Human Recombinant Interleukin-6 and Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Improve Inner Cell Mass Cell Number but Lack Cryoprotective Activities on In Vitro-Produced Bovine Blastocysts
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. In Vitro Embryo Production
2.3. Cytokine Supplementation
2.4. Blastocyst Development Assessment and Cell Counting
2.5. Blastocyst Cryopreservation and Thawing
2.6. Blastocyst Cell Number and Apoptosis Assessment After Freezing and Thawing
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
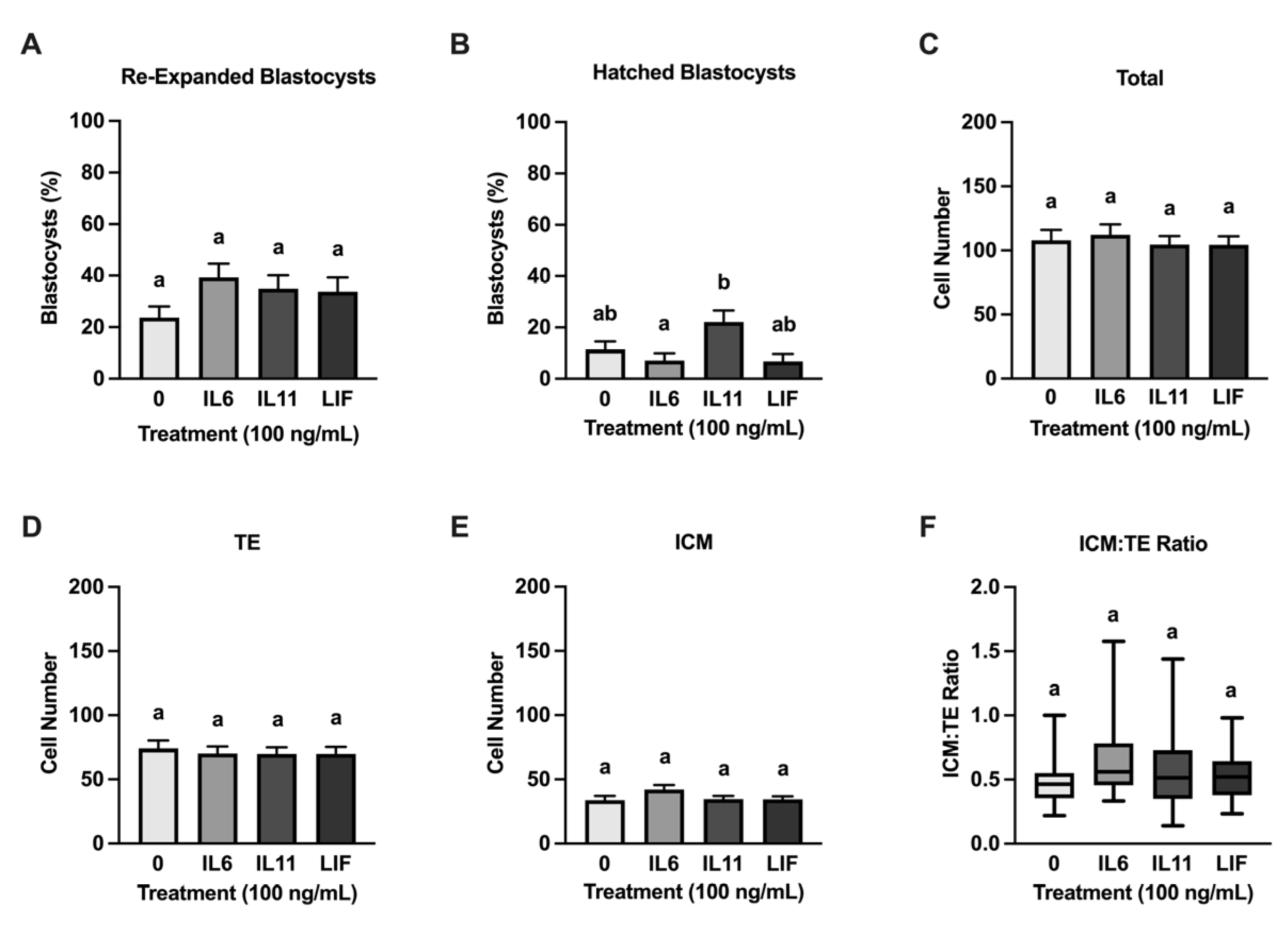
3.1. Effects of IL6, IL11, and LIF on Pre-Freezing Blastocyst Development
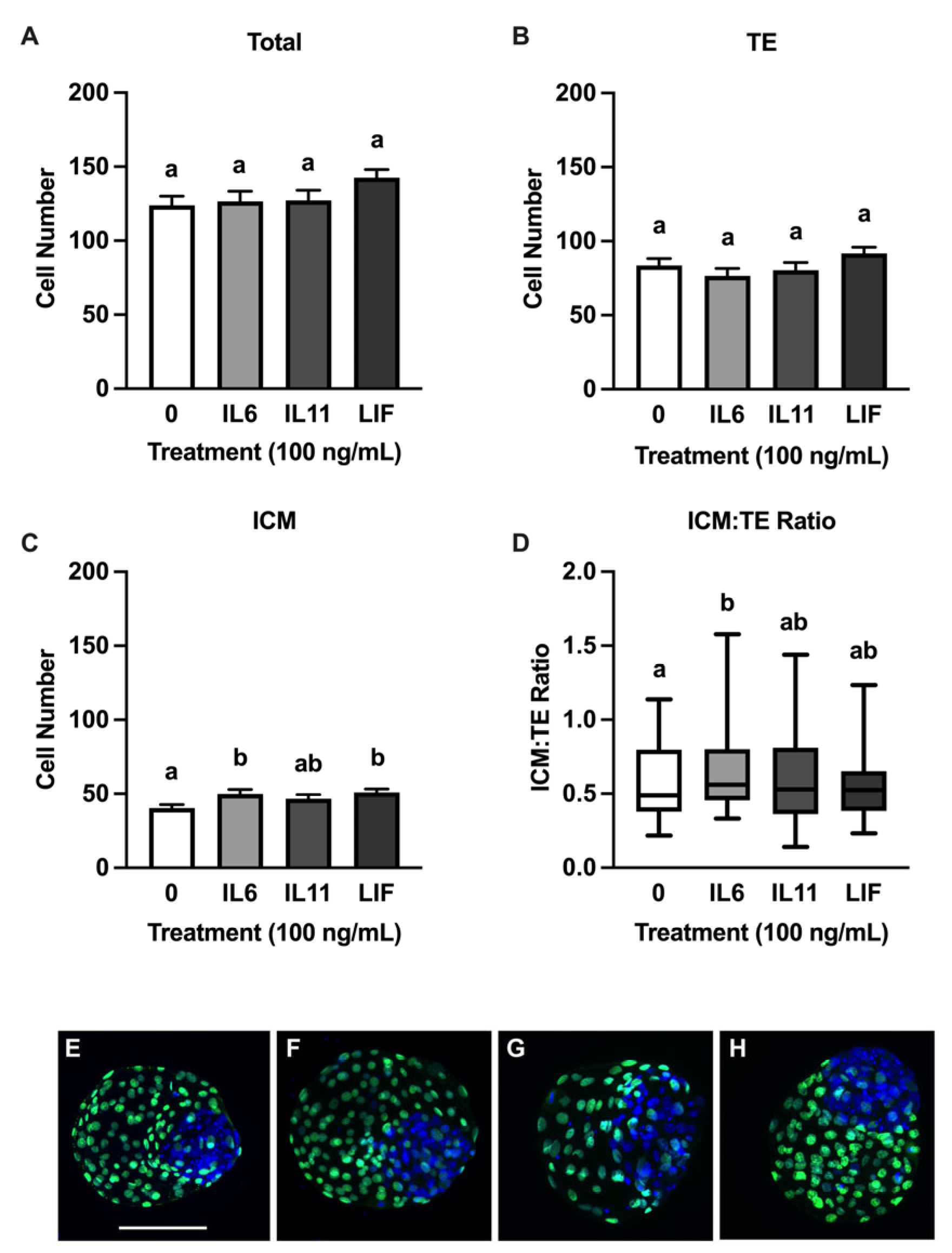
3.2. Effects of IL6, IL11, and LIF on Blastocyst Cell Numbers
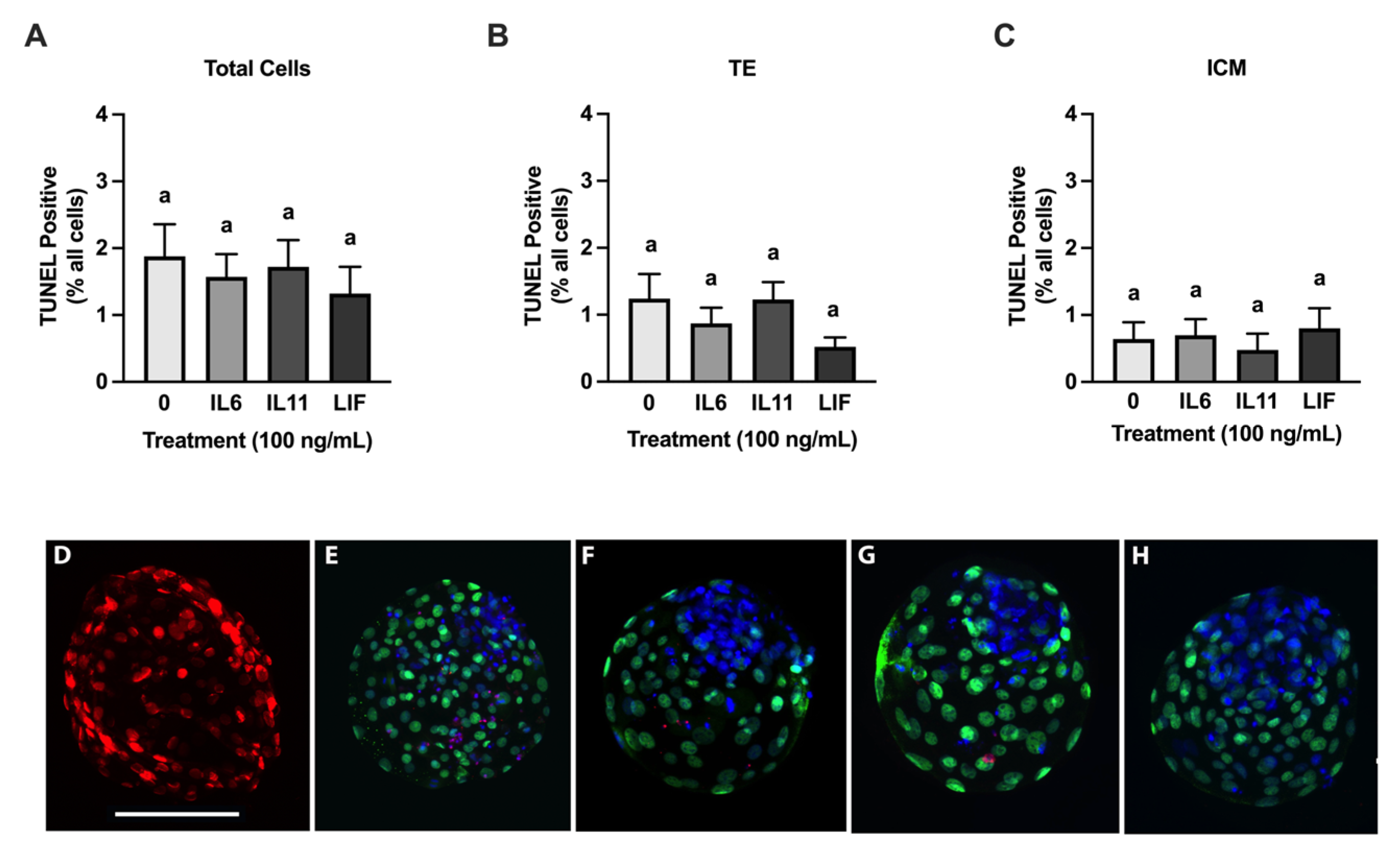
3.3. Cryoprotective Abilities of IL6, IL11, and LIF
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Viana, J. 2021 Statistics of Embryo Production and Transfer in Domestic Farm Animals. Embryo Technol. Newsl. 2022, 40, 22–40. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, P.J. Review: Some Challenges and Unrealized Opportunities toward Widespread Use of the in Vitro-Produced Embryo in Cattle Production. Animal 2023, 17, 100745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonergan, P.; Fair, T. The ART of Studying Early Embryo Development: Progress and Challenges in Ruminant Embryo Culture. Theriogenology 2014, 81, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ealy, A.D.; Wooldridge, L.K.; McCoski, S.R. BOARD INVITED REVIEW: Post-Transfer Consequences of in Vitro-Produced Embryos in Cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 2555–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, P.J. The Incompletely Fulfilled Promise of Embryo Transfer in Cattle—Why Aren’t Pregnancy Rates Greater and What Can We Do about It? J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizos, D.; Clemente, M.; Bermejo-Alvarez, P.; de La Fuente, J.; Lonergan, P.; Gutiérrez-Adán, A. Consequences of in Vitro Culture Conditions on Embryo Development and Quality. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2008, 43, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferre, L.B.; Kjelland, M.E.; Taiyeb, A.M.; Campos-Chillon, F.; Ross, P.J. Recent Progress in Bovine in Vitro-Derived Embryo Cryotolerance: Impact of in Vitro Culture Systems, Advances in Cryopreservation and Future Considerations. