Disorders of the Female Reproductive Tract in Chelonians: A Review
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Anatomy of the Female Reproductive System
1.2. Reproductive Physiology and Endocrinology
- Quiescent phase: there is no follicular development in the ovaries due to immaturity or hibernation.
- Folliculogenesis phase: The ovary matures and follicles develop under hormonal stimulation. The follicles can be distinguished as primordial, primary, secondary, or tertiary according to their developing stage [15]; in Trachemys scripta and Trachemys venusta, four classes of follicles were described and defined according to their diameter as follows: Class I (≤6 mm), Class II (7–13 mm), Class III (14–20 mm), and Class IV (≥21 mm) [16,17,18]. Under FSH stimulation, the follicles produce estradiol, with only some follicles ovulating while others undergo atresia [1].
- 3.
- Fertilization and pregnancy: After ovulation, the oocyte and the sperm meet inside the oviduct, which secretes progesterone to maintain pregnancy. The yolk and eggshell form as the egg progresses, with subsequent shell calcification.
- 4.
- Oviposition: Calcified eggs remain in the oviduct before being laid, with the duration varying by species; some species can retain them for up to 4–6 months [6,8]. This period may lengthen if environmental conditions are unfavorable for laying or if the animal has a concurrent pathological condition [6,8].
2. Clinical Examination
2.1. Collateral Tests
2.1.1. Hematology and Biochemistry
2.1.2. Blood Biochemistry Values
2.1.3. Hematological Findings
2.1.4. Cytology
2.1.5. Histopathology
2.1.6. Parasitology
2.1.7. Microbiology and Virology
2.2. Diagnostic Imaging of the Female Reproductive Apparatus
2.2.1. Ultrasound
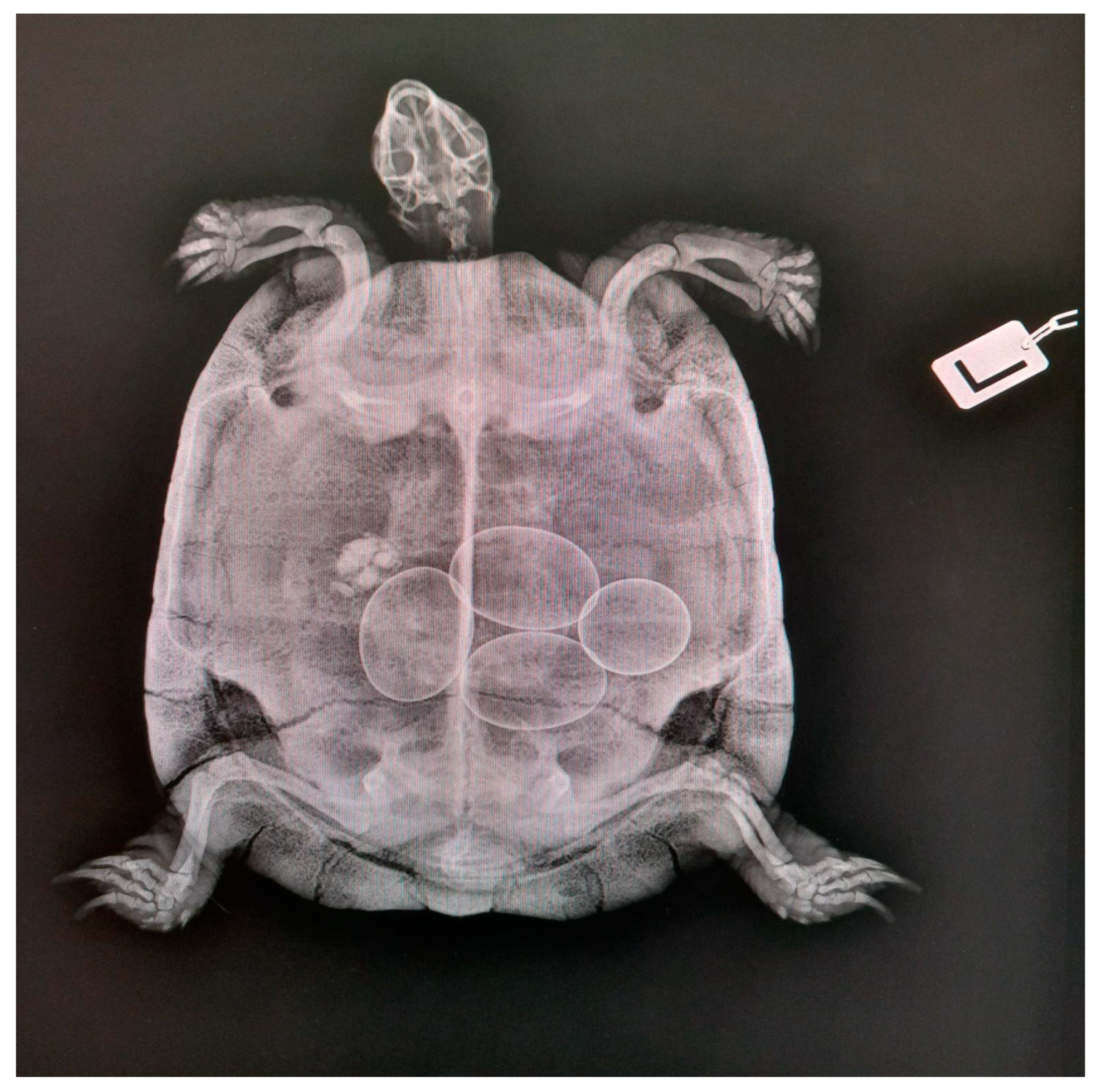
2.2.2. Radiology
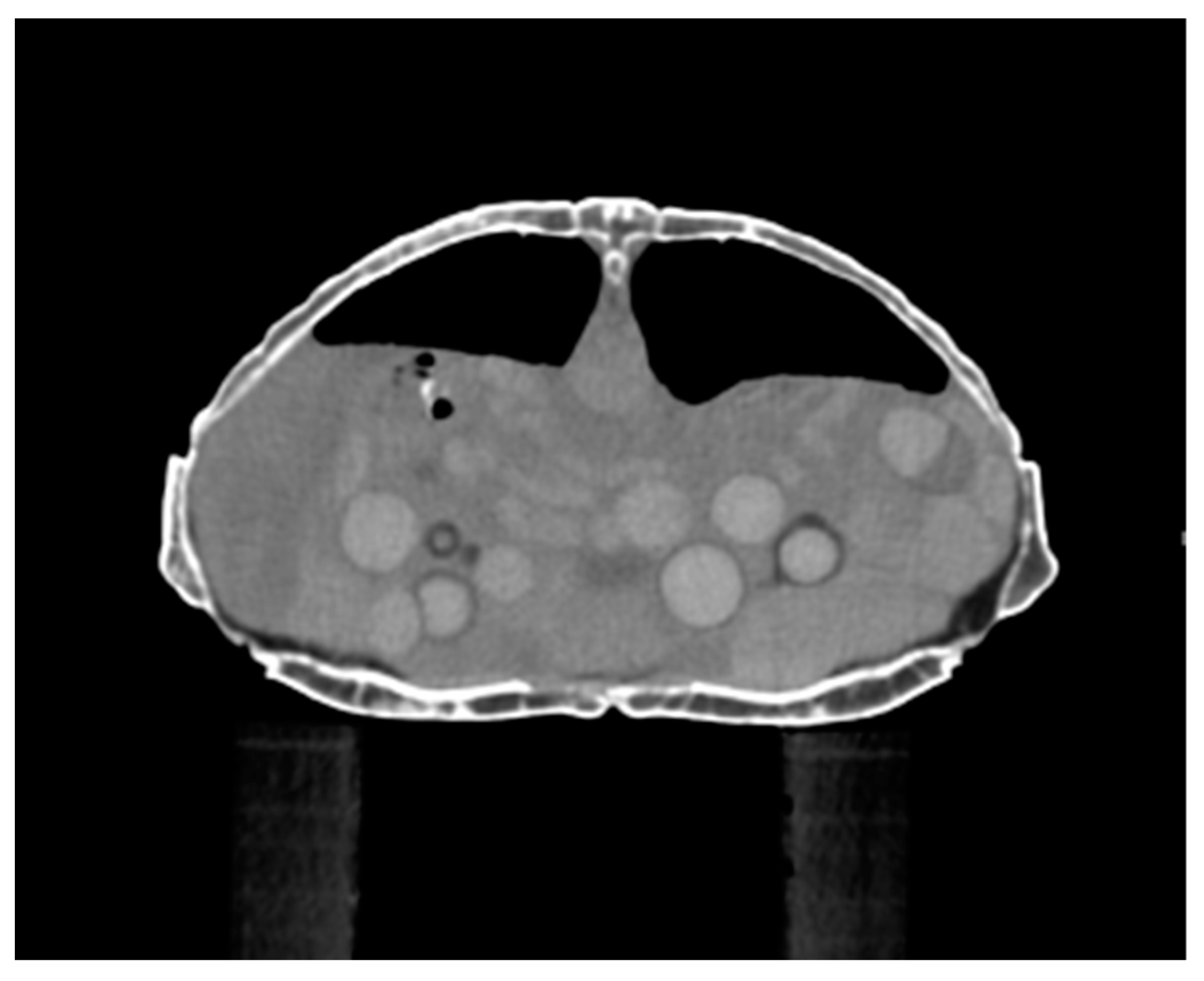
2.2.3. Computed Tomography
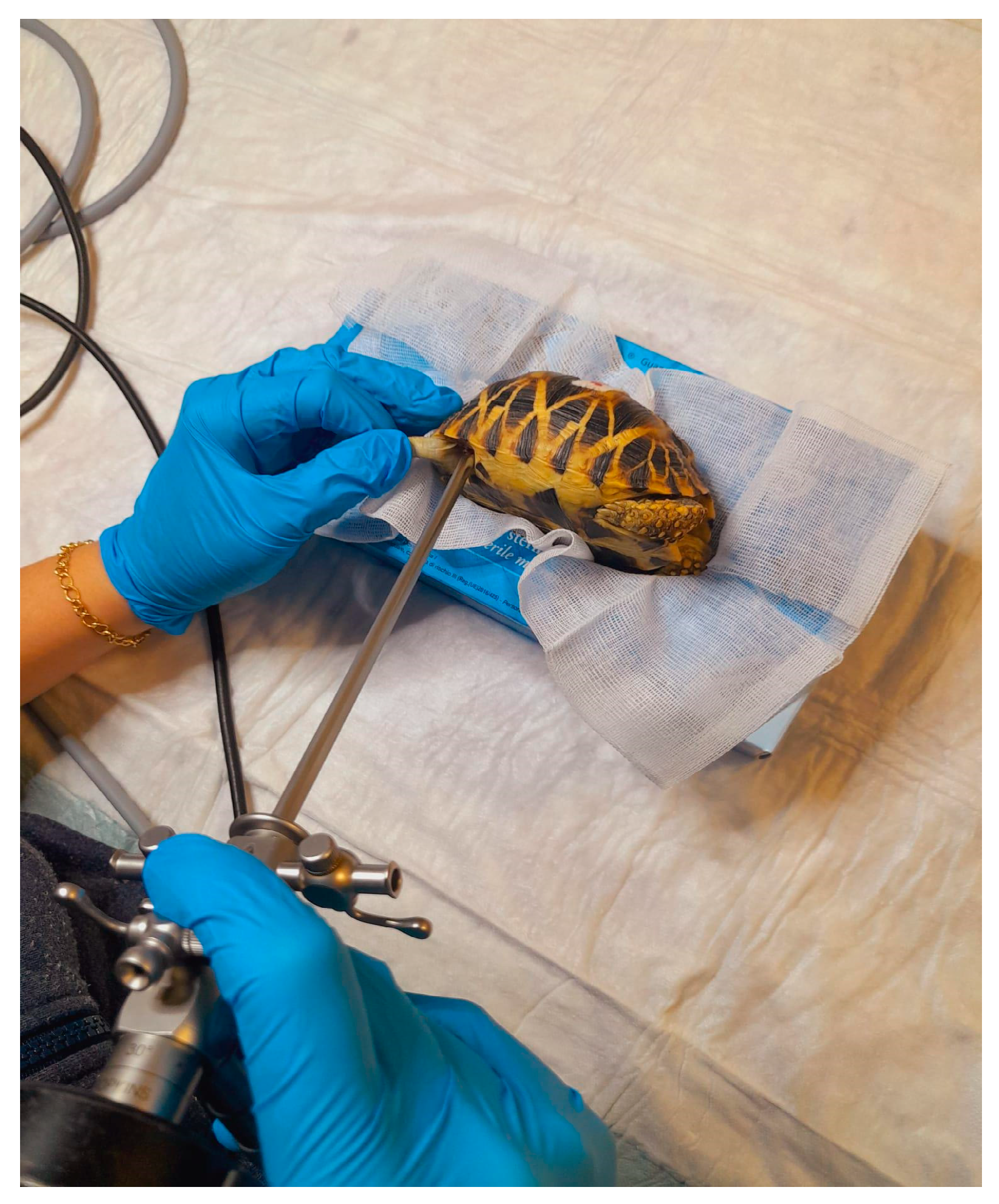
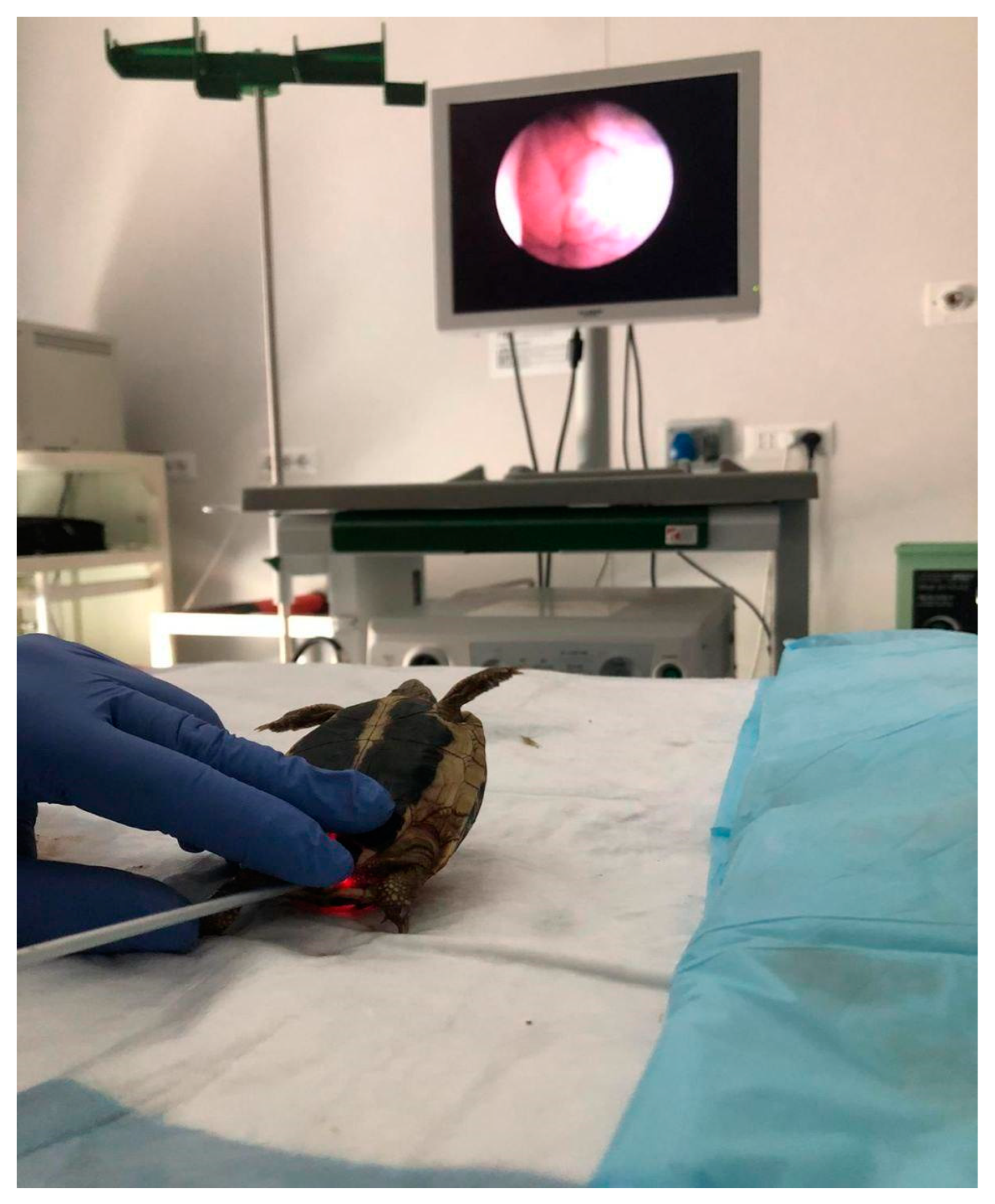
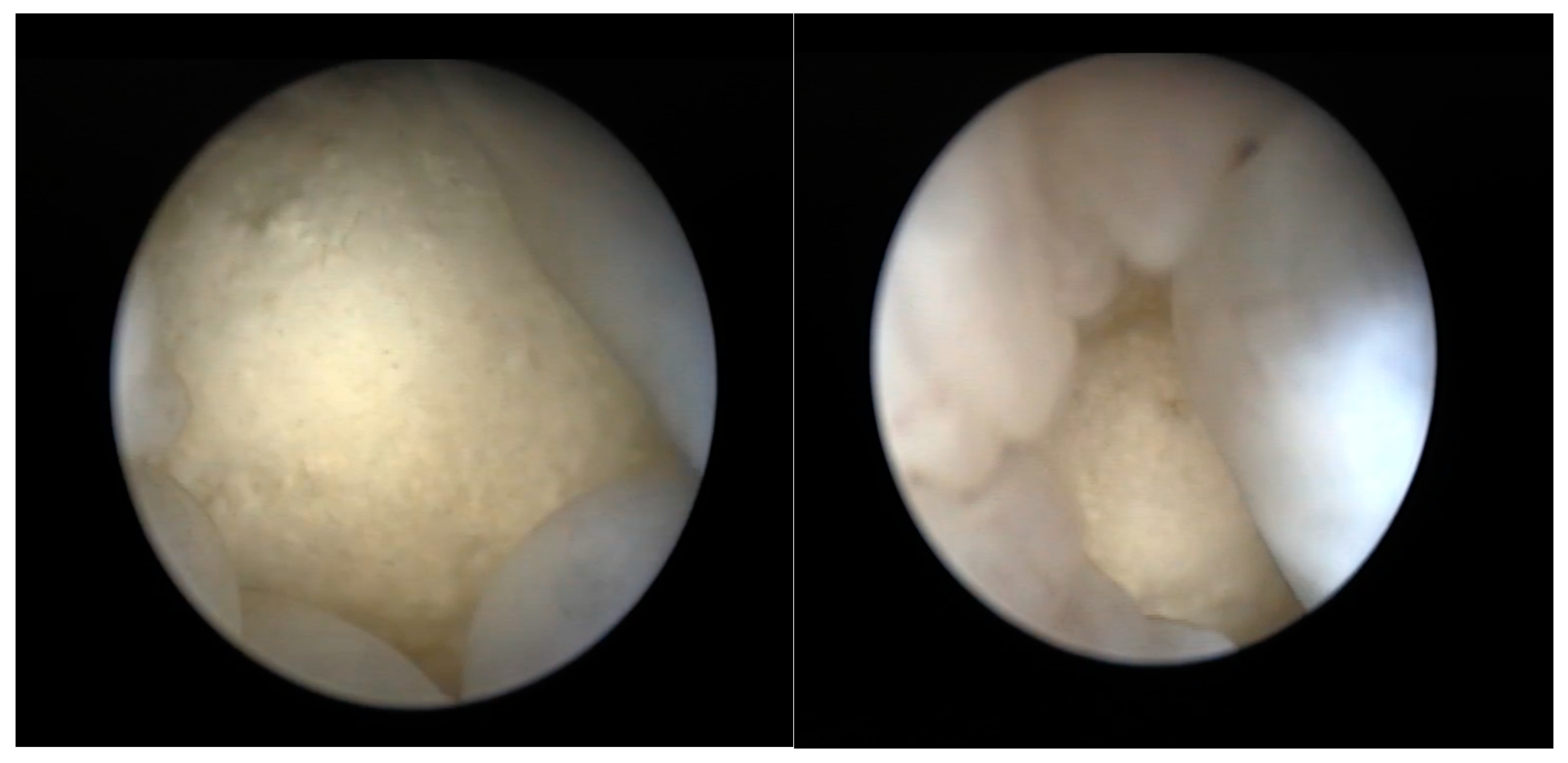
2.2.4. Coelioscopy
2.2.5. Cloacoscopy
3. Main Medical Techniques
3.1. Oxytocin Therapy
3.2. Other Therapies
4. Surgical Techniques
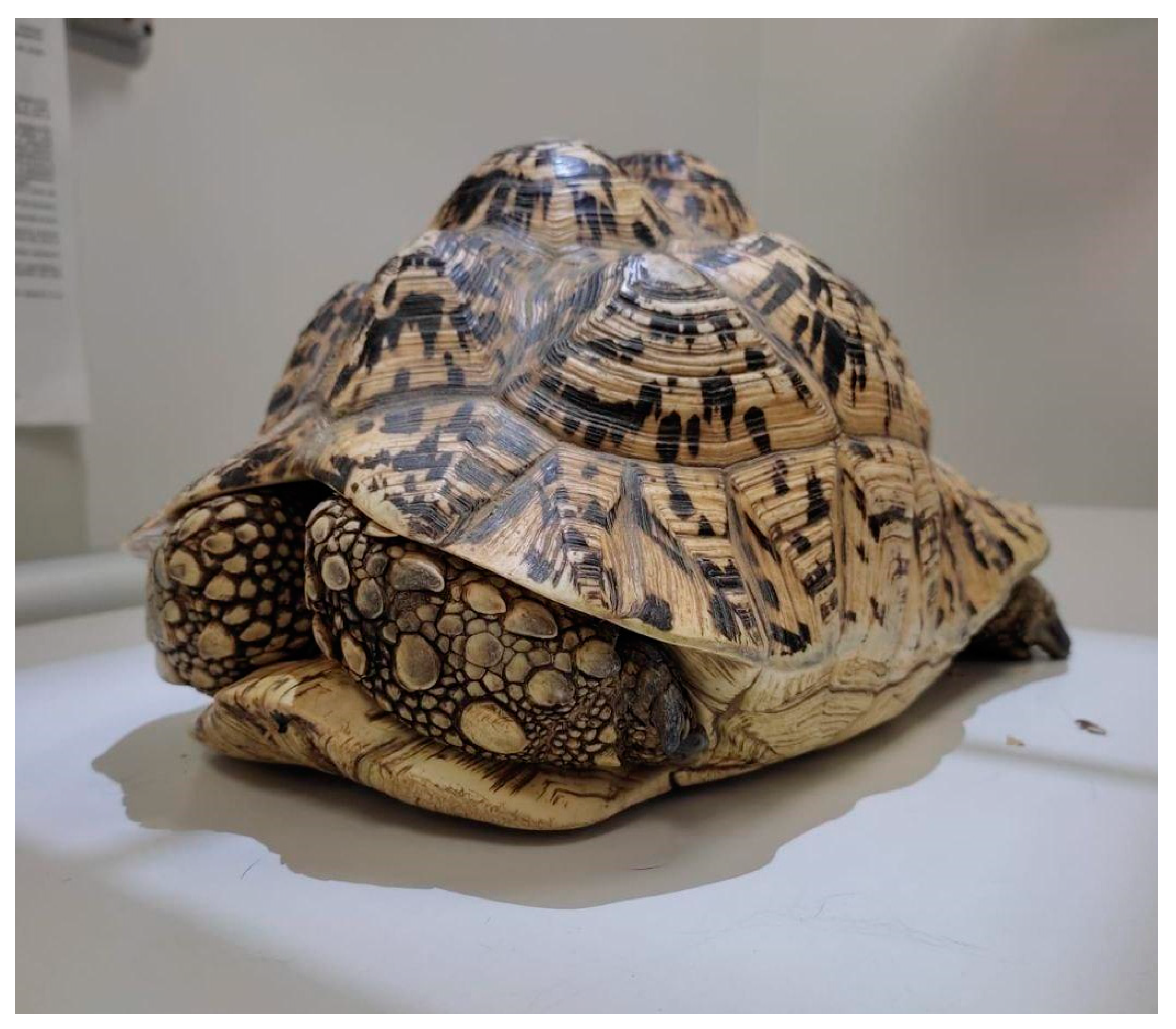
5. Diseases of the Reproductive System
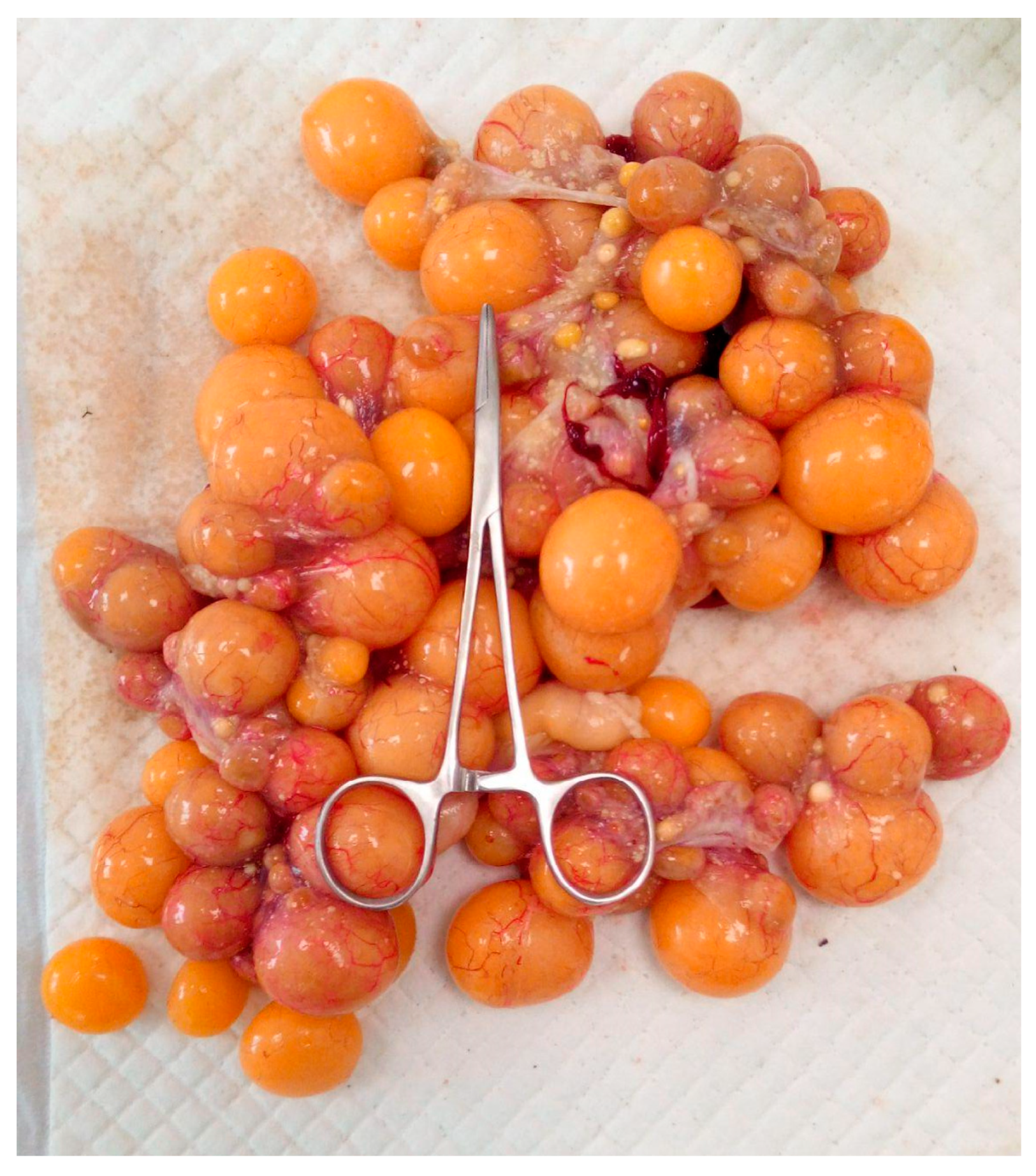
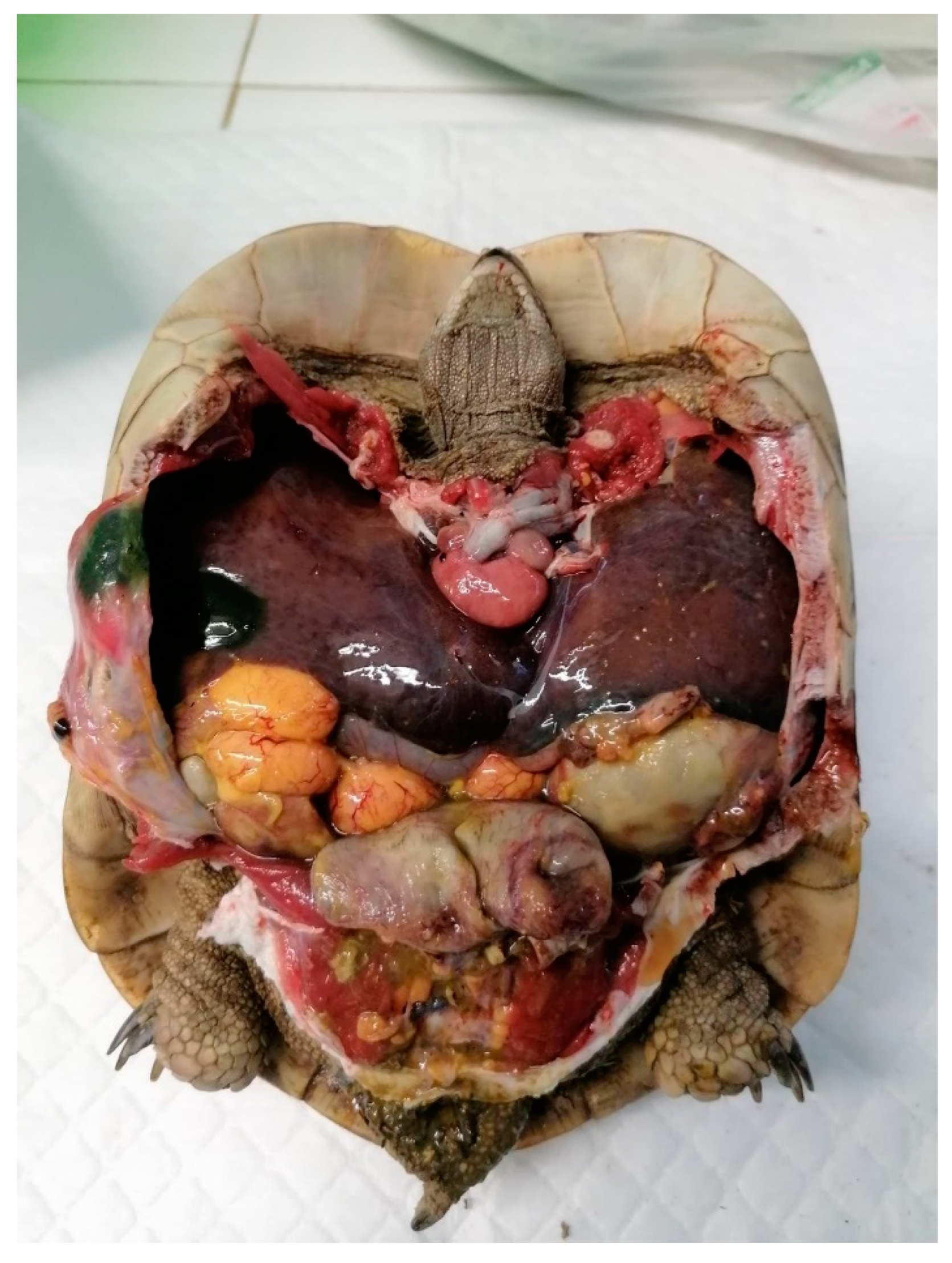
5.1. Preovulatory Follicular Stasis (PFS)
5.1.1. Causes
5.1.2. Clinical Signs
5.1.3. Diagnosis
5.1.4. Treatment
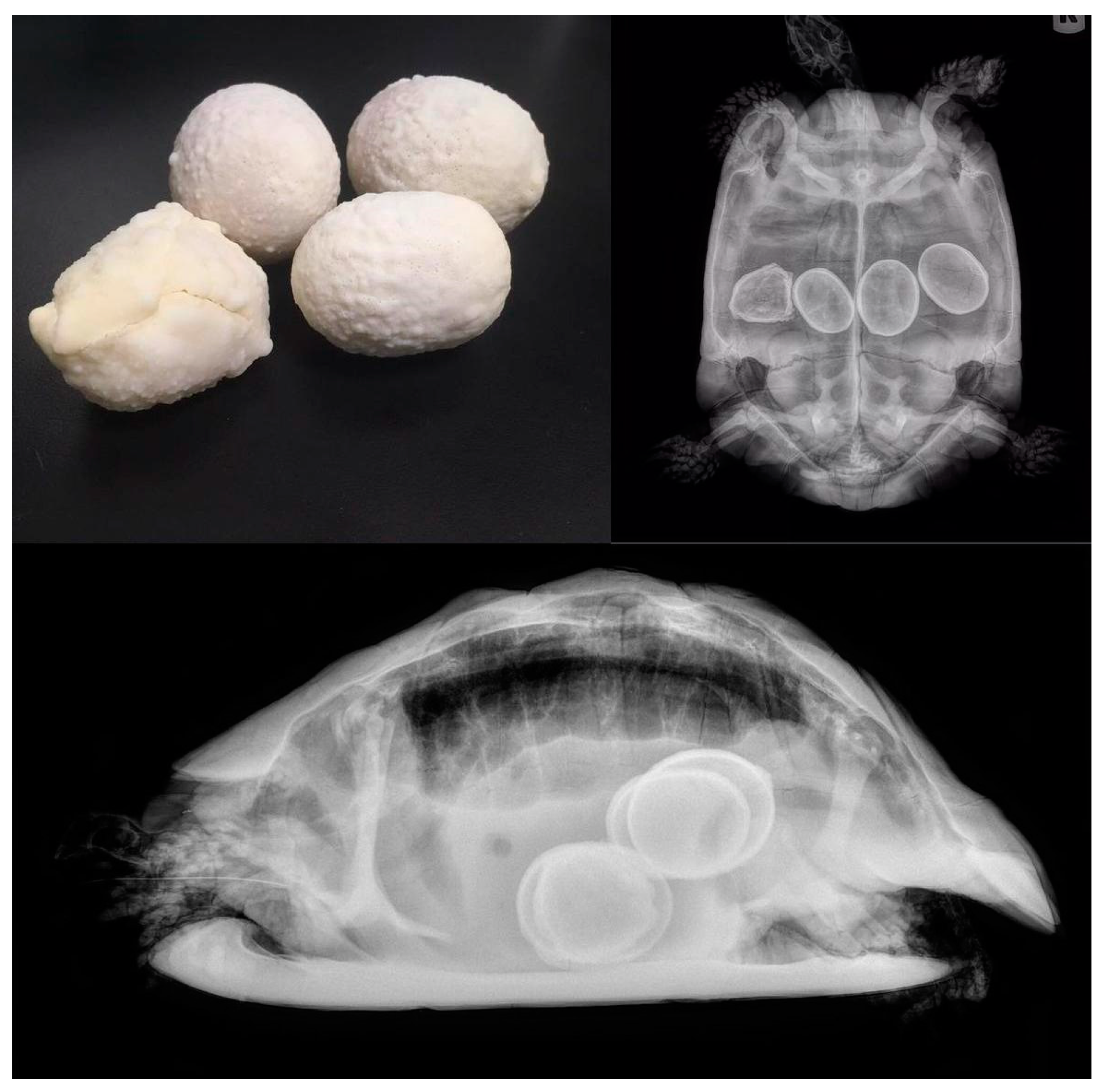
5.2. Dystocia
5.2.1. Causes
5.2.2. Clinical Signs
5.2.3. Diagnosis
5.2.4. Treatment
5.3. Oophoritis
5.4. Salpingitis
5.4.1. Causes
5.4.2. Clinical Signs
5.4.3. Diagnosis
5.4.4. Treatment
5.5. Cloacitis
5.5.1. Causes
5.5.2. Clinical Signs
5.5.3. Diagnosis
5.5.4. Treatment
5.6. Egg Yolk Coelomitis
5.6.1. Causes
5.6.2. Clinical Signs
5.6.3. Diagnosis
5.6.4. Treatment
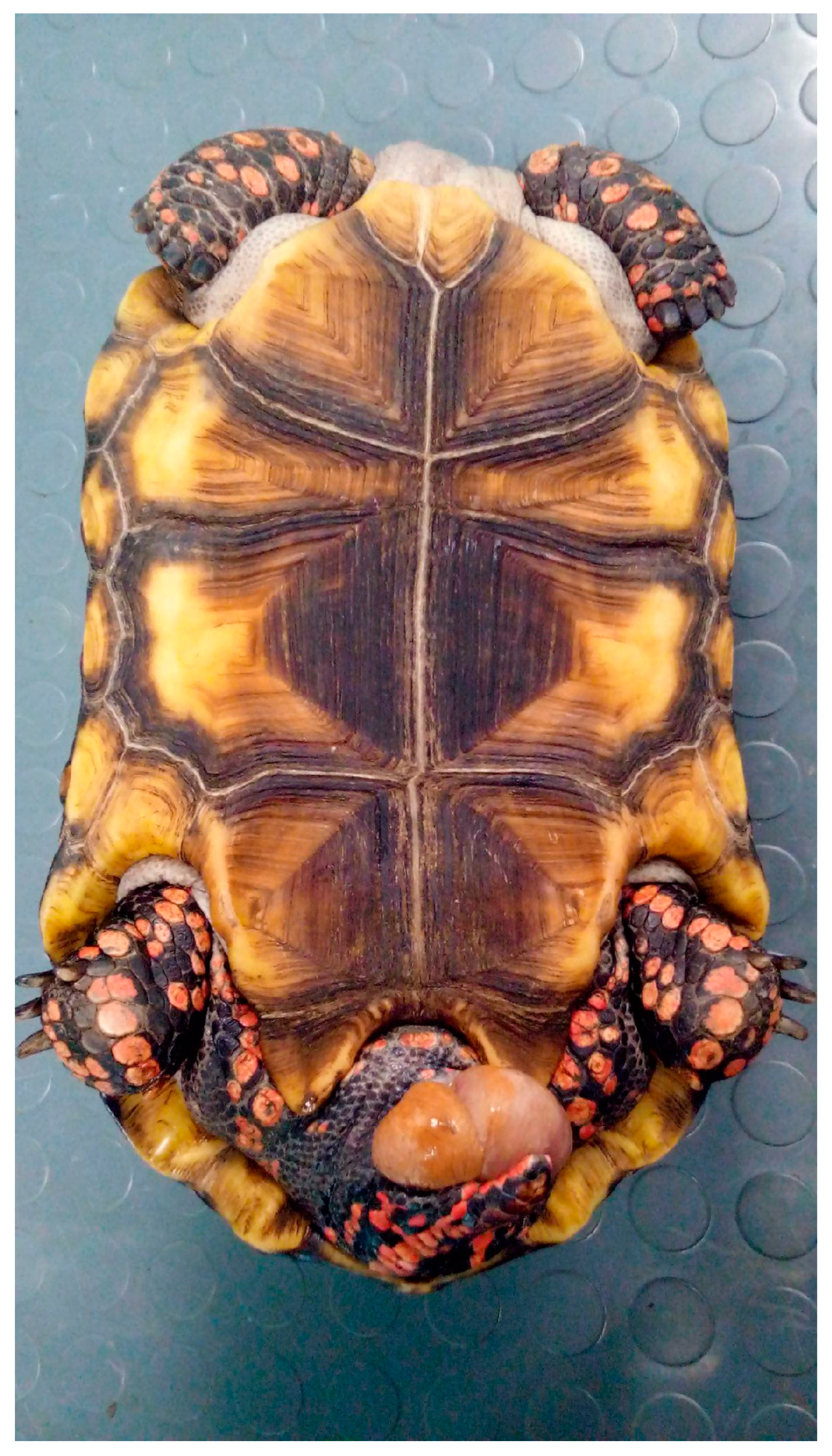
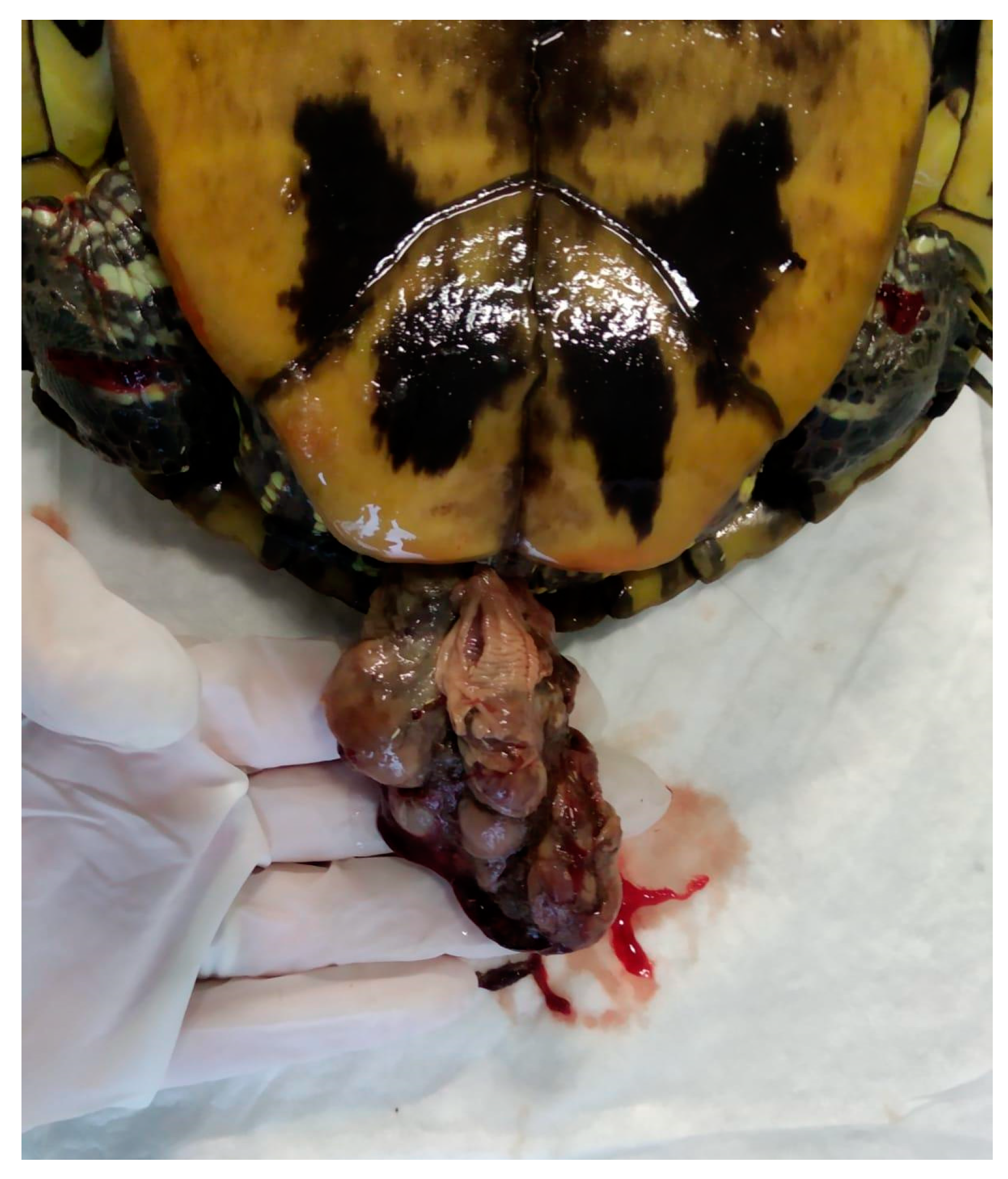
5.7. Oviductal/Cloacal Prolapse
5.7.1. Causes
5.7.2. Clinical Signs
5.7.3. Diagnosis
5.7.4. Treatment
5.8. Infertility
5.8.1. Clinical Signs
5.8.2. Diagnosis
5.9. Neoplasia
5.9.1. Causes
5.9.2. Clinical Signs
5.9.3. Diagnosis and Treatment
5.10. Ovarian Torsion
Diagnosis and Treatment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Innis, C.J.; Boyer, T.H. Chelonian reproductive disorders. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2002, 5, 555–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frye, F.L. Biomedical and Surgical Aspects of Captive Reptile Husbandry. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 1991, 1, 521–550. [Google Scholar]
