Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Fish Density in a Deep-Water Reservoir: Hydroacoustic Assessment of Aggregation Patterns and Key Drivers
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
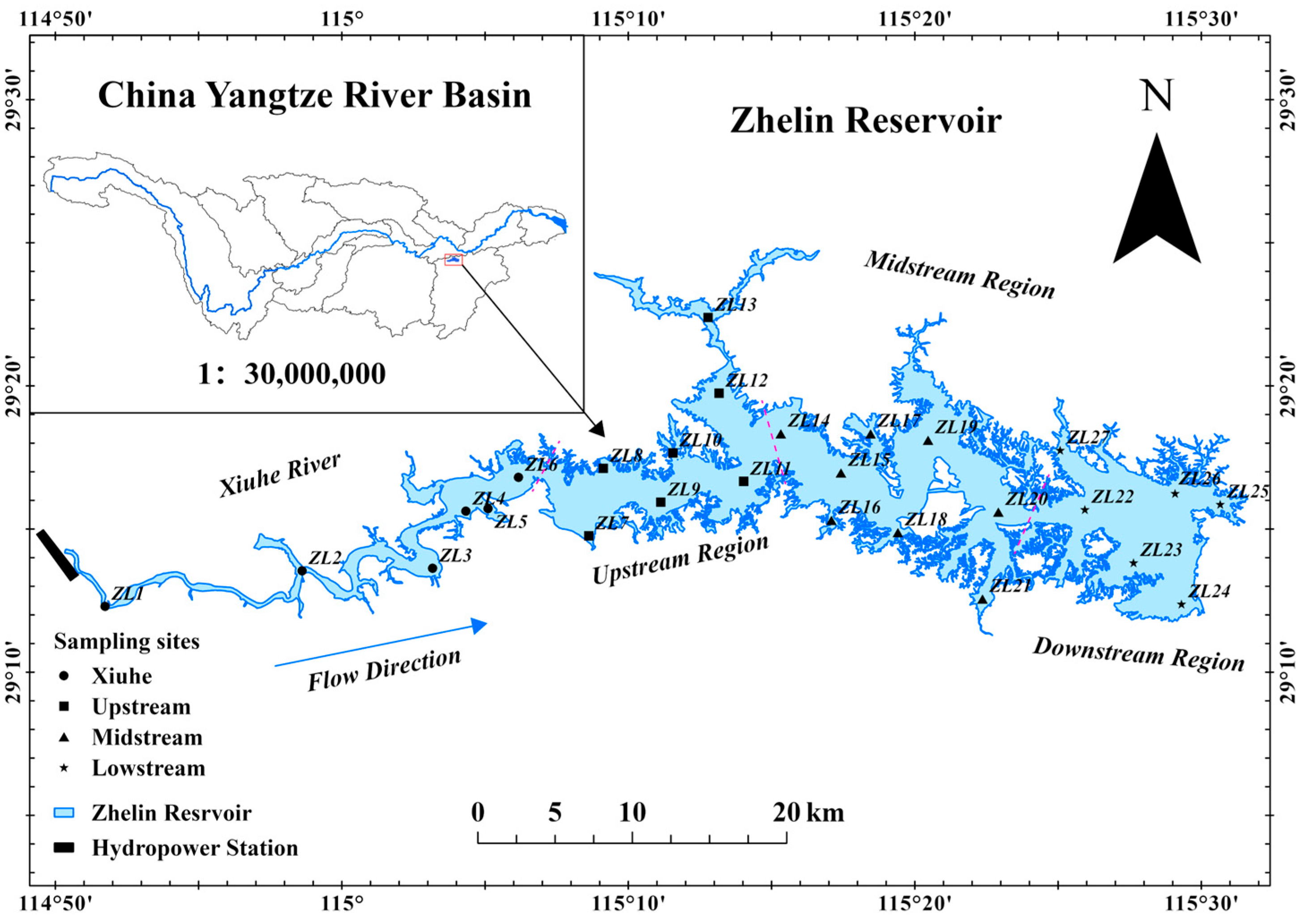
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
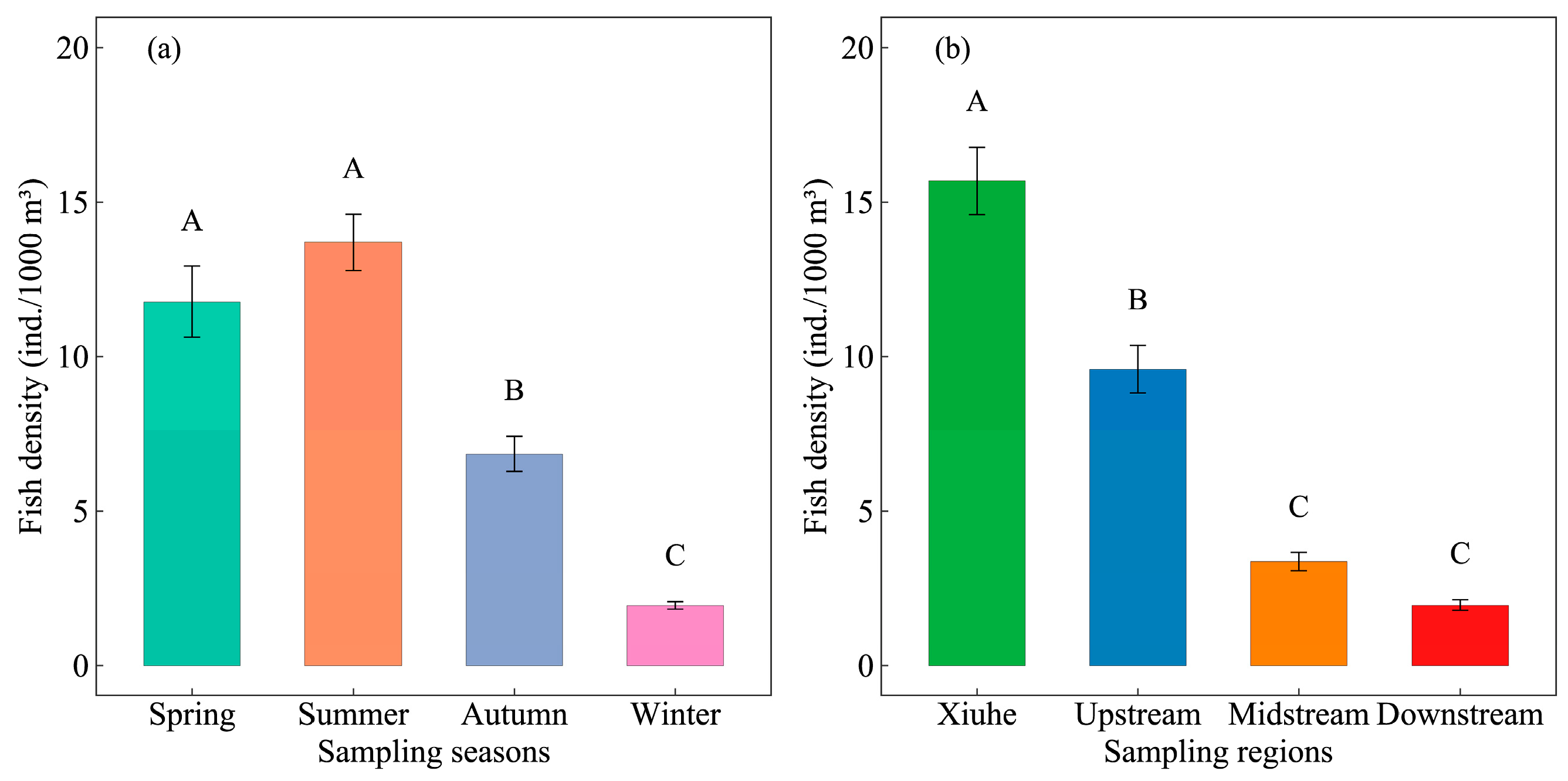
3.1. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Fish Density
3.2. Fish Spatial Aggregation Characteristics
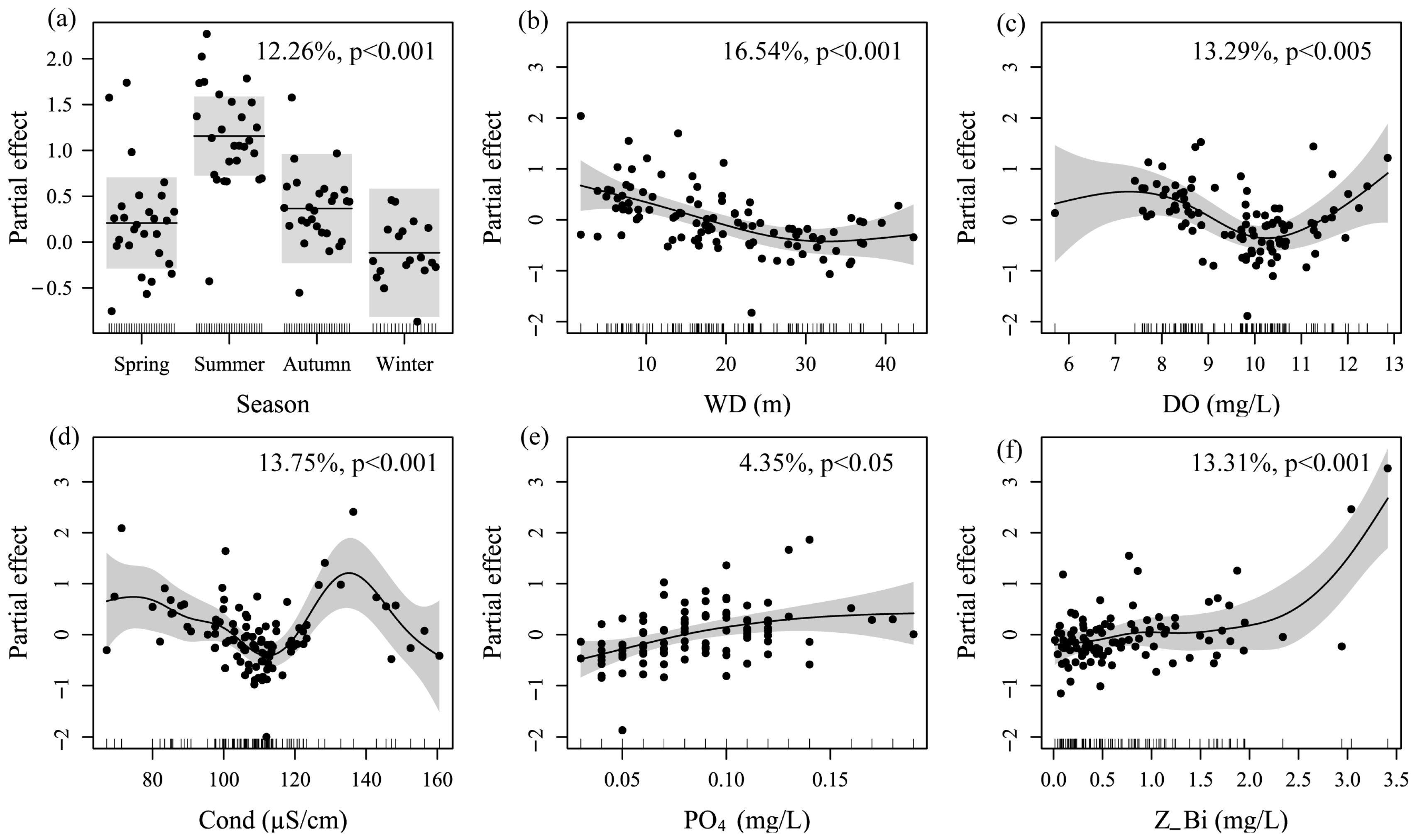
3.3. Key Driving Variables in Fish Distribution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larsson, M. Schooling Fish from a New, Multimodal Sensory Perspective. Animals 2024, 14, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolles, J.W.; Boogert, N.J.; Sridhar, V.H.; Couzin, I.D.; Manica, A. Consistent individual differences drive collective behavior and group functioning of schooling fish. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 2862–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasumyan, A.O.; Pavlov, D.S. Mechanisms of Schooling Behavior of Fish. J. Ichthyol. 2023, 63, 1279–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Arevalo, E.; Cabral, H.N.; Villeneuve, B.; Possémé, C.; Lepage, M. Fish larvae dynamics in temperate estuaries: A review on processes, patterns and factors that determine recruitment. Fish Fish. 2023, 24, 466–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasumyan, A.O.; Pavlov, D.S. Influence of Environmental Factors and the Condition of Fish on Schooling Behavior. J. Ichthyol. 2023, 63, 1362–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, M.; Tayemeh, M.B.; Jo, M.S.; Yu, I.J.; Johari, S.A. Trophic transfer and toxicity of silver nanoparticles along a phytoplankton-zooplankton-fish food chain. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 842, 156807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couzin, I.D.; Krause, J.; Franks, N.R.; Levin, S.A. Effective leadership and decision-making in animal groups on the move. Nature 2005, 433, 513–516. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Sang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, D.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhou, L. Exploring the Drivers of Spatiotemporal Patterns in Fish Community in a Non-Fed Aquaculture Reservoir. Diversity 2023, 15, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, S.J.; Bergman, J.N.; Twardek, W.M.; Piczak, M.L.; Casselberry, G.A.; Lutek, K.; Dahlmo, L.S.; Birnie-Gauvin, K.; Griffin, L.P.; Brownscombe, J.W. The movement ecology of fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2022, 101, 756–779. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, J.A.R.; Reina, A. On aims and methods of collective animal behaviour. Anim. Behav. 2024, 210, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, N.; Jones, E.G.; Reid, D.G. Review of technological advances for the study of fish behaviour in relation to demersal fishing trawls. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2004, 61, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar]
