Development of an Automated Pain Facial Expression Detection System for Sheep (Ovis Aries)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Precision Livestock Farming
3. Facial Expression as a Pain Recognition Tool in Sheep
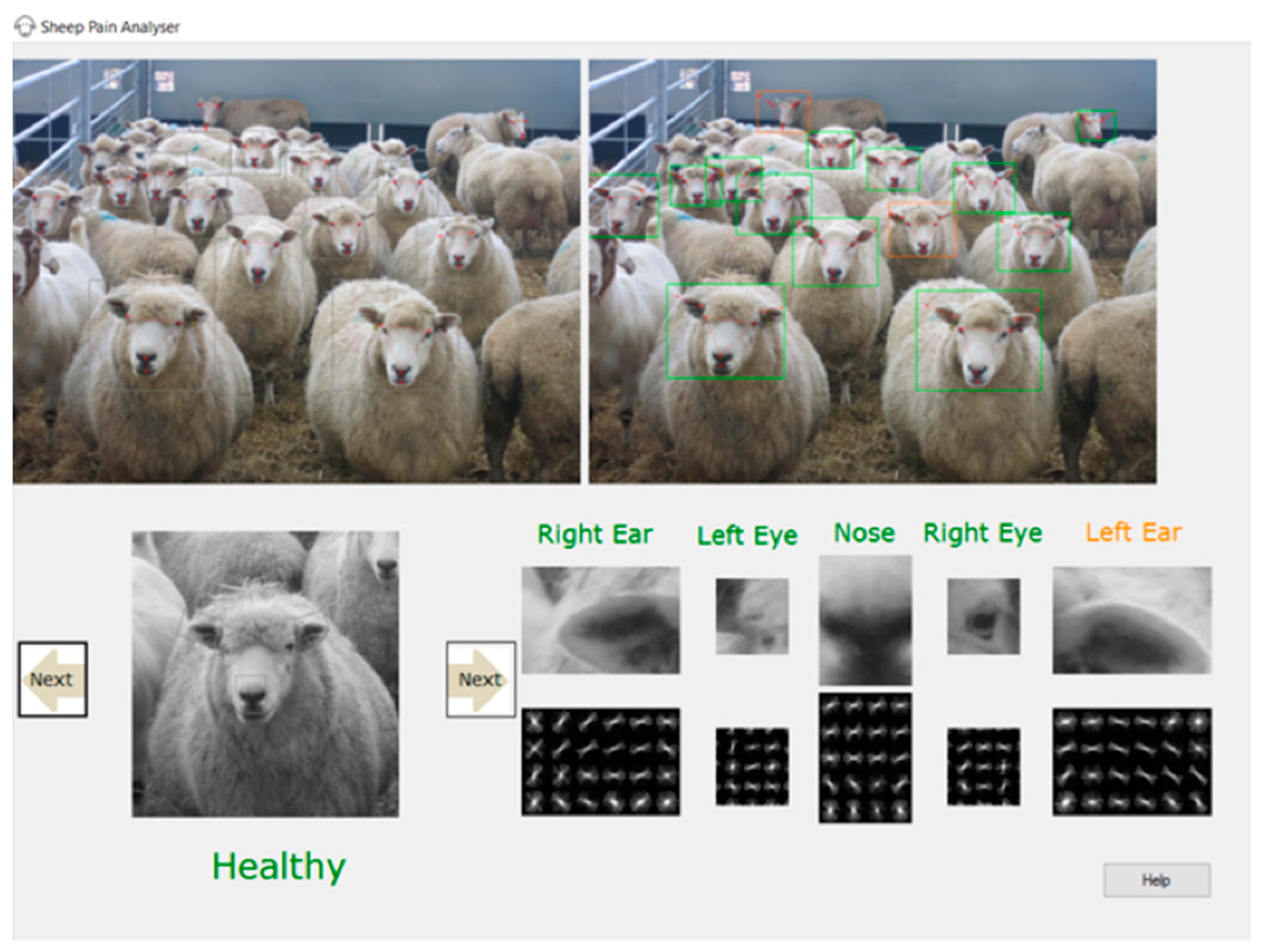
4. Current Status of an Automated Pain Facial Expression Detection System for Sheep
5. Future Direction and Considerations
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunter, M.C.; Smith, R.G.; Schipanski, M.E.; Atwood, L.W.; Mortensen, D.A. Agriculture in 2050: Recalibrating Targets for Sustainable Intensification. Bioscience 2017, 67, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berckmans, D. General introduction to precision livestock farming. Anim. Front. 2017, 7, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, B.; Stewart, G.B.; Panzone, L.A.; Kyriazakis, I.; Frewer, L.J. A Systematic Review of Public Attitudes, Perceptions and Behaviours Towards Production Diseases Associated with Farm Animal Welfare. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2016, 29, 455–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, G.; Weary, D.M.; Spiller, A.; Von Keyserlingk, M.A.G. American and German attitudes towards cow-calf separation on dairy farms. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doughty, A.K.; Coleman, G.J.; Hinch, G.N.; Doyle, R.E. Stakeholder perceptions of welfare issues and indicators for extensively managed sheep in Australia. Animals 2017, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredriksen, B.; Johnsen, A.M.S.; Skuterud, E. Consumer attitudes towards castration of piglets and alternatives to surgical castration. Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 90, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, J.A.; Weary, D.M.; Schuppli, C.A.; Von Keyserlingk, M.A.G. Stakeholder views on treating pain due to dehorning dairy calves. Anim. Welf. 2015, 24, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, B.A.; von Keyserlingk, M.A.G.; Weary, D.M. Animal Welfare Concerns and Values of Stakeholders Within the Dairy Industry. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2014, 28, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaler, J.; Daniels, S.; Wright, J.; Green, L. A randomised factorial design clinical trial to investigate the impact of parenteral long acting oxytetracyline, foot trimming and flunixine meglumine on time to recovery from lameness and foot lesions in sheep lame with footrot. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2010, 24, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieuwhof, G.J.; Bishop, S.C. Costs of the major endemic diseases of sheep in Great Britain and the potential benefits of reduction in disease impact. Anim. Sci. 2005, 81, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.E.T. Mastitis in Sheep. In Breeding for Resistance in Farm Animals; Owen, J.B., Axford, R.E., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 1991; pp. 412–423. [Google Scholar]