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2020, 55, 659–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, A.D.; Sánchez, J.M.; Moore, S.G.; McDonald, M.; McCabe, M.S.; Randi, F.; Lonergan, P.; Butler, S.T. Incidence and Timing of Pregnancy Loss Following Timed Artificial Insemination or Timed Embryo Transfer with a Fresh or Frozen in Vitro-Produced Embryo. J. Dairy Sci. 2025, 108, 1022–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, R.S.; de Almeida, T.G.; Alves, M.F.; Paschoal, D.M.; Basso, A.C.; Sudano, M.J. Cellular and Apoptotic Status Monitoring According to the Ability and Speed to Resume Post-Cryopreservation Embryonic Development. Theriogenology 2020, 158, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomar, F.R.; Teerds, K.J.; Kidson, A.; Colenbrander, B.; Tharasanit, T.; Aguilar, B.; Roelen, B.A.J. Differences in the Incidence of Apoptosis between in Vivo and in Vitro Produced Blastocysts of Farm Animal Species: A Comparative Study. Theriogenology 2005, 63, 2254–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, R.S.; Marsico, T.V.; Sudano, M.J. Basic and Applied Features in the Cryopreservation Progress of Bovine Embryos. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2022, 239, 106970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaba, Y.; Miyashita, S.; Somfai, T.; Geshi, M.; Matoba, S.; Dochi, O.; Nagai, T. Cryopreservation Method Affects DNA Fragmentation in Trophectoderm and the Speed of Re-Expansion in Bovine Blastocysts. Cryobiology 2016, 72, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedambale, T.L.; Dinnyes, A.; Groen, W.; Dobrinsky, J.R.; Tian, X.C.; Yang, X. Comparison on in Vitro Fertilized Bovine Embryos Cultured in KSOM or SOF and Cryopreserved by Slow Freezing or Vitrification. Theriogenology 2004, 62, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, U.; Sagheer, M.; González-Silvestry, F.B.; Hassan, M.; Sosa, F. Vitrification Improves In-Vitro Embryonic Survival in Embryos without Increasing Pregnancy Rate Post Embryo Transfer When Compared to Slow-Freezing: A Systematic Meta-Analysis. Cryobiology 2021, 101, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, T.; Kansaku, K.; Abe, T.; Ueda, S.; Iwata, H. Effects of Resveratrol Treatment on Mitochondria and Subsequent Embryonic Development of Bovine Blastocysts Cryopreserved by Slow Freezing. Anim. Sci. J. 2019, 90, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Ueda, S.; Mori, M.; Baba, T.; Abe, T.; Iwata, H. Influence of Resveratrol Pretreatment on Thawed Bovine Embryo Quality and Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number. Theriogenology 2018, 106, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolini, A.M.; Carrascal-Triana, E.; Ruiz de King, A.; Hansen, P.J.; Alves Torres, C.A.; Block, J. Effect of Addition of