowicz, A.; Januszewska, E.; Pawlas, N.; Pawlas, K. Effects of chronic exposure to lead, cadmium, and manganese mixtures on oxidative stress in rat liver and heart. Arh. Za Hig. Rada I Toksikol. 2015, 66, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzymski, P.; Tomczyk, K.; Rzymski, P.; Poniedzialek, B.; Opala, T.; Wilczak, M. Impact of heavy metals on the female reproductive system. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. AAEM 2015, 22, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.F.; Aarts, M.G. The molecular mechanism of zinc and cadmium stress response in plants. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2012, 69, 3187–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordberg, G.F.; Nogawa, K.; Nordberg, M.; Friberg, L.T. Chapter 23—Cadmium. In Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 445–486. [Google Scholar]
- Brzoska, M.M.; Moniuszko-Jakoniuk, J. Low-level exposure to cadmium during the lifetime increases the risk of osteoporosis and fractures of the lumbar spine in the elderly: Studies on a rat model of human environmental exposure. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2004, 82, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alissa, E.M.; Ferns, G.A. Heavy metal poisoning and cardiovascular disease. J. Toxicol. 2011, 2011, 870125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.; Chowdhury, S.; Biswas, A.K. Regulation of growth and metabolism in rice (oryza sativa L.) by arsenic and its possible reversal by phosphate. J. Plant Interact. 2011, 6, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.; Singh, V.P. The relative impact of toxic heavy metals (THMs) (arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr)(VI), mercury (Hg), and lead (Pb)) on the total environment: An overview. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Rhodes, C.J.; Moncol, J.; Izakovic, M.; Mazur, M. Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2006, 160, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.L.; Bates, P.J.J. The Mammals of Saudi Arabia; Benn: London, UK, 1991; pp. 354–367. [Google Scholar]
- Azizi, K.; Moemenbellah-Fard, M.D.; Fakoorziba, M.R.; Fekri, S. Gerbillus nanus (rodentia: Muridae): A new reservoir host of leishmania major. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2011, 105, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuss, H.G.; Jarrell, S.T.; Scheckenbach, R.; Lieberman, S.; Anderson, R.A. Comparative effects of chromium, vanadium and gymnema sylvestre on sugar-induced blood pressure elevations in shr. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1998, 17, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisham, M.B.; Johnson, G.G.; Lancaster, J.R., Jr. Quantitation of nitrate and nitrite in extracellular fluids. Methods Enzym. 1996, 268, 237–246. [Google Scholar]
- Beutler, E.; Duron, O.; Kelly, B.M. Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1963, 61, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marklund, S.; Marklund, G. Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. FEBS Eur. J. Biochem. 1974, 47, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, G.; Dembiec, D.; Marcus, J. Measurement of catalase activity in tissue extracts. Anal. Biochem. Anal. Biochem. 1970, 34, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Lead Poisoning and Health. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/lead-poisoning-and-health (accessed on 1 May 2019).
- The New Top Six Toxic Threats: A Priority List for Remediation, World’s Worst Pollution Problems Report; Pure Earth: New York, NY, USA, 2015.
