New Data on Rhinogobius chiengmaiensis and Rhinogobius mekongianus in Thailand by DNA Barcoding and Morphological Methods
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Morphological Identification
2.3. Molecular Identification
3. Results
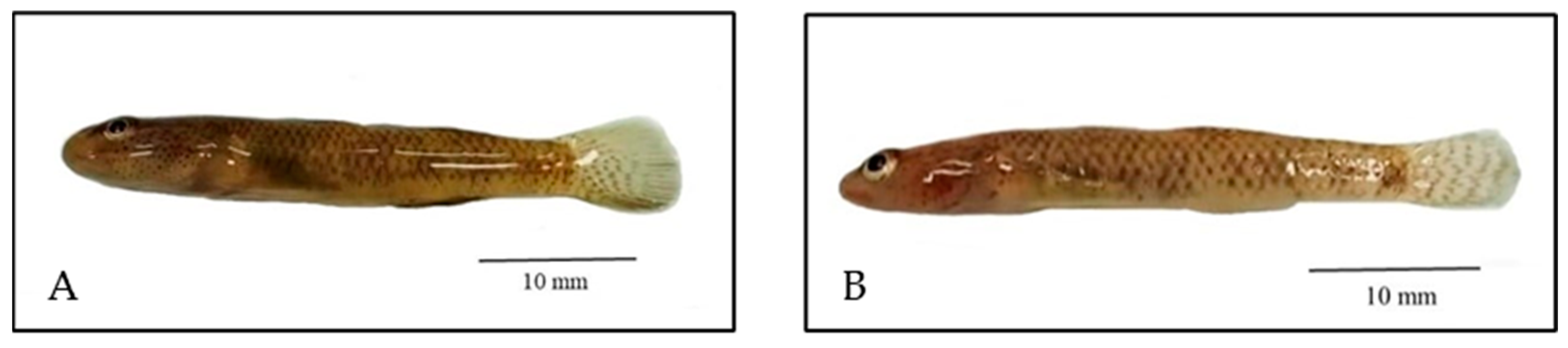
3.1. Morphological Identification
| 1a | Large ctenoid scales; longitudinal scales 24–25; predorsal scales 7; pelvic fins origin slightly behind the opercular margin | 2 |
| 1b | Moderate ctenoid scales; longitudinal scales 29–30; predorsal scales 3–4; pelvic fins origin slightly behind the opercular margin | 3 |
| 2a | Large head, head length 35.86 ± 3.28%SL, head width 62.30 ± 3.15%HL; large mouth (63.24 ± 0.80%HL), maxillary extending well beyond the posterior margin of the eyes; pelvic fin length 22.75 ± 0.36%SL | Pseudogobiopsis oligactis |
| 2b | Small head, head length 32.60 ± 1.24%SL, head width 55.61 ± 3.85%HL; moderately large mouth (48.33 ± 12.41%HL), maxillary extending from the middle of the eyes to well beyond the posterior margin of the eyes; pelvic fin length 24.85 ± 0.35%SL | Eugnathogobius siamensis |
| 3a | Moderately large mouth, maxillary extending to the middle of the eyes (35.50 ± 3.86%HL); moderately slender body, body depth at pelvic fin origin 15.85 ± 0.31%SL; pelvic fin length 19.37 ± 1.15%SL; caudal fin length 24.77 ± 0.54%SL | Rhinogobius chiengmaiensis |
| 3b | Moderately large mouth, maxillary extending to the middle of the eyes (39.19 ± 2.06%HL); very slender body, body depth at pelvic fin origin 13.28 ± 0.54%SL; pelvic fin length 17.88 ± 1.17%SL; caudal fin length 27.34 ± 2.28%SL | Rhinogobius mekongianus |
3.2. Molecular Identification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nelson, J.S.; Grande, T.C.; Wilson, M.V.H. Fishes of the World, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, J.S. Fishes of the World, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Thacker, C.E. Phylogenetic placement of the European sand gobies in Gobionellidae and characterization of gobionellid lineages (Gobiiformes: Gobioidei). Zootaxa 2013, 3619, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.S.; Kottelat, M.; Miller, P.J. Freshwater gobies of the genus Rhinogobius from the Mekong basin in Thailand and Laos, with descriptions of three new species. Zool. Stud. 1999, 38, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, I.S.; Miller, P.J. A new freshwater goby of Rhinogobius (Teleostei: Gobiidae) from Hainan Island, southern China. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2013, 21, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Kottelat, M. Zoogeography of the fishes from Indochinese inland waters with an annotated check-list. Bull. Zool. Mus. Univ. Amst. 1989, 12, 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- McCraney, W.T.; Thacker, C.E.; Alfaro, M.E. Supermatrix phylogeny resolves goby lineages and reveals unstable root of Gobiaria. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2020, 151, 106862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, C.E.; Roje, D.M. Phylogeny of Gobiidae and identification of gobiid lineages. Syst. Biodivers. 2011, 9, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.H.; Wu, H.L.; Li, C.H.; Wu, Y.Q.; Liu, S.H. A new species of Rhinogobius (Pisces: Gobiidae), with analyses of its DNA barcode. Zootaxa 2018, 4407, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.S.; Wang, S.C.; Shao, K.T. A new freshwater gobiid species of Rhinogobius Gill, 1859 (Teleostei: Gobiidae) from northern Taiwan. Zootaxa 2022, 5189, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Oseko, N.; Yamasaki, Y.Y.; Kimura, S.; Shibukawa, K. A new species with two new subspecies of Rhinogobius (Teleostei: Gobiidae) from Yaeyama Group, the Ryukyu Islands, Japan. Bull. Kanagawa Pref. Mus. (Nat. Sci.) 2022, 51, 9–34. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Iida, M.; Tran, H.D. Taxonomy of freshwater gobies of the genus Rhinogobius (Oxudercidae, Gobiiformes) from central Vietnam, with descriptions of two new species. Zootaxa 2024, 5493, 507–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panitvong, N. Freshwater Fishes of Thailand; Parbpim Ltd.: Bangkok, Thailand, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Suvarnaraksha, A.; Utsugi, K. A Field Guild of the Northern Thai Fishes; Maejo University: Chiang Mai, Thailand; Nagao Natural Environment Foundation: Tokyo, Japan, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; deWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.S.; Datta, S.K.; Zhilik, A.A. Molecular diversity of freshwater fishes of Bangladesh assessed by DNA barcoding. Bangladesh J. Zool. 2020, 48, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.S.; Datta, S.K.; Saha, T.; Hossain, Z. Molecular characterization of marine and coastal fishes of Bangladesh through DNA barcodes. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 3696–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingpeng, X.; Heshan, L.; Zhilan, Z.; Chunguang, W.; Yanguo, W.; Jianjun, W. DNA barcoding for identification of fish species in the Taiwan Strait. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetapan, K.; Panprommin, N.; Wangkahart, E.; Ruenkoed, S.; Panprommin, D. COI-high resolution melting analysis for discrimination of four fish species in the family Notopteridae in Thailand. Zool. Anz. 2024, 309, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.D.; Zemlak, T.S.; Innes, B.H.; Last, P.R.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2005, 360, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panprommin, D.; Manosri, R. DNA barcoding as an approach for species traceability and labeling accuracy of fish fillet products in Thailand. Food Control 2022, 136, 108895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitbart, M.; Kerr, M.; Schram, M.J.; Williams, I.; Koziol, G.; Peebles, E.; Stallings, C.D. Evaluation of DNA metabarcoding for identifying fish eggs: A case study on the West Florida Shelf. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Unraveling the drifting larval fish community in a large spawning ground in the Middle Pearl River using DNA barcoding. Animals 2022, 12, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao Natural Environment Foundation. Fishes of the Indochinese Mekong; Nagao Natural Environment Foundation: Tokyo, Japan, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega, accurate alignment of very large numbers of sequences. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1079, 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, I.S.; Cheng, Y.H.; Shao, K.T. A new species of Rhinogobius (Teleostei: Gobiidae) from the Julongjiang Basin in Fujian Province, China. Ichthyol. Res. 2008, 55, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottelat, M. Fishes of Laos; WHT Publications Ltd.: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, H.K. Review of the gobiid fish genera Eugnathogobius and Pseudogobiopsis (Gobioidei: Gobiidae: Gobionellinae), with descriptions of three new species. Raffles Bull. Zool. 2009, 57, 127–181. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.H.; Lim, K.K.P. Rediscovery of the bigmouth stream goby, Pseudogobiopsis oligactis (Actinopterygii: Gobiiformes: Gobionellidae) in Singapore. Nat. Singap. 2011, 4, 363–367. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, H.M. The freshwater fishes of Siam, or Thailand. Bull. U.S. Natl. Mus. 1945, 188, 1–622. [Google Scholar]
