Molecular Identification and Expression Analysis of NOD1/2 and TBK1 in Response to Viral or Bacterial Infection in the Spotted Knifejaw (Oplegnathus punctatus)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Fish
2.2. Sample Processing and Collection
2.3. Total RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.4. Amplification of the CDS Region of the Opnod1, Opnod2 and Optbk1 Genes
2.5. Sequence Analysis of the Opnod1, Opnod2 and Optbk1 Genes
2.6. Detection of Expression Patterns of the Opnod1, Opnod2 and Optbk1 Genes
2.7. In Vitro Stimulation of Kidney Cells of Spotted Knifejaw with Poly I:C and LPS
3. Results
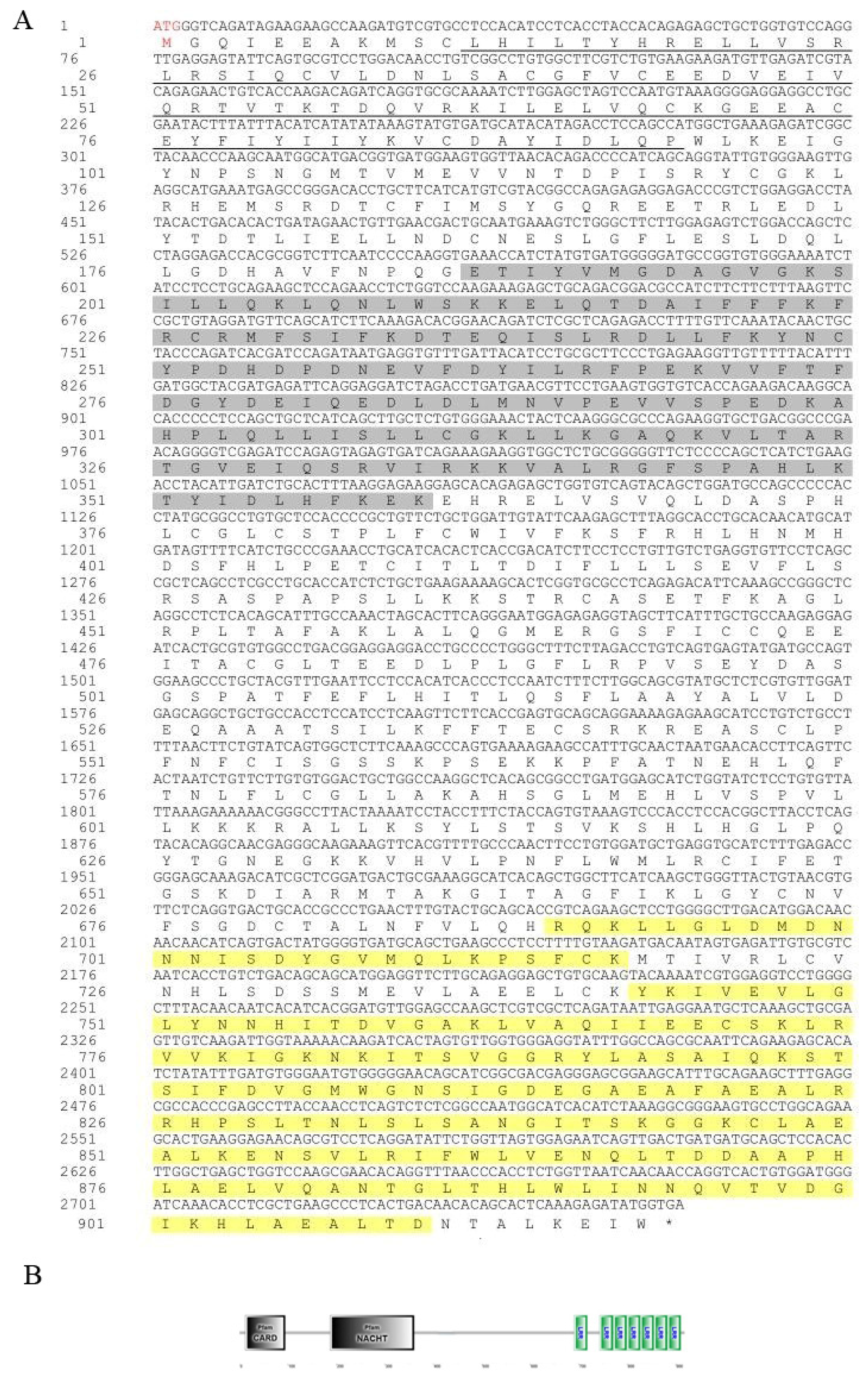
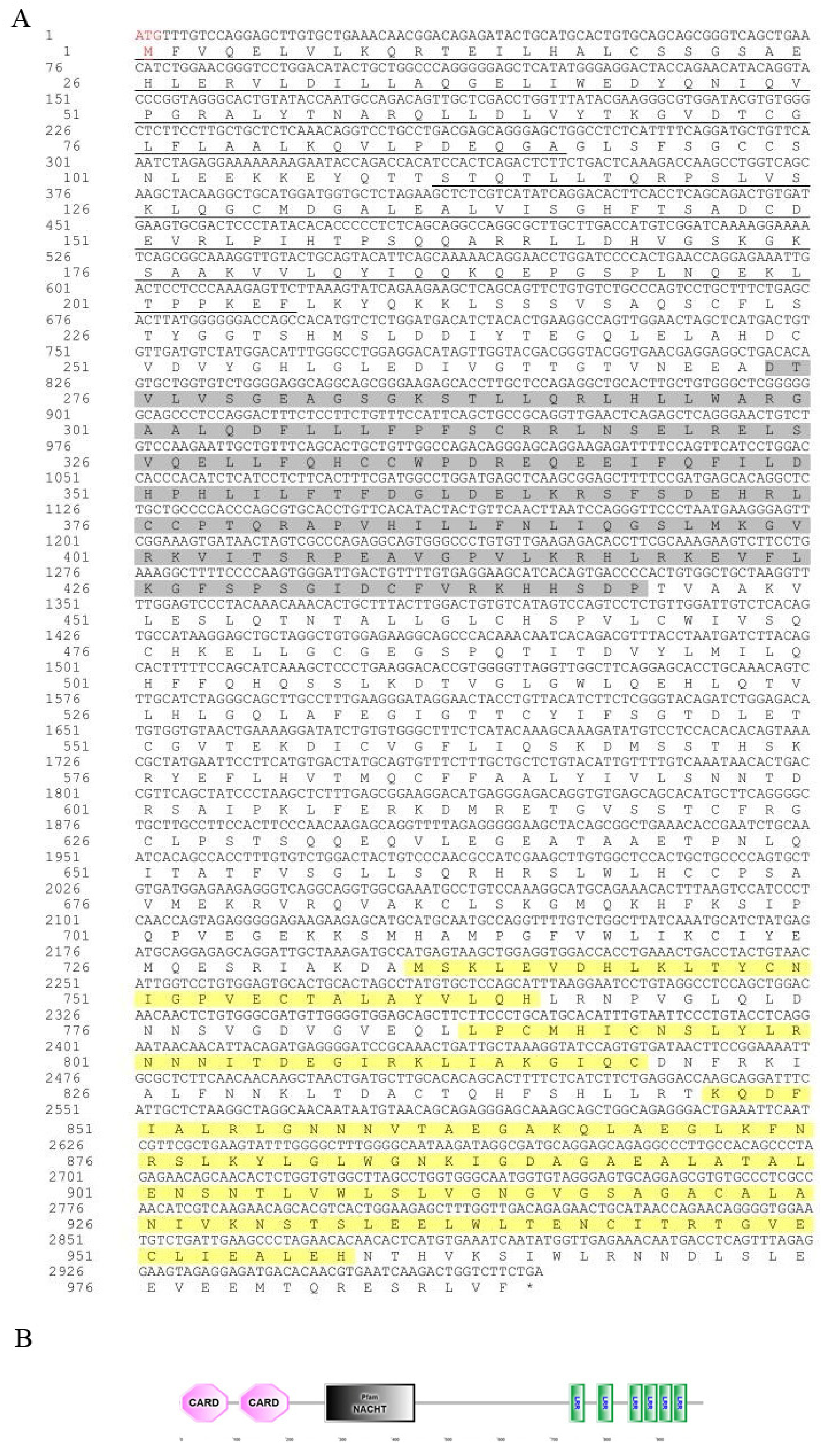
3.1. Sequence Characteristics of the Opnod1, Opnod2 and Optbk1 Genes
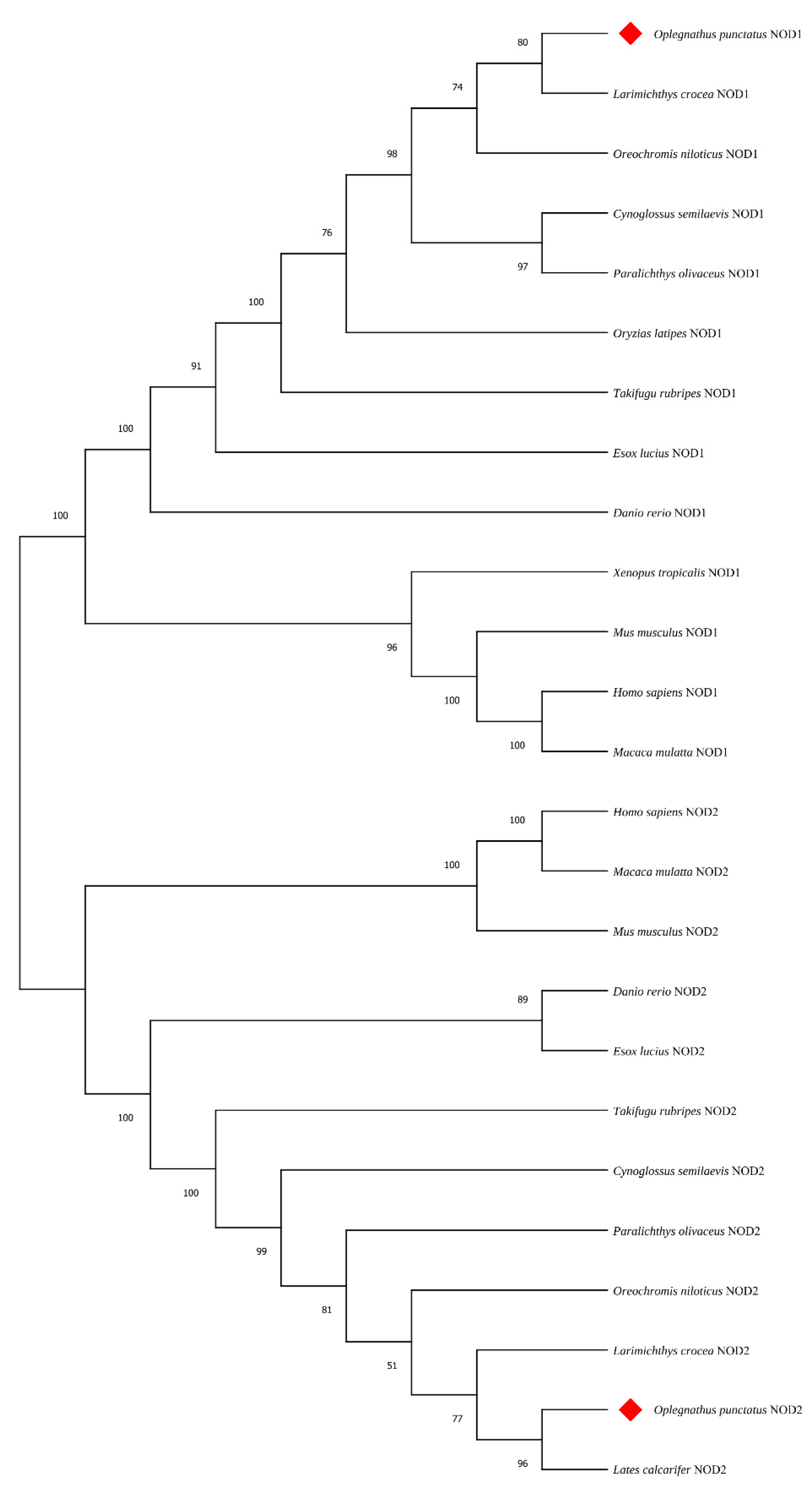
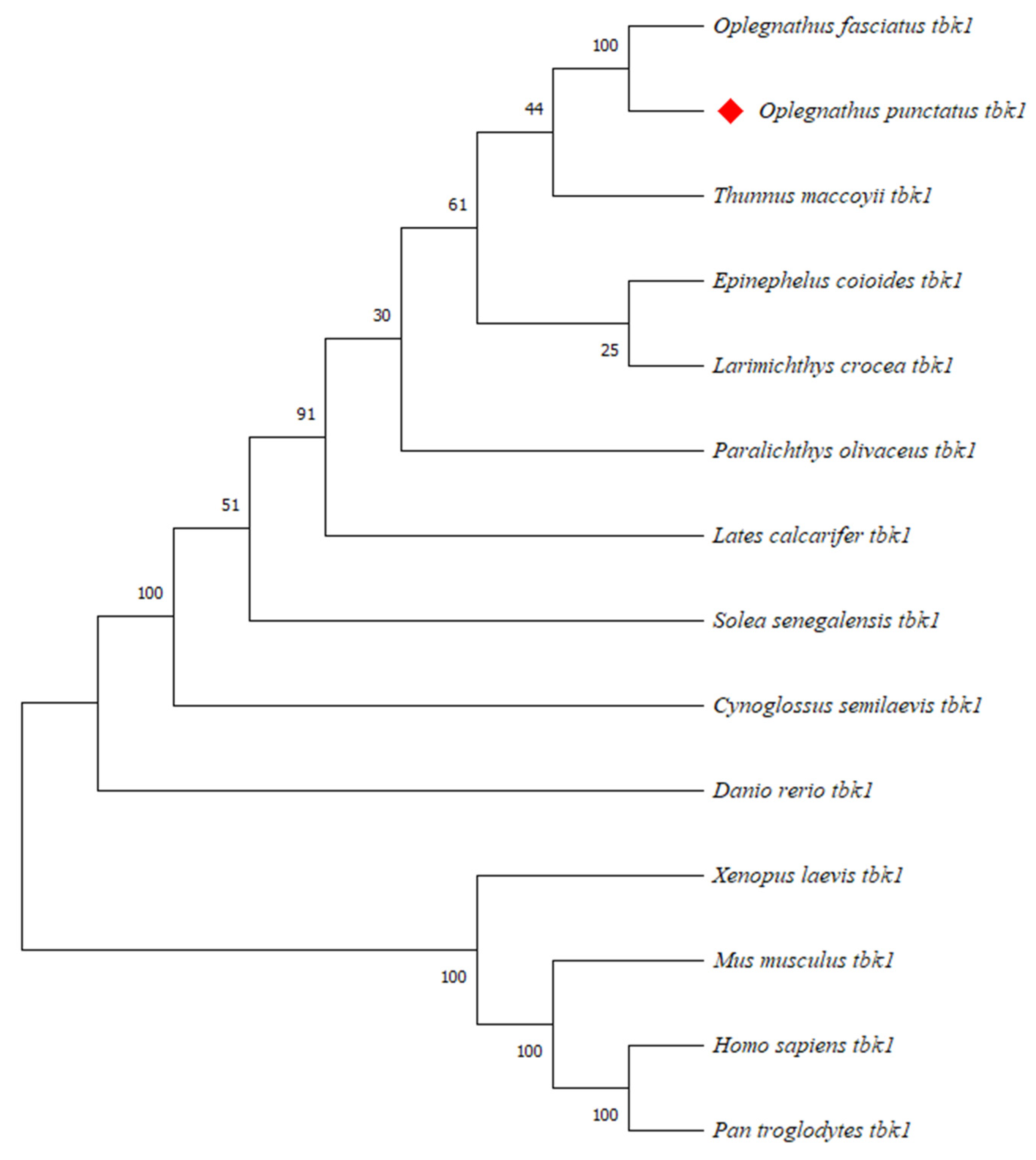
3.2. Amino Acids Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree Analysis
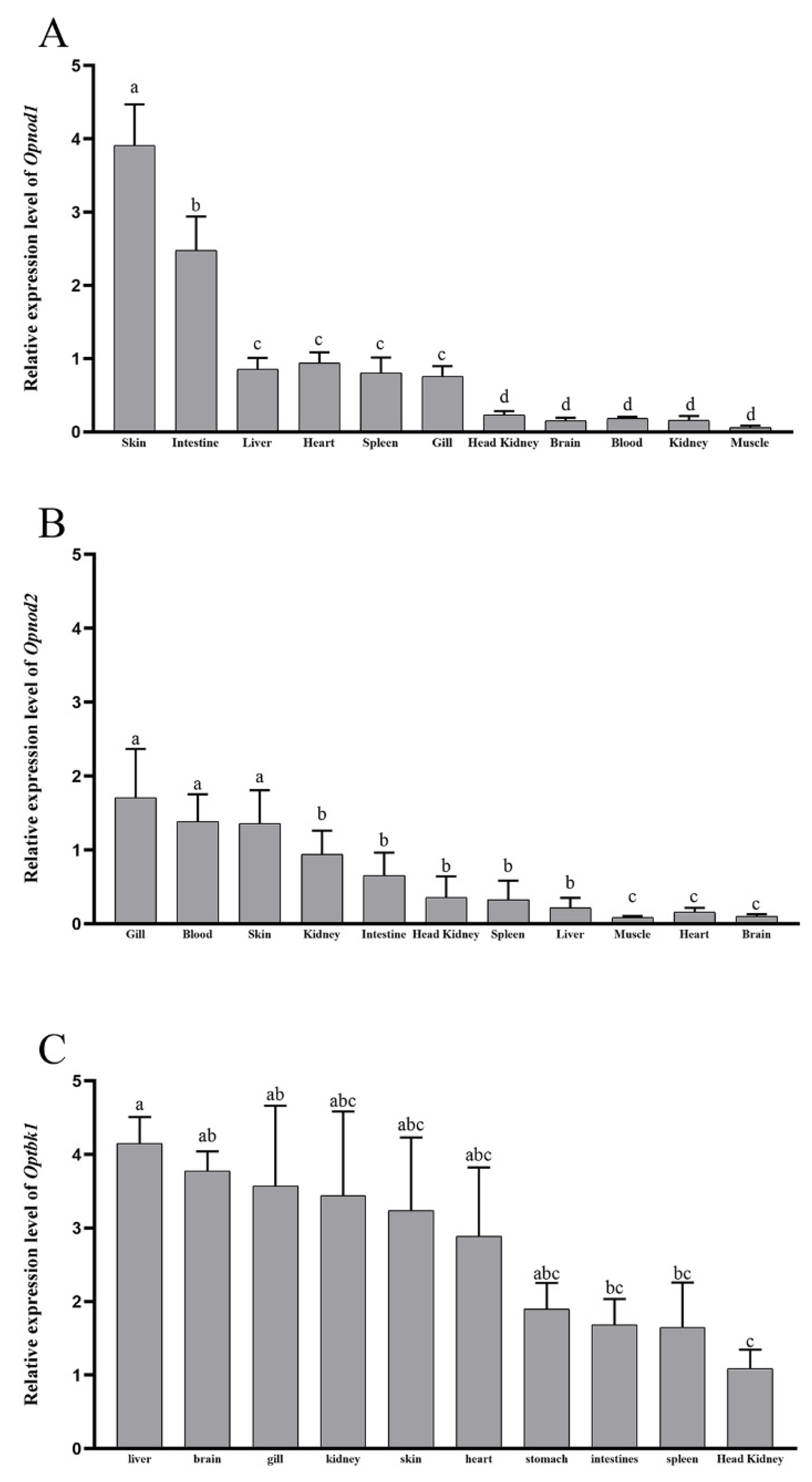
3.3. Expression Patterns of the Opnod1, Opnod2 and Optbk1 Genes in Healthy Individuals
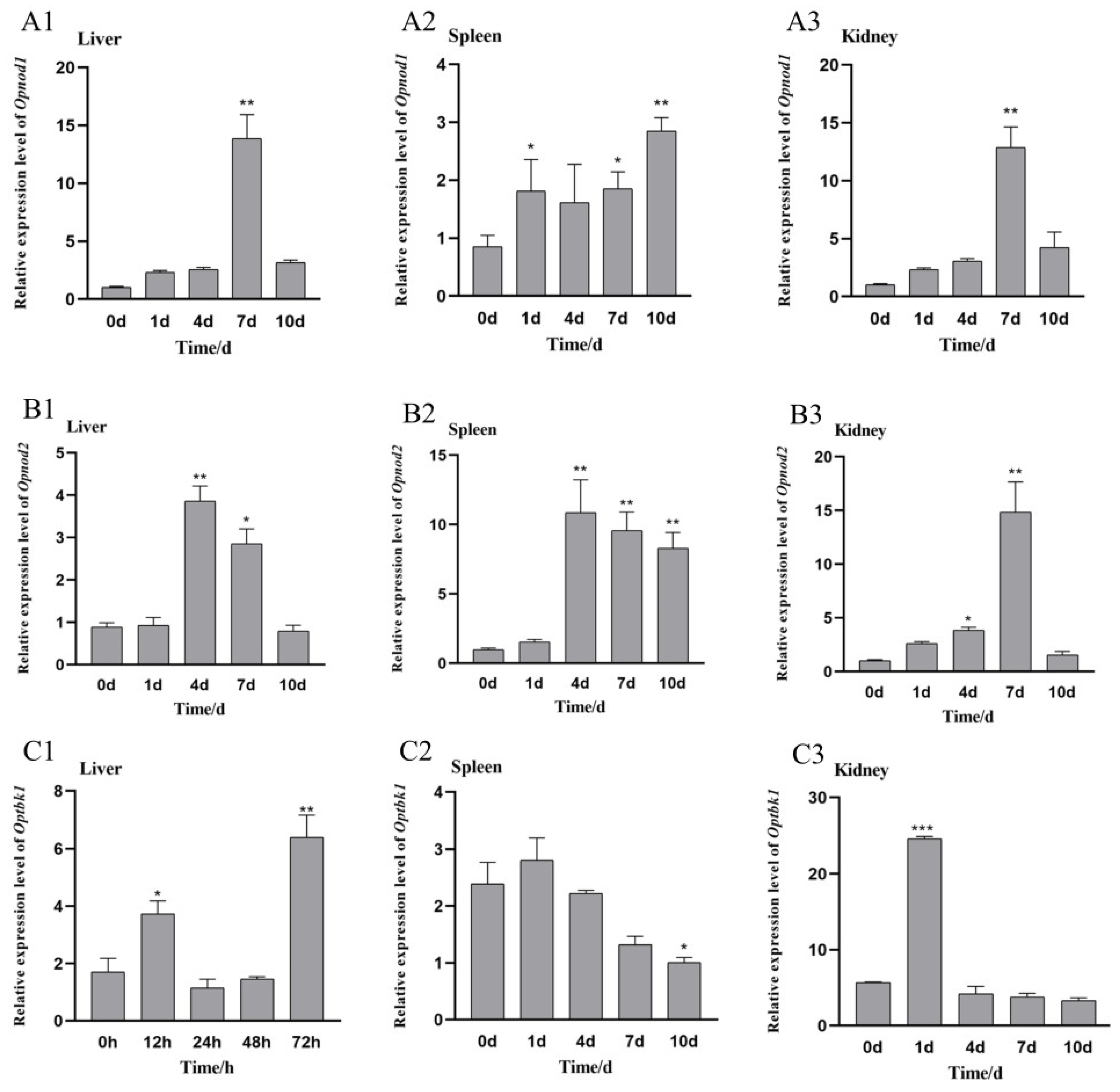
3.4. Changes in the Opnod1, Opnod2 and Optbk1 Gene Expression After Iridovirus Stimulation
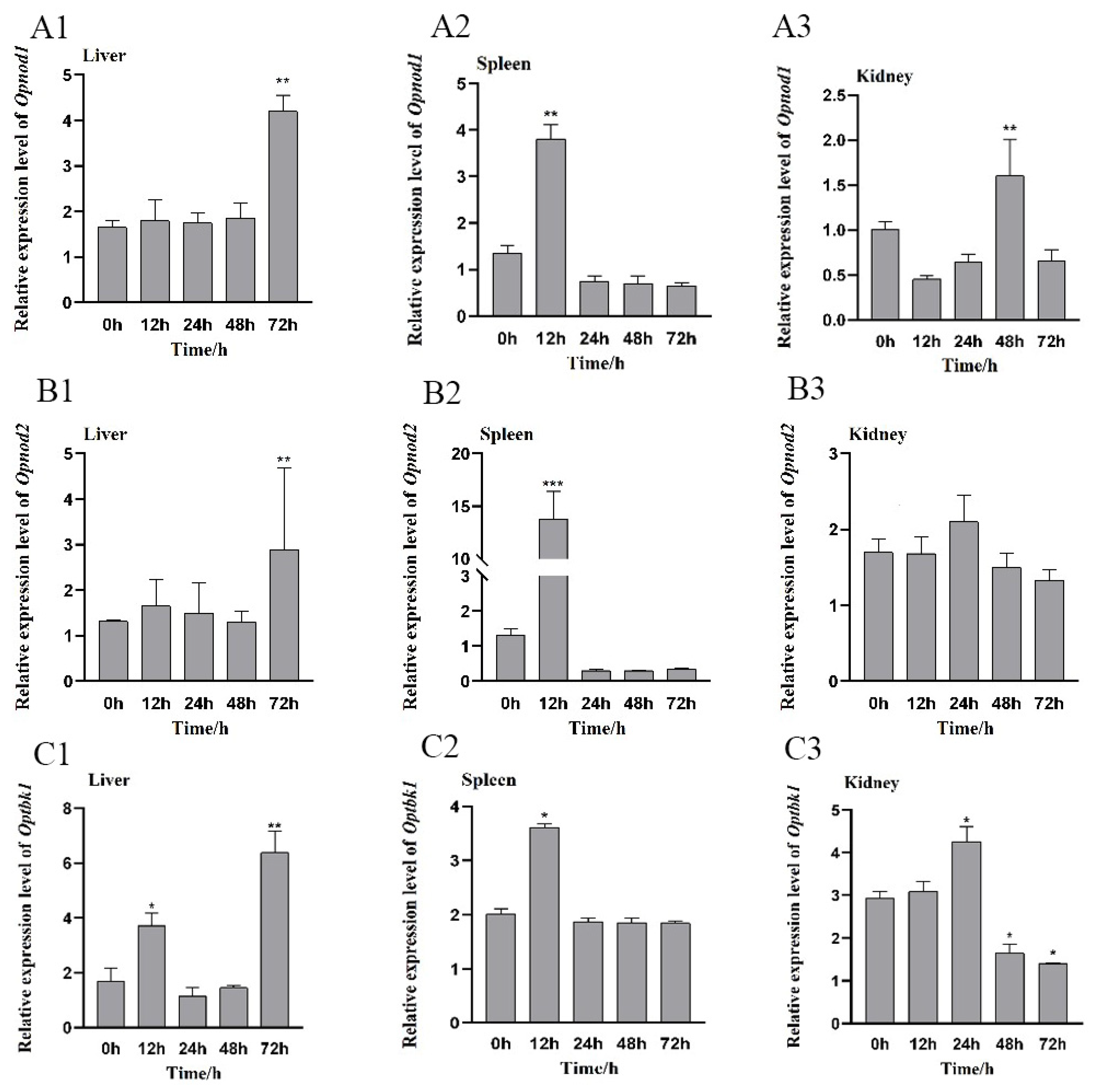
3.5. Changes in the Expression of the Opnod1, Opnod2 and Optbk1 Genes After V. harveyi Stimulation
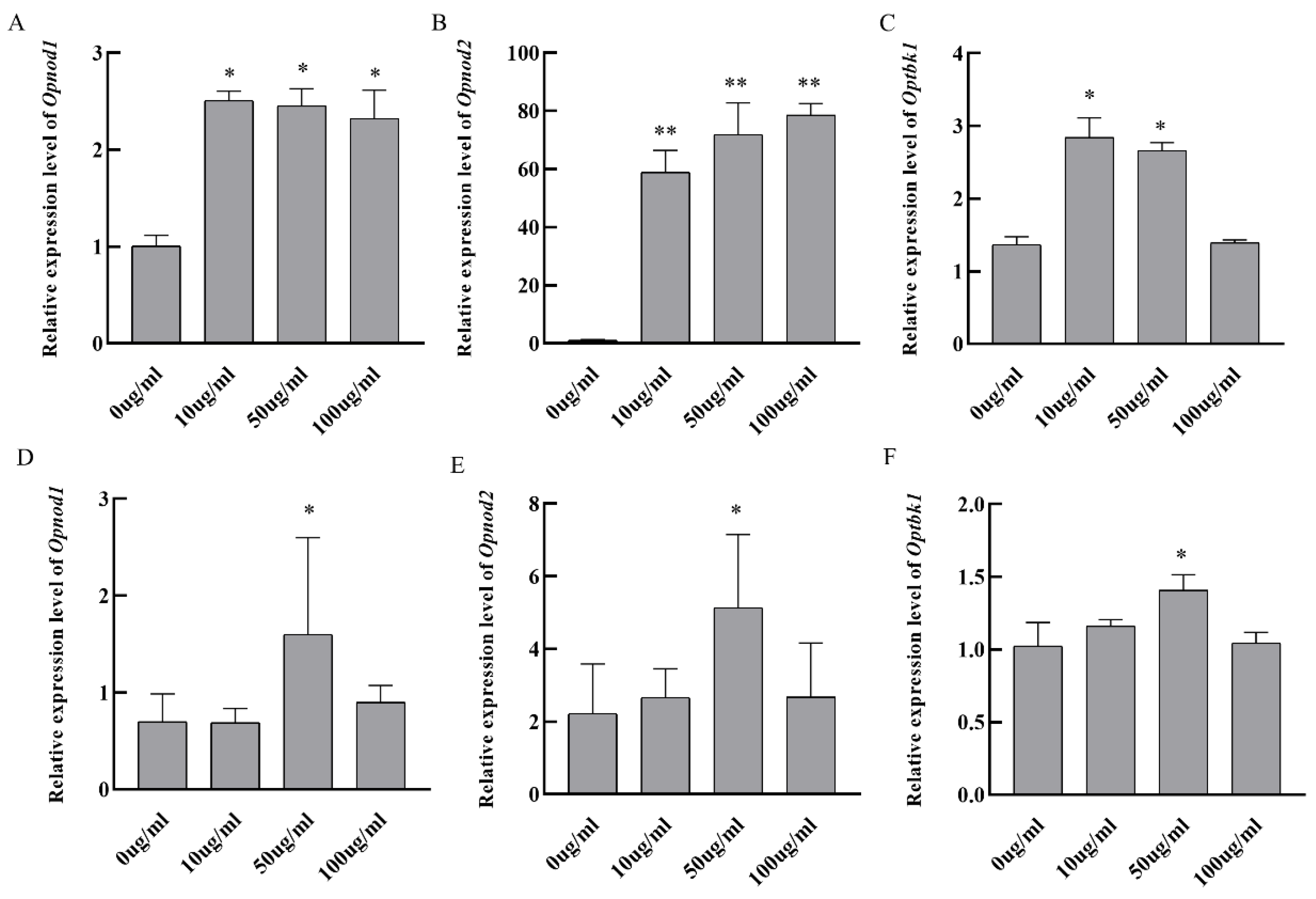
3.6. In Vitro Stimulation of Grouper Kidney Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Netea, M.G. Training innate immunity: The changing concept of immunological memory in innate host defence. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 43, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, G.D.; Balcázar, J.L. A review on the interactions between gut microbiota and innate immunity of fish. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 52, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Su, J. Progresses on three pattern recognition receptor families (TLRs, RLRs and NLRs) in teleost. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 122, 104131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, B.R. Structure of fish Toll-like receptors (TLR) and NOD-like receptors (NLR). