Food Habits of the Wolf in a Low-Density Territory in the Northeast of Trás-os-Montes (Portugal)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
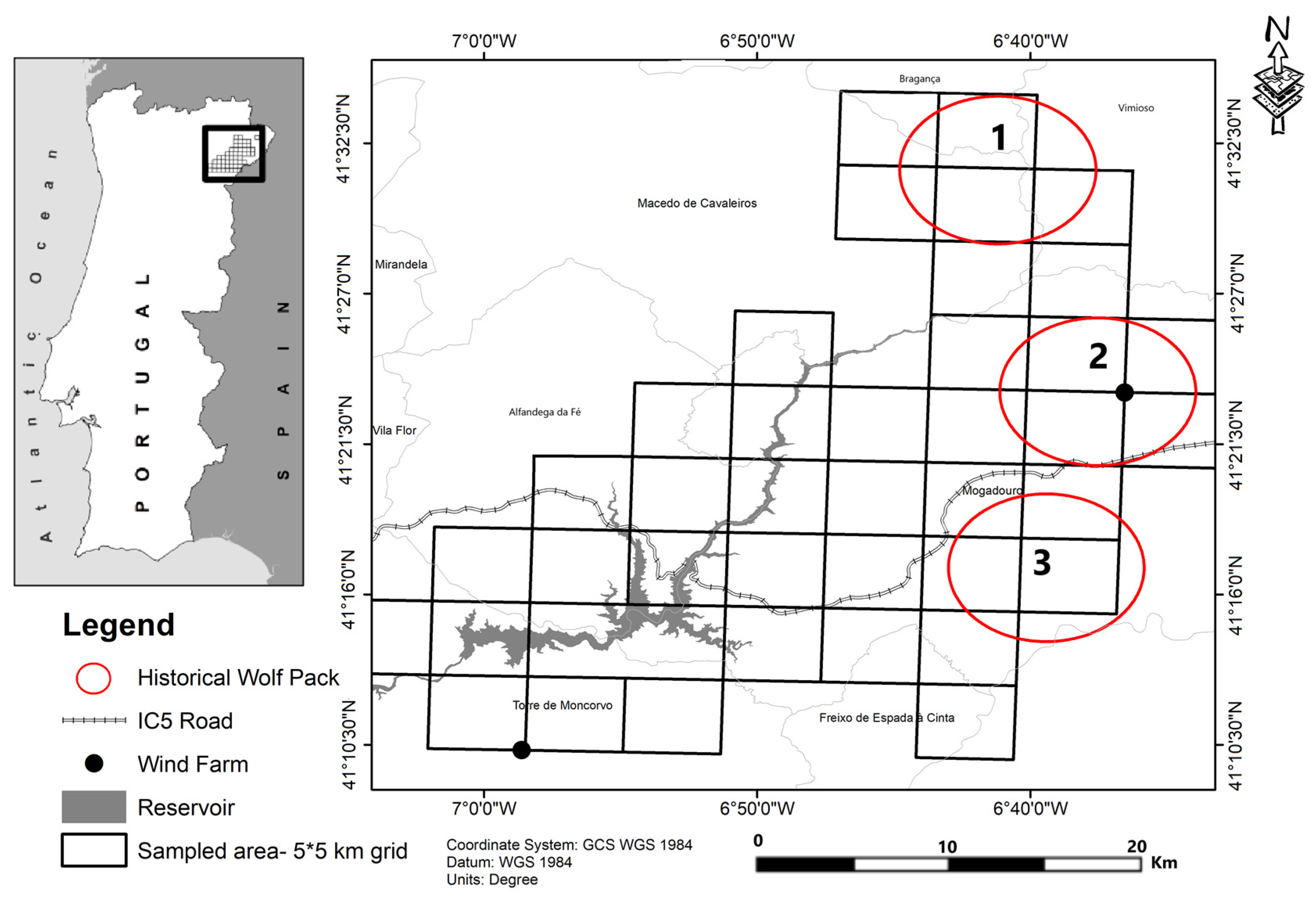
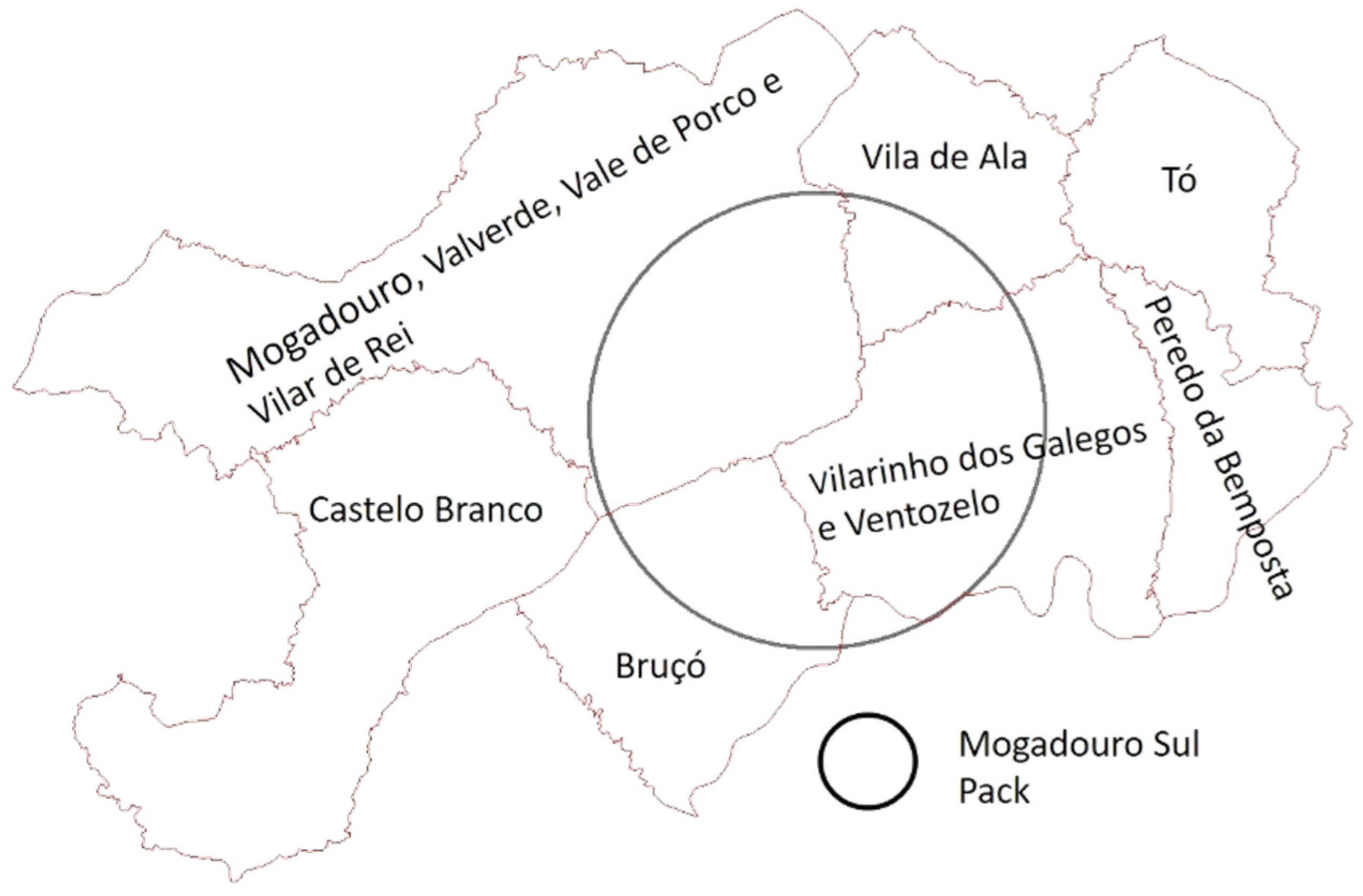
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Scats Analysis
2.4. Wolf Diet Analysis
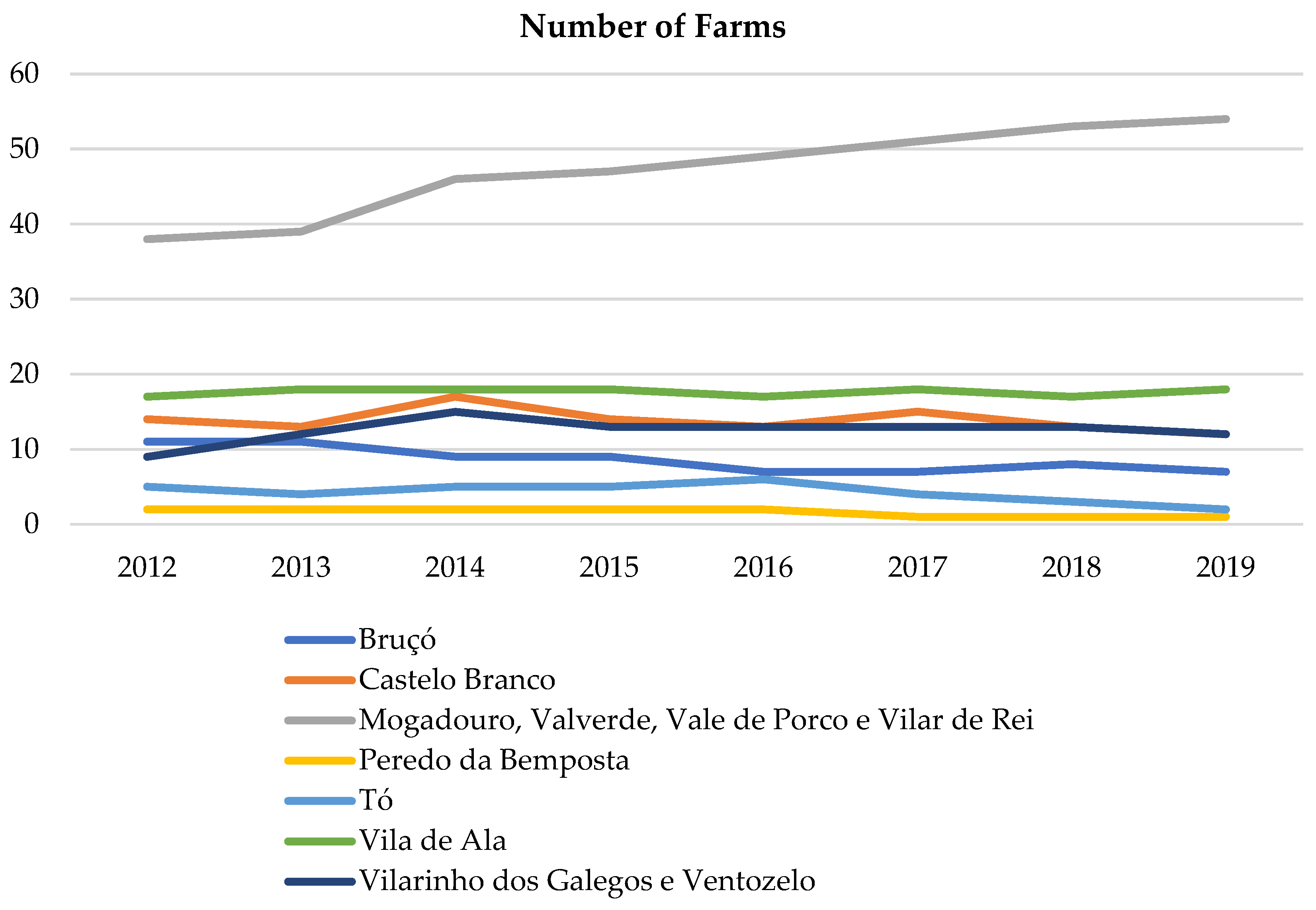
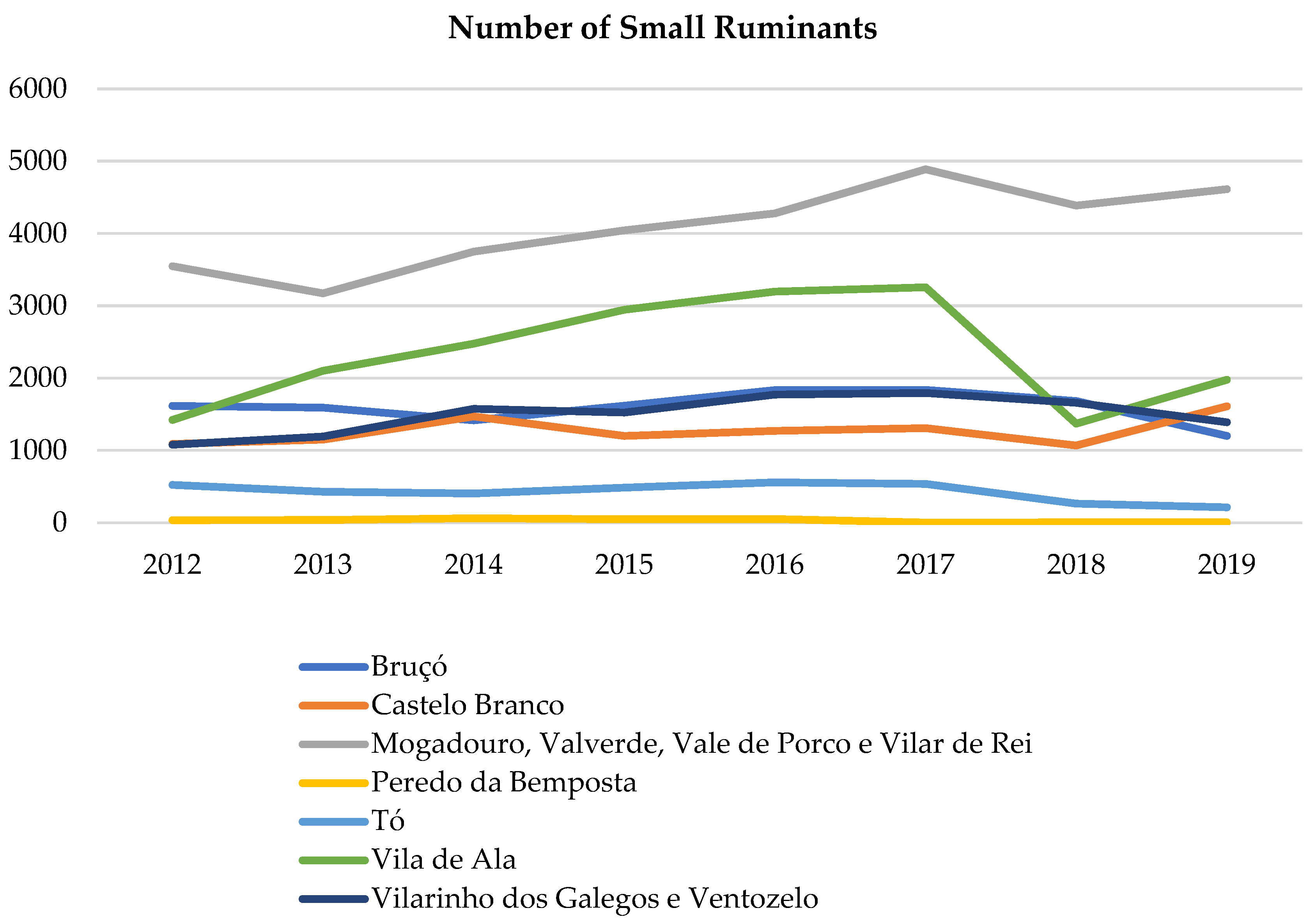
2.5. Domestic Small Ruminants’ Trend
3. Results
3.1. Global Diet Composition
3.2. Seasonal Diet Composition
3.3. Domestic Small Ruminants’ Trend
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Year | Parishes | Farms | Animals |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | Bruçó | 11 | 1615 |
| Castelo Branco | 14 | 1089 | |
| Mogadouro, Valverde, Vale de Porco e Vilar de Rei | 38 | 3547 | |
| Peredo da Bemposta | 2 | 34 | |
| Tó | 5 | 521 | |
| Vila de Ala | 17 | 1420 | |
| Vilarinho dos Galegos e Ventozelo | 9 | 1079 | |
| 2013 | Bruçó | 11 | 1590 |
| Castelo Branco | 13 | 1148 | |
| Mogadouro, Valverde, Vale de Porco e Vilar de Rei | 39 | 3172 | |
| Peredo da Bemposta | 2 | 35 | |
| Tó | 4 | 427 | |
| Vila de Ala | 18 | 2099 | |
| Vilarinho dos Galegos e Ventozelo | 12 | 1191 | |
| 2014 | Bruçó | 9 | 1415 |
| Castelo Branco | 17 | 1468 | |
| Mogadouro, Valverde, Vale de Porco e Vilar de Rei | 46 | 3750 | |
| Peredo da Bemposta | 2 | 61 | |
| Tó | 5 | 402 | |
| Vila de Ala | 18 | 2475 | |
| Vilarinho dos Galegos e Ventozelo | 15 | 1574 | |
| 2015 | Bruçó | 9 | 1616 |
| Castelo Branco | 14 | 1199 | |
| Mogadouro, Valverde, Vale de Porco e Vilar de Rei | 47 | 4042 | |
| Peredo da Bemposta | 2 | 48 | |
| Tó | 5 | 483 | |
| Vila de Ala | 18 | 2945 | |
| Vilarinho dos Galegos e Ventozelo | 13 | 1524 | |
| 2016 | Bruçó | 7 | 1834 |
| Castelo Branco | 13 | 1269 | |
| Mogadouro, Valverde, Vale de Porco e Vilar de Rei | 49 | 4278 | |