- Cagle, K.R.; Lammers, T. Reproductive Diseases in Chelonians. J. Exot. Pet Med. 2017, 26, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Galli, P. Pathologies and Environmental Factors in Chelonian Reproduction: An Overview. Eur. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 24, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, D.L.; Semrad, S.D. Clinical Management of Reproductive Disorders in Reptiles: Environmental Considerations and Treatment Options. J. Herpetol. Med. Surg. 2014, 24, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, S.M.; Mitchell, M.A. Reproductive medicine in freshwater turtles and land tortoises. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2017, 20, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, J.S. Anatomy of the Tortoise; Bibliomania: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, S. Health assessment of the reptilian reproductive tract. J. Exot. Pet Med. 2008, 17, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, T.H.; Boyer, D.M. Tortoises, freshwater turtles, and terrapins. In Mader’s Reptile and Amphibian Medicine and Surgery; Mader, D.R., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2019; pp. 168–179. [Google Scholar]
- Morici, M.; Spadola, F. First evaluation of colonoscopy in Chinese soft-shell turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). Russ. J. Herpetol. 2015, 22, 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Spadola, F.; Insacco, G. Endoscopy of cloaca in 51 Emys trinacris (Fritz et al., 2005): Morphological and diagnostic study. Acta Herpetol. 2009, 4, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadola, F.; Morici, M.; Santoro, M.; Oliveri, M.; Insacco, G. Reproductive disorders and perinatology of sea turtles. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2017, 20, 345–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halámková, L.; Schulte, J.A.; Langen, T.A. Patterns of sexual size dimorphism in chelonia. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2013, 108, 396–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovich, J.E.; Garstka, W.R.; Cooper, W.E. Female participation in courtship behavior of the turtle Trachemys s. scripta. J. Herpetol. 1990, 24, 422–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanvillain, G.; Owens, D.W.; Kuchling, G. Hormones and reproductive cycles in turtles. In Hormones and Reproduction of Vertebrates; Norris, D.O., Lopez, K.H., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2011; pp. 277–303. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, C.H.; Lovich, J.E. Turtles of the United States and Canada; The John Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Moll, E.O.; Legler, J.M. The Life History of a Neotropical Slider Turtle, Pseudemys scripta (Schoepff), in Panama; Bulletin of the Los Angeles County Museum of Natural History Science: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1971; Volume 11, pp. 1–102. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Santigosa, N.; Díaz-Paniagua, C.; Hidalgo-Vila, J. The reproductive ecology of exotic Trachemys scripta elegans in an invaded area of southern Europe. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2008, 18, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, D. Reptilian reproduction, overview. In Encyclopedia of Reproduction; Skinner, M.K., Ed.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998; pp. 254–265. [Google Scholar]
