Using the Footfall Sound of Dairy Cows for Detecting Claw Lesions
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
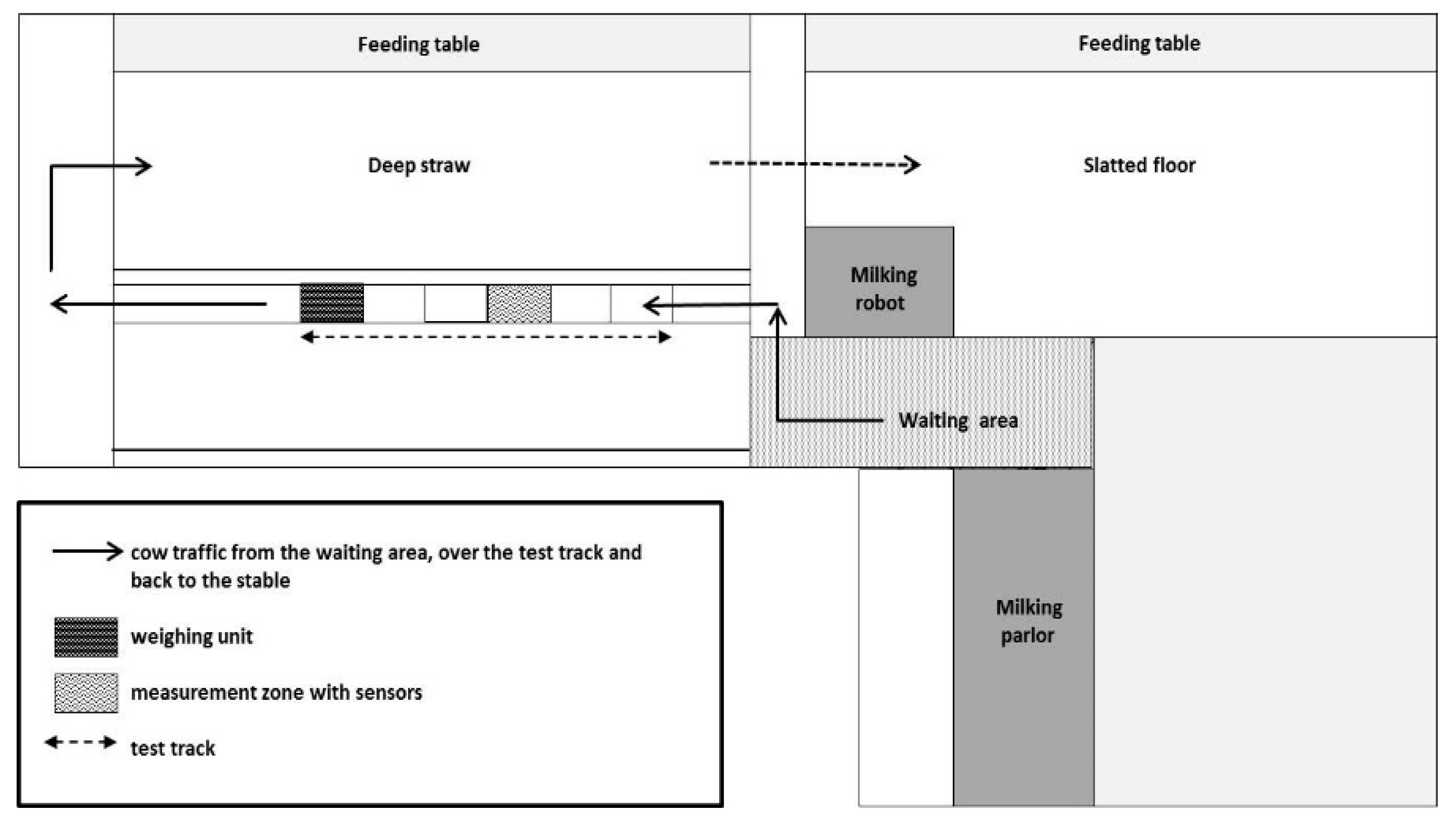
2. Materials and Methods
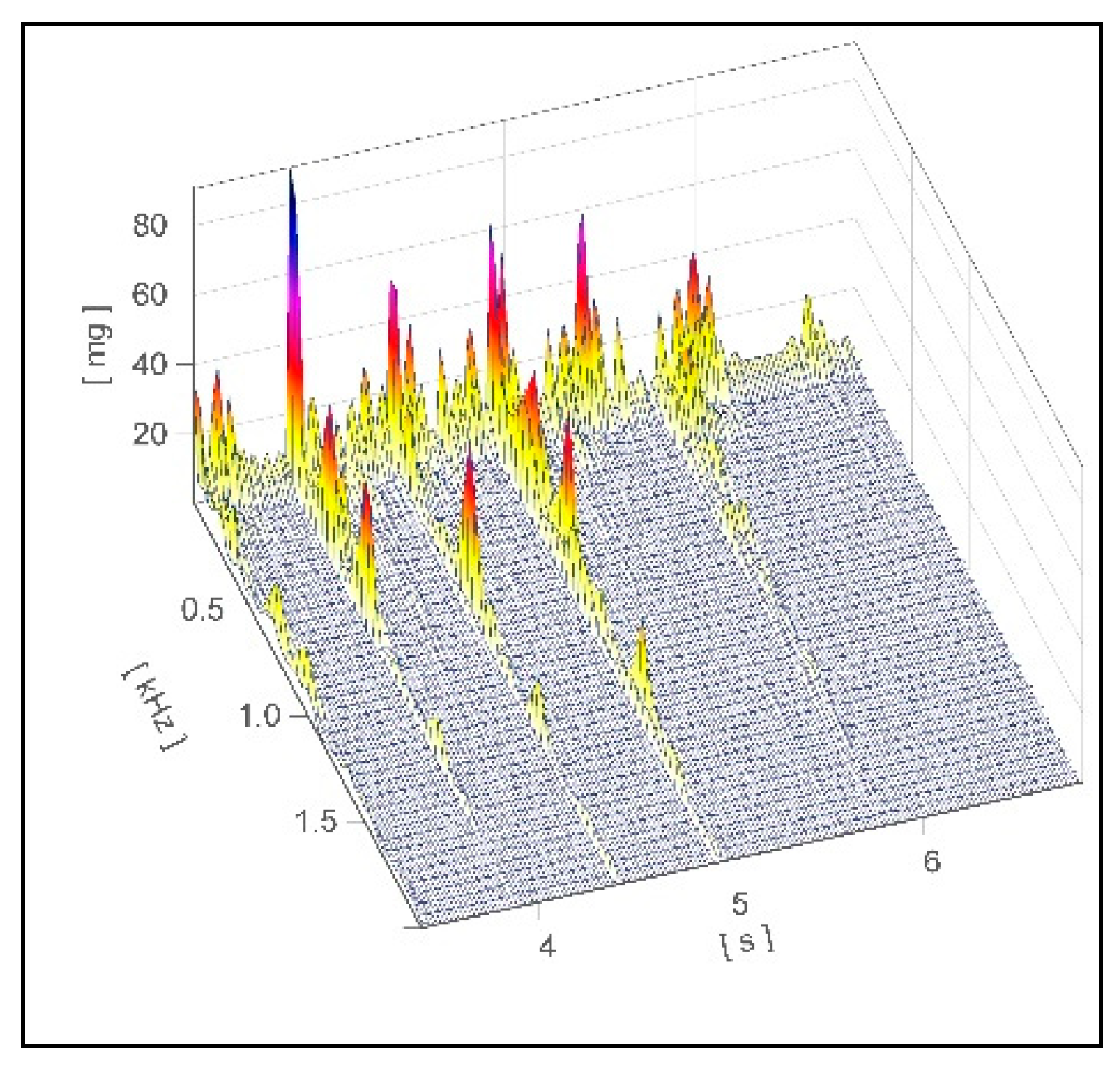
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
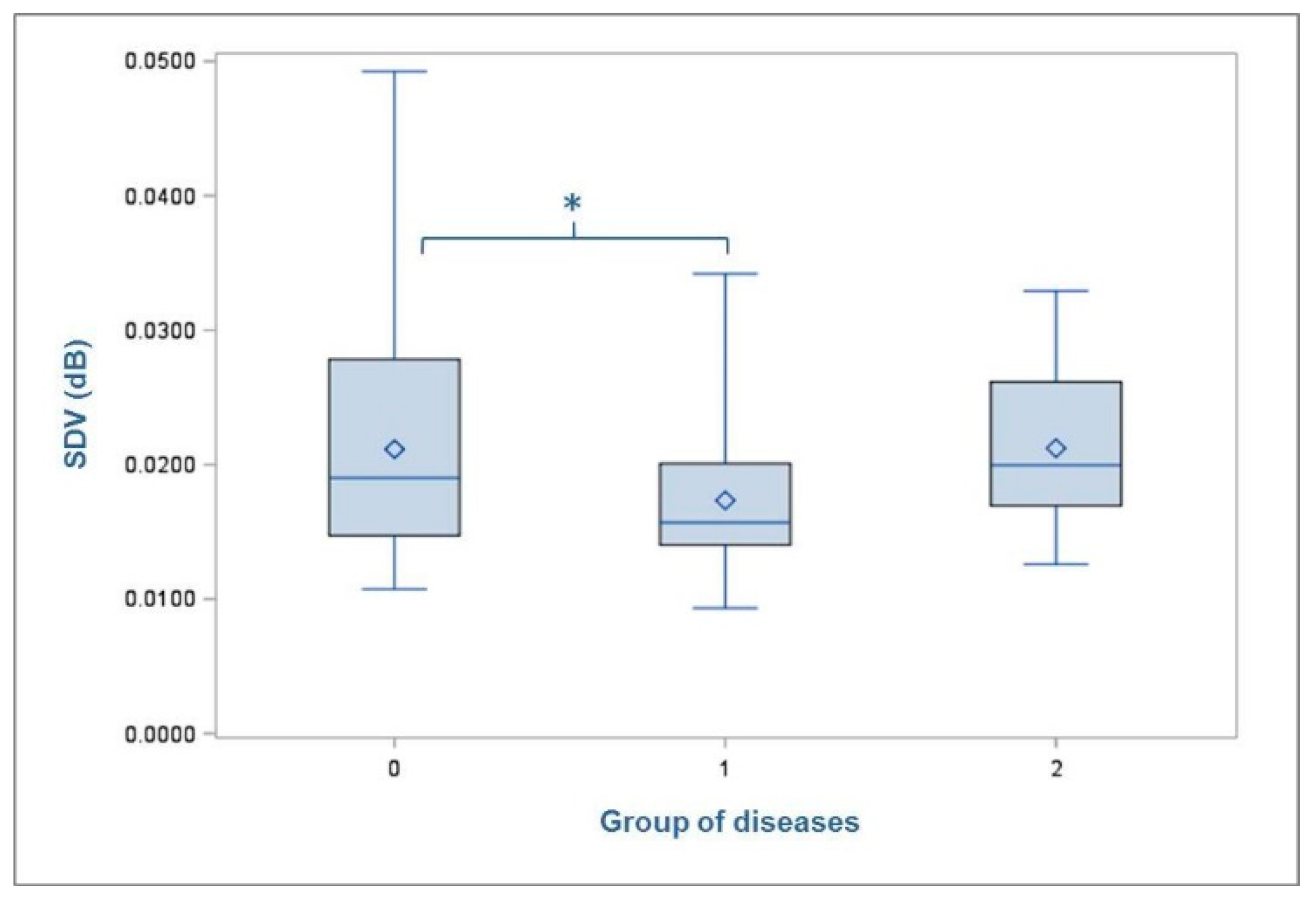
3. Results
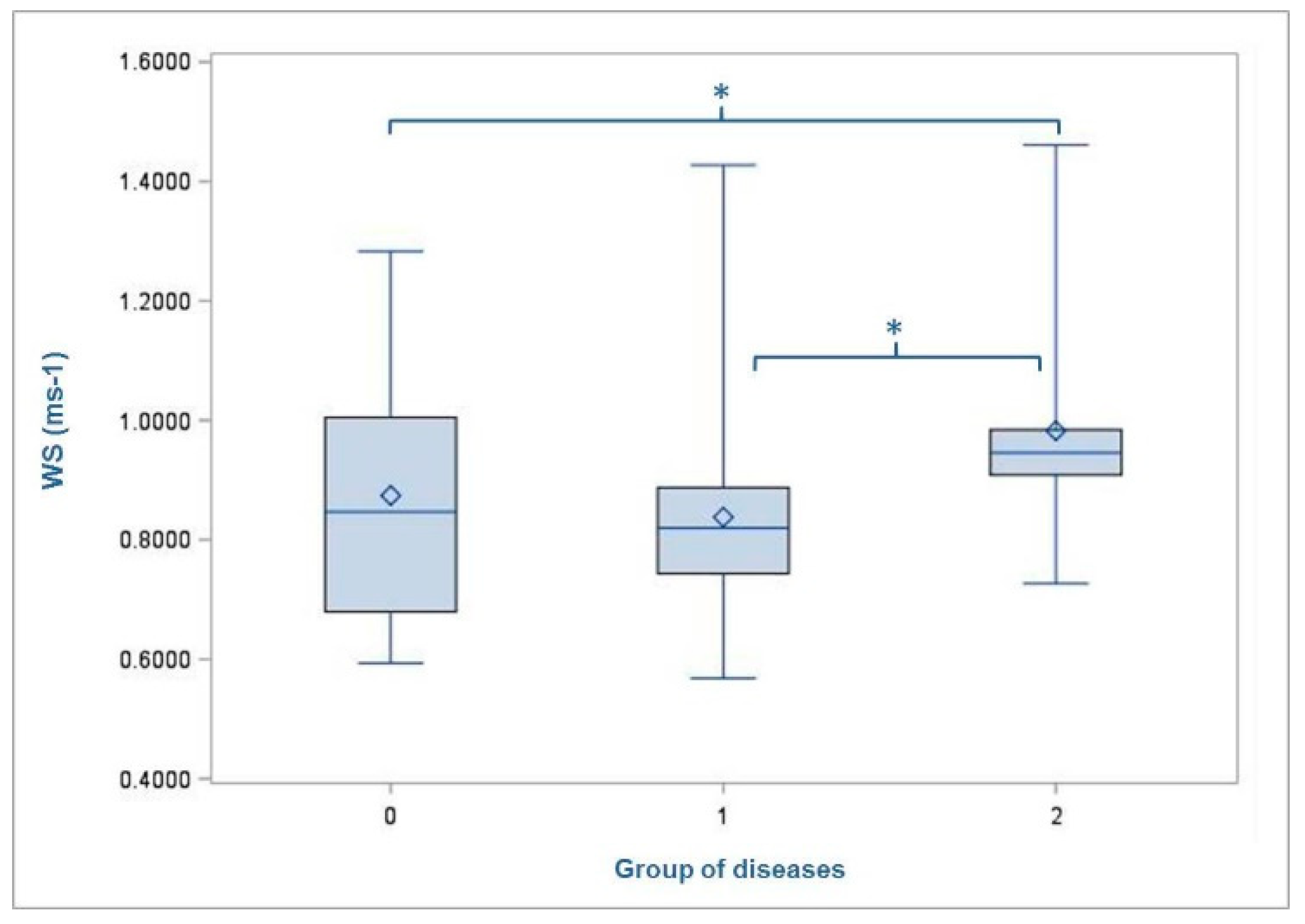
3.1. Walking Speed
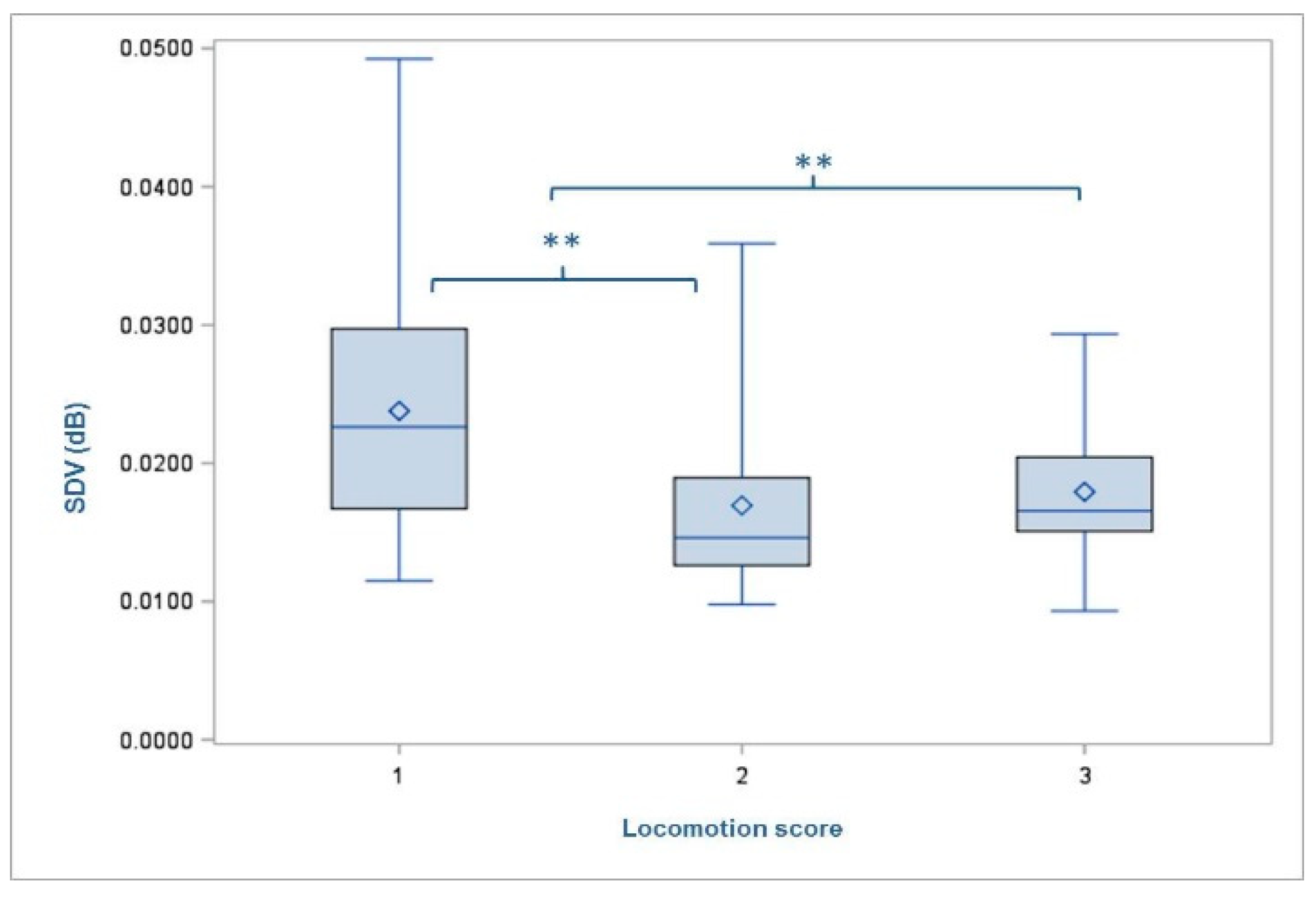
3.2. Standard Deviation of Volume of the Recorded Footfall Sound
4. Discussion
4.1. Walking Speed
4.2. Standard Deviation of Volume of the Recorded Footfall Sound
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grandin, T. Welfare Problems in Cattle, Pigs, and Sheep that Persist Even Though Scientific Research Clearly Shows How to Prevent Them. Animals 2018, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nuffel, A.; Zwertvaegher, I.; Pluym, L.; Van Weyenberg, S.; Thorup, V.M.; Pastell, M.; Sonck, B.; Saeys, W. Lameness Detection in Dairy Cows: Part 1. How to Distinguish between Non-Lame and Lame Cows Based on Differences in Locomotion or Behavior. Animals 2015, 5, 838–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, G.B. Changes in limb loading with lameness for a number of friesian cattle. Br. Vet. J. 1989, 145, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, K.A.; Cripps, P.J.; Downham, D.Y.; Murray, R.D. Subjective and objective assessment of pain and discomfort due to lameness in dairy cattle. Anim. Welf. 2003, 12, 605–610. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, K.; von Keyserlingk, M.A.G.; LeBlanc, S.J.; Weary, D.M. Lying behavior as an indicator of lameness in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 3553–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, C.; Whay, H.; Huxley, J. Recognition and management of pain in cattle. Pract. 2008, 30, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastell, M.; Hanninen, L.; de Passille, A.M.; Rushen, J. Measures of weight distribution of dairy cows to detect lameness and the presence of hoof lesions. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kujala, M.; Pastell, M.; Soveri, T. Use of force sensors to detect and analyse lameness in dairy cows. Vet. Rec. 2008, 162, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapinal, N.; de Passille, A.M.; Rushen, J.; Wagner, S. Automated methods for detecting lameness and measuring analgesia in dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 2007–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maertens, W.; Vangeyte, J.; Baert, J.; Jantuan, A.; Mertens, K.C.; De Campeneere, S.; Pluk, A.; Opsomer, G.; Van Weyenberg, S.; Van Nuffel, A. Development of a real time cow gait tracking and analysing tool to assess lameness using a pressure sensitive walkway: The GAITWISE system. Biosyst. Eng. 2011, 110, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Y.; Leroy, T.; Vranken, E.; Maertens, W.; Sonck, B.; Berckmans, D. Automatic detection of lameness in dairy cattle—Vision-based trackway analysis in cow’s locomotion. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2008, 64, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursaberi, A.; Bahr, C.; Pluk, A.; Van Nuffel, A.; Berckmans, D. Real-time automatic lameness detection based on back posture extraction in dairy cattle: Shape analysis of cow with image processing techniques. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 74, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluk, A.; Bahr, C.; Poursaberi, A.; Maertens, W.; van Nuffel, A.; Berckmans, D. Automatic measurement of touch and release angles of the fetlock joint for lameness detection in dairy cattle using vision techniques. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 1738–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haladjian, J.; Haug, J.; Nüske, S.; Bruegge, B. A Wearable Sensor System for Lameness Detection in Dairy Cattle. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2018, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmann, N.; Stracke, J.; Kemper, N. Evaluation of a gait scoring system for cattle by using cluster analysis and Krippendorff’s α reliability. Vet. Rec. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DLG: Klauengesundheit beim Rind. Available online: http://www.ble-medienservice.de/_assets/downloads_free/1541_2014_klauengesundheit_beim_rind_x000.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- Flower, F.C.; de Passille, A.M.; Weary, D.M.; Sanderson, D.J.; Rushen, J. Softer, higher-friction flooring improves gait of cows with and without sole ulcers. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zillner, J.C.; Tücking, N.; Plattes, S.; Heggemann, T.; Büscher, W. Using walking speed for lameness detection in lactating dairy cows. Livest. Sci. 2018, 218, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telezhenko, E.; Bergsten, C. Influence of floor type on the locomotion of dairy cows. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2005, 93, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espejo, L.A.; Endres, M.I.; Salfer, J.A. Prevalence of lameness in high-producing Holstein cows housed in freestall barns in Minnesota. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 3052–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenough, P.R.; MacCallum, F.J.; Weaver, A.D. Lameness in Cattle; John Wright & Sons: Bristol, UK, 1981; 471p. [Google Scholar]
- Van Nuffel, A.; Van De Gucht, T.; Saeys, W.; Sonck, B.; Opsomer, G.; Vangeyte, J.; Mertens, K.C.; De Ketelaere, B.; Van Weyenberg, S. Environmental and cow-related factors affect cow locomotion and can cause misclassification in lameness detection systems. Animal 2015, 10, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flower, F.C.; Sanderson, D.J.; Weary, D.M. Hoof pathologies influence kinematic measures of dairy cow gait. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 3166–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackie, N.; Bleach, E.C.L.; Amory, J.R.; Scaife, J.R. Associations between locomotion score and kinematic measures in dairy cows with varying hoof lesion types. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 3564–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapinal, N.; de Passille, A.M.; Weary, D.M.; von Keyserlingk, M.A.G.; Rushen, J. Using gait score, walking speed, and lying behavior to detect hoof lesions in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 4365–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distl, O.; Mair, A. Computerized analysis of pedobarometric forces in cattle at the ground surface/floor interface. Comput. Electron. Agric. 1993, 8, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippel, S.; Dolezal, M.; Brenninkmeyer, C.; Brinkmann, J.; March, S.; Knierim, U.; Winckler, C. Risk factors for lameness in freestall-housed dairy cows across two breeds, farming systems, and countries. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 5476–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bicalho, R.C.; Vokey, F.; Erb, H.N.; Guard, C.L. Visual locomotion scoring in the first seventy days in milk: Impact on pregnancy and survival. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 4586–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos, L.T.; da Cruz, E.A.; Fischer, V.; da Porciuncula, G.C.; Werncke, D.; Dalto, A.G.C.; Stumpf, M.T.; Vizzotto, E.F.; da Silveira, I.D.B. Dairy cows change locomotion score and sensitivity to pain with trimming and infectious or non-infectious lesions. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 49, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastell, M.E.; Kujala, M. A probabilistic neural network model for lameness detection. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 2283–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushen, J.; Pombourcq, E.; de Passille, A.M. Validation of two measures of lameness in dairy cows. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 106, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Sample Number | Group 0 | Group 1 | Group 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parity | n | n | % | n | % | n | % |
| 1 | 15 | 10 | 66.7 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 33.3 |
| 2 | 30 | 11 | 36.7 | 15 | 50.0 | 4 | 13.3 |
| 3 | 16 | 2 | 12.5 | 10 | 62.5 | 4 | 25.0 |
| 4 | 9 | 3 | 33.3 | 6 | 66.7 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 3 | 2 | 66.7 | 1 | 33.3 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 3 | 2 | 66.7 | 1 | 33.3 | 0 | 0 |