- Sajjad, A.; Jabeen, F.; Ali, M.; Zafar, S. DNA barcoding and phylogenetics of Wallago attu using mitochondrial COI gene from the River Indus. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2023, 35, 102725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Ratnasingham, S.; de Waard, J.R. Barcoding animal life: Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 2003, 270 (Suppl. S1), S96–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Guan, L.; Wang, D.; Gan, X. DNA barcoding and evaluation of genetic diversity in Cyprinidae fish in the midstream of the Yangtze River. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 2702–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Stoeckle, M.Y.; Zemlak, T.S.; Francis, C.M. Identification of birds through DNA barcodes. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agorreta, A.; San Mauro, D.; Schliewen, U.; Van Tassell, J.L.; Kovačić, M.; Zardoya, R.; Rüber, L. Molecular phylogenetics of Gobioidei and phylogenetic placement of European gobies. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Union for Conservation of Nature. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2023. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/ (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Pornsopin, P.; Sirisuksa, T.; Kantiyawong, S.; Surajit, T. Study on Cultivation of Chiangmai Stream Goby (Rhinogobius Chiengmaiensis Fowler, 1934); Inland Aquaculture Research and Development Division: Bangkok, Thailand, 2022. [Google Scholar]

| Species | GenBank Accession No. | Sample Size | Collection Site |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rhinogobius chiengmaiensis | PQ193904-PQ193905 | 2 | Ping river basin, Chiang Mai province |
| Rhinogobius mekongianus | PQ193906-PQ193910 | 5 | Kok River, Chiang Mai province |
| Eugnathogobius siamensis | PQ193911-PQ193912 | 2 | Surat Thani province |
| Pseudogobiopsis oligactis | PQ193913-PQ193914 | 2 | Satun province |
| Characters | R. chiengmaiensis | R. mekongianus | E. siamensis | P. oligactis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SL (mm) | 28.82 ± 0.51 | 29.16 ± 2.95 | 30.48 ± 2.98 | 29.42 ± 3.68 |
| As % of SL | ||||
| Head length | 31.82 ± 1.67 | 30.50 ± 0.38 | 32.60 ± 1.24 | 35.86 ± 3.28 |
| Head width | 16.46 ± 3.06 | 15.23 ± 1.90 | 18.11 ± 0.57 | 22.39 ± 3.17 |
| Body depth at P2 | 15.85 ± 0.31 | 13.28 ± 0.54 | 18.08 ± 2.29 | 15.88 ± 0.51 |
| Body depth at A | 14.80 ± 0.24 | 11.78 ± 0.37 | 16.49 ± 1.94 | 13.52 ± 0.72 |
| Snout to D1 | 37.28 ± 1.59 | 39.66 ± 2.02 | 39.56 ± 3.06 | 45.14 ± 1.75 |
| Snout to D2 | 59.50 ± 2.57 | 59.01 ± 3.47 | 61.91 ± 2.21 | 58.13 ± 0.89 |
| Snout to A | 65.08 ± 1.89 | 64.27 ± 0.31 | 65.00 ± 1.75 | 63.29 ± 2.38 |
| Snout to P2 | 29.71 ± 2.56 | 29.33 ± 0.18 | 33.31 ± 1.54 | 36.06 ± 0.37 |
| D1 base length | 15.24 ± 2.40 | 14.46 ± 1.18 | 13.16 ± 0.13 | 8.84 ± 0.50 |
| D1 base length | 20.62 ± 2.94 | 17.39 ± 0.98 | 16.95 ± 0.29 | 16.31 ± 1.47 |
| A base length | 14.19 ± 0.01 | 13.72 ± 0.17 | 15.85 ± 1.16 | 13.31 ± 3.12 |
| C length | 24.77 ± 0.54 | 27.34 ± 2.28 | 22.61 ± 3.17 | - |
| Caudal peduncle length | 20.60 ± 1.03 | 19.72 ± 0.15 | 20.53 ± 1.52 | 13.95 ± 2.88 |
| Caudal peduncle depth | 11.55 ± 0.38 | 9.62 ± 0.54 | 11.38 ± 0.44 | 10.56 ± 0.56 |
