Cetobacterium Is a Major Component of the Microbiome of Giant Amazonian Fish (Arapaima gigas) in Ecuador
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethical Notes
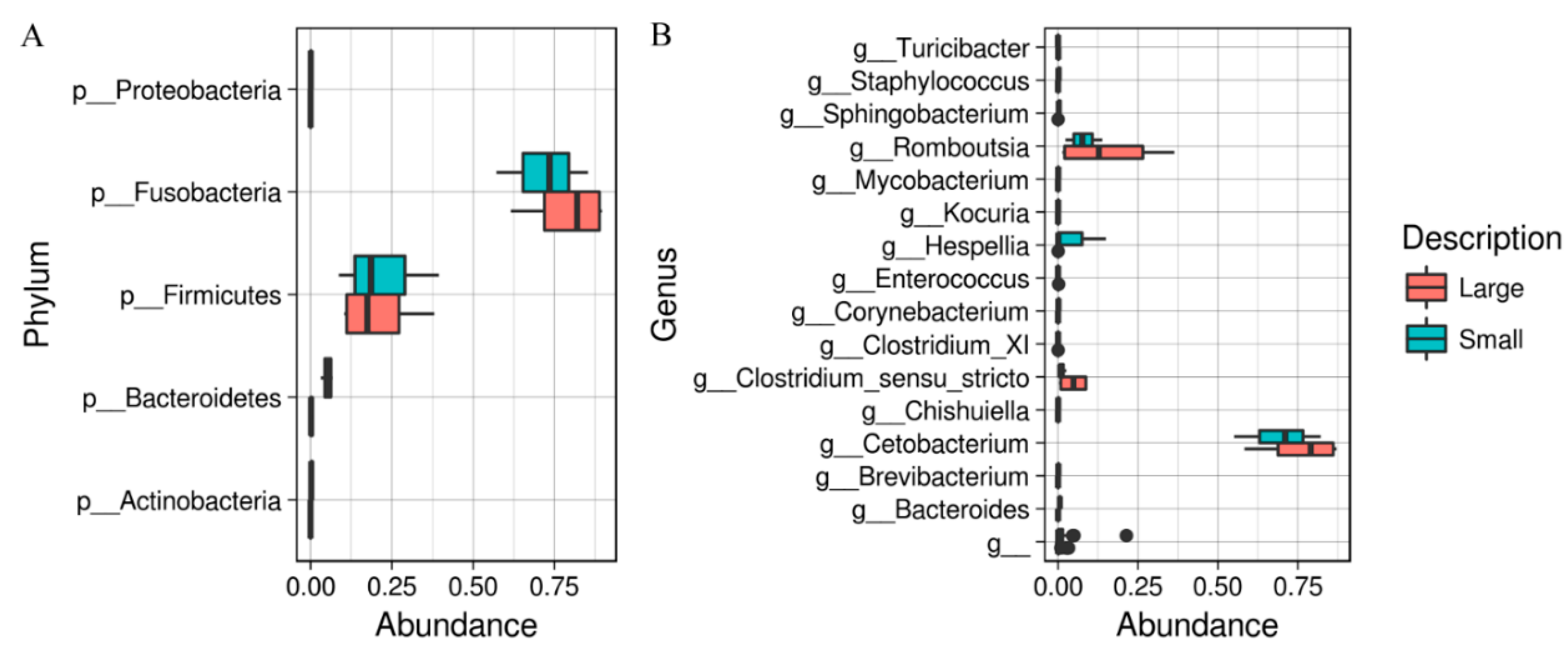
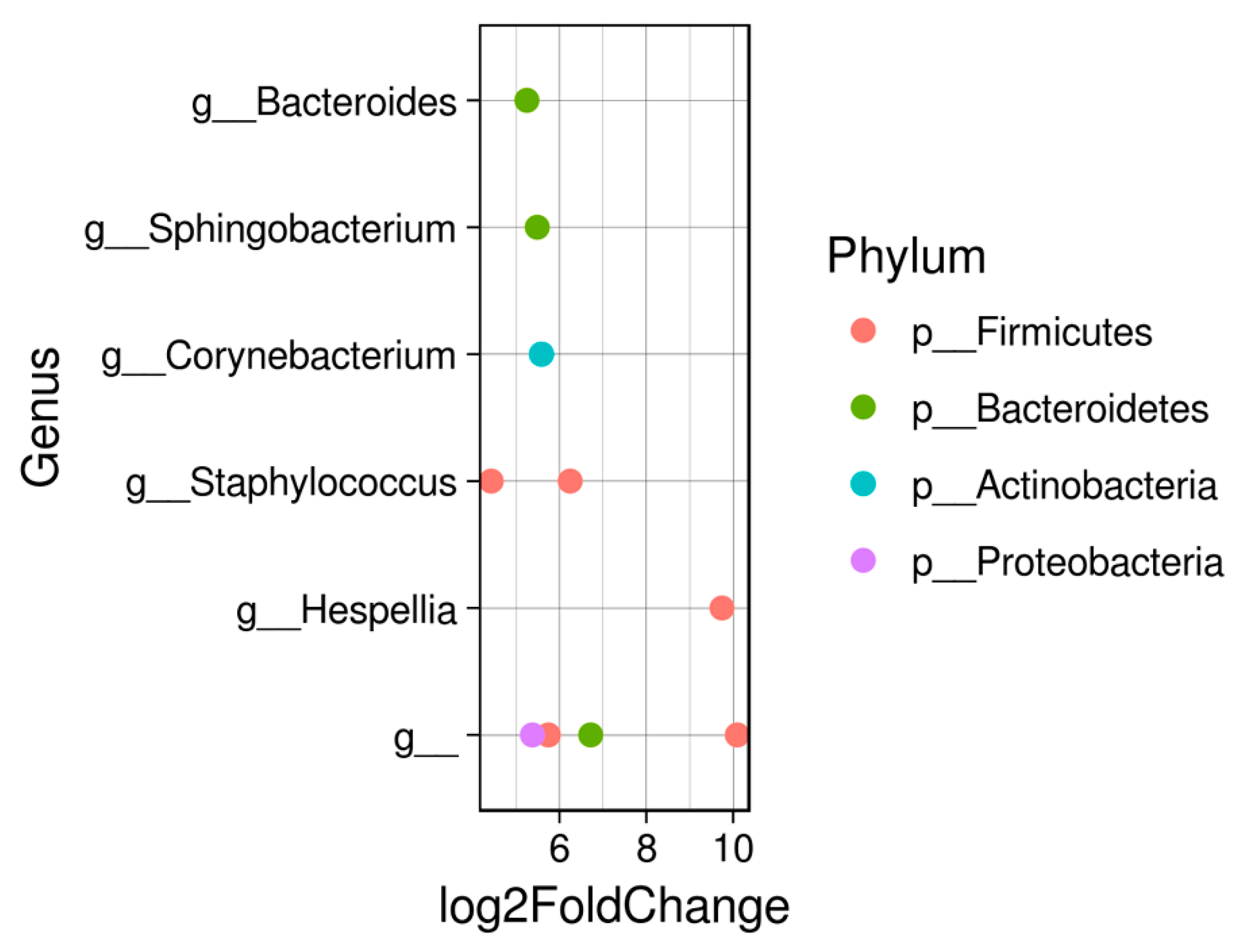
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ono, E.; Roubach, R.; Pereira, M. Pirarucu production advances in central Amazon, Brazil. Glob. Aquacult. Advocate 2003, 6, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Department. Universal Software for Fishery Statistical Time Series, Fisheries and Aquaculture Software, FishStat Plus. Available online: http://www.fao.org/fishery/statistics/software/fishstat/en (accessed on 5 July 2018).