- Mudipalli, A. Lead hepatotoxicity & potential health effects. Indian J. Med Res. 2007, 126, 518–527. [Google Scholar]
- El-Nekeety, A.A.; El-Kady, A.A.; Soliman, M.S.; Hassan, N.S.; Abdel-Wahhab, M.A. Protective effect of Aquilegia vulgaris (L.) against lead acetate-induced oxidative stress in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2009, 47, 2209–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Ha, X.; Yang, Z.; Hui, L.; Yang, X. Oxidative stress: A possible mechanism for lead-induced apoptosis and nephrotoxicity. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2012, 22, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tantawy, W.H. Antioxidant effects of spirulina supplement against lead acetate-induced hepatic injury in rats. J. Tradit. Complementary Med. 2016, 6, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.C.; Peixe, T.S.; Mesas, A.E.; Paoliello, M.M. Lead Exposure and Oxidative Stress: A Systematic Review. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 236, 193–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flora, S.J.S.; Flora, G.; Saxena, G. Environmental occurrence, health effects and management of lead poisoning. In Lead Chemistry, Analytical Aspects, Environmental Impacts and Health Effects; Cascas, S.B., Sordo, J., Eds.; Elsevier Publication: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 158–228. [Google Scholar]
- Adegbesan, B.O.; Adenuga, G.A. Effect of lead exposure on liver lipid peroxidative and antioxidant defense systems of protein-undernourished rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2007, 116, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liu, H.; Alattar, M.; Jiang, S.; Han, J.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, C. The preferential accumulation of heavy metals in different tissues following frequent respiratory exposure to pm2.5 in rats. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarup, L.; Akesson, A. Current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thevenod, F.; Lee, W.K. Toxicology of cadmium and its damage to mammalian organs. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2013, 11, 415–490. [Google Scholar]
- Satarug, S.; Garrett, S.H.; Sens, M.A.; Sens, D.A. Cadmium, environmental exposure, and health outcomes. Cienc. Saude Coletiva 2011, 16, 2587–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalino, E.; Sblano, C.; Landriscina, C. Enzyme activity alteration by cadmium administration to rats: The possibility of iron involvement in lipid peroxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1997, 346, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaprakash, K.; Chinnaswamy, P. Effect of spirulina and liv-52 on cadmium induced toxicity in albino rats. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 43, 773–781. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente-Sanchez, C.; Egido, J.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, P.D.; Perez-Barriocanal, F.; Lopez-Novoa, J.M.; Morales, A.I. Effect of the flavonoid quercetin on cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2008, 46, 2279–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, H.; Yasutake, A.; Hirashima, T.; Takamure, Y.; Kitano, T.; Waalkes, M.P.; Imamura, Y. Strain difference of cadmium accumulation by liver slices of inbred wistar-imamichi and fischer 344 rats. Toxicol. Vitro Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2008, 22, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hao, M.; Liu, C.; Liu, R. Cadmium induced apoptosis in mouse primary hepatocytes: The role of oxidative stress-mediated erk pathway activation and the involvement of histone h3 phosphorylation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 31798–31806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnetto, J.M.; Hennessy, S.W.; Roberts, V.A.; Getzoff, E.D.; Tainer, J.A.; Pique, M.E. Mdb: The metalloprotein database and browser at the scripps research institute. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, J.; Leonard, S.S.; Rao, K.M. Cadmium inhibits the electron transfer chain and induces reactive oxygen species. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 36, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akomolafe, R.O.; Imafidon, C.E.; Olukiran, O.S.; Oladele, A.A.; Ajayi, A.O. Livolin forte ameliorates cadmium-induced kidney injury in wistar rats. Serb. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2016, 17, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognin, M.; Kirschvink, N.; Leemans, J.; De Buscher, V.; Snaps, F.; Gustin, P.; Peeters, D.; Clercx, C. Characterisation of the acute and reversible airway inflammation induced by cadmium chloride inhalation in healthy dogs and evaluation of the effects of salbutamol and prednisolone. Vet. J. 2009, 179, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberdorster, G. Airborne cadmium and carcinogenesis of the respiratory tract. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 1986, 12, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, S.; Oldiges, H.; Konig, H.; Hochrainer, D.; Oberdorster, G. Carcinogenicity of cadmium chloride aerosols in w rats. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1983, 70, 367–373. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Kumar, D.; Sahu, A.P. Arsenic in the environment: Effects on human health and possible prevention. J. Environ. Biol. 2007, 28, 359–365. