Probiotic Lactocaseibacillus casei NK1 Enhances Growth and Gut Microbiota in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Challenged Broilers
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Bacterial Strains and Culturing
2.3. Experimental Design and Chicken Rearing
2.4. Microbial Count
2.5. Body Weight Gain
2.6. Metagenomic Analysis and Microbial Diversity Assessment Using 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.6.1. Cecal Sample Collection
2.6.2. Genomic DNA Isolation
2.6.3. 16S rRNA Gene Amplification and Sequencing
2.6.4. 16S rRNA Sequence Processing and Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
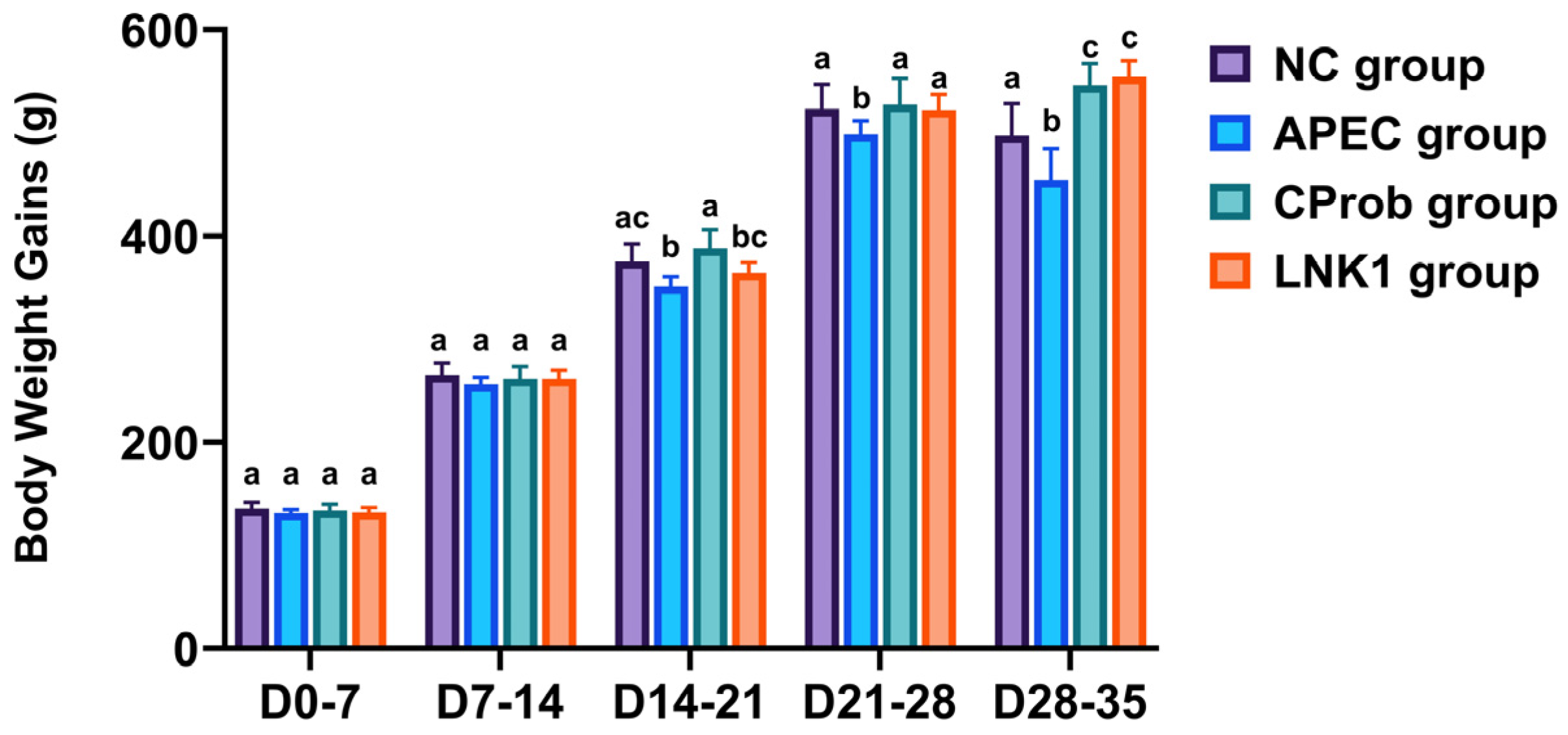
3.1. Body Weight Gain
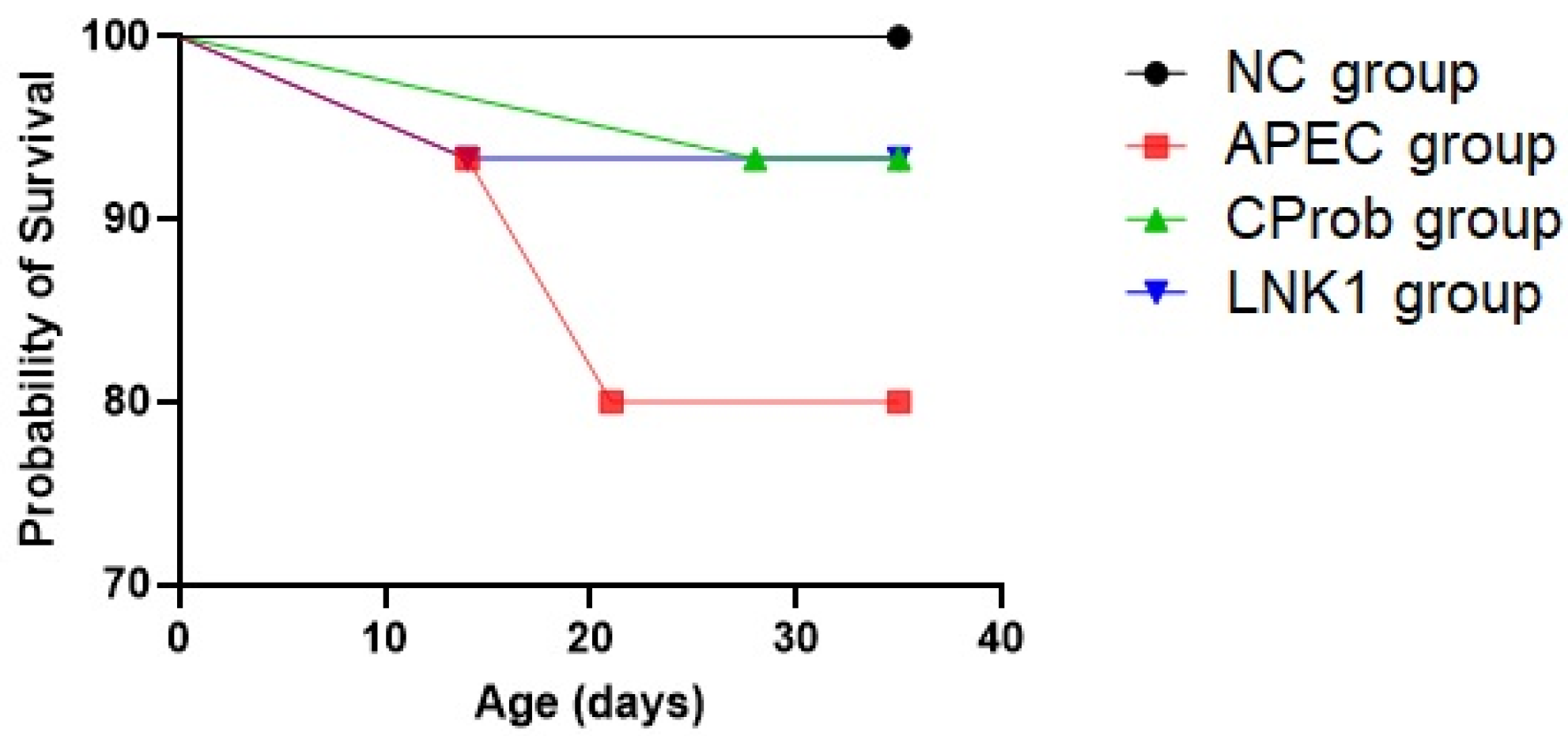
3.2. Mortality
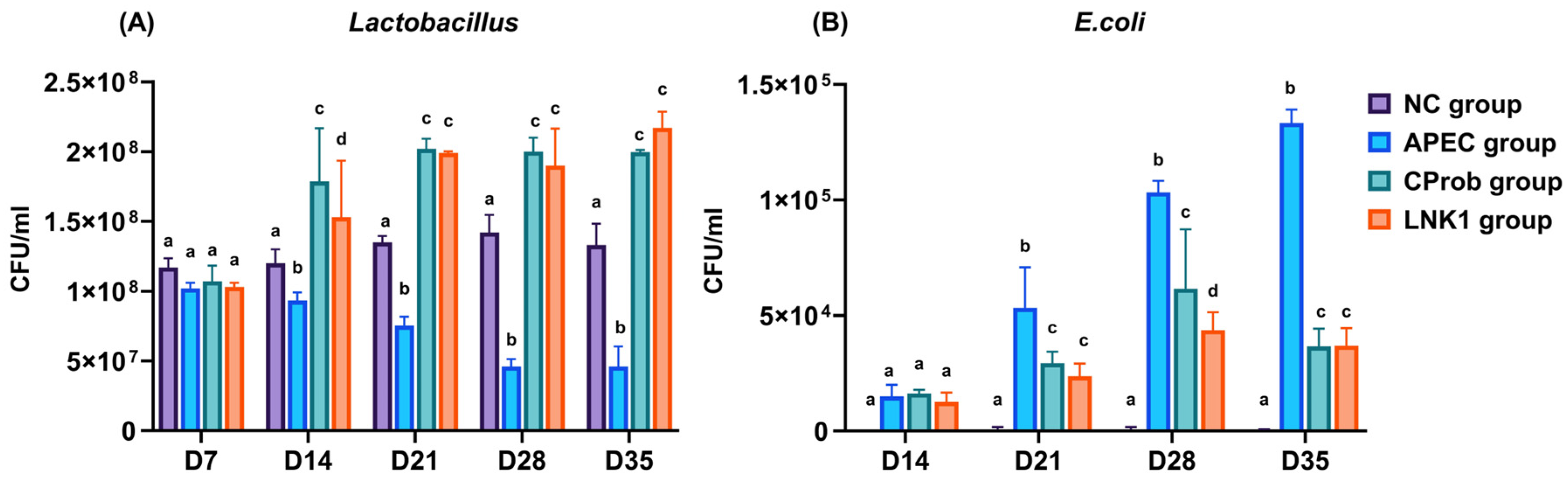
3.3. Microbial Count in Cloacal Swabs
3.4. Metagenomic Analysis Using 16S rRNA Sequencing
3.4.1. The Alpha Diversity Metrics
3.4.2. Microbial Diversity and Community Structure Analysis
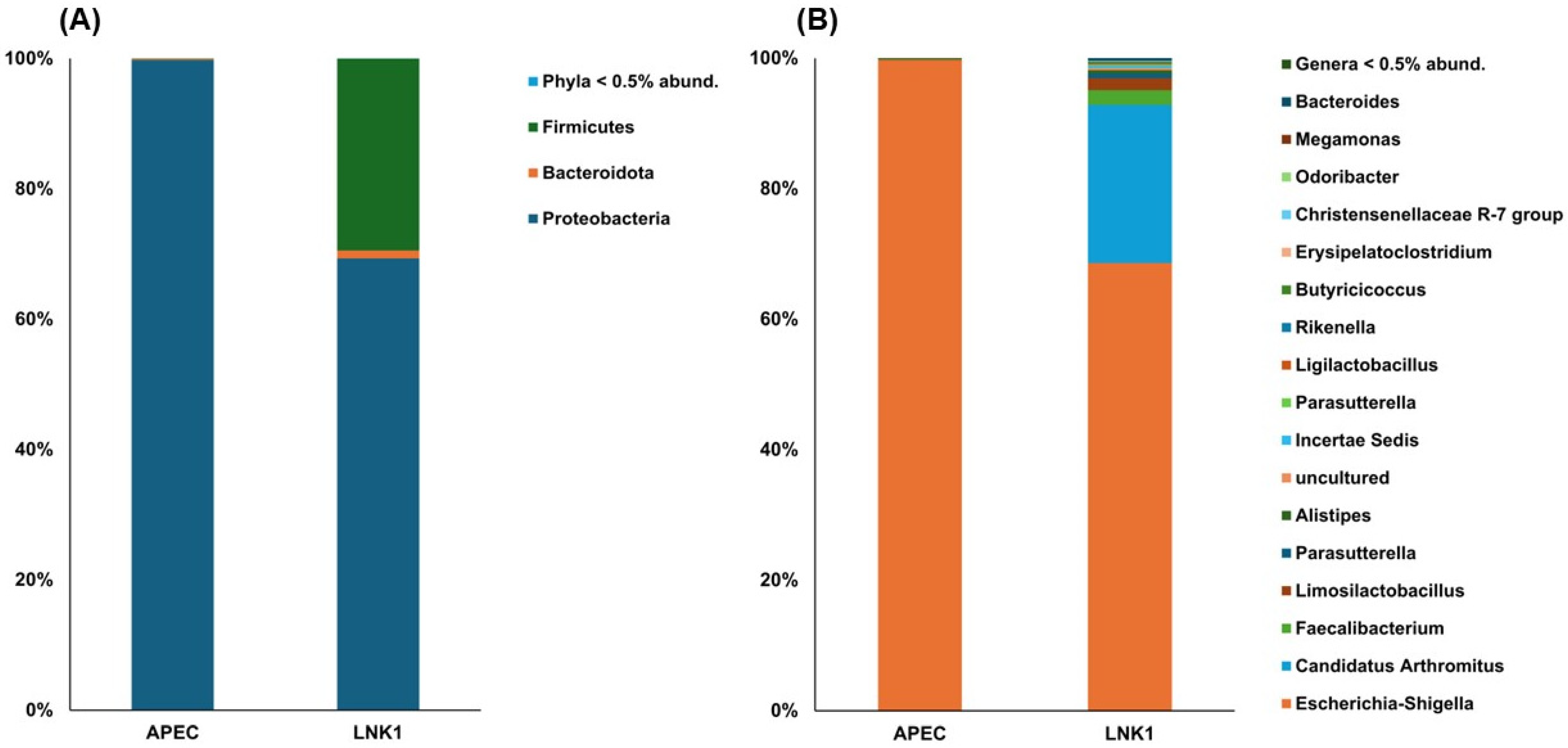
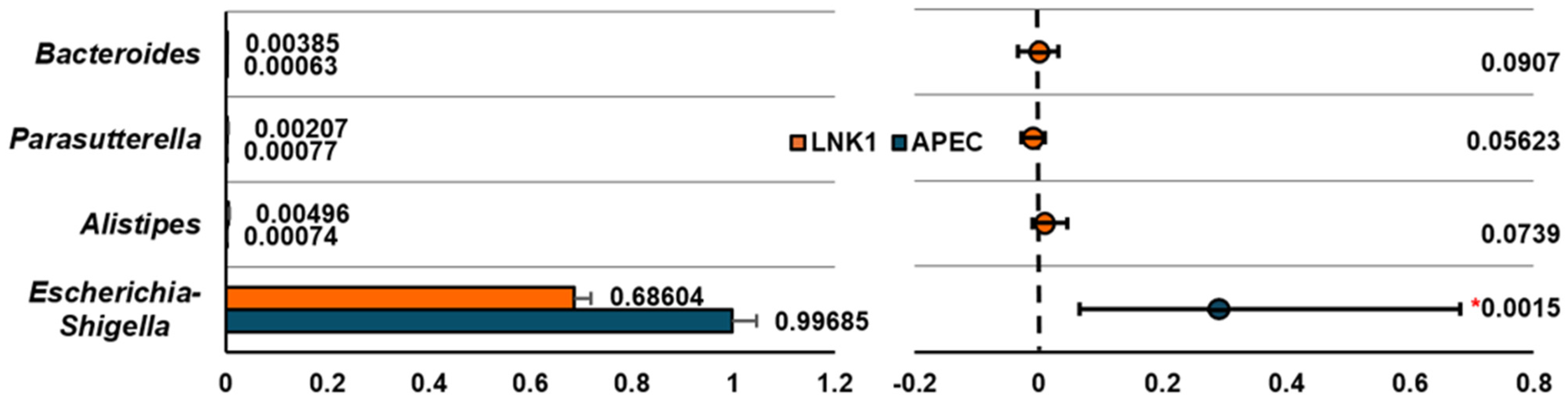
3.4.3. Relative Abundance Comparison
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nolan, L.K.; Barnes, H.J.; Vaillancourt, J.P.; Abdul-Aziz, T.; Logue, C.M. Colibacillosis. In Diseases of Poultry, 13th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 751–805. [Google Scholar]
- Dho-Moulin, M.; Fairbrother, J.M. Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC). Vet. Res. 1999, 30, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guabiraba, R.; Schouler, C. Avian colibacillosis: Still many black holes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, fnv118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellata, M. Human and avian extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli: Infections, zoonotic risks, and antibiotic resistance trends. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 916–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathayat, D.; Lokesh, D.; Ranjit, S.; Rajashekara, G. Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC): An overview of virulence and pathogenesis factors, zoonotic potential, and control strategies. Pathogens 2021, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thøfner, I.; Christensen, J.P. Bacterial diseases in poultry. In Advancements and Technologies in Pig and Poultry Bacterial Disease Control; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 199–227. [Google Scholar]