- Mavrogianni, V.S.; Fthenakis, G.C.; Burriel, A.R.; Gouletsou, P.; Papaioannou, N.; Taitzoglou, I.A. Experimentally Induced Teat Stenosis in Dairy Ewes: Clinical, Pathological and Ultrasonographic Features. J. Comp. Pathol. 2004, 130, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaler, J.; Green, L.E. Recognition of lameness and decisions to catch for inspection among sheep farmers and specialists in GB. BMC Vet. Res. 2008, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, A. Introduction. Pain: An Issue of Animal Welfare. In Pain Management in Veterinary Practice; Egger, C.M., Love, L., Doherty, T., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Huxley, J.N.; Whay, H.R. Current attitudes of cattle practitioners to pain and the use of analgesics in cattle. Vet. Rec. 2006, 159, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flecknell, P. Analgesia from a veterinary perspective. Br. J. Anaesth. 2008, 101, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ison, S.H.; Rutherford, K.M.D. Attitudes of farmers and veterinarians towards pain and the use of pain relief in pigs. Vet. J. 2014, 202, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizarraga, I.; Chambers, J.P. Use of analgesic drugs for pain management in sheep. N. Z. Vet. J. 2012, 60, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, H.C.; Elbers, A.R.W.; Conraths, F.J.; Holsteg, M.; Hoereth-Boentgen, D.; Gethmann, J.; van Schaik, G. Response to an emerging vector-borne disease: Surveillance and preparedness for Schmallenberg virus. Prev. Vet. Med. 2014, 116, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berckmans, D. General introduction to livestock farming. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. int. Epiz 2014, 33, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wathes, C. Precision livestock farming for animal health, welfare and production. Production 2007, 397–404. [Google Scholar]
- Halachmi, I.; Guarino, M. Editorial: Precision livestock farming: A ‘per animal’ approach using advanced monitoring technologies. Animal 2016, 10, 1482–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermeulen, J.; Bahr, C.; Johnston, D.; Earley, B.; Tullo, E.; Fontana, I.; Guarino, M.; Exadaktylos, V.; Berckmans, D. Early recognition of bovine respiratory disease in calves using automated continuous monitoring of cough sounds. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 129, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BBSRC A Vision and High-Level Strategy for UK Animal and Plant Health Research To 2020 and Beyond; BBSRC: Swindon, UK, 2016.