- McArthur, S.; Wilkinson, R.; Meyer, J. Anatomy and physiology. In Medicine and Surgery of Tortoises and Turtles; McArthur, S., Wilkinson, R., Meyer, J., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2004; pp. 35–72. [Google Scholar]
- Gist, D.H.; Congdon, J.D. Oviductal sperm storage as a reproductive tactic of turtles. J. Exp. Zool. 1998, 282, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbraith, D.A. Multiple paternity and sperm storage in turtles. Herpetol. J. 1993, 3, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, S.; Sarkar, N.K.; Maiti, B.R. Oviductal sperm storage structure and their changes during the seasonal (dissociated) reproductive cycle in the soft-shelled turtle Lissemys punctata punctata. J. Exp. Zool. A Comp. Exp. Biol. 2003, 295, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitayama, C.; Tomiyasu, J.; Bochimoto, H.; Kondo, S.; Tokuda, K.; Ogawa, R.; Okubo, S.; Kondoh, D. Histological findings of sperm storage in green turtle (Chelonia mydas) oviduct. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, B.D.; Guillette, L.J. Histology and functional morphology of the female reproductive tract of the tortoise Gopherus polyphemus. Am. J. Anat. 1988, 183, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearse, D.E.; Avise, J.C. Turtle mating systems: Behavior, sperm storage, and genetic paternity. J. Hered. 2001, 92, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Métrailler, S. Elevage et reproduction de Platemys platycephala (Schneider, 1792). Manouria 2001, 4, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Iverson, J.; Barthelmess, E.; Smith, G.; DeRivera, C. Growth and reproduction in the mud turtle Kinosternon hirtipes in Chihuahua, Mexico. J. Herpetol. 1991, 25, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovich, J.E.; Madrak, S.V.; Drost, C.A.; Monatesti, A.J.; Casper, D.; Znari, M. Optimal egg size in a suboptimal environment: Reproductive ecology of female Sonora mud turtles (Kinosternon sonoriense) in central Arizona, USA. Amphib.-Reptil. 2012, 33, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, D.A. Forecasting the viability of sea turtle eggs in a warming world. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrad, J.; Wyneken, J.; Garner, J.; Garner, S. Experimental study of dune vegetation impact and control on leatherback sea turtle Dermochelys coriacea nests. Endanger. Species Res. 2011, 15, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, S.; Wilkinson, R.; Meyer, J.; Wilkinson, R. Clinical pathology. In Medicine and Surgery of Tortoises and Turtles; McArthur, S., Wilkinson, R., Meyer, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 141–186. [Google Scholar]
- McArthur, S.; Wilkinson, R.; Meyer, J.; Wilkinson, R.; Stephen, H.D.; Lafortune, M.; Calvert, I.; Gumpenberger, M.; McArthur, S. Diagnostic imaging techniques. In Medicine and Surgery of Tortoises and Turtles; McArthur, S., Wilkinson, R., Meyer, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 187–238. [Google Scholar]
