Simple Summary
The development of non-lethal sex identification techniques is needed to support broodstock management within geoduck clams. Panopea zelandica is placed forward as an emerging aquaculture species in New Zealand and, as with other species, cannot be accurately sexed prior to spawning, complicating production and subsequent population growth. In this study, liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) metabolomics was used to analyse gill and muscle tissue samples from male and female P. zelandica. From the results, 17 metabolites were identified that significantly differed between the sexes. Herein, lipid biosynthesis is suggested in female clams to support reproductive functions, while carbohydrate pathways sustain sperm production in males. This first-time investigation provides valuable insights into potential sex bio-markers, presenting metabolomics as a non-lethal sex identification method that can be utilised to improve breeding strategies in geoduck aquaculture.
Abstract
Geoduck aquaculture is becoming a key component in meeting international market demand, given the natural and regulatory restrictions on wild geoduck supply. Geoduck clams are not sexually dimorphic, making it practically unfeasible to distinguish between males and females prior to a spawning event. To facilitate increased production of geoduck, a better understanding of reproductive biology and associated targeted bio-markers is required. In this study, metabolomics was utilised as a research tool to distinguish between metabolites related to male and female New Zealand geoduck (Panopea zelandica), gill and muscle samples collected from broodstock individuals housed in an experimental hatchery. A total of 17 metabolites were detected, showing significant differences between sexes. The findings indicate that metabolites associated with lipid biosynthesis were increased in female clams to support reproductive functions. An increase in carbohydrate-linked metabolic pathways was detected in male geoduck, arguably to sustain sperm production. Taurine has been reported as a biomarker to distinguish between male and female bivalves in other studies and is confirmed within this study, with significant elevation in male adductor muscle tissue. Moreover, male geoduck had increased purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis, supporting energy needs. This study provides useful sex biomarkers for future breeding strategies of P. zelandica.
1. Introduction
The large, infaunal, geoduck clam, Panopea zelandica (Quoy and Gaimard, 1835), is found in subtidal areas around New Zealand [1], protected by the Quota Management System which establishes a total allowable commercial catch and ensures sustainable harvesting [2]. Mostly, these clams are harvested by divers for export as live, chilled and frozen animals to traditional South East Asia and Chinese markets [3]. The increasing demand for geoduck in the global market is contributing to the establishment of geoduck aquaculture sectors to avoid overexploitation of natural populations [4], something which has yet to be established as commercial development in New Zealand [5]. Worldwide, geoduck broodstock are predominantly harvested from fisheries for hatchery spawning purposes, making it difficult to accurately age the animals and obtain insight into their genetic diversity [6]. Furthermore, geoduck are not sexually dimorphic [7], with the external morphology of the males and females being indistinguishable from each other [8].
Sex can only be accurately determined once spawning takes place. However, during spawning events not all broodstock may be mature or spawn, causing highly skewed sex ratios in some populations [9]. Currently, the sex of geoduck can be determined via biopsies or microscopic observations of gonadal tissue after post-mortem dissections [8]. The goal is to find non-lethal sex identification methods in broodstock animals to manage captive populations and wild stock. Some progress has been made with the rapid identification of sex and/or maturation in geoduck, with vitellogenin, a precursor protein of egg yolk, found as a biomarker in female Panopea japonica using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay [8]. Another study on Panopea generosa highlights the complexity of sex identification, with pathways of steroid metabolism poorly understood [9], necessitating new research to investigate biochemical mechanisms and biological functions of steroidal metabolism in molluscs.
Omics approaches are powerful biomarker discovery tools enabling the study of complex interactions between genotypes and phenotypes, quantifying biological molecules (genes, proteins, and metabolites) to understand their structure, function, and dynamics within a biological system [10]. The use of transcriptome analyses of gonad tissues has proven successful in differentiating between male and female bivalves as seen amongst others in scallops [11], oysters [12], and clams [13]. Then again, metabolomics allows studying of the metabolome, providing insights into the functional state of cells and serving as a direct signature of biochemical activity [14]. The use of nuclear magnetic resonance metabolomics analyses to find sex-related differences has been successful in other invertebrate species. For example, in abalone, depleted sources of adenosine mono- and triphosphate along with betaine were found in males exposed to organotin compounds [15]. Male clams showed higher alanine and glycine and lower acetoacetate, choline and phosphocholine compared to females [16]. Additionally, metabolomics has revealed species-specific sex differences for both Mytilus edulis and Mytilus galloprovincialis, while also providing the best measure of functional reproductive status when using mantle tissue [17].