| Peredo da Bemposta | 2 | 50 | |
| Tó | 6 | 559 | |
| Vila de Ala | 17 | 3195 | |
| Vilarinho dos Galegos e Ventozelo | 13 | 1771 | |
| 2017 | Bruçó | 7 | 1837 |
| Castelo Branco | 15 | 1307 | |
| Mogadouro, Valverde, Vale de Porco e Vilar de Rei | 51 | 4888 | |
| Peredo da Bemposta | 1 | 3 | |
| Tó | 4 | 536 | |
| Vila de Ala | 18 | 3255 | |
| Vilarinho dos Galegos e Ventozelo | 13 | 1793 | |
| 2018 | Bruçó | 8 | 1683 |
| Castelo Branco | 13 | 1067 | |
| Mogadouro, Valverde, Vale de Porco e Vilar de Rei | 53 | 4386 | |
| Peredo da Bemposta | 1 | 5 | |
| Tó | 3 | 264 | |
| Vila de Ala | 17 | 1370 | |
| Vilarinho dos Galegos e Ventozelo | 13 | 1658 | |
| 2019 | Bruçó | 7 | 1201 |
| Castelo Branco | 12 | 1611 | |
| Mogadouro, Valverde, Vale de Porco e Vilar de Rei | 54 | 4612 | |
| Peredo da Bemposta | 1 | 5 | |
| Tó | 2 | 212 | |
| Vila de Ala | 18 | 1975 | |
| Vilarinho dos Galegos e Ventozelo | 12 | 1387 |
| Year | Parishes | Sheep Farms | Sheep | Goat Farms | Goats |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | Bruçó | 1 | 1744 | 12 | 18 |
| Castelo Branco | 8 | 1558 | 15 | 180 | |
| Peredo da Bemposta | 0 | 174 | 3 | 0 | |
| Tó | 0 | 528 | 4 | 0 | |
| Group of parishes of Mogadouro, Valverde, Vale de Porco e Vilar de Rei | 11 | 3399 | 37 | 767 | |
| Group of parishes of Vilarinho dos Galegos e Ventozelo | 1 | 1428 | 11 | 190 | |
| Vila de Ala | 5 | 1584 | 19 | 213 | |
| 2019 | Bruçó | 2 | 1447 | 8 | 129 |
| Castelo Branco | 3 | 923 | 11 | 115 | |
| Peredo da Bemposta | 1 | 73 | 4 | 3 | |
| Tó | 0 | 227 | 2 | 0 | |
| Group of parishes of Mogadouro, Valverde, Vale de Porco e Vilar de Rei | 18 | 3798 | 47 | 1023 | |
| Group of parishes of Vilarinho dos Galegos e Ventozelo | 6 | 1183 | 14 | 614 | |
| Vila de Ala | 3 | 827 | 12 | 399 |
References
