Spontaneous Learning of Visual Structures in Domestic Chicks
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. General Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Rearing Conditions
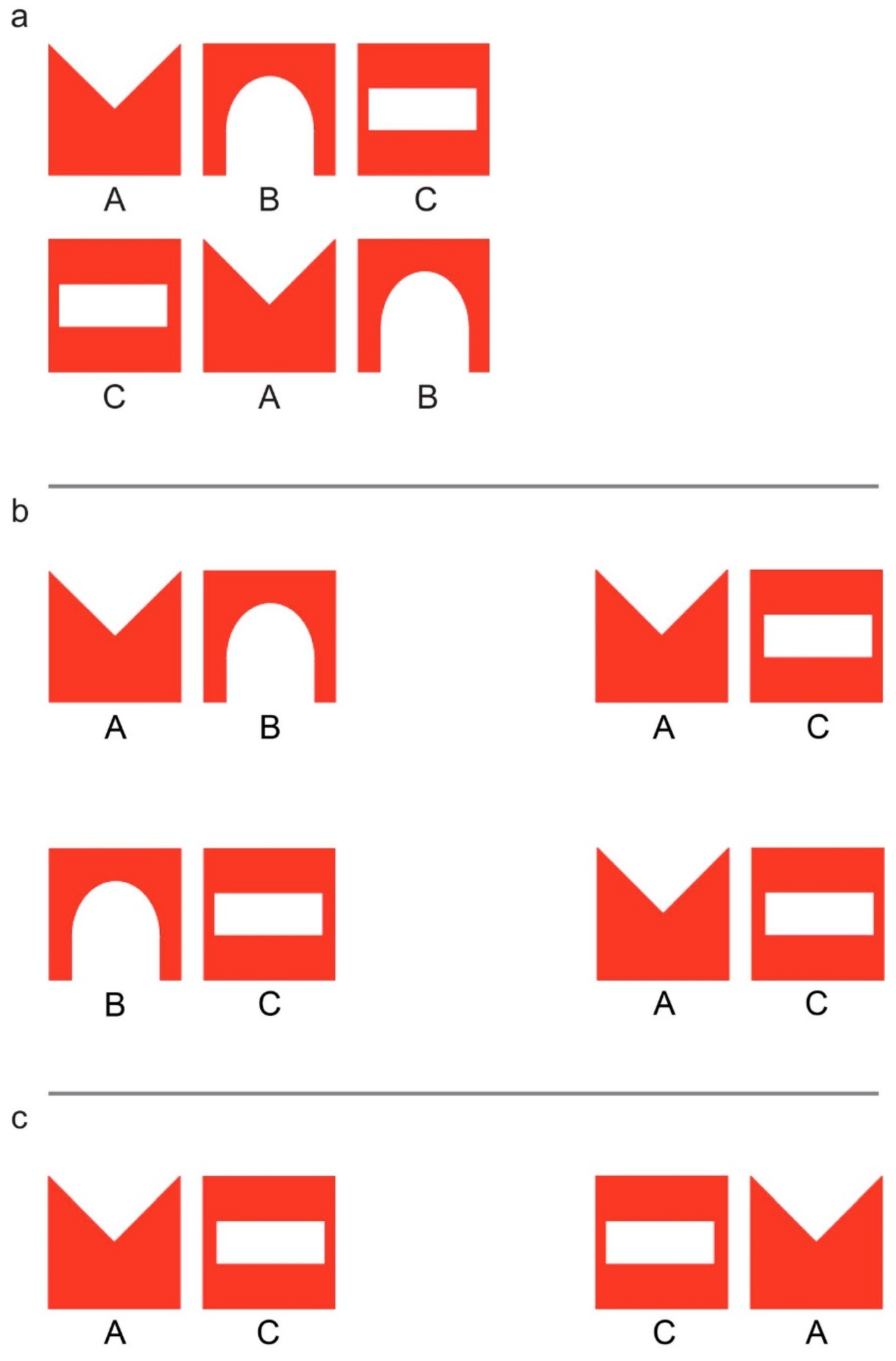
2.2. Imprinting and Test Stimuli
2.3. Test Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Ethical Statement
3. Experiment 1
3.1. Subjects
3.2. Imprinting and Test Stimuli
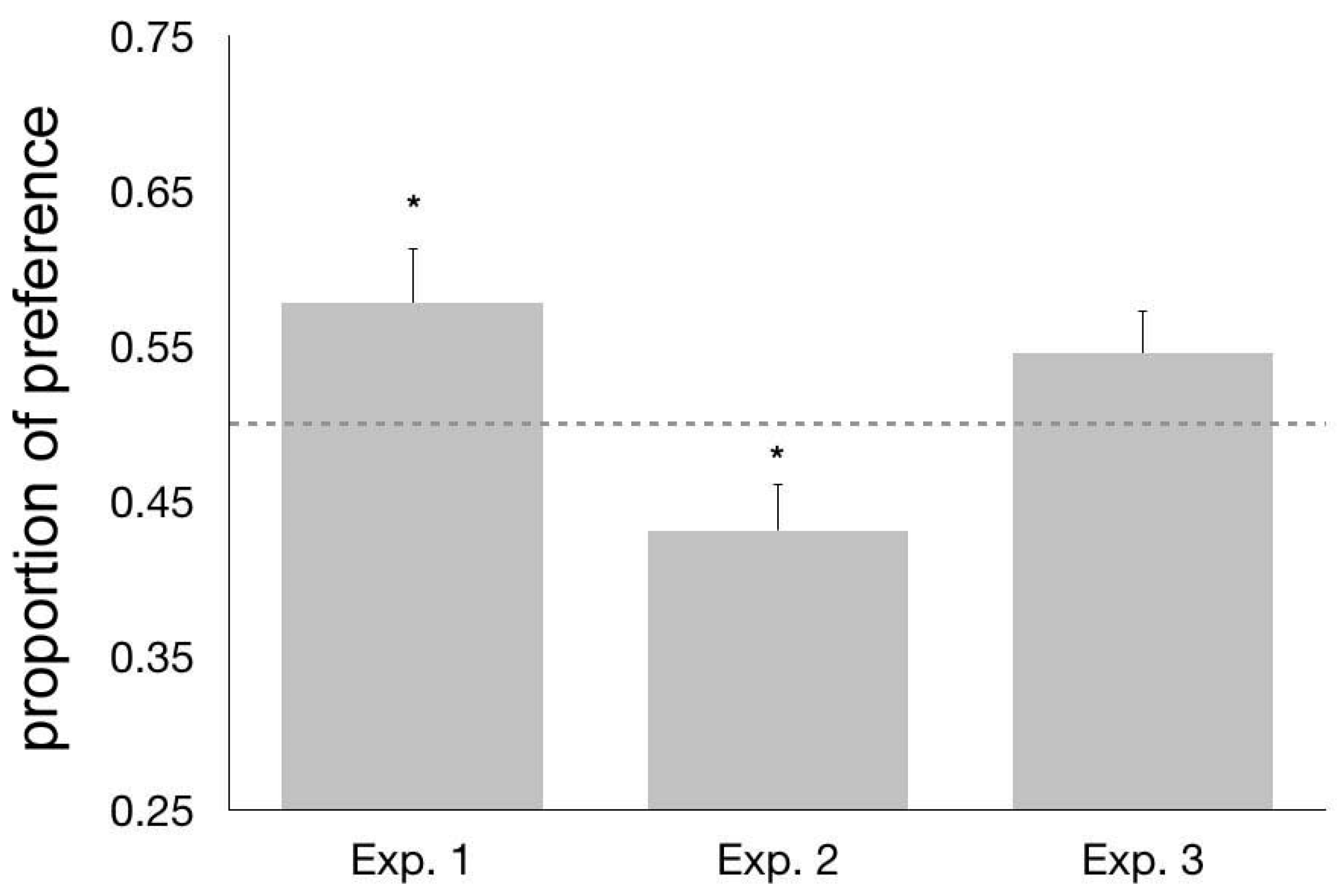
3.3. Results and Discussion
4. Experiment 2
4.1. Subjects
4.2. Imprinting and Test Stimuli
4.3. Results and Discussion
5. Experiment 3
5.1. Subjects
5.2. Imprinting and Test Stimuli
5.3. Results and Discussion
6. General Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fehér, O.; Ljubičić, I.; Suzuki, K.; Okanoya, K.; Tchernichovski, O. Statistical learning in songbirds: From self-tutoring to song culture. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menyhart, O.; Kolodny, O.; Goldstein, M.H.; DeVoogd, T.J.; Edelman, S. Juvenile zebra finches learn the underlying structural regularities of their fathers’ song. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahasi, M.; Yamada, H.; Okanoya, K. Statistical and prosodic cues for song segmentation learning by bengalese finches (Lonchura striata var. domestica). Ethology 2010, 116, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, B.C.; Frost, R.; Christiansen, M.H. The long road of statistical learning research: Past, present and future. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehaene, S.; Meyniel, F.; Wacongne, C.; Wang, L.; Pallier, C. The neural representation of sequences: From transition probabilities to algebraic patterns and linguistic trees. Neuron 2015, 88, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santolin, C.; Saffran, J.R. Constraints on statistical learning across species. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2018, 22, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, C.M.; Christiansen, M.H. Modality-constrained statistical learning of tactile, visual, and auditory sequences. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 2005, 31, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, R.A.; Jakimik, J.; Cooper, W.E. Segmenting speech into words. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1980, 67, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, J.L.; Meier, R.P.; Newport, E.L. Structural packaging in the input to language learning: Contributions of prosodic and morphological marking of phrases to the acquisition of language. Cogn. Psychol. 1987, 19, 498–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelucchi, B.; Hay, J.F.; Saffran, J.R. Statistical learning in a natural language by 8-month-old infants. Child Dev. 2009, 80, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saffran, J.R.; Newport, E.L.; Aslin, R.N.; Tunick, R.A.; Barrueco, S. Incidental language learning: Listening (and learning) out of the corner of your ear. Psychol. Sci. 1997, 8, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffran, J.R.; Aslin, R.N.; Newport, E.L. Statistical learning by 8-month-old infants. Science 1996, 274, 1926–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulf, H.; Johnson, S.P.; Valenza, E. Visual statistical learning in the newborn infant. Cognition 2011, 121, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkham, N.Z.; Slemmer, J.A.; Johnson, S.P. Visual statistical learning in infancy: Evidence for a domain general learning mechanism. Cognition 2002, 83, B35–B42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiser, J.; Aslin, R.N. Statistical learning of new visual feature combinations by infants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15822–15826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toro, J.M.; Trobalón, J.B. Statistical computations over a speech stream in a rodent. Percept. Psychophys. 