Considering the status of Panopea zelandica as high value species with farming potential [5], the use of new technologies to better understand the internal biochemical and/or physiological mechanisms involved in the reproductive processes [7], along with efforts to develop farming practices to increase seed numbers [8], are needed to boost this aquaculture sector. To this end, the aim of the current study was to apply liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) metabolomics as an investigation tool, to distinguish between metabolites relating to male and female Panopea zelandica gill and muscle samples collected from broodstock individuals housed in an experimental hatchery.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Husbandry, Sampling and Sexing
Wild-sourced adult geoduck from the Golden Bay region (New Zealand) were collected and transferred for 120 km to the Cawthron Aquaculture Park. Animals were housed in 100 L tanks with flow-through seawater for 17 months (as part of an ongoing hatchery research program evaluating long term broodstock holding and multiple conditioning and spawning events). During this time, they were fed with standard hatchery grown microalgae species (e.g., Chaetoceros muelleri and Tisochrysis lutea—formerly Isochrysis galbana) aiming to maintain conditions and support gametogenesis until sampling took place in September (Spring in New Zealand).
Prior to sampling, a total of 23 geoduck were removed from the holding tanks, weighed to the nearest 0.01 g, and the shell lengths were measured to the nearest 0.10 mm along the longest axis using callipers. Geoduck were opened by inserting a scalpel above the mantle and cutting through the anterior and posterior adductor muscle attachments. A subsection of gill and anterior adductor muscle tissue was collected, placed in cryovials, snap-frozen using liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80 °C until metabolomics analyses were performed. Gills and muscle tissues were selected for analyses based on their distinct metabolic functions, with rapid metabolite turnover in the gills [18], while muscle tissue has slower protein synthesis and turnover allowing more stable metabolite detection [19]. Importantly, both organs lack reproductive tissue, which would naturally prejudice male/female differences.
To infer the sex and reproductive condition of the animals, a histological tissue section was collected. Using a dissection blade, a cross section of tissue including gonad, gill, digestive tract, digestive gland, heart, kidney, palp, nerve, musculature, mantle, and siphon was obtained for histological assessments. The histology samples were processed by a commercial laboratory for embedding, sectioning, and staining with haematoxylin and eosin. Histology slides were examined using a compound light microscope (Olympus BX40, Tokyo, Japan). Sex was determined by the presence of oocytes or spermatocytes under microscopic examination. All tissues were examined for abnormalities and the presence of any parasites and pathology.
From histological assessments, a total of 11 geoducks were selected after being graded as “good”, where none or a few general features (i.e., haemocyte aggregation, infiltration or ceroid, and pathogens) were found, as well as no tissue-specific issues present in the digestive tract (e.g., epithelium abnormalities), digestive gland (e.g., tubule sloughing), and mantle (e.g., density of connective tissue). The reproductive stage of the selected animals was classified as early active, late active, ripe, spawned, and spent, based on criteria by Gribben et al. (2004) [20]. Gill and muscle tissues from these 11 clams were then utilised for metabolomics analyses, in alignment with proposed replicate sampling suggested by the Metabolomics Standards Initiative [21].
2.2. Metabolomics Sample Preparation and Analysis
Stored tissue samples were freeze-dried overnight and then ground into fine powder using a mortar and pestle. Approximately 10 mg of ground tissue together with 20 μL of internal standard (10 mM L-alanine-2,3,3,3-d4) was extracted using a two-step methanol–water pre-blend extraction solvent mixture [1], resulting in extracts for liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analyses. Quality control (QC) samples were included in each batch to measure repeatability and to identify any potential batch effects in the data. The QC samples were prepared by pooling a mixture of either muscle or gill tissue and analysing them as a biological sample. An Agilent 1260 LC coupled to an Agilent 6470 triple quadrupole (QQQ) mass spectrometer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was used for metabolomics analyses. Agilent MassHunter Workstation Data Acquisition (V 10.0) was used for compound calibration and data acquisition. The LC-MS/MS data were pre-processed with an Agilent MassHunter Workstation QQQ Quantitative Analysis Software (V 10.0) [22]. Two unique transitions were monitored per individual metabolite to provide spectral matching in addition to retention time, resulting in metabolite identities with the highest level of confidence [21,23]. Data were normalised using the mass spectrometry total useful signal normalisation method and generalised log transformed [22].
Metabolite differences between male and female clams were detected via the online webserver MetaboAnalyst (https://www.metaboanalyst.ca, accessed on 2 December 2024), focusing on the findings obtained from the anterior adductor muscle and gill tissues separately [24]. Batch effects were verified using the QC samples by calculating the coefficient of variance percentages. Univariate analyses were used to determine statistically significant metabolites between male and female clams [p-value < 0.05 (false discovery rate ≤ 0.1)], while the effect size was calculated to ensure practical significance (d-value > 0.8, calculated by determining the absolute difference between the means of the two groups divided by the maximum standard deviation of the two groups) [25]. The metabolites of significance were further grouped by tissue-specific findings in a Venn diagram. Multivariate analyses were utilised to provide an overview of the metabolic changes and covariance. The average metabolite abundance of significant metabolites between male and female clams was visualised in a heatmap with metabolite clustering. Principle component analysis (PCA) was used to visualise the major trends between male and female clams by plotting ellipses with a 95% confidence level to effectively indicate grouping [26]. Additionally, a schematic representation of the overall metabolite response with the average (±SE) metabolite abundance detected in male and female clams was manually generated using the significantly detected metabolites.
