Environmental Enrichment in Kennelled Pit Bull Terriers (Canis lupus familiaris)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Housing
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Approval
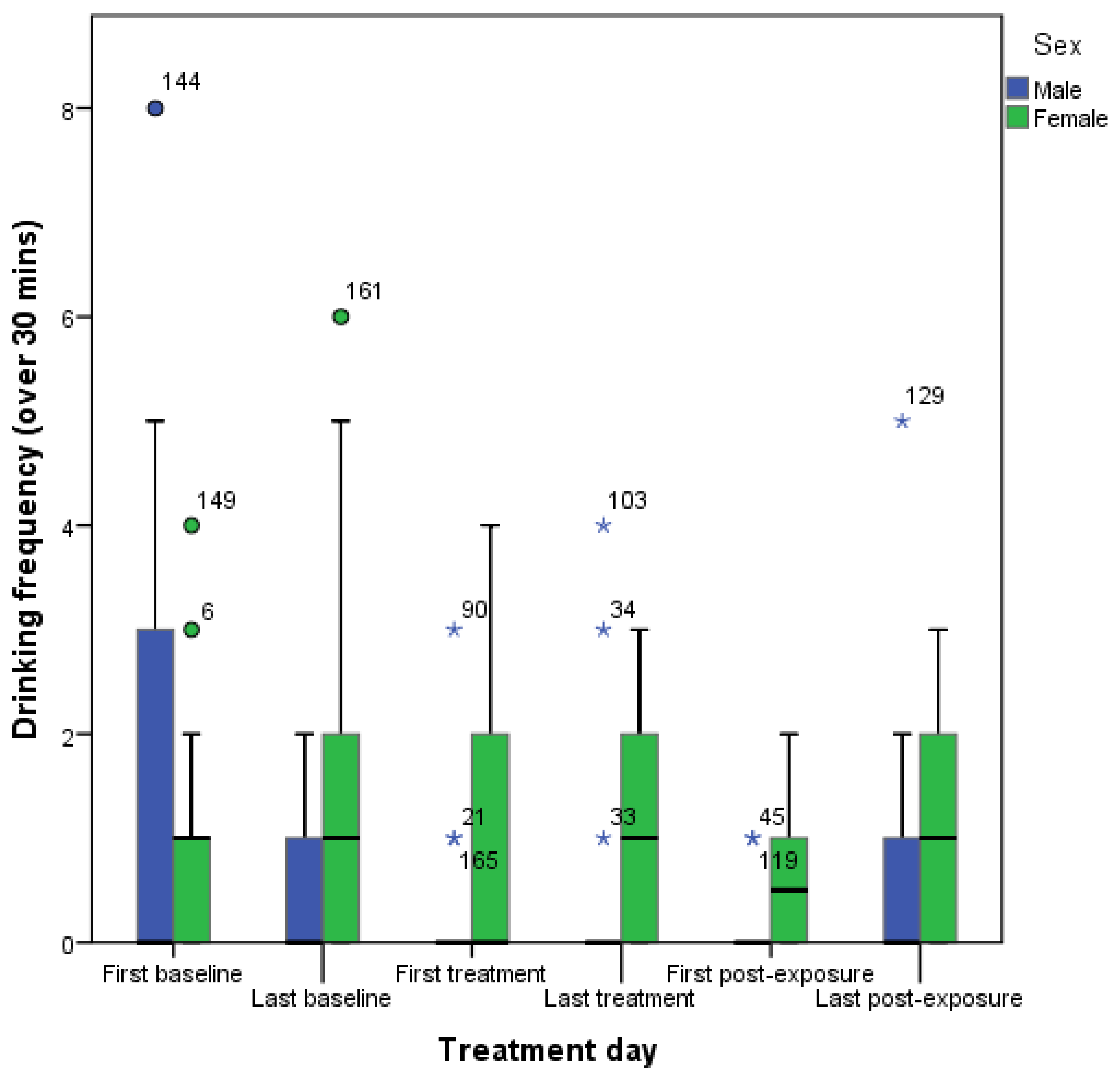
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clark, C.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.; Murray, J. Number of cats and dogs in UK welfare organisations. Vet. Rec. 2012, 170, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavisky, J.; Brennan, M.; Downes, M.; Dean, R. Demographics and economic burden of un-owned cats and dogs in the UK: Results of a 2010 census. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New, J.C.; Kelch, W.J.; Hutchison, J.M.; Salman, M.D.; King, M.; Scarlett, J.M. Birth and death rate estimates of cats and dogs in U.S. households and related factors. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2014, 7, 229–241. [Google Scholar]
- Eckman, H.; Vallentine, S.; Hiby, E. Rabies control and animal welfare. In Proceedings of the Rabies Control—Towards Sustainable Prevention at the Source, Compendium of the OIE Global Conference on Rabies Control, Incheon-Seoul, Korea, 7–9 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, K.; Mills, D. The effect of the kennel environment on canine welfare: A critical review of experimental studies. Anim. Welf. 2007, 16, 435–447. [Google Scholar]
- Beerda, B.; Schilder, M.; Van Hoof, J.; De Vries, H.; Mol, J. Chronic stress in dogs subjected to social and spatial restriction. I. Behavioural responses. Phys. Behav. 1999, 66, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubrecht, R.C. A comparison of social and environmental enrichment methods for laboratory housed dogs. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1993, 37, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, K.N.; Tromborg, C.T. Sources of stress in captivity. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 102, 262–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlstead, K.; Brown, J.L.; Strawn, W. Behavioral and physiological correlates of stress in laboratory cats. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1993, 38, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherdson, D. The role of environmental enrichment in the captive breeding and reintroduction of endangered species. In Creative Conservation Interactive Management of Wild and Captive Animals; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 167–177. [Google Scholar]
- Chamove, A.S.; Moodie, E.M. Are alarming events good for captive monkeys. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1990, 27, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, P.; Pattacini, O.; Beretta, V.; Bertozzi, J.; Zannoni, S.; Viggiani, R.; Accorsi, P.A. Effects of a human social enrichment program on behavior and welfare of sheltered dogs. J. Vet. Behav. Clin. Appl. Res. 2007, 2, 88–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetts, S.; Clark, J.D.; Calpin, J.P.; Arnold, C.E.; Mateo, J.M. Influence of housing conditions on beagle behaviour. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1992, 34, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, L.L.; Vinke, C.M.; Schilder, M.B.; Spruijt, B.M. The effect of feeding enrichment toys on the behaviour of kennelled dogs (Canis familiaris). Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2008, 114, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, L.; Wells, D.L.; Hepper, P.G. The influence of olfactory stimulation on the behaviour of dogs housed in a rescue shelter. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2005, 91, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, D.L.; Hepper, P.G. The influence of auditory stimulation on the behaviour of dogs housed in a rescue shelter. Anim. Welf. 2002, 11, 385–393. [Google Scholar]
