Demographic and Life-History Responses of Rhinella arenarum to Road-Associated Environments
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Classification
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Age Determination
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
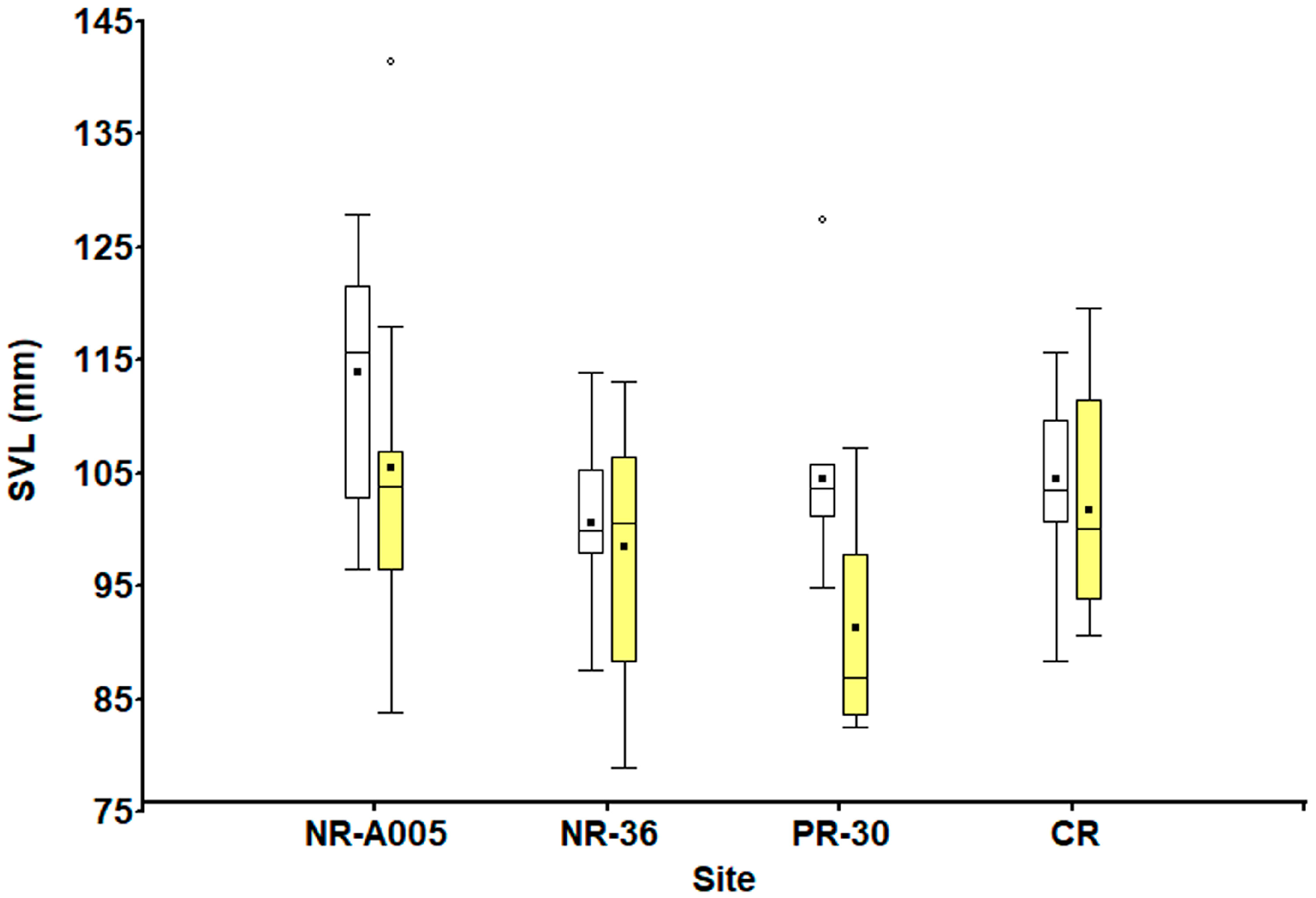
3.1. Body Size and Sexual Variation
3.2. Skeletochronology and Age Analyses
3.3. Growth Patterns
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IUCN SSC Amphibian Specialist Group. Rhinella arenarum. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2023:e.T54576A61393221. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org. (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Luedtke, J.A.; Chanson, J.; Neam, K.; Hobin, L.; Maciel, A.O.; Catenazzi, A.; Borzée, A.; Hamidy, A.; Aowphol, A.; Jean, A.; et al. Ongoing declines for the world’s amphibians in the face of emerging threats. Nature 2023, 622, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, L.F.; Potsch de Carvalho-e-Silva, S.; Paulino Telles de Carvalho-e-Silva, A.M.; Gasparini, J.L.; Baêta, D.; Rebouças, R.; Haddad, C.F.B.; Becker, C.G.; Carvalho, T. A retrospective overview of amphibian declines in Brazil’s Atlantic Forest. Biol. Conserv. 2023, 277, 109845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, S.N.; Hoffmann, M.; Chanson, J.; Cox, N.; Berridge, R.; Ramani, P.; Young, P. Threatened Amphibians of the World; Lynx Edicions: Barcelona, Spain; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland; Conservation International: Arlington, WV, USA, 2008; pp. 1–151. [Google Scholar]
- Jennette, M.A.; Snodgrass, J.W.; Forester, D.C. Variation in age, body size, and reproductive traits among urban and rural amphibian populations. Urban Ecosyst. 2019, 22, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordier, J.M.; Aguilar, R.; Lescano, J.N.; Leynaud, G.C.; Bonino, A.; Miloch, D.; Loyola, R.; Nori, J. A global assessment of amphibian and reptile responses to land-use changes. Biol. Conserv. 2021, 253, 108863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geneletti, D. Biodiversity impact assessment of roads: An approach based on ecosystem rarity. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2003, 23, 343–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibisch, P.L.; Hoffmann, M.T.; Kreft, S.; Pe’er, G.; Kati, V.; Biber-Freudenberger, L.; DellaSala, D.A.; Vale, M.M.; Hobson, P.R.; Selva, N. A global map of roadless areas and their conservation status. Science 2016, 354, 1423–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, D.J.D.; Hamer, A.J.; Preez, L.H.D. Urbanization affects frog communities at multiple scales in a rapidly developing African city. Urban Ecosyst. 2015, 18, 1333–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Carrasco, M.; Martín, J.; Cabido, C. Urban habitats can affect body size and body condition but not immune response in amphibians. Urban Ecosyst. 2017, 20, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, R.T.T.; Sperling, D.; Bissonette, J.A.; Clevenger, A.P.; Cutshall, C.D.; Dale, V.H.; Fahrig, L.; France, R.; Goldman, C.R.; Heanue, K.; et al. Road Ecology: Science and Solutions; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Eigenbrod, F.; Hecnar, S.J.; Fahrig, L. The relative effects of road traffic and forest cover on anuran populations. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevenot, L.; Carré, C.; Pech, P. A Review of the Factors That Determine Whether Stormwater Ponds Are Ecological Traps And/or High-Quality Breeding Sites for Amphibians. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Wu, Y.; Ai, R.; Tie, M.; Duan, Y.; Yuan, Z. Artificial ponds can be ecological traps for amphibians: A case study from Chuxiong Prefecture, Yunnan, China. Biol. Conserv. 