- Sykes, J.M. Updates and practical approaches to reproductive disorders in reptiles. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2010, 13, 349–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, S. Follicular stasis in captive chelonians, Testudo spp. In Proceedings of the Association of Reptilian and Amphibian Veterinarians, Orlando, FL, USA, 13–17 January 2001; pp. 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Di Girolamo, N. Relationship, difference, and diagnostic discordance between blood ionized and total calcium concentrations in client-owned chelonians. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2022, 260, S101–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellebuyck, T.; Vilanova, F.S. The use of prefemoral endoscope-assisted surgery and transplastron coeliotomy in chelonian reproductive disorders. Animals 2022, 12, 3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Vila, J.; Martínez-Silvestre, A.; Díaz-Paniagua, C. Benign ovarian teratoma in a red-eared slider turtle (Trachemys scripta elegans). Vet. Rec. 2006, 159, 122–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirama, S.; Ehrhart, L.M.; Rea, L.D.; Kiltie, R.A. Relating fibropapilloma tumor severity to blood parameters in green turtles Chelonia mydas. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2014, 111, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page-Karjian, A.; Whitmore, L.; Stacy, B.A.; Perrault, J.R.; Farrell, J.A.; Shaver, D.J.; Walker, J.S.; Frandsen, H.R.; Rantonen, E.; Harms, C.A.; et al. Fibropapillomatosis and Chelonid alphaherpesvirus 5 infection in kemp’s ridley sea turtles (Lepidochelys kempii). Animals 2021, 11, 3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Work, T.M.; Balazs, G.H.; Rameyer, R.A.; Morris, R.A. Retrospective pathology survey of green turtles Chelonia mydas with fibropapillomatosis in the Hawaiian Islands, 1993–2003. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2004, 62, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Work, T.M.; Balazs, G.H. Relating tumor score to hematology in green turtles with fibropapillomatosis in Hawaii. J. Wildl. Dis. 1999, 35, 804–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheelings, T.F.; Rafferty, A.R. Hematologic and serum biochemical values of gravid freshwater Australian chelonians. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, T.W. Clinical pathology of reptiles. In Reptile Medicine and Surgery; Mader, D.R., Ed.; Elsevier: St Louis, MO, USA, 2006; pp. 453–470. [Google Scholar]
- Marschang, R.E.; Pasmans, F.; Hyndman, T.; Mitchell, M.; Martel, A. Diagnostic testing. In Reptile Medicine and Surgery in Clinical Practice; Doneley, B., Monks, D., Johnson, R., Carmel, B., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Garner, M.M. Overview of biopsy and necropsy techniques. In Reptile Medicine and Surgery; Mader, D.R., Ed.; Elsevier: St Louis, MO, USA, 2006; pp. 569–580. [Google Scholar]
- Nardoni, S.; Papini, R.; Marcucci, G.M.; Mancianti, F. Survey on the fungal flora of the cloaca of healthy pet reptiles. Rev. Med. Vet. 2008, 159, 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, M.; Hernández, G.; Caballero, M. Aerobic bacterial flora of nesting green turtles (Chelonia mydas) from Tortuguero National Park, Costa Rica. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2006, 37, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakiewicz, A.; Ziółkowska, G.; Zięba, P.; Dziedzic, B.M.; Gnat, S.; Wójcik, M.; Dziedzic, R.; Kostruba, A. Aerobic bacterial microbiota isolated from the cloaca of the European pond turtle (Emys orbicularis) in Poland. J. Wildl. Dis. 2015, 51, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filek, K.; Trotta, A.; Gračan, R.; Di Bello, A.; Corrente, M.; Bosak, S. Characterization of oral and cloacal microbial