- Coya, R.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, A.; Fueyo, Á.; Orduna, C.; Miralles, L.; de Meo, I.; Pérez, T.; Cid, J.R.; Fernández-Delgado, C.; Encina, L. Environmental DNA and Hydroacoustic Surveys for Monitoring the Spread of the Invasive European Catfish (Silurus glanis Linnaeus, 1758) in the Guadalquivir River Basin, Spain. Animals 2025, 15, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yu, X.; Wu, B.; Yu, L.; Wang, D.; Wang, K.; Wang, S.; Chen, D.; Li, Y.; Duan, X. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Fish Resources in a Typical River–Lake Confluence Ecosystem During the Initial Period of Fishing Ban. Fishes 2024, 9, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassir, A.; Andaloussi, S.J.; Ouchetto, O.; Mamza, K.; Serghini, M. Acoustic fish species identification using deep learning and machine learning algorithms: A systematic review. Fish. Res. 2023, 266, 106790. [Google Scholar]
- Meaden, G.J. Applications of GIS to fisheries management. In Marine and Coastal Geographical Information Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; pp. 239–265. [Google Scholar]
- Fauchald, P.; Erikstad, K.E.; Skarsfjord, H. Scale-dependent predator–prey interactions: The hierarchical spatial distribution of seabirds and prey. Ecology 2000, 81, 773–783. [Google Scholar]
- Stenseth, N.C.; Mysterud, A.; Ottersen, G.; Hurrell, J.W.; Chan, K.-S.; Lima, M. Ecological effects of climate fluctuations. Science 2002, 297, 1292–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.N. Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction with R; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Feher, L.C.; Osland, M.J.; Johnson, D.J.; Grace, J.B.; Guntenspergen, G.R.; Stewart, D.R.; Coronado-Molina, C.; Sklar, F.H. Nonlinear patterns of surface elevation change in coastal wetlands: The value of generalized additive models for quantifying rates of change. Estuaries Coasts 2024, 47, 1893–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloret-Lloret, E.; Albo-Puigserver, M.; Giménez, J.; Navarro, J.; Pennino, M.G.; Steenbeek, J.; Bellido, J.M.; Coll, M. Small pelagic fish fitness relates to local environmental conditions and trophic variables. Prog. Oceanogr. 2022, 202, 102745. [Google Scholar]
- Rutterford, L.A.; Simpson, S.D.; Bogstad, B.; Devine, J.A.; Genner, M.J. Sea temperature is the primary driver of recent and predicted fish community structure across Northeast Atlantic shelf seas. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 2510–2521. [Google Scholar]
- De Castro, F.; Colby, J.; Leidy, G.; Sadro, S.; Rypel, A.; Parisek, C. Reservoir ecosystems support large pools of fish biomass. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9428. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Z.; Yang, D.; Hu, F.; Chen, K.; Liu, L.; Xiang, M.; Li, X. Fish resources spatiotemporal distribution patterns and controlling factors in Zhelin Reservoir, Lake Poyang Basin during early fishing ban period. J. Lake Sci. 2023, 35, 2071–2083. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Meng, Z.; Li, X.; Hu, F.; Du, H.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, D. Community structure and functional diversity of fishes in Zhelin Reservoir, Jiangxi Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 4592–4602. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, A.; Kubecka, J. Hydroacoustic Methods of Fish Surveys; National Rivers Authority: Bristol, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Aglen, A. Random errors of acoustic fish abundance estimates in relation to the survey grid density applied. FAO Fish. Rep. 1983, 300, 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- SC/T 9102.3-2007; The Specification for Ecological Environment Monitoringof Fisheries. Part 3: Freshwater. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Utermohl, H. Zur Vervollkommung der quantitativen phytoplankton-methodik. Mitt. Int. Ver. Limnol. 1958, 9, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Hillebrand, H.; Dürselen, C.D.; Kirschtel, D.; Pollingher, U.; Zohary, T. Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 403–424. [Google Scholar]
- Dumont, H.J.; Van de Velde, I.; Dumont, S. The dry weight estimate of biomass in a selection of Cladocera, Copepoda and Rotifera from the plankton, periphyton and benthos of continental waters. Oecologia 1975, 19, 75–97. [Google Scholar]
- Benoit-Bird, K.J.; Lawson, G.L. Ecological insights from pelagic habitats acquired using active acoustic techniques. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2016, 8, 463–490. [Google Scholar]
- McGowan-Yallop, C. Acoustic Target Classification of Zooplankton Using Machine Learning. Ph.D. Thesis, University of the Highlands and Islands, Inverness, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Misund, O.A. Underwater acoustics in marine fisheries and fisheries research. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 1997, 7, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Foote, K.G. Fish target strengths for use in echo integrator surveys. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1987, 82, 981–987. [Google Scholar]
- Dunnett, C.W. New Tables for Multiple Comparisons with a Control. Biometrics 1964, 20, 482–491. [Google Scholar]
- Cressie, N. Statistics for Spatial Data; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, P.A.P. Notes on continuous stochastic phenomena. Biometrika 1950, 37, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cliff, A.D.; Ord, J.K. Spatial Processes: Models & Applications; Pion: London, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Getis, A.; Ord, J.K. The analysis of spatial association by use of distance statistics. Geogr. Anal. 1992, 24, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullagh, P. Generalized Linear Models; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N.; Walker, N.J.; Saveliev, A.A.; Smith, G.M. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 574. [Google Scholar]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, J.; Tang, J.; Li, T.; Zhang, A.; Mao, L. Evaluating the relative importance of predictors in Generalized Additive Models using the gam.hp R package. Plant Divers. 