- Mehdi, Y.; Létourneau-Montminy, M.P.; Gaucher, M.L.; Chorfi, Y.; Suresh, G.; Rouissi, T.; Brar, S.K.; Côté, C.; Ramirez, A.A.; Godbout, S. Use of antibiotics in broiler production: Global impacts and alternatives. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.J.; Thottathil, S.E.; Newman, T.B. Antibiotics overuse in animal agriculture: A call to action for health care providers. Am. J. Public Health 2015, 105, 2409–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew Selaledi, L.; Mohammed Hassan, Z.; Manyelo, T.G.; Mabelebele, M. The current status of the alternative use to antibiotics in poultry production: An African perspective. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, M.; Liu, J.; Qiu, M.; Chen, Y. Isolation and Identification of Chicken-Derived Lactic Acid Bacteria: In Vitro Probiotic Properties and Antagonistic Effects against Salmonella pullorum, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsega, K.T.; Kagira, J.M.; Tessema, N.B.; Mekuria, S.A. Effects of Lactobacillus probiotics supplemented with concentrate feed on growth performance, carcass characteristics, and caecal microflora of RIR chickens. Cogent. Food Agric. 2024, 10, 2311959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishna-Kadawarage, R.N.; Hickey, R.M.; Siwek, M. In-vitro selection of lactic acid bacteria to combat Salmonella enterica and Campylobacter jejuni in broiler chickens. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.Z.; Marquardt, R.R.; Baidoo, S.K. Inhibition of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88, K99 and 987P by the Lactobacillus isolates from porcine intestine. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrmann, M.A.; Kurzak, P.; Bauer, J.; Vogel, R.F. Characterization of lactobacilli towards their use as probiotic adjuncts in poultry. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 92, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Ragione, R.M.; Narbad, A.; Gasson, M.J.; Woodward, M.J. In vivo characterization of Lactobacillus johnsonii FI9785 for use as a defined competitive exclusion agent against bacterial pathogens in poultry. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 38, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, S.; Ajeng, A.A.; Ramli, M.R.; Ameen, F.; Nasir, N.; Lakshmikandan, M. Comparison of novel bacillus salmalaya 139si and lactobacillus as probiotics in the drinking water of chicks. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2024, 34, 362. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hazmi, N.E.; Naguib, D.M. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of nano-probiotics versus free probiotics against gastrointestinal pathogenic bacteria. Indian J. Microbiol. 2024, 64, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idebi, J.A.; Akeredolu, O.S.; Omotosho, T. Isolation and Molecular Identification of Lactic Acid Bacteria from Fermented Maize Grain (Ogi) and their Antimicrobial Activities against Pathogenic Bacteria. IJIRMPS 2024, 12, 230459. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.M.; Harris, H.M.; Mattarelli, P.; O’toole, P.W.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A Taxonomic Note on the Genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 Novel Genera, Emended Description of the Genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and Union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Du, E.; Yuan, J.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Aggrey, S.E.; Guo, Y. Supplemental thymol and carvacrol increases ileum Lactobacillus population and reduces effect of necrotic enteritis caused by Clostridium perfringes in chickens. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, T.C.; Brandão, L.R.; de Oliveira, M.P.; da Costa, W.K.A.; Magnani, M. Health benefits and technological effects of Lacticaseibacillus casei-01: An overview of the scientific literature. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 114, 722–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Yang, S.M.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.Y. Complete genome sequencing and comparative genomics of three potential probiotic strains, Lacticaseibacillus casei FBL6, Lacticaseibacillus chiayiensis FBL7, and Lacticaseibacillus zeae FBL8. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 794315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuy, N.P.; Trai, N.N. Screening of Lactobacillus from Noi chicken gut as potential probiotics against poultry pathogens. Biodivers. J. Biol. Divers. 