Assessing the Speciation of a Cold Water Species, Japanese Sand Lance Ammodytes personatus, in the Northwestern Pacific by AFLP Markers
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. AFLP Analysis
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
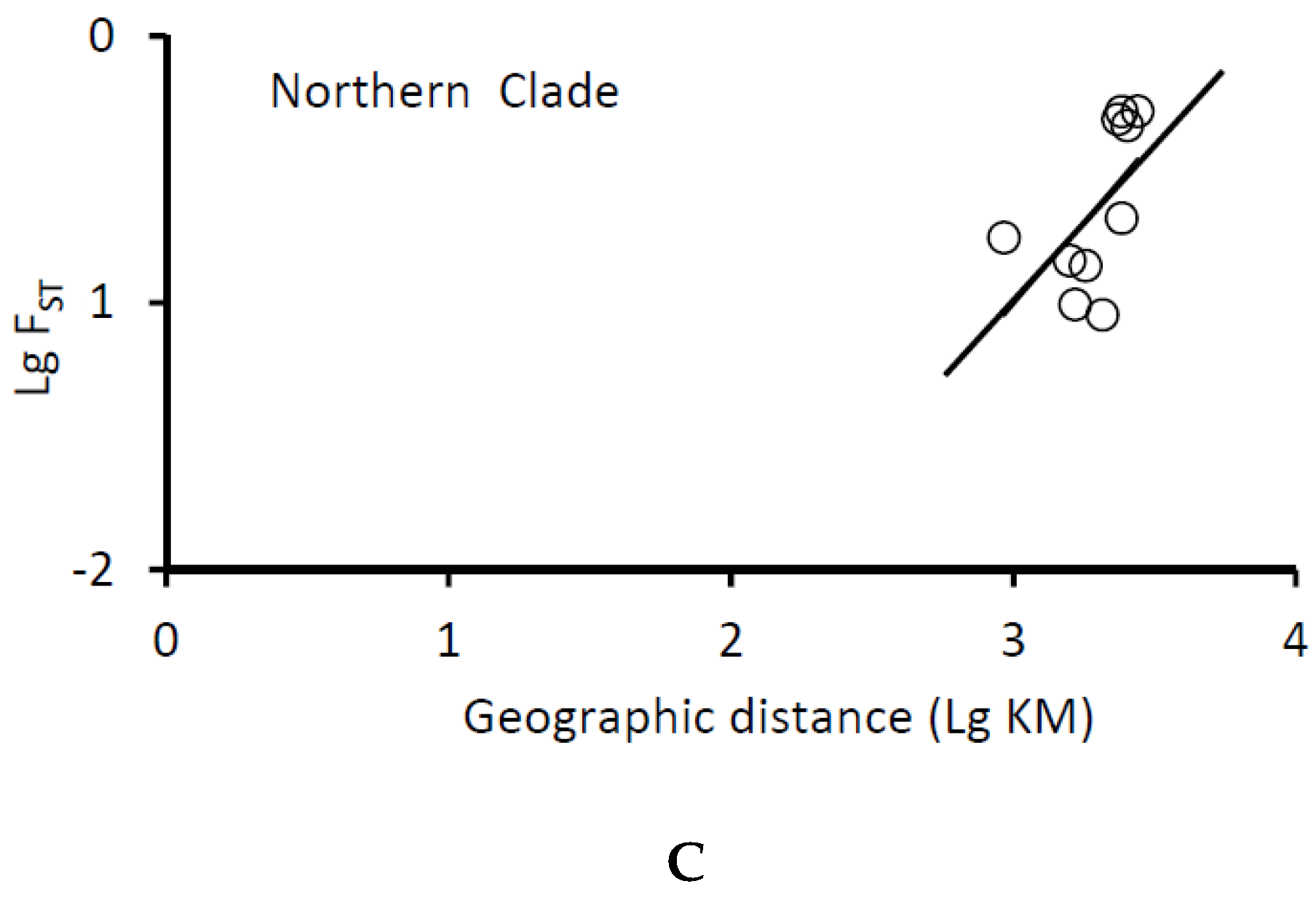
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pauls, S.U.; Nowak, C.; Bálint, M.; Pfenninger, M. The impact of global climate change on genetic diversity within populations and species. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 925–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yannic, G.; Pellissier, L.; Ortego, J.; Lecomte, N.; Couturier, S.; Cuyler, C.; Dussault, C.; Hundertmark, K.J.; Irvine, R.J.; Jenkins, D.A.; et al. Genetic diversity in caribou linked to past and future climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmesan, C. Ecological and evolutionary responses to recent climate change. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2006, 37, 637–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessig, J.M.; Woodley, C.M.; Cech, J.J., Jr.; Hansen, L.J. Effects of global climate change on marine and estuarine fishes and fisheries. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish. 2004, 14, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydeman, W.J.; Poloczanska, E.; Reed, T.E.; Thompson, S.A. Climate change and marine vertebrates. Science 2015, 350, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, R.M. Biological diversity: Differences between land and sea. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 1994, 343, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bálint, M.; Domisch, S.; Engelhardt, C.H.M.; Haase, P.; Lehrian, S.; Sauer, J.; Theissinger, K.; Pauls, S.U.; Nowak, C.; et al. Cryptic biodiversity loss linked to global climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2011, 1, 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Rubidge, E.M.; Patton, J.L.; Lim, M.; Burton, A.C.; Brashares, J.S.; Morit, C. Climate-induced range contraction drives genetic erosion in an alpine mammal. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickford, D.; Lohman, D.J.; Sodhi, N.S.; Ng, P.K.; Meier, R.; Winker, K.; Ingram, K.K.; Das, I. Cryptic species as a window on diversity and conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oba, T.; Irino, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Murayama, M.; Takamura, A.; Aokic, K. Paleoceanographic change off central Japan since the last 144,000 years based on high-resolution oxygen and carbon isotope records. Global Panet. Chang. 2006, 53, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, A.; Kimoto, K. History of the inflow of the warm Tsushima Current into the Sea of Japan between 3.5 and 0.8 Ma. Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl. 2006, 236, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyama, M.; Yanagibashi, S. Effect of temperature, age class, and growth on induction of aestivation in Japanese sandeel (Ammodytes personatus) in Ise Bay, central Japan. Fish. Oceanogr. 2004, 13, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, H. Population structure of the sandeel around Japan. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1984, 50, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H. A Genetic comparison of sympatric populations of sand lance (Genus Ammodytes) from the region east of Cape Soya, Japan. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 46, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.Q.; Yanagimoto, T.; Zhang, Y.P.; Gao, T.X. Phylogeography study of Ammodytes personatus in Northwestern Pacific: Pleistocene isolation, temperature and current conducted secondary contact. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, P.; Hogers, R.; Bleeker, M.; Reijans, M.; van de Lee, T.; Hornes, M.; Frijters, A.; Pot, J.; Peleman, J.; Kuiper, M.; et al. AFLP: A new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 4407–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.Q.; Han, G.; Wang, Z.Y.; Shui, B.N.; Gao, T.X. The genetic divergence and genetic structure of two closely related fish species Lateolabrax maculatus and Lateolabrax japonicus in the Northwestern Pacific inferred from AFLP markers. Genes Genom. 2015, 37, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, H.; Kawasaki, T. Population studies of sandeel, Ammodytes personatus (Girard), in Sendai Bay and its neighborhood. Tohoku J. Agric. Res. 1981, 31, 173–197. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, H.; Yamazaki, F.; Mishima, S. Genetic divergence among sandlance Ammodytes personatus population in Japan. Nippon Suis. Gak. 1988, 54, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Oceanographic Data Centre Home Page. Available online: http://www.jodc.go.jp/jodcweb (accessed on 24 January 2014).
- Wang, Z.; Jayasankar, P.; Khoo, S.K. AFLP fingerprinting reveals genetic variability in common carp stocks from Indonesia. Asian Fish. Sci. 2000, 13, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Nei, M.; Li, W.H. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 6, 5269–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giulia, P.; Valerio, O.; Giulia, S.; Elena, F.; Ettore, R.; Luciano, B. Detecting a hierarchical genetic population structure: the case study of the fire salamander (salamandra salamandra) in northern Italy. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 743–758. [Google Scholar]