2024, 46, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Wickham, M.H. Package ‘ggplot2’. Create elegant data visualisations using the grammar of graphics. In R Package Version; RStudio, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 1–189. [Google Scholar]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, Version 4.4.3; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P.; Fujiwara, M.; Ma, B.; Xia, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, C.; Chang, T.; Gao, X. Ecological drivers shaping mainstem and tributary fish communities in the upper Jinsha River, southeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Process. 2025, 14, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Leibold, M.A.; Govaert, L.; Loeuille, N.; De Meester, L.; Urban, M.C. Evolution and community assembly across spatial scales. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2022, 53, 299–326. [Google Scholar]
- Brandt, S.B. The effect of thermal fronts on fish growth: A bioenergetics evaluation of food and temperature. Estuaries 1993, 16, 142–159. [Google Scholar]
- Gillooly, J.F.; Brown, J.H.; West, G.B.; Savage, V.M.; Charnov, E.L. Effects of size and temperature on metabolic rate. Science 2001, 293, 2248–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olden, J.D.; Naiman, R.J. Incorporating thermal regimes into environmental flows assessments: Modifying dam operations to restore freshwater ecosystem integrity. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 86–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootton, R.J. Ecology of Teleost Fishes; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Thackeray, S.J.; Sparks, T.H.; Frederiksen, M.; Burthe, S.; Bacon, P.J.; Bell, J.R.; Botham, M.S.; Brereton, T.M.; Bright, P.W.; Carvalho, L. Trophic level asynchrony in rates of phenological change for marine, freshwater and terrestrial environments. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 3304–3313. [Google Scholar]
- Gaedke, U. The size distribution of plankton biomass in a large lake and its seasonal variability. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 1202–1220. [Google Scholar]
- Comte, L.; Buisson, L.; Daufresne, M.; Grenouillet, G. Climate-induced changes in the distribution of freshwater fish: Observed and predicted trends. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosse, S.; Lek, S.; Dauba, F. Predicting fish distribution in a mesotrophic lake by hydroacoustic survey and artificial neural networks. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, L.; Lin, H.; Cui, S.; Lu, X.; Shao, J.; Pan, J.; He, G.; Liu, Q.; Hu, Z. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Patterns of Fish in Large Deep-Water Lakes and Their Association with Environmental Factors Assessed Through Hydroacoustic Methods: A Case Study of Qiandao Lake, China. Water 2024, 16, 3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-M.; Setiazi, H.; So, P.-Y. Fisheries hydroacoustic assessment: A bibliometric analysis and direction for future research towards a blue economy. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 60, 102838. [Google Scholar]
- López-Rodríguez, A.; Meerhoff, M.; D’Anatro, A.; de Ávila-Simas, S.; Silva, I.; Pais, J.; de Mello, F.T.; Reynalte-Tataje, D.A.; Zaniboni-Filho, E.; González-Bergonzoni, I. Longitudinal changes on ecological diversity of Neotropical fish along a 1700 km river gradient show declines induced by dams. Perspect. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 22, 186–195. [Google Scholar]