2024, 25, 3943–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.S.; Wang, Y.J.; Qi, H.T.; Wang, L.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J.D.; Zhang, G.H. Effect of cell wall extracts from Lactobacillus acidophilus on pathogenic E. coli O78 binding to chicken intestinal brush border membranes. Chin. J. Prev. Vet. Med. 2012, 34, 283–288. [Google Scholar]
- Fayyaz, I.; Zahoor, M.A.; Shahid, M.; Rasool, M.H.; Nawaz, Z. Effect of Lactobacillus casei on serum interleukins following enteropathogenic E. coli infection in experimental rabbits. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 31, 2131–2136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kabir, S.; Shahid, M.; Waseem, M.; Muzammil, S.; Nawaz, Z.; Rasool, M.H.; Saqalein, M. Dairy origin Lactobacilli: Functional analyses and antagonistic potential against multidrug-resistant foodborne pathogens. Int. Food Res. J. 2020, 27, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, G.; Asif-Iqbal, M.; Riaz, M.; Sajid, M.; Zahid, O.; Wasim-Abbas, S.Y.; Zohaib, M. Comparative effect of different levels of probiotics (Protexin) on hemato-chemical profile in broilers. Adv. Zool. Bot. 2018, 6, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Khalid, N.; Bukhari, S.M.; Ali, W.; Sheikh, A.A. Comparative Study on the Predominance of Lactobacillus spp. and Escherichia Coli in Healthy vs Colibacillosis Diseased Broilers. Braz. J. Poult. Sci. 2023, 25, eRBCA-2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council; Subcommittee on Poultry Nutrition. Nutrient Requirements of Poultry, 9th ed.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; pp. 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Berkhoff, H.A.; Vinal, A.C. Congo red medium to distinguish between invasive and non-invasive Escherichia coli pathogenic for poultry. Avian Dis. 1986, 30, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinroth, M.D.; Belk, A.D.; Dean, C.; Noyes, N.; Dittoe, D.K.; Rothrock, M.J., Jr.; Ricke, S.C.; Myer, P.R.; Henniger, M.T.; Ramírez, G.A.; et al. Considerations and best practices in animal science 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequencing microbiome studies. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, skab346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, D.; Geier, M.S.; Chen, H.; Hughes, R.J.; Moore, R.J. Comparison of fecal and cecal microbiotas reveals qualitative similarities but quantitative differences. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancabelli, L.; Ferrario, C.; Milani, C.; Mangifesta, M.; Turroni, F.; Duranti, S.; Lugli, G.A.; Viappiani, A.; Ossiprandi, M.C.; van Sinderen, D.; et al. Insights into the Biodiversity of the Gut Microbiota of Broiler Chickens. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 4727–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, Z.; Yousaf, M.Z.; Gilani, S.M.H.; Zehra, S.; Ali, A.; Azhar, A.; Galani, S. Comparative Analysis of Chicken Cecal Microbial Diversity and Taxonomic Composition in Response to Dietary Variation Using 16S rRNA Amplicon Sequencing. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 7203–7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.Y.; Wu, W.K.; Chen, C.C.; Panyod, S.; Sheen, L.Y.; Wu, M.S. Evaluation of compatibility of 16S rRNA V3V4 and V4 amplicon libraries for clinical microbiome profiling. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiraei, S.; Anvar, Y.; Hoving, L.; Berbée, J.F.; van Harmelen, V.; Willems van Dijk, K. Evaluation of full-length versus V4-region 16S rRNA sequencing for phylogenetic analysis of mouse intestinal microbiota after a dietary intervention. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; Pirrung, M.; McCue, L.A. FQC Dashboard: Integrates FastQC results into a web-based, interactive, and extensible FASTQ quality control tool. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3137–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and accurate 16S rRNA microbial community analysis using Kraken 2. Microbiome 2020, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ondov, B.D.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Interactive metagenomic visualization in a Web browser. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Bai, G.; Liu, L.; Zhong, R.; Ma, T.; Pan, H.; Zhang, H. Supplementation of multi-enzymes alone or combined with inactivated Lactobacillus benefits growth performance and gut microbiota in broilers fed wheat diets. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 927932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Huang, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Pan, X. Compound Lactobacillus sp. administration ameliorates stress and body growth through gut microbiota optimization on weaning piglets. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 6749–6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, R.; Oh, J.K.; Song, J.H.; Kang, D.K. Gut microbiome-produced metabolites in pigs: A review on their biological functions and the influence of probiotics. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2022, 64, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Alqhtani, A.H.; Swelum, A.A.; Salem, H.M.; Elbestawy, A.R.; Noreldin, A.E.; Babalghith, A.O.; Khafaga, A.F.; Hassan, M.I.; et al. The relationship among avian influenza, gut microbiota and chicken immunity: An updated overview. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 102021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, R.; Das, R.; Oak, S.; Mishra, P. Probiotics (direct-fed microbials) in poultry nutrition and their effects on nutrient utilization, growth and laying performance, and gut health: A systematic review. Animals 2020, 10, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaway, T.R.; Edrington, T.S.; Anderson, R.C.; Harvey, R.B.; Genovese, K.J.; Kennedy, C.N.; Venn, D.W.; Nisbet, D.J. Probiotics, prebiotics and competitive exclusion for prophylaxis against bacterial disease. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2008, 9, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, R. Probiotics in man and animals. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 2000, 66, 365–378. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, S.E.; Higgins, J.P.; Wolfenden, A.D.; Henderson, S.N.; Torres-Rodriguez, A.; Tellez, G.; Hargis, B. Evaluation of a Lactobacillus-based probiotic culture for the reduction of Salmonella enteritidis in neonatal broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindari, Y.R.; Gerber, P.F. Centennial Review: Factors affecting the chicken gastrointestinal microbial composition and their association with gut health and productive performance. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanov, S.; Berlec, A.; Štrukelj, B. The influence of probiotics on the firmicutes/bacteroidetes ratio in the treatment of obesity and inflammatory bowel disease. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looft, T.; Johnson, T.A.; Allen, H.K.; Bayles, D.O.; Alt, D.P.; Stedtfeld, R.D.; Sul, W.J.; Stedtfeld, T.M.; Chai, B.; Cole, J.R.; et al. In-feed antibiotic effects on the swine intestinal microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1691–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Gao, R.; Guo, C.; Mi, S. Disequilibrium in chicken gut microflora with avian colibacillosis is related to microenvironment damaged by antibiotics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, B.B.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Kogut, M.H.; Kim, W.K.; Maurer, J.J.; Pedroso, A.; Lee, M.D.; Collett, S.R.; Johnson, T.J.; Cox, N.A. The chicken gastrointestinal microbiome. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 360, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makled, M.N.; Abouelezz, K.F.; Gad-Elkareem, A.E.; Sayed, A.M. Comparative influence of dietary probiotic, yoghurt, and sodium butyrate on growth performance, intestinal microbiota, blood hematology, and immune response of meat-type chickens. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 51, 2333–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavijo, V.; Flórez, M.J. The gastrointestinal microbiome and its association with the control of pathogens in broiler chicken production: A review. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 1006–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Formation of propionate and butyrate by the human colonic microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokol, H.; Pigneur, B.; Watterlot, L.; Lakhdari, O.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Gratadoux, J.J.; Blugeon, S.; Bridonneau, C.; Furet, J.P.; Corthier, G.; et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an anti-inflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn disease patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16731–16736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afridi, O.K.; Ali, J.; Chang, J.H. Next-generation sequencing based gut resistome profiling of broiler chickens infected with multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli. Animals 2020, 10, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Shi, S.; Tu, J.; Li, S. Comparative metagenomic sequencing analysis of cecum microbiotal diversity and function in broilers and layers. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morotomi, M.; Nagai, F.; Watanabe, Y. Description of Christensenella minuta gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from human faeces, which forms a distinct branch in the order Clostridiales, and proposal of Christensenellaceae fam. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Xia, Y.; Ai, L. The intervention effects of Lactobacillus casei LC2W on Escherichia coli O157: H7-induced mouse colitis. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2020, 9, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Metrics (Unitless) | LNK1 | APEC |
|---|---|---|
| Shannon’s Diversity | 0.935 | 0.026 |
| Simpson’s Index of Diversity | 0.47 | 0.006 |
| Simpson’s Reciprocal Index | 1.885 | 1.006 |
| Berger-Parker’s Diversity | 0.686 | 0.997 |
| Fisher’s Index | 1.438 | 0.389 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khalid, N.; Bukhari, S.M.; Ali, W.; Sheikh, A.A.; Abdullah, H.M.; Nazmi, A. Probiotic Lactocaseibacillus casei NK1 Enhances Growth and Gut Microbiota in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Challenged Broilers. Animals 2025, 15, 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15081136
Khalid N, Bukhari SM, Ali W, Sheikh AA, Abdullah HM, Nazmi A. Probiotic Lactocaseibacillus casei NK1 Enhances Growth and Gut Microbiota in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Challenged Broilers. Animals. 2025; 15(8):1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15081136
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhalid, Nimra, Syed Mohsin Bukhari, Waqas Ali, Ali Ahmad Sheikh, Hafiz Muhammad Abdullah, and Ali Nazmi. 2025. "Probiotic Lactocaseibacillus casei NK1 Enhances Growth and Gut Microbiota in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Challenged Broilers" Animals 15, no. 8: 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15081136
APA StyleKhalid, N., Bukhari, S. M., Ali, W., Sheikh, A. A., Abdullah, H. M., & Nazmi, A. (2025). Probiotic Lactocaseibacillus casei NK1 Enhances Growth and Gut Microbiota in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Challenged Broilers. Animals, 15(8), 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15081136