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 1602–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietdijk, S.T.; Burwell, T.; Bertin, J.; Coyle, A.J. Sensing intracellular pathogens—NOD-like receptors. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, Z.; Yu, L.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J. Nucleotide-binding and oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptors in teleost fish: Current knowledge and future perspectives. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Z.; Abernathy, J.W.; Wang, S.; Li, P.; Kucuktas, H.; Liu, H.; Peatman, E.; Liu, Z. NOD-like subfamily of the nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat containing family receptors and their expression in channel catfish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Lu, L.; Wang, J.; Tian, L.; Wei, W.; Wu, X.; Chen, G. The NOD1 and NOD2 in mandarinfish (Siniperca chuatsi): Molecular characterization, tissue distribution, and expression analysis. BMC Genet. 2018, 19, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Chamaillard, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Horie, Y.; Masumoto, J.; Qiu, S.; Saab, L.; Inohara, N. An essential role for NOD1 in host recognition of bacterial peptidoglycan containing diaminopimelic acid. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 702–707. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, M.; Wang, T.; Nie, P.; Zou, J.; Secombes, C.J. Cloning of two rainbow trout nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 2 (NOD2) splice variants and functional characterization of the NOD2 effector domains. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 30, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motta, V.; Soares, F.; Sun, T.; Philpott, D.J. NOD-like receptors: Versatile cytosolic sentinels. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 149–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philpott, D.J.; Sorbara, M.T.; Robertson, S.J.; Croitoru, K.; Girardin, S.E. NOD proteins: Regulators of inflammation in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Basu, M.; Paichha, M.; Lenka, S.S.; Chakrabarty, R.; Samanta, M. Hypoxic stress: Impact on the modulation of TLR2, TLR4, NOD1 and NOD2 receptor and their down-stream signalling genes expression in catla (Catla catla). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2016, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sabbah, A.; Chang, T.H.; Harnack, R.; Frohlich, V.; Tominaga, K.; Dube, P.H.; Xiang, Y.; Bose, S. Activation of innate immune antiviral responses by Nod2. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, B.; Basu, M.; Samanta, M. Molecular cloning and characterization of nucleotide binding and oligomerization domain-1 (NOD1) receptor in the Indian Major Carp, rohu (Labeo rohita), and analysis of its inductive expression and down-stream signalling molecules following ligands exposure and Gram-negative bacterial infections. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 899–908. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, B.; Basu, M.; Samanta, M. NOD1 and NOD2 receptors in mrigal (Cirrhinus mrigala): Inductive expression and downstream signalling in ligand stimulation and bacterial infections. J. Biosci. 2013, 38, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banikalyan, S.; Kumar, M.N.; Mrinal, S. Nucleotide Binding and Oligomerization Domain 1 (NOD1) Receptor in Catla (Catla catla): Inductive Expression and Down-Stream Signaling in Ligand Stimulation and Bacterial Infections. Int. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 2, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Xu, Q.; Chang, M.; Nie, P.; Peng, K. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of nuclear oligomerization domain proteins NOD1 and NOD2 in grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 28, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Xu, T. Comparative genomic and evolution of vertebrate NOD1 and NOD2 genes and their immune response in miiuy croaker. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 46, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.F.; Chang, M.X.; Li, Y.; Xue, N.N.; Li, J.H.; Chen, S.N.; Nie, P. NOD2 in zebrafish functions in antibacterial and also antiviral responses via NF-kappaB, and also MDA5, RIG-I and MAVS. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 55, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.Y.; Pang, J.C.; Lu, M.X.; Yang, X.L.; Zhu, H.P.; Ke, X.L.; Wang, M. Molecular characterization, expression and functional analysis of NOD1, NOD2 and NLRC3 in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 73, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Swain, B.; Campodonico, V.A.; Curtiss, R. Recombinant Attenuated Edwardsiella piscicida Vaccine Displaying Regulated Lysis to Confer Biological Containment and Protect Catfish against Edwardsiellosis. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, S. A genome-wide survey of NOD-like receptors in Chinese tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis): Identification, characterization and expression analysis in response to bacterial infection. J. Fish Biol. 2021, 99, 1786–1797. [Google Scholar]
- Langevin, C.; Aleksejeva, E.; Passoni, G.; Palha, N.; Levraud, J.-P.; Boudinot, P. The antiviral innate immune response in fish: Evolution and conservation of the IFN System. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 4904–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, A.; Gutiérrez, D.; Epuyao, N.; Modak, B.; Imarai, M.; Valenzuela, B. Alpinone: A positive regulator molecule of immune antiviral response in Atlantic salmon kidney cells. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2022, 126, 104262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Lu, L.-F.; LaPatra, S.E.; Chen, D.-D.; Zhang, Y.-A. Zebrafish STAT6 negatively regulates IFNφ1 production by attenuating the kinase activity of TANK-binding kinase 1. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 67, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Su, J.; Yang, C.; Yan, N.; Rao, Y.; Chen, X. Molecular characterizations of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) TBK1 gene and its roles in regulating IFN-I pathway. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 45, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Xiao, J.