2005, 67, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, T.; Olson, C.R. Statistical learning of visual transitions in monkey inferotemporal cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19401–19406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santolin, C.; Rosa-Salva, O.; Vallortigara, G.; Regolin, L. Unsupervised statistical learning in newly hatched chicks. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R1218–R1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Ten Cate, C. Zebra finches can use positional and transitional cues to distinguish vocal element strings. Behav. Process. 2015, 117, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, M.D.; Newport, E.L.; Aslin, R.N. Segmentation of the speech stream in a non-human primate: Statistical learning in cotton-top tamarins. Cognition 2001, 78, B53–B64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch, W.T.; Friederici, A.D. Artificial grammar learning meets formal language theory: An overview. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 1933–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R. A First Language: The Early Stages; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1973; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, R.L.; Gerken, L. Artificial grammar learning by 1-year-olds leads to specific and abstract knowledge. Cognition 1999, 70, 109–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, G.F.; Vijayan, S.; Bandi Rao, S.; Vishton, P.M. Rule learning by seven-month-old infants. Science 1999, 283, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saffran, J.; Hauser, M.; Seibel, R.; Kapfhamer, J.; Tsao, F.; Cushman, F. Grammatical pattern learning by human infants and cotton-top tamarin monkeys. Cognition 2008, 107, 479–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saffran, J.R. The use of predictive dependencies in language learning. J. Mem. Lang. 2001, 44, 493–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffran, J.R. Constraints on statistical language learning. J. Mem. Lang. 2002, 47, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, B.; Franconeri, S.L.; Waxman, S.R. Very young infants learn abstract rules in the visual modality. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhart, A.L.; Newport, E.L.; Aslin, R.N. Statistical learning of adjacent and nonadjacent dependencies among nonlinguistic sounds. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2009, 16, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.P.; Fernandas, K.J.; Frank, M.C.; Kirkham, N.; Marcus, G.; Rabagliati, H.; Slemmer, J.A. Abstract rule learning for visual sequences in 8- and 11-month-olds. Infancy Off. J. Int. Soc. Infant Stud. 2009, 14, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, K.; Watanabe, D. Songbirds possess the spontaneous ability to discriminate syntactic rules. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; van Rossum, D.; ten Cate, C. Artificial grammar learning in zebra finches and human adults: XYX versus XXY. Anim. Cogn. 2015, 18, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comins, J.A.; Gentner, T.Q. Perceptual categories enable pattern generalization in songbirds. Cognition 2013, 128, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Mora, D.M.; Toro, J.M. Rule learning over consonants and vowels in a non-human animal. Cognition 2013, 126, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endress, A.D.; Carden, S.; Versace, E.; Hauser, M.D. The apes’ edge: Positional learning in chimpanzees and humans. Anim. Cogn. 2010, 13, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentner, T.Q.; Fenn, K.M.; Margoliash, D.; Nusbaum, H.C. Recursive syntactic pattern learning by songbirds. Nature 2006, 440, 1204–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, M.D.; Glynn, D. Can free-ranging rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) extract artificially created rules comprised of natural vocalizations? J. Comp. Psychol. 