- Ripple, W.J.; Estes, J.A.; Beschta, R.L.; Wilmers, C.C.; Ritchie, E.G.; Hebblewhite, M.; Berger, J.; Elmhagen, B.; Letnic, M.; Nelson, M.P.; et al. Status and Ecological Effects of the World’s Largest Carnivores. Science 2014, 343, 1241484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodroffe, R.; Thirgood, S.; Rabinowitz, A. The impact of human–wildlife conflict on natural systems. In People and Wildlife: Conflict and Coexistence; Woodroffe, R., Thirgood, S., Rabinowitz, A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 9, pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, C.; Ripple, W.J. Range contractions of the world’s large carnivores. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapron, G.; Kaczensky, P.; Linnell, J.D.C.; Von Arx, M.; Huber, D.; Andrén, H.; López-Bao, J.V.; Adamec, M.; Álvares, F.; Anders, O.; et al. Recovery of Large Carnivores in Europe’s Modern Human-Dominated Landscapes. Science 2014, 346, 1517–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsey, P.A.; Chapron, G.; Petracca, L.S.; Burnham, D.; Hayward, M.W.; Henschel, P.; Hinks, A.E.; Garnett, S.T.; Macdonald, D.W.; Macdonald, E.A.; et al. Relative efforts of countries to conserve world’s megafauna. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2017, 10, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, L.M.; Pereira, H.M. Rewilding abandoned landscapes in Europe. In Rewilding European Landscapes; Navarro, L.M., Pereira, H.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA; Dordrecht, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2015; pp. 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, V.; Barroso, I.; Álvares, F.; Correia, J.; da Costa, G.F.; Moreira, L.; Nascimento, J.; Petrucci-Fonseca, F.; Roque, S.; Sousa, E. Situação Populacional do Lobo em Portugal. In Resultados do Censo Nacional 2002–2003; Technical Report; ICN/Grupo Lobo: Mafra, Portugal, 2005; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312887510_Situacao_populacional_do_lobo_em_Portugal_resultados_do_censo_nacional_20022003 (accessed on 9 May 2023).
