Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Growth Differences in the Chinese Sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals and Sample Collection
2.2. RNA Extraction, Library Construction, and Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. Validation by Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
3.2. Sequencing Data Statistics
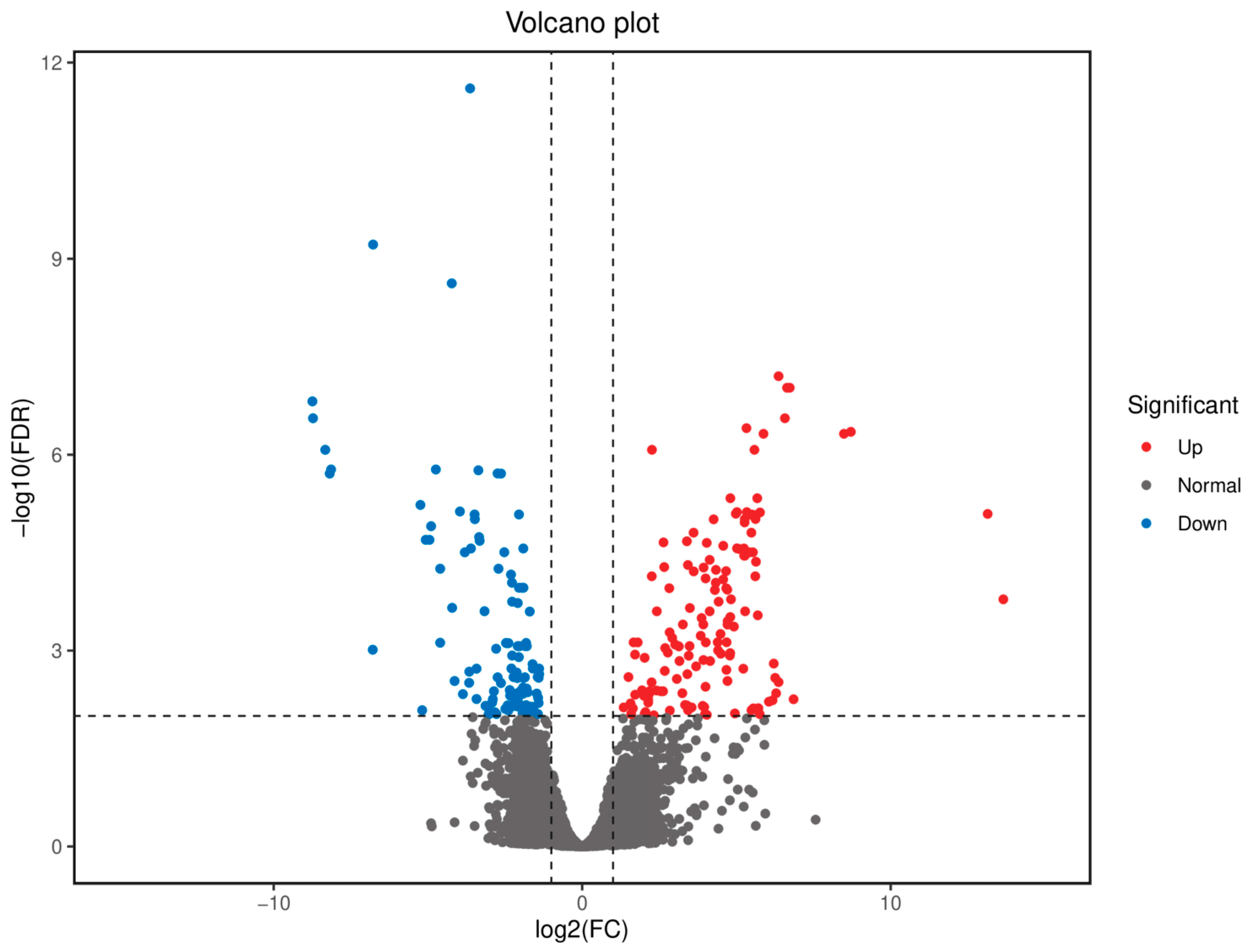
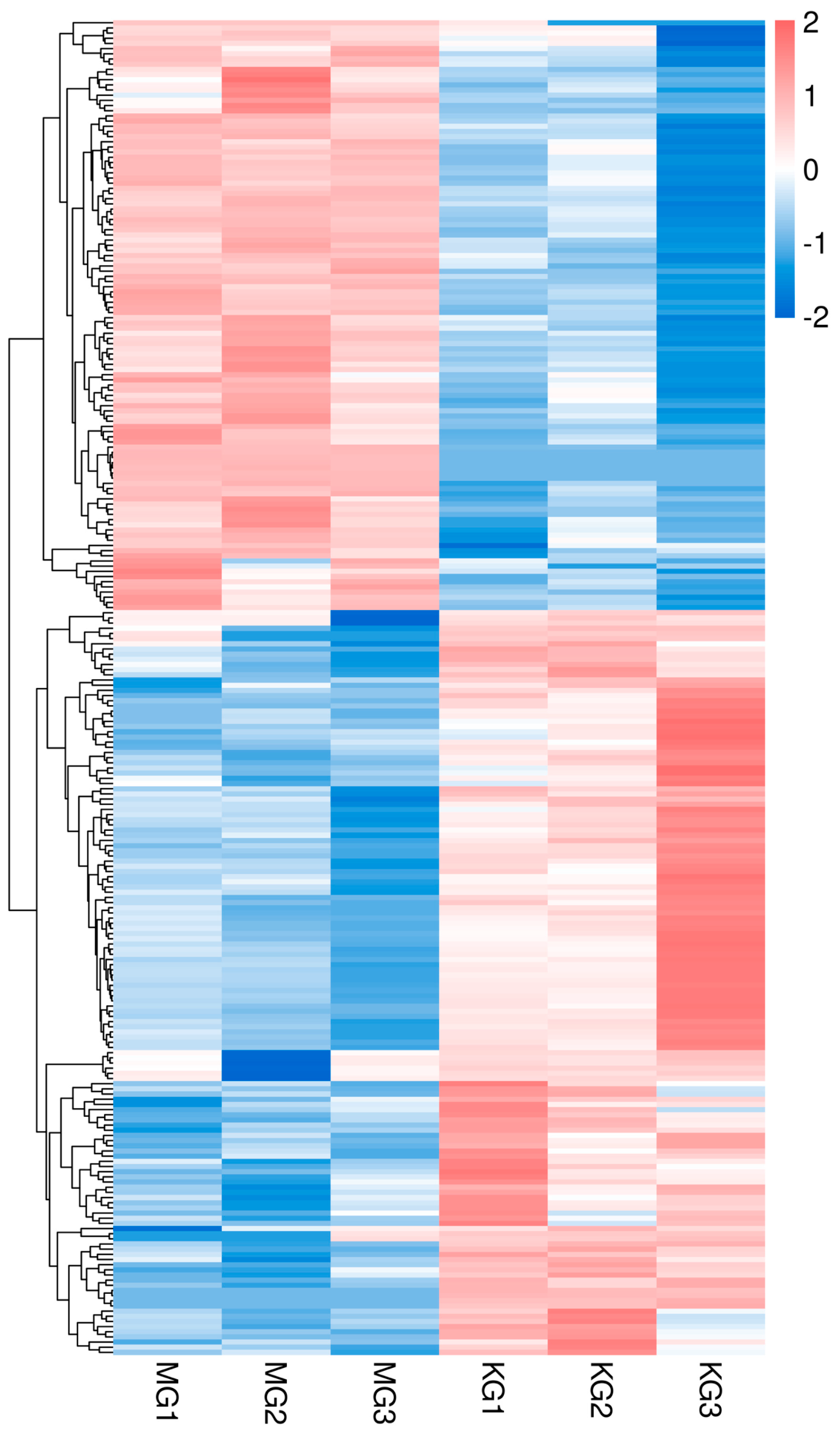
3.3. Differential Gene Expression Analysis
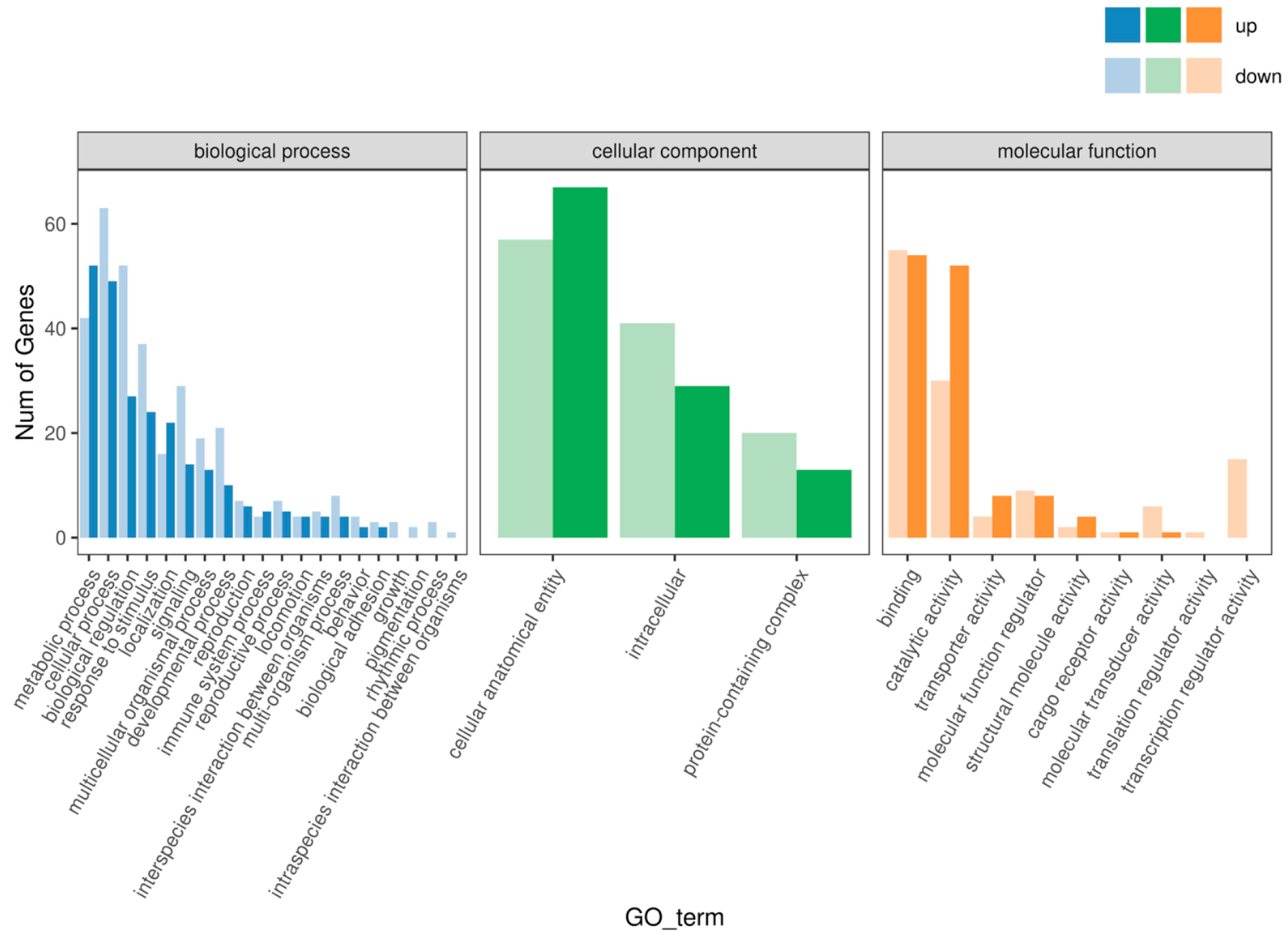
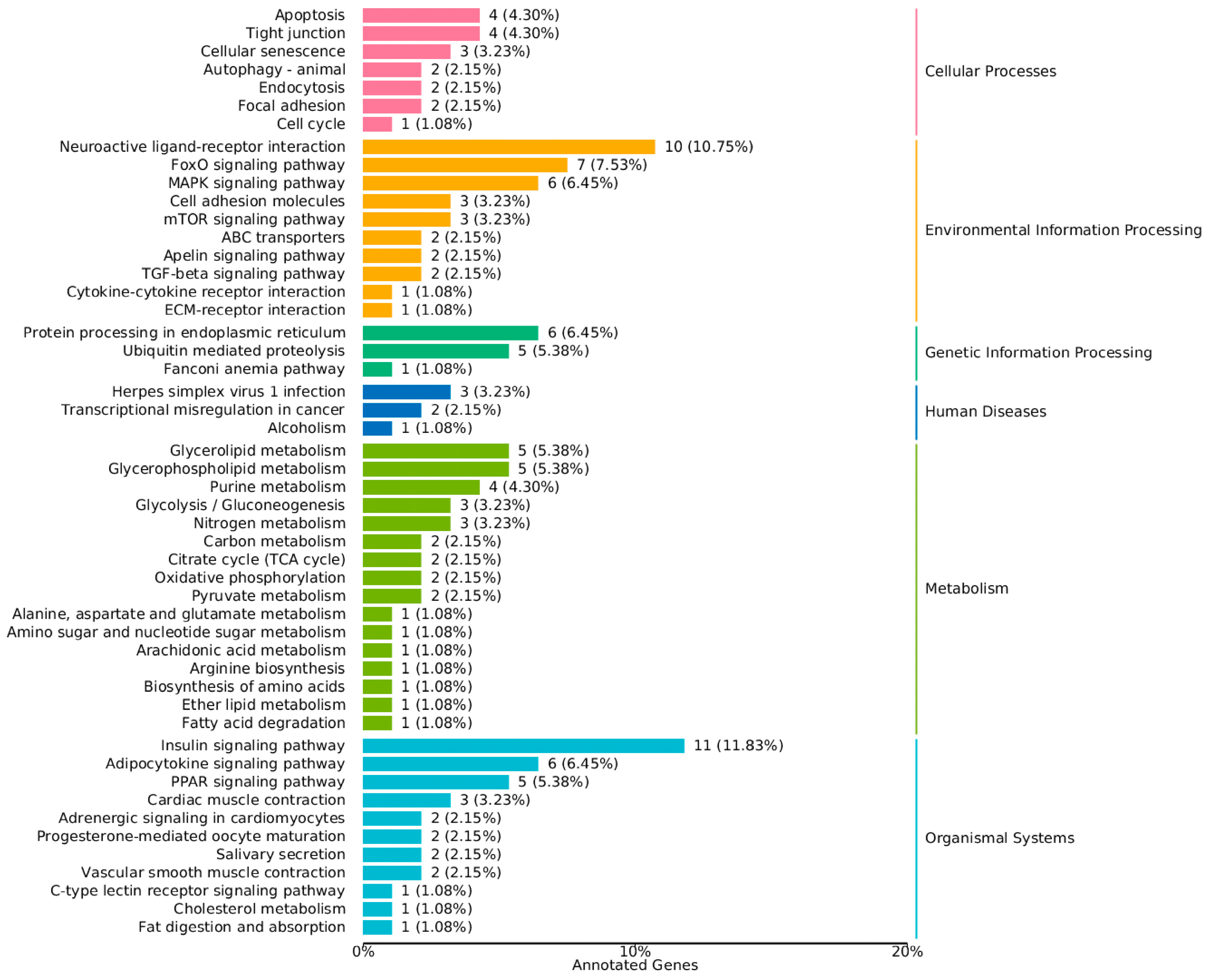
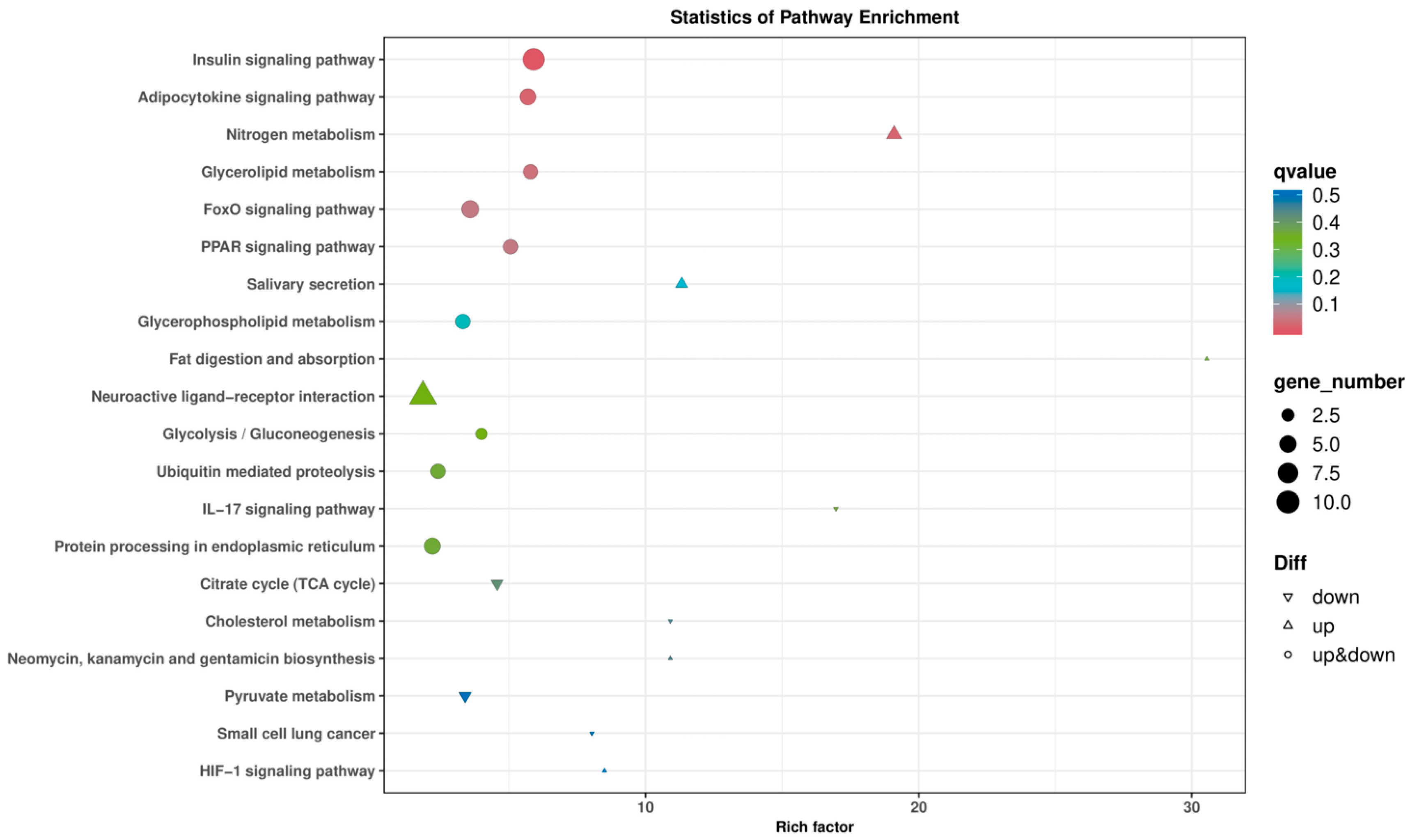
3.4. GO and KEGG Enrichment Analysis
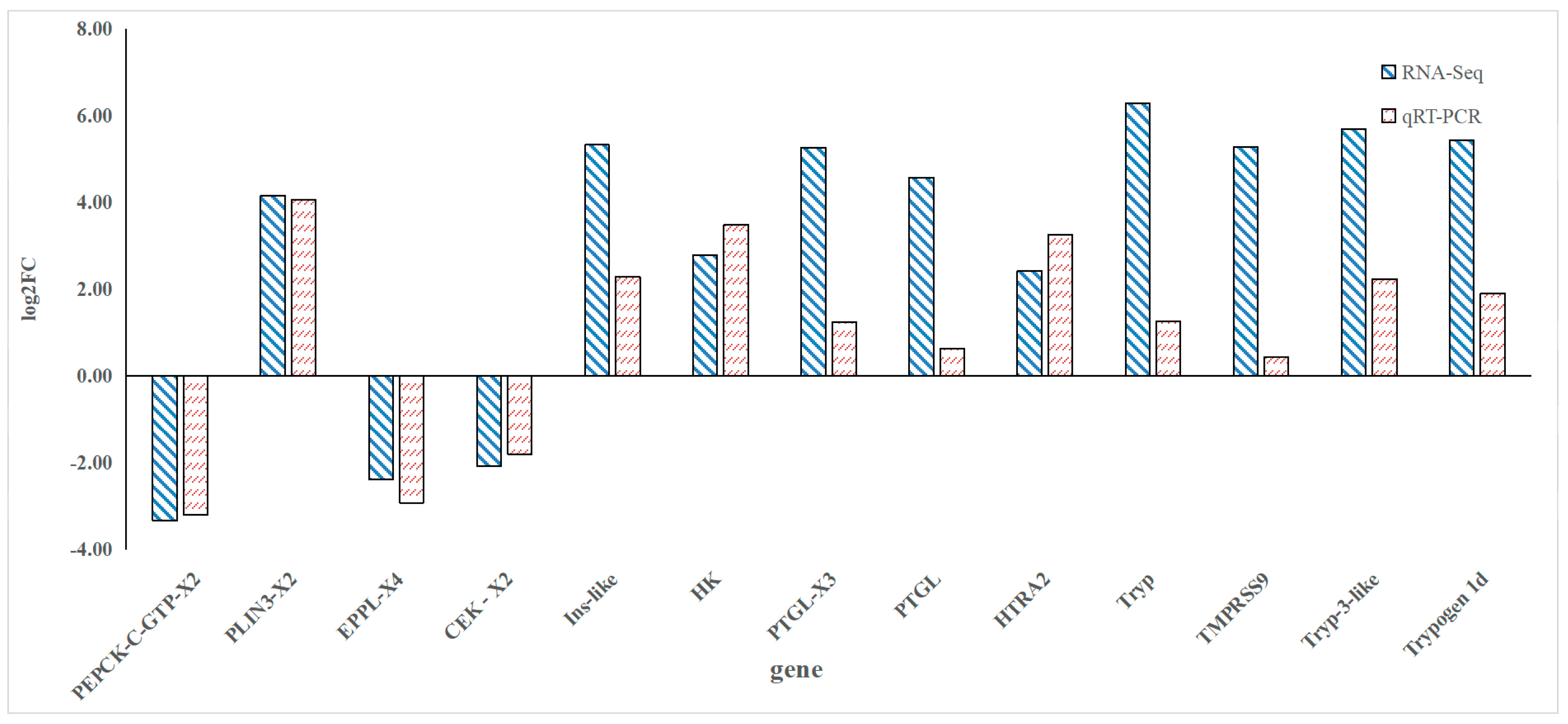
3.5. Validation by qRT-PCR
4. Discussion
4.1. Growth Performance and Differential Gene Expression
4.2. Feed Composition and Feeding Behaviour as Potential Confounders
4.3. Gene Ontology (GO) and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis
4.4. Biological Implications and Conservation Significance
4.5. Comparison with Other Studies
4.6. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Wei, Q.; Du, H.; Kynard, B.; Yang, D.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z. Using drift nets to capture early life stages and monitor spawning of the Yangtze River Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis). J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2013, 25, 100–106. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.; Li, L.; Du, H.