2009, 123, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, R.A.; Mondragón, E.; Murphy, V.A. Rule learning by rats. Science 2008, 319, 1849–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neiworth, J.J.; London, J.M.; Flynn, M.J.; Rupert, D.D.; Alldritt, O.; Hyde, C. Artificial grammar learning in tamarins (Saguinus oedipus) in varying stimulus contexts. J. Comp. Psychol. 2017, 131, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spierings, M.J.; Ten Cate, C. Budgerigars and zebra finches differ in how they generalize in an artificial grammar learning experiment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E3977–E3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Heijningen, C.A.A.; Chen, J.; van Laatum, I.; van der Hulst, B.; ten Cate, C. Rule learning by zebra finches in an artificial grammar learning task: Which rule? Anim. Cogn. 2013, 16, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versace, E.; Regolin, L.; Vallortigara, G. Emergence of grammar as revealed by visual imprinting in newly-hatched chicks. In The Evolution of Language; World Scientific: Singapore, 2006; pp. 457–458. ISBN 978-981-256-656-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, B.; Slater, H.; Kikuchi, Y.; Milne, A.E.; Marslen-Wilson, W.D.; Smith, K.; Petkov, C.I. Auditory artificial grammar learning in macaque and marmoset monkeys. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 18825–18835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, B.; Lew-Williams, C. Communicative signals support abstract rule learning by 7-month-old infants. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, G.F.; Fernandes, K.J.; Johnson, S.P. Infant rule learning facilitated by speech. Psychol. Sci. 2007, 18, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, R.; Armstrong, B.C.; Siegelman, N.; Christiansen, M.H. Domain generality versus modality specificity: The paradox of statistical learning. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2015, 19, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiser, J.; Aslin, R.N. Unsupervised statistical learning of higher-order spatial structures from visual scenes. Psychol. Sci. 2001, 12, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiser, J.; Aslin, R.N. Encoding multielement scenes: Statistical learning of visual feature hierarchies. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2005, 134, 521–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, E.J. Principles of Perceptual Learning and Development; Appleton-Century-Crofts: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Goujon, A.; Fagot, J. Learning of spatial statistics in nonhuman primates: Contextual cueing in baboons (Papio papio). Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 247, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saffran, J.R.; Pollak, S.D.; Seibel, R.L.; Shkolnik, A. Dog is a dog is a dog: Infant rule learning is not specific to language. Cognition 2007, 105, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grainger, J.; Dufau, S.; Montant, M.; Ziegler, J.C.; Fagot, J. Orthographic processing in baboons (Papio papio). Science 2012, 336, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinho, A.; Kacelnik, A. Ducklings imprint on the relational concept of “same or different”. Science 2016, 353, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santolin, C.; Rosa-Salva, O.; Regolin, L.; Vallortigara, G. Generalization of visual regularities in newly hatched chicks (Gallus gallus). Anim. Cogn. 2016, 19, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnweber, R.; Ravignani, A.; Fitch, W.T. Non-adjacent visual dependency learning in chimpanzees. Anim. Cogn. 2015, 18, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stobbe, N.; Westphal-Fitch, G.; Aust, U.; Fitch, W.T. Visual artificial grammar learning: Comparative research on humans, kea (Nestor notabilis) and pigeons (Columba livia). Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 1995–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versace, E.; Spierings, M.J.; Caffini, M.; Ten Cate, C.; Vallortigara, G. Spontaneous generalization of abstract multimodal patterns in young domestic chicks. Anim. Cogn. 2017, 20, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewkowicz, D.J. Perception of serial order in infants. Dev. Sci. 2004, 7, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewkowicz, D.J. Serial order processing in human infants and the role of multisensory redundancy. Cogn. Process. 2004, 5, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Cate, C.; Okanoya, K. Revisiting the syntactic abilities of non-human animals: Natural vocalizations and artificial grammar learning. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 1984–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versace, E. Precocial. In Encyclopedia of Animal Cognition and Behavior; Vonk, J., Shackelford, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–3. ISBN 978-3-319-47829-6. [Google Scholar]
- Versace, E.; Vallortigara, G. Origins of knowledge: Insights from precocial species. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallortigara, G.; Versace, E. Filial Imprinting. In Encyclopedia of Animal Cognition and Behavior; Vonk, J., Shackelford, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–4. ISBN 978-3-319-47829-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bateson, P.P.G. The characteristics and context of imprinting. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1966, 41, 177–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolhuis, J.J. Mechanisms of avian imprinting: A review. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1991, 66, 303–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCabe, B.J. Imprinting. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Cogn. Sci. 2013, 4, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallortigara, G.; Andrew, R.J. Lateralization of response by chicks to change in a model partner. Anim. Behav. 1991, 41, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Cate, C. Stimulus movement, hen behaviour and filial imprinting in Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica). Ethology 1989, 82, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa-Salva, O.; Regolin, L.; Vallortigara, G. Faces are special for newly hatched chicks: Evidence for inborn domain-specific mechanisms underlying spontaneous preferences for face-like stimuli. Dev. Sci. 2010, 13, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouder, J.N.; Speckman, P.L.; Sun, D.; Morey, R.D.; Iverson, G. Bayesian t-tests for accepting and rejecting the null hypothesis. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2009, 16, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateson, P.P.G. How do sensitive periods arise and what are they for? Anim. Behav. 1979, 27, 470–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateson, P.P.G. Preferences for familiarity and novelty: A model for the simultaneous development of both. J. Theor. Biol. 1973, 41, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateson, P.P.G.; Jaeckel, J.B. Chicks’ preferences for familiar and novel conspicuous objects after different periods of exposure. Anim. Behav. 