- Pimenta, V.; Barroso, I.; Álvares, F.; Petrucci-Fonseca, F. Canis lupus lobo. In Livro Vermelho dos Mamíferos de Portugal Continenta; Mathias, L., Fonseca, M.L., Rodrigues, C., Grilo, L., Lopes-Fernandes, C., Palmeirim, M., Santos-Reis, J.M., Alves, M., Cabral, P.C., Ferreira, J.A., et al., Eds.; FCiências.ID, ICNF: Lisboa, Portugal, 2023; pp. 210–211. ISBN 978-989-53724-1-6. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/ip_23_6752 (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Mech, L.D. Where can wolves live and how can we live with them? Biol. Conserv. 2017, 210, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, J.; Sjöström, M. Human attitudes towards wolves, a matter of distance. Biol. Conserv. 2007, 137, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericsson, G.; Heberlein, T.A. Attitudes of hunters, locals, and the general public in Sweden now that the wolves are back. Biol. Conserv. 2003, 111, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiven, J.; Bjerke, T.; Kaltenborn, B.P. Factors influencing the social acceptability of large carnivore behaviours. Biodivers. Conserv. 2004, 13, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrucci-Fonseca, F. O lobo (Canis lupus signatus Cabrera, 1907) em Portugal. Problemática da sua Conservação. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade de Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, S.; De Andrade, L.P.; Fonseca, F. LIFE Project MED-WOLF Best Practice Actions for Wolf Conservation in Mediterranean-Type Areas (LIFE11 NAT/IT/069), Final Report: Action A.3. Ex-Ante Survey of Damages Suffered in the Portuguese Project Areas, Portugal. 2014.