| Sample Number | Group 0 | Group 1 | Group 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LS | n | n | % | n | % | n | % |
| 1 | 24 | 17 | 70.8 | 3 | 12.5 | 4 | 16.7 |
| 2 | 21 | 7 | 33.3 | 10 | 47.7 | 4 | 19.0 |
| 3 | 31 | 6 | 19.4 | 20 | 64.5 | 5 | 16.1 |
| WS | SDV | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | F-value | p-value | F-value | p-value |
| Group of housing | 0.08 | 0.7834 | 0.01 | 0.9240 |
| Parity number | 1.94 | 0.0988 | 0.61 | 0.6933 |
| Bodyweight | 1.46 | 0.2410 | 0.92 | 0.6089 |
| Locomotion score | 10.31 | 0.0001 | 7.17 | 0.0014 |
| Type of disease | 3.20 | 0.0466 | 2.39 | 0.0759 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Volkmann, N.; Kulig, B.; Kemper, N. Using the Footfall Sound of Dairy Cows for Detecting Claw Lesions. Animals 2019, 9, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9030078
Volkmann N, Kulig B, Kemper N. Using the Footfall Sound of Dairy Cows for Detecting Claw Lesions. Animals. 2019; 9(3):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9030078
Chicago/Turabian StyleVolkmann, Nina, Boris Kulig, and Nicole Kemper. 2019. "Using the Footfall Sound of Dairy Cows for Detecting Claw Lesions" Animals 9, no. 3: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9030078
APA StyleVolkmann, N., Kulig, B., & Kemper, N. (2019). Using the Footfall Sound of Dairy Cows for Detecting Claw Lesions. Animals, 9(3), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9030078