communities of wild and rehabilitated loggerhead sea turtles (Caretta caretta). Anim. Microbiome 2021, 3, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bahry, S.N.; Mahmoud, I.Y.; Al-Zadjali, M.; Elshafie, A.; Al-Harthy, A.; Al-Alawi, W. Antibiotic resistant bacteria as bio-indicator of polluted effluent in the green turtles, Chelonia mydas in Oman. Mar. Environ. Res. 2011, 71, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, V.M.; Duck, T.; Schwalbe, C.R.; Jarchow, J.L.; Trueblood, M.H. Nasal and cloacal bacteria in free-ranging desert tortoises from the western United States. J. Wildl. Dis. 2001, 37, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casares, M.; Rübel, A.; Honegger, R.E. Observations on the female reproductive cycle of captive giant tortoises (Geochelone spp.) using ultrasound scanning. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 1997, 28, 267–273. [Google Scholar]
- Gumpenberger, M. Diagnostic imaging of reproductive tract disorders in reptiles. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2017, 20, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumpenberger, M.; Henninger, W. The use of computed tomography in avian and reptile medicine. Semin. Avian Exot. Pet Med. 2001, 10, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innis, C.J. Endoscopy and endosurgery of the chelonian reproductive tract. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2010, 13, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Ianni, F.; Parmigiani, E.; Pelizzone, I.; Bresciani, C.; Gnudi, G.; Volta, A.; Manfredi, S.; Bigliardi, E. Comparison between intramuscular and intravenous administration of oxytocin in captive-bred red-eared sliders (Trachemys scripta elegans) with nonobstructive egg retention. J. Exot. Pet Med. 2014, 23, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.L.; Wilier, C.J.; Wosar, M.A.; Spaulding, K.A.; Lewbart, G.A. Egg-retention in the urinary bladder of a Florida cooter turtle, Pseudemys floridana floridana. J. Herpetol. Med. Surg. 2002, 12, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portas, T.J. Disorders of the reproductive system. In Reptile Medicine and Surgery in Clinical Practice; Doneley, B., Monks, D., Johnson, R., Carmel, B., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 307–321. [Google Scholar]
- McArthur, S.; Wilkinson, R.; Meyer, J.; McArthur, S. Problem-solving approach to common diseases of terrestrial and semi-aquatic chelonians. In Medicine and Surgery of Tortoises and Turtles; McArthur, S., Wilkinson, R., Meyer, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 309–377. [Google Scholar]
- De Nardo, D. Dystocias. In Mader DR Reptile Medicine and Surgery; Mader, D.R., Ed.; Elsevier: St Louis, MO, USA, 2006; pp. 787–791. [Google Scholar]
- Frye, F.L. Surgical and non-surgical procedures dystocia. In Reptile Clinician’s Handbook; Frye, F.L., Ed.; Krieger: Malabar, FL, USA, 1994; p. 179. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R. Dystocia in an injured common eastern long-necked turtle (Chelodina longicollis). Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2006, 9, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mans, C.; Foster, J.D. Endoscopy-guided ectopic egg removal from the urinary bladder in a leopard tortoise (Stigmochelys pardalis). Can. Vet. J. 2014, 55, 569–572. [Google Scholar]