- Torres, R.T.; Silva, N.; Brotas, G.; Fonseca, C. To Eat or Not to Eat? The Diet of the Endangered Iberian Wolf (Canis lupus signatus) in a Human-Dominated Landscape in Central Portugal. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvares, F.; Barroso, I.; Costa, G.; Espírito-Santo, C.; Fonseca, C.; Godinho, R.; Nakamura, M.; Petrucci-Fonseca, F.; Pimenta, V.; Ribeiro, S.; et al. Situação de Referência Para o Plano de Ação Para a Conservação do Lobo-Ibérico em Portugal. ICNF/CIBIO-INBIO/CE3C/UA. Lisboa. 2015. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341368691_PLANO_DE_ACAO_PARA_A_CONSERVACAO_DO_LOBO-IBERICO_EM_PORTUGAL_Situacao_de_Referencia (accessed on 9 May 2023).
- Pimenta, V.; Barroso, I.; Boitani, L.; Beja, P. Wolf predation on cattle in Portugal: Assessing the effects of husbandry systems. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 207, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espírito-Santo, C.; Petrucci-Fonseca, F. Farmers’ acceptance of wolves in Portugal: Just a question of time? Carniv. Damage Prev. News 2018, 17, 52–63. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, R.T.; Fonseca, C. Perspectives on the Iberian wolf in Portugal: Population trends and conservation threats. Biodivers. Conserv. 2016, 25, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.F.; Maia, R.; Moura, R. Implementação de Medidas Compensatórias para a Construção de Aproveitamentos Hidroelétricos-o Caso do Baixo Sabor. In 7as Jornadas de Hidráulica, Recursos Hídricos e Ambiente; Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto: Porto, Portugal, 2012; pp. 53–60. Available online: https://fe.up.pt/shrha/publicacoes/jornadas.html (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- Informação Geográfica. Available online: https://geocatalogo.icnf.pt/catalogo_tema5.html (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Fonseca, C.; Santos, P.; Torres, R.T.; Silva, C.; Monzón, A. Sus scrofa javali. In Livro Vermelho dos Mamíferos de Portugal Continental; Mathias, M.L., Fonseca, C., Rodrigues, L., Grilo, C., Lopes-Fernandes, M., Palmeirim, J.M., Santos-Reis, M., Alves, P.C., Cabral, J.A., Ferreira, M., et al., Eds.; FCiências.ID, ICNF: Lisboa, Portugal, 2023; pp. 238–239. ISBN 978-989-53724-1-6. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, R.T.; Santos, J.; Alvares, F.; Cortez, J.P.; Monzón, A. Capreolus capreolus corço. In Livro Vermelho dos Mamíferos de Portugal Continental; Mathias, M.L., Fonseca, C., Rodrigues, L., Grilo, C., Lopes-Fernandes, M., Palmeirim, J.M., Santos-Reis, M., Alves, P.C., Cabral, J.A., Ferreira, M., et al., Eds.; FCiências.ID, ICNF: Lisboa, Portugal, 2023; pp. 242–243. ISBN 978-989-53724-1-6. [Google Scholar]
- Sistemas Nacional de Informação de Recursos Hídricos. Available online: http://snirh.apambiente.pt/ (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Costa, J.C.; Aguiar, C.; Capelo, J.; Lousã, M.; Neto, C. Biogeografia de Portugal continental. Quercetea 1998, 5–56. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro-Henriques, T.; Aguiar, C. Bioclimatology, biogeography and land use of Trás-os-Montes. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Serpentine Ecology, Flora and Vegetation of Iberian Ultramafics Excursion Guide, Coimbra, Portugal, 12–16 June 2011; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10198/11037 (accessed on 25 July 2017).
- Balestrieri, A.; Remonti, L.; Prigioni, C. Assessing carnivore diet by faecal samples and stomach contents: A case study with Alpine red foxes. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2011, 6, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, D.G. Dieta de la Nutria (Lutra lutra) en un Tramo Fluvial: Variación Estacional; Final Degree Project in Biology; Universidad del País Vasco: Leioa, Spain, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Barja, I.; de Miguel, F.J.; Bárcena, F. The importance of crossroads in faecal marking behaviour of the wolves (Canis lupus). Naturwissenschaften 2004, 91, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, D.J.; Higdon, S.D.; Holub, J.L.; Montague, D.M.; Fies, M.L.; Lisette, W.P.; Marcella, K.J. Bias in Carnivore Diet Analysis Resulting from Misclassification of Predator Scats Based on Field Identification. Wildl. Soc. Bull. 2016, 40, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerloff, U.; Schloetterer, C.; Rassmann, K.; Rambold, I.; Hohmann, G.; Fruth, B.; Tautz, D. Amplification of hypervariable simple sequence repeats (microsatellites) from excremental DNA of wild living bonobos (Pan Paniscus). Mol. Ecol. 1995, 4, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, R.; López-Bao, J.V.; Castro, D.; Llaneza, L.; Lopes, S.; Silva, P.; Ferrand, N. Real-time assessment of hybridization between wolves and dogs: Combining non-invasive samples with ancestry informative markers. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzón, A.; Pereira, A.; Carneiro, C.; Morais, A.; Magalhães, M.; Ferreira, P. Persistência do Lobo-Ibérico no Baixo Sabor. In Proceedings of the Livro de Resumos do IV Congresso Ibérico do Lobo, Castelo Branco, Portugal, 27–30 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- UTAD. Relatório de Monitorização Lobo e Relatório de Monitorização MC8, Programa de Proteção e Valorização do Lobo-ibérico. Project: Aproveitamento Hidrológico do Baixo Sabor. Programa Integrado de Monitorização Ambiental (PIMA), Fase de Exploração (ano 2017); RMLB 02.01. EDP; UTAD: Mafra, Portugal, 2018; p. 48, RMC8.02.01, EDP (Unpublished Work, Internal Report). [Google Scholar]