- Falush, D.; Stephens, M.; Pritchard, J.K. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: Dominant markers and null alleles. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nei, M. Genetic distance between populations. Am. Nat. 1972, 106, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlf, F.J. NTSYS-pc: Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System; Exeter Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourie, S.A.; Green, D.M.; Vincent, A.C.J. Dispersal, habitat differences, and comparative phylogeography of Southeast Asian seahorses (Syngnathidae:Hippocampus). Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 1073–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.X.; Gao, T.X.; Zhuang, Z.M.; Jin, X.S.; Yokogawa, K.; Zhang, Y.P. Late Pleistocene divergence and subsequent population expansion of two closely related fish species, Japanese anchovy (Engraulis japonicus) and Australian anchovy (Engraulis australis). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 40, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.X.; Gao, T.X.; Wu, S.F.; Zhang, Y.P. Pleistocene isolation in the Northwestern Pacific marginal seas and limited dispersal in a marine fish, Chelon haematocheilus (Temminck & Schlegel, 1845). Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 275–288. [Google Scholar]
- Toews, D.P.L.; Brelsford, A. The biogeography of mitochondrial and nuclear discordance in animals. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 16, 3907–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, M.N.; Staton, J.L.; Jacobs, D.K. Phylogeography of the tidewater goby, Eucyclogobius newberryi (Teleostei, Gobiidae), in coastal California. Evolution 2001, 55, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, K.N.; Jamandre, W.B.; Hsu, C.C.; Tzeng, W.N.; Durand, J.D. Plio-pleistocene sea level and temperature fluctuations in the northwestern pacific promoted speciation in the globally-distributed flathead mullet Mugil cephalus. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionne, M.; Caron, F.; Dodson, J.J.; Bernatchez, L. Landscape genetics and hierarchical genetic structure in Atlantic salmon: the interaction of gene flow and local adaptation. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 2382–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, S.; Scheider, H.; Sampaio, I. Genetic differentiation of Macrodon ancylodon (Sciaenidae, Perciformes) populations in Atlantic coastal waters of South America as revealed by mtDNA analysis. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2003, 26, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatkin, M. Isolation by distance in equilibrium and non-equilibrium populations. Evolution 1993, 47, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, W.W.; Lam, V.M.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Kearney, K.; Watson, R.; Pauly, D. Projecting global marine biodiversity impacts under climate change scenarios. Fish Fish. 2009, 10, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
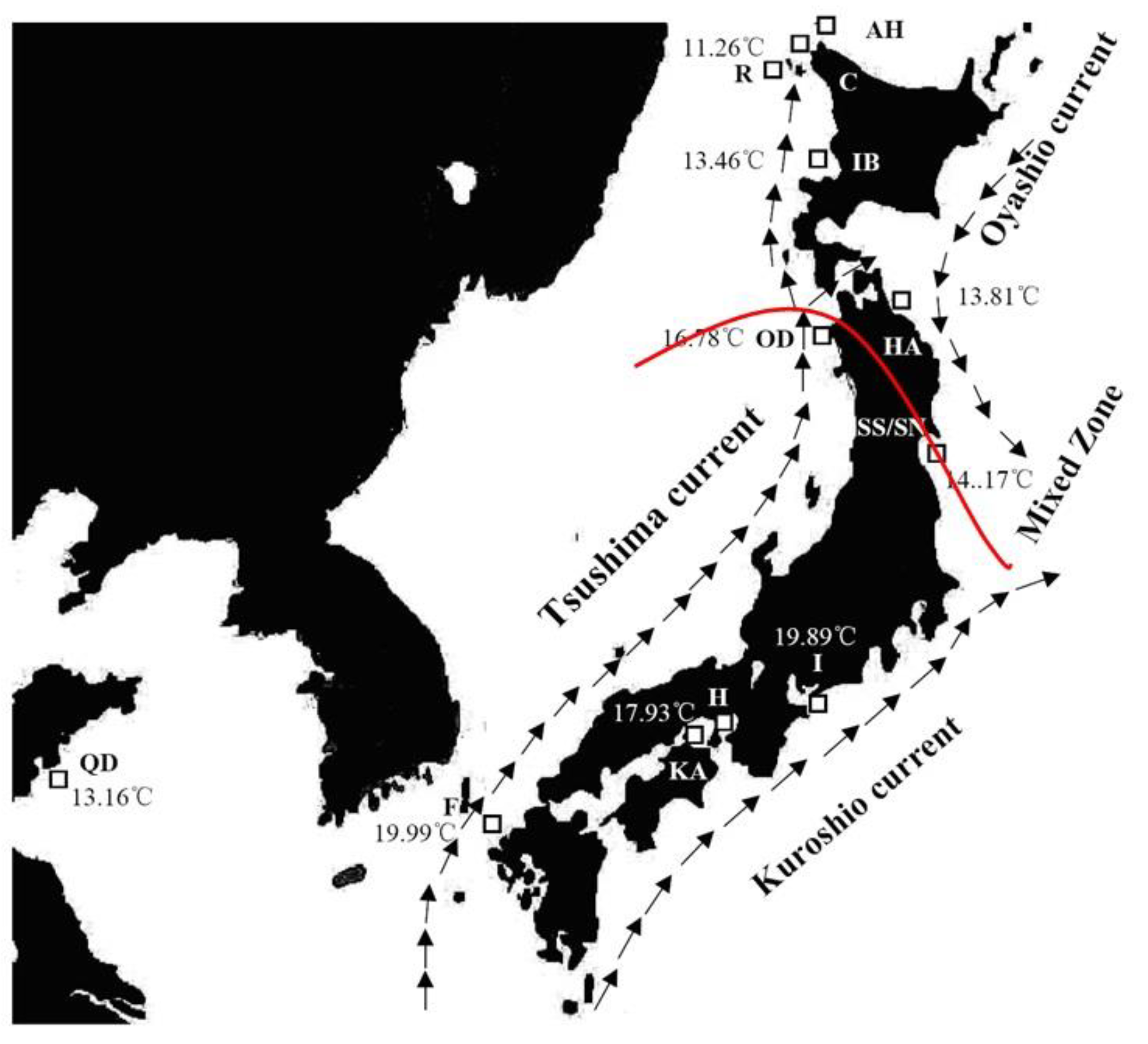
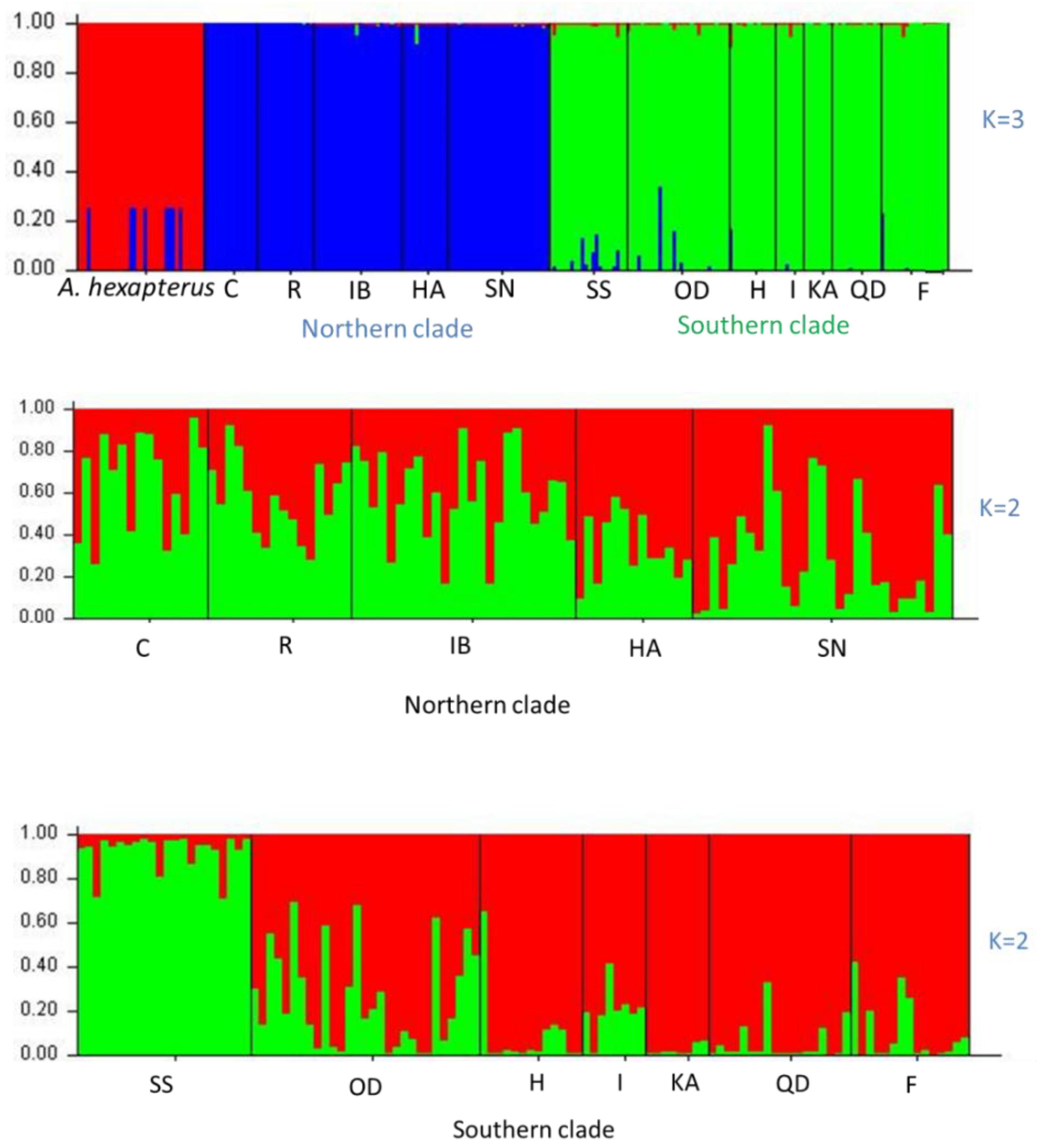
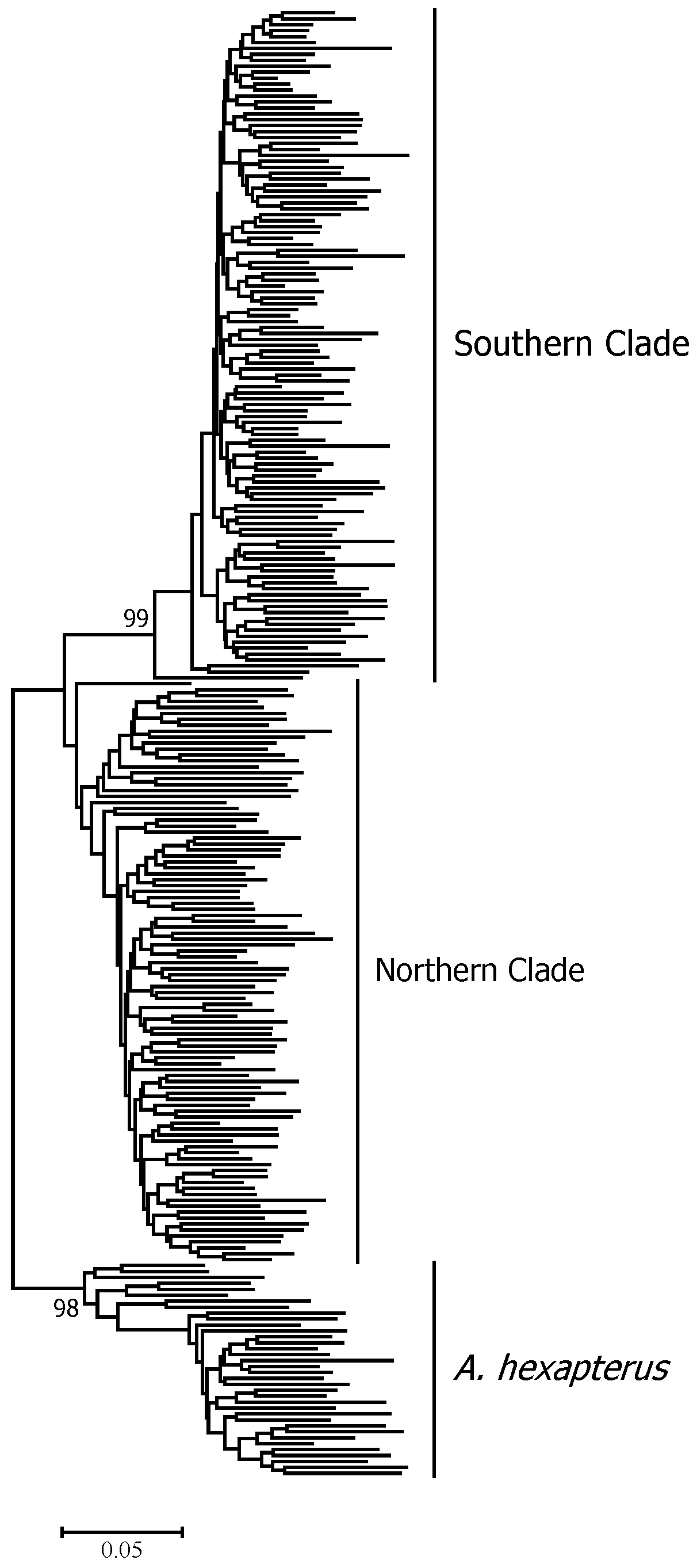
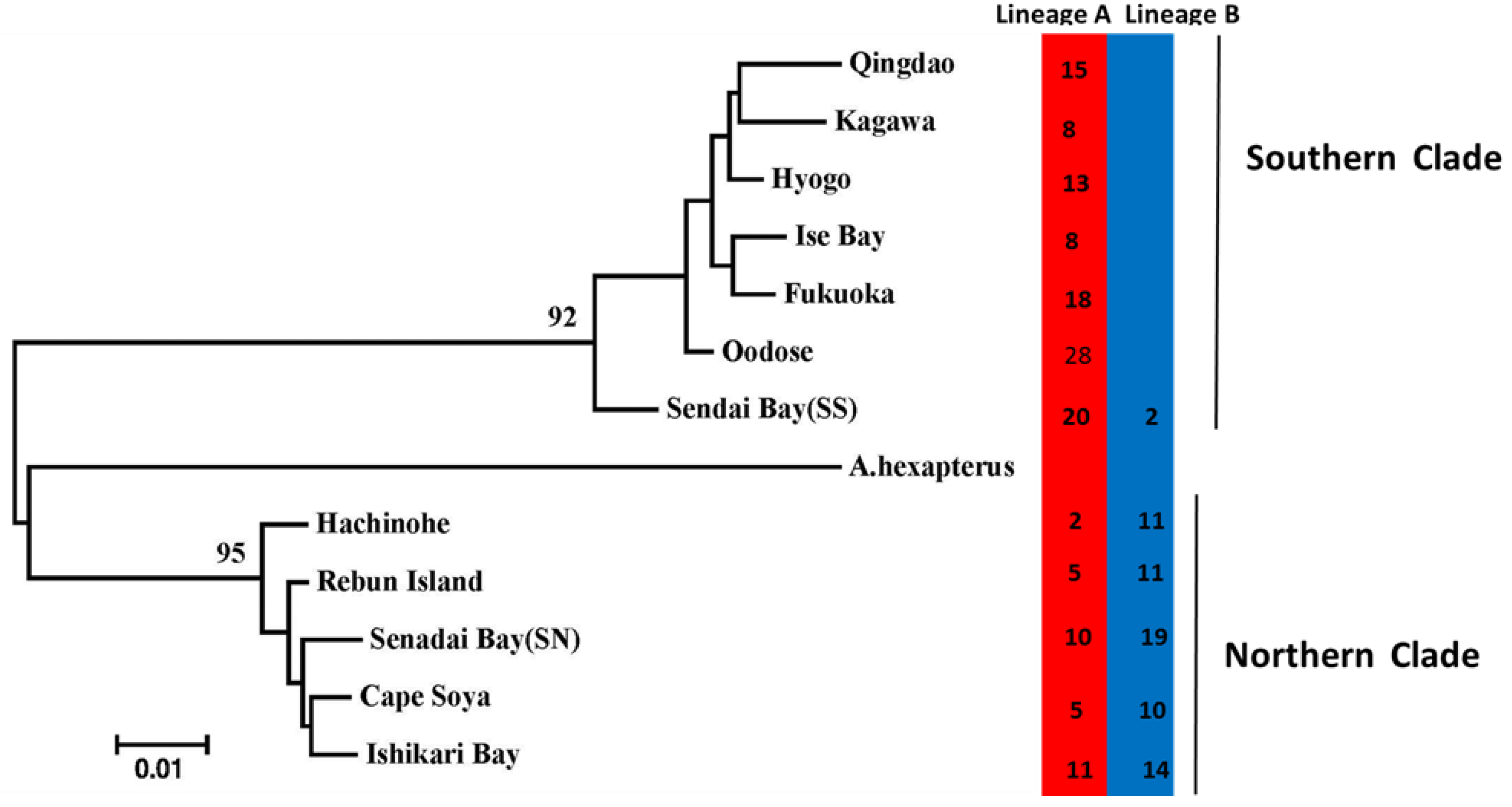
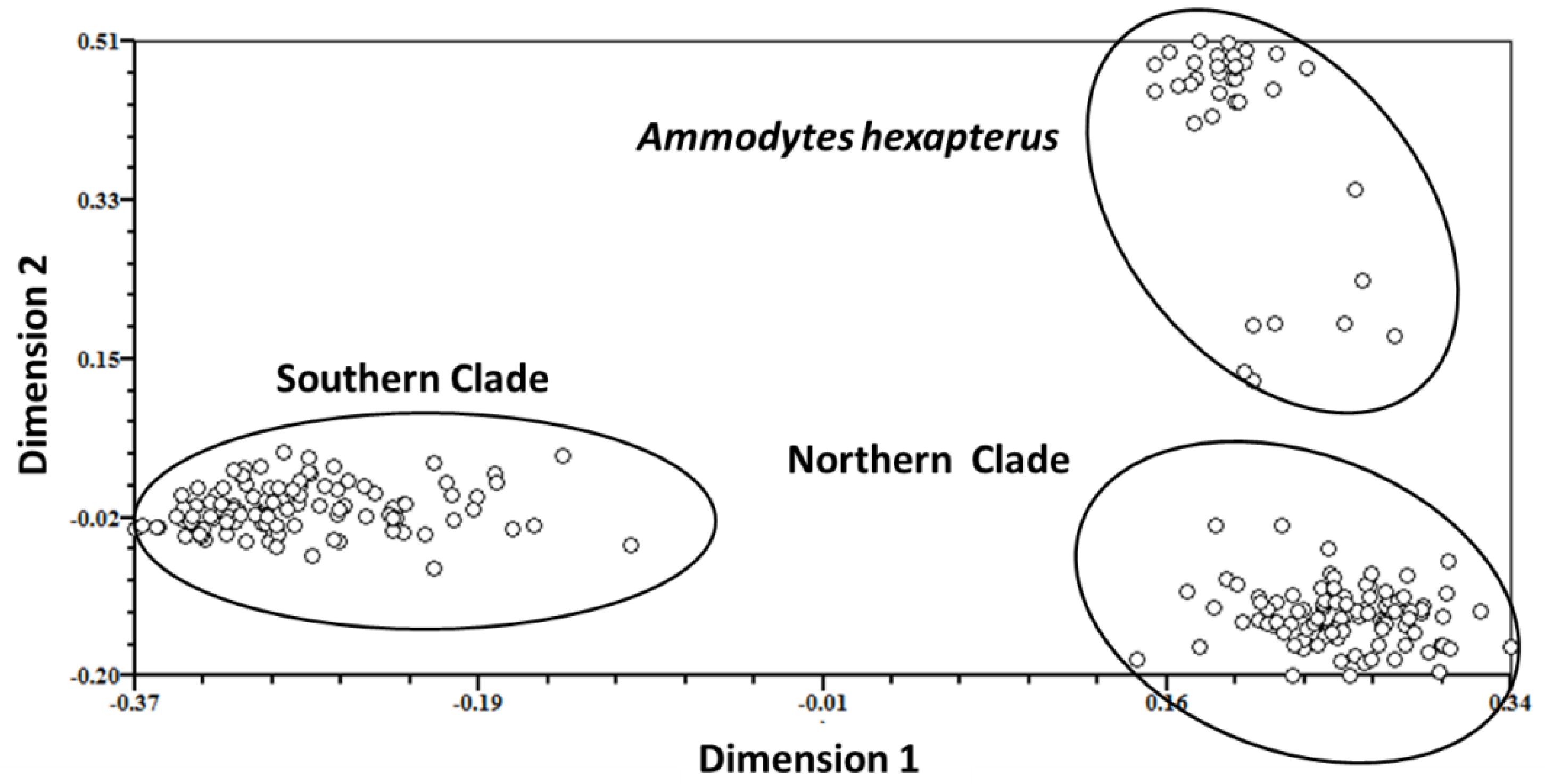
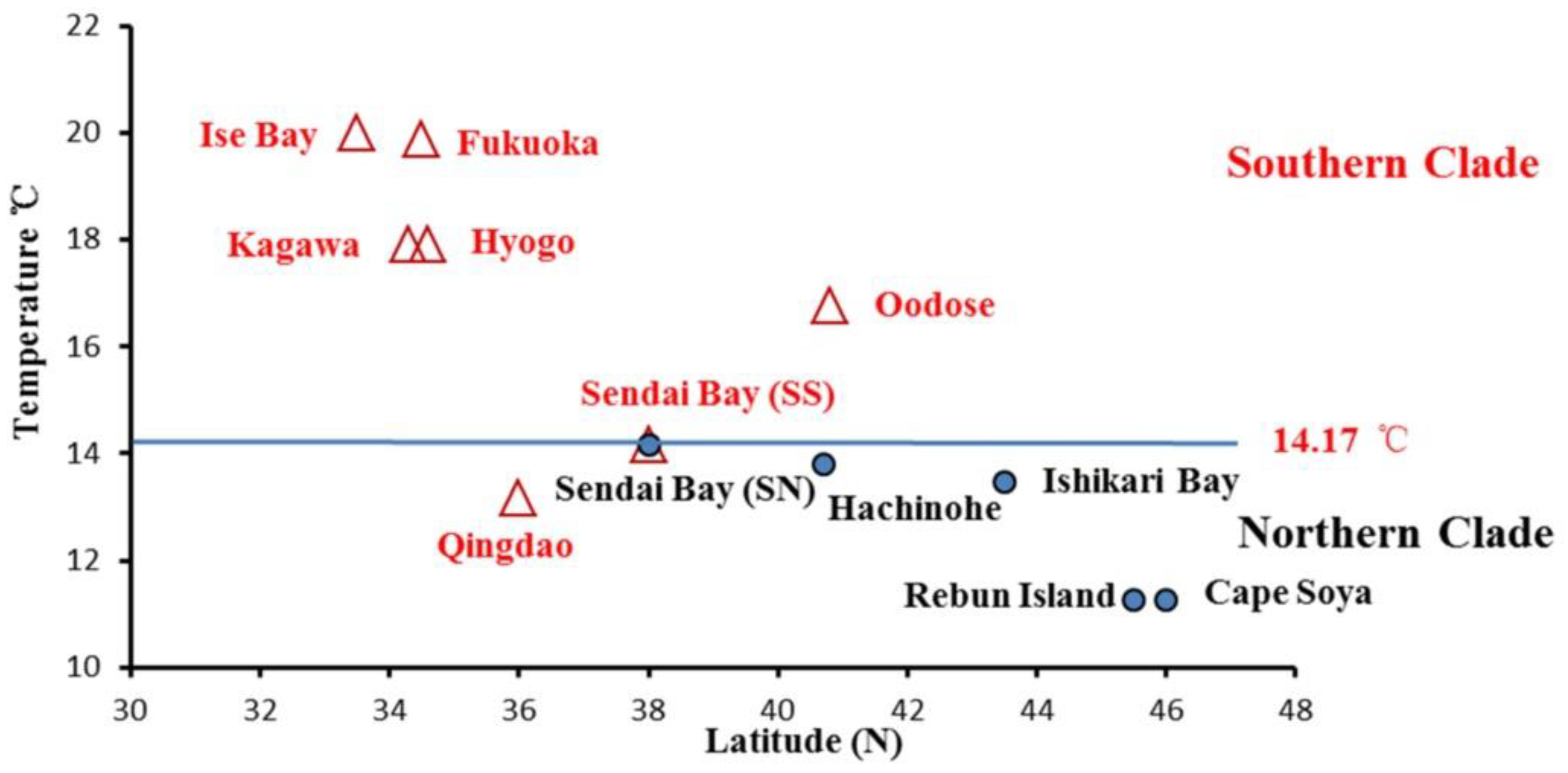