- Cook, N.J.; Chabot, B.; Lui, T.; Bench, C.J.; Schaefer, A.L. Infrared thermography detects febrile and behavioural responses to vaccination of weaned piglets. Animal 2015, 9, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, A.L.; Cook, N.; Tessaro, S.V.; Deregt, D.; Desroches, G.; Dubeski, P.L.; Tong, A.K.W.; Godson, D.L. Early detection and prediction of infection using infrared thermography. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 84, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Jabbar, K.; Hansen, M.F.; Smith, M.L.; Smith, L.N. Early and non-intrusive lameness detection in dairy cows using 3-dimensional video. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 153, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, A. Development of an early detection system for lameness of broilers using computer vision. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 136, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, K.M.; Rebelo, C.J.B.; Corke, M.J.; Holmes, M.A.; Leach, M.C.; Constantino-Casas, F. Development of a facial expression scale using footrot and mastitis as models of pain in sheep. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2016, 176, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, D.J.; Bailey, A.L.; Chanda, M.L.; Clarke, S.E.; Drummond, T.E.; Echols, S.; Glick, S.; Ingrao, J.; Klassen-Ross, T.; Lacroix-Fralish, M.L.; et al. Coding of facial expressions of pain in the laboratory mouse. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, G.D.; Craig, K.D. Judgments of genuine, suppressed, and faked facial expressions of pain. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1992, 63, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, S.; ten Brinke, L.; Wallace, B. Secrets and Lies: Involuntary Leakage in Deceptive Facial Expressions as a Function of Emotional Intensity. J. Nonverbal Behav. 2012, 36, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerner, K.E.; Chambers, C.T.; Craig, K.D.; Pillai Riddell, R.R.; Parker, J.A. Caregiver accuracy in detecting deception in facial expressions of pain in children. Pain 2013, 154, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larochette, A.; Chambers, C.T.; Craig, K.D. Genuine, suppressed and faked facial expressions of pain in children. Pain 2006, 126, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliki, M.N.; Chialvo, D.R.; Geha, P.Y.; Levy, R.M.; Harden, R.N.; Parrish, T.B.; Apkarian, A.V. Chronic pain and the emotional brain: Specific brain activity associated with spontaneous fluctuations of intensity of chronic back pain. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 12165–12173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunz, M.; Chen, J.-I.; Lautenbacher, S.; Vachon-Presseau, E.; Rainville, P. Cerebral Regulation of Facial Expressions of Pain. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 8730–8738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorge, R.E.; Martin, L.J.; Isbester, K.A.; Sotocinal, S.G.; Rosen, S.; Tuttle, A.H.; Wieskopf, J.S.; Acland, E.L.; Dokova, A.; Kadoura, B.; et al. Olfactory exposure to males, inluding men, causes stress and related analgesia in rodents. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guesgen, M.J.; Beausoleil, N.J.; Stewart, M. Effects of early human handling on the pain sensitivity of young lambs. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2013, 40, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Mahmoud, M.; Robinson, P. Estimating Sheep Pain Level Using Facial Action Unit Detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2017), Washington, DC, USA, 30 May–3 June 2017; pp. 394–399. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, R.; Robinson, P. Human and sheep facial landmarks localisation by triplet interpolated features. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer vision (WACV), Lake Placid, NY, USA, 7–10 March 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, M.; Lu, Y.; Hou, X.; McLennan, K.; Robinson, P. Estimation of Pain in Sheep using Computer Vision. In Handbook of Pain and Palliative Care; Moore, R.J., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt, C.; Mahmoud, M. Pose-Informed Face Alignment for Extreme Head Pose Variation in Animals. ACII 2019. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, S.G.; Miller, A.L.; Clapp, J.; Plötz, T.; Kyriazakis, I. Early detection of health and welfare compromises through automated detection of behavioural changes in pigs. Vet. J. 2016, 217, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, E.S.; Swain, D.L.; Cronin, G.; Trotter, M. Autonomous on-animal sensors in sheep research: A systematic review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 150, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McLennan, K.; Mahmoud, M. Development of an Automated Pain Facial Expression Detection System for Sheep (Ovis Aries). Animals 2019, 9, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9040196
McLennan K, Mahmoud M. Development of an Automated Pain Facial Expression Detection System for Sheep (Ovis Aries). Animals. 2019; 9(4):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9040196
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcLennan, Krista, and Marwa Mahmoud. 2019. "Development of an Automated Pain Facial Expression Detection System for Sheep (Ovis Aries)" Animals 9, no. 4: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9040196
APA StyleMcLennan, K., & Mahmoud, M. (2019). Development of an Automated Pain Facial Expression Detection System for Sheep (Ovis Aries). Animals, 9(4), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9040196