- Perrin, M.R.; Campbell, B.S. Key to the mammals of the Andries Vosloo Kudu Reserve (eastern Cape), based on their hair morphology, for use in predator scat analysis. S.-Afr. Tydskr. Natuurnav. 1980, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Chehébar, C.; Martín, S. Guía para el reconocimiento microscópico de los pelos de los mamíferos de la Patagonia. Acta Vertebr. 1989, 16, 247–291. [Google Scholar]
- Teerink, B.J. Hair of West-European Mammals: Atlas and Identification Key; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- De Marinis, A.M.; Agnelli, P. Guide to the microscope analysis of Italian mammals hairs: Insectivora, Rodentia and Lagomorpha. Bolletino Di Zool. 1993, 60, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadros, J.; Monteiro-Filho, E. Coleta e preparação de pêlos de mamíferos para identificação em microscopia óptica. Rev. Bras. Zool. 2006, 23, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.S.; Gheler-costa, C.; Verdade, L.M. Microestruturas de pêlos de pequenos mamíferos não-voadores: Chave para identificação de espécies de agroecossistemas do estado de São Paulo, Brasil. Biota Neotrop. 2009, 9, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.C.; Silva, M.N.; Borges, M.L.; Bantel, C.G.; Pinto, L.C. Análise da Microestrutura de Pelos de Roedores dos Gêneros Euryoryzomys Baird 1858 (Cricetidae: Sigmodontinae) e Proechimys Allen 1899 (Echimyidae: Eumysopinae) Depositados na Coleção de Mamíferos do Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas da Amazônia. In Proceedings of the XX Jornada de Iniciação Científica PIBIC INPA, Manaus, Brazil, 18-22 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Backwell, L.; Taru, P. Hair morphology of some artiodactyls from southern Africa. Ann. Ditsong Natl. Mus. Nat. Hist. 2014, 4, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.; Cho, T.-Y.; Woo, D.; Min, M.-S.M.; Sugita, S.S.; Lee, H. Species Identification Key of Korean Mammal. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2014, 76, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornally, A.; Lawton, C. A guide to the identification of Irish mammal hair. In Irish Wildlife Manuals; National Parks and Wildlife Service, Department of the Arts Heritage. Regional, Rural and Gaeltacht Affairs: Dublin, Ireland, 2016; pp. 1–36. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358646272 (accessed on 23 October 2024).
- Felix, G.A. Identificação de Raças Bovinas Brasileiras por Meio de Análise Tricológica. Ph.D. Thesis, Escola de Veterinária e Zootecnia da Universidade Federal de Goiás, Goiánia, Brazil, 2016. Available online: https://repositorio.bc.ufg.br/tede/items/20ef1c3d-0d95-4891-9d94-9dfbbc0e4186/full (accessed on 6 June 2017).
- Prates, L.; Ballejo, F.; Blasi, A. Analysis of hair remains from a hunter- gatherer grave from Patagonia: Taxonomic identification and archaeological implications. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2016, 8, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvares, F. Ecologia e Conservação do Lobo (Canis lupus L.) no Noroeste de Portugal. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade de Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal, 2011. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10451/5778 (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Ruprecht, A.L. Food of the Barn owl Tyto alba guttata (CL Br.) from Kujawy. Acta Ornithol. 1979, 15, 493–512. [Google Scholar]
- Floyd, T.J.; Mech, L.D.; Jordan, P.A. Relating wolf scat content to prey consumed. J. Wildl. Manag. 1978, 42, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, J.L. Refining the Equation for Interpreting Prey Occurrence in Gray Wolf Scats. J. Wildl. Manag. 1993, 57, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANCRAS. Raça Serrana. Mirandela. 2016. Available online: http://www.caprinet.pt/PDFs/Raça_Serrana.pdf (accessed on 24 July 2017).
- Monteiro, D.O.; Mestre, R.B.; Fontes, A.S.; Azevedo, J.T. A Raça Ovina Churra Badana, Vila Real. 2005. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/234163407_A_Raca_Ovina_Churra_Badana (accessed on 11 August 2017).
- Monteiro, D.O.; Mestre, R.B.; Fontes, A.S.; Azevedo, J.T. A Raça Ovina Churra da Terra Quente, Vila Real. 2005. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/234163404_A_Raca_Ovina_Churra_da_Terra_Quente (accessed on 24 July 2017).
- Associação dos Criadores de Bovinos de Raça Mirandesa. A Raça. Available online: http://www.mirandesa.pt/caracteristicas.htm (accessed on 25 August 2017).
