The Use of an Activity Monitoring System for the Early Detection of Health Disorders in Young Bulls
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, Housing, and Management
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
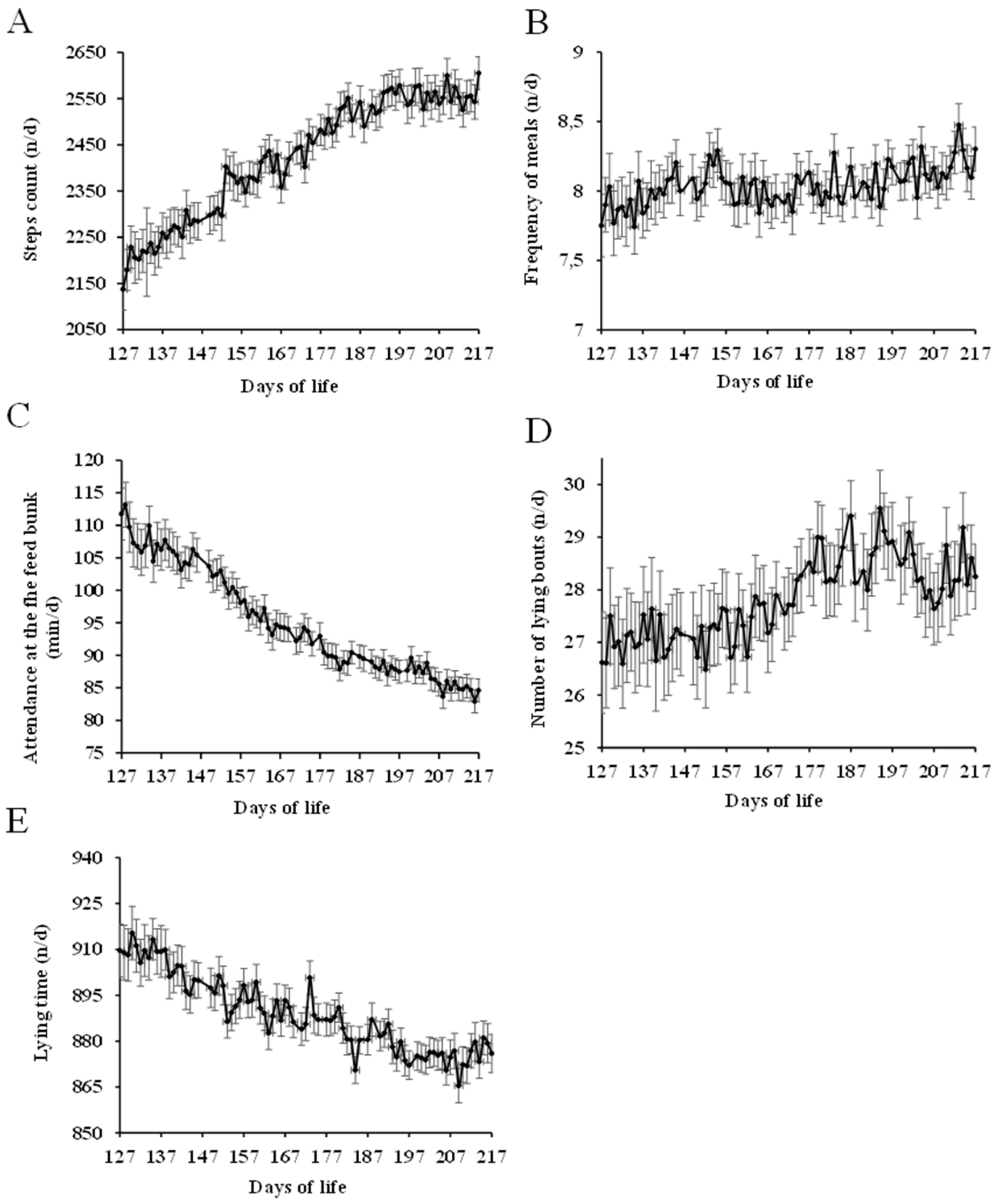
3.1. Normal Behavior
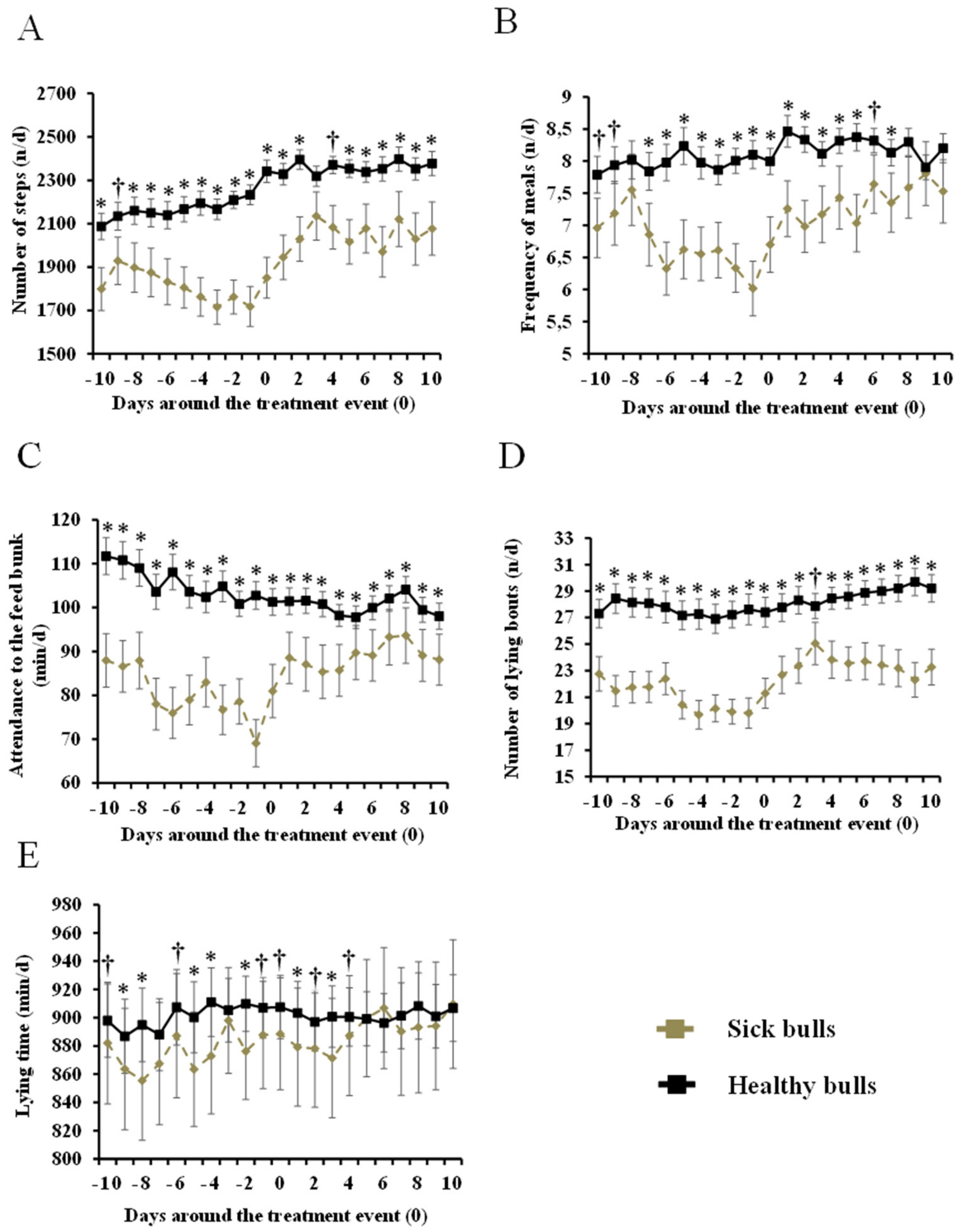
3.2. Differences in Behavior Between Healthy vs. Sick Bulls
3.3. Predictive Models and Validation
4. Discussion
4.1. Normal Behavior
4.2. Differences in Behavior Between Healthy vs. Sick Bulls
4.3. Predictive Models and Validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kelly, A.P.; Janzen, E.D. A review of morbidity and mortality rates and disease occurrence in north american feedlot cattle. Can. Vet. J. 1986, 27, 496–500. [Google Scholar]
- Tennant, T.C.; Ives, S.E.; Harper, L.B.; Renter, D.G.; Lawrence, T.E. Comparison of tulathromycin and tilmicosin on the prevalence and severity of bovine respiratory disease in feedlot cattle in association with feedlot performance, carcass characteristics, and economic factors. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 5203–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catry, B.; Dewulf, J.; Goffin, T.; Decostere, A.; Haesebrouck, F.; De Kruif, A. Antimicrobial resistance patterns of Escherichia colithrough the digestive tract of veal calves. Micro. Drug. Resist. 2007, 13, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, A.; Reid-Smith, R.J.; Irwin, R.J. Antimicrobial resistance in Escherichia coli isolated from retail milk-fed veal meat from Southern Ontario, Canada. J. Food Prot. 2011, 74, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbergeld, E.K.; Graham, J.; Price, L.B. Industrial food animal production, antimicrobial resistance, and human health. Ann. Rev. Pub. Health. 2008, 29, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, P.; Page, K.L.; Hillerton, J.E. The effects of early antibiotic treatment following diagnosis of mastitis detected by a change in the electrical conductivity of milk. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, B.; White, B.J.; Renter, D.G.; Larson, R.L. Evaluation of three-dimensional accelerometers to monitor and classify behavior patterns in cattle. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2009, 67, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutten, C.J.; Velthuis, A.G.; Steeneveld, W.; Hogeveen, H. Invited review: Sensors to support health management on dairy farms. J. Dairy. Sci. 2013, 96, 1928–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quimby, W.F.; Sowell, B.F.; Bowman, J.G.P.; Branine, M.E.; Hubbert, M.E. Application of feeding behaviour to predict morbidity of newly received calves in a commercial feedlot. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 81, 315–320. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfger, B.; Schwartzkopf-Genswein, K.S.; Barkema, H.W.; Pajor, E.A.; Levy, M.; Orsel, K. Feeding behavior as an early predictor of bovine respiratory disease in North American feedlot systems. J. Anim Sci. 2015, 93, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesini, G.; Mottarana, D.; Contiero, B.; Schiavon, E.; Segato, S.; Garbin, E.; Tenti, S.; Andrighetto, I. Use of rumination and activity data as health status and performance indicators in beef cattle during the early fattening period. Vet. J. 2018, 231, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfger, B.; Mang, A.V.; Cook, N.; Orsel, K.; Timsit, E. Evaluation of a system for monitoring individual feeding behavior and activity in beef cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 4110–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohoo, I.; Martin, W.; Stryhn, H. Screening Diagnostic Tests. In Veterinary Epidemiologic Research, 1st ed.; AVC Inc: Charlottetown, PEI, Canada, 2003; Volume 5, pp. 85–113. [Google Scholar]
- Swartz, T.H.; Findlay, A.N.; Petersson-Wolfe, C.S. Automated detection of behavioral changes from respiratory disease in pre-weaned calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 9273–9278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devant, M.; Marti, S.; Bach, A. Effects of castration on eating pattern and physical activity of Holstein bulls fed high-concentrate rations under commercial condition. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 4505–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillen, J.L.; Pinedo, P.J.; Ives, S.E.; Covey, T.L.; Naikare, H.K.; Richeson, J.T. Alteration of activity variables relative to clinical diagnosis of bovine respiratory disease in newly received feedlot cattle. Bov. Pract. 2016, 50, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rouha-Muelleder, C.; Absmanner, E.; Kahrer, E.; Zeiner, H.; Scharl, T.; Leisch, F.; Stanek, C.; Troxler, J. Alternative housing systems for fattening bulls under Austrian condition swith special respect to rubberised slatted floors. Anim. Welf. 2012, 21, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, J.J.; Kegley, E.B.; Lawrence, T.E.; Roberts, S.L.; Powell, J.G.; Richeson, J.T. Zinc injection as a novel castration method in beef bulls: Effects on performance, behavior, and testosterone and haptoglobin concentration. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 890–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prawl, Z.I.; Owens, F.N. Activity patterns of feedlot steers. Okla. Agr. Exp. Sta. Res. Rep. 1998, 96, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Gonyou, H.W.; Stricklin, W.R. Diurnal Behavior Patterns of Feedlot Bulls During Winter and Spring in Northern Latitudes. J. Anim. Sci. 1984, 58, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platz, S.; Ahrens, F.; Bahrs, E.; Nüske, S.; Errhard, M.H. Association between floor type and behaviour, skin lesions and claw dimensions in group-housed fattening bulls. Prev. Vet. Med. 2007, 80, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowell, B.F.; Branine, M.E.; Bowman, J.G.P.; Hubbert, M.E.; Sherwood, H.W.; Quimby, W.F. Feeding and watering behaviour of healthy and morbid steers in a commercial feedlot. J. Anim. Sci. 1999, 77, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, W.; Ketz-Riley, C.J. Klinishe Propädeutick der Inneren Krankeiten und Hautkrankheiten der Haus-und Heimtiere, 4th ed.; Verlag Paul Parey: Berlin, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hanzlicek, G.A.; White, B.J.; Renter, D.G.; Blasi, D.A. A field study evaluating health, performance, and behavior differences in crossbred beef calves administered different vaccine-parasiticide product combinations. Vaccine 2010, 28, 5998–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, B.J.; Anderson, D.E.; Renter, D.G.; Larson, R.L.; Mosier, D.A.; Kelly, L.L.; Theurer, M.E.; Robért, B.D.; Walz, M.L. Clinical, behavioral, and pulmonary changes in calves following inoculation with Mycoplasma bovis. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 73, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, M.A.; Lowe, G.L.; Huddart, F.J.; Waas, J.R.; Stewart, M. Measurement of dairy calf behavior prior to onset of clinical disease and in response to disbudding using automated calf feeders and accelerometers. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8208–8216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theurer, M.E.; Anderson, D.E.; White, B.J. Effect of Mannheimia haemolytica pneumonia on behavior and physiologic responses of calves experiencing hyperthermal environmental conditions. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowell, B.F.; Bowman, J.G.P.; Branine, M.E.; Hubbert, M.E. Radio frequency technology to measure feeding behavior and health of feedlot steers. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1998, 59, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhman, M.J.; Perino, L.J.; Galyean, M.L.; Wittum, T.E.; Montgomery, T.H.; Swingle, R.S. Association between changes in eating and drinking behaviors and respiratory tract disease in newly arrived calves at the feedlot. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2000, 61, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Predictive Variables | Steps Counts | Frequency of Meals | Attendance to the Feed Bunk | Lying Bouts | Lying Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | |
| Season | <0.05 | <0.10 | 0.12 | >0.05 | <0.05 |
| Age | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 |
| Days | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| Health status | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| Days × health status | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | <0.10 | >0.05 |
| Days 1 | AUC 2 | Accuracy, % | Se 3, % | Sp 4, % | FPR 5, % | FNR 6, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −10 | 0.86 | 80 | 84 | 78 | 42 | 7 |
| −9 | 0.88 | 81 | 79 | 81 | 47 | 6 |
| −8 | 0.79 | 75 | 72 | 76 | 57 | 9 |
| −7 | 0.81 | 71 | 74 | 71 | 61 | 9 |
| −6 | 0.83 | 70 | 80 | 67 | 62 | 7 |
| −5 | 0.80 | 66 | 69 | 66 | 66 | 11 |
| −4 | 0.76 | 70 | 69 | 71 | 63 | 10 |
| −3 | 0.86 | 79 | 82 | 78 | 50 | 6 |
| −2 | 0.87 | 76 | 83 | 75 | 55 | 6 |
| −1 | 0.84 | 75 | 76 | 75 | 56 | 8 |
| Parameter | Estimate | Standard Error | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 8.512 | 3.1704 | < 0.05 |
| Age at entry, days | 0.017 | 0.0090 | > 0.05 |
| Attendance to the feed bunk, min/day | −0.036 | 0.0112 | < 0.05 |
| Lying bouts, n/day | −0.127 | 0.0429 | < 0.05 |
| Lying time, min/day | −0.006 | 0.0030 | < 0.05 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belaid, M.A.; Rodriguez-Prado, M.; Chevaux, E.; Calsamiglia, S. The Use of an Activity Monitoring System for the Early Detection of Health Disorders in Young Bulls. Animals 2019, 9, 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110924
Belaid MA, Rodriguez-Prado M, Chevaux E, Calsamiglia S. The Use of an Activity Monitoring System for the Early Detection of Health Disorders in Young Bulls. Animals. 2019; 9(11):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110924
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelaid, Mohammed Anouar, Maria Rodriguez-Prado, Eric Chevaux, and Sergio Calsamiglia. 2019. "The Use of an Activity Monitoring System for the Early Detection of Health Disorders in Young Bulls" Animals 9, no. 11: 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110924
APA StyleBelaid, M. A., Rodriguez-Prado, M., Chevaux, E., & Calsamiglia, S. (2019). The Use of an Activity Monitoring System for the Early Detection of Health Disorders in Young Bulls. Animals, 9(11), 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110924