- Ringo, E.; Zhou, R.Z.; Vecino, J.L.G.; Wadsworth, S.; Romero, J.; Krogdahl, A.; Olsen, R.E.; Dimitroglou, A.; Foey, A.; Davies, S.M.; et al. Effect of dietary components on the gut microbiota of aquatic animals. A never-ending story? Aquacult. Nutr. 2016, 22, 219–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S. Probiotics and immunity: A fish perspective. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez, C.; Romero, J. Fine flounder (Paralichthys adspersus) microbiome showed important differences between wild and reared specimens. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Fish, J.A.; Chai, B.; McGarrell, D.M.; Sun, Y.; Brown, C.T.; Porras-Alfaro, A.; Kuske, C.R.; Tiedje, J.M. Ribosomal Database Project: Data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D633–D642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurdie, P.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, C.; Sakata, T.; Sugita, H. Novel ecological niche of Cetobacterium somerae, an anaerobic bacterium in the intestinal tracts of freshwater fish. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kessel, M.A.; Dutilh, B.E.; Neveling, K.; Kwint, M.P.; Veltman, J.A.; Flik, G.; Jetten, M.S.; Klaren, P.H.; den Camp, H.J. Pyrosequencing of 16s rRNA gene amplicons to study the microbiota in the gastrointestinal tract of carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). AMB Express 2011, 1, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, A.; Mohammed, H.; Arias, C. Characterization of the gut microbiota of three commercially valuable warmwater fish species. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, H.; Miyajima, C.; Deguchi, Y. The vitamin B12-producing ability of the intestinal microflora of freshwater fish. Aquaculture 1991, 92, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Wu, S.; Xiong, F.; Tran, N.; Jakovlíc, I.; Zou, H.; Xiang, W.; Wang, G. Succession and fermentation products of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) hindgut microbiota in response to an extreme dietary shift. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerritsen, J.; Fuentes, S.; Grievink, W.; van Niftrik, L.; Tindall, B.; Timmerman, H.; Rijkers, G.; Smidt, H. Characterization of Romboutsia ilealis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from the gastro-intestinal tract of a rat, and proposal for the reclassification of five closely related members of the genus Clostridium into the genera Romboutsia gen. nov., Intestinibacter gen. nov., Terrisporobacter gen. nov. and Asaccharospora gen. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 1600–1616. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Den Besten, G.; van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.; Bakker, B. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, G.; Mukherjee, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Ray, A. Purification and characterization of extracellular protease and amylase produced by the bacterial strain, Corynebacterium alkanolyticum ATH3 Isolated from Fish Gut. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2016, 41, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.; Ringo, E.; Merrifield, D.L. The gut microbiota of fish. In Aquaculture Nutrition: Gut Health, Probiotics and Prebiotics, 1st ed.; Merrifield, D.L., Ringo, E., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2014; pp. 75–100. ISBN 9780470672716. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, J.; Navarrete, P. 16S rDNA-based analysis of dominant bacterial populations associated with early life stages of coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Microb. Ecol. 2006, 51, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holben, W.E.; Williams, P.; Saarinen, M.; Sarkilahti, L.K.; Apajalahti, J.H. Phylogenetic analysis of intestinal microflora indicates a novel mycoplasma phylotype in farmed and wild salmon. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 44, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Group Size | Sample | Alpha Diversity Index * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTUs | Chao1 | Shannon | Simpson | ||
| Small | C1 | 51 | 60 | 2.087 | 0.823 |
| C2 | 50 | 53 | 1.915 | 0.759 | |
| C4 | 60 | 63 | 2.291 | 0.818 | |
| Est. mean | 54 a | 59 a | 2.098 a | 0.800 a | |
| Large | 7 | 33 | 35 | 1.527 | 0.638 |
| 8 | 37 | 38 | 1.618 | 0.659 | |
| 12 | 42 | 49 | 1.758 | 0.748 | |
| 18 | 40 | 40 | 1.932 | 0.793 | |
| Est. mean | 38 b | 40 b | 1.709 b | 0.709 a | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramírez, C.; Coronado, J.; Silva, A.; Romero, J. Cetobacterium Is a Major Component of the Microbiome of Giant Amazonian Fish (Arapaima gigas) in Ecuador. Animals 2018, 8, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani8110189
Ramírez C, Coronado J, Silva A, Romero J. Cetobacterium Is a Major Component of the Microbiome of Giant Amazonian Fish (Arapaima gigas) in Ecuador. Animals. 2018; 8(11):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani8110189
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamírez, Carolina, Jaime Coronado, Arturo Silva, and Jaime Romero. 2018. "Cetobacterium Is a Major Component of the Microbiome of Giant Amazonian Fish (Arapaima gigas) in Ecuador" Animals 8, no. 11: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani8110189
APA StyleRamírez, C., Coronado, J., Silva, A., & Romero, J. (2018). Cetobacterium Is a Major Component of the Microbiome of Giant Amazonian Fish (Arapaima gigas) in Ecuador. Animals, 8(11), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani8110189