- Funk, R.S.; Diethelm, G. Reptile formulary. In Reptile Medicine and Surgery; Mader, D.R., Ed.; Elsevier: St Louis, MO, USA, 2006; pp. 1119–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, F.B. The dynamics of populations of squamates, crocodilians, and rhynchocephalians. In Biology of the Reptilia; Gans, C., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977; pp. 157–264. [Google Scholar]
- Mans, C.; Sladky, K.K. Diagnosis and management of oviductal disease in three red-eared slider turtles (Trachemys scripta elegans). J. Small Anim. Pract. 2012, 53, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knotek, Z.; Jekl, V.; Knotkova, Z.; Grabensteiner, E. Eggs in chelonian urinary bladder: Is coeliotomy necessary? In Proceedings of the Association of Reptilian and Amphibian Veterinarians—16th Annual Conference, Milwaukee, WI, USA, 8–15 August 2009; Association of Reptilian and Amphibian Veterinarians: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2009; pp. 118–121. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, P.E. Obstetrical problems in two tortoises. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1979, 20, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minter, L.J.; Wood, M.W.; Hill, T.L.; Lewbart, G.A. Cystoscopic guided removal of ectopic eggs from the urinary bladder of the Florida cooter turtle (Pseudemys floridana floridana). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2010, 41, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmann, M.; Möstl, E.; Knotkova, Z.; Knotek, Z. The use of synthetical Gnrh agonist implants (Deslorelin) for the suppression of reptile endocrine reproductive activity. In Proceedings of the 1st ICARE Conference, Wiesbaden, Germany, 20–26 April 2013; p. 248. [Google Scholar]
- Bardi, E.; Manfredi, M.; Capitelli, R.; Lubian, E.; Vetere, A.; Montani, A.; Bertoni, T.; Talon, E.; Ratti, G.; Romussi, S. Determination of efficacy of single and double 4.7 mg deslorelin acetate implant on the reproductive activity of female pond sliders (Trachemys scripta). Animals 2021, 11, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masi, M.; Vetere, A.; Casalini, J.; Corsi, F.; Di Ianni, F.; Nardini, G. Comparison of subcutaneous versus intramuscular dexmedetomidine-midazolam-ketamine-morphine (DMKM) mixture as chemical restraint for endoscopic sex determination in aldabra giant tortoises (Aldabrachelys gigantea). Animals 2023, 13, 3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potier, R.; Monge, E.; Loucachevsky, T.; Hermes, R.; Göritz, F.; Rochel, D.; Risi, E. Effects of deslorelin acetate on plasma testosterone concentrations in captive yellow-bellied sliders (Trachemys scripta sp.). Acta Vet. Hung. 2017, 65, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArthur, S.; Wilkinson, R.; Meyer, J.; McArthur, S.; Hernandez-Divers, S. Surgery. In Medicine and Surgery of Tortoises and Turtles; McArthur, S., Wilkinson, R., Meyer, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 403–464. [Google Scholar]
- Divers, S.J.; Stahl, S.J. Mader’s Reptile and Amphibian Medicine and Surgery; Elsevier Health Sciences: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bardi, E.; Antolini, G.; Lubian, E.; Bronzo, V.; Romussi, S. Comparison of lateral and dorsal recumbency during endoscope-assisted oophorectomy in mature pond sliders (Trachemys scripta). Animals 2020, 10, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innis, C.J.; Hernandez-Divers, S.; Martinez-Jimenez, D. Coelioscopic-assisted prefemoral oophorectomy in chelonians. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2007, 230, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M. An introduction to reptile surgery: A chance to cut is a chance to cure. In Proceedings of the 40th World Small Animal Veterinary Association Congress, Bangkok, Thailand, 15–18 May 2015; pp. 261–262. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, M.C.; Lima, W.C.; Quessada, A.M.; Silva, F.A.; Silva, L.; Souza, A.B.; De Moura, C.R.; Lima, D.A. Celiotomy by plastrotomy in a yellow-footed tortoise (Geochelone denticulata). Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2015, 35, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, G.J. Clinical technique: Chelonian shell repair. J. Exot. Pet Med. 2008, 17, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.A. Diagnosis and management of reptile orthopedic injuries. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2002, 5, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoemaker, N.J. Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone agonists and other contraceptive medications in exotic companion animals. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2018, 21, 443–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetere, A.; Bigliardi, E.; Masi, M.; Rizzi, M.; Leandrin, E.; Di Ianni, F. Egg removal via cloacoscopy in three dystocic leopard geckos (Eublepharis macularius). Animals 2023, 13, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, S.; Wilkinson, R.; Meyer, J.; McArthur, S. Interpretation of presenting signs. In Medicine and Surgery of Tortoises and Turtles; McArthur, S., Wilkinson, R., Meyer, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 273–300. [Google Scholar]
- Backues, K.A.; Ramsay, E.C. Ovariectomy for treatment of follicular stasis in lizards. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 1994, 25, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Divers, S.J.; Stahl, S.J. Mader’s Reptile and Amphibian Medicine and Surgery-E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 849–893. [Google Scholar]
- Takami, Y. Single-incision, prefemoral bilateral oophorosalpingectomy without coelioscopy in an Indian star tortoise (Geochelone elegans) with follicular stasis. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 1675–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostal, D.C.; Robeck, T.R.; Owens, D.W.; Kraemer, D.C. Ultrasound imaging of ovaries and eggs in kemp’s ridley sea turtles (Lepidochelys kempi). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 1990, 21, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- McCracken, H.; Carmel, B.; Chitty, J.; Doneley, B.; Johnson, R.; Lennox, A.M.; Monks, D.; Olsson, A. Differential diagnoses. In Reptile Medicine and Surgery in Clinical Practice; Doneley, B., Monks, D., Johnson, R., Carmel, B., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 217–253. [Google Scholar]
- Divers, S.J.; Mader, D.R. Common Reproductive Disorders of Female Reptiles. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2008, 11, 347–368. [Google Scholar]