2023, 279, 109945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, M.K.; Noss, R.F. Evidence for selective avoidance of traffic noise by anuran Amphibians. Anim. Conserv. 2018, 21, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, A.J.; Barta, B.; Bohus, A.; Gál, B.; Schmera, D. Roads reduce amphibian abundance in ponds across a fragmented landscape. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 28, e01663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenat, P.; Michelli, M.; Pollo, F.; Otero, M.; Baraquet, M.; Martino, A. Traffic noise and breeding site characteristics influencing assemblage composition of anuran species associated to roads. Biodivers. Conserv. 2023, 32, 1931–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Devito, J.; Jones, C.G.; Marentes, A.; Perez, R.; Umeh, L.; Weickum, R.M.; McGovern, K.E.; Wilson, E.W.; Saltzman, W. Effects of anthropogenic noise on endocrine and reproductive function in White’s treefrog, Litoria caerulea. Conserv. Physiol. 2015, 3, cou061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennessen, J.B.; Parks, S.E.; Langkilde, T. Traffic noise causes physiological stress and impairs breeding migration behaviour in frogs. Conserv. Physiol. 2014, 2, cou032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollo, F.; Bionda, C.; Baraquet, M.; Otero, M.; Martino, A.; Grenat, P. Anuran responses to urbanization: Evaluating life history traits of Rhinella arenarum in urban wetlands. Curr. Zool. 2025, 71, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, I.T.; Desrochers, L.; Giacomazzo, M.; Bertolo, A.; Bolduc, P.; Deschesnes, R.; Martin, S.A.; Rainville, V.; Rheault, G.; Proulx, R. Shifting song frequencies in response to anthropogenic noise: A meta-analysis on birds and anurans. Behav. Ecol. 2016, 27, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenat, P.; Pollo, F.; Ferrero, M.; Martino, A. Differential and additive effects of natural biotic and anthropogenic noise on call properties of Odontophrynus americanus (Anura, Odontophryinidae): Implications for the conservation of anurans inhabiting noisy environments. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 99, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenat, P.; Ferrero, M.; Baraquet, M.; Pollo, F.; Otero, M.; Salinas, Z.; Salas, N.; Martino, A. Changes in call properties of Boana pulchella (Anura, Hylidae) in response to different noise conditions. Curr. Zool. 2023, 70, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimmick, C.R.; Pelton, M.R. Criteria of sex and age. In Research and Management Techniques for Wildlife and Habitats; Hout, T.A., Ed.; The Wildlife Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1996; p. 740. [Google Scholar]
- Sinsch, U. Review: Skeletochronological assessment of demographic life-history traits in amphibians. Herpetol. J. 2015, 25, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, F.H.; Hsieh, Y.S.; Hu, S.H.; Kam, Y.C. Altitudinal variation in body size and age structure of the Sauter’s Frog Rana sauteri in Taiwan. Zool. Stud. 2014, 53, 62. Available online: http://www.zoologicalstudies.com/content/53/1/62 (accessed on 12 February 2025). [CrossRef]
- Altunışık, A.; Özdemir, N. Life history traits in Bufotes variabilis (Pallas, 1769) from 2 different altitudes in Turkey. Turk. J. Zool. 2015, 39, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.C.; Lee, T.H.; Kam, Y.C. A skeletochronological study on a subtropical, riparian ranid (Rana swinhoana) from different elevations in Taiwan. Zool. Sci. 2005, 22, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdemir, N.; Altunışık, A.; Ergül, T.; Gül, S.; Tosunoğlu, M.; Cadeddu, G.; Giacoma, C. Variation in body size and age structure among three Turkish populations of the treefrog Hyla arborea. Amphib. Reptil. 