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M.F.; Beck, B.D.; Chen, Y.; Lewis, A.S.; Thomas, D.J. Arsenic exposure and toxicology: A historical perspective. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 123, 305–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangapandiyan, S.; Ramesh, M.; Miltonprabu, S.; Hema, T.; Jothi, G.B.; Nandhini, V. Sulforaphane potentially attenuates arsenic-induced nephrotoxicity via the pi3k/akt/nrf2 pathway in albino wistar rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 12247–12263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Shan, Q.; Liu, P.; Feng, T.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, P.; Chen, K.; Xie, H.; Song, P.; Zhou, L.; et al. Metformin ameliorates arsenic trioxide hepatotoxicity via inhibiting mitochondrial complex i. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariappan, N.; Zafar, I.; Husain, M.; Vaid, M.; Surolia, R.; Kashyap, M.P.; Srivastava, R.; Ahmad, S.; Agarwal, A.; Athar, M.; et al. Pulmonary manifestations of inhaled arsenic trioxide following an acute accidental exposure. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, A2974. [Google Scholar]
- Patrick, L. Mercury toxicity and antioxidants: Part 1: Role of glutathione and alpha-lipoic acid in the treatment of mercury toxicity. Altern. Med. Rev. A J. Clin. Ther. 2002, 7, 456–471. [Google Scholar]
- Boroushaki, M.T.; Mollazadeh, H.; Rajabian, A.; Dolati, K.; Hoseini, A.; Paseban, M.; Farzadnia, M. Protective effect of pomegranate seed oil against mercuric chloride-induced nephrotoxicity in rat. Ren. Fail. 2014, 36, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandao, F.; Cappello, T.; Raimundo, J.; Santos, M.A.; Maisano, M.; Mauceri, A.; Pacheco, M.; Pereira, P. Unravelling the mechanisms of mercury hepatotoxicity in wild fish (Liza aurata) through a triad approach: Bioaccumulation, metabolomic profiles and oxidative stress. Met. Integr. Biometal Sci. 2015, 7, 1352–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altamirano-Lozano, M.A.; Alvarez-Barrera, L.; Mateos-Nava, R.A.; Fortoul, T.I.; Rodriguez-Mercado, J.J. Potential for genotoxic and reprotoxic effects of vanadium compounds due to occupational and environmental exposures: An article based on a presentation at the 8th international symposium on vanadium chemistry, biological chemistry, and toxicology, Washington, DC, USA, 15–18 August 2012. J. Immunotoxicol. 2014, 11, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Castellini, C.; Mourvaki, E.; Sartini, B.; Cardinali, R.; Moretti, E.; Collodel, G.; Fortaner, S.; Sabbioni, E.; Renieri, T. In vitro toxic effects of metal compounds on kinetic traits and ultrastructure of rabbit spermatozoa. Reprod. Toxicol. 2009, 27, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshchin, A.V.; Ordzhonikidze, E.K.; Shalganova, I.V. Vanadium--toxicity, metabolism, carrier state. J. Hyg. Epidemiol. Microbiol. Immunol. 1980, 24, 377–383. [Google Scholar]
- Assem, F.L.; Levy, L.S. Inhalation toxicity of vanadium. In Vanadium: Biochemical and Molecular Biological Approaches; Michibata, H., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 209–224. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, B.R. Essentiality and toxicity in copper health risk assessment: Overview, update and regulatory considerations. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health. Part A 2010, 73, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kox, L.F.; Wosten, M.M.; Groisman, E.A. A small protein that mediates the activation of a two-component system by another two-component system. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 1861–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albretsen, J. The toxicity of iron, an essential element. Vet. Med. Bonn. Springs Edw. 2006, 101, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Ramm, G.A.; Ruddell, R.G. Hepatotoxicity of iron overload: Mechanisms of iron-induced hepatic fibrogenesis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2005, 25, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zager, R.A.; Johnson, A.C.M.; Hanson, S.Y. Parenteral iron nephrotoxicity: Potential mechanisms and consequences1. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almalki, A.M.; Ajarem, J.; Altoom, N.; Al-Otaibi, F.S.; Maodaa, S.N.; Allam, A.A.; Mahmoud, A.M. Effects of Mining Activities on Gerbillus nanus in Saudi Arabia: A Biochemical and Histological Study. Animals 2019, 9, 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9090664
Almalki AM, Ajarem J, Altoom N, Al-Otaibi FS, Maodaa SN, Allam AA, Mahmoud AM. Effects of Mining Activities on Gerbillus nanus in Saudi Arabia: A Biochemical and Histological Study. Animals. 2019; 9(9):664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9090664
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmalki, Ahmed M., Jamaan Ajarem, Naif Altoom, Fahed S. Al-Otaibi, Saleh N. Maodaa, Ahmed A. Allam, and Ayman M. Mahmoud. 2019. "Effects of Mining Activities on Gerbillus nanus in Saudi Arabia: A Biochemical and Histological Study" Animals 9, no. 9: 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9090664
APA StyleAlmalki, A. M., Ajarem, J., Altoom, N., Al-Otaibi, F. S., Maodaa, S. N., Allam, A. A., & Mahmoud, A. M. (2019). Effects of Mining Activities on Gerbillus nanus in Saudi Arabia: A Biochemical and Histological Study. Animals, 9(9), 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9090664