1976, 24, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarf, D.; Colombo, M. Representation of serial order: A comparative analysis of humans, monkeys, and pigeons. Brain Res. Bull. 2008, 76, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straub, R.O.; Terrace, H.S. Generalization of serial learning in the pigeon. Anim. Learn. Behav. 1981, 9, 454–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrace, H.S. Chunking by a pigeon in a serial learning task. Nature 1987, 325, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gierszewski, S.; Bleckmann, H.; Schluessel, V. Cognitive abilities in Malawi cichlids (Pseudotropheus sp.): Matching-to-sample and image/mirror-image discriminations. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmann, A.; Delius, J.D.; Hollard, V.D.; Friesel, M.F. Discrimination of shape reflections and shape orientations by Columba livia. J. Comp. Psychol. 1988, 102, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackintosh, J.; Sutherland, N.S. Visual discrimination by the goldfish: The orientation of rectangles. Anim. Behav. 1963, 11, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, N.S. Visual Discrimination of Orientation and Shape by the Octopus. Nature 1957, 179, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, N.S. Visual discrimination of orientation by octopus: Mirror images. Br. J. Psychol. 1960, 51, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tee, K.S.; Riesen, A.H. Visual right-left confusions in animal and man. Adv. Psychobiol. 1974, 2, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maekawa, F.; Komine, O.; Sato, K.; Kanamatsu, T.; Uchimura, M.; Tanaka, K.; Ohki-Hamazaki, H. Imprinting modulates processing of visual information in the visual wulst of chicks. BMC Neurosci. 2006, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernik, M.; Fearon, P.; Csibra, G. Action anticipation in human infants reveals assumptions about anteroposterior body-structure and action. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20133205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallortigara, G.; Regolin, L. Gravity bias in the interpretation of biological motion by inexperienced chicks. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, R279–R280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallortigara, G.; Regolin, L.; Marconato, F. Visually inexperienced chicks exhibit spontaneous preference for biological motion patterns. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallortigara, G.; Andrew, R.J. Differential involvement of right and left hemisphere in individual recognition in the domestic chick. Behav. Process. 1994, 33, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarf, D.; Colombo, M. Representation of serial order in pigeons (Columba livia). J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process. 2010, 36, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosa-Salva, O.; Fiser, J.; Versace, E.; Dolci, C.; Chehaimi, S.; Santolin, C.; Vallortigara, G. Spontaneous Learning of Visual Structures in Domestic Chicks. Animals 2018, 8, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani8080135
Rosa-Salva O, Fiser J, Versace E, Dolci C, Chehaimi S, Santolin C, Vallortigara G. Spontaneous Learning of Visual Structures in Domestic Chicks. Animals. 2018; 8(8):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani8080135
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosa-Salva, Orsola, József Fiser, Elisabetta Versace, Carola Dolci, Sarah Chehaimi, Chiara Santolin, and Giorgio Vallortigara. 2018. "Spontaneous Learning of Visual Structures in Domestic Chicks" Animals 8, no. 8: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani8080135
APA StyleRosa-Salva, O., Fiser, J., Versace, E., Dolci, C., Chehaimi, S., Santolin, C., & Vallortigara, G. (2018). Spontaneous Learning of Visual Structures in Domestic Chicks. Animals, 8(8), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani8080135