- Llaneza, L.; Fernández, A.; Nores, C. Dieta del lobo en dos zonas de Asturias (España) que difieren en carga ganadera. Acta Vertebrata 1996, 23, 201–213. [Google Scholar]
- Llaneza, L.; Rico, M.; Iglesias, J. Hábitos alimenticios del lobo ibérico en el antiguo Parque Nacional de la Montaña de Covadonga. Galemys 2000, 12, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Álvares, F.B.; Pereira, E.; Petrucci-Fonseca, F. O lobo no Parque Internacional Gerês-Xurés. Situação populacional, aspectos ecológicos e perspectivas de conservação. Galemys 2000, 12, 223–239. [Google Scholar]
- Carreira, R.S.; Petrucci-Fonseca, F. Lobo na região Oeste de Trás-Os-Montes (Portugal). Galemys 2000, 12, 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- Vos, J. Food habits and livestock depredation of two Iberian wolf packs (Canis lupus signatus) in the north of Portugal. Zool. Soc. Lond. 2000, 251, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roque, S.; Álvares, F.; Petrucci-Fonseca, F. Utilización espacio-temporal y hábitos alimentarios de un grupo reproductor de lobos en el noroeste de Portugal. Galemys 2001, 13, 179–198. [Google Scholar]
- Carreira, M. Contribuição Para o Estudo da Ecologia do Lobo Ibérico no Distrito de Vila Real. Master’s Dissertation, Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade de Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Salvador, A.; Abad, P.L. Food habits of a wolf population (Canis lupus) in Leon province, Spain. Mammalia 1897, 51, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, L.; Barcena, F.; Palacios, F.; Reig, S. The trophic ecology of the Iberian Wolf (Canis lupus signatus Cabrera, 1907). A new analysis of stomach’s data. Mammalia 1991, 55, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barja, I. Prey and Prey-Age Preference by the Iberian Wolf Canis Lupus Signatus in a Multiple-Prey Ecosystem. Wildl. Biol. 2009, 15, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urios, V.; Vilà, C.; Castroviejo, J. Estudio de la incidencia real de la depredacion del lobo en la ganaderia comparando dos metodos distintos. Galemys 2000, 12, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo, A.; Valente, A.; Barros, T.; Carvalho, J.; Silva, D.; Fonseca, C.; Madeira de Carvalho, L.; Torres, R. What does the wolf eat? Assessing the diet of the endangered Iberian wolf (Canis lupus signatus) in northeast Portugal. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barja, I.; Navarro-Castilla, Á.; Ortiz-Jiménez, L.; España, Á.; Hinojosa, R.; Sánchez-Sotomayor, D.; Iglesias, Á.; España, J.; Rubio-Sánchez, S.; Martín-Romero, S.; et al. Wild Ungulates Constitute the Basis of the Diet of the Iberian Wolf in a Recently Recolonized Area: Wild Boar and Roe Deer as Key Species for Its Conservation. Animals 2023, 13, 3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.-M.; Hofer, B. Diet of wolves Canis lupus recolonizing Switzerland: A preliminary approach. Rev. Suisse Zool. 2010, 117, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meriggi, A.; Brangi, A.; Schenone, L.; Signorelli, D.; Milanesi, P. Changes of wolf (Canis lupus) diet in Italy in relation to the increase of wild ungulate abundance. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2011, 23, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, S.; Mysłajek, R.W.; Kłosinska, A.; Gabrys, G. Diet and prey selection of wolves (Canis lupus) recolonising Western and Central. Mamm. Biol. 2011, 76, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedrzejewski, W.; Niedzial, M.; Hayward, M.W.; Borowik, T.; Barto, K.A.; Nowak, S.; Juszczyk, A.; Kalamarz, T.; Kloch, A.; Koniuch, J.; et al. Prey choice and diet of wolves related to ungulate communities and wolf subpopulations in Poland. J. Mammal. 2012, 93, 1480–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanszki, J.; Márkus, M.; Újváry, D.; Szabó, Á.; Szemethy, L. Diet of wolves Canis lupus returning to Diet of wolves Canis lupus returning to Hungary. Acta Theriol. 2012, 57, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.; Holzapfel, M.; Kluth, G.; Reinhardt, I.; Ansorge, H. Wolf (Canis lupus) feeding habits during the first eight years of its occurrence in Germany. Mamm. Biol. 2012, 77, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meriggi, A.; Dagradi, V.; Dondina, O.; Perversi, M.; Milanesi, P.; Lombardini, M.; Repossi, A.; Raviglione, S. Short-term responses of wolf feeding habits to changes of wild and domestic ungulate abundance in Northern Italy. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 27, 389–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbert, C.; Caniglia, R.; Fabbri, E.; Milanesi, P.; Randi, E.; Sera, M.; Torretta, E.; Meriggi, A. Why do wolves eat livestock? Factors influencing wolf diet in northern Italy. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 195, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torretta, E.; Brangi, A.; Meriggi, A. Changes in Wolf Occupancy and Feeding Habits in the Northern Apennines: Results of Long-Term Predator–Prey Monitoring. Animals 2024, 14, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, A.S. Food Habits of Wolves in Relation to Livestock Depredations in Northwestern Minnesota. Am. Midl. Nat. 2005, 154, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkle, J.A.; Krausman, P.R.; Stark, D.W.; Oakleaf, J.K.; Ballard, W.B. Summer Diet of the Mexican Gray Wolf (Canis Lupus Baileyi). Southestern Nat. 2009, 54, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebe, N.; Samelius, G.; Alisauskas, R.T.; Bantle, J.L.; Bergman, C.; de Carle, R.; Hendrickson, C.J.; Lusignan, A.; Phipps, K.J.; Pitt, J. Foraging Behaviours and Diets of Wolves in the Queen Maud Gulf Bird Sanctuary, Nunavut, Canada. Arctic 2009, 62, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggard, J. Prey selectivity of wolves in Banff National Park. I. Prey species. Can. J. Zool. 1993, 71, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmegiani, I.; Gazzola, A.; Apollonio, M. Wolf diet and its impact on the ungulates community in a new recolonized area of Western Alps: Gran Paradiso National Park. Folia Zool. 2013, 62, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanesi, P.; Meriggi, A.; Merli, E. Selection of wild ungulates by wolves Canis lupus (L. 1758) in an area of the Northern Apennines (North Italy). Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2012, 24, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, V.; Barroso, I.; Álvares, F.; Barros, T.; Borges, C.; Cadete, D.; Carneiro, C.; Casimiro, J.; Ferrão da Costa, G.; Ferreira, E.; et al. Situação Populacional do Lobo em Portugal: Resultados do Censo Nacional de 2019/2021; ICNF: Lisboa, Portugal, 2023; ISBN 978-972-775-238-6. Available online: https://censo-2019-2021.loboiberico.pt/ (accessed on 16 December 2024).
- Piscopo, N.; Gentile, L.; Scioli, E.; Eguren, V.G.; Carvajal Urueña, A.M.; García, T.Y.; Alberti, J.P.; Esposito, L. Management Models Applied to the Human-Wolf Conflict in Agro-Forestry-Pastoral Territories of Two Italian Protected Areas and One Spanish Game. Area. Animals 2021, 11, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvares, F.; Blanco, J.C.; Salvatori, V.; Pimenta, V.; Barroso, I.; Ribeiro, S. A Predação do Lobo no Gado Bovino: Caracterização do Conflito e Propostas Para a Sua Minimização; Relatório Técnico; Istituto di Ecologia Applicata & LCIE; Comissão Europeia: Brussels, Belgium, 2015; Available online: https://lcie.org/publications (accessed on 23 October 2024).