L-Carnitine to Media for Oocyte Maturation and Embryo Culture on Development and Cryotolerance of Bovine Embryos Produced in Vitro. Theriogenology 2019, 133, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrascal-Triana, E.L.; Zolini, A.M.; de King, A.R.; Penitente-Filho, J.M.; Hansen, P.J.; Torres, C.A.A.; Block, J. Effect of Addition of Ascorbate, Dithiothreitol or a Caspase-3 Inhibitor to Cryopreservation Medium on Post-Thaw Survival of Bovine Embryos Produced in Vitro. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2022, 57, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pero, M.E.; Zullo, G.; Esposito, L.; Iannuzzi, A.; Lombardi, P.; De Canditiis, C.; Neglia, G.; Gasparrini, B. Inhibition of Apoptosis by Caspase Inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK Improves Cryotolerance of in Vitro Derived Bovine Embryos. Theriogenology 2018, 108, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoecklein, K.S.; Ortega, M.S.; Spate, L.D.; Murphy, C.N.; Prather, R.S. Improved Cryopreservation of in Vitro Produced Bovine Embryos Using FGF2, LIF, and IGF1. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0243727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocyigit, A.; Cevik, M. Effects of Leukemia Inhibitory Factor and Insulin-like Growth Factor-I on the Cell Allocation and Cryotolerance of Bovine Blastocysts. Cryobiology 2015, 71, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendrell-Flotats, M.; García-Martínez, T.; Martínez-Rodero, I.; Lopez-Bejar, M.; LaMarre, J.; Yeste, M.; Mogas, T. In Vitro Maturation with Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Prior to the Vitrification of Bovine Oocytes Improves Their Embryo Developmental Potential and Gene Expression in Oocytes and Embryos. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoecklein, K.S.; Garcia-Guerra, A.; Duran, B.J.; Prather, R.S.; Ortega, M.S. Actions of FGF2, LIF, and IGF1 on Bovine Embryo Survival and Conceptus Elongation Following Slow-Rate Freezing. Front. Anim. Sci. 2022, 3, 1040064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocyigit, A.; Cevik, M. Leucemia Inhibitory Factor; Investigating the Time-Dependent Effect on Viability of Vitrified Bovine Embryos. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2017, 52, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, M.A.; Speckhart, S.L.; Edwards, J.L.; Rhoads, M.L.; Ealy, A.D. Human Recombinant Interleukin-6 Improves the Morphological Quality of Cryopreserved in Vitro Produced Bovine Blastocysts. Theriogenology 2024, 226, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinley, E.; Speckhart, S.L.; Keane, J.A.; Oliver, M.A.; Rhoads, M.L.; Edwards, J.L.; Biase, F.H.; Ealy, A.D. In-fluences