| Species | ID | Sample Location | Sample Size | Date of Collection | Genotype Based on AFLP | Genotype Based on Allozyme * | mtDNA lineage * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. personatus | QD | Qingdao | 15 | April 2005 | Southern clade | Southern group | One lineage(A) |
| F | Fukuoka | 18 | April 2005 | Southern clade | Southern group | One lineage(A) | |
| KA | Kagawa | 8 | April 2005 | Southern clade | Southern group | One lineage(A) | |
| H | Hyogo | 13 | April 2005 | Southern clade | Southern group | One lineage(A) | |
| I | Ise Bay | 8 | May 2005 | Southern clade | Southern group | One lineage(A) | |
| OD | Oodose | 29 | May 2006 | Southern clade | Southern group | Two lineages (A: B = 28:1) | |
| SS | Sendai Bay | 22 | April 2006 | Southern clade | Southern group | Two lineages (A: B = 20:2) | |
| SN | Sendai Bay | 29 | April 2006 | Northern clade | Northern group | Two lineages (A: B = 10:19) | |
| HA | Hachinohe | 13 | June 2005 | Northern clade | Northern group | Two lineages (A: B = 2:11) | |
| IB | Ishikari Bay | 25 | April 2006 | Northern clade | Northern group | Two lineages (A: B = 11:14) | |
| R | Rebun Island | 16 | June 2006 | Northern clade | Northern group | Two lineages (A: B = 5:11) | |
| C | Cape Soya | 15 | June 2006 | Northern clade | Northern group | Two lineages (A: B = 5:10) | |
| A. hexapterus | AH | Cape Soya | 36 | June 2006 | |||
| Total | 247 | ||||||
| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| Adapters | |
| EcoRI adapter | 5’-CTCGTAGACTGCGTACC-3’ |
| 5’-AATTGGTACGCAGTCTAC-3’ | |
| MseI adapter | 5’-GACGTGAGTCCTGAG-3’ |
| 5’-TACTCAGGACTCAT-3’ | |
| Pre-amplification primer | |
| EcoRI | 5’-GACTGCGTACCAATTC-3’ |
| MseI | 5’-GATGAGTCCTGAGTAA-3’ |
| Selective amplification primer | |
| E-AAC/M-CTC | 5’-GACTGCGTACCAATTCAAC-3’ 5’-GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACTC-3’ |