- Gazzola, A.; Capitani, C.; Mattioli, L.; Apollonio, M. Livestock damage and wolf presence. J. Zool. 2008, 274, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilo, C.; Lucas, P.M.; Fernández-Gil, A.; Seara, M.; Costa, G.; Roque, S.; Rio-Maior, H.; Nakamura, M.; Álvares, F.; Petrucci-Fonseca, F.; et al. Refuge as major habitat driver for wolf presence in human-modified landscapes. Anim. Conserv. 2018, 22, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, Wild Life and Farmers. Guia de Buenas Práticas Para la Coexistencia: Lobo-Agroganadaria. Proyecto de Cooperación de la Red Rural Nacional. 2014. Available online: https://www.altonarceamuniellos.org/sites/default/files/altonarcea/DOCUMENTOS%20INTERES/Guia_BP_coexistencia_lobo_ganaderia.pdf (accessed on 22 October 2024).
- Llaneza, L.; López-Bao, J.; Sazatornil, V. Insights into wolf presence in human- dominated landscapes: The relative role of food availability, humans and landscape atributes. Divers. Distrib. 2011, 18, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llaneza, L.; García, E.J.; Palacios, V.; Sazatornil, V.; López-Bao, J.V. Resting in risky environments: The importance of cover for wolves to cope with exposure risk in human-dominated landscapes. Biodivers. Conserv. 2016, 25, 1515–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Wolf Identification | Number of Scats | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| Male 1 (cub) | 3 | - | - |
| Male 2 | 6 | 6 | 8 |
| Male 3 (cub) | 1 | - | - |
| Female 1 | 8 | 15 | 7 |
| Female 2 | - | - | 1 |
| Without individual identification | 5 | 13 | 5 |
| Total number of scats (78) | 23 | 34 | 21 |
| Winter | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Annual Cycle | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prey | n | FO | BC | n | FO | BC | n | FO | BC | n | FO | BC | n | FO | BC |
| Domestic Animals | 6 | 54.5 | 55.9 | 7 | 63.6 | 58.1 | 28 | 90.3 | 90.0 | 13 | 81.3 | 79.2 | 54 | 78.3 | 77.1 |
| Dog | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1 | 9.1 | 6.3 | 4 | 12.9 | 9.1 | 2 | 12.5 | 8.3 | 7 | 10.1 | 7.1 |
| Domestic Ungulates | 6 | 54.5 | 55.9 | 6 | 54.5 | 51.8 | 24 | 77.4 | 80.9 | 11 | 68.8 | 70.9 | 47 | 68.1 | 70.0 |
| Goat | 4 | 36.4 | 35.1 | 4 | 36.4 | 32.5 | 13 | 41.9 | 38.3 | 7 | 43.8 | 37.6 | 28 | 40.6 | 36.7 |
| Sheep | 2 | 18.2 | 20.8 | 2 | 18.2 | 19.3 | 10 | 32.3 | 34.9 | 3 | 18.8 | 19.1 | 17 | 24.6 | 26.4 |
| Cow | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1 | 3.2 | 7.7 | 1 | 6.3 | 14.1 | 2 | 2.9 | 6.9 |
| WILD UNGULATES | 5 | 45.5 | 44.1 | 4 | 36.4 | 41.9 | 3 | 9.7 | 10.0 | 3 | 18.8 | 20.8 | 15 | 21.7 | 22.9 |
| Wild boar | 2 | 18.2 | 22.6 | 4 | 36.4 | 41.9 | 2 | 6.5 | 7.6 | 3 | 18.8 | 20.8 | 11 | 15.9 | 18.6 |
| Roe deer | 3 | 27.3 | 21.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1 | 3.2 | 2.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4 | 5.8 | 4.3 |
| Total | 11 | 100 | 100 | 11 | 100 | 100 | 31 | 100 | 100 | 16 | 100 | 100 | 69 | 100 | 100 |
| H′ | 0.58 | 0.55 | 0.60 | 0.62 | 0.65 | ||||||||||
| B′ | 0.53 | 0.45 | 0.46 | 0.51 | 0.55 | ||||||||||
| Parishes | Farms 2009 | Farms 2019 | Sheep 2009 | Sheep 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bruçó | 1 | 2 | 1744 | 1447 |
| Castelo Branco | 8 | 3 | 1558 | 923 |
| Peredo da Bemposta | 0 | 1 | 174 | 73 |
| Tó | 0 | 0 | 528 | 227 |
| Group of parishes of, Valverde, Vale de Porco e Vilar de Rei | 11 | 18 | 3399 | 3798 |
| Group of parishes of Vilarinho dos Galegos e Ventozelo | 1 | 6 | 1428 | 1183 |
| Vila de Ala | 5 | 3 | 1584 | 827 |
| Parishes | Farms 2009 | Farms 2019 | Goats 2009 | Goats 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bruçó | 12 | 8 | 18 | 129 |
| Castelo Branco | 15 | 11 | 180 | 115 |
| Peredo da Bemposta | 3 | 4 | 0 | 3 |
| Tó | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Group of parishes of Mogadouro, Valverde, Vale de Porco e Vilar de Rei | 37 | 47 | 767 | 1023 |
| Group of parishes of Vilarinho dos Galegos e Ventozelo | 11 | 14 | 190 | 614 |
| Vila de Ala | 19 | 12 | 213 | 399 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lemos, S.; Llaneza, L.; Pereira, A.; Monzón, A. Food Habits of the Wolf in a Low-Density Territory in the Northeast of Trás-os-Montes (Portugal). Animals 2025, 15, 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060873
Lemos S, Llaneza L, Pereira A, Monzón A. Food Habits of the Wolf in a Low-Density Territory in the Northeast of Trás-os-Montes (Portugal). Animals. 2025; 15(6):873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060873
Chicago/Turabian StyleLemos, Samuel, Luis Llaneza, Armando Pereira, and Aurora Monzón. 2025. "Food Habits of the Wolf in a Low-Density Territory in the Northeast of Trás-os-Montes (Portugal)" Animals 15, no. 6: 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060873
APA StyleLemos, S., Llaneza, L., Pereira, A., & Monzón, A. (2025). Food Habits of the Wolf in a Low-Density Territory in the Northeast of Trás-os-Montes (Portugal). Animals, 15(6), 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060873