3. Results
From the dissected clams, a total of seven males were present with an average (± SD) wet weight of 405.43 ± 74.29 g and shell length of 109.57 ± 8.81 mm, and reproductive stages were from late active to spent. The remaining four clams were females with an average (± SD) wet weight of 407.50 ± 35.49 g and shell length of 110.25 ± 6.60 mm, and reproductive stages were from spawned to spent.
LC-MS/MS analyses of gill and muscle tissues resulted in a total of 159 detected metabolites, of which the nine metabolites detected in the gill and ten in the muscle showed significant concentration differences between male and female samples, as determined by cut-off values (p < 0.05; d > 0.8). Of the significantly different metabolites, two metabolites (D-sedoheptulose-7-P and malic acid) were detected in both gill and muscle tissues, while an additional seven metabolites were detected in the gills only and eight metabolites detected in the muscle tissue only (Figure 1a). From the seventeen significant metabolites, four [cis-aconitic acid (gill), citric acid (gill), malic acid (gill), and malic acid (muscle)] showed higher concentrations in female geoduck compared to male geoduck, while the remaining metabolites were lower within the female clams (as depicted in the heatmap of Figure 1b). The PCA score plots show a clear separation between male (●) and female (■) metabolites of significance (Figure 1c). An overview of the male and female geoduck metabolite response (Figure 2) encompasses a range of metabolite classes including benzoic acid derivatives, purine and pyrimidine metabolites, tricarboxylic acid cycle metabolites, amino acids, carbohydrates, fatty acid conjugates, hydroxy acids, and organosulfonic acids (Table 1).
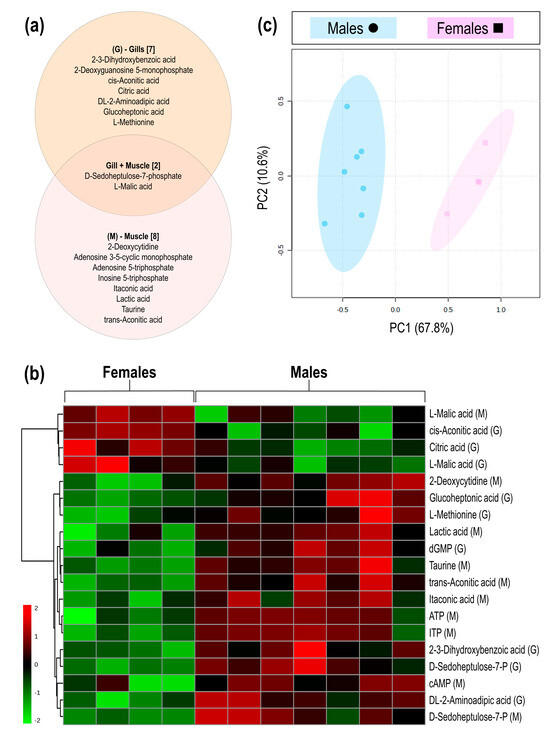
Figure 1.
The metabolite differences between male and female geoduck, Panopea zelandica: (a) Venn diagram of metabolites detected in gill and muscle tissues, (b) Heatmap visualisation of significant metabolites detected in gill (G) and muscle (M) tissue of each individual (column), and (c) PCA score plot of the differential metabolite grouped by sex.
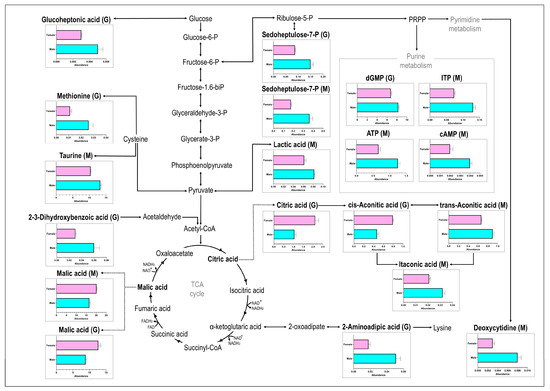
Figure 2.
The metabolite response of female (top bar in pink) and male (bottom bar in blue) geoduck, Panopea zelandica, detected in gill (G) and muscle (M) tissue, reported as average metabolite abundance distributed amongst different metabolite pathways.

Table 1.
Metabolites listed as significantly lower (↓) or higher (↑) in female geoduck, Panopea zelandica, compared to their male counterparts, as detected in gill or muscle tissue. Also reported are the cut-off values (d > 0.8, p < 0.05), a Kyoto Encyclopaedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) identification number, and a metabolite class grouping.