- Fausch, K.D.; Torgersen, C.E.; Baxter, C.V.; Li, H.W. Landscapes to riverscapes: Bridging the gap between research and conservation of stream fishes: A continuous view of the river is needed to understand how processes interacting among scales set the context for stream fishes and their habitat. Bioscience 2002, 52, 483–498. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, J.D.; Castillo, M.M.; Capps, K.A. Stream Ecology: Structure and Function of Running Waters; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, H.H.; Andersen, K.H.; Bergman, E. Projecting fish community responses to dam removal–Data-limited modeling. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá-Oliveira, J.C.; Hawes, J.E.; Isaac-Nahum, V.J.; Peres, C.A. Upstream and downstream responses of fish assemblages to an eastern Amazonian hydroelectric dam. Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 2037–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannote, R.L.; Minshall, G.W.; Cummins, K.W.; Sedell, J.R.; Cushing, C.E. The river continuum concept. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1980, 37, 130–137. [Google Scholar]
- Thorp, J.H.; Thoms, M.C.; Delong, M.D. The riverine ecosystem synthesis: Biocomplexity in river networks across space and time. River Res. Appl. 2006, 22, 123–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Logez, M.; Xu, J.; Tao, S.; Villéger, S.; Brosse, S. Human impacts on global freshwater fish biodiversity. Science 2021, 371, 835–838. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Z.; Yang, D.; Chen, K.; Hu, F.; Liu, L.; Li, X. Temporal-spatial distribution and pollution assessment of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter in surface sediments of Zhelin Reservoir. Environ. Chem. 2023, 42, 138–149. [Google Scholar]
- Rypel, A.L.; Layman, C.A.; Arrington, D.A. Water depth modifies relative predation risk for a motile fish taxon in Bahamian tidal creeks. Estuaries Coasts 2007, 30, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, M.J.; Dale, M.R.T. Spatial autocorrelation in ecological studies: A legacy of solutions and myths. Geogr. Anal. 2009, 41, 392–397. [Google Scholar]
- Leibold, M.A.; Holyoak, M.; Mouquet, N.; Amarasekare, P.; Chase, J.M.; Hoopes, M.F.; Holt, R.D.; Shurin, J.B.; Law, R.; Tilman, D. The metacommunity concept: A framework for multi-scale community ecology. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 601–613. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, L.B.; Oliveira, F.J.M.; De Marco Júnior, P.; Lima-Junior, D.P. Local environmental variables are the best beta diversity predictors for fish communities from the Brazilian Cerrado streams. Aquat. Sci. 2024, 86, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, D.A.; Peres-Neto, P.R.; Olden, J.D. What controls who is where in freshwater fish communities the roles of biotic, abiotic, and spatial factors. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 157–170. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld, J. Assessing the habitat requirements of stream fishes: An overview and evaluation of different approaches. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2003, 132, 953–968. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, D.A.; Harvey, H.H. Fish and benthic invertebrates: Community concordance and community–environment relationships. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1993, 50, 2641–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, F.G.; Legendre, P.; Borcard, D. Modelling directional spatial processes in ecological data. Ecol. Model. 2008, 215, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ding, C.; Heino, J.; Ding, L.; Chen, J.; He, D.; Tao, J. Analysing spatio-temporal patterns of non-native fish in a biodiversity hotspot across decades. Divers. Distrib. 2023, 29, 1492–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, G.C.X.; Medeiros de Abreu, C.H.; Ward, N.D.; Belúcio, L.P.; Brito, D.C.; Cunha, H.F.A.; da Cunha, A.C. Environmental impacts of dam reservoir filling in the East Amazon. Front. Water 2020, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, L.A.; Whitener, Z.T.; Cadrin, S.X.; Morse, M.R.; Secor, D.H.; Golet, W. Mixed stock origin of Atlantic bluefin tuna in the US rod and reel fishery (Gulf of Maine) and implications for fisheries management. Fish. Res. 2020, 224, 105461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puff, N.L.; Allan, J.D.; Bain, M.B.; Karr, J.R.; Prestegaard, K.L.; Richter, B.D.; Sparks, R.E.; Stromberg, J.C. The natural flow regime, a paradigm for river conservation and restoration. Bioscience 1997, 47, 769–784. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, P.E.; Donadi, S.; Sandin, L. Responses of macroinvertebrate communities to small dam removals: Implications for bioassessment and restoration. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 1896–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, L.E.; Coppola, G.; Boxrucker, J. Reservoir fish habitats: A perspective on coping with climate change. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 28, 478–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Duan, X.B.; Liu, S.P.; Chen, D.Q.; Liu, M.D. Acoustic assessment of the fish spatio-temporal distribution during the initial filling of the Three Gorges Reservoir, Yangtze River (China), from 2006 to 2010. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2013, 29, 1395–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doudoroff, P.; Shumway, D.L. Dissolved oxygen requirements of freshwater fishes. FAO Fish. Tech. Pap. 1970, 86, 291. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Ding, S. The responses of stream fish to the gradient of conductivity: A case study from the Taizi River, China. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2019, 22, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, B.; Wells, M.; Midwood, J.D.; Brooks, J.; Kuai, Y.; Li, J. Intense variability of dissolved oxygen and temperature in the internal swash zone of Hamilton Harbour, Lake Ontario. Inland Waters 2021, 11, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrbácek, J.; Brandl, Z.; Straškraba, M. Do the long-term changes in zooplankton biomass indicate changes in fish stock? Hydrobiologia 2003, 504, 203–213. [Google Scholar]