- Pullen, A.J.; Merrill, R.J.; Bradshaw, J. W Preferences for toy types and presentations in kennel housed dogs. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2010, 125, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeder, C.L.; Taylor, D.K. Injury related to environmental enrichment in a dog (Canis familiaris): Gastric foreign body. J. Am. Assoc. Lab Anim. 2009, 48, 76–78. [Google Scholar]
- Kiddie, J.; Collins, L. Identifying environmental and management factors that may be associated with the quality of life of kennelled dogs (Canis familiaris). Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2015, 167, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, M.J.; Morton, D.B.; Anderson, D.; Buckwell, A.; Heath, S.; Hubrecht, R.; Jennings, M.; Robb, D.; Ruane, B.; Swallow, J.; et al. Refining dog husbandry and care. Lab Anim. 2004, 38, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumans, J.M. Environmental enrichment for laboratory rodents and rabbits: requirements of rodents, rabbits, and research. ILAR J. 2005, 46, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boissy, A.; Arnould, C.; Chaillou, E.; Desire, L.; Duvaux-Ponter, C.; Greiveldinger, L.; Leterrier, C.; Richard, S.; Roussel, S.; Saint-Dizier, H.; et al. Emotions and cognition: A new approach to animal welfare. Anim. Welf. 2007, 16, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorf, J.; Panksepp, J. The neurobiology of positive emotions. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2006, 30, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagan, R.; Veasey, J. Challenges of zoo animal welfare. In Wild Mammals in Captivity: Principles & Techniques for Zoo Management; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherdson, D. Principles of and research on environmental enrichment for mammals. In Wild Mammals in Captivity: Principles & Techniques for Zoo Management; Kleiman, D.G., Thompson, K.V., Baer, C.K., Eds.; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hirt, H.; Wechsler, B. Behavioural diversity as a measure of welfare: A study in pigs. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1994, 40, 82–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherdson, D.J.; Mellen, K.; Seidensticker, J. The influence of food presentation on the behaviour of small cats in confined environments. Zoo Biol. 1993, 12, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistler, C.; Hegglin, D.; Wurbel, H.; Konig, B. Feeding enrichment in an opportunistic carnivore: The red fox. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2009, 116, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiddie, J. Assessing Quality of life in Kennelled Dogs. Ph.D. Thesis, The Royal Veterinary College, London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Part, C.E.; Kiddie, J.L.; Hayes, W.A.; Mills, D.S.; Neville, R.F.; Morton, D.B.; Collins, L.M. Physiological, physical and behavioural changes in dogs (Canis familiaris) when kennelled: Testing the validity of stress parameters. Phys. Behav. 2014, 133, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgeois, S.R.; Brent, L. Modifying the behaviour of singly caged baboons: evaluating the effectiveness of four enrichment techniques. Anim. Welf. 2005, 14, 71–81. [Google Scholar]