| E-AAG/M-CAA | 5’-GACTGCGTACCAATTCAAG-3’ 5’-GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACAA-3’ |
| E-AAG/M-CAC | 5’-GACTGCGTACCAATTCAAG-3’ 5’-GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACAC-3’ |
| E-AGC/M-CAC | 5’-GACTGCGTACCAATTCAGC-3’ 5’-GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACAC-3’ |
| QD | F | KA | H | I | SS | SN | OD | HA | IB | R | C | AH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of loci | 188 | 189 | 154 | 183 | 173 | 215 | 228 | 224 | 196 | 231 | 175 | 211 | 245 |
| Percentage of polymorphic loci | 49.47% | 44.97% | 27.27% | 44.81% | 39.88% | 54.42% | 57.02% | 58.48% | 48.98% | 56.71% | 75.43% | 54.98% | 62.45% |
| Nei’s genetic diversity | 0.1081 | 0.0794 | 0.0641 | 0.0907 | 0.0958 | 0.1029 | 0.0932 | 0.0982 | 0.0944 | 0.1047 | 0.1531 | 0.1263 | 0.1218 |
| Shannon diversity index | 0.1772 | 0.1350 | 0.1042 | 0.1506 | 0.1555 | 0.1711 | 0.1578 | 0.1667 | 0.1592 | 0.1750 | 0.2527 | 0.2035 | 0.2011 |
| QD | F | H | KA | I | OD | SS | SN | HA | IB | R | C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | 0.1757* | |||||||||||
| H | 0.0986* | 0.1066* | ||||||||||
| KA | 0.1440* | 0.1665* | 0.0993* | |||||||||
| I | 0.1378* | 0.0632* | 0.0679* | 0.1143* | ||||||||
| OD | 0.0901* | 0.0638* | 0.0473* | 0.0857* | 0.0573* | |||||||
| SS | 0.2078* | 0.2003* | 0.1606* | 0.1951* | 0.1666* | 0.1269* | ||||||
| SN | 0.5222* | 0.5430* | 0.5135* | 0.5549* | 0.4991* | 0.5016* | 0.4652* | |||||
| HA | 0.5223* | 0.5442* | 0.5176* | 0.5669* | 0.4931* | 0.4860* | 0.4596* | 0.0594* | ||||
| IB | 0.4884* | 0.5105* | 0.4770* | 0.5098* | 0.4521* | 0.4661* | 0.4316* | 0.0566* | 0.0685* | |||
| R | 0.4623* | 0.4865* | 0.4545* | 0.4844* | 0.4194* | 0.4461* | 0.3998* | 0.0326* | 0.0503* | 0.0157* | ||