4. Discussion
Male and female animals differ in their physiology [27], yet geoduck show no sexual dimorphism and remain similarly sized [6], with sex only accurately identified due to the presence of spermatozoa or oocytes via histological assessment or through spawning induction [8]. This study investigated, for the first time, metabolite changes between male and female P. zelandica, analysing anterior adductor muscle and gill tissues via LC-MS/MS metabolomics. The results showed differences in metabolite levels between male and female geoduck, with females showing mostly a reduced response in metabolite abundance. In P. zelandica, a sperm to egg ratio of ≤100:1 has been reported to secure successful fertilisation [28], which might necessitate increased metabolite concentrations in muscle and gill tissues of male clams to support spermatozoa energy availability [29]. Considering that the cost of reproduction is believed to be higher in females than in males (considering the large egg size compared to sperm) [30,31], less metabolic energy via gill and muscle sources is suggested in female clams. When a large energy allocation goes to reproduction (i.e., gonad development), a reduction in available aerobic scope is seen [32], supporting the reduced metabolite concentrations detected in adjacent tissues of the female geoduck under investigation.
The metabolites, malic acid (in both gill and muscle tissue), citric acid, and cis-aconitic acid, showed higher concentrations in female geoduck (compared to the males), which are linked directly to the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, the central process of energy metabolism [33]. The TCA cycle utilises acetyl-coenzyme A (-CoA), derived from glucose via the glycolytic pathway, or fatty acids via beta (β)-oxidation, to produce citric acid [34]. During the next steps of the cycle, isocitric acid, alpha (α)-ketoglutaric acid, succinyl-CoA, succinic acid, malic acid, and oxaloacetic acid are formed, providing reducing equivalents that feed the electron transport chain [35,36]. Interestingly, in the cytosol, citric acid can be broken down to oxaloacetic acid (and malic acid which re-enters the TCA cycle) and acetyl-CoA is processed to malonyl-CoA, which in turn supports fatty acid synthesis [34]. It is hypothesised that female geoduck enhance acetyl-CoA production to support lipid biosynthesis, attributed to the increased citric acid and malic acid detected in this study. Increased lipid metabolism has been documented in studies profiling female mice [37], algae [38], and humans [39] as a result of increased hormones linked to reproductive functions. In a study on the clam, Mactra chinensis, the lipid content calculated from adductor muscle samples between males and females did not differ between seasons [40], nor were there any clear differences in haemolymph lipid concentrations between male and female geoduck, P. globosa [7]. In the mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis, lipid metabolism was more impacted in female than male mussels following exposure to anti-depressant drugs [41]. Overall profiling of fatty acid content within male and female P. zelandica will benefit future studies aimed at sex-characterisation.
It is well known that the production of gametes is an energetically costly process, necessitating stored energy in the form of dietary proteins, lipids and carbohydrates [7]. Findings from the current study suggest that male geoduck showed an increase in carbohydrate-based metabolites (D-sedoheptulose-7-phosphate and glucoheptonic acid), likely to support the formation of spermatozoa membrane lipids, which do not accumulate lipid reserves but rather utilise carbohydrates to support motility, as reported in blue mussels [42]. Also, the input of metabolites toward the glycolysis pathway could potentially be lower in the females under investigation as females utilise glycogen during conditioning [43]. Moreover, lactic acid was increased in male geoduck as a result of increased production or decreased clearance thereof. Typically, lactic acid accumulates when energy demand exceeds the supply of oxidative metabolism [44], for example, due to an increased demand, as seen in muscles of the burrowing bivalve Paphies subtriangulatum [45]. Herein, the increased lactic acid in the muscle tissue of male geoduck can be seen as an added pathway to maintain metabolic activity [46] and to support glucose metabolism [47]. It was reported that the adductor muscle of P. generosa does not attribute towards storage functions [7], yet this tissue can still support the active use of metabolites for physiological functions as hypothesised in this study.
Other metabolites, such as aminoadipic acid, methionine, and taurine, were also increased in male geoduck, highlighting the added energy requirements to support gonadal development as seen in male oysters [48]. For instance, aminoadipic acid (derived from lysine metabolism) plays an important role in protein synthesis [49], while proteins coding for methionine have been highlighted as sex-specific in sea cucumbers [50]. In contrast, taurine is not involved in protein synthesis but generally occurs in high intracellular concentrations in marine organisms [51] and has been highlighted as a biomarker to distinguish between male and female mussels [52] and zebrafish [53]. In the geoduck under investigation, males showed higher concentrations of taurine than females, potentially to regulate hormone levels, as stated in sea cucumbers [54], and to support osmoregulation, as seen in salmon [55] and oysters [56].
The process of gametogenesis is known to require substantial purine and pyrimidine investment to produce sperm and oocytes [57], as confirmed in the current study where purine (dGMP, cAMP, ATP, and ITP) and pyrimidine (deoxycytidine) metabolites significantly differed between male and female geoduck. Broadly, purine metabolites can be converted into ATP as a storage source and to cAMP to serve as a messenger molecule to regulate metabolism, as reported in sex-related genes of clams, where purine metabolism dominated in males [58]. Enrichment of purine metabolism pathways was also seen in male scallops [59]. In oysters, purine metabolism was said to be involved in the maintenance of oocyte maturation [60], and in female zebrafish, the depletion of the precursor phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate resulted in reduced intermediates within purine metabolism [53]. Conversely, in female mussels, pyrimidine metabolism was down-regulated in comparison with males following exposure to a stressor [41]. The male geoduck under investigation showed an increase in purine and pyrimidine metabolites (compared to the females), supporting the research mentioned above. It is hypothesised that male geoduck depend on the role of purine metabolism in energy supply [61] to fulfil increased energy needs.