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Feng, C.; Feng, H. TBK1 of black carp plays an important role in host innate immune response against SVCV and GCRV. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 69, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhao, X.; Gong, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Gui, J.F.; Zhang, Y.B. FTRCA1, a Species-Specific Member of finTRIM Family, Negatively Regulates Fish IFN Response through Autophage-Lysosomal Degradation of TBK1. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 2407–2420. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Weng, S.; Luo, Y.; Huang, M.; Ai, H.; Yin, Z.; He, J. A new marine megalocytivirus from spotted knifejaw, Oplegnathus punctatus, and its pathogenicity to freshwater mandarinfish, Siniperca chuatsi. Virus Res. 2010, 147, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Kang, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Z.; Qin, Q.; Wei, J. Isolation and identification of a megalocytivirus strain (SKIV-TJ) from cultured spotted knifejaw (Oplegnathus punctatus) in China and its pathogenicity analysis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 141, 109034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wei, J.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Liu, J.; Hou, Y.; Qin, Q.; Huang, Y. Isolation, identification and genomic analysis of an ISKNV-type megalocytivirus from spotted knifejaw (Oplegnathus punctatus). Aquaculture 2021, 532, 736032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, L.; Song, Y.; Wang, N.; Gong, Z.; Yang, Q.; et al. Transcriptomic analysis reveals the gene expression profiles in the spleen of spotted knifejaw (Oplegnathus punctatus) infected by Vibrio harveyi. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2022, 133, 104432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Han, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Bian, L.; Gao, T. Transcriptomic profiling reveals the immune response mechanism of the Thamnaconus modestus induced by the poly (I:C) and LPS. Gene 2024, 897, 148065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.