of Supplementing Selective Members of the Interleukin-6 Cytokine Family on Bovine Oocyte Compe-tency. Animals 2023, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, F.; Block, J.; Xiao, Y.; Hansen, P.J. Determinants of Survival of the Bovine Blastocyst to Cryopreservation Stress: Treatment with Colony Stimulating Factor 2 during the Morula-to-Blastocyst Transition and Embryo Sex. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2020, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6 Family Cytokines. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a028415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eulenfeld, R.; Dittrich, A.; Khouri, C.; Müller, P.J.; Mütze, B.; Wolf, A.; Schaper, F. Interleukin-6 Signalling: More than Jaks and STATs. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 91, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Narazaki, M.; Metwally, H.; Kishimoto, T. Historical Overview of the Interleukin-6 Family Cytokine. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, L.K.; Ealy, A.D. Interleukin-6 Increases Inner Cell Mass Numbers in Bovine Embryos. BMC Dev. Biol. 2019, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooldridge, L.K.; Johnson, S.E.; Cockrum, R.R.; Ealy, A.D. Interleukin-6 Requires JAK to Stimulate Inner Cell Mass Expansion in Bovine Embryos. Reproduction 2019, 158, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooldridge, L.K.; Ealy, A.D. Interleukin-6 Promotes Primitive Endoderm Development in Bovine Blastocysts. BMC Dev. Biol. 2021, 21, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seekford, Z.K.; Wooldridge, L.K.; Dias, N.W.; Timlin, C.L.; Sales, Á.F.; Speckhart, S.L.; Pohler, K.G.; Cockrum, R.R.; Mercadante, V.R.; Ealy, A.D. Interleukin-6 Supplementation Improves Post-Transfer Embryonic and Fetal Development of in Vitro-Produced Bovine Embryos. Theriogenology 2021, 170, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speckhart, S.L.; Oliver, M.A.; Keane, J.A.; Dias, N.W.; Mercadante, V.R.; Biase, F.H.; Ealy, A.D. Interleukin-6 Supplementation Improves Bovine Conceptus Elongation and Transcriptomic Indicators of Developmental Competence. Biol. Reprod. 2024, 111, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, B.N.; Nix, J.; Wilson, C.; Marrella, M.A.; Speckhart, S.L.; Wooldridge, L.; Yen, C.-N.; Bodmer, J.S.; Kirkpatrick, L.T.; Moorey, S.E.; et al. Tight Gene Co-Expression in BCB Positive Cattle Oocytes and Their Surrounding Cumulus Cells. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2022, 20, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, L.J.; Mansourri-Attia, N.; Fahey, A.G.; Browne, J.; Forde, N.; Roche, J.F.; Lonergan, P.; Fair, T. Characterization of the Th Profile of the Bovine Endometrium during the Oestrous Cycle and Early Pregnancy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speckhart, S.L.; Wooldridge, L.K.; Ealy, A.D. An Updated Protocol for in Vitro Bovine Embryo Production. STAR Protoc. 2023, 4, 101924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, S.D.; Hansen, P.J.; Ealy, A.D. Fibroblast Growth Factor Requirements for in Vitro Development of Bovine Embryos. Theriogenology 2011, 75, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bó, G.A.; Mapletoft, R.J. Evaluation and Classification of Bovine Embryos. Anim. Reprod. AR 2018, 10, 344–348. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, E.; Carrocera, S.; Martin, D.; Perez-Janez, J.J.; Prendes, J.; Prendes, J.M.; Vazquez, A.; Murillo, A.; Gimeno, I.; Munoz, M. Efficient One-Step Direct Transfer to Recipients of Thawed Bovine Embryos Cultured in Vitro and Frozen in Chemically Defined Medium. Theriogenology 2020, 146, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Ibeas, P.; Lamas-Toranzo, I.; Martínez-Moro, Á.; de Frutos, C.; Quiroga, A.C.; Zurita, E.; Bermejo-Álvarez, P. Embryonic Disc Formation Following Post-Hatching Bovine Embryo Development in Vitro. Reprod. Camb. Engl. 2020, 160, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zech, N.; Lejeune, B.; Zech, H.; Vanderzwalmen, P. Vitrification of Hatching and Hatched Human Blastocysts: Effect of an Opening in the Zona Pellucida before Vitrification. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2005, 11, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, K.S.; Harris, D.C.; Daneshmand, S.T.; Shapiro, B.S. Quantitative Grading of a Human Blastocyst: Optimal Inner Cell Mass Size and Shape. Fertil. Steril. 2001, 76, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.-Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.-W. Overall Blastocyst Quality, Trophectoderm Grade, and Inner Cell Mass Grade Predict Pregnancy Outcome in Euploid Blastocyst Transfer Cycles. Chin. Med. J. 2018, 131, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irani, M.; Reichman, D.; Robles, A.; Melnick, A.; Davis, O.; Zaninovic, N.; Xu, K.; Rosenwaks, Z. Morphologic Grading of Euploid Blastocysts Influences Implantation and Ongoing Pregnancy Rates. Fertil. Steril. 2017, 107, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacic, B.; Vlaisavljevic, V.; Reljic, M.; Cizek-Sajko, M. Developmental Capacity of Different Morphological Types of Day 5 Human Morulae and Blastocysts. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2004, 8, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Abbeel, E.; Balaban, B.; Ziebe, S.; Lundin, K.; Cuesta, M.J.G.; Klein, B.M.; Helmgaard, L.; Arce, J.-C. Association between Blastocyst Morphology and Outcome of Single-Blastocyst Transfer. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2013, 27, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooldridge, L.K.; Ealy, A.D. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Stimulates Primitive Endoderm Expansion in the Bovine Inner Cell Mass. Front. Anim. Sci. 2021, 2, 796489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neira, J.A.; Tainturier, D.; Pena, M.A.; Martal, J. Effect of the Association of IGF-I, IGF-II, bFGF, TGF-Beta1, GM-CSF, and LIF on the Development of Bovine Embryos Produced in Vitro. Theriogenology 2010, 73, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, J.; Niemann, H. mRNA Expression of Leukaemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) and Its Receptor Subunits Glycoprotein 130 and LIF-Receptor-Beta in Bovine Embryos Derived in Vitro or in Vivo. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 1998, 4, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vejlsted, M.; Avery, B.; Gjorret, J.O.; Maddox-Hyttel, P. Effect of Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) on in Vitro Produced Bovine Embryos and Their Outgrowth Colonies. Mol. Reprod. Dev. Inc. Gamete Res. 2005, 70, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, L.; Ortiz, W.; Xiao, Y.; Estrada-Cortes, E.; Jannaman, E.A.; Hansen, P.J. Actions of Putative Embryokines on Development of the Preimplantation Bovine Embryo to the Blastocyst Stage. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 11930–11944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, Y.; Matsuyama, K. Development of in Vitro Matured and Fertilized Bovine Embryos Cultured in Media Containing Human Leukemia Inhibitory Factor. Theriogenology 1994, 42, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirisathien, S.; Hernandez-Fonseca, H.J.; Bosch, P.; Hollet, B.R.; Lott, J.D.; Brackett, B.G. Effect of Leukemia Inhibitory Factor on Bovine Embryos Produced in Vitro under Chemically Defined Conditions. Theriogenology 2003, 59, 1751–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, A.; De Frutos, C.; Diez, C.; Caamano, J.N.; Facal, N.; Duque, P.; Garcia-Ochoa, C.; Gomez, E. Effects of Human versus Mouse Leukemia Inhibitory Factor on the in Vitro Development of Bovine Embryos. Theriogenology 2007, 67, 1092–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Devi, S.; Bowen-Shauver, J.; Ferguson-Gottschall, S.; Robb, L.; Gibori, G. The Role of Interleukin-11 in Pregnancy Involves Up-Regulation of A2-Macroglobulin Gene through Janus Kinase 2-Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Pathway in the Decidua. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 3240–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Meng, F.; Forrester-Gauntlett, B.; Turner, P.; Henderson, H.; Oback, B. Signal Inhibition Reveals JAK/STAT3 Pathway as Critical for Bovine Inner Cell Mass Development. Biol. Reprod. 2015, 93, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, M.; Sakatani, M.; Yao, J.; Shanker, S.; Yu, F.; Yamashita, R.; Wakabayashi, S.; Nakai, K.; Dobbs, K.B.; Sudano, M.J.; et al. Global Gene Expression of the Inner Cell Mass and Trophectoderm of the Bovine Blastocyst. BMC Dev. Biol. 2012, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Wu, G.; Yuan, D.; Jia, B.; Liu, C.; Zhu, S.; Hou, Y. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Enhances Bovine Oocyte Maturation and Early Embryo Development. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2014, 81, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliver, M.A.; Alward, K.J.; Rhoads, M.L.; Ealy, A.D. Human Recombinant Interleukin-6 and Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Improve Inner Cell Mass Cell Number but Lack Cryoprotective Activities on In Vitro-Produced Bovine Blastocysts. Animals 2025, 15, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15050668
Oliver MA, Alward KJ, Rhoads ML, Ealy AD. Human Recombinant Interleukin-6 and Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Improve Inner Cell Mass Cell Number but Lack Cryoprotective Activities on In Vitro-Produced Bovine Blastocysts. Animals. 2025; 15(5):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15050668
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliver, Mary A., Kayla J. Alward, Michelle L. Rhoads, and Alan D. Ealy. 2025. "Human Recombinant Interleukin-6 and Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Improve Inner Cell Mass Cell Number but Lack Cryoprotective Activities on In Vitro-Produced Bovine Blastocysts" Animals 15, no. 5: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15050668
APA StyleOliver, M. A., Alward, K. J., Rhoads, M. L., & Ealy, A. D. (2025). Human Recombinant Interleukin-6 and Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Improve Inner Cell Mass Cell Number but Lack Cryoprotective Activities on In Vitro-Produced Bovine Blastocysts. Animals, 15(5), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15050668