As a rule, differentiation between sexes on a physiological level (i.e., energetics and metabolism) is driven by various factors, such as hormone levels [62], sex steroids [63], biochemical signatures from egg and sperm [64], and sex chromosomes [65]. Within the current investigation, none of the above factors were directly measured, yet sex-specific variations in metabolites were detected between male and female P. zelandica. This study indicates that metabolites associated with lipid biosynthesis were increased in female clams, while all other affected metabolites were decreased in the female cohort. The results additionally support an increase in carbohydrate-associated metabolic pathways in male geoduck, arguably meant to sustain sperm production. Taurine has been reported as a biomarker to distinguish between sexes in bivalves and is confirmed within this study as a metabolite to distinguish between male and female geoduck. Moreover, male geoduck had increased purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis, supporting energy needs.
5. Conclusions and Future Recommendations
This study provides advancements in geoduck sex identification on a metabolite level using muscle and gill tissues. Considering that geoduck, lack clear sexual dimorphism, the application of biomarker approaches, such as metabolomics, to infer sex differences becomes a useful tool within a wider aquaculture context [66]. As a next step, a non-destructive biological sample, such as haemolymph, can be analysed to determine if the same metabolites can be reliably detected [67]. Also, future studies will benefit from targeting lipid metabolism, as proven by research on Apostichopus japonicus [54] and Odontobutis potamophila [68], as well as phospholipid metabolism seen in Perna viridis [69]. The use of gonads and digestive gland as tissues to infer meaning to sex differences has also proven productive [69] and is worth considering for future metabolomics studies on geoduck sex characterisation. It is also important to include information relating to gonad development to allow the tracking of gametogenesis, which can assist biomarker development for different developmental stages [70]. Ultimately, sex-specific omics responses from geoduck tissues are lacking in the literature; hence, this study creates a new dataset that can contribute to the characterisation of male and female geoduck. This information provides valuable references for future breeding of P. zelandica in New Zealand.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ani15060860/s1, Raw metabolomics data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation: A.C.A., L.N.Z. and N.L.C.R.; Methodology: L.V., L.N.Z. and P.J.J.v.R.; Formal Analysis: L.V., L.N.Z. and P.J.J.v.R.; Investigation: L.V., A.C.A., L.N.Z., N.J.D., N.L.C.R. and P.J.J.v.R.; Resources: A.C.A., N.L.C.R., and L.N.Z.; Data Curation: L.V., P.J.J.v.R. and J.Z.L.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation: A.C.A. and L.V.; Writing—Review and Editing: A.C.A., L.V., L.N.Z., N.L.C.R., N.J.D., P.J.J.v.R. and J.Z.L.; Visualisation: L.V. and J.Z.L.; Supervision: L.N.Z.; Project Administration: A.C.A.; Funding Acquisition: A.C.A. and N.L.C.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the New Zealand government Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment Shellfish Aquaculture Research Platform, hosted by the Cawthron Institute (Strategic Science Investment Fund contract CAWX1801).
Institutional Review Board Statement
No ethical approval was required for this study. According to the New Zealand Animal Welfare Act, ethical approval for work using molluscs is not needed (except for cephalopods).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Raw metabolomics data are provided as Supplementary Material with this manuscript. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Thank you to Steve Webb for the valuable histological assessments. Thank you to the Aquaculture Biotechnology Research group, Auckland University of Technology, the Biomedical and Molecular Metabolism Research team at the North-West University and the team of Cawthron Aquaculture Park for continued support and scientific input. We would also like to thank the Cawthron Aquaculture Park technical staff for their constant support in animal husbandry and experimental work. A special thank you to Thao V. Nguyen for your contribution towards this experiment and the larger project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ATP | Adenosine 5-triphosphate |
| cAMP | Adenosine 3-5-cyclic monophosphate |
| CoA | Coenzyme A |
| dGMP | 2-Deoxyguanosine 5-monophosphate |
| ITP | Inosine 5-triphosphate |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopaedia of Genes and Genomes |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry |
| PCA | Principle component analysis |
| QC | Quality control |
| QQQ | Triple quadrupole |
| TCA | Tricarboxylic acid |
References
- Sharma, S.; Venter, L.; Alfaro, A.C.; Ragg, N.L.; Delorme, N.J.; Zamora, L.N. Physiological responses of juvenile New Zealand geoduck (Panopea zelandica) following emersion and recovery. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2022, 41, 100929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisheries New Zealand, Fisheries Assessment Plenary, May 2021: Stock Assessments and Stock Status. Compiled by the Fisheries Science Team, Fisheries New Zealand, Wellington, New Zealand. 2021, 1782p. Available online: https://www.mpi.govt.nz/science/fisheries-science-research/about-our-fisheries-research/ (accessed on 25 November 2024).