| P1 length | 20.74 ± 6.94 | 25.48 ± 1.84 | 28.63 ± 0.56 | 22.70 ± 0.37 |
| P2 length | 19.37 ± 1.15 | 17.88 ± 1.17 | 24.85 ± 0.35 | 22.75 ± 0.36 |
| As % of HL | ||||
| Snout length | 29.76 ± 1.44 | 27.92 ± 2.71 | 27.98 ± 0.75 | 27.79 ± 0.01 |
| Eye diameter | 20.16 ± 1.39 | 19.74 ± 0.57 | 13.16 ± 0.72 | 12.63 ± 0.19 |
| Postorbital length | 50.08 ± 0.04 | 52.34 ± 2.13 | 58.87 ± 0.03 | 59.58 ± 0.17 |
| Interorbital space | 21.93 ± 0.01 | 16.35 ± 1.22 | 19.13 ± 0.03 | 19.99 ± 1.23 |
| snout to maxilla | 35.50 ± 3.86 | 39.19 ± 2.06 | 48.33 ± 12.41 | 63.24 ± 0.80 |
| Head width | 51.54 ± 6.93 | 49.97 ± 6.87 | 55.61 ± 3.85 | 62.30 ± 3.15 |
| Species | GenBank Accession No. | GenBank | BOLD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | % Identity | Query Cover (%) | Species | % Identity | ||
| R. chiengmaiensis | PQ193904- PQ193905 | Rhinogobius virgigena | 95.85 | 99 | Rhinogobius virgigena | 96.22 |
| R. mekongianus | PQ193906- PQ193910 | Rhinogobius virgigena | 95.44–95.72 | 99 | Rhinogobius virgigena | 95.91–96.22 |
| E. siamensis | PQ193911- PQ193912 | Pseudogobiopsis oligactis | 98.14 | 99 | Pseudogobiopsis oligactis | 98.93 |
| P. oligactis | PQ193913- PQ193914 | Pseudogobiopsis oligactis | 99.29 | 100 | Pseudogobiopsis oligactis | 99.85 |
| Species | Nucleotide Composition (%) | %GC Content | %AT Content | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | C | A | G | |||
| R. chiengmaiensis | 29.7 ± 0.0 | 28.8 ± 0.0 | 22.3 ± 0.0 | 19.2 ± 0.0 | 48.0 ± 0.0 | 52.0 ± 0.0 |
| R. mekongianus | 30.0 ± 0.1 | 28.5 ± 0.0 | 22.2 ± 0.1 | 19.3 ± 0.1 | 47.8 ± 0.1 | 52.2 ± 0.1 |
| E. siamensis | 27.4 ± 0.0 | 28.6 ± 0.0 | 24.3 ± 0.0 | 19.7 ± 0.0 | 48.3 ± 0.0 | 51.7 ± 0.0 |
| P. oligactis | 27.3 ± 0.0 | 28.7 ± 0.0 | 23.6 ± 0.0 | 20.4 ± 0.0 | 49.1 ± 0.0 | 50.9 ± 0.0 |
| Average | 29.0 ± 1.3 | 28.6 ± 0.1 | 22.9 ± 0.9 | 19.5 ± 0.5 | 48.2 ± 0.5 | 51.8 ± 0.5 |
| Species | R. chiengmaiensis | R. mekongianus | E. siamensis | P. oligactis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R. chiengmaiensis | 0.00 | |||
| R. mekongianus | 0.86 | 0.28 | ||
| E. siamensis | 15.38 | 11.02 | 0.00 | |
| P. oligactis | 16.63 | 12.00 | 1.64 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tuncharoen, S.; Panase, P.; Panprommin, N.; Wangkahart, E.; Ruenkoed, S.; Mongkolwit, K.; Panprommin, D. New Data on Rhinogobius chiengmaiensis and Rhinogobius mekongianus in Thailand by DNA Barcoding and Morphological Methods. Animals 2025, 15, 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060871
Tuncharoen S, Panase P, Panprommin N, Wangkahart E, Ruenkoed S, Mongkolwit K, Panprommin D. New Data on Rhinogobius chiengmaiensis and Rhinogobius mekongianus in Thailand by DNA Barcoding and Morphological Methods. Animals. 2025; 15(6):871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060871
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuncharoen, Siriluck, Paiboon Panase, Nontree Panprommin, Eakapol Wangkahart, Supranee Ruenkoed, Keatipong Mongkolwit, and Dutrudi Panprommin. 2025. "New Data on Rhinogobius chiengmaiensis and Rhinogobius mekongianus in Thailand by DNA Barcoding and Morphological Methods" Animals 15, no. 6: 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060871
APA StyleTuncharoen, S., Panase, P., Panprommin, N., Wangkahart, E., Ruenkoed, S., Mongkolwit, K., & Panprommin, D. (2025). New Data on Rhinogobius chiengmaiensis and Rhinogobius mekongianus in Thailand by DNA Barcoding and Morphological Methods. Animals, 15(6), 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060871