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, W.; Zhang, H.; Shen, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C. Research on technology for controlled propagation of cultured Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis). J. Fish. China 2013, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Brosse, S.; Chen, Y.B.; Lek, S.; Chang, J.B. Effects of damming on population sustainability of Chinese sturgeon, Acipenser sinensis: Evaluation of optimal conservation measures. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2009, 86, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, P.; Kynard, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Cao, W.; Wei, Q. Ontogenetic behavior and migration of Chinese sturgeon, Acipenser sinensis. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2002, 65, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Lin, P.; Li, M.; Duan, Z.; Liu, H. Effects of water temperature and discharge on natural reproduction time of the Chinese sturgeon, Acipenser sinensis, in the Yangtze River, China and impacts of the impoundment of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Zool. Sci. 2014, 31, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Gao, X.; Shen, Z.; Fujiwara, M.; Yang, P.; Chang, T.; Liu, H. Novel insights into the reproductive strategies of wild Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis) populations based on the kinship analysis. Water Biol. Secur. 2023, 2, 100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennions, M.D.; Petrie, M. Why do females mate multiply? A review of the genetic benefits. Biol. Rev. 2000, 75, 21–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribolli, J.; Miño, C.I.; Zaniboni-Filho, E.; de Souza Guerreiro, T.C.; Reynalte-Tataje, D.A.; de Freitas, P.D.; Galetti, P.M., Jr. Preliminary insights into the genetic mating system of Neotropical Salminus brasiliensis: Kinship assignment and parental reconstruction reveal polygynandry. Ichthyol. Res. 2016, 63, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Gao, X.; Danley, P.D.; Lin, P.; Li, M.; Liu, H. Potential hydrological regime requirements for spawning success of the Chinese sturgeon Acipenser sinensis in its present spawning ground of the Yangtze River. Ecohydrology 2021, 14, e2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y.; Kong, N. Potential causes of habitat degradation and spawning time delay of the Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis). Ecol. Inform. 2018, 43, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlesworth, D.; Willis, J.H. The genetics of inbreeding depression. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, A.R.; Shaw, K.; Routman, E.; Davis, S.K. The genetic consequences of habitat fragmentation. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1990, 77, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bemis, W.E.; Kynard, B. Sturgeon rivers: An introduction to acipenseriform biogeography and life history. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1997, 48, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikitch, E.K.; Doukakis, P.; Lauck, L.; Chakrabarty, P.; Erickson, D.L. Status, trends and management of sturgeon and paddlefish fisheries. Fish Fish. 2005, 6, 233–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williot, P.; Chebanov, M.; Nonnotte, G. Welfare in the cultured Siberian sturgeon, Acipenser baerii Brandt: State of the art. The Siberian Sturgeon (Acipenser baerii, Brandt, 1869). Farming 2017, 2, 403–450. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Kang, M.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Du, H.; Wei, Q. Increasing river temperature shifts impact the Yangtze ecosystem: Evidence from the endangered Chinese sturgeon. Animals 2019, 9, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, L.; Crespo, B.; Sanchez-Baizan, N.; Xavier, D.; Kuhl, H.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Piferrer, F. Characterization of the European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) gonadal transcriptome during sexual development. Mar. Biotechnol. 2019, 21, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Salbu, B.; Teien, H.C.; Sørlie Heier, L.; Rosseland, B.O.; Høgåsen, T.; Tollefsen, K.E. Hepatic transcriptomic profiling reveals early toxicological mechanisms of uranium in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Xu, S.; Luo, K.; Hu, M.; Luan, S.; Shao, H.; Kong, J.; Hu, H. Estimation of genetic parameters for growth and egg related traits in Russian sturgeon (Acipenser gueldenstaedtii). Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestin, A.; Brunel, O.; Malledant, A.; Debeuf, B.; Benoit, P.; Mahla, R.; Chapuis, H.; Guémené, D.; Vandeputte, M.; Haffray, P. Genetic parameters of caviar yield, color, size and firmness using parentage assignment in an octoploid fish species, the Siberian sturgeon Acipenser baerii. Aquaculture 2021, 540, 736725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Lv, H.; Yin, X.; Li, W.; Chu, Z. Transcriptome analysis of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) at different growth rates. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 50, 1745–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Solberg, M.F.; Chen, Z.; Wei, M.; Zhu, F.; Jia, C.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, Z. Comparative transcriptome analysis of mixed tissues of black porgy (Acanthopagrus schlegelii) with differing growth rates. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 5800–5813. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ling, L.; Jin, H.; Li, Z.; Gao, Y.; Liu, F.; Luo, H.; Ye, H. Identification of genes related to growth from transcriptome profiles of the muscle and liver of Chinese longsnout catfish (Leiocassis longirostris). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D 2024, 49, 101180. [Google Scholar]
- Loukovitis, D.; Siasiou, A.; Mitsopoulos, I.; Lymberopoulos, A.G.; Laga, V.; Chatziplis, D. Genetic diversity of Greek sheep breeds and transhumant populations utilizing microsatellite markers. Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 136, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besson, M.; Rombout, N.; Salou, G.; Vergnet, A.; Cariou, S.; Bruant, J.S.; Vandeputte, M. Potential for genomic selection on feed efficiency in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata), based on individual feed conversion ratio, carcass and lipid traits. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 24, 101132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2022, 34, 884–890. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Wu, B.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Ming, Y.; Bai, M.; Du, H. Whole-genome sequencing reveals autooctoploidy in Chinese sturgeon and its evolutionary trajectories. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2024, 22, qzad002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-Seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Mao, X.; Huang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Dong, S.; Kong, L.; Gao, G.; Li, C.Y.; Wei, L. KOBAS 2.0: A web server for annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W316–W322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.; Cao, L.; Cao, Z.; Bing, X. Characterization of the growth-related transcriptome in the liver and brain of mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi) through RNA-Seq analysis. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2024, 52, 2440045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Liu, W.; Qi, M.; Liang, Q.; Yao, G.; Ma, C.; Ding, X.; Yu, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. Integrated transcriptome and microbiome analyses reveal growth- and stress-response-related genes and microbes in mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Fishes 2025, 10, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Name | Primer Sequence | Product Length (bp) | Annealing Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| beta-actin-S | GCTATGTACGTTGCCATCCAGG | 220 | 60 |
| beta-actin-A | CCGTGGTAGTGAAGCTGTAGCC | ||
| PEPCK-C-GTP-X2-S | TGGATGTCGGAGGAGGAGTTC | 190 | 60 |
| PEPCK-C-GTP-X2-A | CCGATCCCATCCTGGTCAT | ||
| PLIN3-X2-S | TAGCTGTCAATAACCTTGCCTGTAA | 118 | 60 |
| PLIN3-X2-A | ACCGTGTTCGTAACCACCTCTG | ||
| EPPL-X4-S | ATTCTGATACAAACGACTGCCAAAC | 173 | 60 |
| EPPL-X4-A | GCCTTTGGCACGGATTATCTTA | ||
| CEK-X2-S | GAGGCGTTCCAGATCAGCATAA | 121 | 60 |
| CEK-X2-A | CATACAAGCGAAGCAGCACATT | ||
| Ins-like-S | CGGAGAACGATGTGGACGAG | 106 | 60 |
| Ins-like-A | AAATCGTACAGGGAGCAGGG | ||
| HK-S | CGAGGCTGGAAAGTGGAGAC | 176 | 60 |
| HK-A | CGCACAGGGAAGGAGAAGGT | ||
| PTGL-X3-S | TGGCAAGGAGGGTCAAGAAC | 272 | 60 |
| PTGL-X3-A | ACCGCATCACTAGCATCCAAT | ||
| PTGL-S | GTCGGCCACCTTGACTTCTATC | 103 | 60 |
| PTGL-A | TTCCTTCCCAAATGCCATCC | ||
| HTRA2-S | CGGCGTGTCCTACCGAAAT | 287 | 60 |
| HTRA2-A | TGACAATCAGCCCGTCTTCC | ||
| Tryp-S | GATGAGATCACTTGTTGCGTTTGT | 104 | 60 |
| Tryp-A | GCTTGGAGTTGGGTCTGCATT | ||
| TMPRSS9-S | CAGGATTGTGAACGGTGAGGAG | 117 | 60 |
| TMPRSS9-A | ACGACCCATTGAGCCGAGAT | ||
| Tryp-3-like-S | CACGACATCTTCAGCTCCGA | 144 | 60 |
| Tryp-3-like-A | CACGTACTGGTTGAACTGGGC |
| Samples | Clean Reads | Clean Bases | GC/% | Q30/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGL1 | 20,953,792 | 6,273,734,949 | 46.36% | 93.85% |
| FGL2 | 21,099,905 | 6,314,319,433 | 46.71% | 94.04% |
| FGL3 | 21,494,398 | 6,436,870,627 | 51.23% | 94.10% |
| SGL1 | 26,083,923 | 7,796,224,713 | 46.68% | 93.75% |
| SGL2 | 21,448,768 | 6,405,909,053 | 45.40% | 93.58% |
| SGL3 | 20,360,203 | 6,092,883,104 | 46.19% | 94.05% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Tian, T.; He, R.; Jiang, W.; Hu, Y. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Growth Differences in the Chinese Sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis). Animals 2025, 15, 3550. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15243550
Zhang J, Tian T, He R, Jiang W, Hu Y. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Growth Differences in the Chinese Sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis). Animals. 2025; 15(24):3550. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15243550
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jianming, Tian Tian, Rui He, Wei Jiang, and Yacheng Hu. 2025. "Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Growth Differences in the Chinese Sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis)" Animals 15, no. 24: 3550. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15243550
APA StyleZhang, J., Tian, T., He, R., Jiang, W., & Hu, Y. (2025). Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Growth Differences in the Chinese Sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis). Animals, 15(24), 3550. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15243550