-H.; Yi, S.-B.; Ding, X.; Zhang, H.-X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.-C.; Lu, D.-Q.; Lin, H.-R. Differential expression analysis of nuclear oligomerization domain proteins NOD1 and NOD2 in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, K.J.; Purcell, M.K.; Winton, J.R.; Hansen, J.D. A genomic view of the NOD-like receptor family in teleost fish: Identification of a novel NLR subfamily in zebrafish. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shang, D. NOD1 and NOD2: Essential Monitoring Partners in the Innate Immune System. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 9463–9479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.Y.; Wang, K.L.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Wu, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.W.; Chen, S.N. Transcription of NOD1 and NOD2 and their interaction with CARD9 and RIPK2 in IFN signaling in a perciform fish, the Chinese perch, Siniperca chuatsi. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1374368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, B.; Basu, M.; Lenka, S.S.; Das, S.; Jayasankar, P.; Samanta, M. Characterization and Inductive Expression Analysis of Interferon Gamma-Related Gene in the Indian Major Carp, Rohu (Labeo rohita). DNA Cell Biol. 2015, 34, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, M.; Swain, B.; Sahoo, B.R.; Maiti, N.K.; Samanta, M. Induction of toll-like receptor (TLR) 2, and MyD88-dependent TLR-signaling in response to ligand stimulation and bacterial infections in the Indian major carp, mrigal (Cirrhinus mrigala). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 6015–6028. [Google Scholar]
- Caruso, R.; Núñez, G. Innate Immunity: ER Stress Recruits NOD1 and NOD2 for Delivery of Inflammation. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R508–R511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Feng, H.; Liu, H.; Kong, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Hu, W.; Guo, Q. Expression profiles of carp IRF-3/-7 correlate with the up-regulation of RIG-I/MAVS/TRAF3/TBK1, four pivotal molecules in RIG-I signaling pathway. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.L.; Yu, D.H.; Chen, J.; Fan, S.; Wang, Z.Y. Expression profiles and interaction suggest TBK1 can be regulated by Nrdp1 in response to immune stimulation in large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 46, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Z.C.; Lu, L.F.; Li, P.; Li, X.Y.; Li, S. Functional Characterization of Dark Sleeper (Odontobutis obscura) TBK1 on IFN Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 985. [Google Scholar]

| Primer | Sequence(5′-3′) | Use Application |
|---|---|---|
| Opnod1-ORF-F | ATGGGTCAGATAGAAGAAGCCAAG | ORF verification |
| Opnod1-ORF-R | TCACCATATCTCTTTGAGTGCTGTG | |
| Opnod2-ORF-F | ATGTTTGTCCAGGAGCTTGTGCTG | |
| Opnod2-ORF-R | TCAGAAGACCAGTCTTGATTCACG | |
| Optbk1-ORF-F | ATGCAGAGCACCACTAACTACCTG | |
| Optbk1-ORF-R | TCAGCCTCTCAGACCTCCGTCCAG | |
| Opnod1-qRT-F | GTTGGTGGGAGGTATTTGG | qRT-PCR |
| Opnod1-qRT-R | GTTGGTAAGGCTCGGGTG | |
| Opnod2-qRT-F | GGGGCAATAAGATAGGCG | |
| Opnod2-qRT-R | TGACGATGTTGGCGAGGG | |
| Optbk1-qRT-F | AGGACGACGAGCACTTTGTG | |
| Optbk1-qRT-R | CGTATTTCTTCTGGTGGTCTTTT | |
| β-actin-F | GCTGTGCTGTCCCTGT | |
| β-actin-R | GAGTAGCCACGCTCTGTC |
| Species | GenBank Access Number | Similarity/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NOD 1 | Oreochromis niloticus | XP_005472430.1 | 86.27 |
| Larimichthys crocea | XP_019134818.2 | 85.07 | |
| Paralichthys olivaceus | XP_019946646.1 | 84.39 | |
| Cynoglossus semilaevis | XP_008322367.1 | 81.05 | |
| Oryzias latipes | XP_020565632.1 | 78.45 | |
| Takifugu rubripes | XP_003965935.3 | 74.4 | |
| Esox lucius | XP_010883447.1 | 71.35 | |
| Danio rerio | XP_002665106.3 | 65.25 | |
| Macaca mulatta | XP_028701734.1 | 50.71 | |
| Mus musculus | NP_001164478.1 | 50.33 | |
| Homo sapiens | XP_011513383.1 | 49.6 | |
| Xenopus laevis | XP_031759856.1 | 48.74 | |
| NOD2 | Lates calcarifer | XP_018522174 | 89.59 |
| Larimichthys crocea | XP_010727419.3 | 85.64 | |
| Oreochromis niloticus | XP_003437591.1 | 83.82 | |
| Paralichthys olivaceus | XP_019935411.1 | 83.22 | |
| Cynoglossus semilaevis | XP_008335431.1 | 79.27 | |