| C | 0.4945* | 0.5161* | 0.4902* | 0.5144* | 0.4570* | 0.4670* | 0.4201* | 0.0588* | 0.0791* | 0.0336* | 0.0112 | |
| AH | 0.5547* | 0.5718* | 0.5356* | 0.5724* | 0.5386* | 0.5397* | 0.5263* | 0.4613* | 0.4471* | 0.4539* | 0.4256* | 0.4472* |
| Isolation by Temperature | Mantel test | All Populations | Northern Clade | Southern Clade |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolation by distance | r | 0.41 | 0.04 | 0.46 |
| P | 0.02 | 0.33 | 0.02 | |
| r | 0.26 | 0.76 | 0.14 | |
| P | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.35 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Z.; Wang, Z.; Gao, T.; Yanagimoto, T.; Iida, K. Assessing the Speciation of a Cold Water Species, Japanese Sand Lance Ammodytes personatus, in the Northwestern Pacific by AFLP Markers. Animals 2018, 8, 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani8120224
Han Z, Wang Z, Gao T, Yanagimoto T, Iida K. Assessing the Speciation of a Cold Water Species, Japanese Sand Lance Ammodytes personatus, in the Northwestern Pacific by AFLP Markers. Animals. 2018; 8(12):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani8120224
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Zhiqiang, Zhiyong Wang, Tianxiang Gao, Takashi Yanagimoto, and Koji Iida. 2018. "Assessing the Speciation of a Cold Water Species, Japanese Sand Lance Ammodytes personatus, in the Northwestern Pacific by AFLP Markers" Animals 8, no. 12: 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani8120224
APA StyleHan, Z., Wang, Z., Gao, T., Yanagimoto, T., & Iida, K. (2018). Assessing the Speciation of a Cold Water Species, Japanese Sand Lance Ammodytes personatus, in the Northwestern Pacific by AFLP Markers. Animals, 8(12), 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani8120224