2012, 33, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturino, A.; Rosenbaum, E.; Caballero de Castro, A.; Anguiano, O.L.; Gauna, L.; Fonovich De Schroeder, T.; Pechen de D’Angelo, A.M. Biomarkers of effect in toads and frogs. Biomarkers 2003, 8, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bionda, C.L.; Lajmanovich, R.; Salas, N.E.; Martino, A.L.; di Tada, I. Demografía poblacional de Rhinella arenarum (Anura: Bufonidae) y Physalaemus biligonigerus (Anura: Leiuperidae) en agroecosistemas de la provincia de Córdoba, Argentina. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2013, 61, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bionda, C.L.; Kost, S.; Salas, N.E.; Lajmanovich, R.; Sinsch, U.; Martino, A.L. Age structure, growth and longevity in the common toad, Rhinella arenarum, from Argentina. Acta Herpetol. 2015, 10, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bionda, C.; Babini, M.S.; Martino, A.; Salas, N.; Lajmanovich, R. Impact assessment of agriculture and livestock over age, longevity and growth of populations of common toad Rhinella arenarum (Anura: Bufonidae), central area of Argentina. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 14, e00398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babini, S.; Bionda, C.; Salas, N.; Martino, A. Health status of tadpoles and metamorphs of Rhinella arenarum (Anura, Bufonidae) that inhabit agroecosystems and its implications for land use. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 118, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, F.A.S.; Clevengerb, A.P.; Griloa, C. Effects of roads on terrestrial vertebrate species in Latin America. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2020, 81, 106337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyer, W.R. Variation within the Leptodactylus podicipinuswagneri complex of frogs (Amphibia: Leptodactylidae). Smithson. Contrib. Zool. 1994, 546, 1–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cei, J.M. Amphibians of Argentina. Monit. Zool. Ital. N. S. Monografia 1980, 2, 1–609. [Google Scholar]
- Lovich, J.E.; Gibbons, J.W. A review of techniques for quantifying sexual size dimorphism. Growth Dev. Aging 1992, 56, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Green, D.E. Anesthesia of Amphibians in the Field. ARMI SOP No. 104. An Online Reference Amphibian Research & Monitoring Initiative National Wildlife Health Center 6006 Schroeder Road Madison. 2018. Available online: https://www.yumpu.com/en/document/read/22948540/anesthesia-of-amphibians-in-the417field-nationalwildlife-health (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Rozenblut, B.; Ogielska, M. Development and growth of long bones in European water frogs (Amphibia: Anura: Ranidae), with remarks on age determination. J. Morphol. 2005, 265, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.B.; Lu, X. Age structure and body size of the Chuanxi tree frog Hyla annectans chuanxiensis from two different elevations in Sichuan (China). Zool. Anz. 2010, 248, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, F.M.; De Pous, P.; Crottini, A.; Mezzasalma, M.; Andreone, F. Age structure and growth in a population of Pelobates varaldii (Anura, Pelobatidae) from northwestern Morocco. Amphib-Reptilia 2011, 32, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraquet, M.; Otero, M.; Valetti, J.A.; Grenat, P.; Martino, A. Age, body size, and growth of Boana cordobae (Anura: Hylidae) along an elevational gradient in Argentina. Herpetol. Conserv. Biol. 2018, 13, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bertalanffy, L. A quantitative theory of organic growth. Hum. Biol. 1938, 10, 181–213. [Google Scholar]