| Takifugu rubripes | XP_029701512.1 | 77.25 | |
| Esox lucius | XP_010894874.4 | 67.4 | |
| Danio rerio | NP_001314973.1 | 64.18 | |
| Macaca mulatta | XP_014981593.2 | 46.26 | |
| Homo sapiens | NP_071445.1 | 46.26 | |
| Mus musculus | AAN84594.1 | 45.54 | |
| TBK1 | Oplegnathus fasciatus | AHX37216.1 | 99.86 |
| Thunnus maccoyii | XP_042259009.1 | 98.47 | |
| Larimichthys crocea | AKM77645.1 | 98.06 | |
| Epinephelus coioides | ATI15615.1 | 97.93 | |
| Lates calcarifer | XP_018530412.1 | 97.92 | |
| Paralichthys olivaceus | XP_019966450.1 | 97.09 | |
| Solea senegalensis | XP_043878151.1 | 96.26 | |
| Cynoglossus semilaevis | XP_008313509.1 | 95.29 | |
| Danio rerio | NP_001038213.2 | 85.48 | |
| Mus musculus | NP_062760.3 | 71.78 | |
| Homo sapiens | NP_037386.1 | 71.65 | |
| Pan troglodytes | XP_509194.2 | 71.64 | |
| Xenopus laevis | NP_001086516.1 | 64.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, M.; Chen, S. Molecular Identification and Expression Analysis of NOD1/2 and TBK1 in Response to Viral or Bacterial Infection in the Spotted Knifejaw (Oplegnathus punctatus). Animals 2025, 15, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15071006
Song Y, Wang L, Li K, Zhang M, Chen S. Molecular Identification and Expression Analysis of NOD1/2 and TBK1 in Response to Viral or Bacterial Infection in the Spotted Knifejaw (Oplegnathus punctatus). Animals. 2025; 15(7):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15071006
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yu, Lei Wang, Kaimin Li, Mengqian Zhang, and Songlin Chen. 2025. "Molecular Identification and Expression Analysis of NOD1/2 and TBK1 in Response to Viral or Bacterial Infection in the Spotted Knifejaw (Oplegnathus punctatus)" Animals 15, no. 7: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15071006
APA StyleSong, Y., Wang, L., Li, K., Zhang, M., & Chen, S. (2025). Molecular Identification and Expression Analysis of NOD1/2 and TBK1 in Response to Viral or Bacterial Infection in the Spotted Knifejaw (Oplegnathus punctatus). Animals, 15(7), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15071006