- Lubian, E.; Martino, P.A. Composizione Della Flora Batterica Cloacale in Testudo hermanni Sane E Con Cloacite. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Milan, Milano, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, P.R.; Singh, I.; Kamal, K.K.; Saini, M.; Arvinder. Management of uterine prolapse in a turtle. CIBTech J. Zool. 2018, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Simard, J. Oviductal prolapse associated with a leiomyoma in a Hermann’s tortoise (Testudo hermanni). Vlaams Diergeneeskd. Tijdschr. 2021, 90, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, S.J.; Brown, C.J.; Patnaik, A.K. Malignant ovarian teratoma in a red-eared slider (Trachemys scripta elegans). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2003, 15, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frye, F.L.; Eichelberger, S.A.; Harshbarger, J.C.; Cuzzocrea, A.D. Dysgerminomas in two red-eared slider turtles (Trachemys scripta elegans) from the same household. J. Zoo Anim. Med. 1988, 19, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machotka, S.V.; Wisser, J.; Ippen, R.; Nawab, E. Report of dysgerminoma in the ovaries of a snapping turtle (Chelydra serpentina) with discussion of ovarian neoplasms reported in reptilians and women. Vivo 1992, 6, 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Frye, F.L. Diagnosis and surgical treatment of reptilian neoplasms with a compilation of cases 1966–1993. Vivo 1994, 8, 885–892. [Google Scholar]
- Arthur, K.; Limpus, C.; Balazs, G.; Capper, A.; Udy, J.; Shaw, G.; Keuper-Bennett, U.; Bennett, P. The exposure of green turtles (Chelonia mydas) to tumour promoting compounds produced by the cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula and their potential role in the aetiology of fibropapillomatosis. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Houtan, K.S.; Hargrove, S.K.; Balazs, G.H. Land use, macroalgae, and a tumor-forming disease in marine turtles. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paillusseau, C.; Gandar, F.; Francois, C.; Schilliger, L. Unilateral ovarian torsion in five geckos: Clinical and ultrasound findings. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2024, 55, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan-Sallés, C.; Garner, M.M.; Monreal, T.; Burgos-Rodriguez, A.G. Ovarian Torsion in a Green, Iguana iguana, and a Rhinoceros, Cyclura cornuta, Iguana. J. Herpetol. Med. Surg. 2008, 18, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetere, A.; Di Ianni, F.; Bertocchi, M.; Castiglioni, V.; Nardini, G. Unilateral ovarian torsion in a Moroccan eyed lizard (Timon tangitanus). J. Exotic Pet Med. 2022, 41, 46–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetere, A.; Gavezzoli, M.; Bel, L.V.; Lecce, R.D.; Fumeo, M.; Bonazzi, M.; Ianni, F.D. Partial unilateral ovarian torsion in a Red-Eared Slider Turtle (Trachemys scripta elegans). Front. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 1524568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lubian, E.; Palotti, G.; Di Ianni, F.; Vetere, A. Disorders of the Female Reproductive Tract in Chelonians: A Review. Animals 2025, 15, 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091275
Lubian E, Palotti G, Di Ianni F, Vetere A. Disorders of the Female Reproductive Tract in Chelonians: A Review. Animals. 2025; 15(9):1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091275
Chicago/Turabian StyleLubian, Emanuele, Giulia Palotti, Francesco Di Ianni, and Alessandro Vetere. 2025. "Disorders of the Female Reproductive Tract in Chelonians: A Review" Animals 15, no. 9: 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091275
APA StyleLubian, E., Palotti, G., Di Ianni, F., & Vetere, A. (2025). Disorders of the Female Reproductive Tract in Chelonians: A Review. Animals, 15(9), 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091275