- Fisheries and Oceans Canada. Geoduck and Horse Clam Integrated Fisheries Management Plan 2022/23; Fisheries and Oceans Canada: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2022; Volume 22-2134, 198p. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Méndez, L.; Castro-Longoria, E.; Araujo-Palomares, C.; García-Esquivel, Z.; Castellanos-Martínez, S. Hemocyte cell types of the Cortes Geoduck, Panopea globosa (Dall 1898), from the Gulf of California, Mexico. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 100, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenton-Dozey, J.M.; Heath, P.; Ren, J.S.; Zamora, L.N. New Zealand aquaculture industry: Research, opportunities and constraints for integrative multitrophic farming. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2021, 55, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, S.L. Geoduck aquaculture: A review of reproduction, farming and potential ecological impacts of Panopea generosa and other Panopea spp. Curr. Top. Molluscan Aquac. 2020, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Arcos-Ortega, F.G.; León-Hing, S.J.S.; Rodriguez-Jaramillo, C.; Burgos-Aceves, M.A.; Giffard-Mena, I.; García-Esquivel, Z. Biochemical and histochemical changes associated with gonad development of the Cortez geoduck, Panopea globosa (Dall 1898), from the Gulf of California, Mexico. J. Shellfish Res. 2015, 34, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-S.; Ma, Y.; So, J.-H.; Lee, D.-H.; Maeng, C.-H.; Yoo, H.-K.; Lim, H.-J.; Nam, M.-M.; Sohn, S.; Park, J.-S. Development of elisa system using vitellogenin for sex identification of geoduck (Panopea japoniia). J. Shellfish Res. 2018, 37, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmins-Schiffman, E.B.; Crandall, G.A.; Vadopalas, B.; Riffle, M.E.; Nunn, B.L.; Roberts, S.B. Integrating discovery-driven proteomics and selected reaction monitoring to develop a noninvasive assay for geoduck reproductive maturation. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 3298–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.V.; Alfaro, A.C.; Mundy, C.; Petersen, J.; Ragg, N.L. Omics research on abalone (Haliotis spp.): Current state and perspectives. Aquaculture 2021, 547, 737438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Yang, C.; Liao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Deng, Y. Transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses reveal sex-related differences in the gonads of Pinctada fucata martensii. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2024, 52, 101304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proestou, D.A.; Delomas, T.A.; Sullivan, M.E.; Markey Lundgren, K. Sex-specific gene expression in eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica, gonad and mantle tissues. Invertebr. Biol. 2024, 143, e12418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ni, H.; Rong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yan, S.; Liao, X.; Dong, Z. Gonad transcriptome analysis reveals the differences in gene expression related to sex-biased and reproduction of clam Cyclina sinensis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1110587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.; Alfaro, A.C. Metabolomic strategies for aquaculture research: A primer. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 26–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Feng, J.; Cai, S.; Chen, Z. Metabolomic responses of Haliotis diversicolor to organotin compounds. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aru, V.; Balling Engelsen, S.; Savorani, F.; Culurgioni, J.; Sarais, G.; Atzori, G.; Cabiddu, S.; Cesare Marincola, F. The effect of season on the metabolic profile of the European clam Ruditapes decussatus as studied by 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Metabolites 2017, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, A.; Yeung, W.H.; Craft, J.; Brown, M.; Kennedy, J.; Bignell, J.; Stentiford, G.D.; Viant, M.R. Comparison of histological, genetic, metabolomics, and lipid-based methods for sex determination in marine mussels. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 369, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meechonkit, P.; Asuvapongpatana, S.; Jumromn, W.; Kovitvadhi, U.; Weerachatyanukul, W. Sexual differences in serotonin distribution and induction of synchronous larval release by serotonin in the freshwater mussel Hyriopsis bialatus. J. Molluscan Stud. 2012, 78, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacher, L.S.; Horstmann, L.; Hardy, S.M. A field-based study of metabolites in sacculinized king crabs Paralithodes camtschaticus (Tilesius, 1815) and Lithodes aequispinus Benedict, 1895 (Decapoda: Anomura: Lithodidae). J. Crustac. Biol. 2018, 38, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribben, P.; Helson, J.; Jeffs, A. Reproductive cycle of the New Zealand geoduck, Panopea zelandica, in two North Island populations. Veliger 2004, 47, 53–65. [Google Scholar]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.-M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis: Chemical analysis working group (CAWG) metabolomics standards initiative (MSI). Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizan, A.; Venter, L.; Jansen van Rensburg, P.J.; Ericson, J.A.; Ragg, N.L.C.; Alfaro, A.C. Metabolite changes of Perna canaliculus following a laboratory marine heatwave exposure: Insights from metabolomic analyses. Metabolites 2023, 13, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Jeon, J.; Gulde, R.; Fenner, K.; Ruff, M.; Singer, H.P.; Hollender, J. Identifying small molecules via high resolution mass spectrometry: Communicating confidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2097–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.; Soufan, O.; Li, C.; Caraus, I.; Li, S.; Bourque, G.