- Research Randomizer. Available online: https://www.randomizer.org/ (accessed on 13 July 2014).
- Friard, O. BORIS. Available online: http://www.boris.unito.it/ (accessed on February 2015).
- Wells, D.L.; Hepper, P.G. A note on the influence of visual conspecific contact on the behaviour of sheltered dogs. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1998, 60, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, J.M.; Ledger, R.A. An audit of behavioural indicators of poor welfare in kennelled dogs in the United Kingdom. J. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2005, 8, 79–95. [Google Scholar]
- Beerda, B.; Schilder, M.B.; van Hoof, J.A.; de Vries, H.W.; Mol, J.A. Behavioural and hormonal indicators of enduring environmental stress in dogs. Anim. Welf. 2000, 9, 49–62. [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy, M.B.; Morris, A.; Linden, F. Evaluation of the effects of a socialization program in a prison on behavior and pituitary-adrenal hormone levels of shelter dogs. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2006, 99, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolles, J.; Rompa-Barendregt, J.; Gispen, W.H. ACTH-induced excessive grooming in the rat: The influence of environmental and motivational factors. Horm. Behav. 1979, 12, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, A.; Poggioli, R.; Vergoni, A.V. Cross-species comparison of the ACTH-induced behavioral syndrome. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 525, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manz, A.; Wentz, A. 24-h hydration status: Parameters, epideiology and recommendations. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 57, S10–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnier, F.; Benoit, E.; Virat, M.; Ochoa, R.; Delatour, P. Adrenal cortical response in clinically normal dogs before and after adaptation to a housing environment. Lab. Anim. 1990, 24, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales, G.; Hubrecht, R.; Peyvandi, A.; Milligan, S.; Shield, B. Noise in dog kenelling: Is barking a welfare problem for dogs? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1997, 52, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, M.W. Behaviour of Wolves, Dogs and Related Canids; Dogwise Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, J.K.; Dale, A.R.; D’Eath, R.B.; Wemelsfelder, F. Welfare assessment in dogs: Reducing the invasiveness of welfare assessment methodology through trial and validation of a qualitative, behavioral-based approach. J. Vet. Behav: Clin. Appl. Res. 2009, 4, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Behaviour | Description |
|---|---|
| Lie | Part of both upper and lower body in contact with the bottom of the cage. |
| Sit | Hindquarters in contact with the bottom of the cage, front legs extended. |
| Interact with coconut or cardboard bed | Part of both upper and lower body in contact with cardboard bed, or chewing the coconut or cardboard. |
| Stand | Standing with all four paws in contact with the bottom of the cage. |