- Vander Zanden, M.J.; Casselman, J.M.; Rasmussen, J.B. Stable isotope evidence for the food web consequences of species invasions in lakes. Nature 1999, 401, 464–467. [Google Scholar]
- Elser, J.J.; Bracken, M.E.S.; Cleland, E.E.; Gruner, D.S.; Harpole, W.S.; Hillebrand, H.; Ngai, J.T.; Seabloom, E.W.; Shurin, J.B.; Smith, J.E. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Dodds, W.K. Freshwater Ecology: Concepts and Environmental Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Holling, C.S. Cross-scale morphology, geometry, and dynamics of ecosystems. Ecol. Monogr. 1992, 62, 447–502. [Google Scholar]


| Region | Season | WD (°C) | DO (mg/L) | Cond (µS/cm) | Z_Bi (mg/L) | PO4 (mg/L) | TN (mg/L) | NH4 (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xiuhe | Winter | 9.67 ± 7.07 | 10.24 ± 0.50 | 138.67 ± 16.37 | 0.30 ± 0.15 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 1.48 ± 0.48 | 0.11 ± 0.10 |
| Spring | 5.60 ± 3.21 | 9.75 ± 2.43 | 78.90 ± 10.84 | 0.86 ± 0.72 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 1.31 ± 0.09 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | |
| Summer | 12.28 ± 6.26 | 9.10 ± 1.09 | 112.30 ± 3.95 | 2.24 ± 1.08 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.82 ± 0.24 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | |
| Autumn | 11.78 ± 6.74 | 9.48 ± 1.19 | 138.88 ± 13.12 | 0.61 ± 0.31 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.84 ± 0.10 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | |
| Upstream | Winter | 16.08 ± 5.27 | 10.47 ± 0.14 | 111.35 ± 6.45 | 0.35 ± 0.23 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 0.69 ± 0.22 | 0.09 ± 0.04 |
| Spring | 13.43 ± 6.02 | 11.95 ± 0.57 | 113.79 ± 21.15 | 0.97 ± 0.34 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 1.30 ± 0.16 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | |
| Summer | 16.60 ± 6.40 | 9.89 ± 0.24 | 111.37 ± 2.58 | 1.83 ± 0.30 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 0.78 ± 0.14 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | |
| Autumn | 15.23 ± 5.20 | 8.52 ± 0.33 | 128.61 ± 12.24 | 0.54 ± 0.25 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 0.78 ± 0.21 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | |
| Midstream | Winter | 25.02 ± 10.13 | 10.48 ± 0.18 | 90.05 ± 7.53 | 0.23 ± 0.14 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.55 ± 0.25 | 0.07 ± 0.09 |
| Spring | 21.93 ± 9.91 | 11.16 ± 0.44 | 108.00 ± 3.79 | 1.09 ± 0.28 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 1.12 ± 0.33 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | |
| Summer | 22.51 ± 8.00 | 9.89 ± 0.27 | 104.67 ± 2.92 | 0.54 ± 0.29 | 0.10 ± 0.06 | 0.82 ± 0.10 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | |
| Autumn | 25.70 ± 9.16 | 8.21 ± 0.45 | 113.77 ± 2.38 | 0.40 ± 0.10 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 0.57 ± 0.18 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | |
| Downstream | Winter | 29.03 ± 14.15 | 10.34 ± 0.17 | 83.60 ± 1.61 | 0.19 ± 0.10 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.44 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| Spring | 26.30 ± 10.76 | 10.09 ± 0.17 | 109.70 ± 2.82 | 0.60 ± 0.37 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.94 ± 0.21 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | |
| Summer | 28.19 ± 11.22 | 8.63 ± 0.28 | 99.44 ± 2.61 | 0.36 ± 0.60 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.96 ± 0.16 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | |
| Autumn | 28.11 ± 9.96 | 7.85 ± 0.26 | 104.14 ± 2.65 | 0.33 ± 0.42 | 0.09 ± 0.06 | 0.62 ± 0.14 | 0.01 ± 0.01 |
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I | 0.9977 | 0.9959 | 0.9988 | 0.9953 |
| Z-score | 625.23 | 623.98 | 625.83 | 623.80 |
| p-value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Distribution patterns | Clustered | Clustered | Clustered | Clustered |
| Types | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold spots 99% confidence | 0.00% | 29.48% | 22.49% | 26.32% |
| Cold spots 95% confidence | 0.00% | 18.74% | 26.46% | 10.61% |
| Cold spots 90% confidence | 49.43% | 8.62% | 12.17% | 4.75% |
| No Significant | 41.20% | 27.43% | 25.35% | 42.81% |
| Hotspots 99% confidence | 2.31% | 0.86% | 0.58% | 1.92% |
| Hotspots 95% confidence | 0.98% | 1.54% | 0.75% | 2.51% |
| Hotspots 90% confidence | 6.09% | 13.33% | 12.21% | 11.09% |
| Factor | Estimate | Standard Error (SE) | t-Value (t) | Effective Degrees of Freedom (edf) | Reference Degrees of Freedom (Ref.df) | F-Statistic (F) | p-Value (p) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept (season: Spring) | 1.14 | 0.20 | 5.80 | <0.001 | |||
| Season: Summer | 0.95 | 0.26 | 3.60 | <0.001 | |||
| Season: Autumn | 0.16 | 0.37 | 0.43 | 0.67 | |||
| Season: Winter | −0.33 | 0.34 | −0.95 | 0.35 | |||
| s(WD) | 2.40 | 3.00 | 6.35 | <0.001 | |||
| s(DO) | 3.71 | 4.61 | 4.04 | <0.005 | |||
| s(Z_Bi) | 3.81 | 4.69 | 6.29 | <0.001 | |||
| s(Cond) | 6.14 | 7.25 | 4.23 | <0.001 | |||
| s(PO4) | 1.78 | 2.23 | 5.27 | <0.05 | |||
| s(NH4) | 2.26 | 2.75 | 2.36 | 0.10 | |||
| s(TN) | 1.86 | 2.30 | 0.79 | 0.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, Z.; Hu, F.; Xiang, M.; Fu, X.; Li, X. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Fish Density in a Deep-Water Reservoir: Hydroacoustic Assessment of Aggregation Patterns and Key Drivers. Animals 2025, 15, 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15071068
Meng Z, Hu F, Xiang M, Fu X, Li X. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Fish Density in a Deep-Water Reservoir: Hydroacoustic Assessment of Aggregation Patterns and Key Drivers. Animals. 2025; 15(7):1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15071068
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Zihao, Feifei Hu, Miao Xiang, Xuejun Fu, and Xuemei Li. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Fish Density in a Deep-Water Reservoir: Hydroacoustic Assessment of Aggregation Patterns and Key Drivers" Animals 15, no. 7: 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15071068
APA StyleMeng, Z., Hu, F., Xiang, M., Fu, X., & Li, X. (2025). Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Fish Density in a Deep-Water Reservoir: Hydroacoustic Assessment of Aggregation Patterns and Key Drivers. Animals, 15(7), 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15071068