- Otero, M.; Baraquet, M.; Pollo, F.; Grenat, P.; Salas, N.; Martino, A. Sexual size dimorphism in relation to age and growth in Hypsiboas cordobae (Anura: Hylidae) from Córdoba, Argentina. Herpetol. Conserv. Biol. 2017, 12, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Otero, M.A.; Valetti, J.A.; Bionda, C.L.; Salas, N.E.; Martino, A.L. Are ploidy and age size-related? A comparative study on tetraploid Pleurodema kriegi and octoploid P. cordobae (Anura: Leptodactylidae) from Central Argentina. Zool. Anz. 2017, 268, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraquet, M.; Pollo, F.E.; Otero, M.; Grenat, P.; Salas, N.E.; Martino, A. Body size, age and growth in males populations of Boana pulchella (Anura, Hylidae). An. Acad. Bras. Ciênc. 2021, 93, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, M.A.; Pollo, F.; Grenat, P.R.; Salas, N.E.; Martino, A.L. Differential effects on life history traits and body size of two anuran species inhabiting an environments related to fluorite mine. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, S.; Zamora-Camacho, F.; Eriksson, F.A.A.; Goeder, D.; Comas, M.; Calsbeek, R. Fitter frogs from polluted ponds: The complex impacts of human-altered environments. Evol. Appl. 2018, 2, 1360–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinsch, U.; Hecht, K.; Kost, S.; Grenat, P.R.; Martino, A.L. Asymmetric Male Mating Success in Lek-Breeding Rhinella arenarum. Animals 2022, 12, 3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, J.; Naretto, S.; Carezzano, F.; Quinzio, S. Sexual Size Dimorphism in Multiple Traits: An Integrative Perspective in Several Anuran Species. J. Herpetol. 2024, 58, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arantes, I.C.; Vasconcellos, M.M.; Boas, T.C.V.; Veludo, L.B.A.; Colli, G.R. Sexual Dimorphism, Growth, and Longevity of Two Toad Species (Anura, Bufonidae) in a Neotropical Savanna. Copeia 2015, 103, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matías-Ferrer, N.; Escalante, P. Size, body condition, and limb asymmetry in two hylid frogs at different habitat disturbance levels in Veracruz, México. Herpetol. J. 2015, 25, 169–176. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Shu, X.; Pei, E.; Yuan, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z. The Impacts of Urbanization on the Distribution and Body Condition of the Rice-paddy Frog (Fejervarya multistriata) and Gold-striped Pond Frog (Pelophylax plancyi) in Shanghai, China. Asian Herpetol. Res. 2016, 7, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogălniceanu, D.; Stănescu, F.; Székely, D.; Topliceanu, T.-S.; Iosif1, R.; Székely, P. Age, size and body condition do not equally reflect population response to habitat change in the common spadefoot toad Pelobates fuscus. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettencourt-Amarante, S.; Abensur, R.; Furet, R.; Ragon, C.; Herrel, A. Do human-induced habitat changes impact the morphology of a common amphibian, Bufo bufo? Urban Ecosyst. 2025, 28, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffers, B.R.; Paszkowski, C.A. Large body size for metamorphic wood frogs in urban stormwater wetlands. Urban Ecosyst. 2016, 19, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, T.R.; Verrell, P.A. Body size and age in amphibians and reptiles. J. Herp. 1988, 22, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, T.A.; Juncá, F.A. Effects of temperature and volume of water on the growth and development of tadpoles of Pleurodema diplolister and Rhinella granulosa (Amphibia: Anura). Zoologia 2009, 26, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orton, F.; Routledge, E. Agricultural intensity in ovo affects growth, metamorphic development and sexual differentiation in the Common toad (Bufo bufo). Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babini, M.S.; Bionda, C.L.; Salas, N.E.; Martino, A.L. Adverse effect of agroecosystem pond water on biological endpoints of common toad (Rhinella arenarum) tadpoles. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, M.A.; Grenat, P.R.; Pollo, F.; Baraquet, M.; Martino, A.L. Effect on growth and development of common toad (Rhinella arenarum) tadpoles in environment related to fluorite mine. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollo, F.E.; Grenat, P.R.; Otero, M.A.; Salas, N.E.; Martino, A.L. Assessment in situ of genotoxicity in tadpoles and adults of frog Hypsiboas cordobae (Barrio 1965) inhabiting aquatic ecosystems associated with fluorite mine. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 133, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga, L.B.; Sanabria, E.A.; Acosta, J.C. Size- and Sex-Dependent variation in diet of Rhinella arenarum (Anura: Bufonidae) in a wetland of San Juan, Argentina. J. Herpetol. 2009, 43, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyrea, N.E.; Rangob, J.; Faganb, W.F.; Faethb, S.H. Ground arthropod community structure in a heterogeneous urban environment. Landsc. Urban Plann. 2001, 52, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komine, H.; Koike, S.; Schwarzkopf, L. Impacts of artificial light on food intake in invasive toads. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duellman, W.E.; Trueb, L. Biology of Amphibians; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Buono, V.; Guarino, F.M.; Vignoli, L. Maximum body size and age distribution in the Italian Stream Frog, Rana italica Dubois 1987 (Amphibia: Anura). Acta Herpetol. 2014, 9, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, F.M.; Erismis, U.C. Age determination and growth by skeletochronology of Rana holtzi, an endemic frog from Turkey. Ital. J. Zool. 2008, 75, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, M.; Sánchez-Herráiz, M.J.; Barbadillo, L.J.; Castanet, J.; Márquez, R. Effect of age, size and temperature on the advertisement calls of two Spanish populations of Pelodytes punctatus. Amphib-Reptilia 2002, 23, 249–258. [Google Scholar]
- Zamora-Camacho, F.J.; Comas, M. Greater reproductive investment, but shorter lifespan, in agrosystem than in natural-habitat toads. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babini, M.S.; Bionda, C.L.; Martino, A.L.; Peltzer, P.M. Impacts of horticultural environments on Rhinella arenarum (Anura, Bufonidae) populations: Exploring genocytotoxic damage and demographic life history traits. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 21235–21248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beebee, T.J.C. Effects of Road Mortality and Mitigation Measures on Amphibian Populations. Conserv. Biol. 2013, 27, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shu, G.; Li, Y.; Xiong, S.; Liang, C.; Li, C. Daytime driving decreases amphibian roadkill. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirose, L.J.; Brooks, R.J.; Barta, J.R.; Desser, S.S. Intersexual differences in growth, mortality and size at maturity in bullfrogs in central Ontario. Can. J. Zool. 1993, 71, 2363–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkwood, T.B.L.; Austad, S.N. Why do we age? Nature 2000, 408, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsch, U.; Leskovar, C.; Drobig, A.; König, A.; Grosse, W.-R. Life-history traits in green toad (Bufo viridis) populations: Indicators of habitat quality. Can. J. Zool. 2007, 85, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miaud, C.; Guyetant, R.; Faber, H. Age, size, and growth of the Alpine newt, Triturus alpestris (Urodela: Salamandridae), at high altitude and a review of life-history trait variation throughout its range. Herpetologica 2000, 56, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Oromia, N.; Sanuya, D.; Sinsch, U. Altitudinal variation of demographic life-history traits does not mimic latitudinal variation in natterjack toads (Bufo calamita). Zoology 2012, 115, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, F.M.; Crottini, A.; Mezzasalma, M.; Randrianirina, J.E.; Andreone, F. A skeletochronological estimate of age and growth in a large riparian frog from Madagascar (Anura, Mantellidae, Mantidactylus). Herpetozoa 2019, 32, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogălniceanu, D.; Miaud, C. Population age structure and growth in four syntopic amphibian species inhabiting a large river floodplain. Can. J. Zool. 2003, 81, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturra-Cid, M.; Ortiz, J.C.; Ibargüengoytía, N.R. Age, size, and growth of the Chilean frog Pleurodema thaul (Anura: Leiuperidae): Latitudinal and altitudinal effects. Copeia 2010, 2010, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogălniceanu, D.; Roşioru, D.; Székely, P.; Buhaciuc, E.; Stănescu, F.; Miaud, C. Age and body size in populations of two syntopic spadefoot toads (genus Pelobates) at the limit of their ranges. J. Herpetol. 2014, 48, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangoni, F.; Tejedo, M.; Cogălniceanu, D. Can age and growth patterns explain the geographical variation in the body size of two toad species? An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2021, 93, e20190470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, D.A. Skeletochronological assessment of age structure and population stability for two threatened frog species. Aust. J. Ecol. 1999, 24, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Males | Females | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR-A005 n = 12 | NR-36 n = 7 | PR-30 n = 9 | CR n = 11 | NR-A005 n = 12 | NR-36 n = 7 | PR-30 n = 10 | CR n = 11 | |
| Urbanization categories | High | Medium-High | Medium-Low | Urban open space | High | Medium-High | Medium-Low | Urban open space |
| SVL (mm) | 105.44 ± 14.67 (83.87–141.41) | 98.38 ± 10.63 (78.88–113.09) | 91.26 ± 8.96 (82.45–107.17) | 101.77 ± 9.65 (90.66–119.6) | 113.94 ± 10.74 (96.56–127.83) | 100.53 ± 7.95 (87.5–113.87) | 103.52 ± 11.14 (87.25–127.5) | 104.53 ± 97.55 (88.38–114.7) |
| Age (years) | 3.67 ± 0.89 | 4.28 ± 0.48 | 3.12 ± 0. 35 | 4.18 ± 0.87 | 3.90 ± 0.83 | 4.28 ± 0.75 | 3.6 ± 0.51 | 4.18 ± 0.98 |
| Longevity (years) | 5 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 6 |
| Age at sexual maturity (years) | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| Potential reproductive lifespan (years) | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 |
| Modal age | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| SVL at sexual maturity (mm) | 105.67 | 93.77 | 93.16 | 93.32 | 112. 92 | 99.9 | 101.8 | 88.38 |
| SVLmax (mm) | 109.67 ± 7.16 (94.67–124.66) | 100.33 ± 4.69 (90.27–110.4) | 97.47 ± 5.52 (83.42–106.84) | 108.17 ± 4.36 (99–117.34) | 118.5 ± 6.07 (105.75–131.25) | 104.68 ± 3.78 (96.58–112.79) | 111.15 ± 7.73 (94.66–127.64) | 108.31 ± 1.98 (104.15–112.47) |
| K | 0.95 ± 0.37 (0.16–1.73) | 0.80 ± 0.22 (0.32–1.28) | 0.93 ± 0.26 (0.33–1.05) | 0.95 ± 0.16 (0.41–1.09 | 0.85 ± 0.24 (0.34–1.36) | 0.80 ± 0.16 (0.44–1.16) | 0.81 ± 0.29 (0.18–1.44) | 0.93 ± 0.12 (0.69–1.17) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baraquet, M.; Pollo, F.; Otero, M.; Martino, A.; Grenat, P. Demographic and Life-History Responses of Rhinella arenarum to Road-Associated Environments. Animals 2025, 15, 1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091343
Baraquet M, Pollo F, Otero M, Martino A, Grenat P. Demographic and Life-History Responses of Rhinella arenarum to Road-Associated Environments. Animals. 2025; 15(9):1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091343
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaraquet, Mariana, Favio Pollo, Manuel Otero, Adolfo Martino, and Pablo Grenat. 2025. "Demographic and Life-History Responses of Rhinella arenarum to Road-Associated Environments" Animals 15, no. 9: 1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091343
APA StyleBaraquet, M., Pollo, F., Otero, M., Martino, A., & Grenat, P. (2025). Demographic and Life-History Responses of Rhinella arenarum to Road-Associated Environments. Animals, 15(9), 1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091343