| Panting | Breathing deeply and quickly with mouth open. |
| Barking | Vocalisation, one or a series of short sharp sounds. |
| Yawn | Opens mouth wide and closes eyes. |
| Playing with bowl * | Interacting with water bowl, pushing, picking up. |
| Chewing cage * | Chewing any part of the cage. |
| Licking cage * | Licking any part of the cage. |
| Drink | Laps water. |
| Autogroom | Licks or chews part of own body. |
| Defecate * | Squats to defecate. |
| Urinate | Squats or cocks leg to urinate. |
| Walk | Ambulates at any speed. |
| Kennel rear | Stands on hind legs with forelegs against side of kennel. |
| Other | Behaviours that are not defined, especially coprophagy. |
| Day | Mean/SE | Sit | Walk | Stand | Lie | Groom | Pant | Bark | Urinate | Drink | Kennel Rear | Yawn | Interact with Coconut/Bed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First baseline | Mean | 9.37 | 8.47 | 22.01 | 38.69 | 4.10 | 8.45 | 41.03 | 0.31 | 1.28 | 4.69 | 1.34 | 0.00 |
| SE | 2.85 | 1.91 | 3.06 | 5.81 | 1.19 | 2.35 | 15.42 | 0.10 | 0.36 | 3.80 | 0.24 | 0.00 | |
| Last baseline | Mean | 6.31 | 7.20 | 22.76 | 41.83 | 1.90 | 12.70 | 69.03 | 0.33 | 0.94 | 2.81 | 1.28 | 0.00 |
| SE | 1.62 | 1.35 | 2.41 | 4.80 | 0.89 | 2.61 | 27.41 | 0.09 | 0.24 | 1.79 | 0.27 | 0.00 | |
| First treatment | Mean | 2.98 | 4.76 | 22.58 | 36.33 | 2.31 | 11.32 | 36.44 | 0.28 | 0.61 | 1.97 | 0.64 | 22.89 |
| SE | 0.88 | 1.33 | 2.61 | 4.84 | 0.77 | 2.07 | 19.41 | 0.09 | 0.18 | 1.44 | 0.23 | 3.58 | |
| Last treatment | Mean | 4.94 | 7.41 | 30.15 | 28.45 | 1.27 | 8.71 | 79.72 | 0.44 | 0.75 | 3.97 | 0.75 | 13.81 |
| SE | 1.26 | 1.59 | 3.52 | 5.01 | 0.54 | 2.24 | 29.05 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 2.39 | 0.15 | 3.91 | |
| First post-exposure | Mean | 11.82 | 5.19 | 24.75 | 45.08 | 2.36 | 4.32 | 41.92 | 0.33 | 0.42 | 1.00 | 1.14 | 0.00 |
| SE | 3.09 | 0.96 | 3.61 | 5.79 | 0.69 | 1.63 | 17.60 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.62 | 0.23 | 0.00 | |
| Last post-exposure | Mean | 5.73 | 8.43 | 26.29 | 38.57 | 1.29 | 11.22 | 88.08 | 0.67 | 0.83 | 2.39 | 1.06 | 0.00 |
| SE | 1.69 | 1.60 | 3.36 | 5.02 | 0.45 | 2.55 | 19.27 | 0.12 | 0.19 | 0.88 | 0.19 | 0.00 | |
| Total | Mean | 6.78 | 6.86 | 24.85 | 38.14 | 2.14 | 9.49 | 59.99 | 0.40 | 0.79 | 2.74 | 1.02 | 6.20 |
| SE | 0.83 | 0.60 | 1.28 | 2.13 | 0.31 | 0.93 | 9.13 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.79 | 0.09 | 1.17 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiddie, J.; Bodymore, A.; Dittrich, A. Environmental Enrichment in Kennelled Pit Bull Terriers (Canis lupus familiaris). Animals 2017, 7, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani7040027
Kiddie J, Bodymore A, Dittrich A. Environmental Enrichment in Kennelled Pit Bull Terriers (Canis lupus familiaris). Animals. 2017; 7(4):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani7040027
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiddie, Jenna, Anna Bodymore, and Alex Dittrich. 2017. "Environmental Enrichment in Kennelled Pit Bull Terriers (Canis lupus familiaris)" Animals 7, no. 4: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani7040027
APA StyleKiddie, J., Bodymore, A., & Dittrich, A. (2017). Environmental Enrichment in Kennelled Pit Bull Terriers (Canis lupus familiaris). Animals, 7(4), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani7040027