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 4.0: Towards more transparent and integrative metabolomics analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W486–W494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venter, L.; Loots, D.T.; Mienie, L.J.; Jansen van Rensburg, P.J.; Mason, S.; Vosloo, A.; Lindeque, J.Z. The cross-tissue metabolic response of abalone (Haliotis midae) to functional hypoxia. Biol. Open 2018, 7, bio031070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venter, L.; Young, T.; Alfaro, A.C.; Lindeque, J.Z. Establishing sampling confidence parameters: Effect of sampling and transport conditions on haemocyte and metabolite profiles of Greenshell mussels. Aquaculture 2021, 538, 736538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galtsoff, P.S. Physiology of reproduction in molluscs. Am. Zool. 1961, 1, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.V.; Young, T.; Alfaro, A.C.; Ragg, N.L.; Hilton, Z.; Watts, E.; King, N. Practical fertilization procedure and embryonic development of the New Zealand geoduck clam (Panopea zelandica). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2018, 98, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulais, M.; Demoy-Schneider, M.; Alavi, S.M.H.; Cosson, J. Spermatozoa motility in bivalves: Signaling, flagellar beating behavior, and energetics. Theriogenology 2019, 136, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribben, P.; Creese, R. Protandry in the New Zealand geoduck, Panopea zelandica (Mollusca, Bivalvia). Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 2003, 44, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brokordt, K.B.; Guderley, H.E. Energetic requirements during gonad maturation and spawning in scallops: Sex differences in Chlamys islandica (Muller 1776). J. Shellfish Res. 2004, 23, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, P.J.; Vorsatz, L.D.; Costa, T.M.; Cannicci, S. Temperature extremes and sex-related physiology, not environmental variability, are key in explaining thermal sensitivity of bimodal-breathing intertidal crabs. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 858280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, O.E.; Kalhan, S.C.; Hanson, R.W. The key role of anaplerosis and cataplerosis for citric acid cycle function. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 30409–30412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, N.C.; O’Neill, L.A. A role for the Krebs cycle intermediate citrate in metabolic reprogramming in innate immunity and inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akram, M. Citric acid cycle and role of its intermediates in metabolism. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 68, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; He, H.; Meng, Y.; Luo, S.; Lu, Z. Determiners of cell fates: The tricarboxylic acid cycle versus the citrate-malate shuttle. Protein Cell 2023, 14, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, E.-Y.; Yoon, M.-K.; Kim, S.-W.; Jung, Y.; Bae, H.-W.; Lee, D.; Park, S.G.; Lee, C.-H.; Hwang, G.-S.; Chi, S.-W. Gender-specific metabolomic profiling of obesity in leptin-deficient ob/ob mice by 1H NMR spectroscopy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zang, Y.; Chen, J.; Shang, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Tang, X. The differing responses of central carbon cycle metabolism in male and female Sargassum thunbergii to ultraviolet-B radiation. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 904943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochhar, S.; Jacobs, D.M.; Ramadan, Z.; Berruex, F.; Fuerholz, A.; Fay, L.B. Probing gender-specific metabolism differences in humans by nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabonomics. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 352, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, L.; Ke, Q.; Kong, L. Gametogenic cycle and biochemical composition of the clam Mactra chinensis (Mollusca: Bivalvia): Implications for aquaculture and wild stock management. Mar. Biol. Res. 2011, 7, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, G.; Gomez, E.; Dumas, T.; Rosain, D.; Mathieu, O.; Fenet, H.; Courant, F. Early biological modulations resulting from 1-week venlafaxine exposure of marine mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis determined by a metabolomic approach. Metabolites 2022, 12, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laudicella, V.A.; Carboni, S.; Whitfield, P.D.; Doherty, M.K.; Hughes, A.D. Sexual dimorphism in the gonad lipidome of blue mussels (Mytilus sp.): New insights from a global lipidomics approach. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2023, 48, 101150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, D.; Putnam, J.; Steiner, J.N.; Fisher, B.; Burcham, G.N.; Oliver, J.; Smith, S.B.; Erickson, R.; Remek, A.; Bodoeker, N. Targeted metabolomics characterizes metabolite occurrence and variability in stable freshwater mussel populations. Conserv. Physiol. 2023, 11, coad040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowitz, J.D.; Enerbäck, S. Lactate: The ugly duckling of energy metabolism. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, J.L.; Wells, R.M. Strategies of anaerobiosis in New Zealand infaunal bivalves: Adaptations to environmental and functional hypoxia. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1995, 29, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, D.R. Origins and evolution of pathways of anaerobic metabolism in the animal kingdom. Am. Zool. 1991, 31, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, H.; Wei, L.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Yuan, D.; Wang, Z. Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses identify key factors in the vitellogenesis of juvenile Sichuan bream (Sinibrama taeniatus). Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1243767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Li, R.; Liao, Q.; Shi, G.; Zhou, Y.; Wan, W.; Li, J.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z. Comparison of biochemical composition, nutritional quality, and metals concentrations between males and females of three different Crassostrea sp. Food Chem. 2023, 398, 133868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, D.; Bos, C. Lysine requirement through the human life cycle. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1642S–1645S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.-K.; Yu, Z.-H.; Wang, W.-J.; Jia, W.-Z. Transcriptome and metabolome analyses reveal gender-specific expression genes in sea cucumber (Holothuria leucospilota). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2023, 47, 101117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yihua, C.; Min, D.; Zhiguo, D.; Yifeng, L.; Donghong, N. Function of taurine and its synthesis-related genes in hypertonic regulation of Sinonovacula constricta. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2023, 287, 111536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; Jia, X.; Cai, W. Gender-specific metabolic responses in gonad of mussel Perna viridis to triazophos. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 123, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giommi, C.; Ladisa, C.; Carnevali, O.; Maradonna, F.; Habibi, H.R. Metabolomic and transcript analysis revealed a sex-specific effect of glyphosate in zebrafish liver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ru, X.; Zhang, L.; Gonçalves, D.; Yang, H. Examination of sex-related differences in intestinal and gonadal lipid metabolism in the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Aquaculture 2023, 562, 738787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benskin, J.P.; Ikonomou, M.G.; Liu, J.; Veldhoen, N.; Dubetz, C.; Helbing, C.C.; Cosgrove, J.R. Distinctive metabolite profiles in in-migrating Sockeye salmon suggest sex-linked endocrine perturbation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11670–11678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Lu, J.; Yao, T.; Ye, L.; Wang, J. Gender-specific metabolic responses of Crassostrea hongkongensis to infection with Vibrio harveyi and lipopolysaccharide. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagné, F.; Blaise, C. Review of biomarkers and new techniques for in situ aquatic studies with bivalves. Environ. Toxic. Test. 2005, 206–228. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Xiao, G.; Chai, X.; Lin, X.; Fang, J.; Teng, S. Transcriptome analysis of sex-related genes in the blood clam Tegillarca granosa. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Sun, X.; Wu, B.; Yu, T.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, A.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, D. Transcriptomics analysis revealing candidate genes and networks for sex differentiation of yesso scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis). BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corporeau, C.; Vanderplancke, G.; Boulais, M.; Suquet, M.; Quéré, C.; Boudry, P.; Huvet, A.; Madec, S. Proteomic identification of quality factors for oocytes in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 5554–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.-W.; Li, S.-Y.; Zhang, X.-L.; Chen, C.-Y.; Sun, W.-J.; Gu, Z.-Q.; Huang, J.; He, J.-Y.; Qi, P.-Z.; Guo, B.-Y. Morphological change and differential proteomics analysis of gill in Mytilus coruscus under starvation. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleps, R.A.; Myers, T.C.; Lipcius, R.N.; Henderson, T.O. A sex-specific metabolite identified in a marine invertebrate utilizing phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubero-Leon, E.; Minier, C.; Rotchell, J.M.; Hill, E.M. Metabolomic analysis of sex specific metabolites in gonads of the mussel, Mytilus edulis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2012, 7, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, R.P.; Spicer, J.I.; Byrne, J.J.; Sommer, U.; Viant, M.R.; White, D.A.; Widdicombe, S. 1H NMR metabolomics reveals contrasting response by male and female mussels exposed to reduced seawater pH, increased temperature, and a pathogen. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7044–7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Xu, W.; Hong, Q.; Yang, C.X.L.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tan, H.; Tang, X.; Gao, Y. Rapid comparison of metabolites in humans and rats of different sexes using untargeted ultraperformance liquid chromatography coupled to time-of-flight mass spectrometry and an in-house software platform. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 21, 801–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaro, A.C.; Young, T. Showcasing metabolomic applications in aquaculture: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, N.J.; Venter, L.; Rolton, A.; Ericson, J.A. Integrating animal health and stress assessment tools using the green-lipped mussel Perna canaliculus as a case study. J. Shellfish Res. 2021, 40, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, H.; Wen, X.; Yin, S.; Jia, Y. Integrated analysis of proteomics and metabolomics reveals the potential sex determination mechanism in Odontobutis potamophila. J. Proteom. 2019, 208, 103482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, F.; Chen, H. Sex-specific metabolic dysregulation in digestive glands of green mussels following exposure to triazophos. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 194, 105514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné, F.; Burgeot, T.; Hellou, J.; St-Jean, S.; Farcy, E.; Blaise, C. Spatial variations in biomarkers of Mytilus edulis mussels at four polluted regions spanning the Northern Hemisphere. Environ. Res. 2008, 107, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).